3.2.9 Alkenes. Polymerisation. 152 minutes. 149 marks. Page 1 of 22
|
|
|
- Philippa Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ..9 Alkenes Polymerisation 5 minutes 49 marks Page of
2 M. Oxygen or air () Can score from the equation Silver catalyst () Linked to process: e.g. Consequence of leaks etc. () Hazard = flammable or explosive () Hazard : = toxic or causes respiratory failure or neurological effects () (CH CH )O +H O HOCH CH OH () Not (CH CH ) O, CH CH O, C H 4 O, but only penalise once Uses include antifreeze or polyester formation / terylene (), Not plastics, polymers, surfactants n(ch CH )O + CH CH OH CH CH O(CH CH O) n H () Uses include brake fluids or plasticisers () OR surfactant or detergent CH CH (OCH CH ) n OH and H(CH CH O) n+ OH are OK in last equation [8] M. (a) ethan(e)-,-diol OR,-ethan(e)diol () antifreeze () OR production of Terylene / polyester feedstock for polyester / PET NOT surfactant NOT plasticizer NOT solvent NOT de-icer (b) Reaction H O or steam () Reaction O () NOT air Ignore reaction Reaction 4 H O () Reaction 5 NH () For Reaction 4; credit dil H SO 4 OR H SO 4 (aq) OR HCl (aq) but NOT steam and NOT NaOH(aq) 4 (c) Penalise M incorrect δ+ / δ Penalise δ on alkene (M) Penalise dots on bonds once Penalise M4 (structure) for use of wrong alkene Penalise M for use of Br 4 Page of
3 (d) Water OR aqueous solution OR (aq) in equation () Yeast OR enzyme/zymase OR T 45 C but T not below 0 C and allow warm N.B. yeast and T=60 con Ignore ph Ignore anaerobic / oxygen Ignore time Ignore pressure M M C 6 H O 6 C H 5 OH (or CH CH OH) + CO Allow C H O if balanced equation M4 OR M5 needs the use of good English and correct chemistry to gain credit M M4: The rate of fermentation is slower () OR The rate of hydration is faster QoL OR (The rate of) fermentation is slow and (the rate of) hydration is fast reference correctly to time rather than rate gains credit M5: The product of fermentation is less pure or lower purity OR The product of hydration is more pure or higher purity OR The product of fermentation is impure and that of hydration is pure OR Specific reference to 0 5% versus 90 00% OR correct reference to higher or lower yield 5 [5] M. (a) (i) C 6 H O 6 C H 5 OH + CO (Or CH CH OH) (Ignore state symbols in the equation) Fermentation Page of
4 (Or C H 6 O or CH CH OH) (In equation, allow additional O on both sides of the equation) (b) (i) C H 5 OH + O CO + H O CO or carbon monoxide or C or carbon ONLY (iii) CO + NO CO + N OR NO N + O OR NO + C N + CO OR C 8 H 8 + 5NO 8CO + ½N + 9H O (c) Elimination (Penalise additional words such as electrophilic ) M structure of protonated alcohol (allow CH CH ) M arrow to show breakage of C O bond on protonated alcohol M structure of carbocation (allow ) M4 arrow from correct C H bond on carbocation (penalise sticks once only for structures M and M) (synchronous mechanism using correct structure required for M, loses M) Page 4 of
5 (d) Silver OR silver-based (NOT silver oxide) M correct structure for epoxyethane (Allow CH =CH or C H 4 in the equation) (Credit the structure of epoxyethane independently) (Credit M provided O has been used and the atoms balance, but the structure is poor e.g. C H 4 O or CH OCH but NOT CH CHO) [] M4. (a) M X is,-dibromoethane only M electrophilic addition (both words needed) M the double bond is a centre of electron density OR electron-rich OR nucleophilic OR a source of an electron pair OR a pi cloud/bond of electrons M4 a dipole or polarity is induced/created/formed in the Br-Br bond/molecule - award this mark only if the quality of language justifies the award. Page 5 of
6 (b) nucleophilic substitution (both words needed) Mechanism M curly arrow from lone pair on oxygen of hydroxide ion to C atom of C-Br Mechanism M curly arrow from C-Br bond to side of Br atom (a possible repeat error here from Question 4a) (award a maximum of one mark for the wrong haloalkane) (credit an SNl mechanism in which Ml will be a curly arrow from the lone pair on oxygen of the hydroxide ion to the correct positive carbon atom) Y is susceptible to attack by hydroxide ions for one of the following reasons o o o the C-Br bond is polar the carbon atom is partially positive (or shown as such) the carbon atom is electron deficient (c) M oxygen (ignore air ) M silver or silver-based (penalise silver nitrate) M Z is epoxyethane M4 epoxyethane o has a strained ring structure o has a bond angle of 60 o has a bond angle significantly less than tetrahedral (ignore unstable, has strained bonds, is stressed ) Page 6 of
7 (d) Ethane-,-diol is used in antifreeze OR in the manufacture of PET/Terylene/polyester (penalise solvent or plasticiser ) Hazard in Route via X/Y o o bromine is toxic or corrosive sodium hydroxide is corrosive or caustic Hazard in Route via epoxyethane o risk of explosion in reaction 4 o epoxyethane is toxic o epoxyethane is a respiratory irritant o epoxyethane causes neurological damage [5] M5. (a) (i) Electron pair/ lone pair acceptor OR seeking/bonds with an electron pair (insist on reference to a pair of electrons) M curly arrow from middle of C=C bond of the alkene towards/ alongside the H atom of the H-Br; (penalise arrows which go towards one of the carbon atoms) (ignore a partial negative charge on the C=C) M curly arrow from H-Br bond to side of Br atom; (penalise M if there are formal charges on HBr or if there are partial charges which are the wrong) (penalise M if the single bond has two dots in addition to the line) M correct structure for carbocation; (penalise M if the positive charge is placed on the end of a bond) (penalise M if any alkene other than ethene is used - all other marks can score) M4 curly arrow from lone pair on bromide ion to the positive carbon of carbocation, ensuring that bromide ion has a negative charge; Page 7 of
8 (b) (i) M Oxygen OR O ; (do not credit air alone, but otherwise ignore) (iii) M silver OR Ag OR silver-based (penalise silver nitrate) correct structure for epoxyethane; (penalise poorly presented C-O bonds) water OR H O; (credit steam OR H SO 4 (aqueous OR dilute) OR NaOH(aq) OR HCl(aq), OR H PO 4 (aq), but insist that (aq) is included) (do not credit HCl or H SO 4 (concentrated or without water present)) (c) (i) M: potassium cyanide OR KCN OR sodium Cyanide OR NaCN; (ignore conditions - dissolved in (aq) or (alc) or KOH(aq) all work) (penalise HCN) M: propanenitrile; (credit propan--nitrile OR propan nitrile, but not propanitrile) M: ammonia OR NH ; (iii) (If formula is written, insist that it is correct) (ignore conditions, but penalise acidic) M: ethylamine; (credit aminoethane) M: curly arrow from lone pair on nitrogen of (correct formula for) ammonia towards/alongside C atom of C-Br; (penalise M if formula of ammonia is wrong or has a negative charge or has no lone pair or arrow is from negative charge) M: curly arrow from C-Br bond towards/alongside side Br atom; (credit M independently) (penalise M if formal positive charge on C atom of C-Br) Page 8 of
9 M: correct structure of the ethylammonium ion; (credit the structure drawn out with all four bonds around the nitrogen atom OR written as C H 5 NH + OR CH CH NH + ) M4: curly arrow from the middle of one of the H-N bonds towards the positive N atom; (possible to credit M4 on an incorrect ethylammonium ion with no positive charge) (ignore use of ammonia or bromide ion etc. to remove proton from ethylammonium ion) (If the wrong haloalkane is used, award MAX. marks for the mechanism) (If S N mechanism is used, give full credit in which M is for a curly arrow from the lone pair of the N atom of (correct formula for) ammonia towards/alongside the positive carbon atom of CH CH + ) [7] M6. (a) Ag or silver or silver-based or silver on an alumina base epoxyethane (penalise specific silver compounds) Page 9 of
10 (b) electrophilic addition M: curly arrow from C=C bond towards/alongside the side of H atom on H-OSO OH (penalise M if arrow to H SO 4 OR to formal charge on H of H-O bond) (ignore partial charges on H and O of H SO 4, but penalise if these are incorrect on the H atom being attacked) (credit M and M if correct curly arrow to H+ provided the anion is present) M: curly arrow from H O bond towards/alongside the side of the O atom on H OSO OH (credit the arrow even if there are partial or formal charges on H and O but the structure of H SO 4 is correct) M: correct structure of the carbocation (penalise use of sticks in this structure) M4: curly arrow from lone pair on an individual oxygen atom of (correct formula for) hydrogensulphate ion towards/alongside C atom bearing the positive charge (insist that the an ion has the correct formula with a lone pair of electrons and a negative charge) (c) (i) ethanal correct structure for ethanal (aldehyde functional group must be drawn out) oxidation or redox [0] M7. (a) (i) M curly arrow from lone pair of electrons on oxygen of hydroxide ion (insist on a lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom and a negative charge, but only credit this mark if the attack is to a correct H atom) M curly arrow from the middle of the C H bond to the middle of the C C bond. (only credit this mark if the arrow originates from the correct C H bond and if an attempt has been made at M) Page 0 of
11 M curly arrow from the middle of the C Br bond towards/alongside the Br atom. (credit M independently unless the bond breaking is contradicted by an additional arrow) (penalise M curly arrow if the C Br has a formal positive charge) (ignore partial charges on the C Br bond, but penalise if incorrect) (credit full marks for an E mechanism, with M awarded for a correct curly arrow on the correct carbocation) (award a maximum of two marks for an incorrect haloalkane) (ignore products) Haloalkane/C H 5 Br is made from ethane OR haloalkane is not (readily) available OR haloalkane is expensive OR it is (too) expensive/costly OR (reaction) yield is too low/poor OR it is too slow OR a valid reference to nucleophilic substitution/alcohol formation occurring as an alternative reaction. (ignore references to temperature or to energy consumption) (do not credit statements which refer to the idea that this route is not chosen, because industry chooses another route e.g. cracking) (b) (i) Strained ring/ bonds/ structure/molecule OR three membered ring OR 60 o bond angle OR bond angle much less than tetrahedral (penalise stressed ring ) (ignore weak bonds, ignore unstable ) ethane, diol OR correct structure (penalise ethylene glycol OR, dihydroxyethane if these appear alone) (credit ethan, diol) (If both a structure and a formula are given, credit either correct one of these provided the other is a good, if imperfect, attempt) (used in) antifreeze OR for OR in the manufacture/making/formation of terylene, polyester, PET only (ignore reference to terylene etc. if they accompany antifreeze (penalise de icer, solvent, surfactant, plasticizer ) (If the candidate indicates that the product is antifreeze,then this can gain credit, but not if contradicted in its use e.g. as de icer) [7] Page of
12 M8. (a) (i) Nucleophilic substitution (iii) M must show an arrow from the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom of the negatively charged hydroxide ion to the central C atom. M must show the movement of a pair of electrons from the C-Br bond to the Br atom. Mark M independently. Penalise M if covalent KOH is used Penalise M for formal charge on C or incorrect partial charges Penalise once only for a line and two dots to show a bond. Max mark for the mechanism for the wrong reactant and/or sticks Ignore product Award full marks for an S N mechanism in which M is the attack of the hydroxide ion on the intermediate carbocation. -bromopropane ONLY Polar C Br OR polar carbon bromine bond OR dipole on C Br OR δ+ (δ ) C atom of carbon bromine bond is δ+/electron deficient OR C Br (Credit carbon halogen bond as an alternative to carbon bromine bond) It must be clear that the discussion is about the carbon atom of the C Br bond. NOT just reference to a polar molecule. Ignore X for halogen Page of
13 (b) Elimination Credit base elimination but NOT nucleophilic elimination No other prefix. M must show an arrow from the lone pair on oxygen of a negatively charged hydroxide ion to the correct H atom M must show an arrow from the correct C-H bond to the C-C bond and should only be awarded if an attempt has been made at M M is independent. Mechanism Penalise M if covalent KOH Penalise M for formal charge on C or incorrect partial charges Penalise once only for a line and two dots to show a bond. Max marks for the mechanism for wrong reactant and/or sticks Ignore product Award full marks for an E mechanism in which M is on the correct carbocation. (c) Any one condition from this list to favour elimination; Apply the list principle alcohol(ic)/ethanol(ic) (solvent) high concentration of KOH/alkali/hydroxide OR concentrated KOH/hydroxide Ignore aqueous high temperature or hot or heat under reflux or T = 78 to 00 C Ignore excess (d) (i) Addition (polymerisation) ONLY Penalise additional But--ene ONLY (hyphens not essential) Ignore references to cis and trans or E/Z Ignore butane [] Page of
14 M9. (a) (i) M (yellow precipitate is) silver iodide OR AgI (which may be awarded from the equation) M Ag + + I AgI (Also scores M unless contradicted) M sodium chloride OR NaCl For M Accept multiples Ignore state symbols Allow crossed out nitrate ions, but penalise if not crossed out The silver nitrate is acidified to react with / remove ions that would interfere with the test prevent the formation of other silver precipitates / insoluble silver compounds that would interfere with the test remove (other) ions that react with the silver nitrate react with / remove carbonate / hydroxide / sulfite (ions) Ignore reference to false positive (iii) M and M in either order M Fluoride (ion) OR F M Silver fluoride / AgF is soluble / dissolves (in water) no precipitate would form / no visible /observable change Do not penalise the spelling fluoride, Penalise fluride once only Mark M and M independently Page 4 of
15 (b) M Ba + + SO 4 - BaSO 4 (or the ions together) M white precipitate / white solid / white suspension M Barium meal or ( internal ) X-ray or to block X-rays M4 BaSO 4 / barium sulfate is insoluble (and therefore not toxic) For M, ignore state symbols Allow crossed out sodium ions, but penalise if not crossed out For M, ignore milky If BaSO OR BaS used in M and M4, penalise once only For M Ignore radio-tracing For M4 NOT barium ions NOT barium NOT barium meal NOT It unless clearly BaSO 4 4 (c) M (.00000) + 4(.00794) = M Ethene and CO or they have an imprecise M r of 8.0 / 8 OR Ethene and CO or they have the same M r to one d.p. OR These may be shown by two clear, simple sums identifying both compounds M C H 4 + O CO + H O (H C=CH ) M4 Displayed formula Page 5 of
16 M5 Type of polymer = Addition (polymer) M must show working using 5 d.p.for hydrogen Penalise similar or close to, if this refers to the imprecise value in M, since this does not mean the same For M, accept CH =CH OR CH CH For M4, all bonds must be drawn out including those on either side of the unit. Penalise sticks Ignore brackets around correct repeating unit but penalise n Penalise additional 5 [5] M0. (a) M electrophilic addition For M, both words required Accept phonetic spelling For the mechanism M Ignore partial negative charge on the double bond M must show an arrow from the double bond towards the H atom of the H Br molecule M Penalise partial charges on H Br bond if wrong way and penalise formal charges M must show the breaking of the H Br bond Penalise once only in any part of the mechanism for a line and two dots to show a bond M5 must show an arrow from the lone pair of electrons on the negatively charged bromide ion towards the correct (positively charged) carbon atom Maximum any of 4 marks for the mechanism for wrong (organic) reactant OR wrong organic product (if shown) OR primary carbocation Accept the correct use of sticks NB These are double-headed arrows 5 Page 6 of
17 (b) M Nucleophilic substitution For M, both words required Accept phonetic spelling For the mechanism Penalise M if NH is negatively charged M must show an arrow from the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom of an ammonia molecule to the correct C atom Penalise M for formal charge on C of the C Br or incorrect partial charges on C Br Penalise M for an additional arrow from the Br to something else M must show the movement of a pair of electrons from the C Br bond to the Br atom. Mark M independently provided it is from their original molecule The second mole of ammonia is not essential for M5; therefore ignore any species here M4 is for the structure of the alkylammonium ion, which could be a condensed formula. A positive charge must be shown on / or close to, the N atom Penalise once only for a line and two dots to show a bond M5 is for an arrow from the N H bond to the N atom Maximum any of 4 marks for the mechanism for wrong organic reactant OR wrong organic product if shown Award full marks for an S N mechanism in which M is the attack of the ammonia on the intermediate carbocation Accept the correct use of sticks NB These are double-headed arrows 5 (c) M (addition) polymerisation OR poly-addition Ignore additional Credit polyprop--ene and polypropylene M poly(propene) / polypropene Penalise condensation polymerisation Page 7 of
18 (d) Penalise M if covalent KOH M must show an arrow from the lone pair on the oxygen of a negatively charged hydroxide ion to a correct H atom Penalise M for formal charge on C of C Br or incorrect partial charges on C Br. M must show an arrow from a correct C H bond adjacent to the C Br bond to the appropriate C C bond. Only award if an arrow is shown attacking the H atom of a correct C H bond in M Ignore other partial charges Penalise once only in any part of the mechanism for a line and two dots to show a bond M is independent provided it is from their original molecule, but CE=0 if nucleophilic substitution Maximum any of marks for wrong organic reactant Award full marks for an E mechanism in which M is on the correct carbocation. Accept the correct use of sticks for the molecule except for the C H being attacked NB These are double-headed arrows [5] M. (a) (i) M c(oncentrated) phosphoric acid / c(onc.) H PO 4 OR c(oncentrated) sulfuric acid / c(onc.) H SO 4 In M, the acid must be concentrated. Ignore an incorrect attempt at the correct formula that is written in addition to the correct name. M Re-circulate / re-cycle the (unreacted) ethene (and steam) / the reactants OR pass the gases over the catalyst several / many times In M, ignore remove the ethanol. Credit re-use. Page 8 of
19 M (By Le Chatelier s principle) the equilibrium is driven / shifts / moves to the right / L to R / forwards / in the forward direction M depends on a correct statement of M The equilibrium moves / shifts to oppose the addition of / increased concentration of / increased moles / increased amount of water / steam to decrease the amount of steam / water Mark M independently M Yield of product / conversion increase OR ethanol increases / goes up / gets more (iii) M Poly(ethene) / polyethene / polythene / HDPE / LDPE M At higher pressures More / higher cost of electrical energy to pump / pumping cost OR Cost of higher pressure equipment / valves / gaskets / piping etc. OR expensive equipment Credit all converse arguments for M (b) M for balanced equation M for state symbols in a correctly balanced equation C(s / graphite) + H (g) + ½O (g) CH CH OH(l) (C H 5 OH) Not multiples but credit correct state symbols in a correctly balanced equation. Penalise C H 6 O but credit correct state symbols in a correctly balanced equation. (c) (i) M The enthalpy change / heat change at constant pressure when mol of a compound / substance / element If standard enthalpy of formation CE=0 M is burned / combusts / reacts completely in oxygen OR burned / combusted / reacted in excess oxygen M with (all) reactants and products / (all) substances in standard / specified states OR (all) reactants and products / (all) substances in normal states under standard conditions / 00 kpa / bar and specified T / 98 K For M Ignore reference to atmosphere Page 9 of
20 M Correct answer gains full marks ΣB(reactants) ΣB(products) = ΔH Credit mark for (+) 79 (kj mol ) OR Sum of bonds broken Sum of bonds formed = ΔH OR B(C-C) + B(C-O) + B(O-H) + 5B(C-H) + B(O=O) (LHS) 4B(C=O) 6B(O H) (RHS) = ΔH M (also scores M) (4)+(496) [LHS = 479] (060) (488) 4(805) 6(46) [RHS = 5998] = ΔH (0) (778) OR using only bonds broken and formed ( ) For other incorrect or incomplete answers, proceed as follows check for an arithmetic error (AE), which is either a transposition error or an incorrect multiplication; this would score marks (M and M) If no AE, check for a correct method; this requires either a correct cycle with C and 6H and 7O OR a clear statement of M which could be in words and scores only M M ΔH= 79 (kj mol ) Allow a maximum of one mark if the only scoring point is LHS = 479 OR RHS = 5998 Award mark for +79 Candidates may use a cycle and gain full marks (d) (i) Reducing agent OR reductant OR electron donor OR to reduce the copper oxide Not reduction. Not oxidation. Not electron pair donor. CH COOH [7] Page 0 of
21 M. (a) (i) Structure of (Z)-but--enenitrile with or without either or both of the CH and the CN groups displayed Penalise C NC Do not penalise C H C Ignore bond angles. Restricted rotation / no (free) rotation about the double bond / about the C=C OR does not rotate (about the double bond) Must use the word rotate / rotation. (b) Repeating unit of polyalkene All the bonds relevant to the unit must be drawn out including those on either side of the unit. There is no need to expand either the CH or the CN Penalise C NC Penalise sticks. Ignore brackets. Penalise n (c) Feature Absorption / peak in the range 0 to 60 cm or specified value in this range or marked correctly on spectrum and (characteristic absorption / peak for) C N / CN group / nitrile / cyanide group Feature Allow the words dip OR spike OR trough OR low transmittance as alternatives for absorption. Allow a peak at 00 cm to 0 cm in this case. Absorption / peak in the range 60 to 680 cm or specified value in this range or marked correctly on spectrum and (characteristic absorption / peak for) C=C group / alkene / carbon-carbon double bond Ignore reference to other absorptions eg C-H Either order. [5] Page of
22 Page of
Page 2. M1.(a) P 3,3 dimethylbut 1 ene OR accept 3,3 dimethylbutene Ignore absence of commas, hyphens and gaps Require correct spelling Q OR
 M.(a) P 3,3 dimethylbut ene OR accept 3,3 dimethylbutene Ignore absence of commas, hyphens and gaps Require correct spelling Q OR 3 chloro 2,2 dimethylbutane accept 2 chloro 3,3 dimethylbutane In Q, chloro
M.(a) P 3,3 dimethylbut ene OR accept 3,3 dimethylbutene Ignore absence of commas, hyphens and gaps Require correct spelling Q OR 3 chloro 2,2 dimethylbutane accept 2 chloro 3,3 dimethylbutane In Q, chloro
2.8 EXTRA QUESTIONS MS. (iii) C 6 H 5 CHCl 2 / C 6 H 5 CCl 3 / C 6 H 5 CHCHC 6 H 5 / other correct possible answer (1) 1
 .8 EXTRA QUESTIONS MS 1. (i) l l / ½ l l 1 (ii) l 6 5 6 5 l 6 5 l l 6 5 l (iii) 6 5 l / 6 5 l / 6 5 6 5 / other correct possible answer 1 [4]. (a) (i) (free)radical substitution 1 (both words required
.8 EXTRA QUESTIONS MS 1. (i) l l / ½ l l 1 (ii) l 6 5 6 5 l 6 5 l l 6 5 l (iii) 6 5 l / 6 5 l / 6 5 6 5 / other correct possible answer 1 [4]. (a) (i) (free)radical substitution 1 (both words required
3.2.9 Alkenes. Addition Reactions. 271 minutes. 268 marks. Page 1 of 39
 ..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 7 minutes 68 marks Page of 9 M. (a) Electrophile: e pair / lone pair acceptor or e deficient species or e seeking species () For species accept atom, molecule, ion NOT +
..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 7 minutes 68 marks Page of 9 M. (a) Electrophile: e pair / lone pair acceptor or e deficient species or e seeking species () For species accept atom, molecule, ion NOT +
Version 1.0: 1006 abc. General Certificate of Education examination - June series
 Version.0: 006 abc General Certificate of Education Chemistry 542 CHM3/W Introduction to Organic Chemistry Mark Scheme 2006 examination - June series Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
Version.0: 006 abc General Certificate of Education Chemistry 542 CHM3/W Introduction to Organic Chemistry Mark Scheme 2006 examination - June series Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
M1. (a) Yellow (solution) 1. Orange solution 1 SO 4. Yellow / purple (solution) Allow orange / brown (solution) 1. Brown precipitate / solid 1 + 3H 2
 M. (a) Yellow (solution) range solution Cr + H + Cr 7 + H Allow equation with H S (b) Yellow / purple (solution) Allow orange / brown (solution) Brown precipitate / solid [Fe(H ) 6 ] + + H Fe(H ) (H) +
M. (a) Yellow (solution) range solution Cr + H + Cr 7 + H Allow equation with H S (b) Yellow / purple (solution) Allow orange / brown (solution) Brown precipitate / solid [Fe(H ) 6 ] + + H Fe(H ) (H) +
must show C=C Penalise sticks once per pair 1 H 10 Penalise sticks once per pair 1 or CH 3 C 2 Penalise sticks once per pair 1
 M. (a) A allow CH COCH B must show C=C Penalise sticks once per pair (b) C CH CH CH CH CH D NOT cyclopentane which is only C 5 H 0 Penalise sticks once per pair (c) E CH CH COOCH Allow C H 5 CO CH F CH
M. (a) A allow CH COCH B must show C=C Penalise sticks once per pair (b) C CH CH CH CH CH D NOT cyclopentane which is only C 5 H 0 Penalise sticks once per pair (c) E CH CH COOCH Allow C H 5 CO CH F CH
3.2.9 Alkenes. Addition Reactions. 271 minutes. 268 marks. Page 1 of 35
 ..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
Unit 2. Answers to examination-style questions. Answers Marks Examiner s tips. 1 (a) heat energy change at constant pressure
 (a) heat energy change at constant pressure This is in the spec but not so well known. Learn it. (b) N 2 (g) + ½O 2 (g) N 2 O(g) (c) (i) D = (bonds broken) (bonds made) = ½(945) + (3/2)(59) 3(278) = 23
(a) heat energy change at constant pressure This is in the spec but not so well known. Learn it. (b) N 2 (g) + ½O 2 (g) N 2 O(g) (c) (i) D = (bonds broken) (bonds made) = ½(945) + (3/2)(59) 3(278) = 23
2.9 ALKENES EXTRA QUESTIONS MS. (b) Addition 1 (ignore self or chain as a preface to addition ) (penalise additional)
 2.9 ALKENES EXTRA QUESTIONS MS 1. (a) 2 6 2 4 2 1 (b) Addition 1 (ignore self or chain as a preface to addition ) (penalise additional) 2. Electrophilic addition 1 M1: curly arrow from = bond towards/alongside
2.9 ALKENES EXTRA QUESTIONS MS 1. (a) 2 6 2 4 2 1 (b) Addition 1 (ignore self or chain as a preface to addition ) (penalise additional) 2. Electrophilic addition 1 M1: curly arrow from = bond towards/alongside
Alcohols. Ethanol Production. 182 minutes. 181 marks. Page 1 of 26
 ..0 Alcohols Ethanol Production 8 minutes 8 marks Page of 6 M. Condition = two from yeast (anywhere in question) Air excluded or sterile / clean () Ignore references to pressure / temperature / aqueous
..0 Alcohols Ethanol Production 8 minutes 8 marks Page of 6 M. Condition = two from yeast (anywhere in question) Air excluded or sterile / clean () Ignore references to pressure / temperature / aqueous
A mass spectrometer can be used to distinguish between samples of butane and propanal. The table shows some precise relative atomic mass values.
 Butane and propanal are compounds with M r = 58.0, calculated using data from your Periodic Table. (a) A mass spectrometer can be used to distinguish between samples of butane and propanal. The table shows
Butane and propanal are compounds with M r = 58.0, calculated using data from your Periodic Table. (a) A mass spectrometer can be used to distinguish between samples of butane and propanal. The table shows
Marking Guidance Mark Comments
 Energetics Answers Chemistry - AQA GCE Mark Scheme 200 June series Q Part Sub Part Marking Guidance Mark Comments a i M drawn curve starts at reactants and ends at products M2 curve peak is below the one
Energetics Answers Chemistry - AQA GCE Mark Scheme 200 June series Q Part Sub Part Marking Guidance Mark Comments a i M drawn curve starts at reactants and ends at products M2 curve peak is below the one
Alkenes and Alcohols Answers
 Alkenes and Alcohols Answers Chemistry - AQA GCE Mark Scheme 200 June series Q Part Sub Part Marking Guidance Mark Comments 8 a Three conditions in any order for M to M3 4 Mark independently M M2 M3 yeast
Alkenes and Alcohols Answers Chemistry - AQA GCE Mark Scheme 200 June series Q Part Sub Part Marking Guidance Mark Comments 8 a Three conditions in any order for M to M3 4 Mark independently M M2 M3 yeast
Answer Marks Guidance
 Question number (a) molecular formula: C 4 H 8 Answer Marks Guidance empirical formula: CH 2 This is a revision of earlier chapters. (b) (i) name of mechanism: electrophilic addition Remember that reactions
Question number (a) molecular formula: C 4 H 8 Answer Marks Guidance empirical formula: CH 2 This is a revision of earlier chapters. (b) (i) name of mechanism: electrophilic addition Remember that reactions
Which of the following is a correct mechanism for the formation of 2-methylbut-2-ene from 2-bromo-3-methylbutane?
 Which of the following is a correct mechanism for the formation of 2-methylbut-2-ene from 2-bromo-3-methylbutane? A B C D (Total mark) 2 2-bromo-2-methylpentane is heated with potassium hydroxide dissolved
Which of the following is a correct mechanism for the formation of 2-methylbut-2-ene from 2-bromo-3-methylbutane? A B C D (Total mark) 2 2-bromo-2-methylpentane is heated with potassium hydroxide dissolved
3.2.1 Energetics. Bond Enthalpy. 98 minutes. 96 marks. Page 1 of 16
 3..1 Energetics Bond Enthalpy 98 minutes 96 marks Page 1 of 16 Q1. (a) State what is meant by the term mean bond enthalpy. () (b) Ethanal has the structure Gaseous ethanal burns as shown by the equation
3..1 Energetics Bond Enthalpy 98 minutes 96 marks Page 1 of 16 Q1. (a) State what is meant by the term mean bond enthalpy. () (b) Ethanal has the structure Gaseous ethanal burns as shown by the equation
Electrophilic substitution Both words needed Ignore minor misspellings 1
 M.(a) Electrophilic substitution Both words needed Ignore minor misspellings (b) (i) Sn / HCl OR H 2 / Ni OR H 2 / Pt OR Fe / HCl OR Zn / HCl OR SnCl 2 / HCl Ignore conc or dil with HCl, Allow (dil) H
M.(a) Electrophilic substitution Both words needed Ignore minor misspellings (b) (i) Sn / HCl OR H 2 / Ni OR H 2 / Pt OR Fe / HCl OR Zn / HCl OR SnCl 2 / HCl Ignore conc or dil with HCl, Allow (dil) H
3.2.8 Haloalkanes. Nucleophilic Substitution. 267 minutes. 264 marks. Page 1 of 36
 3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide.
 Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
Haloalkanes. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers for C 5 H 11 Br
 Haloalkanes The basics: The functional group is a halogen atom: F, Cl, Br or I General formula C n H 2n+1 X Use the prefixes: fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers
Haloalkanes The basics: The functional group is a halogen atom: F, Cl, Br or I General formula C n H 2n+1 X Use the prefixes: fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers
3.2.2 Kinetics. Effect of Concentration. 135 minutes. 134 marks. Page 1 of 13
 3.. Kinetics Effect of Concentration 35 minutes 34 marks Page of 3 M. (a) Activation energy;- The minimum energy needed for a reaction to occur / start () Catalyst effect:- Alternative route (or more molecules
3.. Kinetics Effect of Concentration 35 minutes 34 marks Page of 3 M. (a) Activation energy;- The minimum energy needed for a reaction to occur / start () Catalyst effect:- Alternative route (or more molecules
3.2.1 Energetics. Enthalpy Change. 263 minutes. 259 marks. Page 1 of 33
 .. Energetics Enthalpy Change 6 minutes 59 marks Page of M. (a) (Enthalpy change) when mol () of a compound is formed from its constituent elements () in their standard states () Allow energy or heat,
.. Energetics Enthalpy Change 6 minutes 59 marks Page of M. (a) (Enthalpy change) when mol () of a compound is formed from its constituent elements () in their standard states () Allow energy or heat,
When 2-bromopentane reacts with ethanolic KOH, two structurally isomeric alkenes are formed.
 Q1. Organic reaction mechanisms help chemists to understand how the reactions of organic compounds occur. The following conversions illustrate a number of different types of reaction mechanism. (a) When
Q1. Organic reaction mechanisms help chemists to understand how the reactions of organic compounds occur. The following conversions illustrate a number of different types of reaction mechanism. (a) When
Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction?
 Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of -bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A Electrophilic addition B Electrophilic substitution
Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of -bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A Electrophilic addition B Electrophilic substitution
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level. Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis
 OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
Alcohols. Nomenclature. 57 minutes. 57 marks. Page 1 of 9
 ..0 Alcohols Nomenclature 57 minutes 57 marks Page of 9 M. (a) % O =.6 % () If % O not calculated only M available C O () = 5. =.5 =.5 Ratio: : 0: ( C 0 O) () If arithmetic error in any result lose M If
..0 Alcohols Nomenclature 57 minutes 57 marks Page of 9 M. (a) % O =.6 % () If % O not calculated only M available C O () = 5. =.5 =.5 Ratio: : 0: ( C 0 O) () If arithmetic error in any result lose M If
Cherry Hill Tuition A Level Chemistry OCR (A) Paper 9 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE CHEMISTRY A Chains, Energy and Resources F322 * OCE / 1 9 2 3 4* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE CHEMISTRY A Chains, Energy and Resources F322 * OCE / 1 9 2 3 4* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry
TOPIC 13 ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES a) (i) UV light / temperatures > 500 ºC (ii) CH 4 (g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl(g) + HCl(g) Cl(g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl 2 (l) + HCl(g) Cl 2 (l) + Cl 2 (g) CHCl 3 (l) + HCl(g) CHCl 3 (l) + Cl 2 (g)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES a) (i) UV light / temperatures > 500 ºC (ii) CH 4 (g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl(g) + HCl(g) Cl(g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl 2 (l) + HCl(g) Cl 2 (l) + Cl 2 (g) CHCl 3 (l) + HCl(g) CHCl 3 (l) + Cl 2 (g)
3.2.1 Energetics. Hess's Law. 183 minutes. 181 marks. Page 1 of 21
 .. Energetics Hess's Law 8 minutes 8 marks Page of M. (a) (Enthalpy change) when mol () of a compound is formed from its constituent elements () in their standard states () Allow energy or heat, Ignore
.. Energetics Hess's Law 8 minutes 8 marks Page of M. (a) (Enthalpy change) when mol () of a compound is formed from its constituent elements () in their standard states () Allow energy or heat, Ignore
International Advanced Level Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 2: Application of Core Principles of Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 2: Application of Core Principles of Chemistry Friday
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 2: Application of Core Principles of Chemistry Friday
M1.(a) (i) 2Cl Cl 2 + 2e Ignore state symbols Credit loss of electrons from LHS Credit multiples Do not penalise absence of charge on electron 1
 M.(a) (i) 2Cl Cl 2 + 2e Credit loss of electrons from LHS Credit multiples Do not penalise absence of charge on electron (ii) (iii) +7 7 VII +VII Allow Mn +7 and 7+ MnO 4 + 8H + + 5e Mn 2+ + 4H 2 O Credit
M.(a) (i) 2Cl Cl 2 + 2e Credit loss of electrons from LHS Credit multiples Do not penalise absence of charge on electron (ii) (iii) +7 7 VII +VII Allow Mn +7 and 7+ MnO 4 + 8H + + 5e Mn 2+ + 4H 2 O Credit
10.2 ALCOHOLS EXTRA QUESTIONS. Reaction excess conc, H SO 180 C
 10.2 ALOOLS EXTRA QUESTIONS 1. onsider the reaction scheme below which starts from butanone. N Reaction 1 3 2 3 3 2 3 O Reaction 2 O A 3 O B 2 3 excess conc, SO 180 2 4 but 1 ene and but 2 ene (a) When
10.2 ALOOLS EXTRA QUESTIONS 1. onsider the reaction scheme below which starts from butanone. N Reaction 1 3 2 3 3 2 3 O Reaction 2 O A 3 O B 2 3 excess conc, SO 180 2 4 but 1 ene and but 2 ene (a) When
Question Answer Mark Guidance 1 (a) Method 1: 100% OR (only) one product OR no waste 2 product OR addition (reaction)
 1 (a) Method 1: 100% OR (only) one product OR no waste 2 product OR addition (reaction) ALLOW co-product or by-product for waste product Method 2: < 100% AND two products OR (also) produces NaBr OR (There
1 (a) Method 1: 100% OR (only) one product OR no waste 2 product OR addition (reaction) ALLOW co-product or by-product for waste product Method 2: < 100% AND two products OR (also) produces NaBr OR (There
3.2.8 Haloalkanes. Elimination. 148 minutes. 145 marks. Page 1 of 22
 3.2.8 Haloalkanes Elimination 148 minutes 145 marks Page 1 of 22 Q1. Reaction of 2-bromobutane with potassium hydroxide can produce two types of product depending on the solvent used. In aqueous solution,
3.2.8 Haloalkanes Elimination 148 minutes 145 marks Page 1 of 22 Q1. Reaction of 2-bromobutane with potassium hydroxide can produce two types of product depending on the solvent used. In aqueous solution,
Deduce the empirical and molecular formulas of the carboxylic acid formed. Empirical formula =... Molecular formula =... (4)
 Glucose can decompose in the presence of microorganisms to form a range of products. One of these is a carboxylic acid (M r = 88.0) containing 40.9% carbon and 4.5% hydrogen by mass. (a) Deduce the empirical
Glucose can decompose in the presence of microorganisms to form a range of products. One of these is a carboxylic acid (M r = 88.0) containing 40.9% carbon and 4.5% hydrogen by mass. (a) Deduce the empirical
Chemistry 2.5 AS WORKBOOK. Working to Excellence Working to Excellence
 Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Organic Chemistry Review: Topic 10 & Topic 20
 Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
CHEM2. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June Unit 2 Chemistry in Action. Friday 27 May pm to 3.
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2011 Question 1 2 Mark
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2011 Question 1 2 Mark
Chapter 16. Answers to examination-style questions. Answers Marks Examiner s tips. 1 (a) (i) C 6 H 12 O 6 2C 2 H 5 OH + 2CO 2 (ii) fermentation
 Chapter 6 (a) (i) C 6 O 6 C 5 O + CO (ii) fermentation (b) (i) C 5 O + 3O CO + 3 O (ii) CO or carbon monoxide or C or carbon (a) (i) potassium (or sodium) dichromate(vi) or correct formula or potassium
Chapter 6 (a) (i) C 6 O 6 C 5 O + CO (ii) fermentation (b) (i) C 5 O + 3O CO + 3 O (ii) CO or carbon monoxide or C or carbon (a) (i) potassium (or sodium) dichromate(vi) or correct formula or potassium
Properties of Compounds
 Chapter 6. Properties of Compounds Comparing properties of elements and compounds Compounds are formed when elements combine together in fixed proportions. The compound formed will often have properties
Chapter 6. Properties of Compounds Comparing properties of elements and compounds Compounds are formed when elements combine together in fixed proportions. The compound formed will often have properties
Bond C=O C H C O O H. Use the enthalpy change for the reaction and data from the table to calculate a value for the H H bond enthalpy.
 Many chemical processes release waste products into the atmosphere. Scientists are developing new solid catalysts to convert more efficiently these emissions into useful products, such as fuels. One example
Many chemical processes release waste products into the atmosphere. Scientists are developing new solid catalysts to convert more efficiently these emissions into useful products, such as fuels. One example
Unit 4: General Principles of Chemistry I Rates, Equilibria and Further Organic Chemistry (including synoptic assessment)
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Unit 4: General Principles of Chemistry I Rates, Equilibria and Further Organic Chemistry
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Unit 4: General Principles of Chemistry I Rates, Equilibria and Further Organic Chemistry
GCE AS/A level 1092/01 CHEMISTRY CH2
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1092/01 CHEMISTRY CH2 S15-1092-01 P.M. TUESDAY, 2 June 2015 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded Section A
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS/A level 1092/01 CHEMISTRY CH2 S15-1092-01 P.M. TUESDAY, 2 June 2015 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded Section A
Name: Class: Redox revision questions. 50 minutes. Time: Marks: 50. Comments: Page 1 of 17
 Name: Class: Redox revision questions Time: 50 minutes Marks: 50 Comments: Page of 7 Aqueous C 2 O ions react with MnO ions in acidic solution according to the equation 5 C 2 O + 2MnO + 6H + 2Mn 2+ + 0CO
Name: Class: Redox revision questions Time: 50 minutes Marks: 50 Comments: Page of 7 Aqueous C 2 O ions react with MnO ions in acidic solution according to the equation 5 C 2 O + 2MnO + 6H + 2Mn 2+ + 0CO
3.2.1 Energetics. Enthalpy Change. 263 minutes. 259 marks. Page 1 of 41
 ..1 Energetics Enthalpy Change 6 minutes 59 marks Page 1 of 41 Q1. (a) Define the term standard molar enthalpy of formation, ΔH f. (b) State Hess s law. (c) Propanone, CO, burns in oxygen as shown by the
..1 Energetics Enthalpy Change 6 minutes 59 marks Page 1 of 41 Q1. (a) Define the term standard molar enthalpy of formation, ΔH f. (b) State Hess s law. (c) Propanone, CO, burns in oxygen as shown by the
Version : /2010. klm. General Certificate of Education. Chemistry Chemistry in Action. Mark Scheme examination - January series
 Version : 1.0 02/2010 klm General Certificate of Education Chemistry 1421 CHEM2 Chemistry in Action Mark Scheme 2010 examination - January series Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and
Version : 1.0 02/2010 klm General Certificate of Education Chemistry 1421 CHEM2 Chemistry in Action Mark Scheme 2010 examination - January series Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and
UNIT 2 REVISION CHECKLIST. a) understand that reactions are either exothermic or endothermic and apply the sign convention
 UNIT 2 REVISION CHECKLIST Topic 2.1 Energetics a) understand that reactions are either exothermic or endothermic and apply the sign convention b) define the term enthalpy change, recall what standard conditions
UNIT 2 REVISION CHECKLIST Topic 2.1 Energetics a) understand that reactions are either exothermic or endothermic and apply the sign convention b) define the term enthalpy change, recall what standard conditions
EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES. 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction....
 EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction. C 6 H 5 3 + Cl 2 C 6 H 5 2 Cl + HCl Write an equation for the initiation
EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction. C 6 H 5 3 + Cl 2 C 6 H 5 2 Cl + HCl Write an equation for the initiation
Final. Mark Scheme. Chemistry CHEM2. (Specification 2420) Unit 2: Chemistry in Action. General Certificate of Education (A-level) January 2011 PMT
 Version 1 General Certificate of Education (A-level) January 2011 Chemistry CHEM2 (Specification 2420) Unit 2: Chemistry in Action Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
Version 1 General Certificate of Education (A-level) January 2011 Chemistry CHEM2 (Specification 2420) Unit 2: Chemistry in Action Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
2.9 ALKENES EXTRA QUESTIONS
 .9 ALKENES EXTRA QUESTIONS 1. (a) Most of the ethene used by industry is produced when ethane is heated to 900 C in the absence of air. Write an equation for this reaction.... Name the type of polymerisation
.9 ALKENES EXTRA QUESTIONS 1. (a) Most of the ethene used by industry is produced when ethane is heated to 900 C in the absence of air. Write an equation for this reaction.... Name the type of polymerisation
M1.B [1] M2.B [1] OR H PO 4. M1 (1) heat (1) M2 OR 150 C C Condition mark linked to correct reagent but award M2 if H 2.
![M1.B [1] M2.B [1] OR H PO 4. M1 (1) heat (1) M2 OR 150 C C Condition mark linked to correct reagent but award M2 if H 2. M1.B [1] M2.B [1] OR H PO 4. M1 (1) heat (1) M2 OR 150 C C Condition mark linked to correct reagent but award M2 if H 2.](/thumbs/87/97087846.jpg) Penalise reagent and condition if dilute H S 4 / H P 4 4 M.B [] M.B [] M. (a) Reaction : NaH KH () M alcohol (ic) ethanol (ic)() M ignore heat Condition mark linked to correct reagent but award M if H
Penalise reagent and condition if dilute H S 4 / H P 4 4 M.B [] M.B [] M. (a) Reaction : NaH KH () M alcohol (ic) ethanol (ic)() M ignore heat Condition mark linked to correct reagent but award M if H
Alcohols. Ethanol Production. 182 minutes. 181 marks. Page 1 of 25
 3..10 Alcohols Ethanol Production 18 minutes 181 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Ethanol is produced commercially by fermentation of aqueous glucose, C 6 H 1 O 6 State two conditions, other than temperature, which
3..10 Alcohols Ethanol Production 18 minutes 181 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Ethanol is produced commercially by fermentation of aqueous glucose, C 6 H 1 O 6 State two conditions, other than temperature, which
Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCE Centre Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry Candidate Number Thursday 13 January 2011 Morning Time: 1 hour
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCE Centre Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry Candidate Number Thursday 13 January 2011 Morning Time: 1 hour
Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level Centre Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry Candidate Number Thursday 9 January
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level Centre Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry Candidate Number Thursday 9 January
Collision Theory. Mark Scheme 2. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision
 Collision Theory Mark Scheme Level A Level Subject Chemistry Exam Board AQA Module 3. Physical Chemistry Topic 3..5 Kinetics Sub-Topic 3..5. Collision Theory Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 5 minutes
Collision Theory Mark Scheme Level A Level Subject Chemistry Exam Board AQA Module 3. Physical Chemistry Topic 3..5 Kinetics Sub-Topic 3..5. Collision Theory Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 5 minutes
AS-LEVEL Chemistry. AS Paper 2 Mark scheme. 7404/2 June Version: 1.0 Final
 AS-LEVEL Chemistry AS Paper 2 Mark scheme 7404/2 June 207 Version:.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject
AS-LEVEL Chemistry AS Paper 2 Mark scheme 7404/2 June 207 Version:.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject
# Ans Workings / Remarks
 # Ans Workings / Remarks 1 B Atomic mass and temperature affects the rate of diffusion of gas. The lower the atomic mass, the lighter the substance. The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of collision
# Ans Workings / Remarks 1 B Atomic mass and temperature affects the rate of diffusion of gas. The lower the atomic mass, the lighter the substance. The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of collision
Chemistry. Student Number. Mark / 64. Final Examination Preliminary Course General Instructions. Total Marks 64
 Student Number Mark / 64 Chemistry Final Examination Preliminary Course 2003 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 120 minutes Write using black or blue pen Draw diagrams using pencil
Student Number Mark / 64 Chemistry Final Examination Preliminary Course 2003 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 120 minutes Write using black or blue pen Draw diagrams using pencil
CHEM2. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January Unit 2 Chemistry in Action
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January 2011 Question 1 2
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January 2011 Question 1 2
WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY
 WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY enthalpy change of reaction, enthalpy change of combustion and standard molar enthalpy change of formation, Δ fh ϴ Hess s law and energy cycles concept
WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY enthalpy change of reaction, enthalpy change of combustion and standard molar enthalpy change of formation, Δ fh ϴ Hess s law and energy cycles concept
2 Answer all the questions. 1 Nitrogen monoxide is formed when nitrogen and oxygen from the air combine. (g) + O 2
 2 Answer all the questions. 1 Nitrogen monoxide is formed when nitrogen and oxygen from the air combine. N 2 (g) + 2 (g) 2N(g) equation 1.1 Under normal atmospheric conditions, a further reaction occurs
2 Answer all the questions. 1 Nitrogen monoxide is formed when nitrogen and oxygen from the air combine. N 2 (g) + 2 (g) 2N(g) equation 1.1 Under normal atmospheric conditions, a further reaction occurs
(13) WMP/Jun14/CHEM2
 13 Do not write outside the box 6 This question is about Group 7 chemistry. 6 (a) Sea water is a major source of iodine. The iodine extracted from sea water is impure. It is purified in a two-stage process.
13 Do not write outside the box 6 This question is about Group 7 chemistry. 6 (a) Sea water is a major source of iodine. The iodine extracted from sea water is impure. It is purified in a two-stage process.
Chapter 4. The Major Classes of Chemical Reactions 4-1
 Chapter 4 The Major Classes of Chemical Reactions 4-1 The Major Classes of Chemical Reactions 4.1 The Role of Water as a Solvent 4.2 Writing Equations for Aqueous Ionic Reactions 4.3 Precipitation Reactions
Chapter 4 The Major Classes of Chemical Reactions 4-1 The Major Classes of Chemical Reactions 4.1 The Role of Water as a Solvent 4.2 Writing Equations for Aqueous Ionic Reactions 4.3 Precipitation Reactions
Question number 1 (a) Statement. Answer Notes Marks. 1 mark for each line correct. Fractional distillation. Cracking. Crude oil is heated
 (a) Statement Crude oil is heated Fractional distillation ( ) Cracking mark for each line correct 5 A catalyst may be used Alkenes are formed Decomposition reactions occur Fuels are obtained (b) i i ii
(a) Statement Crude oil is heated Fractional distillation ( ) Cracking mark for each line correct 5 A catalyst may be used Alkenes are formed Decomposition reactions occur Fuels are obtained (b) i i ii
Enthalpy changes
 2.3.1. Enthalpy changes In an exothermic change energy is transferred from the system (chemicals) to the surroundings. The have less energy than the If an enthalpy change occurs then energy is transferred
2.3.1. Enthalpy changes In an exothermic change energy is transferred from the system (chemicals) to the surroundings. The have less energy than the If an enthalpy change occurs then energy is transferred
Based on the kinetic molecular theory of gases, which one of the following statements is INCORRECT?
 1 Based on the kinetic molecular theory of gases, which one of the following statements is INCORRECT? A) The collisions between gas molecules are perfectly elastic. B) At absolute zero, the average kinetic
1 Based on the kinetic molecular theory of gases, which one of the following statements is INCORRECT? A) The collisions between gas molecules are perfectly elastic. B) At absolute zero, the average kinetic
(10) WMP/Jan12/CHEM2
 0 Do not write outside the box 5 Iodine reacts with concentrated nitric acid to produce nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ). 5 (a) (i) Give the oxidation state of iodine in each of the following. I 2... HIO 3...
0 Do not write outside the box 5 Iodine reacts with concentrated nitric acid to produce nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ). 5 (a) (i) Give the oxidation state of iodine in each of the following. I 2... HIO 3...
dihalogenoalkane H 2, Nickel Catalyst KOH alcoholic HBr, HCl Br Cl Elimination KOH aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution
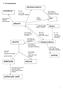 7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
Acceptable Answers Reject Mark. The sulfur trioxide can accept a pair of electrons An electron 1
 (a)(i sulfuric acid / fuming H SO 4 / oleum / H S O 7 Conc. (for fuming) Fuming dilute sulfuric acid Just sulfuric acid Just H SO 4 (a)(ii) Sulfur is δ+ and on at least one oxygen δ- Full + or charge(s)
(a)(i sulfuric acid / fuming H SO 4 / oleum / H S O 7 Conc. (for fuming) Fuming dilute sulfuric acid Just sulfuric acid Just H SO 4 (a)(ii) Sulfur is δ+ and on at least one oxygen δ- Full + or charge(s)
IB Chemistry Solutions Gasses and Energy
 Solutions A solution is a homogeneous mixture it looks like one substance. An aqueous solution will be a clear mixture with only one visible phase. Be careful with the definitions of clear and colourless.
Solutions A solution is a homogeneous mixture it looks like one substance. An aqueous solution will be a clear mixture with only one visible phase. Be careful with the definitions of clear and colourless.
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE CHEMISTRY A Chains, Energy and Resources F322 * OCE / 1 9 2 3 4* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE CHEMISTRY A Chains, Energy and Resources F322 * OCE / 1 9 2 3 4* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry
Reactions of Haloalkanes
 Reactions of aloalkanes N Goalby chemrevise.org aloalkanes ontain a halogen atom covalently bonded to a carbon atom General formula: R-X where X is a halogen atom (F, l,, I) and R is the carbon chain.
Reactions of aloalkanes N Goalby chemrevise.org aloalkanes ontain a halogen atom covalently bonded to a carbon atom General formula: R-X where X is a halogen atom (F, l,, I) and R is the carbon chain.
F322 Chains, Energy and Resources
 F322 Chains, Energy and Resources 1 (a) C n 2n+2 1 ALLOW C n 2(n+1) IGNORE size of subscripts (b) (i) C 8 18 + 8½O 2 8CO + 9 2 O 1 ALLOW any correct multiples IGNORE state symbols (ii) limited supply of
F322 Chains, Energy and Resources 1 (a) C n 2n+2 1 ALLOW C n 2(n+1) IGNORE size of subscripts (b) (i) C 8 18 + 8½O 2 8CO + 9 2 O 1 ALLOW any correct multiples IGNORE state symbols (ii) limited supply of
(24) WMP/Jun12/CHEM2
 24 Do not write outside the box 9 A student investigated the chemistry of the halogens and the halide ions. 9 (a) In the first two tests, the student made the following observations. Test 1. Add chlorine
24 Do not write outside the box 9 A student investigated the chemistry of the halogens and the halide ions. 9 (a) In the first two tests, the student made the following observations. Test 1. Add chlorine
M1. (a) Functional group (isomerism) 1
 M. (a) Functional group (isomerism) (b) M Tollens (reagent) (Credit ammoniacal silver nitrate a description of making Tollens ) (Ignore either AgNO or [Ag(NH ) 2 + ] or the silver mirror test on their
M. (a) Functional group (isomerism) (b) M Tollens (reagent) (Credit ammoniacal silver nitrate a description of making Tollens ) (Ignore either AgNO or [Ag(NH ) 2 + ] or the silver mirror test on their
Chapter 6. Chemical Reactions. Sodium reacts violently with bromine to form sodium bromide.
 Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions Sodium reacts violently with bromine to form sodium bromide. Evidence of Chemical Reactions Chemical Equations Reactants Products Reactant(s): Substance(s) present before the
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions Sodium reacts violently with bromine to form sodium bromide. Evidence of Chemical Reactions Chemical Equations Reactants Products Reactant(s): Substance(s) present before the
Paper Reference. Advanced Unit Test 6B (Synoptic) Monday 25 June 2007 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 6 2 4 6 0 2 Signature Paper Reference(s) 6246/02 Edexcel GCE Chemistry Examiner s use only Team Leader s use only Advanced Unit Test 6B (Synoptic)
Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 6 2 4 6 0 2 Signature Paper Reference(s) 6246/02 Edexcel GCE Chemistry Examiner s use only Team Leader s use only Advanced Unit Test 6B (Synoptic)
ORGANIC REACTIONS 11 MARCH 2014
 ORGANIC REACTIONS 11 MARCH 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at the chemical reactions of organic molecules Summary Organic molecules can undergo several important chemical reactions. 1.
ORGANIC REACTIONS 11 MARCH 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Look at the chemical reactions of organic molecules Summary Organic molecules can undergo several important chemical reactions. 1.
Q1. (a) State what is meant by the term activation energy of a reaction. (1)
 Q1. (a) State what is meant by the term activation energy of a reaction. (c) State in general terms how a catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction. The curve below shows the Maxwell Boltzmann
Q1. (a) State what is meant by the term activation energy of a reaction. (c) State in general terms how a catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction. The curve below shows the Maxwell Boltzmann
18.1 Arenes benzene compounds Answers to Exam practice questions
 Pages 230 232 1 a) Benzene has a planar molecule ; with six carbon atoms in a regular hexagon. Each carbon atom forms a normal covalent ( ) bond with its two adjacent carbons atoms and a hydrogen atom.
Pages 230 232 1 a) Benzene has a planar molecule ; with six carbon atoms in a regular hexagon. Each carbon atom forms a normal covalent ( ) bond with its two adjacent carbons atoms and a hydrogen atom.
Stoichiometry: Chemical Calculations. Chemistry is concerned with the properties and the interchange of matter by reaction i.e. structure and change.
 Chemistry is concerned with the properties and the interchange of matter by reaction i.e. structure and change. In order to do this, we need to be able to talk about numbers of atoms. The key concept is
Chemistry is concerned with the properties and the interchange of matter by reaction i.e. structure and change. In order to do this, we need to be able to talk about numbers of atoms. The key concept is
TOPIC 11 ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES QUESTIONSHEET 1 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF THE HALOGENS
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF THE HALOGENS a) (i) F 2 gas (½) yellow (½) Cl 2 gas (½) green / yellow-green (½) Br 2 liquid (½) dark red / brown (½) I 2 solid (½) violet-black / black (½) (ii)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF THE HALOGENS a) (i) F 2 gas (½) yellow (½) Cl 2 gas (½) green / yellow-green (½) Br 2 liquid (½) dark red / brown (½) I 2 solid (½) violet-black / black (½) (ii)
A-LEVEL Chemistry. 7405/3 Paper 3 Mark scheme June Version: 1.0 Final
 A-LEVEL Chemistry 7405/3 Paper 3 Mark scheme 7405 June 207 Version:.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject
A-LEVEL Chemistry 7405/3 Paper 3 Mark scheme 7405 June 207 Version:.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject
... [1] (ii) Draw a dot-and-cross diagram to show the bonding in NH 3
![... [1] (ii) Draw a dot-and-cross diagram to show the bonding in NH 3 ... [1] (ii) Draw a dot-and-cross diagram to show the bonding in NH 3](/thumbs/76/73434679.jpg) 1 Chemists have developed models for bonding and structure which are used to explain different properties. (a) Ammonia, NH 3, is a covalent compound. Explain what is meant by a covalent bond. Draw a dot-and-cross
1 Chemists have developed models for bonding and structure which are used to explain different properties. (a) Ammonia, NH 3, is a covalent compound. Explain what is meant by a covalent bond. Draw a dot-and-cross
M1 (could be scored by a correct mathematical expression) M1 ΔH = ΣΔH f (products) ΣΔH f (reactants) OR a correct cycle of balanced equations
 M.(a) M (could be scored by a correct mathematical expression) M ΔH = ΣΔH f (products) ΣΔH f (reactants) a correct cycle of balanced equations M2 = 5( 635) ( 560) = 375 + 560 (This also scores M) M3 =
M.(a) M (could be scored by a correct mathematical expression) M ΔH = ΣΔH f (products) ΣΔH f (reactants) a correct cycle of balanced equations M2 = 5( 635) ( 560) = 375 + 560 (This also scores M) M3 =
For the element X in the ionic compound MX, explain the meaning of the term oxidation state.
 1. (a) By referring to electrons, explain the meaning of the term oxidising agent.... For the element X in the ionic compound MX, explain the meaning of the term oxidation state.... (c) Complete the table
1. (a) By referring to electrons, explain the meaning of the term oxidising agent.... For the element X in the ionic compound MX, explain the meaning of the term oxidation state.... (c) Complete the table
Chemistry Assessment Unit AS 2
 Centre Number 71 Candidate Number ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education January 2009 Chemistry Assessment Unit AS 2 assessing Module 2: Organic, Physical and Inorganic Chemistry ASC21
Centre Number 71 Candidate Number ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education January 2009 Chemistry Assessment Unit AS 2 assessing Module 2: Organic, Physical and Inorganic Chemistry ASC21
Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCE Centre Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry Candidate Number Monday 23 May 2011 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCE Centre Number Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry Candidate Number Monday 23 May 2011 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *6897461207* CHEMISTRY 9701/22 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions May/June 2016 1 hour 15 minutes
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *6897461207* CHEMISTRY 9701/22 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions May/June 2016 1 hour 15 minutes
CHEM2. (JUN14CHEM201) WMP/Jun14/CHEM2/E9w. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June Unit 2 Chemistry in Action
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Chemistry General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2014 CHEM2
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Chemistry General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2014 CHEM2
UNIT 2: CHEMICAL BONDING, APPLICATION OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOUNDATION TIER SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS
 GCSE CHEMISTRY Sample Assessment Materials 71 Surname Other Names Centre Number Candidate Number GCSE CHEMISTRY UNIT 2: CHEMICAL BONDING, APPLICATION OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOUNDATION
GCSE CHEMISTRY Sample Assessment Materials 71 Surname Other Names Centre Number Candidate Number GCSE CHEMISTRY UNIT 2: CHEMICAL BONDING, APPLICATION OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOUNDATION
Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Chemical Reactions Reactants: Zn + I 2 Product: ZnI 2 Chemical Reactions Evidence of a chemical reaction: Gas Evolution
Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Chemical Reactions Reactants: Zn + I 2 Product: ZnI 2 Chemical Reactions Evidence of a chemical reaction: Gas Evolution
International School of Johannesburg. Diploma Chemistry. Organic Chemistry (HL) Revision Questions. D. ( HNCH 2 CH 2 NHCOCH 2 NH ) (Total 1 mark)
 International School of Johannesburg Diploma Chemistry Organic Chemistry (HL) Revision Questions 1. The compounds H 2 NCH 2 CH 2 NH 2 and HOOCCH 2 COOH react to form a polymer. What is the structure of
International School of Johannesburg Diploma Chemistry Organic Chemistry (HL) Revision Questions 1. The compounds H 2 NCH 2 CH 2 NH 2 and HOOCCH 2 COOH react to form a polymer. What is the structure of
B410U20-1 S17-B410U20-1. CHEMISTRY AS component 2 Energy, Rate and Chemistry of Carbon Compounds
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS NEW B410U20-1 S17-B410U20-1 CHEMISTRY AS component 2 Energy, Rate and Chemistry of Carbon Compounds FRIDAY, 9 JUNE 2017 AFTERNOON 1 hour 30 minutes
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE AS NEW B410U20-1 S17-B410U20-1 CHEMISTRY AS component 2 Energy, Rate and Chemistry of Carbon Compounds FRIDAY, 9 JUNE 2017 AFTERNOON 1 hour 30 minutes
AQA Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
2 CH 2 O (-) Na (+) This equation scores (2) marks. CH 2 OHCH 2 O (-) Na (+)
 (a) Na + O (-) Na (+) O (-) Na (+) O (-) Na (+) + This equation scores () marks Accept multiples and ( ) and ( O (-) Na (+) ) Organic product (harges not needed) Na (+) O (-) Na (+) O (-) Reject bond from
(a) Na + O (-) Na (+) O (-) Na (+) O (-) Na (+) + This equation scores () marks Accept multiples and ( ) and ( O (-) Na (+) ) Organic product (harges not needed) Na (+) O (-) Na (+) O (-) Reject bond from
3.2.5 Group VII. Trends in reducing abilities. 222 minutes. 218 marks. Page 1 of 21
 3..5 Group VII Trends in reducing abilities minutes 18 marks Page 1 of 1 Q1. (a) Samples of solid sodium fluoride, sodium chloride, sodium bromide and sodium iodide are each warmed separately with concentrated
3..5 Group VII Trends in reducing abilities minutes 18 marks Page 1 of 1 Q1. (a) Samples of solid sodium fluoride, sodium chloride, sodium bromide and sodium iodide are each warmed separately with concentrated
Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The Core Principles of Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GE entre Number hemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The ore Principles of hemistry andidate Number Thursday 10 January 2013 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GE entre Number hemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: The ore Principles of hemistry andidate Number Thursday 10 January 2013 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
GCE A level 1094/01 CHEMISTRY CH4
 Surname ther Names Centre 2 Candidate GCE A level 1094/01 CHEMISTRY CH4 P.M. MNDAY, 14 January 2013 1¾ hours ADDITINAL MATERIALS In addition to this examination paper, you will need: Data Sheet Periodic
Surname ther Names Centre 2 Candidate GCE A level 1094/01 CHEMISTRY CH4 P.M. MNDAY, 14 January 2013 1¾ hours ADDITINAL MATERIALS In addition to this examination paper, you will need: Data Sheet Periodic
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *5604890866* CHEMISTRY 9701/22 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions May/June 2018 1 hour 15 minutes
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *5604890866* CHEMISTRY 9701/22 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions May/June 2018 1 hour 15 minutes
