SAM Teachers Guide Atoms and Energy Overview Learning Objectives: Possible student pre/misconceptions
|
|
|
- Kathleen Margaret Fletcher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SAM Teachers Guide Atoms and Energy Overview Students will explore how the Law of Conservation of Energy (the First Law of Thermodynamics) applies to atoms as well as the implications of heating or cooling a system. This unit focuses on potential energy and kinetic energy as well as energy conservation. The goal is to apply what is learned to both our human scale world and the world of atoms and molecules. Learning Objectives: Students will be able to: Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. Explain how kinetic energy can be converted to potential energy and vice versa. Analyze energy graphs and the motion of objects in a system to learn about the Law of Conservation of Energy. Apply the first Law of Thermodynamics when heating or cooling a system. Differentiate between energy transfer in an open system and energy conversion. Possible student pre/misconceptions Energy is associated only with movement. Energy is destroyed in transformations from one type to another. Gravitational potential energy is the only type of potential energy. Models to Highlight and Possible Discussion Questions After completion of Part 1 of the activity: Models to highlight: Page 3 Pendulum Model o Discuss how kinetic and gravitational potential energy are converted and vice versa. Point out that gravitational potential energy is not the only type of potential energy in light of common student misconceptions. o Link to other SAM Activity: Gravitational potential energy is compared to electric potential energy in future lesson studying electric current. Page 4 The Model of the Spring (Elastic PE) and Corresponding Graph o Discuss the relationship between the position of the spring and the curves for potential, kinetic and total energy in the graph. Ask students to share ideas for the snapshots they chose to illustrate the point of lowest kinetic energy and energy conservation.
2 Possible Discussion Questions: Have student s brainstorms examples of objects that have kinetic energy and the factors that impact kinetic energy (mass and velocity). List situations besides the pendulum where students can explain how potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and vice versa. Try to encourage students to think of examples in addition to those involving gravitational potential energy. Demo Idea: Use spring or slinky in class to illustrate the principles of elastic potential energy and conversion to kinetic energy. After completion of Part 2 of the activity: Models to highlight: Page 5 Model of Interatomic PE and Corresponding Graph o Point out the relationship between KE and PE as the atoms move both toward and away from each other. Differentiate the importance of atoms being in close proximity to that of the spring example from Day 1. Discuss how total energy still remains constant. o Link to other SAM Activity: Connect interatomic potential energy to future lessons such as Electrostatics (attraction and repulsion between atoms) and Newton s Laws (forces between atoms at work at close enough distances). Page 6 Model of Atomic Motion and Corresponding Graph o Discuss how the color of the atoms indicates the gain or loss of kinetic energy in the system. Stress how the First Law of Thermodynamics can be seen in both the model and the graph. Page 8 Model of Energy Transfer o Differentiate between energy conversion and energy transfer. Discuss what happens as the divider is withdrawn and what the effect is on the temperature of both containers. Link to Other SAM Activity: Models of Pages 6,7,8 link strongly to the next activity, Heat and Temperature. Use discussion of the models to lead into the upcoming differences between heat and temperature. Possible Discussion Questions: Why is the example of interatomic potential energy both similar to and different from the spring example? (Discuss how the sum of total energy is still conserved but how distance between atoms now plays a role.)
3 Have students explain their understanding of the First Law of Thermodynamics and give examples of how it applies with heating and cooling. Have students brainstorm/share examples of energy transfer in an open system. How is this different from a closed system?
4 Connections to Other SAM Activities: The focus of this activity is for students to understand kinetic energy, the interconversion of potential and kinetic energy and how energy is conserved according to the Law of Conservation of Energy. The Atoms and Energy unit is supported by both Atomic Structure and Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale. Atomic Structure sets up a connection between an atom s composition and how this plays a role in both attraction and repulsion. In Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale students focus on force, mass and acceleration, which connects to how the forces at work between atoms. Atoms and Energy supports Heat and Temperature. Temperature is defined by the kinetic energy of the substance, where atoms are colliding. Students can recognize that energy is conserved in atomic collisions. In addition, kinetic energy is converted into an excited state in Atoms, Excited States, and Photons. Once atoms are excited, energy can be converted into light, photons. Phase Change is related to the energy atoms have to use to overcome forces of attraction. Finally, Atoms and Energy supports Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport and ATP Biological Energy. The connections are more indirect but still present when discussing active transport and ATP. Chemical energy is converted into another form of potential energy, electrostatic potential energy. The fundamental principles of energy conversion and conservation, as shown in the Atoms and Energy unit are highlighted once again.
5 Activity Answer Guide Page 1: Introduction Sample Snapshot 2: Page 2: 1. The faster the ball on the left moved the kinetic energy of the ball... (b) 2. The kinetic energy is related to both an object's speed and its mass. Predict what would happen to the kinetic energy if the ball on the left were twice its current mass but the speed of the ball remains the same. The kinetic energy of the ball on the left would double if the mass were twice the current mass. This is true if the speed of the ball remains constant. Page 3: The kinetic energy is lowest in this snapshot where the spring is fully compressed. 2. Take a snapshot of the graph and label it with the annotation tools to explain how we know that energy is conserved in this spring system. 1. Where is the pendulum when the kinetic energy is maximum? (a) 2. What happens to the kinetic and potential energy as the pendulum swings from its highest point to its lowest point? The potential energy decreases and the kinetic energy increases. Page 4: 1. Take a snapshot of the model on the left that shows one of the 2 possible locations of the balls on the spring when the kinetic energy is lowest. Sample Snapshot 1: The kinetic energy is the lowest in this snapshot because the spring is fully extended. The total energy of the spring system remains constant. The total energy is shown as the straight black line. The graph shows that when potential energy is increasing the kinetic energy is decreasing and vice versa. 3. Use the step back or step forward button to describe the change in kinetic energy as the spring moves from the most compressed position to the most stretched position. At the most compressed position, the kinetic energy is low. When the spring is released, the stored potential energy is converted into kinetic energy to stretch the spring. By the time the spring is fully extended to its most stretched position, the kinetic energy is low again as it has been converted back into potential energy.
6 Page 5: 1. The total energy is the sum of the potential and kinetic energy. What happens to it over time, if you do not adjust the strength of the interaction? (c) 2. Take a snapshot of the graph and annotate it to show the point where there is no force. Page 8: 1. The energy level of the circular area on the right rose because: When the separator between the two containers is withdrawn, heat energy from the container on the left is transferred to the system on the right until the temperature of the two circular areas is almost equal. 2. Give one example of something that comes close to having the same characteristics of energy transfer as seen in the model. Explain your choice. 3. Why does the kinetic energy increase as the atoms move toward each other? The attraction between atoms causes the kinetic energy to increase as they move towards one another. Page 6: 1. As long as you leave the atoms alone, what happens to the total energy of the atoms over time? (c) 2. When atoms collide with each other, they exchange energy. How does the model show this? How does the graph show this? The model shows the exchange of energy because the atoms with low energy (the lighter colors) become darker in color after they collide. The graph shows that as a system the kinetic energy will increase and decrease but the total energy (black line) will stay constant. Page 7: 1. Describe how the energy of the system changes when it is heated or cooled. When the system is heated, the total energy of the system increases. When the system is cooled, the total energy of the system decreases. Answers will vary. One example is putting a hot pot on a cool countertop. The heat from the pot will be transferred to the countertop. The pot's temperature will decrease as the countertop's temperature increases. Page 9: 1. When two or more atoms collide... (e) 2. Explain what it means to say energy is conserved when two atoms move toward and away from each other. Energy will be converted from potential energy to kinetic and back but the total energy in the system of the two atoms is conserved. 3. What happens to an atom's kinetic energy if it collides with an atom that has even less kinetic energy? When two atoms with different amounts of energy collide, energy will be transferred from one atom to the other. 4. How can you increase a cup of water's kinetic energy? Adding heat energy to a cup of water will increase its kinetic energy. The addition of heat to the system will cause the water molecules to speed up their motion and therefore increase their energy.
7 SAM HOMEWORK QUESTIONS: Atoms and Energy Directions: After completing the unit, answer the following questions to review. 1. What does the Law of Conservation of Energy state? 2. The equation for kinetic energy is: KE = ½ mv 2. This means that the kinetic energy of an object is based on what two factors? 3. Look at the pendulum below. Label where you think the kinetic energy will be highest and lowest. Do the same for potential energy. 4. In a closed system, the First Law of Thermodynamics can be seen. Look at the image below. What will happen to the kinetic energy of the individual atoms as they are in motion? What happens to the total energy of the system over time? 5. How would your answers to the above question differ if heat were added to the system? Or, if the system was cooled?
SAM Teachers Guide Phase Change Overview Learning Objectives Possible Student Pre/Misconceptions
 SAM Teachers Guide Phase Change Overview Students review the atomic arrangements for each state of matter, following trajectories of individual atoms to observe their motion and observing and manipulating
SAM Teachers Guide Phase Change Overview Students review the atomic arrangements for each state of matter, following trajectories of individual atoms to observe their motion and observing and manipulating
SAM Teachers Guide Phase Change Overview Learning Objectives Possible Student Pre/Misconceptions
 SAM Teachers Guide Phase Change Overview Students review the atomic arrangements for each state of matter, following trajectories of individual atoms to observe their motion. Students observe and manipulate
SAM Teachers Guide Phase Change Overview Students review the atomic arrangements for each state of matter, following trajectories of individual atoms to observe their motion. Students observe and manipulate
SAM Teachers Guide Atoms, Excited States, and Photons
 SAM Teachers Guide Atoms, Excited States, and Photons Overview This activity focuses on the ability of atoms to store energy and re emit it at a later time. Students explore atoms in an ʺexcitedʺ state
SAM Teachers Guide Atoms, Excited States, and Photons Overview This activity focuses on the ability of atoms to store energy and re emit it at a later time. Students explore atoms in an ʺexcitedʺ state
SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Learning Objectives Possible Student Pre/Misconceptions
 SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Students explore how Newton s three laws apply to the world of atoms and molecules. Observations start with the originally contradictory observation
SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Students explore how Newton s three laws apply to the world of atoms and molecules. Observations start with the originally contradictory observation
SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Learning Objectives Possible Student Pre/Misconceptions
 SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Students explore how Newton s three laws apply to the world of atoms and molecules. Observations start with the originally contradictory observation
SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Students explore how Newton s three laws apply to the world of atoms and molecules. Observations start with the originally contradictory observation
Lab/Demo 5 Periodic Motion and Momentum PHYS 1800
 Lab/Demo 5 Periodic Motion and Momentum PHYS 1800 Objectives: Learn to recognize and describe periodic motion. Develop some intuition for the principle of conservation of energy in periodic systems. Use
Lab/Demo 5 Periodic Motion and Momentum PHYS 1800 Objectives: Learn to recognize and describe periodic motion. Develop some intuition for the principle of conservation of energy in periodic systems. Use
SAM Teachers Guide Intermolecular Forces Overview Learning Objectives: Possible student pre/misconceptions
 SAM Teachers Guide Intermolecular Forces Overview This unit focuses on the attractive forces felt between molecules. Both London Dispersion and Dipole Dipole intermolecular attractions will be discussed
SAM Teachers Guide Intermolecular Forces Overview This unit focuses on the attractive forces felt between molecules. Both London Dispersion and Dipole Dipole intermolecular attractions will be discussed
Healy/DiMurro. Vibrations 2016
 Name Vibrations 2016 Healy/DiMurro 1. In the diagram below, an ideal pendulum released from point A swings freely through point B. 4. As the pendulum swings freely from A to B as shown in the diagram to
Name Vibrations 2016 Healy/DiMurro 1. In the diagram below, an ideal pendulum released from point A swings freely through point B. 4. As the pendulum swings freely from A to B as shown in the diagram to
SAM Teacher s Guide Protein Partnering and Function
 SAM Teacher s Guide Protein Partnering and Function Overview Students explore protein molecules physical and chemical characteristics and learn that these unique characteristics enable other molecules
SAM Teacher s Guide Protein Partnering and Function Overview Students explore protein molecules physical and chemical characteristics and learn that these unique characteristics enable other molecules
Potential Energy. Serway 7.6, 7.7;
 Potential Energy Conservative and non-conservative forces Gravitational and elastic potential energy Mechanical Energy Serway 7.6, 7.7; 8.1 8.2 Practice problems: Serway chapter 7, problems 41, 43 chapter
Potential Energy Conservative and non-conservative forces Gravitational and elastic potential energy Mechanical Energy Serway 7.6, 7.7; 8.1 8.2 Practice problems: Serway chapter 7, problems 41, 43 chapter
Lesson 8: Work and Energy
 Name Period Lesson 8: Work and Energy 8.1 Experiment: What is Kinetic Energy? (a) Set up the cart, meter stick, pulley, hanging mass, and tape as you did in Lesson 5.1. You will examine the distance and
Name Period Lesson 8: Work and Energy 8.1 Experiment: What is Kinetic Energy? (a) Set up the cart, meter stick, pulley, hanging mass, and tape as you did in Lesson 5.1. You will examine the distance and
Understanding KMT using Gas Properties and States of Matter
 Understanding KMT using Gas Properties and States of Matter Learning Goals: Students will be able to describe matter in terms of particle motion. The description should include Diagrams to support the
Understanding KMT using Gas Properties and States of Matter Learning Goals: Students will be able to describe matter in terms of particle motion. The description should include Diagrams to support the
WHAT IS ENERGY???? Energy can have many different meanings and. The ability of an object to do work. Measured in joules (J)
 WHAT IS ENERGY???? Energy can have many different meanings and forms The ability of an object to do work Measured in joules (J) N m = J Work in Progress So what is are the different types of energy? DIFFERENT
WHAT IS ENERGY???? Energy can have many different meanings and forms The ability of an object to do work Measured in joules (J) N m = J Work in Progress So what is are the different types of energy? DIFFERENT
- Conservation of Energy Notes Teacher Key -
 NAME: DATE: PERIOD: PHYSICS - Conservation of Energy Notes Teacher Key - - Is Energy Conserved? - Determine the max height that a 5kg cannonball will reach if fired vertically with an initial velocity
NAME: DATE: PERIOD: PHYSICS - Conservation of Energy Notes Teacher Key - - Is Energy Conserved? - Determine the max height that a 5kg cannonball will reach if fired vertically with an initial velocity
Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes
 Physics 1 Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes Date 1. Define work. 2. Define energy. 3. Determine the work done by a constant force. Period 4. Determine the work done by a
Physics 1 Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes Date 1. Define work. 2. Define energy. 3. Determine the work done by a constant force. Period 4. Determine the work done by a
SAM Teachers Guide Chemical Bonds
 SAM Teachers Guide Chemical Bonds Overview Students discover that the type of bond formed ionic, non polar covalent, or polar covalent depends on the electronegativity of the two atoms that are bonded
SAM Teachers Guide Chemical Bonds Overview Students discover that the type of bond formed ionic, non polar covalent, or polar covalent depends on the electronegativity of the two atoms that are bonded
Background Information
 Background Information The lesson we will encounter today is the 7 th lesson in an energy unit that is being developed at the University of Michigan for middle school students. There are four learning
Background Information The lesson we will encounter today is the 7 th lesson in an energy unit that is being developed at the University of Michigan for middle school students. There are four learning
5. A car moves with a constant speed in a clockwise direction around a circular path of radius r, as represented in the diagram above.
 1. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is 20. Newtons. If the mass of each object were doubled, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the objects would be A) 5.0 N B)
1. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is 20. Newtons. If the mass of each object were doubled, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the objects would be A) 5.0 N B)
s_3x03 Page 1 Physics Samples
 Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY
 KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY IMPORTANT CHARACTERISTICS OF GASES 1) Gases are highly compressible An external force compresses the gas sample and decreases its volume, removing the external force allows the
KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY IMPORTANT CHARACTERISTICS OF GASES 1) Gases are highly compressible An external force compresses the gas sample and decreases its volume, removing the external force allows the
Name: Class: Date: 1. Students will be able to define, correctly use, and provide examples of the following terms:
 ENERGY BASICS PACKET Packet Includes: I. Objectives II. Energy Reading III. Energy Notes IV. Review Questions 1-7 & 11-17 (answer on separate sheet) V. Quiz Review I. Unit Objectives: 1. Students will
ENERGY BASICS PACKET Packet Includes: I. Objectives II. Energy Reading III. Energy Notes IV. Review Questions 1-7 & 11-17 (answer on separate sheet) V. Quiz Review I. Unit Objectives: 1. Students will
SAM Teachers Guide Photosynthesis
 SAM Teachers Guide Photosynthesis Overview This activity focuses on how certain molecules called pigments interact with light and determine the color of plants. Students explore how molecules such as chlorophyll
SAM Teachers Guide Photosynthesis Overview This activity focuses on how certain molecules called pigments interact with light and determine the color of plants. Students explore how molecules such as chlorophyll
Physics. The study of energy & matter and how they interact
 Physics The study of energy & matter and how they interact Forces a push or pull on an object. Drawn as a vector - have direction and strength Measured in. newtons 5 n Net Force when in the same direction
Physics The study of energy & matter and how they interact Forces a push or pull on an object. Drawn as a vector - have direction and strength Measured in. newtons 5 n Net Force when in the same direction
Clicker Ques,ons for NEXUS/Physics. Atomic Interactions & Chemical Energy
 Clicker Ques,ons for NEXUS/Physics Atomic Interactions & Chemical Energy A note on usage: The clicker slides in this booklet are meant to be used as stimuli to encourage class discussion. They are intended
Clicker Ques,ons for NEXUS/Physics Atomic Interactions & Chemical Energy A note on usage: The clicker slides in this booklet are meant to be used as stimuli to encourage class discussion. They are intended
SAM Teachers Guide Electricity
 SAM Teachers Guide Electricity Overview Students explore the role of electron voltage and density on electric current. They compare the movement of electrons in a conductor and an insulator. They derive
SAM Teachers Guide Electricity Overview Students explore the role of electron voltage and density on electric current. They compare the movement of electrons in a conductor and an insulator. They derive
Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic
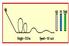 Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster related to these values?
Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster related to these values?
General Physics I Work & Energy
 General Physics I Work & Energy Forms of Energy Kinetic: Energy of motion. A car on the highway has kinetic energy. We have to remove this energy to stop it. The brakes of a car get HOT! This is an example
General Physics I Work & Energy Forms of Energy Kinetic: Energy of motion. A car on the highway has kinetic energy. We have to remove this energy to stop it. The brakes of a car get HOT! This is an example
Name Class Date. Energy Energy
 CHAPTER 13 3 What Is Energy? SECTION Work and Energy KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How are energy and work related? Why is potential energy called energy of position?
CHAPTER 13 3 What Is Energy? SECTION Work and Energy KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How are energy and work related? Why is potential energy called energy of position?
5.3: Calculate kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy, and elastic potential energy. Do Now: 1. Hand in your Forms of Energy Wheel
 Do Now: 1. Hand in your Forms of Energy Wheel 2. Identify the following forms of energy: a. A hiker at the top of a mountain b. A dog chasing a cat c. A rubber band being stretched Agenda: How can we calculate
Do Now: 1. Hand in your Forms of Energy Wheel 2. Identify the following forms of energy: a. A hiker at the top of a mountain b. A dog chasing a cat c. A rubber band being stretched Agenda: How can we calculate
What is Work? W = Fd. Whenever you apply a force to an object and the object moves in the direction of the force, work is done.
 Year 10 Physics What is Work? Whenever you apply a force to an object and the object moves in the direction of the force, work is done. If force is measured in newtons (N) and distance moved in metres,
Year 10 Physics What is Work? Whenever you apply a force to an object and the object moves in the direction of the force, work is done. If force is measured in newtons (N) and distance moved in metres,
As the mass travels along the track, the maximum height it will reach above point E will be closest to A) 10. m B) 20. m C) 30. m D) 40.
 1. As a pendulum swings from position A to position B as shown in the diagram, its total mechanical energy (neglecting friction) A) decreases B) increases C) remains the same 2. Base your answer to the
1. As a pendulum swings from position A to position B as shown in the diagram, its total mechanical energy (neglecting friction) A) decreases B) increases C) remains the same 2. Base your answer to the
Student Exploration: Energy of a Pendulum
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Energy of a Pendulum Vocabulary: conservation of energy, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, pendulum, potential energy, velocity Prior Knowledge Questions
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Energy of a Pendulum Vocabulary: conservation of energy, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, pendulum, potential energy, velocity Prior Knowledge Questions
1. A force acts on a particle and displaces it through. The value of x for zero work is 1) 0.5 2) 2 4) 6
 1. A force acts on a particle and displaces it through. The value of x for zero work is 1) 0.5 2) 2 3) +2 4) 6 2. Two bodies with K.E. in the ratio 4 : 1 are moving with same linear momenta. The ratio
1. A force acts on a particle and displaces it through. The value of x for zero work is 1) 0.5 2) 2 3) +2 4) 6 2. Two bodies with K.E. in the ratio 4 : 1 are moving with same linear momenta. The ratio
5.3. Conservation of Energy
 5.3. Conservation of Energy Conservation of Energy Energy is never created or destroyed. Any time work is done, it is only transformed from one form to another: Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Gravitational,
5.3. Conservation of Energy Conservation of Energy Energy is never created or destroyed. Any time work is done, it is only transformed from one form to another: Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Gravitational,
Lab: Energy-Rubber Band Cannon C O N C E P T U A L P H Y S I C S : U N I T 4
 Name Date Period Objectives: Lab: Energy-Rubber Band Cannon C O N C E P T U A L P H Y S I C S : U N I T 4 1) Find the energy stored within the rubber band cannon for various displacements. 2) Find the
Name Date Period Objectives: Lab: Energy-Rubber Band Cannon C O N C E P T U A L P H Y S I C S : U N I T 4 1) Find the energy stored within the rubber band cannon for various displacements. 2) Find the
Scaler Quantity (definition and examples) Average speed. (definition and examples)
 Newton s First Law Newton s Second Law Newton s Third Law Vector Quantity Scaler Quantity (definition and examples) Average speed (definition and examples) Instantaneous speed Acceleration An object at
Newton s First Law Newton s Second Law Newton s Third Law Vector Quantity Scaler Quantity (definition and examples) Average speed (definition and examples) Instantaneous speed Acceleration An object at
Grade 8 Science, Quarter 3, Unit 3.1. Energy. Overview
 Energy Overview Number of instructional days: 20 (1 day = 50 minutes) Content to be learned Show that within a system, energy transforms from one form to another. Show the transfer of potential energy
Energy Overview Number of instructional days: 20 (1 day = 50 minutes) Content to be learned Show that within a system, energy transforms from one form to another. Show the transfer of potential energy
Clicker Question: Momentum. If the earth collided with a meteor that slowed it down in its orbit, what would happen: continued from last time
 Momentum continued from last time If the earth collided with a meteor that slowed it down in its orbit, what would happen: A: It would maintain the same distance from the sun. B: It would fall closer in
Momentum continued from last time If the earth collided with a meteor that slowed it down in its orbit, what would happen: A: It would maintain the same distance from the sun. B: It would fall closer in
Physical Science Final Examination-Review Sheet (14-15) KEY. 1. A process used to answer questions or solve problems is called scientific inquiry.
 Physical Science Final Examination-Review Sheet (14-15) KEY 1. A process used to answer questions or solve problems is called scientific inquiry. 2. Anything that has mass and takes up space is matter.
Physical Science Final Examination-Review Sheet (14-15) KEY 1. A process used to answer questions or solve problems is called scientific inquiry. 2. Anything that has mass and takes up space is matter.
law of conservation of energy energy
 What happens when? 6.8A compare and contrast potential and kinetic energy 6.9 Law of Conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. How does it work? Explanation If you
What happens when? 6.8A compare and contrast potential and kinetic energy 6.9 Law of Conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. How does it work? Explanation If you
Physical Science midterm study guide. Chapter 1 and 2
 Physical Science midterm study guide Chapter 1 and 2 1. Explain the difference between a scientific law and a scientific theory a. Laws generalize observations b. Theories explain observations 2. Select
Physical Science midterm study guide Chapter 1 and 2 1. Explain the difference between a scientific law and a scientific theory a. Laws generalize observations b. Theories explain observations 2. Select
The Story of Energy. Forms and Functions
 The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 7
 INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 7 EXPLAINING MELTING AND SOLIDIFYING A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals Students should be able to explain melting and solidifying, by reference to the molecular
INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 7 EXPLAINING MELTING AND SOLIDIFYING A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals Students should be able to explain melting and solidifying, by reference to the molecular
Problem Solver Skill 5. Defines multiple or complex problems and brainstorms a variety of solutions
 Motion and Forces Broad Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. LS 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (such as, displacement, velocity,
Motion and Forces Broad Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. LS 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (such as, displacement, velocity,
Magnets and Potential Energy
 efinitions of Energy Magnets and Potential Energy 1 Potential energy (PE), also known as stored energy, is the energy stored within a physical system. Since energy can be defined as the ability to do work
efinitions of Energy Magnets and Potential Energy 1 Potential energy (PE), also known as stored energy, is the energy stored within a physical system. Since energy can be defined as the ability to do work
Connections to NGSS, CCSS-Mathematics, and CCSS-ELA/Literacy are at the end of this document.
 Conservation of Energy at the Skate Park Student Prior Knowledge: The equations for KE and PE and relationships of these with speed and height. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transported
Conservation of Energy at the Skate Park Student Prior Knowledge: The equations for KE and PE and relationships of these with speed and height. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transported
4 A mass-spring oscillating system undergoes SHM with a period T. What is the period of the system if the amplitude is doubled?
 Slide 1 / 52 1 A block with a mass M is attached to a spring with a spring constant k. The block undergoes SHM. Where is the block located when its velocity is a maximum in magnitude? A 0 B + or - A C
Slide 1 / 52 1 A block with a mass M is attached to a spring with a spring constant k. The block undergoes SHM. Where is the block located when its velocity is a maximum in magnitude? A 0 B + or - A C
Physics A - PHY 2048C
 Kinetic Mechanical Physics A - PHY 2048C and 11/01/2017 My Office Hours: Thursday 2:00-3:00 PM 212 Keen Building Warm-up Questions Kinetic Mechanical 1 How do you determine the direction of kinetic energy
Kinetic Mechanical Physics A - PHY 2048C and 11/01/2017 My Office Hours: Thursday 2:00-3:00 PM 212 Keen Building Warm-up Questions Kinetic Mechanical 1 How do you determine the direction of kinetic energy
1 Forces. 2 Energy & Work. GS 104, Exam II Review
 1 Forces 1. What is a force? 2. Is weight a force? 3. Define weight and mass. 4. In European countries, they measure their weight in kg and in the United States we measure our weight in pounds (lbs). Who
1 Forces 1. What is a force? 2. Is weight a force? 3. Define weight and mass. 4. In European countries, they measure their weight in kg and in the United States we measure our weight in pounds (lbs). Who
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up What is energy, and what are energy transformations? What do you think?
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up What is energy, and what are energy transformations? What do you think?
Energy Notes. Name: Hr:
 Energy Notes Name: Hr: Guided Outline 5-1 Nature of Energy Directions: As you read through Chapter 5 in your textbook, fill in the missing information. I. Section 1: Nature of Energy A. What is Energy?
Energy Notes Name: Hr: Guided Outline 5-1 Nature of Energy Directions: As you read through Chapter 5 in your textbook, fill in the missing information. I. Section 1: Nature of Energy A. What is Energy?
Gases have important properties that distinguish them from solids and liquids:
 Kinetic molecular theory Gases have important properties that distinguish them from solids and liquids: Gases diffuse to occupy available space. For example, the molecules responsible for the scent of
Kinetic molecular theory Gases have important properties that distinguish them from solids and liquids: Gases diffuse to occupy available space. For example, the molecules responsible for the scent of
Energy ~ Learning Guide Name:
 Energy ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
Energy ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up What is energy, and what are energy transformations? What do you think?
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up What is energy, and what are energy transformations? What do you think?
Work changes Energy. Do Work Son!
 1 Work changes Energy Do Work Son! 2 Do Work Son! 3 Work Energy Relationship 2 types of energy kinetic : energy of an object in motion potential: stored energy due to position or stored in a spring Work
1 Work changes Energy Do Work Son! 2 Do Work Son! 3 Work Energy Relationship 2 types of energy kinetic : energy of an object in motion potential: stored energy due to position or stored in a spring Work
PHYS 154 Practice Test 3 Spring 2018
 The actual test contains 1 multiple choice questions and 2 problems. However, for extra exercise, this practice test includes 4 problems. Questions: N.B. Make sure that you justify your answers explicitly
The actual test contains 1 multiple choice questions and 2 problems. However, for extra exercise, this practice test includes 4 problems. Questions: N.B. Make sure that you justify your answers explicitly
WORK, ENERGY & POWER Work scalar W = F S Cosθ Unit of work in SI system Work done by a constant force
 WORK, ENERGY & POWER Work Let a force be applied on a body so that the body gets displaced. Then work is said to be done. So work is said to be done if the point of application of force gets displaced.
WORK, ENERGY & POWER Work Let a force be applied on a body so that the body gets displaced. Then work is said to be done. So work is said to be done if the point of application of force gets displaced.
Final Review. If a car has 3,000kg-m/s of momentum, and a mass of 1,000kg. How fast is it moving? A ball that has momentum must also have energy.
 Physics Name: Date: Period: Final Review Write the appropriate formulas with all units below. Impulse Momentum Conservation of Momentum Rank these in order from least to most momentum:.01kg mass moving
Physics Name: Date: Period: Final Review Write the appropriate formulas with all units below. Impulse Momentum Conservation of Momentum Rank these in order from least to most momentum:.01kg mass moving
ENERGY IN CHEMISTRY. R. Ashby Duplication by permission only.
 CH 11 TOPIC 28 CHANGING STATES OF MATTER 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) define or describe: ENERGY, POTENTIAL ENERGY, KINETIC ENERGY & KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY 2) define or describe HEAT
CH 11 TOPIC 28 CHANGING STATES OF MATTER 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) define or describe: ENERGY, POTENTIAL ENERGY, KINETIC ENERGY & KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY 2) define or describe HEAT
First Year Physics: Prelims CP1 Classical Mechanics: DR. Ghassan Yassin
 First Year Physics: Prelims CP1 Classical Mechanics: DR. Ghassan Yassin MT 2007 Problems I The problems are divided into two sections: (A) Standard and (B) Harder. The topics are covered in lectures 1
First Year Physics: Prelims CP1 Classical Mechanics: DR. Ghassan Yassin MT 2007 Problems I The problems are divided into two sections: (A) Standard and (B) Harder. The topics are covered in lectures 1
Lesson 6: How to Calculate Kinetic Energy
 KREUTTER:WORK AND ENERGY 1 Lesson 6: How to Calculate Kinetic Energy 6.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) In a car crash testing facility, engineers evaluate the reaction of a car to a front impact.
KREUTTER:WORK AND ENERGY 1 Lesson 6: How to Calculate Kinetic Energy 6.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) In a car crash testing facility, engineers evaluate the reaction of a car to a front impact.
Gravitational Potential Energy
 Name: Directions: Read and answer the following questions. You can then go on to my web page and check your answers. At the conclusion, go to schoology.com and complete the PE assignment. Gravitational
Name: Directions: Read and answer the following questions. You can then go on to my web page and check your answers. At the conclusion, go to schoology.com and complete the PE assignment. Gravitational
Name. Date. Period. Engage
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 7.a Work, Gravitational Potential, and Kinetic Energy Outcomes 1. Define work. 2. Define energy. 3. Determine the work done by a constant force. 4. Determine the work done by a force
AP Physics 1 Lesson 7.a Work, Gravitational Potential, and Kinetic Energy Outcomes 1. Define work. 2. Define energy. 3. Determine the work done by a constant force. 4. Determine the work done by a force
AP PHYSICS 1 UNIT 4 / FINAL 1 PRACTICE TEST
 AP PHYSICS 1 UNIT 4 / FINAL 1 PRACTICE TEST NAME FREE RESPONSE PROBLEMS Put all answers on this test. Show your work for partial credit. Circle or box your answers. Include the correct units and the correct
AP PHYSICS 1 UNIT 4 / FINAL 1 PRACTICE TEST NAME FREE RESPONSE PROBLEMS Put all answers on this test. Show your work for partial credit. Circle or box your answers. Include the correct units and the correct
Reviewing the Alignment of IPS with NGSS
 Reviewing the Alignment of IPS with NGSS Harold A. Pratt & Robert D. Stair Introductory Physical Science (IPS) was developed long before the release of the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS); nevertheless,
Reviewing the Alignment of IPS with NGSS Harold A. Pratt & Robert D. Stair Introductory Physical Science (IPS) was developed long before the release of the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS); nevertheless,
FM: WARM-UP. Students gather evidence about the velocity change of objects in a collision. (10 min)
 CH.3 COLLISIONS FM: 3.3.1 WARM-UP Students gather evidence about the velocity change of objects in a collision. (10 min) Both Objects will Change Velocity Only 1 Object will Change Velocity Neither Object
CH.3 COLLISIONS FM: 3.3.1 WARM-UP Students gather evidence about the velocity change of objects in a collision. (10 min) Both Objects will Change Velocity Only 1 Object will Change Velocity Neither Object
Energy Unit Test * Required
 Energy Unit Test * Required 1. First and Last Name 2. Class Period 2nd 4th Forms of Energy Standard 6.PS3.1 Analyze the properties and compare sources of kinetic, elastic potential, gravitational potential,
Energy Unit Test * Required 1. First and Last Name 2. Class Period 2nd 4th Forms of Energy Standard 6.PS3.1 Analyze the properties and compare sources of kinetic, elastic potential, gravitational potential,
Universal Gravitation. A Core Learning Goals Activity for Science and Mathematics
 CoreModels Universal Gravitation A Core Learning Goals Activity for Science and Mathematics Summary: Students construct a STELLA model to demonstrate the effect of universal gravitation between two objects.
CoreModels Universal Gravitation A Core Learning Goals Activity for Science and Mathematics Summary: Students construct a STELLA model to demonstrate the effect of universal gravitation between two objects.
Key Performance Task
 COURSE UNIT PERIOD PAGE SPH3U Energy Conservation of Mechanical Energy 1 of 2 Overall Expectation D2. investigate energy transformations and the law of conservation of energy, and solve related problems
COURSE UNIT PERIOD PAGE SPH3U Energy Conservation of Mechanical Energy 1 of 2 Overall Expectation D2. investigate energy transformations and the law of conservation of energy, and solve related problems
Lesson Plan: Modeling the Melting of Ice FOR THE TEACHER
 Lesson Plan: Modeling the Melting of Ice FOR THE TEACHER Instructional Notes and Answers In our exploration of the tiles, we ended with a macroscopic model of thermal energy transfer as well as a model
Lesson Plan: Modeling the Melting of Ice FOR THE TEACHER Instructional Notes and Answers In our exploration of the tiles, we ended with a macroscopic model of thermal energy transfer as well as a model
Electric energy Radiant energy Nuclear energy
 CHAPTER 7 LESSON 1: FORMS OF ENERGY Potential Energy Stored Energy Energy Kinetic Potential Work What is Energy? Mechanical Sound Thermal Electric Radiant Nuclear Potential is stored due to the interactions
CHAPTER 7 LESSON 1: FORMS OF ENERGY Potential Energy Stored Energy Energy Kinetic Potential Work What is Energy? Mechanical Sound Thermal Electric Radiant Nuclear Potential is stored due to the interactions
Energy, Work, and Power
 Matthew W. Milligan, Work, and Power Conservation Laws an Alternative to Newton s Laws Matthew W. Milligan, Work, and Power I. - kinetic and potential - conservation II. Work - dot product - work-energy
Matthew W. Milligan, Work, and Power Conservation Laws an Alternative to Newton s Laws Matthew W. Milligan, Work, and Power I. - kinetic and potential - conservation II. Work - dot product - work-energy
Energy Conservation AP
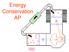 Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
The Story of Energy. Forms and Functions
 The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
Forces in Two Dimensions Teacher s Guide
 Forces in Two Dimensions Teacher s Guide 1.0 Summary Forces in Two Dimensions is the sixth activity in the Dynamica sequence. This activity should be done after Balancing Force and it should take students
Forces in Two Dimensions Teacher s Guide 1.0 Summary Forces in Two Dimensions is the sixth activity in the Dynamica sequence. This activity should be done after Balancing Force and it should take students
Introduction to Energy Study Guide (also use your notes!!!!)
 Introduction to Energy Study Guide (also use your notes!!!!) 1. What is energy? The ability to do work 2. What is kinetic energy? The energy of motion (movement) 3. Can objects with kinetic energy do work?
Introduction to Energy Study Guide (also use your notes!!!!) 1. What is energy? The ability to do work 2. What is kinetic energy? The energy of motion (movement) 3. Can objects with kinetic energy do work?
A Correlation of Pearson Physics 2014
 A Correlation of Pearson Physics Ohio s New Learning Standards for Science, 2011 Physics, High School Science Inquiry and Application Course Content A Correlation of, INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates
A Correlation of Pearson Physics Ohio s New Learning Standards for Science, 2011 Physics, High School Science Inquiry and Application Course Content A Correlation of, INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates
HOMEWORK ANSWERS. Lesson 4.1: Simple Harmonic Motion
 DEVIL PHYSICS HOMEWORK ANSWERS Tsokos, Chapter 3 Test Lesson 4.1: Simple Harmonic Motion 1. Objectives. By the end of this class you should be able to: a) Understand that in simple harmonic motion there
DEVIL PHYSICS HOMEWORK ANSWERS Tsokos, Chapter 3 Test Lesson 4.1: Simple Harmonic Motion 1. Objectives. By the end of this class you should be able to: a) Understand that in simple harmonic motion there
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist
 Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Physics Paper 2
 6.5.1 Forces and their interactions 6.5.2 Work done and energy transfer AQA TRILOGY Physics (8464) from 2016 Topics T6.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and
6.5.1 Forces and their interactions 6.5.2 Work done and energy transfer AQA TRILOGY Physics (8464) from 2016 Topics T6.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist
 Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Alief ISD Middle School Science STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Force, Motion, & Energy
 8.6.A demonstrate and calculate how unbalanced forces change the speed or direction of an object s motion Alief ISD Middle School Science STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Force, Motion, & Energy Force
8.6.A demonstrate and calculate how unbalanced forces change the speed or direction of an object s motion Alief ISD Middle School Science STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Force, Motion, & Energy Force
States of Matter. Changes in State
 CHAPTER 8 States of Matter LESSON 2 Changes in State What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
CHAPTER 8 States of Matter LESSON 2 Changes in State What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
RELEASED. Spring 2013 North Carolina Measures of Student Learning: NC s Common Exams
 Released Form Spring 2013 North arolina Measures of Student Learning: N s ommon Exams Physics RELESE Public Schools of North arolina State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction Raleigh, North
Released Form Spring 2013 North arolina Measures of Student Learning: N s ommon Exams Physics RELESE Public Schools of North arolina State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction Raleigh, North
Chapter 10 Notes: Gases
 Chapter 10 Notes: Gases Watch Bozeman Videos & other videos on my website for additional help: Big Idea 2: Gases 10.1 Characteristics of Gases Read p. 398-401. Answer the Study Guide questions 1. Earth
Chapter 10 Notes: Gases Watch Bozeman Videos & other videos on my website for additional help: Big Idea 2: Gases 10.1 Characteristics of Gases Read p. 398-401. Answer the Study Guide questions 1. Earth
Grade 7 Science. Enduring Understanding and Essential Questions Competencies Concepts Key Vocabulary
 Unit: The Scientific Method Length: 3 WEEKS Grade 7 Science Enduring Understanding and Essential Questions Competencies Concepts Key Vocabulary The scientific method is problem solving guide based on identification
Unit: The Scientific Method Length: 3 WEEKS Grade 7 Science Enduring Understanding and Essential Questions Competencies Concepts Key Vocabulary The scientific method is problem solving guide based on identification
Gravitation & Kepler s Laws
 Gravitation & Kepler s Laws What causes YOU to be pulled down to the surface of the earth? THE EARTH.or more specifically the EARTH S MASS. Anything that has MASS has a gravitational pull towards it. F
Gravitation & Kepler s Laws What causes YOU to be pulled down to the surface of the earth? THE EARTH.or more specifically the EARTH S MASS. Anything that has MASS has a gravitational pull towards it. F
Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1
 Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1 Name Multiple Choice Questions 1. A block with a mass M is attached to a spring with a spring constant k. The block undergoes SHM. Where is the
Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1 Name Multiple Choice Questions 1. A block with a mass M is attached to a spring with a spring constant k. The block undergoes SHM. Where is the
Since reactions want to minimize energy you would think that the reaction would be spontaneous like a ball rolling down a hill
 Notes 1.1 Exothermic reactions give off heat 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 2 4 6 Heat Content Since reactions want to minimize energy you would think that the reaction would be spontaneous like a ball rolling
Notes 1.1 Exothermic reactions give off heat 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 2 4 6 Heat Content Since reactions want to minimize energy you would think that the reaction would be spontaneous like a ball rolling
Seminary 3 and 4 Work, energy, momentum and conservation laws
 Seminary 3 and 4 Work, energy, momentum and conservation laws SEMINARY 3 The unsolved problems are given as homework. 1/ Work, Kinetic, Potential, Total Energy. Conservation laws DISCUSSION: Briefly remember
Seminary 3 and 4 Work, energy, momentum and conservation laws SEMINARY 3 The unsolved problems are given as homework. 1/ Work, Kinetic, Potential, Total Energy. Conservation laws DISCUSSION: Briefly remember
Chapter 14: Periodic motion
 Chapter 14: Periodic motion Describing oscillations Simple harmonic motion Energy of simple harmonic motion Applications of simple harmonic motion Simple pendulum & physical pendulum Damped oscillations
Chapter 14: Periodic motion Describing oscillations Simple harmonic motion Energy of simple harmonic motion Applications of simple harmonic motion Simple pendulum & physical pendulum Damped oscillations
Section 1: Work, Power, and Machines. Preview Key Ideas Bellringer What Is Work? Math Skills Power Machines and Mechanical Advantage
 Section 1 Section 1: Work, Power, and Machines Preview Key Ideas Bellringer What Is Work? Math Skills Power Machines and Mechanical Advantage Section 1 Key Ideas How is work calculated? What is the relationship
Section 1 Section 1: Work, Power, and Machines Preview Key Ideas Bellringer What Is Work? Math Skills Power Machines and Mechanical Advantage Section 1 Key Ideas How is work calculated? What is the relationship
Temperature, Thermal Energy, and Heat
 Temperature, Thermal Energy, and Heat Textbook pages 424 435 Section 10.1 Summary Before You Read We often use the terms heat and temperature interchangeably. Do you think they mean the same thing? Explain
Temperature, Thermal Energy, and Heat Textbook pages 424 435 Section 10.1 Summary Before You Read We often use the terms heat and temperature interchangeably. Do you think they mean the same thing? Explain
2. What is the force weight of a 45 kg desk? 3. Give a scenario example for each of Newton s Laws.
 Catalyst 1.What is the unit for force? Newton (N) 2. What is the force weight of a 45 kg desk? 3. Give a scenario example for each of Newton s Laws. HANDS UP!! 441 N 4. What is net force? Give an example.
Catalyst 1.What is the unit for force? Newton (N) 2. What is the force weight of a 45 kg desk? 3. Give a scenario example for each of Newton s Laws. HANDS UP!! 441 N 4. What is net force? Give an example.
1.2 Energy of Charged Particles
 1.2 Energy of Charged Particles Objective 1: Recall Coulomb s Law which states that the electrostatic force between 2 charged particles is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
1.2 Energy of Charged Particles Objective 1: Recall Coulomb s Law which states that the electrostatic force between 2 charged particles is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Work and Energy Experiments
 Work and Energy Experiments Experiment 16 When a juggler tosses a bean ball straight upward, the ball slows down until it reaches the top of its path and then speeds up on its way back down. In terms of
Work and Energy Experiments Experiment 16 When a juggler tosses a bean ball straight upward, the ball slows down until it reaches the top of its path and then speeds up on its way back down. In terms of
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS LSN 11-1: SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION LSN 11-: ENERGY IN THE SIMPLE HARMONIC OSCILLATOR LSN 11-3: PERIOD AND THE SINUSOIDAL NATURE OF SHM Introductory Video:
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS LSN 11-1: SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION LSN 11-: ENERGY IN THE SIMPLE HARMONIC OSCILLATOR LSN 11-3: PERIOD AND THE SINUSOIDAL NATURE OF SHM Introductory Video:
Purpose of the experiment
 Work and Energy PES 1160 General Physics Lab I Purpose of the experiment What is Work and how is related to Force? To understand the work done by a constant force and a variable force. To see how gravitational
Work and Energy PES 1160 General Physics Lab I Purpose of the experiment What is Work and how is related to Force? To understand the work done by a constant force and a variable force. To see how gravitational
Science Is A Verb! Part 7. Let s do it! ISBN
 Let s do it! Science Is A Verb! Part 7 ISBN 978-1-847003-60-7 Contents INTRODUCTION Lab Title Where are we positioned? Students know position is defined in relation to some choice of a standard reference
Let s do it! Science Is A Verb! Part 7 ISBN 978-1-847003-60-7 Contents INTRODUCTION Lab Title Where are we positioned? Students know position is defined in relation to some choice of a standard reference
1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B km C. 25 km D. 45 km E. 50 km
 Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
