Advanced Organic Chemistry
|
|
|
- Leslie Ward
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Advanced rganic Chemistry Gareth J. Rowlands
2 2 Enantioselective synthesis Why is enantioselective synthesis important? ature yields an enormous variety of chiral compounds A change in stereochemistry can have profound effects Ac 2 C C 2 azadiractin anti-feedant (S)-3-(1-methylpyrrolidin- 2-yl)pyridine nicotine toxin / stimulant (1R,2R,3S,5S)-2-acetyl-8-methyl-8- aza-bicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-yl benzoate cocaine stimulant 2 C 2 (S)-2-aminopropanoic acid L-alanine mammalian amino acid 2 C 2 (R)-2-aminopropanoic acid D-alanine bacterial cell wall (S)-2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3- yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione (S)-thalidomide teratogen (birth defects)
3 3 Chirality and biology IV protease + inhibitor icotinic receptor Enzymes & receptors are invariably chiral Chiral drugs can interact with these to give two diastereomeric complexes Imagine the hand below is the enzyme, it can form two very different complexes depending on the chirality or handness of the drug it interacts with...
4 4 Chirality and biology II S C 2 S C (R)-1-(isopropylamino)-4- (naphthalen-1-yl)butan-2-ol ( )-propanolol β-blocker for heart disease (S)-1-(isopropylamino)-4- (naphthalen-1-yl)butan-2-ol (+)-propanolol contraceptive (S)-2-amino-3-mercapto-3- methylbutanoic acid D-penicillamine treats chronic arthritus (R)-2-amino-3-mercapto-3- methylbutanoic acid L-penicillamine toxic Et Et (S,S)-2-[2-(1-ydroxymethylpropylamino)-ethylamino]-butan-1-ol Ethambutol tuberculostatic (anti-tb) Et Et (R,R)-2-[2-(1-ydroxymethylpropylamino)-ethylamino]-butan-1-ol causes blindness As you can imagine, these two complexes can have very different effects The three drugs above highlight the possible effects of using the wrong compound As a result we must have methods to prepare the correct enantiomers
5 5 Revision: terminology Stereoisomers - Isomers that differ only by the arrangement of substituents in space Stereogenic element - the focus of stereoisomerism, be it a stereogenic centre, axis or plane, within the molecule such that the change of two substituents about this element leads to different stereoisomers The easiest to identify are the cis-trans isomers found with sp 2 systems Alkenes should be assigned E or Z using Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules We are not going to look at these BUT will see their effects in enolate chemistry A C A C B D A & C have highest priority alkene = Z B D A & D have highest priority alkene = E Imines are treated in a similar manner A B C A has highest priority imine = Z or cis A B C B has highest priority imine = E or trans
6 6 ne stereogenic centre: chirality on an atom Chiral compounds - simply a molecule (or object) that cannot be superimposed upon its mirror image Most obvious example is our hands... image Left & right hands on-superimposable Chiral centre - In a tetrahedral (Xabcd) or trigonal pyramidal (Xabc) structure, the...atom X to which the four (or three, respectively) substituents abc(d) are attached Ph Ph P chiral centre
7 7 ne stereogenic centre: chirality on an atom plane plane rotate rotate Chiral images are non-superimposable Each mirror image is an enantiomer nly differ by their absolute...configuration or actual 3D shape Simplistically - 4 different groups Do not have a plane of symmetry R 4 R 3 R 1 R 2 achiral R 4 R 3 R 1 =R 1 R 3 R 4 chiral R 1 R 2 R 3 R 4 Achiral images are superimposable Compound has a plane of symmetry R 1 R 1 plane of symmetry running through central carbon, hydrogen and ACIRAL
8 8 Enantiomers & optical rotation α light source light (λ) polariser plane polarised light sample cell length l (dm) reading Each enantiomer has identical physical & chemical properties (in an achiral environment) nly differ by how they rotate plane polarised light (rotate in opposite directions Enantiomers are said to be optically active ot very useful as value is very unreliable (dependent on solvent & all factors below) Even sign (+/ ) can change depending on concentration!! Ph C 2 (R)-(-)-mandelic acid C [α] D Ph C 2 (S)-(+)-mandelic acid C [α] D optical rotation [α] t = D α l x c α = observed rotation; l = cell path (dm); c = concentration g/ ml (or g/100ml); t = temperature
9 9 Defining absolute configuration 2 C 2 alanine eed to be able to define the absolute configuration of a chiral centre First assign priorities according to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules (highest atomic number) C 2 2 rotate around axis until lowest priority points away from you 2 C 2 2 C C 2 2 ext rotate molecule until lowest priority (4) is pointing away from viewer Draw a line connecting 1 to 3 If line clockwise (right) the (R) If line anti-clockwise (left) the (S) 1 2 C 2 (S)-alanine (S)-2-aminopropanoic acid
10 10 Defining absolute configuration II P 2 P Ph 4 3 Define priorities according to CIP Point lowest priority (4) away from viewer Draw line from 1 to 3 Line is anti-clockwise so (S) 1 P 2 Ar Ph S S 3 2 Define priorities according to CIP Point lowest priority (4) away from viewer Draw line from 1 to 3 Line is anti-clockwise so (R) 1 S Tol 3 2 P (S)-(4- methoxyphenyl)methylphenyl phosphine oxide S (R)-methyl-4- methylphenylsulfoxide
11 11 Central chirality at elements other than carbon Chiral itrogen compounds As last two examples indicated it is not just carbon that can have central chirality Any tetrahedral or pyramidal atom with four (three) different substituents can be chiral itrogen / amines have the potential to be chiral... R 1 R 3 R 2 R 1 R 2 R3 Tröger's base (5S)-2,8-Dimethyl-6,12-5,11- methano-dibenzo[b,f][1,5]diazocine But rapid pyramidal inversion normally prevents isolation of either enantiomer If substituents are constrained in a ring then rigid structure prevents inversion Quaternary ammonium salts (below) can be isolated enantiomerically pure Racemisation has been observed, presumably via dissociation... Ph Et i-pr Cl
12 12 Central chirality at phosphorus Trigonal pyramidal phosphorus (III) is configurationally stable below 200 C P-chiral phosphines have a rich history as chiral ligands P (S)-cyclohexyl(4- methoxyphenyl)(methyl) phosphine X P Tetrahedral phosphorus (V) is configurationally stable P t-bu Ph (S)-naphthalen-1-yl tertbutyl(phenyl)phosphinate
13 13 Central chirality at sulfur Sulfoxides are tetrahedral; remember they have a lone pair! Configurationally stable at room temperature Certain anions (Cl ) can cause racemisation (interconversion of the enantiomers) S (R)-1-methyl-4- (methylsulfinyl)benzene S S (R)-S-tert-butyl 2- methylpropane-2- sulfinothioate t-bu S Ph (S)--benzylidene-2- methylpropane-2-sulfinamide It should be stressed that the definition of a chiral compound is that it cannot be superimposed upon its mirror image A stereogenic centre (central chirality) is sufficient for the existence of chirality it is not a requirement Furthermore, as we shall see, not all compounds with a stereogenic centre are chiral!!
14 14 Axial chirality Axial chirality - onplanar arrangement of four groups about an axis Spiro-compounds axis of chirality 2 C C 2 D-Fecht acid (S)-spiro[3.3]heptane-2,6- dicarboxylic acid 2 C C 2 L-Fecht acid (R)-spiro[3.3]heptane-2,6- dicarboxylic acid C 2 C 2 2 C C 2 Viewed along axis axis of chirality olean (R)-1,7- dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane attracts male olive flies olean (S)-1,7- dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane attracts female olive flies 4 R 2 C 2 C 2 R 3 R R 1 anti-clockwise = (S)
15 15 Axial chirality II axis of chirality Cl C Cl (R)-1,3-dichloropropa- 1,2-diene Allenes Cl C Cl (S)-1,3-dichloropropa- 1,2-diene Axial chirality and atropisomerism Atropisomers - stereoisomers resulting from restricted rotation about a single bond Mostly commonly found in hindered biaryls axis of chirality PPh 2 PPh 2 Ph 2 P Ph 2 P (R)-(+)-BIAP (R)-2-(diphenylphosphino)-1-(2- (diphenylphosphino)naphthalen -1-yl)naphthalene (S)-(-)-BIAP (S)-2-(diphenylphosphino)-1-(2- (diphenylphosphino)naphthalen -1-yl)naphthalene
16 16 Axial chirality III Atropisomerism is not just found in biaryl compounds Any molecule in which rotation is restricted sufficiently to allow isolation of each isomer can be chiral... rotation around central bond C X C Atropisomerism is found in nature Vancomycin is an anti-bacterial Kotanin is from rice mold 2 Cl 2 C Cl 2 kotanin Vancomycin
17 17 elicity Molecules that twist like a helix, propeller or screw Right-handed helix is denoted P (clockwise as you travel away from viewer) Interestingly, [8]helicene racemises (1:1 mixture of enantiomers) readily at 293 C! P [8]helicene M [8]helicene
18 18 Planar chirality Planar chirality - chirality resulting from the arrangement of out-of-plane groups with respect to a plane, called the chiral plane In [2.2]paracyclophane the more substituted benzene ring is considered the chiral plane 2 2 (R)-4-amino[2.2]paracyclophane (S)-4-amino[2.2]paracyclophane 2 plane of chirality
19 19 Planar chirality II Probably the most important planar chiral compounds are ferrocene derivatives These have found considerable use in enantioselective catalysis Ph Fe PPh 2 Ph Ph 2 P Fe (S)-2-phenyl-1- (diphenylphosphanyl) ferrocene (R)-2-phenyl-1- (diphenylphosphanyl) ferrocene An interesting example of planar chirality is found in some (E)-cycloalkenes (R)-(E)-cyclooctene (S)-(E)-cyclooctene
Unit One Part 8: stereochemistry
 Unit ne Part 8: stereochemistry 1 Describe the difference between stereoisomers & structural isomers omenclature used for double bonds (cis-trans or E-Z) Predict conformations of cyclohexanes Define chirality
Unit ne Part 8: stereochemistry 1 Describe the difference between stereoisomers & structural isomers omenclature used for double bonds (cis-trans or E-Z) Predict conformations of cyclohexanes Define chirality
Stereochemistry. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition
 Stereochemistry Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition Stereochemistry! Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry)! A right-hand glove
Stereochemistry Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition Stereochemistry! Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry)! A right-hand glove
CH 3 C 2 H 5. Tetrahedral Stereochemistry
 Ch 5 Tetrahedral Stereochemistry Enantiomers - Two non-superimposable mirror image molecules - They are stereoisomers with the same atoms and bonds, but different spatial geometries. - The two molecules
Ch 5 Tetrahedral Stereochemistry Enantiomers - Two non-superimposable mirror image molecules - They are stereoisomers with the same atoms and bonds, but different spatial geometries. - The two molecules
9. Stereochemistry. Stereochemistry
 9. Stereochemistry Stereochemistry Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry) A right-hand glove is different than a left-hand glove (See Figure
9. Stereochemistry Stereochemistry Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry) A right-hand glove is different than a left-hand glove (See Figure
Stereochemistry. In organic chemistry, subtle differences in spatial arrangements can give rise to prominent effects.
 Stereochemistry This is study of the 3 dimensional arrangement in space of molecules. In organic chemistry, subtle differences in spatial arrangements can give rise to prominent effects. E.g. the isomers
Stereochemistry This is study of the 3 dimensional arrangement in space of molecules. In organic chemistry, subtle differences in spatial arrangements can give rise to prominent effects. E.g. the isomers
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH.3 - STEREOISOMERISM AND CHIRALITY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: TYPES OF ISOMERS Isomers are used to describe relationships between similar molecules. We can order these relationships in order of increasing similarity Page 2 CONCEPT:
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: TYPES OF ISOMERS Isomers are used to describe relationships between similar molecules. We can order these relationships in order of increasing similarity Page 2 CONCEPT:
CHAPTER 5. Stereoisomers
 CHAPTER 5 Stereoisomers We have already covered two kinds of isomerism: Constitutional Isomers (structural isomers) Stereoisomers Examples of Constitutional Isomers: Examples of Stereoisomers: Another
CHAPTER 5 Stereoisomers We have already covered two kinds of isomerism: Constitutional Isomers (structural isomers) Stereoisomers Examples of Constitutional Isomers: Examples of Stereoisomers: Another
Basic Stereochemical Considerations
 Basic Stereochemical Considerations Key words: chirality, chiral carbon, enantiomers, diastereomers, absolute configuration, relative configuration, optical activity 1 Key Concepts Basics of projection
Basic Stereochemical Considerations Key words: chirality, chiral carbon, enantiomers, diastereomers, absolute configuration, relative configuration, optical activity 1 Key Concepts Basics of projection
240 Chem. Stereochemistry. Chapter 5
 240 Chem Stereochemistry Chapter 5 1 Isomerism Isomers are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. Constitutional isomers are isomers that differ because their atoms are connected in
240 Chem Stereochemistry Chapter 5 1 Isomerism Isomers are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. Constitutional isomers are isomers that differ because their atoms are connected in
CHEMISTRY PAPER No. : 7 MODULE No. : 23 (Optical Isomerism)
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 7 : Inorganic Chemistry-II (Metal-Ligand Bonding, Electronic Spectra and Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal Complexes) 23
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 7 : Inorganic Chemistry-II (Metal-Ligand Bonding, Electronic Spectra and Magnetic Properties of Transition Metal Complexes) 23
Chapter 5 Stereochemistry
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 5 Stereochemistry Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 5 Stereochemistry Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 5 Stereochemistry. Stereoisomers
 Chapter 5 Stereochemistry Stereoisomers Same bonding sequence Different arrangement in space Example: OOC-C=C-COO has two geometric (cis-trans) isomers: COO COO COO COO Stereochemistry Slide 5-2 1 Chirality
Chapter 5 Stereochemistry Stereoisomers Same bonding sequence Different arrangement in space Example: OOC-C=C-COO has two geometric (cis-trans) isomers: COO COO COO COO Stereochemistry Slide 5-2 1 Chirality
Organic Chemistry. M. R. Naimi-Jamal. Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology
 Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 6. Stereochemistry Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition Stereochemistry Some objects
Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 6. Stereochemistry Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition Stereochemistry Some objects
Stereochemistry. 3-dimensional Aspects of Tetrahedral Atoms
 Stereochemistry 3-dimensional Aspects of Tetrahedral Atoms Chiral Entire molecules or simply atoms that do not possess a plane of symmetry are called chiral. Conversely, the term achiral is applied to
Stereochemistry 3-dimensional Aspects of Tetrahedral Atoms Chiral Entire molecules or simply atoms that do not possess a plane of symmetry are called chiral. Conversely, the term achiral is applied to
Stereochemistry Terminology
 Stereochemistry Terminology Axis of symmetry: When an operation on an axis C n, where n = 360 /rotation, leads to a structure indistinguishable from the original. C 2 180 Plane of symmetry: (σ) A plane
Stereochemistry Terminology Axis of symmetry: When an operation on an axis C n, where n = 360 /rotation, leads to a structure indistinguishable from the original. C 2 180 Plane of symmetry: (σ) A plane
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 Introduction to rganic Chemistry 25 Introduction to rganic Chemistry andout 2 - Stereochemistry A N 2 enantiomers B N 2 diastereomers diastereomers diastereomers C N 2 enantiomers D N 2 http://burton.chem.ox.ac.uk/teaching.html
Introduction to rganic Chemistry 25 Introduction to rganic Chemistry andout 2 - Stereochemistry A N 2 enantiomers B N 2 diastereomers diastereomers diastereomers C N 2 enantiomers D N 2 http://burton.chem.ox.ac.uk/teaching.html
Chapter 5 Stereochemistry
 Chapter 5 Stereochemistry References: 1. Title: Organic Chemistry (fifth edition) Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice Publisher: Pearson International Edition 2. Title: Stereokimia Author: Poh Bo Long Publisher:
Chapter 5 Stereochemistry References: 1. Title: Organic Chemistry (fifth edition) Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice Publisher: Pearson International Edition 2. Title: Stereokimia Author: Poh Bo Long Publisher:
10/4/2010. Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration. Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration. 5.5 Sequence Rules for Specifying.
 5.5 Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration Configuration The three-dimensional arrangement of substituents at a chirality center Sequence rules to specify the configuration of a chirality center:
5.5 Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration Configuration The three-dimensional arrangement of substituents at a chirality center Sequence rules to specify the configuration of a chirality center:
SECOND YEAR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - REVISION COURSE Lecture 1 MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 1: STEREOCHEMISTRY & CONFORMATIONAL ANALYSIS
 Prof Ben Davis SECND YEAR RGANIC CEMISTRY - REVISIN CURSE Lecture 1 MLECULAR STRUCTURE 1: STERECEMISTRY & CNFRMATINAL ANALYSIS Good books and reading: Carey and Sundberg, Part A, Ch 2 & 3 Stereochemistry
Prof Ben Davis SECND YEAR RGANIC CEMISTRY - REVISIN CURSE Lecture 1 MLECULAR STRUCTURE 1: STERECEMISTRY & CNFRMATINAL ANALYSIS Good books and reading: Carey and Sundberg, Part A, Ch 2 & 3 Stereochemistry
Organic Chemistry. Chemical Bonding and Structure (2)
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Structure (2) by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty of Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Structure (2) by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty of Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my
Chapter 4: Stereochemistry
 Chapter 4: Stereochemistry Introduction To Stereochemistry Consider two of the compounds we produced while finding all the isomers of C 7 16 : C 3 C 3 2-methylhexane 3-methylhexane C 2-methylhexane Bu
Chapter 4: Stereochemistry Introduction To Stereochemistry Consider two of the compounds we produced while finding all the isomers of C 7 16 : C 3 C 3 2-methylhexane 3-methylhexane C 2-methylhexane Bu
CHEM 263 Oct 18, Do they have the same molecular formula?
 EM 263 ct 8, 206 To compare the relationship of 2 structures: Do they have the same molecular formula? o ot isomers Do they have the same sequence of atoms (i.e. connectivity)? o onstitutional or tructural
EM 263 ct 8, 206 To compare the relationship of 2 structures: Do they have the same molecular formula? o ot isomers Do they have the same sequence of atoms (i.e. connectivity)? o onstitutional or tructural
geometric isomers (diastereomers)
 Symmetry Monarch butterfly: bilateral symmetry= mirror symmetry Whenever winds blow butterflies find a new place on the willow tree -Basho (~6-69) 5 hapter 7: Stereochemistry - three-dimensional arrangement
Symmetry Monarch butterfly: bilateral symmetry= mirror symmetry Whenever winds blow butterflies find a new place on the willow tree -Basho (~6-69) 5 hapter 7: Stereochemistry - three-dimensional arrangement
It is possible for organic molecules with the same molecular formula to have different structures
 Isomerism It is possible for organic molecules with the same molecular formula to have different structures Definition- Structural isomers: same molecular formula different structures (or structural formulae)
Isomerism It is possible for organic molecules with the same molecular formula to have different structures Definition- Structural isomers: same molecular formula different structures (or structural formulae)
Topic 5 Stereochemistry and optical isomers Isomerism
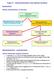 Topic 5 Stereochemistry and optical isomers Isomerism Recap lassification of isomers same molecular formula onstitutional Different nature/sequence of bonds Stereoisomers Different arrangement of groups
Topic 5 Stereochemistry and optical isomers Isomerism Recap lassification of isomers same molecular formula onstitutional Different nature/sequence of bonds Stereoisomers Different arrangement of groups
C 4 H 10 O. butanol. diethyl ether. different carbon skeleton different functional group different position of FG
 hapter 5: Stereoisomerism- three-dimensional arrangement of atoms (groups) in space 5. verview of Isomerism Isomers: different chemical compounds with the same formula onstitutional isomers: same formula,
hapter 5: Stereoisomerism- three-dimensional arrangement of atoms (groups) in space 5. verview of Isomerism Isomers: different chemical compounds with the same formula onstitutional isomers: same formula,
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry Topic 1: Organic Chemistry
 Concept Check: Topic 1: Conformation Winter 2009 Page 112 Concept Check: Topic 1: Conformation Winter 2009 Page 113 1 STEREOCHEMISTRY Winter 2009 Page 114 We have already covered two kinds of isomerism:
Concept Check: Topic 1: Conformation Winter 2009 Page 112 Concept Check: Topic 1: Conformation Winter 2009 Page 113 1 STEREOCHEMISTRY Winter 2009 Page 114 We have already covered two kinds of isomerism:
18 Isomerism and stereochemistry
 s manual for Burrows et.al. hemistry Third edition 8 Isomerism and stereochemistry s to worked examples WE 8. Structural isomers (on p. 88 in hemistry ) For the following four compounds, A D, identify
s manual for Burrows et.al. hemistry Third edition 8 Isomerism and stereochemistry s to worked examples WE 8. Structural isomers (on p. 88 in hemistry ) For the following four compounds, A D, identify
Stereochemistry Structural or constitutional isomers... have the same molecular formula but different connectivity (skeletal, positional, functional)
 Stereochemistry Structural or constitutional isomers... have the same molecular formula but different connectivity (skeletal, positional, functional) Stereoisomers... have the same connectivity but a different
Stereochemistry Structural or constitutional isomers... have the same molecular formula but different connectivity (skeletal, positional, functional) Stereoisomers... have the same connectivity but a different
CSUS - CH6B Fischer projection and R/S configurations Instructor: J.T., P: 1. a) Fischer Projection can be rotated by 180 only!
 CSUS - C6B Fischer projection and R/S configurations Instructor: J.T., P: () Fischer Projection: orizontal line is coming out of the plane of the page. Vertical line is going back behind of the plane of
CSUS - C6B Fischer projection and R/S configurations Instructor: J.T., P: () Fischer Projection: orizontal line is coming out of the plane of the page. Vertical line is going back behind of the plane of
ISOMERISM - A general survey
 Isomerism 1 ISOMERISM - A general survey STRUTURAL ISOMERS have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae They occur due to variations in... the carbon skeleton AIN ISOMERISM 2 2 positions
Isomerism 1 ISOMERISM - A general survey STRUTURAL ISOMERS have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae They occur due to variations in... the carbon skeleton AIN ISOMERISM 2 2 positions
9. Stereochemistry: Introduction to Using Molecular Models
 9. Stereochemistry: Introduction to Using Molecular Models The first part of this document reviews some of the most important stereochemistry topics covered in lecture. Following the introduction, a number
9. Stereochemistry: Introduction to Using Molecular Models The first part of this document reviews some of the most important stereochemistry topics covered in lecture. Following the introduction, a number
HO C. Explain briefly (in one or two short sentences) the meaning of the following basic stereochemical terms.
 Chem 232 D. J. Wardrop wardropd@uic.edu Problem et 3 Answers Question 1. Four compounds, each having the molecular formula C 3 5, have the I spectra summarized below. What are their structures? a. ne sharp
Chem 232 D. J. Wardrop wardropd@uic.edu Problem et 3 Answers Question 1. Four compounds, each having the molecular formula C 3 5, have the I spectra summarized below. What are their structures? a. ne sharp
Stereochemistry. Conformers: Compounds that differ by orientation of atoms in space. They are interconvertible via rotation about single bonds.
 Stereochemistry Terms onformers: ompounds that differ by orientation of atoms in space. They are interconvertible via rotation about single bonds. onstitutional isomers (also called structural isomers):
Stereochemistry Terms onformers: ompounds that differ by orientation of atoms in space. They are interconvertible via rotation about single bonds. onstitutional isomers (also called structural isomers):
Lecture Topics: I. Stereochemistry Stereochemistry is the study of the three dimensional structure of molecules
 Stereochemistry eading: Wade chapter 5, sections 5-- 5-7 Study Problems: 5-26, 5-3, 5-32, 5-33, 5-34 Key oncepts and Skills: assify molecules as chiral or achiral, and identify planes of symmetry. Identify
Stereochemistry eading: Wade chapter 5, sections 5-- 5-7 Study Problems: 5-26, 5-3, 5-32, 5-33, 5-34 Key oncepts and Skills: assify molecules as chiral or achiral, and identify planes of symmetry. Identify
Chapter 5: Stereoisomerism
 hapter 5: Stereoisomerism [Sections: 5.1-5.9] 1. dentifying Types of somers Same MolecularFormula? A B compounds are not isomers Same onnectivity? D E constitutional isomers have different names (parent
hapter 5: Stereoisomerism [Sections: 5.1-5.9] 1. dentifying Types of somers Same MolecularFormula? A B compounds are not isomers Same onnectivity? D E constitutional isomers have different names (parent
E30 ENANTIOMERS Chirality in organic chemistry
 E30 ENANTIMERS hirality in organic chemistry TE TASK To investigate the nature of chirality in organic chemistry. TE SKILLS By the end of the experiment you should be able to: use molecular modelling kits
E30 ENANTIMERS hirality in organic chemistry TE TASK To investigate the nature of chirality in organic chemistry. TE SKILLS By the end of the experiment you should be able to: use molecular modelling kits
CHEM J-10 June The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below.
 CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
Lecture 8: September 13, 2012
 CHM 223 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2012, Des Plaines Prof. Chad Landrie Lecture 8: September 13, 2012 Skillbuilder 2 Ch. 5: Stereochemistry (Sec8ons 5.1-5.5) CHM 223 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2012, Des Plaines
CHM 223 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2012, Des Plaines Prof. Chad Landrie Lecture 8: September 13, 2012 Skillbuilder 2 Ch. 5: Stereochemistry (Sec8ons 5.1-5.5) CHM 223 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2012, Des Plaines
Solutions 80 CHAPTER a) trans b) not stereoisomeric c) trans d) trans e) trans f) not stereoisomeric g) cis
 80 CAPTE 5 killbuilder 5.9 Assigning configuration from a Fischer projection AIG TE CFIGUATI F TE CIALITY CETE I TE FLLWIG CMPUD C 2 olutions 5.1. trans not stereoisomeric trans trans trans f) not stereoisomeric
80 CAPTE 5 killbuilder 5.9 Assigning configuration from a Fischer projection AIG TE CFIGUATI F TE CIALITY CETE I TE FLLWIG CMPUD C 2 olutions 5.1. trans not stereoisomeric trans trans trans f) not stereoisomeric
STEREOGENIC CENTER (Chiral Center,Asymmetric Center) Atom (usually carbon) to which 4 different groups are attached: W Z C X Y
 STEREOGENI ENTER (hiral enter,asymmetric enter) Atom (usually carbon) to which 4 different groups are attached: W Z X Y Many, but not all, molecules which contain a stereogenic center are chiral. (A molecule
STEREOGENI ENTER (hiral enter,asymmetric enter) Atom (usually carbon) to which 4 different groups are attached: W Z X Y Many, but not all, molecules which contain a stereogenic center are chiral. (A molecule
Chapter 6. Isomers and Stereochemistry
 Chapter 6. Isomers and Stereochemistry Learning objectives: 1. Differentiate chiral and achiral molecules. 2. Recognize and draw structural isomers (constitutional isomers), stereoisomers including enantiomers
Chapter 6. Isomers and Stereochemistry Learning objectives: 1. Differentiate chiral and achiral molecules. 2. Recognize and draw structural isomers (constitutional isomers), stereoisomers including enantiomers
02/07/2017. Isomerism. Structural isomerism. 1. Structural isomerism different linkages of atoms. Same molecular formula Different structural formulae
 hain isomerism Position isomerism Metamerism Tautomerism Functional group isomerism Geometrical isomerism Optical isomerism 02/07/2017 Isomerism The presence of two or more compounds which has the same
hain isomerism Position isomerism Metamerism Tautomerism Functional group isomerism Geometrical isomerism Optical isomerism 02/07/2017 Isomerism The presence of two or more compounds which has the same
Optical Isomerism. Types of isomerism. chemrevise.org 20/08/2013. N Goalby Chemrevise.org. Isomerism. Structural isomerism.
 ptical Isomerism N Goalby hemrevise.org Types of isomerism Isomerism Structural isomerism Stereoisomerism Geometric isomerism ptical isomerism 1 ptical Isomerism ptical isomerism occurs in carbon compounds
ptical Isomerism N Goalby hemrevise.org Types of isomerism Isomerism Structural isomerism Stereoisomerism Geometric isomerism ptical isomerism 1 ptical Isomerism ptical isomerism occurs in carbon compounds
Chapter 6. Isomers and Stereochemistry
 hapter 6. Isomers and Stereochemistry Learning objectives: 1. Differentiate chiral and achiral molecules. 2. Recognize and draw structural isomers (constitutional isomers), stereoisomers including enantiomers
hapter 6. Isomers and Stereochemistry Learning objectives: 1. Differentiate chiral and achiral molecules. 2. Recognize and draw structural isomers (constitutional isomers), stereoisomers including enantiomers
MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY I EXAM #1
 MEDICIAL CEMISTRY I EXAM #1 1 September 30, 2005 ame SECTI A. Answer each question in this section by writing the letter corresponding to the best answer on the line provided (2 points each; 50 points
MEDICIAL CEMISTRY I EXAM #1 1 September 30, 2005 ame SECTI A. Answer each question in this section by writing the letter corresponding to the best answer on the line provided (2 points each; 50 points
Eliel, E.L.: Wilen, S.H. Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds, Wiley, New York, 1994.
 Chem 233 Course Glossary George O Doherty For an authoritative treatment of Organic stereochemistry see: Eliel, E.L.: Wilen, S.H. Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds, Wiley, New York, 1994. Relationships
Chem 233 Course Glossary George O Doherty For an authoritative treatment of Organic stereochemistry see: Eliel, E.L.: Wilen, S.H. Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds, Wiley, New York, 1994. Relationships
Introduction to Organic Chemistry, Unit 3: Chirality at Carbon Centers Bring your model kits to class!
 Introduction to rganic hemistry, Unit 3: hirality at arbon enters Bring your model kits to class! rganic hemistry #3 1 bjectives: by the end of this unit, you should be able to... Identify the chiral centres
Introduction to rganic hemistry, Unit 3: hirality at arbon enters Bring your model kits to class! rganic hemistry #3 1 bjectives: by the end of this unit, you should be able to... Identify the chiral centres
STEREOCHEMISTRY CHIRALITY
 TERECEMITRY CIRALITY A A C C B C D D C B Chirality - tereoisomers 2 Chirality Enantiomers - molecules that are not superimposable on their mirror image. Molecules that can exist as enantiomers are called
TERECEMITRY CIRALITY A A C C B C D D C B Chirality - tereoisomers 2 Chirality Enantiomers - molecules that are not superimposable on their mirror image. Molecules that can exist as enantiomers are called
STEREOGENIC CENTER (Chiral Center,Asymmetric Center)
 STEREOGENI ENTER (hiral enter,asymmetric enter) Atom (usually carbon) to which 4 different groups are attached: W Z X Y Many, but not all, molecules which contain a stereogenic center are chiral. (A molecule
STEREOGENI ENTER (hiral enter,asymmetric enter) Atom (usually carbon) to which 4 different groups are attached: W Z X Y Many, but not all, molecules which contain a stereogenic center are chiral. (A molecule
Three-Dimensional Structures of Drugs
 Three-Dimensional Structures of Drugs Moore, T. (2016). Acids and Bases. Lecture presented at PHAR 422 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. Chiral drugs are sometimes sold as one enantiomer (pure
Three-Dimensional Structures of Drugs Moore, T. (2016). Acids and Bases. Lecture presented at PHAR 422 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. Chiral drugs are sometimes sold as one enantiomer (pure
3.7 Organic naming and Isomerism continued
 3.7 rganic naming and Isomerism continued See chapter 3.1 for basic naming of organic molecules. This chapter extends the naming for functional groups met in next few chapters homologous series functional
3.7 rganic naming and Isomerism continued See chapter 3.1 for basic naming of organic molecules. This chapter extends the naming for functional groups met in next few chapters homologous series functional
Chapter 7 Cyclic Compounds. Stereochemistry of Reactions
 Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 7 Cyclic Compounds. Stereochemistry of Reactions Solutions to In-Text Problems 7.3 Following the procedure in the
Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 7 Cyclic Compounds. Stereochemistry of Reactions Solutions to In-Text Problems 7.3 Following the procedure in the
Fall Organic Chemistry Experiment #6 Fractional Crystallization (Resolution of Enantiomers)
 Suggested Reading: Fall Organic Chemistry Experiment #6 Fractional Crystallization (Resolution of Enantiomers) Jones Section 4.9 Physical Properties of Diastereomers: Optical Resolution pages 176-178 Introduction
Suggested Reading: Fall Organic Chemistry Experiment #6 Fractional Crystallization (Resolution of Enantiomers) Jones Section 4.9 Physical Properties of Diastereomers: Optical Resolution pages 176-178 Introduction
Enantiomers. nonsuperimposable mirror image Both Configuration will be opposite. Both Configuration will be opposite
 Optical Isomerism Isomerism of Organic Molecules: Two chiral centers Many organic compounds have more than one asymmetric carbon. The more asymmetric carbons a compound has, the more number of stereoisomers
Optical Isomerism Isomerism of Organic Molecules: Two chiral centers Many organic compounds have more than one asymmetric carbon. The more asymmetric carbons a compound has, the more number of stereoisomers
(S)-(-)-Dopa, used to treat Parkinson's disease, and its medically ineffective (R)-(+) enantiomer
 C h a p t e r F i v e: Stereoisomerism N 2 2 N (S)-(-)-Dopa, used to treat Parkinson's disease, and its medically ineffective (R)-(+) enantiomer CM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter
C h a p t e r F i v e: Stereoisomerism N 2 2 N (S)-(-)-Dopa, used to treat Parkinson's disease, and its medically ineffective (R)-(+) enantiomer CM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter
(2/94)(6,7,9/95)(8,9/97)(12/99)(1/00) Neuman Chapter 4
 4: Stereochemistry Tetrahedral Carbon Configurations Stereoisomers and R,S Assignments The Number and Types of Stereoisomers Drawing Structures of Stereoisomers Cyclic Molecules Optical Activity Preview
4: Stereochemistry Tetrahedral Carbon Configurations Stereoisomers and R,S Assignments The Number and Types of Stereoisomers Drawing Structures of Stereoisomers Cyclic Molecules Optical Activity Preview
(1) Check to see if the two compounds are identical. (2) Recall the definitions of stereoisomers, conformational isomers, and constitutional isomers.
 MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 04: Stereochemistry Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Determine the relationship of the molecules shown: O O Question #01 (A) Identical (B) Constitutional isomers (C)
MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 04: Stereochemistry Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Determine the relationship of the molecules shown: O O Question #01 (A) Identical (B) Constitutional isomers (C)
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises Topic 8 Unit 30
 Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises In-text activities Checkpoint (page 60) 1 Any two of the following: 2 a) A 2-bromo-2-methylpropane B 1-bromobutane b) 3 4 a) position isomers
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises In-text activities Checkpoint (page 60) 1 Any two of the following: 2 a) A 2-bromo-2-methylpropane B 1-bromobutane b) 3 4 a) position isomers
General Glossary. General Glossary
 General Glossary Absolute configuration The actual three-dimensional structure of a chiral molecule. Absolute configurations are specified verbally by the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog R,S convention and are represented
General Glossary Absolute configuration The actual three-dimensional structure of a chiral molecule. Absolute configurations are specified verbally by the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog R,S convention and are represented
Stereoselective Organic Synthesis
 Stereoselective rganic Synthesis Prabhat Arya Professor and Leader, Chemical Biology Program Dean, Academic Affairs, Institute of Life Sciences (An Associate Institute of University of yderabad Supported
Stereoselective rganic Synthesis Prabhat Arya Professor and Leader, Chemical Biology Program Dean, Academic Affairs, Institute of Life Sciences (An Associate Institute of University of yderabad Supported
Two enantiomers of a racemic carboxylic acid (to be separated)
 7.8 FISCER PRJECTINS 237 (R)-RC 2 (S)-RC 2 Two enantiomers of a racemic carboxylic acid (to be separated) Figure 7.5 RESLUTIN F A RACEMIC CARBYLIC ACID. (S)-RN 2 ne enantiomer of a chiral amine + (R)-RC
7.8 FISCER PRJECTINS 237 (R)-RC 2 (S)-RC 2 Two enantiomers of a racemic carboxylic acid (to be separated) Figure 7.5 RESLUTIN F A RACEMIC CARBYLIC ACID. (S)-RN 2 ne enantiomer of a chiral amine + (R)-RC
For more info visit
 Bond Fission: a) Homolytic fission: Each atom separates with one electron, leading to the formation of highly reactive entities called radicals, owing their reactivity to their unpaired electron. b) Heterolytic
Bond Fission: a) Homolytic fission: Each atom separates with one electron, leading to the formation of highly reactive entities called radicals, owing their reactivity to their unpaired electron. b) Heterolytic
Chapter 6 Principles of Stereochemistry
 6.1 (a) This compound is chiral. Methane is achiral. Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 6 Principles of Stereochemistry Solutions to In-Text Problems
6.1 (a) This compound is chiral. Methane is achiral. Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 6 Principles of Stereochemistry Solutions to In-Text Problems
Isomerism. Introduction
 Isomerism Introduction The existence of two or more compounds with same molecular formula but different properties (physical, chemical or both) is known as isomerism; and the compounds themselves are called
Isomerism Introduction The existence of two or more compounds with same molecular formula but different properties (physical, chemical or both) is known as isomerism; and the compounds themselves are called
STEREOCHEMISTRY AND STEREOELECTRONICS NOTES
 - 1 - STEREOCHEMISTRY AND STEREOELECTRONICS NOTES Stereochemistry in Organic Molecules Conventions used in drawing molecules Also, Fischer projections can sometimes be useful for acyclic molecules with
- 1 - STEREOCHEMISTRY AND STEREOELECTRONICS NOTES Stereochemistry in Organic Molecules Conventions used in drawing molecules Also, Fischer projections can sometimes be useful for acyclic molecules with
Chapter 5 Stereoisomerism
 Chapter 5 tereoisomerism eview of Concepts Fill in the blanks below. To verify that your answers are correct, look in your textbook at the end of Chapter 5. Each of the sentences below appears verbatim
Chapter 5 tereoisomerism eview of Concepts Fill in the blanks below. To verify that your answers are correct, look in your textbook at the end of Chapter 5. Each of the sentences below appears verbatim
PRESENTATION ISOMERISM. Dr. Susmita Bajpai
 PRESENTATION OF ISOMERISM Dr. Susmita Bajpai Department Chemistry B.N.D. College, Kanpur ISOMERISM What is isomerism:- The compounds which have the some molecular formula but differ from each other in
PRESENTATION OF ISOMERISM Dr. Susmita Bajpai Department Chemistry B.N.D. College, Kanpur ISOMERISM What is isomerism:- The compounds which have the some molecular formula but differ from each other in
Lecture 4: 12.4 Isomerism
 Lecture 4: 12.4 Isomerism Learning Outcomes: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to : Define isomerism. Explain constitutional isomerism. chain isomers positional isomers functional group
Lecture 4: 12.4 Isomerism Learning Outcomes: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to : Define isomerism. Explain constitutional isomerism. chain isomers positional isomers functional group
CHEM1902/ N-9 November 2014
 CEM1902/4 2014-N-9 November 2014 The elimination of 2 O from alcohol A can form the isomeric alkenes B and C. Elimination of Br from the alkyl halide D can generate the same two alkenes. 7 Assign the absolute
CEM1902/4 2014-N-9 November 2014 The elimination of 2 O from alcohol A can form the isomeric alkenes B and C. Elimination of Br from the alkyl halide D can generate the same two alkenes. 7 Assign the absolute
Assigning Stereochemistry I What is stereochemistry?
 S. Lievens, March 0 University of alifornia, Davis For use in UDavis hemistry 8/8 Series Assigning Stereochemistry I What is stereochemistry? Types of isomers As organic molecules get larger (more than
S. Lievens, March 0 University of alifornia, Davis For use in UDavis hemistry 8/8 Series Assigning Stereochemistry I What is stereochemistry? Types of isomers As organic molecules get larger (more than
1. Use appropriate curved arrows to indicate the complete mechanism of each of these reactions. KH (1 equiv.) + KCl THF. + HBr.
 1. Use appropriate curved arrows to indicate the complete mechanism of each of these reactions. K (1 equiv.) TF K 3 2 2 3 enantiomer While writing the mechanism, justify both the regiochemistry the relative
1. Use appropriate curved arrows to indicate the complete mechanism of each of these reactions. K (1 equiv.) TF K 3 2 2 3 enantiomer While writing the mechanism, justify both the regiochemistry the relative
10/4/2010. Chapter 5 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers. Handedness. 5.1 Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon
 John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 5 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Handedness Right and left hands are not identical
John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 5 Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Handedness Right and left hands are not identical
Assign (R) or (S) configurations to the chiral carbons in the following molecules: enantiomers
 CAPTER 5: STERECEMISTRY (cont.) Assign (R) or (S) configurations to the chiral carbons in the following molecules: 3 C 3 C N 2 Molecules With Multiple Chiral Atoms. 1-chloro-2-methylcyclohexane has four
CAPTER 5: STERECEMISTRY (cont.) Assign (R) or (S) configurations to the chiral carbons in the following molecules: 3 C 3 C N 2 Molecules With Multiple Chiral Atoms. 1-chloro-2-methylcyclohexane has four
Lesson 4. Molecular Geometry and Isomers II. Lesson 4 CH 3 HO H OH
 Lesson 4 Molecular Geometry and Isomers II 4 Lesson 4 3 O O 3 Organic Edge A. Structural Isomers (onstitutional Isomers) 1. Structural isomers are molecules that share the same molecular formula but differ
Lesson 4 Molecular Geometry and Isomers II 4 Lesson 4 3 O O 3 Organic Edge A. Structural Isomers (onstitutional Isomers) 1. Structural isomers are molecules that share the same molecular formula but differ
Stereochemistry: Chiral Molecules. Constitutional Isomers - Review. Enantiomers and Chiral Molecules. Mirror images = handedness
 Isomerism: Constitutional Isomers and Stereoisomers Chapter 5 Constitutional Isomers = same molecular formula, different connectedness Stereoisomers = same molecular formula, same connectivity of atoms
Isomerism: Constitutional Isomers and Stereoisomers Chapter 5 Constitutional Isomers = same molecular formula, different connectedness Stereoisomers = same molecular formula, same connectivity of atoms
Organic: module 4 revision guide. Basic definitions to know. Drawing Displayed formulae
 opyright Goalby Bancroft's School rganic: module 4 revision guide ydrocarbon is a compound consisting of hydrogen and carbon only Basic definitions to know Saturated: ontain single carbon-carbon bonds
opyright Goalby Bancroft's School rganic: module 4 revision guide ydrocarbon is a compound consisting of hydrogen and carbon only Basic definitions to know Saturated: ontain single carbon-carbon bonds
CHEM 261 Feb. 2, Stereochemistry and Chirality
 70 EM 261 eb. 2, 2017 Stereochemistry and hirality hiral object or molecule: has a non-superimposable mirror image Achiral object: not chiral, has a superimposable mirror image 1848 - Louis Pasteur separated
70 EM 261 eb. 2, 2017 Stereochemistry and hirality hiral object or molecule: has a non-superimposable mirror image Achiral object: not chiral, has a superimposable mirror image 1848 - Louis Pasteur separated
IN-CLASS PROBLEM. ChemistryOnline, STEREOCHEMISTRY OF TETRAHEDRAL CENTERS. ChemistryOnline, No Plane of Symmetry
 hapter 5 Draw the structure of bromocyclopentane. Stereochemistry Reproduction or distribution of any of the content, or any of the images in this presentation is strictly prohibited without the expressed
hapter 5 Draw the structure of bromocyclopentane. Stereochemistry Reproduction or distribution of any of the content, or any of the images in this presentation is strictly prohibited without the expressed
Unless otherwise stated, all images in this file have been reproduced from:
 Unless otherwise stated, all images in this file have been reproduced from: Blackman, Bottle, Schmid, Mocerino and Wille, hemistry, 2007 (John Wiley) ISBN: 9 78047081 0866 1 hemistry 1B EM1002 Lecture
Unless otherwise stated, all images in this file have been reproduced from: Blackman, Bottle, Schmid, Mocerino and Wille, hemistry, 2007 (John Wiley) ISBN: 9 78047081 0866 1 hemistry 1B EM1002 Lecture
Chapter 27: Structure and Bonding
 Chapter 27: Structure and Bonding 1 Atomic Orbitals: Wave functions that represent the probability of finding electrons in a specific region of space s, p, d, f orbitals In organic chemistry, need to concentrate
Chapter 27: Structure and Bonding 1 Atomic Orbitals: Wave functions that represent the probability of finding electrons in a specific region of space s, p, d, f orbitals In organic chemistry, need to concentrate
Stereochemistry & Polarimetry notes
 Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the laboratory manual. Stereochemistry & Polarimetry notes History Application: Approximately 25% of all drugs are marketed as either racemates
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the laboratory manual. Stereochemistry & Polarimetry notes History Application: Approximately 25% of all drugs are marketed as either racemates
Enantiomers 2:22 PM 1
 1 Definition (Revisited) Enantiomers are stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images. Note that all the chiral centres in a pair of enantiomers are mirror images of each other. 2 Practice Questions
1 Definition (Revisited) Enantiomers are stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images. Note that all the chiral centres in a pair of enantiomers are mirror images of each other. 2 Practice Questions
C h a p t e r E i g h t: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions. 5-Androstene, the parent alkene for most anabolic steroids
 C h a p t e r E i g h t: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions 5-Androstene, the parent alkene for most anabolic steroids CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter
C h a p t e r E i g h t: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions 5-Androstene, the parent alkene for most anabolic steroids CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter
MOLECULAR MODELS : STEREOISOMERS
 MM.1 MOLEULAR MODELS : STEREOISOMERS Note: No pre-laboratory summary is required for this experiment, but there are some topics you most probably need to review from 351 and you may want to start work
MM.1 MOLEULAR MODELS : STEREOISOMERS Note: No pre-laboratory summary is required for this experiment, but there are some topics you most probably need to review from 351 and you may want to start work
Connexions module: m Stereochemistry. Andrew R. Barron. Figure 1: The two stereo isomers of butane: (a) n-butane and (b) iso-butane.
 Connexions module: m34480 1 Stereochemistry Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 1 Stereo isomers Stereo isomers
Connexions module: m34480 1 Stereochemistry Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 1 Stereo isomers Stereo isomers
a. Does the model have a plane of symmetry? Yes No The central carbon is said to be a stereocenter, stereogenic center, or chiral carbon.
 Name: TA Name Lab Section: Day Time OPTICAL ISOMERISM 1. Construct a model that has a central carbon atom with 4 different colored spheres attached to it, representing four different atoms or groups. Draw
Name: TA Name Lab Section: Day Time OPTICAL ISOMERISM 1. Construct a model that has a central carbon atom with 4 different colored spheres attached to it, representing four different atoms or groups. Draw
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions
 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Names. Chiral: A chiral object is not superimposable upon its mirror image. A chiral object contains the property of "handedness.
 CEM 241 IN-CLASS #3 MOLECULAR MODELS EXERCISE Names Stereoisomerism Construct a model containing a tetrahedral carbon (black ball) that is attached to four different atoms (use the green, orange, purple
CEM 241 IN-CLASS #3 MOLECULAR MODELS EXERCISE Names Stereoisomerism Construct a model containing a tetrahedral carbon (black ball) that is attached to four different atoms (use the green, orange, purple
Practice Hour Examination # 1-2
 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Practice Hour Examination # 1-2 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Practice Hour Examination # 1-2 Monday,
CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Practice Hour Examination # 1-2 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Practice Hour Examination # 1-2 Monday,
4Types of Isomers. 1. Structural Isomers/(Constitutional) 2. Geometric Isomers/(Cis/Trans) 3. Optical Isomers A. Enantiomers B.
 4Types of Isomers 1. Structural Isomers/(Constitutional) 2. Geometric Isomers/(Cis/Trans) 3. Optical Isomers A. Enantiomers B. Diastereomers 4Types of Isomers C 4 10 C 4 10 O O O O O O O O O O O O C 3
4Types of Isomers 1. Structural Isomers/(Constitutional) 2. Geometric Isomers/(Cis/Trans) 3. Optical Isomers A. Enantiomers B. Diastereomers 4Types of Isomers C 4 10 C 4 10 O O O O O O O O O O O O C 3
STEREOCHEMISTRY A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: STEREOCHEMISTRY 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define the following terms, and give examples of pairs
A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: STEREOCHEMISTRY 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define the following terms, and give examples of pairs
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
STEREOISOMERS ARRANGEMENTS IN 3D- SPACE
 STEREOISOMERS ARRANGEMENTS IN 3D- SPACE 1 Isomers 2 Physiological Proper@es of Stereoisomers (Enan@omers) Enan@omers can have very different physiological proper@es. 3 Oranges and Lemons found in oranges
STEREOISOMERS ARRANGEMENTS IN 3D- SPACE 1 Isomers 2 Physiological Proper@es of Stereoisomers (Enan@omers) Enan@omers can have very different physiological proper@es. 3 Oranges and Lemons found in oranges
Pentane (C5H12) exists in three form
 ISOMERISM The phenomenon of existence of two or more compounds with same molecular formula but different properties ( physical, chemical or both) is known as isomerism and the compound exhibiting this
ISOMERISM The phenomenon of existence of two or more compounds with same molecular formula but different properties ( physical, chemical or both) is known as isomerism and the compound exhibiting this
CHEM 261 Feb. 2, Pheromone: from Greek pherein horman meaning to carry excitement. Only about 50 % of the population can smell this compound
 70 EM 61 eb., 017 Pheromone: from Greek pherein horman meaning to carry excitement O Only about 50 % of the population can smell this compound omenclature of Alkynes Rules: - ind longest chain with max
70 EM 61 eb., 017 Pheromone: from Greek pherein horman meaning to carry excitement O Only about 50 % of the population can smell this compound omenclature of Alkynes Rules: - ind longest chain with max
Problem Set 7: Stereochemistry-ANSWER KEY
 Problem Set 7: Stereochemistry-ANSWER KEY Chemistry 260 Organic Chemistry 1. The answer is (2). Circled isomers have a stereogenic carbon (*) and hence a stereogenic centre. C 2 C 2 C 2 C 2 C 2 C 2 C 2
Problem Set 7: Stereochemistry-ANSWER KEY Chemistry 260 Organic Chemistry 1. The answer is (2). Circled isomers have a stereogenic carbon (*) and hence a stereogenic centre. C 2 C 2 C 2 C 2 C 2 C 2 C 2
Química Orgânica I 2008/09. w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A3 1
 Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A3 1 O O O 3 C 3 C O O O C 3 N O C 3 O O O O O O C 3 O w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A3 2 Adaptado de: Jo Blackburn; 2006, Prentice all; Organic Chemistry,
Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A3 1 O O O 3 C 3 C O O O C 3 N O C 3 O O O O O O C 3 O w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A3 2 Adaptado de: Jo Blackburn; 2006, Prentice all; Organic Chemistry,
lectures Handout 1 - Bonding Jonathan Burton
 Introduction to rganic hemistry jonathan.burton@chem.ox.ac.uk 1 Introduction to rganic hemistry 2017 5 lectures andout 1 - Bonding Jonathan Burton http://burton.chem.ox.ac.uk/teaching.html rganic hemistry
Introduction to rganic hemistry jonathan.burton@chem.ox.ac.uk 1 Introduction to rganic hemistry 2017 5 lectures andout 1 - Bonding Jonathan Burton http://burton.chem.ox.ac.uk/teaching.html rganic hemistry
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes
 Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
