6. How many nonmetal atoms are there in the formula: NaH 2 PO 4? a. 1 b. 2 c. 4 d. 6 e. 7
|
|
|
- Richard Baldwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C101 Chapters 1 and 2 90 representative questions from old exams The questions are grouped by topic. Do these problems as homework to prepare for Exam Carbon is a metal/nonmetal that has the symbol. a. metal, C b. metal, Ca c. nonmetal, C d. nonmetal, Ca e. nonmetal, Cl 2. The elements tin, titanium, tantalum and thallium are represented respectively by the symbols: a. Ti, Tm, Ta, Th b. Sb, Ti, Tl, Tm c. Sn, Ti, Tl, Th d. Sn, Ti, Ta, Tl e. W, Tc, Tl, Hg 3. Barium and beryllium are examples of a. alkaline earth metals. b. rare earth metals. c. transition metals. d. alkali metals. e. halogens. 4. Which is a transition metal? a. indium b. cadmium c. rubidium d. selenium e. antimony 5. Which of the following elements is misspelled? a. scandium b. vanadium c. tellerium d. iridium e. lanthanum 6. How many nonmetal atoms are there in the formula: NaH 2 PO 4? a. 1 b. 2 c. 4 d. 6 e. 7
2 7. Alkali metals a. react violently with water. b. have one valence electron. c. form 1:1 compounds with halogens. d. all of the above e. none of the above 8. Which of the following would you expect to be chemically similar to chlorine? a. Ar b. F and Br c. Se and Ne d. O and Kr e. P and S 9. Which element is likely to have chemical properties similar to elemental potassium? a. Ar b. Ca c. Sc d. Rb e. Sr 10. Which of the following is equivalent to ? a b c d e Express in scientific notation. a b c d e Which digit is uncertain in the following mass? g a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 e. 4
3 13. Which of the following has exactly 4 significant figures? a b c d e The number should be rounded to what value in order to have exactly 3 significant figures? a b c d e Evaluate the following expression to the correct number of significant figures: ml ml ml a ml b ml c ml d ml e ml 16. What temperature is 75.0 F on the Kelvin scale? a K b K c. 215 K d. 297 K e. 348 K 17. Which of the following describes a chemical change? a. new materials are formed b. the change is reversible c. the change is not reversible d. a and b e. a and c 18. Identify the physical change (or changes) in the following list. a. diluting bleach with water b. explosion of gasoline in an automobile engine c. making rock candy by evaporating water from a sugar solution d. a and b e. a and c
4 19. When a substance undergoes a physical change a. it always undergoes a change of state. b. the process cannot be reversed. c. a new substance is produced. d. its chemical composition remains unchanged. e. heat is always given off. 20. When an electrical current is used to make hydrogen gas and oxygen gas from water, a. a chemical change has occurred. b. a simple change of state (physical change) has occurred. c. water is a reactant and hydrogen and oxygen are products. d. a and c e. b and c 21. A compound is a liquid at 250 F. Which of the following could be the correct melting point and boiling point for this material? a. 0 C and 100 C b. 390 C and 840 C c. 100 C and 212 C d. 20 C and 120 C e. 130 C and 180 C 22. Benzyl salicylate, a sunscreen, melts at 75 F and boils at 608 F. At which temperature would benzyl salicylate be a gas? a. 0 F b. 0 C c. 100 C d. 300 C e. none of the above 23. Which of the following would be described as a heterogeneous mixture? a. air, a mixture of O 2, N 2, CO 2 and other gases b. propane gas, C 3 H 8 c. 95% ethyl alcohol (C 2 H 6 O dissolved in water) d. elemental sulfur, S 8 e. none of the above 24. Which of the following pairs consists of an example of a mixture and an example of a pure substance? a. concrete, air b. rubbing alcohol, liquid hand soap c. salt water, helium gas d. anhydrous ammonia, aluminum foil e. air, motor oil
5 25. Which of the following can be classified as a pure compound? a. glucose, C 6 H 12 O 6 b. mercury metal, Hg c. chlorine gas, Cl 2 d. rubbing alcohol, C 3 H 8 O in H 2 O e. all of the above 26. Which should be classified as a heterogeneous mixture? a. salsa b. salt water c. table salt, NaCl d. a and b e. all of the above 27. A piece of lead floats when it is dropped into a pool of mercury. This means that a. the density of lead is less than one. b. the density of Pb is less than the specific gravity of Pb. c. the density of mercury is greater than the density of lead. d. the atomic weight of lead is less than the atomic weight of mercury. e. the specific gravity of lead is greater than the specific gravity of mercury. 28. A liquid sample has a density of 1.3 g/ml. What is the volume occupied by 10. g of this liquid? a. 7.7 ml b. 10. ml c. 13 ml d ml e ml 29. The density of a solution is g/ml. What is the mass of 3.0 ml of this solution (with proper attention to correct significant digits)? a g b. 4.0 g c. 3.9 g d g e. 2.3 g 30. What is the density if g of a metal occupies a volume of 9.0 cubic centimeters? Make sure your answer has the correct number of significant figures. a g/ml b. 6.5 g/ml c. 7 g/ml d g/ml e g/ml
6 31. The densities of ethylene glycol, water and wood alcohol are 1.11 g/ml, 1.00 g/ml and 0.79 g/ml respectively. Suppose an object floats in water and ethylene glycol but sinks when placed in wood alcohol. Which of the following could be the density of the object? a g/ml b g/ml c g/ml d g/ml e g/ml 32. What is the mass of 2.00 in 3 of mercury? Note: The density of mercury is 13.6 g/cm 3. a g b g c g d. 223 g e. 446 g 33. The density of air is cg/kl. Express this density in mg/l. a mg/l b mg/l c mg/l d mg/l e mg/l 34. What temperature change results if 10.0 g of iron absorbs 50.0 calories? Note: C Fe = cal/g C. a C b C c C d C e C 35. How much heat (in kcal) is released when 125 g of water cools from 90.0ºC to 9.5ºC? (Note: the specific heat value for water is 1.00 cal/g C.) a kcal b kcal c kcal d kcal e kcal 36. Suppose an equal amount of heat is absorbed by different masses of each of the following metals and you discover that the temperature of the magnesium sample changes the most. Which of the following could be a correct statement of the relative masses of the metal samples studied? Au: cal/g C Fe: cal/g C Mg: cal/g C a. mass Mg > mass Au > mass Fe b. mass Mg > mass Fe > mass Au c. mass Au > mass Fe > mass Mg d. mass Au > mass Mg > mass Fe e. mass Fe > mass Mg > mass Au
7 37. How many micrograms are in a kilogram? a b c d e Which of the following is equivalent to 75.0 grams? a mg b mg c mg d mg e mg 39. Convert 3.5 liters to milliliters. a ml b ml c ml d ml e ml 40. Convert 6.0 pints to nanoliters. (Note: 1 pint = L) a nl b nl c nl d nl e nl 41. Which of the following is equivalent to the volume of a cube that is 100 cm on each side? Note: The volume of a cube is length width height. a. 1 kiloliter b. 1 megaliter c centiliters d microliters e milliliters 42. Convert cm to units of Å. Note that 1 Å is exactly m. a Å b. 5.0 Å c. 50 Å d Å e Å
8 43. An extra-strength aspirin tablet contains grams of aspirin. How many grains is this? Note: 1 grain = 64.8 mg a grains b grains c grains d grains e grains 44. Which of the following types of electromagnetic radiation has the highest energy? a. red light b. blue light c. yellow light d. infrared radiation e. ultraviolet radiation 45. Put the following types of electromagnetic radiation in order of increasing energy. I: orange light II: UV radiation III: red light IV: microwaves a. IV < I < II < III b. IV < III < I < II c. I < IV < III < II d. III < IV < I < II e. II < I < III < IV 46. What is the subatomic particle that has a positive charge and a mass of approximately 1 amu? a. electron b. proton c. neutron d. protium e. deuterium 47. The nucleus is held together by a. electromagnetic radiation. b. nuclear strong force. c. electrostatic attraction. d. gravitational force. e. all of the above 48. An atom that contains 47 protons, 47 electrons and 60 neutrons is an isotope of: a. Ag b. Al c. Nd d. Bh e. cannot be determined from the information given
9 49. How many protons are in an isotope of strontium that has 50 neutrons? a. 50 b. 87 c. 36 d. 38 e A certain isotope has 17 protons, 18 neutrons, and 18 electrons. The correct symbol for this is: a. b. c. d. e. 35 Ar 35 Cl 17 Cl + 36 K 2 53 I 51. Which has more neutrons than electrons? a S 2 b K c P 3 d. e. 24 Mg 2+ 9 B 52. An atom with mass number (A) 69 and atomic number (Z) 31 contains: a. 31 protons and 69 neutrons b. 69 protons and 31 neutrons c. 31 protons and 38 neutrons d. 38 protons and 31 neutrons e. 31 protons and 100 neutrons 53. Consider 54 Co 2+. The atomic number, mass number, number of protons, number of neutrons and number of electrons are (in order): a. 27, 54, 27, 27, 29 b. 27, 54, 27, 27, 25 c. 54, 59, 27, 27, 25 d. 54, 59, 29, 27, 27 e. none of the above 54. A charged atom (-1) has 76 electrons and has a mass number (A) of 190. How many protons and neutrons are in the nucleus of this atom? a. 114 p 190 n b. 115 p 75 n c. 75 p 190 n d. 75 p 115 n e. 76 p 114 n
10 55. Which of the following contains exactly 44 neutrons? a. I-131 b. Ti-22 c. Se-78 d. Sc-44 e. Ru The atomic weight listed for an element in the periodic table is a. the same as the mass number (A) for the element. b. a weighted average of the weights of naturally-occurring isotopes of the element. c. the average of the mass number (A) and the atomic number (Z). d. the mass of an atom with the weight adjusted to reflect loss or gain of electrons. e. the weight of the predominant isotope found on earth. 57. Put the following in order of increasing mass. I: beryllium ion, Be 2+ II: electron III: neutron IV: tritium, 1 3 H a. II < III < IV < I b. II < III < I < IV c. I < IV < III < II d. III < IV < I < II e. IV < III < II < I 58. What is the approximate mass of 10 chromium atoms? a. 10 amu b. 24 amu c. 52 amu d. 240 amu e. 520 amu 59. What is the approximate mass in amu of 33 atoms of gold-203? a amu b amu c amu d amu e amu 60. What is the mass in grams of 135 atoms of bromine? Note: 1 amu = grams a g b g c g d g e g
11 61. How many atoms are there in a 10.0 g sample of aluminum? Note: 1 amu = grams a atoms b atoms c atoms d atoms e atoms 62. The atomic weight of hydrogen from the periodic table is amu. From this information, what is the likely approximate isotopic composition of naturally occurring hydrogen on earth? a. mostly protium (no neutrons) b. mostly deuterium (1 neutron) c. mostly tritium (2 neutrons) d. equal amounts of protium, deuterium and tritium e. equal amounts of protium and deuterium, with a lesser amount of tritium 63. Which of the following sets of isotopic abundance data does NOT make sense based on the atomic weights listed in the periodic table for these elements? a. vanadium-50, 0.25% and vanadium-51, 99.75% b. bromine-79, 50.7% and bromine-81, 49.3% c. lithium-6, 72.3% and lithium-7, 27.7% d. neon-20, 90.5% and neon-22, 9.5% e. boron-10, 19.8% and boron-11, 80.2% 64. There are 4 naturally occurring isotopes of strontium. The mass numbers of these isotopes are 84, 86, 87 and 88. One isotope makes up about 82% of a typical sample of strontium. Based on the atomic weight listed in the periodic table, which isotope is the most abundant? a. strontium-84 b. strontium-86 c. strontium-87 d. strontium-88 e. It is impossible to answer this question from the available information. 65. A single orbital (for example: a d orbital in the 3 rd shell or a 2p orbital) has a maximum capacity of a. 2 protons. b. 2 neutrons. c. 2 electrons. d. 6 electrons. e. 10 electrons. 66. Which of these orbitals has the highest energy? a. 1s b. 2s c. 3s d. 4s e. 5s
12 67. Which is a spherically-shaped region of electron density? a. any orbital in an s subshell b. any orbital in a p subshell c. 3d orbital d. 4f orbital e. none of the above 68. How many distinct d-orbitals exist? Remember, the d-block is ten elements wide. a. 3 b. 5 c. 6 d. 10 e How many electrons can occupy the shell having n = 2? a. 2 b. 6 c. 8 d. 18 e How many electrons are in an atom with electron configuration: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6? a. 5 b. 8 c. 10 d. 11 e What is the electron configuration for an uncharged (neutral) cadmium atom? a. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 b. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 c. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 d. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 e. 1s 4 2s 4 2p 12 3s 4 3p 12 4s 4 3d The neutral element with electron configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4 is: a. Be b. C c. O d. Si e. S
13 73. Which have the following electron configuration? 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 a. S and Cl b. K + and P 3 c. Ar and Ca 2+ d. a and b e. b and c 74. Which is the correct electron configuration for an uncharged selenium atom in the ground state? a. [Ar]3s 2 3d 10 3p 4 b. [Ar]4s 2 4d 1 0 4p 4 c. [Ar]4s 2 3d 10 4p 4 d. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 e. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 4d 10 4p Which is the correct ground state electron configuration for a neutral scandium atom? a. [Ar]4d 3 b. [Ar]4s 2 3d 1 c. [Ar]3s 2 3p 1 d. 1s 2 1p 6 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 3 e. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 4d Which is the correct ground state electron configuration for aluminum ion, Al 3+? a. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 b. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 c. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 3s 2 d. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 1 e. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 3s 2 3p Which of the following represents a ground state electron configuration? a. 1s 2s 2p 3s b. 1s 2s 2p 3s c. 1s 2s 2p 3s d. 1s 2s 2p 3s e. 1s 2s 2p 3s 78. Which could be represented by the following electron configuration? 1s 2s 2p 3s a. an oxygen ion in an excited state b. a carbon atom in an excited state c. a nitrogen atom in the ground state d. a phosphorus atom in the ground state e. a fluorine atom that has gained two electrons
14 79. Which represents the electron configuration of a neutral sodium atom in an excited state? a. [He]2s 2 2p 6 3s 1 3p 1 b. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 c. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5 3s 1 d. [Ne]3p 1 e. [Ne]3s The valence shell for a neutral atom of rubidium is n =. a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 e Elements that have one, two or three valence electrons are likely a. metals. b. nonmetals. c. nearly inert. d. liquids at room temperature. e. gases at room temperature. 82. Antimony is a that has valence electrons. a. metal, 3 b. nonmetal, 3 c. metalloid, 4 d. nonmetal, 5 e. metalloid, The valence electrons in a neutral atom of gallium are: a. 3p 1 b. 4p 1 c. 3s 2 3p 1 d. 4s 2 4p 1 e. 4s 2 4p Sodium and lithium have similar chemical properties because a. they have the same number of valence electrons. b. sodium ion and lithium ion are isoelectronic. c. they are both alkaline earth metals d. a and b e. a and c
15 85. The neutral element that has exactly four valence electrons is: a. H b. Na c. Mg d. Si e. S 86. In terms of atomic structure, the common characteristic of elements in the same group is: a. number of electrons b. number of valence electrons c. number of neutrons d. number of protons e. mass number 87. A polonium atom that has gained 2 electrons has the same number of electrons as: a. a neutral atom of lead b. a neutral atom of radium c. an atom of astatine that has lost 1 electron d. an atom of barium that has lost 2 electrons e. an atom of radium that has lost 2 electrons 88. The term isoelectronic refers to species that a. have the same charge. b. have identical mass numbers, A. c. have identical electron configurations. d. reside in the same period in the periodic table. e. have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. 89. A sulfur atom that has gained two electrons has the same number of electrons as a neutral atom of: a. C b. Ne c. Mg d. Si e. Ar 90. Rb + is isoelectronic with: a. K + b. Cs + c. Kr d. a and b e. all of the above
Chapter 2 Atoms and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 2 1 Chapter 2 Atoms and the Periodic Table Solutions to In-Chapter Problems 2.1 Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. Use the periodic table to find the symbol for each element.
Chapter 2 1 Chapter 2 Atoms and the Periodic Table Solutions to In-Chapter Problems 2.1 Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. Use the periodic table to find the symbol for each element.
Full file at
 16 Chapter 2: Atoms and the Periodic Table Solutions to In-Chapter Problems 2.1 Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. Use the periodic table to find the symbol for each element. a.
16 Chapter 2: Atoms and the Periodic Table Solutions to In-Chapter Problems 2.1 Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. Use the periodic table to find the symbol for each element. a.
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach 2e (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements
 Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach 2e (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements 1) Which of the following is an example of the law of multiple proportions? A) A sample of chlorine is found to contain
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach 2e (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements 1) Which of the following is an example of the law of multiple proportions? A) A sample of chlorine is found to contain
Note that the protons and neutrons are each almost 2,000 times more massive than an electron; What is the approximate diameter of an atom?
 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Evolution of Atomic Theory The ancient Greek scientist Democritus is often credited with developing the idea of the atom Democritus proposed that matter was, on
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Evolution of Atomic Theory The ancient Greek scientist Democritus is often credited with developing the idea of the atom Democritus proposed that matter was, on
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 2e (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements. Multiple Choice Questions
 Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 2e (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements Multiple Choice Questions 1) In a chemical reaction, matter is neither created or destroyed. Which law does this refer to? A) Law
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 2e (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements Multiple Choice Questions 1) In a chemical reaction, matter is neither created or destroyed. Which law does this refer to? A) Law
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 3e (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements
 Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 3e (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements 1) Which of the following is an example of the law of multiple proportions? A) A sample of chlorine is found to contain
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 3e (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements 1) Which of the following is an example of the law of multiple proportions? A) A sample of chlorine is found to contain
Regular Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam
 Regular Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam Mr. Matthew Totaro MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which statement about the
Regular Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam Mr. Matthew Totaro MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which statement about the
Chapter 4 Atoms Practice Problems
 Chapter 4 Atoms Practice Problems 1) The primary substances of which all other things are composed are A) molecules. B) compounds. C) elements. D) electrons. E) protons. 2) Which of the following is a
Chapter 4 Atoms Practice Problems 1) The primary substances of which all other things are composed are A) molecules. B) compounds. C) elements. D) electrons. E) protons. 2) Which of the following is a
Chapter 2: Atoms and the Periodic Table
 1. Which element is a nonmetal? A) K B) Co C) Br D) Al Ans: C Difficulty: Easy 2. Which element is a metal? A) Li B) Si C) Cl D) Ar E) More than one of the elements above is a metal. Ans: A Difficulty:
1. Which element is a nonmetal? A) K B) Co C) Br D) Al Ans: C Difficulty: Easy 2. Which element is a metal? A) Li B) Si C) Cl D) Ar E) More than one of the elements above is a metal. Ans: A Difficulty:
1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A atomic mass C molar mass
 1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A atomic mass C molar mass A Br, Ga, Hg C O, S, Se B atomic number D oxidation number 2. Which list includes elements with the
1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A atomic mass C molar mass A Br, Ga, Hg C O, S, Se B atomic number D oxidation number 2. Which list includes elements with the
1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A atomic mass C molar mass
 1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A atomic mass C molar mass A Br, Ga, Hg C O, S, Se B atomic number D oxidation number 2. Which list includes elements with the
1. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order of increasing A atomic mass C molar mass A Br, Ga, Hg C O, S, Se B atomic number D oxidation number 2. Which list includes elements with the
Chapter 2: Atoms and the Periodic Table
 1. Which element is a nonmetal? A) K B) Co C) Br D) Al Ans: C Difficulty: Easy 2. Which element is a metal? A) Li B) Si C) Cl D) Ar E) More than one of the elements above are metals. 3. Which element is
1. Which element is a nonmetal? A) K B) Co C) Br D) Al Ans: C Difficulty: Easy 2. Which element is a metal? A) Li B) Si C) Cl D) Ar E) More than one of the elements above are metals. 3. Which element is
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements
 Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements 1) Which of the following is an example of the law of multiple proportions? A) A sample of chlorine is found to contain
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (Tro) Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements 1) Which of the following is an example of the law of multiple proportions? A) A sample of chlorine is found to contain
Unit 3. Atoms and molecules
 Unit 3. Atoms and molecules Index. s and compounds...2.. Dalton's Atomic theory...2 2.-The atom...2 3.-Atomic number and mass number...2 4.-Isotopes, atomic mass unit and atomic mass...3 5.- configuration...3
Unit 3. Atoms and molecules Index. s and compounds...2.. Dalton's Atomic theory...2 2.-The atom...2 3.-Atomic number and mass number...2 4.-Isotopes, atomic mass unit and atomic mass...3 5.- configuration...3
Honors Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam
 Honors Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam Mr. Matthew Totaro MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which statement about the
Honors Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam Mr. Matthew Totaro MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which statement about the
Ch. 3 Answer Key. O can be broken down to form two atoms of H and 1 atom of O. Hydrogen and oxygen are elements.
 Ch. 3 Answer Key 1. The Greeks believed that all matter is made of elements. We currently believe the same thing. However, the Greeks believed that there were 4 elements: earth, water, air and fire. Instead,
Ch. 3 Answer Key 1. The Greeks believed that all matter is made of elements. We currently believe the same thing. However, the Greeks believed that there were 4 elements: earth, water, air and fire. Instead,
Periodic Table Practice 11/29
 Periodic Table Practice 11/29 1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the
Periodic Table Practice 11/29 1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the
In addition to the information at the end of the exam, you will be given a periodic table.
 In addition to the information at the end of the exam, you will be given a periodic table. 1. Express 3143 in scientific notation. a. 3.143 x 10-3 b. 3143 x 10 +3 c. 3.143 x 10 +3 d. 3.143 x 10 +4 2. Express
In addition to the information at the end of the exam, you will be given a periodic table. 1. Express 3143 in scientific notation. a. 3.143 x 10-3 b. 3143 x 10 +3 c. 3.143 x 10 +3 d. 3.143 x 10 +4 2. Express
UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
 UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 2.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into simpler substances. Each element is represented by an abbreviation called
UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 2.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into simpler substances. Each element is represented by an abbreviation called
Regents review Atomic & periodic
 2011-2012 1. The diagram below represents the nucleus of an atom. What are the atomic number and mass number of this atom? A) The atomic number is 9 and the mass number is 19. B) The atomic number is 9
2011-2012 1. The diagram below represents the nucleus of an atom. What are the atomic number and mass number of this atom? A) The atomic number is 9 and the mass number is 19. B) The atomic number is 9
3.1 Classification of Matter. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements 3.1 Classification of Matter Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Matter Matter is the stuff that makes up all things. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 2 Pure
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements 3.1 Classification of Matter Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Matter Matter is the stuff that makes up all things. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 2 Pure
Metric System: 1. The basic unit of length in the metric system is the (a) kilometer (b) mile (c) foot (d) meter (e) none of these 2.
 Metric System: 1. The basic unit of length in the metric system is the (a) kilometer (b) mile (c) foot (d) meter (e) none of these 2. The basic unit of mass in the metric system is the _ (a) gram (b) kilogram
Metric System: 1. The basic unit of length in the metric system is the (a) kilometer (b) mile (c) foot (d) meter (e) none of these 2. The basic unit of mass in the metric system is the _ (a) gram (b) kilogram
1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on
 1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the number of oxidation states 2.
1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the number of oxidation states 2.
Teacher Workbooks. Science and Nature Series. Atomic Structure, Electron Configuration, Classifying Matter and Nuclear Chemistry, Vol.
 Teacher Workbooks Science and Nature Series Atomic Structure, Electron Configuration, Classifying Matter and Nuclear Chemistry, Vol. 1 Copyright 23 Teachnology Publishing Company A Division of Teachnology,
Teacher Workbooks Science and Nature Series Atomic Structure, Electron Configuration, Classifying Matter and Nuclear Chemistry, Vol. 1 Copyright 23 Teachnology Publishing Company A Division of Teachnology,
Test Topics: Periodic Table, Atomic Theory, Physical/Chemical Properties, Atom, Isotopes, Average Atomic Mass
 Elemental Properties Review Worksheet Test Topics: Periodic Table, Atomic Theory, Physical/Chemical Properties, Atom, Isotopes, Average Atomic Mass Periodic Table 1. List the element symbols for the following
Elemental Properties Review Worksheet Test Topics: Periodic Table, Atomic Theory, Physical/Chemical Properties, Atom, Isotopes, Average Atomic Mass Periodic Table 1. List the element symbols for the following
Exam Accelerated Chemistry Study Sheet Chap 04 The Atom/Periodic Table
 Exam Accelerated Chemistry Study Sheet Chap 04 The Atom/Periodic Table Name /87 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. Correct the False statements by changing
Exam Accelerated Chemistry Study Sheet Chap 04 The Atom/Periodic Table Name /87 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. Correct the False statements by changing
What are the isotopes of hydrogen? H, 2 H, and 3 H
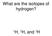 What are the isotopes of hydrogen? 1 H, 2 H, and 3 H The average mass of a boron atom is 10.81. Assuming you were able to isolate only one boron atom, the chance that you would randomly get one with a
What are the isotopes of hydrogen? 1 H, 2 H, and 3 H The average mass of a boron atom is 10.81. Assuming you were able to isolate only one boron atom, the chance that you would randomly get one with a
M T W R. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. (3 pts ea)
 Exam 1 A Fall 2016 a Seat # Name M T W R MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. (3 pts ea) 1) Which of the following is a chemical property?
Exam 1 A Fall 2016 a Seat # Name M T W R MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. (3 pts ea) 1) Which of the following is a chemical property?
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chemi1100pretest1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Accordingly to the periodic law the properties of elements repeat at regular intervals
Chemi1100pretest1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Accordingly to the periodic law the properties of elements repeat at regular intervals
Test Review # 4. Chemistry: Form TR4-5A 6 S S S
 Chemistry: Form TR4-5A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Development of the Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) prepared a card for each of the known elements listing the symbol, the atomic mass,
Chemistry: Form TR4-5A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Development of the Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) prepared a card for each of the known elements listing the symbol, the atomic mass,
1 Arranging the Elements
 CHAPTER 11 1 Arranging the Elements SECTION The Periodic Table BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are elements arranged on the periodic table?
CHAPTER 11 1 Arranging the Elements SECTION The Periodic Table BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are elements arranged on the periodic table?
Periodic Table Workbook
 Key Ideas: The placement or location of elements on the Periodic Table gives an indication of physical and chemical properties of that element. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order
Key Ideas: The placement or location of elements on the Periodic Table gives an indication of physical and chemical properties of that element. The elements on the Periodic Table are arranged in order
Unit 02 Review: Atomic Theory and Periodic Table Review
 Practice Multiple Choice Questions Unit 02 Review: Atomic Theory and Periodic Table Review 1. The number of neutrons in an atom of radioactive C 14 is: a) 6 c) 8 b) 12 d) 14 2. When a radioactive nucleus
Practice Multiple Choice Questions Unit 02 Review: Atomic Theory and Periodic Table Review 1. The number of neutrons in an atom of radioactive C 14 is: a) 6 c) 8 b) 12 d) 14 2. When a radioactive nucleus
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7e (McMurry) Chapter 2 Atoms and the Periodic Table
 Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7e (McMurry) Chapter 2 Atoms and the Periodic Table 1) The smallest amount of an element that retains that element's characteristics is the A)
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7e (McMurry) Chapter 2 Atoms and the Periodic Table 1) The smallest amount of an element that retains that element's characteristics is the A)
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 25 g sample of sugar is found to contain 51.4% oxygen by mass. Another 250 g sample
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 25 g sample of sugar is found to contain 51.4% oxygen by mass. Another 250 g sample
Unit 7 Study Guide: Name: KEY Atomic Concepts & Periodic Table
 Unit 7 Study Guide: Name: KEY Atomic Concepts & Periodic Table Focus Questions for the unit... How has the modern view of the atom changed over time? How does a chemist use symbols and notation to communicate
Unit 7 Study Guide: Name: KEY Atomic Concepts & Periodic Table Focus Questions for the unit... How has the modern view of the atom changed over time? How does a chemist use symbols and notation to communicate
Chapter 2: Atoms. 2.1 (a) NaClO3 (b) AlF (a) The mass number is = 31. (b) The mass number is = 222.
 2.1 (a) NaClO3 (b) AlF3 2.2 (a) The mass number is 15 + 16 = 31. (b) The mass number is 86 + 136 = 222. 2.3 (a) The element has 15 protons, making it phosphorus (P); its symbol is 31 P 15. (b) The element
2.1 (a) NaClO3 (b) AlF3 2.2 (a) The mass number is 15 + 16 = 31. (b) The mass number is 86 + 136 = 222. 2.3 (a) The element has 15 protons, making it phosphorus (P); its symbol is 31 P 15. (b) The element
5. The outermost principal energy level electron configuration of the element bromine is: a. 4s 2 c. 4s 2 4p 5 b. 4p 5 d.
 1 c E = h 1. Sodium and potassium have similar properties because they have the same a. atomic radii. c. number of valence electrons. b. ionization energy. d. electronegativity. 2. Electrons must be added
1 c E = h 1. Sodium and potassium have similar properties because they have the same a. atomic radii. c. number of valence electrons. b. ionization energy. d. electronegativity. 2. Electrons must be added
EXAM 2 PRACTICE PROBLEMS PACKET ANSWER KEY
 EXAM 2 PRACTICE PROBLEMS PACKET ANSWER KEY CHEM 110 1) Write the conversion factor between milliliters and liters (use symbols): 1000 ml = 1 L 2) Write the conversion factor between meters and centimeters
EXAM 2 PRACTICE PROBLEMS PACKET ANSWER KEY CHEM 110 1) Write the conversion factor between milliliters and liters (use symbols): 1000 ml = 1 L 2) Write the conversion factor between meters and centimeters
There is more here than would be on the test, but this is a good example of the types of questions you will encounter.
 Test Study Materials There is more here than would be on the test, but this is a good example of the types of questions you will encounter. Chapter 1 38. Define matter. Explain what is meant by mass and
Test Study Materials There is more here than would be on the test, but this is a good example of the types of questions you will encounter. Chapter 1 38. Define matter. Explain what is meant by mass and
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHM 210 Chemistry Homework #2 Atoms and Elements (Ch. 3) Due: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Helium is a(n) A) heterogeneous mixture.
CHM 210 Chemistry Homework #2 Atoms and Elements (Ch. 3) Due: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Helium is a(n) A) heterogeneous mixture.
6.3 Classifying Elements with the Periodic Table
 6.3 Classifying Elements with the Periodic Table The Periodic Table was developed by scientists to organize elements in such a way as to make sense of the growing information about their properties. The
6.3 Classifying Elements with the Periodic Table The Periodic Table was developed by scientists to organize elements in such a way as to make sense of the growing information about their properties. The
Units 1, 2 study guide- atomic structure
 Name: Units 1, 2 study guide- atomic structure 1) Complete the required information for each subatomic particle (T1.3) symbol name charge location Mass (AMU) p + e - n 0 2) Define the following terms:
Name: Units 1, 2 study guide- atomic structure 1) Complete the required information for each subatomic particle (T1.3) symbol name charge location Mass (AMU) p + e - n 0 2) Define the following terms:
The Periodic Table of the Elements
 The Periodic Table of the Elements All matter is composed of elements. All of the elements are composed of atoms. An atom is the smallest part of an element which still retains the properties of that element.
The Periodic Table of the Elements All matter is composed of elements. All of the elements are composed of atoms. An atom is the smallest part of an element which still retains the properties of that element.
Chapter 2 The Structure of Matter and the Chemical Elements
 9 Chapter 2 The Structure of Matter and the Chemical Elements Review Skills 2.1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases Solids Liquids Gases Internet: The Structure of Matter 2.2 The Chemical Elements Internet: Element
9 Chapter 2 The Structure of Matter and the Chemical Elements Review Skills 2.1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases Solids Liquids Gases Internet: The Structure of Matter 2.2 The Chemical Elements Internet: Element
Reporting Category 1: Matter and Energy
 Name: Science Teacher: Reporting Category 1: Matter and Energy Atoms 8.5A Fill in the missing information to summarize what you know about atomic structure. Name of Subatomic Particle Location within the
Name: Science Teacher: Reporting Category 1: Matter and Energy Atoms 8.5A Fill in the missing information to summarize what you know about atomic structure. Name of Subatomic Particle Location within the
Unit 1: Analyzing Data 1. Measure the following using the appropriate number of significant digits. Name Hour Date. b. o C
 Name Hour Date Chemistry Semester 1 Review!!! If you have completed ALL of the review on the assigned days you are allowed to use a cheat sheet that is created on the back of the periodic table found on
Name Hour Date Chemistry Semester 1 Review!!! If you have completed ALL of the review on the assigned days you are allowed to use a cheat sheet that is created on the back of the periodic table found on
Test Review # 5. Chemistry: Form TR5-8A. Average Atomic Mass. Subatomic particles.
 Chemistry: Form TR5-8A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 5 Subatomic particles. Type of Particle Location Mass Relative Mass Charge Proton Center 1.67 10-27 kg 1 +1 Electron Outside 9.11 10-31 kg 0-1
Chemistry: Form TR5-8A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 5 Subatomic particles. Type of Particle Location Mass Relative Mass Charge Proton Center 1.67 10-27 kg 1 +1 Electron Outside 9.11 10-31 kg 0-1
Chemistry CRT Study Guide First Quarter
 Number AL COS # 1. #1.0 Classify sodium chloride as an element, mixture, compound, or colloid. Compound 2. #1.0 Classify air as an element, mixture, compound, or colloid. Mixture 3. #1.0 Classify a blueberry
Number AL COS # 1. #1.0 Classify sodium chloride as an element, mixture, compound, or colloid. Compound 2. #1.0 Classify air as an element, mixture, compound, or colloid. Mixture 3. #1.0 Classify a blueberry
Identify the five scientists that progressed atomic structure Illustrate each scientist s model of the atom
 Semester Review What happens to electronegativity down a group? electrons for aluminum Identify the five scientists that progressed atomic structure Illustrate each scientist s model of the atom Circle
Semester Review What happens to electronegativity down a group? electrons for aluminum Identify the five scientists that progressed atomic structure Illustrate each scientist s model of the atom Circle
A sample of carbon dioxide has a volume of 28.7 L and a mass of 52.5 g at 20 C. Determine the density of carbon dioxide at this temperature.
 Semester Review A sample of carbon dioxide has a volume of 28.7 L and a mass of 52.5 g at 20 C. Determine the density of carbon dioxide at this temperature. 1.83 g/l Describe what defines an element s
Semester Review A sample of carbon dioxide has a volume of 28.7 L and a mass of 52.5 g at 20 C. Determine the density of carbon dioxide at this temperature. 1.83 g/l Describe what defines an element s
Test Review # 4. Chemistry: Form TR4-9A
 Chemistry: Form TR4-9A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Location of electrons. Electrons are in regions of the atom known as orbitals, which are found in subdivisions of the principal energy levels
Chemistry: Form TR4-9A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Location of electrons. Electrons are in regions of the atom known as orbitals, which are found in subdivisions of the principal energy levels
1. Ham radio operators often broadcast on the 6 meter band. The frequency of this electromagnetic radiation is MHz. a. 500 b. 200 c. 50 d. 20 e. 2.
 Name: Score: 0 / 60 points (0%) [1 open ended question not graded] Chapters 6&7 Practice Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Ham radio
Name: Score: 0 / 60 points (0%) [1 open ended question not graded] Chapters 6&7 Practice Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Ham radio
THE PERIODIC TABLE, OBSERVABLE PROPERTIES & ATOMIC THEORY
 CH 11 T7 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC THEORY 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) relate stability of the NOBLE GASSES to electron arrangement within the atom. 2) relate the charge of MONATOMIC
CH 11 T7 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC THEORY 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) relate stability of the NOBLE GASSES to electron arrangement within the atom. 2) relate the charge of MONATOMIC
Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT.
 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
Chapter 2: Atoms. 2.1 (a) NaClO 3 (b) AlF (a) The mass number is = 31. (b) The mass number is = 222.
 2.1 (a) NaClO 3 (b) AlF 3 2.2 (a) The mass number is 15 + 16 = 31. (b) The mass number is 86 + 136 = 222. 2.3 (a) The element has 15 protons, making it phosphorus (P); its symbol is 31 P 15. (b) The element
2.1 (a) NaClO 3 (b) AlF 3 2.2 (a) The mass number is 15 + 16 = 31. (b) The mass number is 86 + 136 = 222. 2.3 (a) The element has 15 protons, making it phosphorus (P); its symbol is 31 P 15. (b) The element
THE PERIODIC TABLE, OBSERVABLE PROPERTIES & ATOMIC THEORY
 CH 11 T7 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC THEORY 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) relate stability of the NOBLE GASSES to electron arrangement within the atom. 2) relate the charge of MONATOMIC
CH 11 T7 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC THEORY 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) relate stability of the NOBLE GASSES to electron arrangement within the atom. 2) relate the charge of MONATOMIC
Chem 1A Chapter 5 and 21 Practice Test Grosser ( )
 Class: Date: Chem A Chapter 5 and 2 Practice Test Grosser (203-204) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. The periodic law states that the properties
Class: Date: Chem A Chapter 5 and 2 Practice Test Grosser (203-204) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. The periodic law states that the properties
Part A Unit-based exercise
 Topic 2 Microscopic World I / Microscopic World (Combined Science) Part A Unit-based exercise Unit 5 Atomic structure Fill in the blanks 1 atoms 2 solids; liquids; gases 3 metals; metalloids; non-metals
Topic 2 Microscopic World I / Microscopic World (Combined Science) Part A Unit-based exercise Unit 5 Atomic structure Fill in the blanks 1 atoms 2 solids; liquids; gases 3 metals; metalloids; non-metals
protons electrons neutrons nucleus Center of the atom; contains protons and neutrons. The Atom Molecules are made up of two or more atoms.
 _ Period: The Atom Ch. 18:1 Everything is made of atoms. Atoms are the smallest part of matter. Atoms are made up of 3 subatomic particles (particles smaller than the atom): electrons, protons, and neutrons.
_ Period: The Atom Ch. 18:1 Everything is made of atoms. Atoms are the smallest part of matter. Atoms are made up of 3 subatomic particles (particles smaller than the atom): electrons, protons, and neutrons.
Reporting Category 1: Matter and Energy
 Name: Science Teacher: Reporting Category 1: Matter and Energy Atoms Fill in the missing information to summarize what you know about atomic structure. Name of Subatomic Particle Location within the Atom
Name: Science Teacher: Reporting Category 1: Matter and Energy Atoms Fill in the missing information to summarize what you know about atomic structure. Name of Subatomic Particle Location within the Atom
Unit 3 Atomic Structure
 Name: Unit 3 Atomic Structure Scientist Year Contribution and/ or Experimental Work Democritus Aristotle Alchemists Boyle Franklin Dalton Avogadro Mendeleev Moseley 1 Scientist Year Contribution and/ or
Name: Unit 3 Atomic Structure Scientist Year Contribution and/ or Experimental Work Democritus Aristotle Alchemists Boyle Franklin Dalton Avogadro Mendeleev Moseley 1 Scientist Year Contribution and/ or
General Chemistry 1 (CHEM 1141) Shawnee State University Fall 2018 September 27, 2018
 General Chemistry 1 (CHEM 1141) Shawnee State University Fall 2018 September 27, 2018 Exam # 1 A Name Please write your full name, and the exam version (1 A) that you have on the scantron sheet! (Bubble
General Chemistry 1 (CHEM 1141) Shawnee State University Fall 2018 September 27, 2018 Exam # 1 A Name Please write your full name, and the exam version (1 A) that you have on the scantron sheet! (Bubble
In this activity, you will use the same information they had to construct your own periodic table.
 Building the Periodic Table from Scratch Name: Period: Introduction: Before the periodic table could be built, the individual elements had to be found and their properties tested. Although elements such
Building the Periodic Table from Scratch Name: Period: Introduction: Before the periodic table could be built, the individual elements had to be found and their properties tested. Although elements such
HSVD Ms. Chang Page 1
 Name: Chemistry, PERIODIC TABLE 1. A solid element that is malleable, a good conductor of electricity, and reacts with oxygen is classified as a (1) noble gas (2) metalloid (3) metal (4) nonmetal 2. Which
Name: Chemistry, PERIODIC TABLE 1. A solid element that is malleable, a good conductor of electricity, and reacts with oxygen is classified as a (1) noble gas (2) metalloid (3) metal (4) nonmetal 2. Which
Homework Packet Unit 2. b. Al 3+, F, Na +, Mg 2+, O 2
 Name Period Homework Packet Unit 2 1. Which of the following is the correct empirical formula for a compound that has 37.5% C, 12.6% H, and 49.9% O? (A) C 2 H 4 O (B) CH 4 O 2 (C) CH 5 O 2 (D) CH 4 O (E)
Name Period Homework Packet Unit 2 1. Which of the following is the correct empirical formula for a compound that has 37.5% C, 12.6% H, and 49.9% O? (A) C 2 H 4 O (B) CH 4 O 2 (C) CH 5 O 2 (D) CH 4 O (E)
Chemistry. Chemistry is the study of the interactions between atoms and molecules. Atoms and Molecules
 Chemistry Chemistry is the study of the interactions between atoms and molecules. Atoms and Molecules An atom is a particle of matter that cannot be further divided without changing the chemical identity
Chemistry Chemistry is the study of the interactions between atoms and molecules. Atoms and Molecules An atom is a particle of matter that cannot be further divided without changing the chemical identity
Q. Why is hydrogen located on the left side of the periodic table with the active metals, even
 REPRESENTATIVE GROUPS Q. Why is hydrogen located on the left side of the periodic table with the active metals, even though it is a gas? Hydrogen s location is related to its electron configuration, not
REPRESENTATIVE GROUPS Q. Why is hydrogen located on the left side of the periodic table with the active metals, even though it is a gas? Hydrogen s location is related to its electron configuration, not
Chem A Practice Exam f2013
 Class: Date: Chem A Practice Exam f2013 Short Answer 1. The following length measurements were taken by students using several different measuring devices. Find the average of the measurements. Make sure
Class: Date: Chem A Practice Exam f2013 Short Answer 1. The following length measurements were taken by students using several different measuring devices. Find the average of the measurements. Make sure
Regan & Johnston Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period
 Regan & Johnston Name Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period 1. An atom of which element has the largest atomic radius? (1) Si (2) Fe (3) Zn (4) Mg 2. Which characteristics both generally
Regan & Johnston Name Chemistry Unit 3 Exam: The Periodic Table Class Period 1. An atom of which element has the largest atomic radius? (1) Si (2) Fe (3) Zn (4) Mg 2. Which characteristics both generally
1 Arranging the Elements
 CHAPTER 12 1 Arranging the Elements SECTION The Periodic Table BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are elements arranged on the periodic table?
CHAPTER 12 1 Arranging the Elements SECTION The Periodic Table BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are elements arranged on the periodic table?
The Atom/Periodic Table After School Regents Review Practice
 1. An ion that consists of 7 protons, 9 neutrons, and 10 electrons has a net charge of A) 2 B) 2+ C) 3+ D) 3 2. The mass of a proton is approximately equal to the mass of A) an electron B) a neutron C)
1. An ion that consists of 7 protons, 9 neutrons, and 10 electrons has a net charge of A) 2 B) 2+ C) 3+ D) 3 2. The mass of a proton is approximately equal to the mass of A) an electron B) a neutron C)
new experimental data, and can be modified
 Mass in grams 10 20 30 40 50 Name: Date: Period: CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review CHAPTERS 1 & 2: Scientific Method, Density, Metric Conversions, Accuracy/Precision, Significant Figures 1. Know
Mass in grams 10 20 30 40 50 Name: Date: Period: CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review CHAPTERS 1 & 2: Scientific Method, Density, Metric Conversions, Accuracy/Precision, Significant Figures 1. Know
Electronic Structure and Bonding Review
 Name: Band: Date: Electronic Structure and Bonding Review 1. For electrons: a. What is the relative charge? b. What is the relative mass? c. What is the symbol? d. Where are they located in the modern
Name: Band: Date: Electronic Structure and Bonding Review 1. For electrons: a. What is the relative charge? b. What is the relative mass? c. What is the symbol? d. Where are they located in the modern
Note Taking Guide: Episode 401. arranged elements by. predicted of missing. discovered that each has a unique. arranged elements by
 Note Taking Guide: Episode 401 Dmitri Mendeleev: arranged elements by. predicted of missing. Henry Moseley: discovered that each has a unique. arranged elements by. now all elements fit into place based
Note Taking Guide: Episode 401 Dmitri Mendeleev: arranged elements by. predicted of missing. Henry Moseley: discovered that each has a unique. arranged elements by. now all elements fit into place based
5E Essential Lesson-SC.8.P.8.6. Element Name: Hydrogen (H) Element Name: Helium (He) Number of orbitals: 1. Number of valence electrons: 2
 Element Name: Hydrogen (H) Number of orbitals: 1 Number of protons: 1 Atomic Mass: 1.01 AMU Properties: gas, bonds with other elements, flammable Element Name: Helium (He) Number of orbitals: 1 Number
Element Name: Hydrogen (H) Number of orbitals: 1 Number of protons: 1 Atomic Mass: 1.01 AMU Properties: gas, bonds with other elements, flammable Element Name: Helium (He) Number of orbitals: 1 Number
1 The atomic mass of titanium is atomic mass units. This atomic mass represents the
 Direct: Answer the following question(s). 1 The atomic mass of titanium is 47.88 atomic mass units. This atomic mass represents the A. total mass of all the protons and neutrons in an atom of Ti B. total
Direct: Answer the following question(s). 1 The atomic mass of titanium is 47.88 atomic mass units. This atomic mass represents the A. total mass of all the protons and neutrons in an atom of Ti B. total
1. Electronic Structure 2. Electron Configuration 3. Core Notation 4. EC Relationship to Periodic Table 5. Electron Configuration of Ions
 Pre-AP Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory II Name: Date: Block: 1. Electronic Structure 2. Electron Configuration 3. Core Notation 4. EC Relationship to Periodic Table 5. Electron Configuration of Ions Electronic
Pre-AP Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory II Name: Date: Block: 1. Electronic Structure 2. Electron Configuration 3. Core Notation 4. EC Relationship to Periodic Table 5. Electron Configuration of Ions Electronic
Unit 4 - Periodic Table Exam Name: PRACTICE QUESTIONS Date: 2/23/2016
 Name: PRACTICE QUESTIONS Date: 2/23/2016 1. Which pair of symbols represents a metalloid and a noble gas? 1) Si and Bi 2) As and Ar 3) Ge and Te 4) Ne and Xe 2. What determines the order of placement of
Name: PRACTICE QUESTIONS Date: 2/23/2016 1. Which pair of symbols represents a metalloid and a noble gas? 1) Si and Bi 2) As and Ar 3) Ge and Te 4) Ne and Xe 2. What determines the order of placement of
Writing Chemical formula with polyatomic groups
 Writing Chemical formula with polyatomic groups 1. Use the Periodic table to determine the combining powers of single elements. Eg. Magnesium is in Group 2 and has a combining power of 2. 2. Use Table
Writing Chemical formula with polyatomic groups 1. Use the Periodic table to determine the combining powers of single elements. Eg. Magnesium is in Group 2 and has a combining power of 2. 2. Use Table
Part I: Structure of Matter
 Part I: Structure of Matter What is Matter? Matter is anything with mass and volume (occupies space). Matter is composed of atoms. Note: Atoms are different from cells. Cells are the basic unit of all
Part I: Structure of Matter What is Matter? Matter is anything with mass and volume (occupies space). Matter is composed of atoms. Note: Atoms are different from cells. Cells are the basic unit of all
Modern Atomic Theory
 Modern Atomic Theory Review of the Discovery of the Atom 1803 John Dalton discovered that elements are made of atoms. He thought that atoms were solid, like a marble. 1875 Crooks discovered the electron.
Modern Atomic Theory Review of the Discovery of the Atom 1803 John Dalton discovered that elements are made of atoms. He thought that atoms were solid, like a marble. 1875 Crooks discovered the electron.
Chemistry 9 Weeks Exam Review Guide
 Name Date: Chemistry 9 Weeks Exam Review Guide 9 Weeks Exam: Tuesday, October 15 th Topics Covered Unit 1 Measurement: Accuracy & Precision, metric system, Conversions, Significant Figures, Percent Error,
Name Date: Chemistry 9 Weeks Exam Review Guide 9 Weeks Exam: Tuesday, October 15 th Topics Covered Unit 1 Measurement: Accuracy & Precision, metric system, Conversions, Significant Figures, Percent Error,
Electron Configurations
 Section 3 Electron Configurations Key Terms electron configuration Pauli exclusion principle noble gas Aufbau principle Hund s rule noble-gas configuration Main Ideas Electrons fill in the lowest-energy
Section 3 Electron Configurations Key Terms electron configuration Pauli exclusion principle noble gas Aufbau principle Hund s rule noble-gas configuration Main Ideas Electrons fill in the lowest-energy
Chemistry Chapter 9 Review. 2. Calculate the wavelength of a photon of blue light whose frequency is 6.3 x s -1.
 Chemistry Chapter 9 Review 1. What is the frequency of radiation that has a wavelength of 4.7 x 10-5 cm? 2. Calculate the wavelength of a photon of blue light whose frequency is 6.3 x 10 14 s -1. 3. The
Chemistry Chapter 9 Review 1. What is the frequency of radiation that has a wavelength of 4.7 x 10-5 cm? 2. Calculate the wavelength of a photon of blue light whose frequency is 6.3 x 10 14 s -1. 3. The
5. All isotopes of a given element must have the same (A) atomic mass (B) atomic number (C) mass number (D) number of neutrons
 1. Which substance can be decomposed by a chemical change? (A) beryllium (B) boron (C) methanol (D) magnesium 2. The particles in a crystalline solid are arranged (A) randomly and far apart (B) randomly
1. Which substance can be decomposed by a chemical change? (A) beryllium (B) boron (C) methanol (D) magnesium 2. The particles in a crystalline solid are arranged (A) randomly and far apart (B) randomly
Honors Chemistry: Chapter 4- Problem Set (with some 6)
 Honors Chemistry: Chapter 4- Problem Set (with some 6) All answers and work on a separate sheet of paper! Classify the following as always true (AT), sometimes true (ST), or never true (NT) 1. Atoms of
Honors Chemistry: Chapter 4- Problem Set (with some 6) All answers and work on a separate sheet of paper! Classify the following as always true (AT), sometimes true (ST), or never true (NT) 1. Atoms of
Organizing the Periodic Table
 Organizing the Periodic Table How did chemists begin to organize the known elements? Chemists used the properties of the elements to sort them into groups. The Organizers JW Dobereiner grouped the elements
Organizing the Periodic Table How did chemists begin to organize the known elements? Chemists used the properties of the elements to sort them into groups. The Organizers JW Dobereiner grouped the elements
A. Element 1. The number of protons and neutrons of an atom.
 Unit 03: Test Review Atoms and Elements Key Term Definition A. Element 1. The number of protons and neutrons of an atom. B. Atom 2. The smallest particle of an element. C. Atomic Number 3. A primary substance
Unit 03: Test Review Atoms and Elements Key Term Definition A. Element 1. The number of protons and neutrons of an atom. B. Atom 2. The smallest particle of an element. C. Atomic Number 3. A primary substance
8. Which of the following could be an isotope of chlorine? (A) 37 Cl 17 (B) 17 Cl 17 (C) 37 Cl 17 (D) 17 Cl 37.5 (E) 17 Cl 37
 Electronic Structure Worksheet 1 Given the following list of atomic and ionic species, find the appropriate match for questions 1-4. (A) Fe 2+ (B) Cl (C) K + (D) Cs (E) Hg + 1. Has the electron configuration:
Electronic Structure Worksheet 1 Given the following list of atomic and ionic species, find the appropriate match for questions 1-4. (A) Fe 2+ (B) Cl (C) K + (D) Cs (E) Hg + 1. Has the electron configuration:
1) What is the name given to the element with the symbol "K"? A) Potassium B) Krypton C) Phosphorus D) Kallium
 Practice Exam 1 (Chapters 1-4) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the name given to the element with the symbol "K"?
Practice Exam 1 (Chapters 1-4) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the name given to the element with the symbol "K"?
Solid Gas Liquid Plasma
 Unit 1: MATTER 1. Define CHEMISTRY: 2. Define MATTER: Use one of the states of matter to complete each statement. (Words will be used more than once.) Solid Gas Liquid Plasma 3. A has definite volume and
Unit 1: MATTER 1. Define CHEMISTRY: 2. Define MATTER: Use one of the states of matter to complete each statement. (Words will be used more than once.) Solid Gas Liquid Plasma 3. A has definite volume and
Test 3: Lab Safety, Measurements, Matter and Periodic Table
 Name: Grade/Group: Subject: Chemistry-7 Teacher: Mrs. Raj Date: Test 3: Lab Safety, Measurements, Matter and Periodic Table Directions: Determine the best answer for each question. Circle your answer on
Name: Grade/Group: Subject: Chemistry-7 Teacher: Mrs. Raj Date: Test 3: Lab Safety, Measurements, Matter and Periodic Table Directions: Determine the best answer for each question. Circle your answer on
Worksheet #1: Atomic Spectra Answer the following questions using your Unit 3 notes.
 Worksheet #1: Atomic Spectra 1. How did Bohr expand on Rutherford s model of the atom? 2. Compare the energy of an electron in the ground state and an electron in the excited state. 3. When an electron
Worksheet #1: Atomic Spectra 1. How did Bohr expand on Rutherford s model of the atom? 2. Compare the energy of an electron in the ground state and an electron in the excited state. 3. When an electron
Chemistry Released Questions
 Name: Date: 1. What was Niels Bohr s prediction about the location of the electrons in an atom? 3. An atom with which atomic diagram has chemical properties most similar to calcium? A. Electrons pair with
Name: Date: 1. What was Niels Bohr s prediction about the location of the electrons in an atom? 3. An atom with which atomic diagram has chemical properties most similar to calcium? A. Electrons pair with
Chapter 4. Lecture Presentation
 Chapter 4 Lecture Presentation 4.1 Elements and Symbols 4.2 The Periodic Table 4.3 The Atom 4.4 Atomic Number and Mass Number 4.5 Isotopes and Atomic Mass 4.6 Electron Energy Levels 4.7 Electron Configurations
Chapter 4 Lecture Presentation 4.1 Elements and Symbols 4.2 The Periodic Table 4.3 The Atom 4.4 Atomic Number and Mass Number 4.5 Isotopes and Atomic Mass 4.6 Electron Energy Levels 4.7 Electron Configurations
"In Terms Of" 1. Explain, in terms of electron configuration, why arsenic and antimony are chemically similar.
 Name: Mrs. Vandergoot "In Terms Of" Regents Chemistry 1. Explain, in terms of electron configuration, why arsenic and antimony are chemically similar. 2. Base your answer to the following question on the
Name: Mrs. Vandergoot "In Terms Of" Regents Chemistry 1. Explain, in terms of electron configuration, why arsenic and antimony are chemically similar. 2. Base your answer to the following question on the
CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review
 Mass in grams 10 20 30 40 50 CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review 1. Know the symbol and the power of 10 for the following metric prefixes: A. Mega M 10 6 D. deka da 10 1 G. milli m 10 6 B. kilo k
Mass in grams 10 20 30 40 50 CP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Test Review 1. Know the symbol and the power of 10 for the following metric prefixes: A. Mega M 10 6 D. deka da 10 1 G. milli m 10 6 B. kilo k
Chemistry 110 Lecture Notes. EXAM I Material. The Universe According to Physical Sciences: Chemistry: Physics: Areas of Application in Chemistry:
 The Universe According to Physical Sciences: Chemistry 110 Lecture Notes EXAM I Material Chemistry: Physics: Areas of Application in Chemistry: 1 MATH TOOLS FOR CHEMISTRY I. Scientific Notation Scientific
The Universe According to Physical Sciences: Chemistry 110 Lecture Notes EXAM I Material Chemistry: Physics: Areas of Application in Chemistry: 1 MATH TOOLS FOR CHEMISTRY I. Scientific Notation Scientific
3. (3) For each of the following measurements, state the number of significant figures, the uncertainty, and the range of possible values.
 Exam 1 Chem 30A, Fall 11 Fossum Name: Note: there are 5 points of extra credit built in to this exam. 1. (2) Shown here is a close-up of part of a ruler. The units are centimeters. If you were measuring
Exam 1 Chem 30A, Fall 11 Fossum Name: Note: there are 5 points of extra credit built in to this exam. 1. (2) Shown here is a close-up of part of a ruler. The units are centimeters. If you were measuring
