Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
- Jonathan Hoover
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemi1100pretest1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Accordingly to the periodic law the properties of elements repeat at regular intervals when the elements are arranged in order of a. their increasing atomic mass. b. their increasing atomic size. c. their increasing number of neutrons in the nucleus. d. their increasing number of isotopes. e. their increasing number of protons in the nucleus. 2. Which electrons have the greatest influence on the properties of elements? a. those electrons in s orbitals b. those electrons in d orbitals c. core electrons d. the outermost electrons e. none of these 3. is a d-transition metal. a. Cr b. Ga c. Sn d. Sb e. Li 4. Which one of the following is an inner transition (f-transition) element? a. Rb b. Ho c. Co d. Ru e. Bi 5. Which of the following is not a representative element? a. Cl b. Sr c. Co d. K e. N 6. What would be the outer electron configuration of group VIA (O, S, Se,...)? a. ns 2 np 6 b. ns 2 np 2 c. ns 2 np 4 d. np 6 e. ns 0 np 6 7. What would be the outer electron configuration of alkaline earth metals? a. ns 2 np 2 b. np 2 c. ns 0 np 2
2 d. nd 2 e. ns 2 8. Choose the term that best describes all members of this series of elements: Xe, Rn, He, Ne, Kr a. metalloids b. noble gases c. alkaline earth metals d. alkali metals e. representative elements 9. Which element has the largest atomic radius? a. Al b. Si c. P d. S e. Cl 10. Arrange the following elements in order of increasing atomic radii. K, Na, Mg, Cs, Cl a. Na < Mg < Cl < K < Cs b. Cl < Mg < Na < K < Cs c. Cs < K < Cl < Mg < Na d. Cl < Mg < Cs < K < Na e. Cl < Mg < Na < Cs < K 11. Which element has the lowest first ionization energy? a. Cs b. Rb c. Ca d. Ba e. Na 12. Which of the following elements has the most negative electron affinity? a. Si b. P c. S d. Se e. Te 13. Which one of the following species is not isoelectronic with neon? a. Mg 2+ b. Na + c. O 2 d. Si 2+ e. Al Which ion has the largest radius? a. Li + b. Na + c. Be 2+
3 d. Mg 2+ e. Al Simple positively charged ions are always than the neutral atoms from which they are formed. a. smaller b. larger c. isoelectronic d. the same size e. more anionic 16. Arrange the following elements in order of decreasing electronegativities. Al, Cs, Mg, Na, P a. P > Al > Mg > Na > Cs b. Cs > Na > Mg > Al > P c. Al > Mg > Na > Cs > P d. P > Al > Mg > Cs > Na e. P > Cs > Na > Mg > Al 17. Which of the following pairs of elements would be expected to form an ionic compound? a. S / F b. H / C c. Rb / Cl d. As / Br e. C / I 18. Which of the following oxides does not give an acidic solution when dissolved in water? a. SO 2 b. CO 2 c. N 2 O 5 d. P 4 O 10 e. Na 2 O 19. An amphoteric compound exhibits a. acidic properties. b. acidic and basic properties. c. metallic properties. d. basic properties. e. ionic properties. 20. Atoms consist of three fundamental particles. What are these particles and their charges? a. proton (+1), neutron (neutral) and electron ( 1) b. proton ( 1), neutron (+1) and electron (neutral) c. proton (+1), neutron ( 1) and electron (neutral) d. proton (neutral), neutron (+1) and electron ( 1) e. proton ( 1), neutron (neutral) and electron (+1) 21. One of the following does not describe solids. Which one is it? a. Particles in definite positions. b. Definite shape. c. Easily compressed. d. Relatively high densities.
4 e. Particles compact. 22. All of the following are properties of antimony. Which one is not a physical property? a. It is a solid at room temperature. b. It has both yellow and gray forms (allotropes) in the solid state. c. It burns in an atmosphere of chlorine. d. It is one of the few substances that expands upon freezing. e. The gray form melts at 631 C. 23. The following statements describe some physical and chemical properties of sucrose (table sugar). Which response includes all that describe chemical properties, and none that describe physical properties? I. It is a colorless solid. II. It chars or blackens when heated gently. III. Its density is 1.6 g/ml. IV. It ignites and burns with a yellow flame when heated strongly. V. It is usually in the form of small crystals although it can occur as a powder. a. I, III, and IV b. II and IV c. II, IV, and V d. I and V e. another combination is the answer 24. Which of the following is not an intensive property of matter? a. color b. density c. melting point d. weight e. boiling point 25. Which response includes all of the following that involve chemical changes, and none that involve physical changes? I. converting milk to cheese II. converting water to steam III. composting leaves IV. burning of gasoline V. melting wax a. II and V b. I, III, and IV c. I, II, and III d. IV and V e. III, IV, and V 26. Which mixture is incorrectly labeled? a. homogeneous / sugar dissolved in water b. homogeneous / sand stirred into water c. heterogeneous / orange juice with pulp d. heterogeneous / chocolate chip cookie e. heterogeneous / concrete sidewalk 27. What is the symbol for the element potassium?
5 a. K b. P c. Pt d. W e. Po 28. Water is always 11.1% hydrogen and 88.9 % oxygen by mass. This is a statement of the a. Law of Conservation of Matter. b. Law of Definite Proportions. c. Law of Multiple Proportions. d. Law of Conservation of Matter and Energy. e. none of these. 29. Below is a list of physical properties and the fundamental unit used in the SI system to measure each. Which unit is not the correct fundamental unit for the property? physical property / unit a. length / meter b. time / second c. mass / gram d. temperature / kelvin e. electric current / ampere 30. Below is a list of common prefixes used in the SI and metric systems. Included with each is an abbreviation and meaning. Which set contains an error? a. mega- M 10 6 b. deci- d 10 1 c. centi- c 10 2 d. micro- m 10 6 e. kilo- k Which of the following is equivalent to 10 cm? a. 1 m b. 0.1 dm c. 100 mm d m e. 1 mm 32. Which of the following numbers has 4 significant figures? a b c d e The sum expressed to the proper number of significant figures is: a. 439 b c d e
6 34. Perform the indicated mathematical operations and express the answer in scientific notation rounded off to the proper number of significant figures: ( ) ( ) = a b c d e If neon atoms (spherical) were laid in a line, each touching the next, the line would measure 2.54 miles. What is the diameter of a neon atom in Å? (1 Å=1x10 10 m) a Å b Å c Å d Å e Å 36. What is the area in square millimeters of a rectangle that is cm long and mm wide? a mm 2 b mm 2 c mm 2 d mm 2 e mm At 25 C, one milliliter of mercury has a mass of 13.6 grams. How many liters of mercury are required to have a mass of 500 kg of mercury? a. 500 L b L c L d L e L 38. A metal cube having a mass of 112 grams is dropped into a graduated cylinder containing ml of water. This causes the water level to rise to ml. What is the density of the cube? a g/ml b g/ml c g/ml d g/ml e g/ml 39. The density of mercury is 13.6 g/cm 3. What is the mass of 6.50 cm 3 of mercury? a g b g c g d g e g 40. Gallium, a metal, has a freezing point near room temperature so it can be melted by holding it in your hands. If gallium's melting point is K, what is that temperature in C?
7 a. 0.0 C b C c C d C e C 41. If a sample of butane, C 4 H 10, contains a total of atoms of carbon, how many molecules of butane are in the sample? a b c d e Each response below lists an ion by name and by chemical symbol or formula. Also each ion is classified as monatomic or polyatomic and as a cation or anion. Which response contains an error? a. hydroxide / OH / monatomic / anion b. carbonate / CO 2 3 / polyatomic / anion c. + ammonium / NH 4 / polyatomic / cation d. magnesium / Mg 2+ / monatomic / cation e. sulfite / SO 2 3 / polyatomic / anion 43. What is the formula for ammonium fluoride? a. AlF b. Al 2 F 3 c. NH 3 F d. NH 4 F 2 e. NH 4 F 44. What is the formula for aluminum oxide? a. Al 2 O 3 b. Ag 2 O 3 c. AlO 3 d. AlO e. AlO Calculate the number of moles of oxygen atoms in 35.2 grams of oxygen. a moles b moles c moles d moles e moles 46. Determine the number of sulfur atoms in 27.1 g of molecular sulfur (S 8 ). a b c d e
8 47. Calculate the formula weight of NaHSO 4. a. 193 amu b. 104 amu c. 120 amu d. 215 amu e. 185 amu 48. What is the mass in grams of water molecules? a g b g c g d g e g 49. Which of the following has no charge? a. nucleus b. neutron c. proton d. electron e. alpha particle 50. In interpreting the results of his "oil drop" experiment in 1909, Robert Millikan was able to determine. a. the charge on a proton b. that electrically neutral particles (neutrons) are present in the nuclei of atoms c. that the masses of protons and neutrons are nearly identical d. the charge on an electron e. the extremely dense nature of the nuclei of atoms 51. In the Rutherford gold foil experiment, the fact that most of the alpha particles were not deflected as they passed through the gold foil indicates that a. the nucleus is positively charged. b. the atom is mostly empty space. c. atoms are solid spheres touching each other in the solid state. d. gold is very dense. e. none of these is correct. 52. The number of electrons in a neutral atom of an element is always equal to the of the element. a. mass number b. atomic number c. atomic mass unit d. isotope number e. Avogadro's number 53. The atomic number of an element gives the number of and in the atom while the mass number gives the total number of and. a. neutrons; protons; neutrons; electrons b. neutrons; electrons; protons; electrons c. neutrons; electrons; neutrons; protons d. protons; electrons; neutrons; electrons e. protons; electrons; neutrons; protons
9 54. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that a. have different numbers of electrons. b. have different numbers of protons. c. have different atomic numbers. d. have different numbers of neutrons. e. have different nuclear charges. 55. Give the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom of the 90 Sr isotope. a. 38 p; 38 n; 38 e b. 38 p; 90 n; 38 e c. 52 p; 38 n; 52 e d. 38 p; 52 n; 38 e e. 90 p; 38 n; 90 e Chapter 4 Values The following values may be useful for solving some of the problem(s) below. speed of light = m/s 1 joule = 1 kg m 2 /s 2 Planck's constant = J s 1 Ångstrom = m 56. What is the wavelength of yellow light having a frequency of Hz? a m b m c m d m e m 57. What is the energy, in J/photon, of ultraviolet light with a frequency of Hz? a J/photon b J/photon c J/photon d J/photon e J/photon 58. Calculate the energy (J/photon) of a photon of wavelength m. a J b J c J d J e. none of these 59. The Rydberg equation is an empirical equation that describes mathematically. a. the lines in the emission spectrum of hydrogen b. the results of the oil drop experiment c. the results of the cathode ray experiments d. the Bohr model of the atom e. the possible paths of two isotopes of the same element in a mass spectrometer 60. What is the velocity of a neutron of mass kg that has a de Broglie wavelength of 2.05 Å?
10 a. 19 m/s b m/s c m/s d m/s e m/s 61. What statement regarding quantum numbers is false? a. The spin quantum number has values of either +1 or 1. b. The principle quantum number has only integer values. c. The angular momentum quantum number also has letter designations. d. The magnetic quantum number has its values restricted by the l quantum number. e. The magnetic quantum number is represented by m l. 62. Which response lists all the true statements about the four quantum numbers? I. n = principal quantum number, n = 1,2,3,... II. l = angular momentum quantum number, l = 0,1,2,3,..., (n 1) III. m l = magnetic quantum number, m l = 0, 1,..., l IV. m s = spin quantum number, m s = ± a. I, II, and IV b. I, II, and III c. I and III d. II and III e. II, III, and IV 63. The third energy level or shell of an atom can hold a maximum of electrons. a. 8 b. 2 c. 16 d. 18 e Which of the following is not a valid magnetic quantum number for the 3d set of orbitals? a. 1 b. 2 c. 0 d. 2 e What is the value of the angular momentum quantum number, l, for the following orbital? a. b. 1 c. 0 d. 1 e. 2
11 66. All orbitals of a given degenerate set must be singly occupied before pairing begins in that set is a statement of. a. the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle b. the Bohr Theory c. the Aufbau Principle d. Planck's Theory e. Hund's Rule 67. Which element has the electron configuration below? 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 3 a. V b. Ca c. P d. As e. Se 68. What is the electron configuration of tin, Sn? a. [Kr]5s 2 3d 10 3f 14 5p 4 b. [Kr]5s 2 3d 10 4d 14 5p 4 c. [Kr]5s 2 3d 10 4f 14 5p 2 d. [Kr]5s 2 4d 10 5p 2 e. [Xe]5s 2 4d 10 5p What is the electron configuration of the iron(iii) ion? a. Fe 3+ [Ar]4s 2 3d 3 b. Fe 3+ [Ar]3d 5 c. Fe 2+ [Ar]4s 2 3d 3 d. Fe 2+ [Ar]3d 5 e. Fe 3+ [Kr]3d Which of the following sets of quantum numbers could represent the highest energy electron in V 2+? a. b. c. d. e. n l m l m s Which of the following atoms has the greatest number of unpaired electrons in its ground state? a. Fe b. N c. S d. Ti
12 e. Cu
13 Chemi1100pretest1 Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: More About the Periodic Table 2. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: More About the Periodic Table 3. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: More About the Periodic Table 4. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: More About the Periodic Table 5. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: More About the Periodic Table 6. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: More About the Periodic Table 7. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: More About the Periodic Table 8. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: More About the Periodic Table 9. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Atomic Radii 10. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Atomic Radii 11. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Ionization Energy 12. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: Electron Affinity 13. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: Ionic Radii 14. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Ionic Radii 15. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Ionic Radii 16. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Electronegativity 17. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: Electronegativity 18. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: Oxygen and the Oxides 19. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Oxygen and the Oxides 20. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Chemistry A Molecular View of Matter 21. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: States of Matter 22. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: Chemical and Physical Properties 23. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Chemical and Physical Properties 24. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: Chemical and Physical Properties 25. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Chemical and Physical Changes 26. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Mixtures, Substances, Compounds, and Elements 27. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Mixtures, Substances, Compounds, and Elements 28. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Mixtures, Substances, Compounds, and Elements 29. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: Measurements in Chemistry 30. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: Measurements in Chemistry 31. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: Measurements in Chemistry 32. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Use of Numbers 33. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Use of Numbers 34. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: Use of Numbers 35. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: The Unit Factor Method (Dimensional Analysis) 36. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: The Unit Factor Method (Dimensional Analysis)
14 37. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: The Unit Factor Method (Dimensional Analysis) 38. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Density and Specific Gravity 39. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Density and Specific Gravity 40. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: Heat and Temperature 41. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: Chemical Formulas 42. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Ions and Ionic Compounds 43. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: Names and Formulas of Some Ionic Compounds 44. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Names and Formulas of Some Ionic Compounds 45. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: The Mole 46. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: The Mole 47. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: Formula Weights, Molecular Weights, and Moles 48. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Formula Weights, Molecular Weights, and Moles 49. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Fundamental Particles 50. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: The Discovery of Electrons 51. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Rutherford and the Nuclear Atom 52. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Atomic Number 53. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: Mass Number and Isotopes 54. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: Mass Number and Isotopes 55. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: Mass Number and Isotopes 56. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: Electromagnetic Radiation 57. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: Electromagnetic Radiation 58. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Electromagnetic Radiation 59. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Atomic Spectra and the Bohr Atom 60. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: The Wave Nature of the Electron 61. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: The Quantum Mechanical Picture of the Atom 62. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Quantum Numbers 63. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: Atomic Orbitals 64. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: Atomic Orbitals 65. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: Atomic Orbitals 66. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: Electron Configurations 67. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: Electron Configurations 68. ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: Electron Configurations 69. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Electron Configurations 70. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: Electron Configurations 71. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Paramagnetism and Diamagnetism
8. Which of the following could be an isotope of chlorine? (A) 37 Cl 17 (B) 17 Cl 17 (C) 37 Cl 17 (D) 17 Cl 37.5 (E) 17 Cl 37
 Electronic Structure Worksheet 1 Given the following list of atomic and ionic species, find the appropriate match for questions 1-4. (A) Fe 2+ (B) Cl (C) K + (D) Cs (E) Hg + 1. Has the electron configuration:
Electronic Structure Worksheet 1 Given the following list of atomic and ionic species, find the appropriate match for questions 1-4. (A) Fe 2+ (B) Cl (C) K + (D) Cs (E) Hg + 1. Has the electron configuration:
Chemistry CRT Study Guide First Quarter
 Number AL COS # 1. #1.0 Classify sodium chloride as an element, mixture, compound, or colloid. Compound 2. #1.0 Classify air as an element, mixture, compound, or colloid. Mixture 3. #1.0 Classify a blueberry
Number AL COS # 1. #1.0 Classify sodium chloride as an element, mixture, compound, or colloid. Compound 2. #1.0 Classify air as an element, mixture, compound, or colloid. Mixture 3. #1.0 Classify a blueberry
1. Ham radio operators often broadcast on the 6 meter band. The frequency of this electromagnetic radiation is MHz. a. 500 b. 200 c. 50 d. 20 e. 2.
 Name: Score: 0 / 60 points (0%) [1 open ended question not graded] Chapters 6&7 Practice Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Ham radio
Name: Score: 0 / 60 points (0%) [1 open ended question not graded] Chapters 6&7 Practice Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Ham radio
Test Topics: Periodic Table, Atomic Theory, Physical/Chemical Properties, Atom, Isotopes, Average Atomic Mass
 Elemental Properties Review Worksheet Test Topics: Periodic Table, Atomic Theory, Physical/Chemical Properties, Atom, Isotopes, Average Atomic Mass Periodic Table 1. List the element symbols for the following
Elemental Properties Review Worksheet Test Topics: Periodic Table, Atomic Theory, Physical/Chemical Properties, Atom, Isotopes, Average Atomic Mass Periodic Table 1. List the element symbols for the following
b. Na. d. So. 1 A basketball has more mass than a golf ball because:
 Chem I Semester Review All of the following are general characteristics of a substance in the liquid state except a. definite volume. c. not easily compressed. b. able to flow. d. definite shape. In the
Chem I Semester Review All of the following are general characteristics of a substance in the liquid state except a. definite volume. c. not easily compressed. b. able to flow. d. definite shape. In the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which one of the following is not one of the postulates of Dalton's atomic theory? A)
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which one of the following is not one of the postulates of Dalton's atomic theory? A)
Professor K. Section 8 Electron Configuration Periodic Table
 Professor K Section 8 Electron Configuration Periodic Table Schrödinger Cannot be solved for multielectron atoms We must assume the orbitals are all hydrogen-like Differences In the H atom, all subshells
Professor K Section 8 Electron Configuration Periodic Table Schrödinger Cannot be solved for multielectron atoms We must assume the orbitals are all hydrogen-like Differences In the H atom, all subshells
Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT.
 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
Unit 7 Study Guide: Name: KEY Atomic Concepts & Periodic Table
 Unit 7 Study Guide: Name: KEY Atomic Concepts & Periodic Table Focus Questions for the unit... How has the modern view of the atom changed over time? How does a chemist use symbols and notation to communicate
Unit 7 Study Guide: Name: KEY Atomic Concepts & Periodic Table Focus Questions for the unit... How has the modern view of the atom changed over time? How does a chemist use symbols and notation to communicate
CHEMISTRY I - HONORS MIDTERM REVIEW* *Test may cover other topics not included on this review, yet have been covered throughout the semester.
 Name Period CHEMISTRY I - HONORS MIDTERM REVIEW* *Test may cover other topics not included on this review, yet have been covered throughout the semester. Chapter 2 Measurement & Calculations Describe the
Name Period CHEMISTRY I - HONORS MIDTERM REVIEW* *Test may cover other topics not included on this review, yet have been covered throughout the semester. Chapter 2 Measurement & Calculations Describe the
Unit Two Test Review. Click to get a new slide. Choose your answer, then click to see if you were correct.
 Unit Two Test Review Click to get a new slide. Choose your answer, then click to see if you were correct. According to the law of definite proportions, any two samples of water, H2O, A. will be made up
Unit Two Test Review Click to get a new slide. Choose your answer, then click to see if you were correct. According to the law of definite proportions, any two samples of water, H2O, A. will be made up
Honors Chemistry: Chapter 4- Problem Set (with some 6)
 Honors Chemistry: Chapter 4- Problem Set (with some 6) All answers and work on a separate sheet of paper! Classify the following as always true (AT), sometimes true (ST), or never true (NT) 1. Atoms of
Honors Chemistry: Chapter 4- Problem Set (with some 6) All answers and work on a separate sheet of paper! Classify the following as always true (AT), sometimes true (ST), or never true (NT) 1. Atoms of
ATOMIC THEORY, PERIODICITY, and NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
 ATOMIC THEORY, PERIODICITY, and NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY Note: For all questions referring to solutions, assume that the solvent is water unless otherwise stated. 1. The nuclide is radioactive and decays by the
ATOMIC THEORY, PERIODICITY, and NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY Note: For all questions referring to solutions, assume that the solvent is water unless otherwise stated. 1. The nuclide is radioactive and decays by the
E J The electron s energy difference between the second and third levels is J. = J
 The wavelength of light emitted is 654 nm. = c f c 3.00 10 8 m/s f c 3.00 108 m 1s 6.54 10 7 m f 4.59 4.59 10 14 z 1 s 10 14 The frequency of the light emitted is 4.59 10 14 z. E hf h 6.63 10 34 J/z E
The wavelength of light emitted is 654 nm. = c f c 3.00 10 8 m/s f c 3.00 108 m 1s 6.54 10 7 m f 4.59 4.59 10 14 z 1 s 10 14 The frequency of the light emitted is 4.59 10 14 z. E hf h 6.63 10 34 J/z E
Ch. 1: Introduction to Chemistry. Ch. 2: Matter and Change
 Review Sheet for Chemistry First Semester Final Refer to your class notes, worksheets, and the textbook to complete this review sheet. Study early so that you will have time to ask questions about what
Review Sheet for Chemistry First Semester Final Refer to your class notes, worksheets, and the textbook to complete this review sheet. Study early so that you will have time to ask questions about what
CDO AP Chemistry Unit 5
 1. a. Calculate the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation that has a frequency of 5.56 MHz. b. Calculate the frequency of electromagnetic radiation that has a wavelength equal to 667 nm. 2. Electromagnetic
1. a. Calculate the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation that has a frequency of 5.56 MHz. b. Calculate the frequency of electromagnetic radiation that has a wavelength equal to 667 nm. 2. Electromagnetic
new experimental data, and can be modified
 Mass in grams 10 20 30 40 50 Name: Date: Period: CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review CHAPTERS 1 & 2: Scientific Method, Density, Metric Conversions, Accuracy/Precision, Significant Figures 1. Know
Mass in grams 10 20 30 40 50 Name: Date: Period: CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review CHAPTERS 1 & 2: Scientific Method, Density, Metric Conversions, Accuracy/Precision, Significant Figures 1. Know
A.P. Chemistry Practice Test - Ch. 7, Atomic Structure and Periodicity
 A.P. Chemistry Practice Test - Ch. 7, Atomic Structure and Periodicity 1) Ham radio operators often broadcast on the 6-meter band. The frequency of this electromagnetic radiation is MHz. A) 50 B) 20 C)
A.P. Chemistry Practice Test - Ch. 7, Atomic Structure and Periodicity 1) Ham radio operators often broadcast on the 6-meter band. The frequency of this electromagnetic radiation is MHz. A) 50 B) 20 C)
CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review
 Mass in grams 10 20 30 40 50 CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review 1. Know the symbol and the power of 10 for the following metric prefixes: A. Mega M 10 6 D. deka da 10 1 G. milli m 10 6 B. kilo k
Mass in grams 10 20 30 40 50 CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review 1. Know the symbol and the power of 10 for the following metric prefixes: A. Mega M 10 6 D. deka da 10 1 G. milli m 10 6 B. kilo k
5. The outermost principal energy level electron configuration of the element bromine is: a. 4s 2 c. 4s 2 4p 5 b. 4p 5 d.
 1 c E = h 1. Sodium and potassium have similar properties because they have the same a. atomic radii. c. number of valence electrons. b. ionization energy. d. electronegativity. 2. Electrons must be added
1 c E = h 1. Sodium and potassium have similar properties because they have the same a. atomic radii. c. number of valence electrons. b. ionization energy. d. electronegativity. 2. Electrons must be added
AP Chapter 6 Study Questions
 Class: Date: AP Chapter 6 Study Questions True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The wavelength of radio waves can be longer than a football field. 2. Black body radiation is the
Class: Date: AP Chapter 6 Study Questions True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The wavelength of radio waves can be longer than a football field. 2. Black body radiation is the
Chemistry Mid-Term Practice Exam
 Chemistry Mid-Term Practice Exam Multiple Choice. Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A measure of the 3-D space matter occupies is a. density. c. volume.
Chemistry Mid-Term Practice Exam Multiple Choice. Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A measure of the 3-D space matter occupies is a. density. c. volume.
CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review 1. Know the symbol and the power of 10 for the following metric prefixes: A. Mega B.
 Mass in grams 10 20 30 40 50 CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review 1. Know the symbol and the power of 10 for the following metric prefixes: A. Mega B. kilo D. deka E. deci G. milli H. micro C. hecto
Mass in grams 10 20 30 40 50 CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review 1. Know the symbol and the power of 10 for the following metric prefixes: A. Mega B. kilo D. deka E. deci G. milli H. micro C. hecto
1. What is the difference between a qualitative and quantitative observation? Give at least one example of each.
 1 st 9wks Exam Review Name Per. Chemistry 1H Scientific Skills Unit - Lab Safety & Equipment: KEY EQUIPMENT TO KNOW: +beaker +Erlenmeyer flask +beaker tongs +balance +graduated cylinder +test tube +test
1 st 9wks Exam Review Name Per. Chemistry 1H Scientific Skills Unit - Lab Safety & Equipment: KEY EQUIPMENT TO KNOW: +beaker +Erlenmeyer flask +beaker tongs +balance +graduated cylinder +test tube +test
6. How many nonmetal atoms are there in the formula: NaH 2 PO 4? a. 1 b. 2 c. 4 d. 6 e. 7
 C101 Chapters 1 and 2 90 representative questions from old exams The questions are grouped by topic. Do these problems as homework to prepare for Exam 1. 1. Carbon is a metal/nonmetal that has the symbol.
C101 Chapters 1 and 2 90 representative questions from old exams The questions are grouped by topic. Do these problems as homework to prepare for Exam 1. 1. Carbon is a metal/nonmetal that has the symbol.
ATOMIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRONS, AND PERIODICITY
 ATOMIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRONS, AND PERIODICITY All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms; these are the elements. (EU 1.A) Development of Atomic Theory Atoms are so small
ATOMIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRONS, AND PERIODICITY All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms; these are the elements. (EU 1.A) Development of Atomic Theory Atoms are so small
What are the isotopes of hydrogen? H, 2 H, and 3 H
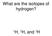 What are the isotopes of hydrogen? 1 H, 2 H, and 3 H The average mass of a boron atom is 10.81. Assuming you were able to isolate only one boron atom, the chance that you would randomly get one with a
What are the isotopes of hydrogen? 1 H, 2 H, and 3 H The average mass of a boron atom is 10.81. Assuming you were able to isolate only one boron atom, the chance that you would randomly get one with a
CHAPTER 2. Atoms,Elements, Periodic Table
 CHAPTER Atoms,Elements, Periodic Table 1 Vocabulary Chemistry Science that describes matter its properties, the changes it undergoes, and the energy changes that accompany those processes Matter Anything
CHAPTER Atoms,Elements, Periodic Table 1 Vocabulary Chemistry Science that describes matter its properties, the changes it undergoes, and the energy changes that accompany those processes Matter Anything
Chemistry Mid-Term Exam Review Spring 2017
 Unit 1 Measurement & Math Accuracy & Precision (recognizing given lab data) Density calculations Number of SFs in a measurement, Round answers to correct number of SFs Percent Error Unit conversions in
Unit 1 Measurement & Math Accuracy & Precision (recognizing given lab data) Density calculations Number of SFs in a measurement, Round answers to correct number of SFs Percent Error Unit conversions in
Mid-Term Review Multiple Choice: Ch. 3 Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 HONORS CHEMISTRY MID-TERM PRACTICE January 2013 Mrs. Allen from HS North put together a collection of multiple choice questions for you to use as a study tool. Not all of the midterm topics are covered
HONORS CHEMISTRY MID-TERM PRACTICE January 2013 Mrs. Allen from HS North put together a collection of multiple choice questions for you to use as a study tool. Not all of the midterm topics are covered
The Electronic Structures of Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation has the symbol λ.
 CHAPTER 7 Atomic Structure Chapter 8 Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity 1 The Electronic Structures of Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation has the symbol
CHAPTER 7 Atomic Structure Chapter 8 Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity 1 The Electronic Structures of Atoms Electromagnetic Radiation The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation has the symbol
ATOMIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRONS, AND PERIODICITY
 ATOMIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRONS, AND PERIODICITY All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms; these are the elements. (EU 1.A) Development of Atomic Theory Atoms are so small
ATOMIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRONS, AND PERIODICITY All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms; these are the elements. (EU 1.A) Development of Atomic Theory Atoms are so small
Honors Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam
 Honors Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam Mr. Matthew Totaro MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which statement about the
Honors Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam Mr. Matthew Totaro MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which statement about the
7. How many unpaired electrons are there in an atom of tin in its ground state? 2
 Name period AP chemistry Unit 2 worksheet 1. List in order of increasing energy: 4f, 6s, 3d,1s,2p 1s, 2p, 6s, 4f 2. Explain why the effective nuclear charge experienced by a 2s electron in boron is greater
Name period AP chemistry Unit 2 worksheet 1. List in order of increasing energy: 4f, 6s, 3d,1s,2p 1s, 2p, 6s, 4f 2. Explain why the effective nuclear charge experienced by a 2s electron in boron is greater
Periodic Table Practice 11/29
 Periodic Table Practice 11/29 1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the
Periodic Table Practice 11/29 1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the
Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
 Name KEY Block Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table In the 1790's Antoine Lavoisier compiled a list of the known elements at that time. There were only 23 elements. By the 1870's
Name KEY Block Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table In the 1790's Antoine Lavoisier compiled a list of the known elements at that time. There were only 23 elements. By the 1870's
Test Bank for General Chemistry Atoms First 2nd Edition by John E. McMurry and Robert C. Fay
 Test Bank for General Chemistry Atoms First 2nd Edition by John E. McMurry and Robert C. Fay Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-for-general-chemistry-atoms-f irst-2nd-edition-by-mcmurry-and-fay/
Test Bank for General Chemistry Atoms First 2nd Edition by John E. McMurry and Robert C. Fay Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-for-general-chemistry-atoms-f irst-2nd-edition-by-mcmurry-and-fay/
Name: Midterm Review Date:
 Name: Midterm Review Date: 1. Which statement concerning elements is true? A) Different elements must have different numbers of isotopes. B) Different elements must have different numbers of neutrons.
Name: Midterm Review Date: 1. Which statement concerning elements is true? A) Different elements must have different numbers of isotopes. B) Different elements must have different numbers of neutrons.
Name Midterm Review Date
 Name Midterm Review Date 1. In which process does a solid change directly into a vapor? A) sublimation B) deposition C) condensation D) solidification 2. What is the molecular formula of a compound that
Name Midterm Review Date 1. In which process does a solid change directly into a vapor? A) sublimation B) deposition C) condensation D) solidification 2. What is the molecular formula of a compound that
Atomic Theory. H. Cannon, C. Clapper and T. Guillot Klein High School
 Atomic Theory Unit 3 Development of the Atomic Theory 1. Where is the mass of the atom concentrated? 2. What is located in the nucleus? 3. What is the negative particle that orbits the nucleus? 4. What
Atomic Theory Unit 3 Development of the Atomic Theory 1. Where is the mass of the atom concentrated? 2. What is located in the nucleus? 3. What is the negative particle that orbits the nucleus? 4. What
Period: Chemistry Semester 1 Final Exam Review Packet. 1. What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory?
 Chemistry Name: Period: Chemistry Semester 1 Final Exam Review Packet 1. What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory? 2. Distinguish between quantitative and qualitative observations. States
Chemistry Name: Period: Chemistry Semester 1 Final Exam Review Packet 1. What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory? 2. Distinguish between quantitative and qualitative observations. States
Chemistry B11 Chapter 3 Atoms
 Chapter 3 Atoms Element: is a substance that consists of identical atoms (hydrogen, oxygen, and Iron). 116 elements are known (88 occur in nature and chemist have made the others in the lab). Compound:
Chapter 3 Atoms Element: is a substance that consists of identical atoms (hydrogen, oxygen, and Iron). 116 elements are known (88 occur in nature and chemist have made the others in the lab). Compound:
Test Review # 4. Chemistry: Form TR4-9A
 Chemistry: Form TR4-9A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Location of electrons. Electrons are in regions of the atom known as orbitals, which are found in subdivisions of the principal energy levels
Chemistry: Form TR4-9A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Location of electrons. Electrons are in regions of the atom known as orbitals, which are found in subdivisions of the principal energy levels
Chemistry 1-2E Semester I Study Guide
 Chemistry 1-2E Semester I Study Guide Name Hour Chapter 1 1. Define the following terms. Matter Mass Law of Conservation of Mass 2. Define and give 2 examples of the following: Pure substance Element Compound
Chemistry 1-2E Semester I Study Guide Name Hour Chapter 1 1. Define the following terms. Matter Mass Law of Conservation of Mass 2. Define and give 2 examples of the following: Pure substance Element Compound
1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on
 1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the number of oxidation states 2.
1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the number of oxidation states 2.
Chemistry Final Exam Review
 Chemistry Final Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following are physical properties of matter EXCEPT.
Chemistry Final Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following are physical properties of matter EXCEPT.
Regular Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam
 Regular Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam Mr. Matthew Totaro MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which statement about the
Regular Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam Mr. Matthew Totaro MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which statement about the
Regents review Atomic & periodic
 2011-2012 1. The diagram below represents the nucleus of an atom. What are the atomic number and mass number of this atom? A) The atomic number is 9 and the mass number is 19. B) The atomic number is 9
2011-2012 1. The diagram below represents the nucleus of an atom. What are the atomic number and mass number of this atom? A) The atomic number is 9 and the mass number is 19. B) The atomic number is 9
Q1 and Q2 Review large CHEMISTRY
 Q1 and Q2 Review large CHEMISTRY Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. E = hv relates the following a. Energy to Planck s constant & wavelength
Q1 and Q2 Review large CHEMISTRY Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. E = hv relates the following a. Energy to Planck s constant & wavelength
Electromagnetic spectrum
 All course materials, including lectures, class notes, quizzes, exams, handouts, presentations, and other materials provided to students for this course are protected intellectual property. As such, the
All course materials, including lectures, class notes, quizzes, exams, handouts, presentations, and other materials provided to students for this course are protected intellectual property. As such, the
Modern Atomic Theory
 Modern Atomic Theory Review of the Discovery of the Atom 1803 John Dalton discovered that elements are made of atoms. He thought that atoms were solid, like a marble. 1875 Crooks discovered the electron.
Modern Atomic Theory Review of the Discovery of the Atom 1803 John Dalton discovered that elements are made of atoms. He thought that atoms were solid, like a marble. 1875 Crooks discovered the electron.
M T W R. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. (3 pts ea)
 Exam 1 A Fall 2016 a Seat # Name M T W R MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. (3 pts ea) 1) Which of the following is a chemical property?
Exam 1 A Fall 2016 a Seat # Name M T W R MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. (3 pts ea) 1) Which of the following is a chemical property?
2. For the following two compounds between oxygen and hydrogen: 3. Tell what discoveries were made by each of the following scientists:
 EXTRA HOMEWORK 1A 1. When Dalton proposed that matter was composed of atoms, why was his Atomic Theory accepted? 2. For the following two compounds between oxygen and hydrogen: Mass of O Mass of H Compound
EXTRA HOMEWORK 1A 1. When Dalton proposed that matter was composed of atoms, why was his Atomic Theory accepted? 2. For the following two compounds between oxygen and hydrogen: Mass of O Mass of H Compound
I. The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table. Electronic Configuration and Periodicity. Announcements Newland Law of Octaves
 Announcements EM radiation --Exam 3 Oct 3...Includes chapters 7/8/9/10 The excluded items include: 1. Classical distinction between energy and matter (p. 217) 2. Numerical problems involving the Rydberg
Announcements EM radiation --Exam 3 Oct 3...Includes chapters 7/8/9/10 The excluded items include: 1. Classical distinction between energy and matter (p. 217) 2. Numerical problems involving the Rydberg
Additional Problem 1.13
 Task 1 Due: 11:59pm on Friday, April 27, 2018 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy Additional Problem 1.13 Classify each of the following as a pure
Task 1 Due: 11:59pm on Friday, April 27, 2018 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy Additional Problem 1.13 Classify each of the following as a pure
Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity
 Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity The Periodic Table Periodic law (Mendeleev, Meyer, 1870) periodic reoccurrence of similar physical and chemical properties of the elements arranged by increasing
Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity The Periodic Table Periodic law (Mendeleev, Meyer, 1870) periodic reoccurrence of similar physical and chemical properties of the elements arranged by increasing
Atomic Theory and Atomic structure. Part A. d) Distance of electrons from the nucleus
 Grade Subject Topic : AP : Science : Atomic Theory and Atomic Structure Atomic Theory and Atomic structure Part A (1) The Principal quantum number represents a) Shape of an orbital b) Number of electrons
Grade Subject Topic : AP : Science : Atomic Theory and Atomic Structure Atomic Theory and Atomic structure Part A (1) The Principal quantum number represents a) Shape of an orbital b) Number of electrons
Chapter 9: Electrons and the Periodic Table
 C h e m i s t r y 1 2 C h 9 : E l e c t r o n s a n d P e r i o d i c T a b l e P a g e 1 Chapter 9: Electrons and the Periodic Table Work on MasteringChemistry assignments What we have learned: Dalton
C h e m i s t r y 1 2 C h 9 : E l e c t r o n s a n d P e r i o d i c T a b l e P a g e 1 Chapter 9: Electrons and the Periodic Table Work on MasteringChemistry assignments What we have learned: Dalton
CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Review KEY. Unit 1
 CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Review KEY Unit 1 Practice Problems 1. What tool do you use to measure volume of water? Describe how to make a proper measurement of a volume of water using a 50 ml graduated
CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Review KEY Unit 1 Practice Problems 1. What tool do you use to measure volume of water? Describe how to make a proper measurement of a volume of water using a 50 ml graduated
Test Review # 5. Chemistry: Form TR5-8A. Average Atomic Mass. Subatomic particles.
 Chemistry: Form TR5-8A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 5 Subatomic particles. Type of Particle Location Mass Relative Mass Charge Proton Center 1.67 10-27 kg 1 +1 Electron Outside 9.11 10-31 kg 0-1
Chemistry: Form TR5-8A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 5 Subatomic particles. Type of Particle Location Mass Relative Mass Charge Proton Center 1.67 10-27 kg 1 +1 Electron Outside 9.11 10-31 kg 0-1
1) Which electron would be most likely to emit x-ray electromagnetic energy?
 AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 7) Multiple Choice (40%) 1) Which electron would be most likely to emit x-ray electromagnetic energy? A) n = 1 n = 6 B) n = 2 n = 3 C) n = 6 n = 1 D) n = 3 n = 2 2) Which statement
AP Chemistry Test (Chapter 7) Multiple Choice (40%) 1) Which electron would be most likely to emit x-ray electromagnetic energy? A) n = 1 n = 6 B) n = 2 n = 3 C) n = 6 n = 1 D) n = 3 n = 2 2) Which statement
Memorize: Understand: Know how to:
 NAME: CLASS PERIOD: REVIEW FOR HONORS CHEMISTRY SEMESTER 1 EXAM Memorize: Understand: Know how to: 1 SI units for different measurements (length, volume, number, mass, temperature, density) Definition
NAME: CLASS PERIOD: REVIEW FOR HONORS CHEMISTRY SEMESTER 1 EXAM Memorize: Understand: Know how to: 1 SI units for different measurements (length, volume, number, mass, temperature, density) Definition
Chapter 2: The Structure of the Atom and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 2: The Structure of the Atom and the Periodic Table 1. What are the three primary particles found in an atom? A) neutron, positron, and electron B) electron, neutron, and proton C) electron, proton,
Chapter 2: The Structure of the Atom and the Periodic Table 1. What are the three primary particles found in an atom? A) neutron, positron, and electron B) electron, neutron, and proton C) electron, proton,
Unit 1: Analyzing Data 1. Measure the following using the appropriate number of significant digits. Name Hour Date. b. o C
 Name Hour Date Chemistry Semester 1 Review!!! If you have completed ALL of the review on the assigned days you are allowed to use a cheat sheet that is created on the back of the periodic table found on
Name Hour Date Chemistry Semester 1 Review!!! If you have completed ALL of the review on the assigned days you are allowed to use a cheat sheet that is created on the back of the periodic table found on
Electrons. Unit H Chapter 6
 Electrons Unit H Chapter 6 1 Electrons were discovered by 1. Dalton 2. Lavoisier 3. Proust 4. Mendeleev 6. Rutherford 7. Bohr 8. Schrodinger 9. Dirac 5. Thomson 2 Electrons were discovered by 1. Dalton
Electrons Unit H Chapter 6 1 Electrons were discovered by 1. Dalton 2. Lavoisier 3. Proust 4. Mendeleev 6. Rutherford 7. Bohr 8. Schrodinger 9. Dirac 5. Thomson 2 Electrons were discovered by 1. Dalton
Chapter 7 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 7 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 7.1 Development of the Periodic Table 1864 - John Newlands - Law of Octaves- every 8 th element had similar properties
Chapter 7 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 7.1 Development of the Periodic Table 1864 - John Newlands - Law of Octaves- every 8 th element had similar properties
8. (5 pts) Draw a sketch of an atom. Label the nucleus, protons, neutrons. nucleus, containing protons and neutrons
 1. (2 pts) Atoms of the same element, regardless of charge, all have the same number of protons. 2. (2 pts) Comparing the mass of an electron to the mass of a proton, one could say that the electron is
1. (2 pts) Atoms of the same element, regardless of charge, all have the same number of protons. 2. (2 pts) Comparing the mass of an electron to the mass of a proton, one could say that the electron is
Multiple Choice Do Now!
 Name: Period: Date: KIPP NYC College Prep General Chemistry Quarter 1: Let s Review Multiple Choice Do Now! 1. Which substance can be decomposed by chemical means? (1) Aluminum (2) Octane (3) Silicon (4)
Name: Period: Date: KIPP NYC College Prep General Chemistry Quarter 1: Let s Review Multiple Choice Do Now! 1. Which substance can be decomposed by chemical means? (1) Aluminum (2) Octane (3) Silicon (4)
Unit 1, Lesson 01: Summary of Atomic Structure so far
 Unit 1, Lesson 01: Summary of Atomic Structure so far Atoms are made of sub-atomic particles: Protons: found in the nucleus, charge of 1+, mass of 1 amu (u) Neutrons: found in nucleus, no charge, mass
Unit 1, Lesson 01: Summary of Atomic Structure so far Atoms are made of sub-atomic particles: Protons: found in the nucleus, charge of 1+, mass of 1 amu (u) Neutrons: found in nucleus, no charge, mass
Key Equations. Determining the smallest change in an atom's energy.
 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND PERIODICITY Matter and Energy Key Equations λν = c ΔE = hν Relating speed of a wave to its wavelength and frequency. Determining the smallest change in an atom's energy. H( λ =R n
ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND PERIODICITY Matter and Energy Key Equations λν = c ΔE = hν Relating speed of a wave to its wavelength and frequency. Determining the smallest change in an atom's energy. H( λ =R n
How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas?
 EXAMPLE PROBLEM: How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas? 1 - Convert 2545 grams of chlorine to moles chlorine using formula weight 2 - Convert moles
EXAMPLE PROBLEM: How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas? 1 - Convert 2545 grams of chlorine to moles chlorine using formula weight 2 - Convert moles
1) What is the name given to the element with the symbol "K"? A) Potassium B) Krypton C) Phosphorus D) Kallium
 Practice Exam 1 (Chapters 1-4) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the name given to the element with the symbol "K"?
Practice Exam 1 (Chapters 1-4) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the name given to the element with the symbol "K"?
Review Multiple Choice Questions
 Chapter 2 Matter and Changes Review Multiple Choice Questions 1. The random molecular motion of a substance is greatest when the substance is a. condensed b. a liquid c. frozen d. a gas 2. After elements
Chapter 2 Matter and Changes Review Multiple Choice Questions 1. The random molecular motion of a substance is greatest when the substance is a. condensed b. a liquid c. frozen d. a gas 2. After elements
Chapter 10: Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table. How does atomic structure relate to the periodic table? 10.1 Electromagnetic Radiation
 Chapter 10: Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table How does atomic structure relate to the periodic table? 10.1 Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic (EM) radiation is a form of energy that exhibits
Chapter 10: Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table How does atomic structure relate to the periodic table? 10.1 Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic (EM) radiation is a form of energy that exhibits
Unit 0 Measurements and Calculations in Chemistry
 Unit 0 Measurements and Calculations in Chemistry Question Difficulty: * Normal ** Difficult *** Very difficult A. Measurements and Units (O-0.2 O-0.5) 1. SI units and prefixes a. A measured quantity/property
Unit 0 Measurements and Calculations in Chemistry Question Difficulty: * Normal ** Difficult *** Very difficult A. Measurements and Units (O-0.2 O-0.5) 1. SI units and prefixes a. A measured quantity/property
Homework Packet Unit 2. b. Al 3+, F, Na +, Mg 2+, O 2
 Name Period Homework Packet Unit 2 1. Which of the following is the correct empirical formula for a compound that has 37.5% C, 12.6% H, and 49.9% O? (A) C 2 H 4 O (B) CH 4 O 2 (C) CH 5 O 2 (D) CH 4 O (E)
Name Period Homework Packet Unit 2 1. Which of the following is the correct empirical formula for a compound that has 37.5% C, 12.6% H, and 49.9% O? (A) C 2 H 4 O (B) CH 4 O 2 (C) CH 5 O 2 (D) CH 4 O (E)
Chapter 2: Atoms and the Periodic Table
 1. Which element is a nonmetal? A) K B) Co C) Br D) Al Ans: C Difficulty: Easy 2. Which element is a metal? A) Li B) Si C) Cl D) Ar E) More than one of the elements above are metals. 3. Which element is
1. Which element is a nonmetal? A) K B) Co C) Br D) Al Ans: C Difficulty: Easy 2. Which element is a metal? A) Li B) Si C) Cl D) Ar E) More than one of the elements above are metals. 3. Which element is
First Semester Review Worksheet
 First Semester Review Worksheet 1. Determine the number of significant figures in each of the numbers below a. 1000 b. 4.567 c. 2030 d. 0.0240 e. 0.02677 f. 200.00 g. 4.65 x 10 4 h. 100.300 2. Convert
First Semester Review Worksheet 1. Determine the number of significant figures in each of the numbers below a. 1000 b. 4.567 c. 2030 d. 0.0240 e. 0.02677 f. 200.00 g. 4.65 x 10 4 h. 100.300 2. Convert
Part A. Answer all questions in this part.
 Part A Directions (1-20): For each statement or question, record on your separate answer sheet the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question.
Part A Directions (1-20): For each statement or question, record on your separate answer sheet the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question.
Honors Chemistry Unit 4 ( )
 Honors Chemistry Unit 4 (2017-2018) Families (research and present) Metals/nonmetals Trends o Atomic radius o Electronegativity o Ionization energy o Metallic and nonmetallic character Review Ions Oxidation
Honors Chemistry Unit 4 (2017-2018) Families (research and present) Metals/nonmetals Trends o Atomic radius o Electronegativity o Ionization energy o Metallic and nonmetallic character Review Ions Oxidation
Section 11: Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends
 Section 11: Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 11.01 The Bohr Model of the Atom
Section 11: Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 11.01 The Bohr Model of the Atom
CHM 1045 Test #4 December 4, 2000
 CHM 1045 Test #4 December 4, 2000 1. The scientist who was first to propose that electrons in an atom could have only certain energies was a. Planck. b. Einstein. c. Bohr. d. Rydberg. 2. Select the arrangement
CHM 1045 Test #4 December 4, 2000 1. The scientist who was first to propose that electrons in an atom could have only certain energies was a. Planck. b. Einstein. c. Bohr. d. Rydberg. 2. Select the arrangement
Atoms, Electrons and Light MS. MOORE CHEMISTRY
 Atoms, Electrons and Light MS. MOORE CHEMISTRY Atoms Remember Rutherford??? What did he discover with his gold foil experiment. A: Atoms contain a dense nucleus where the protons and neutrons reside. ATOMS
Atoms, Electrons and Light MS. MOORE CHEMISTRY Atoms Remember Rutherford??? What did he discover with his gold foil experiment. A: Atoms contain a dense nucleus where the protons and neutrons reside. ATOMS
4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table. GCSE Chemistry
 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table GCSE Chemistry All substances are made of atoms this is cannot be chemically broken down it is the smallest part of an element. Elements are made of only one
4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table GCSE Chemistry All substances are made of atoms this is cannot be chemically broken down it is the smallest part of an element. Elements are made of only one
THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS. ATOMS Atoms consist of a number of fundamental particles, the most important ones are...
 Atomic Structure THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS ATOMS Atoms consist of a number of fundamental particles, the most important ones are... Mass / kg Charge / C Relative mass Relative Charge PROTON NEUTRON ELECTRON
Atomic Structure THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS ATOMS Atoms consist of a number of fundamental particles, the most important ones are... Mass / kg Charge / C Relative mass Relative Charge PROTON NEUTRON ELECTRON
SAMPLE PROBLEMS! 1. From which of the following is it easiest to remove an electron? a. Mg b. Na c. K d. Ca
 SAMPLE PROBLEMS! 1. From which of the following is it easiest to remove an electron? a. Mg b. Na c. K d. Ca 2. Which of the following influenced your answer to number one the most? a. effective nuclear
SAMPLE PROBLEMS! 1. From which of the following is it easiest to remove an electron? a. Mg b. Na c. K d. Ca 2. Which of the following influenced your answer to number one the most? a. effective nuclear
2008 Brooks/Cole 2. Frequency (Hz)
 Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter Oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Magnetic field Electric field Chapter 7: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Traveling wave moves through space
Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter Oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Magnetic field Electric field Chapter 7: Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Traveling wave moves through space
Chemistry 121: Atomic and Molecular Chemistry Topic 3: Atomic Structure and Periodicity
 Text Chapter 2, 8 & 9 3.1 Nature of light, elementary spectroscopy. 3.2 The quantum theory and the Bohr atom. 3.3 Quantum mechanics; the orbital concept. 3.4 Electron configurations of atoms 3.5 The periodic
Text Chapter 2, 8 & 9 3.1 Nature of light, elementary spectroscopy. 3.2 The quantum theory and the Bohr atom. 3.3 Quantum mechanics; the orbital concept. 3.4 Electron configurations of atoms 3.5 The periodic
Test Review # 4. Chemistry: Form TR4-5A 6 S S S
 Chemistry: Form TR4-5A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Development of the Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) prepared a card for each of the known elements listing the symbol, the atomic mass,
Chemistry: Form TR4-5A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Development of the Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) prepared a card for each of the known elements listing the symbol, the atomic mass,
How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas?
 146 EXAMPLE PROBLEM: How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas? 1 - Convert 2545 grams of chlorine gas to moles. Use formula weight. 2 - Convert moles
146 EXAMPLE PROBLEM: How many grams of sodium metal is required to completely react with 2545 grams of chlorine gas? 1 - Convert 2545 grams of chlorine gas to moles. Use formula weight. 2 - Convert moles
Electron Arrangement - Part 2
 Brad Collins Electron Arrangement - Part 2 Chapter 9 Some images Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Review Energy Levels Multi-electron 4d 4d 4d 4d 4d n = 4 4s 4p 4p 4p 3d 3d 3d 3d 3d n=3, l = 2
Brad Collins Electron Arrangement - Part 2 Chapter 9 Some images Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Review Energy Levels Multi-electron 4d 4d 4d 4d 4d n = 4 4s 4p 4p 4p 3d 3d 3d 3d 3d n=3, l = 2
Chapter 7 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 7 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 7.1 Development of the Periodic Table 1864 - John Newlands - Law of Octaves- every 8th element had similar properties
Chapter 7 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 7.1 Development of the Periodic Table 1864 - John Newlands - Law of Octaves- every 8th element had similar properties
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 3e (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements
 Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 3e (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements 1) Which of the following is an example of the law of multiple proportions? A) A sample of chlorine is found to contain
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 3e (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements 1) Which of the following is an example of the law of multiple proportions? A) A sample of chlorine is found to contain
Exam Accelerated Chemistry Study Sheet Chap 04 The Atom/Periodic Table
 Exam Accelerated Chemistry Study Sheet Chap 04 The Atom/Periodic Table Name /87 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. Correct the False statements by changing
Exam Accelerated Chemistry Study Sheet Chap 04 The Atom/Periodic Table Name /87 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. Correct the False statements by changing
A) first electron shell D) are located in orbitals outside the nucleus A) 2-3 D) 18 A) K and Na C) a mixture C) Sb2O5
 1. In a calcium atom in the ground state, the electrons that possess the least amount of energy are located in the A) first electron shell B) second electron shell C) third electron shell D) fourth electron
1. In a calcium atom in the ground state, the electrons that possess the least amount of energy are located in the A) first electron shell B) second electron shell C) third electron shell D) fourth electron
Chapter Test B. Chapter: Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms. possible angular momentum quantum numbers? energy level? a. 4 b. 8 c. 16 d.
 Assessment Chapter Test B Chapter: Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms PART I In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question
Assessment Chapter Test B Chapter: Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms PART I In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question
Chapter 1 Introduction to Chemistry 1. What is chemistry?
 FIRST SEMESTER EXAM REVIEW Chapter 1 Introduction to Chemistry 1. What is chemistry? 2. Identify the independent and dependent variables using the graph above. IV: DV: 3. Write a hypothesis for this experiment.
FIRST SEMESTER EXAM REVIEW Chapter 1 Introduction to Chemistry 1. What is chemistry? 2. Identify the independent and dependent variables using the graph above. IV: DV: 3. Write a hypothesis for this experiment.
1 st Semester Final Review Sheet (Chapters 2-7)
 CP Chemistry Name: Period: 1 st Semester Final Review Sheet (Chapters 2-7) Matter (Chapter 2) 1. What is the definition of an element? 2. What is the definition of a compound? 3. What is the definition
CP Chemistry Name: Period: 1 st Semester Final Review Sheet (Chapters 2-7) Matter (Chapter 2) 1. What is the definition of an element? 2. What is the definition of a compound? 3. What is the definition
CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM 1 SEPTEMBER 20, 2010 FORM A
 CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM 1 SEPTEMBER 20, 2010 FORM A 1. What are the correct numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons in a 39 K + ion? p n e A. 20 19 18 B. 20 19 19 C. 19 20 18 D. 19 20 19 E. 20 19 20 2. Which
CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM 1 SEPTEMBER 20, 2010 FORM A 1. What are the correct numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons in a 39 K + ion? p n e A. 20 19 18 B. 20 19 19 C. 19 20 18 D. 19 20 19 E. 20 19 20 2. Which
PART 2 Electronic Structure and the Periodic Table. Reference: Chapter 7 8 in textbook
 PART 2 Electronic Structure and the Periodic Table Reference: Chapter 7 8 in textbook 1 Experiment to Discover Atom Structure -particle: He 2+ mass number = 4 Nucleus and Electron Model 2 Atomic Structure
PART 2 Electronic Structure and the Periodic Table Reference: Chapter 7 8 in textbook 1 Experiment to Discover Atom Structure -particle: He 2+ mass number = 4 Nucleus and Electron Model 2 Atomic Structure
