Nov. 20, 1973 U. NEUMANN 3,773,902. PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF POTASSIUM CARBONATE HYDRATE Filed May 26, 1971
|
|
|
- Baldric Webb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nov., 1973 U. NEUMANN 3,773,902 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF POTASSIUM CARBONATE HYDRATE Filed May 26, 1971 S
2 United States Patent Office 3,773,902 Patented Nov., ,773,902 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF POTASSUM CARBONATE HYDRATE Ulrich Neumann, Rodenkirchen, Germany, assignor to Chemical Dr. A. Zieren, GmbH & Co. KG, Cologne Braunsfeld, Germany Filed May 26, 1971, Ser. No. 146,986 Claims priority, application Germany, May 26, 1970, P U.S. C nt. C. C01d 7/00 10 Claims ABSTRACT OF THE DISCLOSURE An economically feasible continuous process for the production of potassium carbonate by the carbonation of a potassium hydroxide solution with CO2 on a com mercial scale which is trouble-free and requires simple apparatus in which a stream of the potassium hydroxide solution is fed to a reaction zone where it is reacted with CO at C. and 1 torr-atmospheric pressure; sufficient water is evaporated from the solution in the reaction zone to precipitate K2CO3 1/2 H2O; a stream of the precipitated potassium carbonate and a portion of the solution is removed from the reaction zone as a slurry; the liquid and solid phases of the slurry are separated; and the separated liquid phase is recycled to the reaction zone, preferably after heating to a temperature above that of the reaction zone. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION This invention relates to a process for the preparation of potassium carbonate hydrate, more particularly by re acting an aqueous potassium hydroxide solution with a carbon dioxide-containing gas. It is known to produce potassium carbonate from elec trolytically obtained potassium hydroxide solution of ap proximately 50% strength by the reaction with waste gases containing carbon dioxide, such as, for example, flue gas or lime kiln gas, in absorption towers. The hy drate K2CO31.5H2O crystallizes during cooling from the hot concentrated solutions obtained by evaporation in a suitable evaporator. The salt separated by centrifuging or suction-filtering is dried at about 1' C., so that the hydrate with 1/2 molecules of water is obtained as the product. The mother liquor can be again worked up in a mixture with fresh solution (Ullmann, vol. 9 (1957), p. 235). This process, due to the separation of reaction, evaporation, and crystallization processes, has the disad vantages of a high heat energy consumption and consid erable initial investment costs, It is known from Austrian patent application A3191/ 68 to react sodium hydroxide solution with carbon di oxide to obtain soda ash. During this process, water is evaporated above 90 C. and sodium carbonate monohy drate is precipitated. This process is not suitable for the production of potassium carbonate hydrate, because si multaneous hydrate deposition and water vaporization according to the process as described therein is possible only at temperatures which are uneconomically high. A work by N. K. Kishinevskij in "Zhur. Priklad. Khim. (1957), pp , deals with the kinetics of CO2 absorption in potassium hydroxide solution un der laminar and turbulent flow agitation conditions. How ever, no potassium carbonate hydrate was precipitated in this process, and the reaction temperature was 57 C. at a maximum. It is an object of this invention to provide a process for the preparation of potassium carbonate hydrate from potassium hydroxide solution formed, for example, by potassium amalgam decomposition, with lower external heat energy requirements for the water vaporization than the known processes of the prior art. It is another object to provide such a novel method which requires the use of only few apparatus components. Other objects will be apparent to those skilled in the art to which this inven tion pertains. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION These objects are attained in accordance with this in vention by continuous process which comprises the steps of feeding a potassium hydroxide solution to a reaction stage; reacting the potassium hydroxide in the reaction stage with carbon dioxide at a temperature of between 80 and 135 C. and a pressure of between 1 torr mm. Hg) and atmospheric pressure; evaporating water from the reaction stage, thus precipitating potassium carbon ate hydrate from the solution in the reaction stage; re moving from the reaction stage as a slurry the thus-pre cipitated potassium carbonate hydrate separating the solid phase of the slurry from the liquid phase; and recycling the separated liquid phase to the reaction zone. The com bination of the reaction between potassium hydroxide solution and carbon dioxide, the water vaporization, and the precipitation of the potassium carbonate hydrate in a single stage, as effected by the present invention, makes possible the direct utilization of the thus-liberated heat of neutralization for vaporization of the water, which va porization is a prerequisite for the crystallization of the potassium carbonate hydrate. The evaporator and the crystallizer are eliminated, whereby the plant becomes less trouble-prone. The liberated heat of neutralization and crystallization is fully utilized for the evaporation of the water, since this heat is liberated directly in the re action mixture. By the use of subatmospheric pressure, the temperature at which the vaporization and simultane ously the hydrate deposition occur is lowered. This also lessens the heat energy requirements of the process and eliminates the necessity of cooling means to prevent over heating of the reaction solution. The thermal load on the materials is also reduced. The hydrate thus precipitated in the reaction mixture corresponds approximately to the formula K2COs' 1.5H2O. The thus-separated hydrate can be separated from the mother liquor by centrifuging or by filtration. The mother liquor, which is a solution con sisting of about 58-67% by weight of KaCO3, is recycled into the reaction vessel. The gas employed for the reaction can be, for exam ple, a CO2 rich gas consisting of more than 90% by vol ume of CO2, a lime kiln gas consisting of about 40-45% by volume of CO2, or a flue gas consisting of about 8 14% by volume of CO. In accordance with the preferred embodiment of this invention, the potassium hydroxide solution is reacted with the carbon dioxide at temperatures of between 80 and 1 C. and under pressures of between 1 and 700 torr, especially at temperatures of between 90 and 110 C. and under pressures of between 0 and 600 torr. These subatmospheric pressures can be maintained eco nomically by means of steam jet air ejectors. The separated mother liquor is preferably heated, prior to being recycled into the reactor, to a temperature above the reaction temperature. In this manner, there is sup plied to the reaction mixture the amount of heat which is required, above and beyond the heat liberated within the reaction mixture, to vaporize the water in the potassium hydroxide solution which is introduced into the reaction Zone. In a modification of this process, this external heat can also be introduced into the system at some other point, for example by preheating the potassium hydroxide solu tion or the CO2-containing gas or by directly heating the reaction mixture. In all of these cases, a minimum of ex ternal heat is required, since the heat of reaction and
3 3 crystallization is fully utilized for the water vaporization. In accordance with the preferred embodiment of the invention, the reaction mixture is stirred or otherwise agitated by turbulence. This results in an increase in the reaction rate, since the rate of diffusion of the CO2 into the solution increases, with the further result that there is a uniform temperature distribution and concentration distribution in the mixture. The potassium carbonate sesquihydrate obtained after separation from the mother liquor can be dehydrated to anhydrous KCO at temperatures of above 240 C. This step is preferably carried out in a steam-heated cal cining drum. The waste gases therefrom are preferably purified in a conventional manner to remove any en trained fine particles of potassium carbonate. The invention will be described below in greater detail with reference to the drawing, wherein a plant for con ducting the process of this invention is illustrated in a schematic view. As shown in the drawing, stirred reactor 1 is fed with a stream of potassium hydroxide solution from storage tank 2 and with a stream of CO-containing gas via con duit 3. A vacuum is produced in the reaction vessel 1 by steam jet air ejector 4 connected thereto. In reactor 1, the aqueous potassium hydroxide solution, obtained, for example, from an alkaline chloride electrolysis state connected upstream of this plant, is reacted with the car bon dioxide in the gas fed to the reactor, during which step potassium carbonate sesquihydrate is precipitated. At the same time, water is evaporated from the reaction mix ture and is removed by the vacuum produced by ejector 4. The reaction mixture with the precipitated potassium carbonate sesquihydrate flows, as a suspension, via conduit 6 into agitator-equipped vessel 5, the gas space of which is in communication with that of reactor 1 via line 7, and thus is likewise maintained under a vacuum. From vessel 5, the suspension is pumped, via conduit 8, into centrifuge 9, where the precipitated hydrate is sepa rated from the mother liquor. The moist hydrate obtained at 10 can be dried and optionally dehydrated in a subse quent drying stage. The mother liquor passes, via line 11, into container 12 containing steam heated heat exchange coils, is heated therein, and recycled via line 13 into reactor 1. In general, the amount of water in the incoming KOH solution should not exceed about 70% by weight of the total solution, and is preferably in the range of 60 to 40%" by weight. The carbonation zone, by virtue of tur bulence is usually kept at a uniform temperature within the C. operable range. Due to minor turbulence or laminar flow, temperature variations may exist in the reactor. In this case the average temperature should be at least 80 C. According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, more than 70% by weight of the water of the potassium hydroxide solution is evaporated. Where the potassium hydroxide solution contains not more than 50% by weight of water, the heat of neutralization and of pre cipitation evolved during the carbonation is nearly suf ficient to evaporate the above-mentioned portion of water. However, in a preferred embodiment, the mother liquor separated from the slurry which is removed from the re action Zone is heated to a temperature from about to 60 C. higher than the reaction temperature because the heats of neutralization and precipitation in the carbonat ing Zone are usually insufficient to evaporate enough of the water of the KOH solution to maintain the solution at the desired KCO concentration. This preheating step thus supplements the heats of neutralization and precipita tion to offset the heat demand for water evaporation and the heat loss with slurry removal. Generally, the lower the KOH concentration, the more external heating is nec essary to maintain the system in balance. Specific examples of this relationship are shown in Table I, 3,778, TABLE I Recycle mother Reactor liquor Pressure tempera- tempera (torr) ture, C. ture, C. KQE concentration, percent by weight: Because the separated mother liquor is recirculated to the carbonation reactor, the entire carbonation stage thus comprises a cyclic process in which most of the water is removed with the separated precipitated potassium car bonate. It is surprising that the water can be removed by evaporation under reduced pressure at high thermal efficiency and with relatively little loss of CO2 and high conversion of KOH to K2CO3. Without further elaboration, it is believed that one skilled in the art can, using the preceding description, utilize the present invention to its fullest extent. The fol lowing preferred specific embodiments are, therefore, to be construed as merely illustrative, and not limitative of the remainder of the disclosure in any way whatsoever. EXAMPLE 1. In the plant illustrated in the drawing, 1,000 kg./h. of 50% strength potassium hydroxide solution available at 50 C. from an alkaline chloride electrolysis stage, is re acted with 115 Nm.8/h. of approximately 98% CO2 gas at about 100 C. The reaction mixture is under a pressure of about 0 torr. 405 kg/h. of water evaporates, during which step 592 kg./h. of potassium carbonate sesquihy drate is precipitated. From the reactor, 6,772 kg./h. of suspension is with drawn and separated, by centrifuging, into 5,980 kg/h. of mother liquor and 792 kg/h. of moist potassium car bonate sesquihydrate. The moist hydrate, after drying and dehydration, yields 615 kg./h. of K2CO3. The mother liquor, obtained at a temperature of 90 C., is heated by indirect heat exchange with steam of 5 atmospheres to its boiling point (about 1 C.) and is recycled into the reactor. EXAMPLE 2 In the plant illustrated in the drawing, 440 kg./h. of 50% strength potassium hydroxide solution obtained at 85 C. from an alkaline chloride electrolysis, is reacted with 472 Nm.8/h. of a flue gas having a temperature of 180 C. and containing 9.3% by volume of CO and 18.0% by volume of H.O. The reaction mixture has a temperature of about 100 C. and is under atmospheric pressure. 775 Nm.8/h. of waste gas is discharged having 1.4% by volume of CO and 43.3% by volume of H.O. From the reaction vessel, 1,660 kg./h. of suspension is withdrawn. By centrifuging, 1,3 kg./h. of mother liquor and 340 kg./h. of moist potassium carbonate hydrate are produced. From the moist hydrate, kg/h. of KCO is obtained after drying and dehydration. The mother liquor, obtained at 90 C., is heated by means of steam of 5 atmospheres to 1 C. and recycled into the reactor. The preceding examples can be repeated with similar success by Substituting the generically or specifically de scribed reactants and/or operating conditions of this in vention for those used in the preceding examples. From the foregoing description, one skilled in the art can easily ascertain the essential characteristics of this in vention, and without departing from the spirit and scope thereof, can make various changes and modifications of the invention to adapt it to various usages and conditions.
4 What is claimed is: 5 1. A continuous single stage process for the prepara tion of crystalline potassium carbonate hydrate, com prising: (a) reacting an aqueous solution consisting essentially of 70% by weight potassium hydroxide with a gas containing carbon dioxide by bubbling said gas through said aqueous solution at a temperature of C. and at a pressure of between 1 mm. Hg and atmospheric pressure with sufficient evapora tion of water to precipitate potassium carbonate hydrate crystals; (b) removing a stream of precipitated potassium car bonate hydrate crystals and a portion of the mother liquor as a slurry from the reaction zone; (c) separating the precipitated potassium carbonate hydrate crystals from the mother liquor of said slurry; and (d) recycling the separated mother liquor back into the reaction zone. 2. A process according to claim 1, wherein the potas sium hydroxide solution is reacted with the carbon dioxide containing gas at a temperature of between 80 and 1 C. and a pressure of between 1 and 700 mm. Hg. 3. A process according to claim 1, wherein the potas sium hydroxide solution is reacted with carbon dioxide containing gas at a temperature of between 90 and 110 C. and a pressure of between 0 and 600 mm. Hg. 4. A process according to claim 2 wherein the mother liquor, prior to being recycled, is heated to a tempera ture from about to 60 C. above the temperature of the reaction solution in the reaction zone which maintains the latter at the selected reaction temperature and wherein 3,778, the reaction solution is agitated in a turbulent manner in the reaction zone. 5. A process according to claim 4 wherein the slurry is transferred to a second zone in liquid and gaseous com munication with the reaction zone prior to separation of the precipitated potassium carbonate therein. 6. A process according to claim 1 wherein the mother liquor, prior to being recycled, is heated to a temperature from about to 60 C. above the temperature of the reaction solution in the reaction zone which maintains the latter at the selected reaction temperature. 7. A process according to claim 1 wherein the reaction solution is agitated in a turbulent manner in the reaction ZOC. 8. A process according to claim 1 wherein more than 70% by weight of the water in the potassium hydroxide solution is evaporated in the reaction zone. 9. A process according to claim 8 wherein said aqueous potassium hydroxide solution contains not more than 50% by weight water. 10. A process according to claim 9 wherein the recycled mother liquor consists essentially of about 58-67% by weight of K2CO3. References Cited UNITED STATES PATENTS 2,135,605 11/1938 Stevenson ,2,477 8/1965 Loeffler et al ,4,946 6/1966 Hass et al ,644,089 2/1972 Minz et al OSCAR R. VERTIZ, Primary Examiner J. COOPER, Assistant Examiner
5 UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE CERTIFICATE OF CORRECTION Patent No. 3,773,902 pated November, 1973 Inventor(s) Ulrich. Neumann, et al. It is certified that error appears in the above-identified patent and that said Letters Patent are hereby corrected as shown below: IN THE HEADING, COLUMN l: The Assignee of Record should read -- CHEMIEBAU DR. A. ZIEREN, GmbH & Co. KG. Signed and sealed this 10th day of September (SEAL) Attest: McCOY M. GIBSON, JR. Attesting Officer C. MARSHALL DANN Commissioner of Patents drm PO-1050 (10-69) USCOMMedC 60376ap69 A U.S. GOWERNMENT PrintNG office: 1989 o ,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
: X''' gy? î. * March 21, 1967 L. H. COOK ETA 3,310, ß. Filled Sept. 9, 1963 PROCESS FOR COMBINED PRODUCTION OF AMMONIA AND UREA
 s March 21, 1967 L. H. COOK ETA 3,310,376 PROCESS FOR COMBINED PRODUCTION OF AMMONIA AND UREA OF) O CN r) Filled Sept. 9, 1963 8 O C) LAO O 3 : X''' 8 8 ß LUCIEN H. COOK VO MAVROVIC INVENTORS. gy?47.244
s March 21, 1967 L. H. COOK ETA 3,310,376 PROCESS FOR COMBINED PRODUCTION OF AMMONIA AND UREA OF) O CN r) Filled Sept. 9, 1963 8 O C) LAO O 3 : X''' 8 8 ß LUCIEN H. COOK VO MAVROVIC INVENTORS. gy?47.244
BY ye; v P. April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY 3,441,626. TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 INVENTOR. PRODUCT C. S.
 April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 PRODUCT INVENTOR. C. S. KELLEY BY ye; v P. A 77OAPAWAYS United States Patent Office Patented Apr. 29, 1969 1.
April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 PRODUCT INVENTOR. C. S. KELLEY BY ye; v P. A 77OAPAWAYS United States Patent Office Patented Apr. 29, 1969 1.
June 9, R. C. DATIN ETAL SYNTHESIS OF NITROSODIMETHYLAMINE Filed Jan. 7, ,136,821
 June 9, 1964 R. C. DATIN ETAL SYNTHESIS OF NITROSODIMETHYLAMINE Filed Jan. 7, 19 United States Patent Office Patented June 9, 1964 SYNTHESS OF NTROSO/IETHYLAMINE Richard C. Datin and George A. Eliott,
June 9, 1964 R. C. DATIN ETAL SYNTHESIS OF NITROSODIMETHYLAMINE Filed Jan. 7, 19 United States Patent Office Patented June 9, 1964 SYNTHESS OF NTROSO/IETHYLAMINE Richard C. Datin and George A. Eliott,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0286850 A1 Peterson et al. US 20140286850A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) METHOD OF MAKING SODIUM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0286850 A1 Peterson et al. US 20140286850A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) METHOD OF MAKING SODIUM
United States Patent (19) Sakowski et al.
 United States Patent (19) Sakowski et al. 54) PROCESS FOR MANUFACTURE OF CALCUM HYPOCHLORITE (75) Inventors: Walter J. Sakowski; John H. Shaffer; Larry G. Carty, all of Cleveland, Tenn. 73) Assignee: Olin
United States Patent (19) Sakowski et al. 54) PROCESS FOR MANUFACTURE OF CALCUM HYPOCHLORITE (75) Inventors: Walter J. Sakowski; John H. Shaffer; Larry G. Carty, all of Cleveland, Tenn. 73) Assignee: Olin
United States Patent (19) Gudmundsen et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gudmundsen et al. 54 RECOVERY OF ANHYDROUS HCL GAS BY EXTRACTIVE DISTILLATION WITH A HALDE SALT (75 Inventors: Sigmund Gudmundsen, Saetre I Hurum; Egil Ronaess, Porsgrunn; Sver
United States Patent (19) Gudmundsen et al. 54 RECOVERY OF ANHYDROUS HCL GAS BY EXTRACTIVE DISTILLATION WITH A HALDE SALT (75 Inventors: Sigmund Gudmundsen, Saetre I Hurum; Egil Ronaess, Porsgrunn; Sver
(30) Foreign Application Priority Data Jan. 21, 1975 Italy (5) Int. Cl... CO1C 1/ /239.3 P, A
 United States Patent (19) Donati et al. 4 PROCESS FOR THE NEUTRALIZATION OF ACID SOLUTIONS OF CAPROLACTAM 7 Inventors: Ivo Donati, Rieti; Werner Muench, Milan; Mario Fidecicchi, Torviscosa, all of Italy
United States Patent (19) Donati et al. 4 PROCESS FOR THE NEUTRALIZATION OF ACID SOLUTIONS OF CAPROLACTAM 7 Inventors: Ivo Donati, Rieti; Werner Muench, Milan; Mario Fidecicchi, Torviscosa, all of Italy
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B01D 9/00 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 505 243 A1 (43) Date of publication: 03.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/40 (51) Int Cl.: B01D 9/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 12162017.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 505 243 A1 (43) Date of publication: 03.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/40 (51) Int Cl.: B01D 9/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 12162017.3 (22) Date of filing:
United States Patent (19) (11) 4,390,512 Loehr et al. l (45) Jun. 28, 1983
 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,390,512 Loehr et al. l () Jun. 28, 1983 (54) PROCESS FOR PRODUCING CALCIUM 3,251,647 5/1966 Nicolaisen... 23/86 HYPOCHLORITE 3,572,989 3/1971 Tatara et al..... 23/86 3,767,775
United States Patent (19) (11) 4,390,512 Loehr et al. l () Jun. 28, 1983 (54) PROCESS FOR PRODUCING CALCIUM 3,251,647 5/1966 Nicolaisen... 23/86 HYPOCHLORITE 3,572,989 3/1971 Tatara et al..... 23/86 3,767,775
Sept. 5, 1972 HidEO FURUKAWA ET AL 3,689,37 SEPARATING CLOSE BOILING, TWO COMPONENT MIXTURE BY DISTILLING IN PRESENCE OF SELECTIVE THIRD COMPONENT
 Sept., 1972 HidEO FURUKAWA ET AL 3,689,37 SEPARATING CLOSE BOILING, TWO COMPONENT MIXTURE BY DISTILLING IN PRESENCE OF SELECTIVE THIRD COMPONENT Filed June 1, 1970 (OM/AO/WAM// C / 7WO COMAWA/W7 (AAA)
Sept., 1972 HidEO FURUKAWA ET AL 3,689,37 SEPARATING CLOSE BOILING, TWO COMPONENT MIXTURE BY DISTILLING IN PRESENCE OF SELECTIVE THIRD COMPONENT Filed June 1, 1970 (OM/AO/WAM// C / 7WO COMAWA/W7 (AAA)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Leonard 54 PREPARATION OF FORMIC ACID BY HYDROLYSIS OF METHYL FORMATE (76) Inventor: Jackson D. Leonard, 7002 Blvd. East, Guttenberg, N.J. 07093 (21) Appl. No. 912,189 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Leonard 54 PREPARATION OF FORMIC ACID BY HYDROLYSIS OF METHYL FORMATE (76) Inventor: Jackson D. Leonard, 7002 Blvd. East, Guttenberg, N.J. 07093 (21) Appl. No. 912,189 22 Filed:
(51) Int. Cl... D06F tank. The liquid level detector includes a first resistance
 US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Dodge 54). PROCESS AND APPARATUS FOR PRODUCING CYANURCACD 75) Inventor: William B. Dodge, Montgomery Township, Somerset County, N.J. 73 Assignee: Olin Corporation, Cheshire, Conn.
United States Patent (19) Dodge 54). PROCESS AND APPARATUS FOR PRODUCING CYANURCACD 75) Inventor: William B. Dodge, Montgomery Township, Somerset County, N.J. 73 Assignee: Olin Corporation, Cheshire, Conn.
Lecture 25: Manufacture of Maleic Anhydride and DDT
 Lecture 25: Manufacture of Maleic Anhydride and DDT 25.1 Introduction - In this last lecture for the petrochemicals module, we demonstrate the process technology for Maleic anhydride and DDT. - Maleic
Lecture 25: Manufacture of Maleic Anhydride and DDT 25.1 Introduction - In this last lecture for the petrochemicals module, we demonstrate the process technology for Maleic anhydride and DDT. - Maleic
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
July 11, ,330,864 K. P. BELLINGER METHOD FOR MAKING UREA NITRATE. Filed April 29, 1965 ;---- INVENTOR. KENNETH. P. BELLINGER ATTORNEY
 July 11, 1967 K. P. BELLINGER METHOD FOR MAKING UREA NITRATE Filed April 29, 196 ;---- \!--------- ^ A----------^--------------- INVENTOR. KENNETH. P. BELLINGER ATTORNEY United States Patent Office Patented
July 11, 1967 K. P. BELLINGER METHOD FOR MAKING UREA NITRATE Filed April 29, 196 ;---- \!--------- ^ A----------^--------------- INVENTOR. KENNETH. P. BELLINGER ATTORNEY United States Patent Office Patented
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001 0042523A1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0042523 A1 Kesala (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FEEDING GAS PHASE REACTANT INTO A REACTION
(19) United States US 2001 0042523A1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0042523 A1 Kesala (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FEEDING GAS PHASE REACTANT INTO A REACTION
United States Patent (19) Mix
 United States Patent (19) Mix 54 (75) (73) 21 22) (63) 51 (52) (58 56) AZEOTROPIC DEHYDRATION DISTILLATION PROCESS Inventor: Assignee: Thomas W. Mix, Wellesley, Mass. Merix Corporation, Wellesley, Mass.
United States Patent (19) Mix 54 (75) (73) 21 22) (63) 51 (52) (58 56) AZEOTROPIC DEHYDRATION DISTILLATION PROCESS Inventor: Assignee: Thomas W. Mix, Wellesley, Mass. Merix Corporation, Wellesley, Mass.
M7Mae /2 roy t?a Hav. /nventors Ace-air /fo/ee. July 6, 1971 E. MOLLER ETAL 3,591,490. Filed Nov. 14, 1969
 July 6, 1971 E. MLLER ETAL 3,91,490 PRCESS F SEPARATING PURE ARMATIC HYDRCARBNS FRM HYDRCARBN MIXTURES Filed Nov. 14, 1969 /nventors Ace-air /fo/ee M7Mae /2 roy t?a Hav United States Patent ffice 3,91,490
July 6, 1971 E. MLLER ETAL 3,91,490 PRCESS F SEPARATING PURE ARMATIC HYDRCARBNS FRM HYDRCARBN MIXTURES Filed Nov. 14, 1969 /nventors Ace-air /fo/ee M7Mae /2 roy t?a Hav United States Patent ffice 3,91,490
United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al.
 United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al. 11 3,983,170 (45) Sept. 28, 1976 (54) (75) 73 22 21 52) 51 58) PROCESS FOR THE PURIFICATION OF MALIC ACID Inventors: Shozo Sumikawa, Hofu, Rikichi Maida; Yuriaki
United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al. 11 3,983,170 (45) Sept. 28, 1976 (54) (75) 73 22 21 52) 51 58) PROCESS FOR THE PURIFICATION OF MALIC ACID Inventors: Shozo Sumikawa, Hofu, Rikichi Maida; Yuriaki
United States Patent (19) Needham et al.
 United States Patent (19) Needham et al. 54 PREPARATION OF AZINES BY A CASCADE SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Brian John Needham, Newton; Michael Arthur Smith, Harton, both of England 73) Assignee: Fisons Limited,
United States Patent (19) Needham et al. 54 PREPARATION OF AZINES BY A CASCADE SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Brian John Needham, Newton; Michael Arthur Smith, Harton, both of England 73) Assignee: Fisons Limited,
Filed: Jun. 1, 1981 Int. Cl... CO1B 11/06 U.S. C /474. 2,441,337 5/1948 Sprauer /474 2,469,901 5/1949 Sprauer...
 United States Patent (19) Welch et al. 54) 75) (73) (21) 22 (51) (52) 58 56 PROCESS FOR PRODUCING CALCIUM HYPOCHLORITE Inventors: Cletus N. Welch, Clinton; Clifford E. Loehr, Norton; Roger A. Crawford,
United States Patent (19) Welch et al. 54) 75) (73) (21) 22 (51) (52) 58 56 PROCESS FOR PRODUCING CALCIUM HYPOCHLORITE Inventors: Cletus N. Welch, Clinton; Clifford E. Loehr, Norton; Roger A. Crawford,
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/19
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 40 336 A1 (43) Date of publication: 09.0.2012 Bulletin 2012/19 (21) Application number: 19081.8 (1) Int Cl.: C07C 41/6 (2006.01) C07C 43/30 (2006.01) C07C
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 40 336 A1 (43) Date of publication: 09.0.2012 Bulletin 2012/19 (21) Application number: 19081.8 (1) Int Cl.: C07C 41/6 (2006.01) C07C 43/30 (2006.01) C07C
Espacenet Bibliographic data: DE (A1)
 Espacenet Bibliographic data: DE102012100315 (A1) 2013-07-18 REAGENTLESS, ENERGETIC METHOD AND CORRESPONDING SYSTEM FOR PRODUCING HUMIN-CONTAINING SUSPENSIONS Inventor(s): WERNER UWE [DE]; OSTROVSKIJ MIHAIL
Espacenet Bibliographic data: DE102012100315 (A1) 2013-07-18 REAGENTLESS, ENERGETIC METHOD AND CORRESPONDING SYSTEM FOR PRODUCING HUMIN-CONTAINING SUSPENSIONS Inventor(s): WERNER UWE [DE]; OSTROVSKIJ MIHAIL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,229,054 B1. Dai et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, THEREFOR 3,644,534 2/1972 Reabe.
 USOO6229054B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,229,054 B1 Dai et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, 2001 (54) DERIVATIVE OF CARDANOLAND USES 3,283,030 11/1966 Bean et al.... 568/630 THEREFOR
USOO6229054B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,229,054 B1 Dai et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, 2001 (54) DERIVATIVE OF CARDANOLAND USES 3,283,030 11/1966 Bean et al.... 568/630 THEREFOR
Ways to Improve the Energy Efficiency of AN Solution Plants
 Ways to Improve the Energy Efficiency of AN Solution Plants by Axel Erben Uhde GmbH Dortmund, Germany Prepared for Presentation at NITROGEN 2009 International Conference Rome, Italy 22-25 February 2009
Ways to Improve the Energy Efficiency of AN Solution Plants by Axel Erben Uhde GmbH Dortmund, Germany Prepared for Presentation at NITROGEN 2009 International Conference Rome, Italy 22-25 February 2009
2 5 t/ 2 weams suicidity itains
 F. HABER & R. LE ROSSIGNOl. PRODUCTION OF AMMONA. APPCATION FLED AUG, 13, 1909. Patented 0ct, 31, 1916. SN 3. 2. s: St. SEAL t -> Ei. Aa 44 / A. g; Ag/fader 2 t/ 2 weams suicidity itains UNITED STATES
F. HABER & R. LE ROSSIGNOl. PRODUCTION OF AMMONA. APPCATION FLED AUG, 13, 1909. Patented 0ct, 31, 1916. SN 3. 2. s: St. SEAL t -> Ei. Aa 44 / A. g; Ag/fader 2 t/ 2 weams suicidity itains UNITED STATES
'" is "s" 165,443 3/1965 U.S.S.R. 260/531
 United States Patent 3,678,107 Yonemitsu et al. () July 18, 1972 54 PRCESS FR THE PRDUCTIN F 2,867,7 1/1959 Sehvitz,... 2/531 R x XALCACD FREIGN PATENTS RAPPLICATINS 72 tors: Eichi Yonemitsu, Kashiwa;
United States Patent 3,678,107 Yonemitsu et al. () July 18, 1972 54 PRCESS FR THE PRDUCTIN F 2,867,7 1/1959 Sehvitz,... 2/531 R x XALCACD FREIGN PATENTS RAPPLICATINS 72 tors: Eichi Yonemitsu, Kashiwa;
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Muders et al. 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF 1-AMINO-4-BROMOANTHRAQUINONE-2- SULPHONCACD 75 Inventors: Rolf Muders, Cologne; Heinrich Leister; Helmut Dittmer, both of Leverkusen;
United States Patent (19) Muders et al. 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF 1-AMINO-4-BROMOANTHRAQUINONE-2- SULPHONCACD 75 Inventors: Rolf Muders, Cologne; Heinrich Leister; Helmut Dittmer, both of Leverkusen;
Mathis. 58) Field of Search /603 56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 2,826,610 3/1958 Morris et al /603
 United States Patent (19) Correia et al. US00540 1876A 11 Patent Number: Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 1995 (54 SYNTHESIS F CHLRACETIC ACIDS 75 Inventors: Yves Correia, Chateau Arnoux; Daniel Pellegrin, Grenoble,
United States Patent (19) Correia et al. US00540 1876A 11 Patent Number: Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 1995 (54 SYNTHESIS F CHLRACETIC ACIDS 75 Inventors: Yves Correia, Chateau Arnoux; Daniel Pellegrin, Grenoble,
Structure of the chemical industry
 CEE-Lectures on Industrial Chemistry Lecture 1. Crystallization as an example of an industrial process (ex. of Ind. Inorg. Chemistry) Fundamentals (solubility (thermodynamics), kinetics, principle) Process
CEE-Lectures on Industrial Chemistry Lecture 1. Crystallization as an example of an industrial process (ex. of Ind. Inorg. Chemistry) Fundamentals (solubility (thermodynamics), kinetics, principle) Process
CHLORINE RECOVERY FROM HYDROGEN CHLORIDE
 CHLORINE RECOVERY FROM HYDROGEN CHLORIDE The Project A plant is to be designed for the production of 10,000 metric tons per year of chlorine by the catalytic oxidation of HCl gas. Materials Available 1.
CHLORINE RECOVERY FROM HYDROGEN CHLORIDE The Project A plant is to be designed for the production of 10,000 metric tons per year of chlorine by the catalytic oxidation of HCl gas. Materials Available 1.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,059 B1
 USOO6337059B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Schubert et al. () Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2002 (54) ABSORBENT COMPOSITIONS FOR THE 4997,630 A 3/1991 Wagner et al... 423/228 REMOVAL OF ACID GASES
USOO6337059B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Schubert et al. () Date of Patent: Jan. 8, 2002 (54) ABSORBENT COMPOSITIONS FOR THE 4997,630 A 3/1991 Wagner et al... 423/228 REMOVAL OF ACID GASES
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1
 US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
"All-4-4 / daysza///zer. Oct. 13, G. S. SiM PSON 2,057,119. Mo/her A/zoor. Mozaera/zoo/ 6eorye S 5/7 as or. Filed Aug. 9,
 Oct. 13, 1936. G. S. SiM PSON 2,07,119 /0 26 METHOD OF PRODUCING OXALIC ACID Filed Aug. 9, 1933 8. Mo/her A/zoor A07/7er4/avor so/v7/6/7 A/xed acal 24/ /6 /feaction Jan. A daysza///zer 3/ /2 Mozaera/zoo/
Oct. 13, 1936. G. S. SiM PSON 2,07,119 /0 26 METHOD OF PRODUCING OXALIC ACID Filed Aug. 9, 1933 8. Mo/her A/zoor A07/7er4/avor so/v7/6/7 A/xed acal 24/ /6 /feaction Jan. A daysza///zer 3/ /2 Mozaera/zoo/
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taniguchi et al. (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING FERULIC ACD 75 Inventors: Hisaji Taniguchi; Eisaku Nomura; Takuo Tsuno; Seiko Minami, all of Wakayama; Koji Kato, Hashimoto; Chieko
United States Patent (19) Taniguchi et al. (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING FERULIC ACD 75 Inventors: Hisaji Taniguchi; Eisaku Nomura; Takuo Tsuno; Seiko Minami, all of Wakayama; Koji Kato, Hashimoto; Chieko
He'? United States Patent (19) Foer. 11) Patent Number: 4,595,469 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 17, 1986 NOOH /6. PRODUCT NaCl + H2O FEED (54)
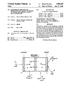 United States Patent (19) Foer 11) Patent Number: 4,595,469 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 17, 1986 (54) I75 (73) 21 22 63 (51) (52) 58 ELECTROLYTIC PROCESS FOR PRODUCTION OF GASEOUS HYDROGEN CHLORIDE AND AOUEOUS
United States Patent (19) Foer 11) Patent Number: 4,595,469 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 17, 1986 (54) I75 (73) 21 22 63 (51) (52) 58 ELECTROLYTIC PROCESS FOR PRODUCTION OF GASEOUS HYDROGEN CHLORIDE AND AOUEOUS
United States Patent (113,554,265
 United States Patent (113,554,265 72) 21 22) 45) 73 (54) (52) 51 50 Inventor Gonzalo D. Milian 56) References Cited Hasbrouck, N.J. UNITED STATES PATENTS Appl. No. 825.59 *2,193,336 3/1940 Lecher... 260/621
United States Patent (113,554,265 72) 21 22) 45) 73 (54) (52) 51 50 Inventor Gonzalo D. Milian 56) References Cited Hasbrouck, N.J. UNITED STATES PATENTS Appl. No. 825.59 *2,193,336 3/1940 Lecher... 260/621
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Scremin et al.
 United States Patent (19) Scremin et al. 54) DISTILLATION IN RASCHIG-PHENOL PROCESS 75) inventors: Eric Hermann Scremin, Niagara Falls, N.Y.; Jay Peter Eggert, Bellefonte, Ky. 73 Assignee: Hooker Chemicals
United States Patent (19) Scremin et al. 54) DISTILLATION IN RASCHIG-PHENOL PROCESS 75) inventors: Eric Hermann Scremin, Niagara Falls, N.Y.; Jay Peter Eggert, Bellefonte, Ky. 73 Assignee: Hooker Chemicals
United States Patent (19) Lin et al.
 United States Patent (19) Lin et al. (54) (75) (73) (21) 22) 51 (52) 58) (56) PROCESS FOR PRODUCING SS-ETHYLENEDIAMENE-N,N'-DISUCCINIC ACID Inventors: Ronny W. Lin, Baton Rouge; Eldon E. Atkinson, Jr.,
United States Patent (19) Lin et al. (54) (75) (73) (21) 22) 51 (52) 58) (56) PROCESS FOR PRODUCING SS-ETHYLENEDIAMENE-N,N'-DISUCCINIC ACID Inventors: Ronny W. Lin, Baton Rouge; Eldon E. Atkinson, Jr.,
Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte 12-21-1993 Clovis Linkous University of Central Florida
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte 12-21-1993 Clovis Linkous University of Central Florida
(51) Int. Cl."... C07C 209/00 The invention provides a novel process for producing a
 USOO5977412A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,977,412 Bremmer et al. () Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1999 54 PROCESS FOR PREPARING 3,5-5,510,533 4/1996 Kobayashi et al.. DIFLUOROANILINE FOREIGN
USOO5977412A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,977,412 Bremmer et al. () Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1999 54 PROCESS FOR PREPARING 3,5-5,510,533 4/1996 Kobayashi et al.. DIFLUOROANILINE FOREIGN
(51) Int Cl.: C09C 1/02 ( ) D21H 17/67 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z874 A_T (11) EP 3 08 742 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26..16 Bulletin 16/43 (1) Int Cl.: C09C 1/02 (06.01) D21H 17/67 (06.01) (21) Application number: 16434.9
(19) TEPZZ Z874 A_T (11) EP 3 08 742 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26..16 Bulletin 16/43 (1) Int Cl.: C09C 1/02 (06.01) D21H 17/67 (06.01) (21) Application number: 16434.9
United States Patent Office
 United States Patent Office Patented May 5, 1964 solid ALKALI. Ioff EcoMPOSETIONS AND PROCESS FOR PRODUCING THE SAME Abraham Sidney Behrman, Chicago, E., assignor to Chilean Nitrate Sales Corporation,
United States Patent Office Patented May 5, 1964 solid ALKALI. Ioff EcoMPOSETIONS AND PROCESS FOR PRODUCING THE SAME Abraham Sidney Behrman, Chicago, E., assignor to Chilean Nitrate Sales Corporation,
United States Patent (19 Ramachandran et al.
 United States Patent (19 Ramachandran et al. 54 75) 73) 21 22) (63) 51 52) 58) (56) PROCESS FOR THE PRODUCTION OF ETHANOLAND SOPROPANOL Inventors: Ramakrishnan Ramachandran, Allendale, Loc H. Dao, Bound
United States Patent (19 Ramachandran et al. 54 75) 73) 21 22) (63) 51 52) 58) (56) PROCESS FOR THE PRODUCTION OF ETHANOLAND SOPROPANOL Inventors: Ramakrishnan Ramachandran, Allendale, Loc H. Dao, Bound
FDE 211 Material & Energy Balances. Instructor: Dr. Ilgin Paker Yikici Fall 2015
 FDE 211 Material & Energy Balances Instructor: Dr. Ilgin Paker Yikici Fall 2015 Agenda Process classification General mass balance equation Basic functions of Processes Process Flow Diagram Degree of Freedom
FDE 211 Material & Energy Balances Instructor: Dr. Ilgin Paker Yikici Fall 2015 Agenda Process classification General mass balance equation Basic functions of Processes Process Flow Diagram Degree of Freedom
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4906,789 Grzywa et al. 45 Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 1990
 United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4906,789 Grzywa et al. Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 1990 54 METHODS-FORBISPHENOLA 56 References Cited PRODUCTION U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS Marai 3,049,569 8/1962 Apel
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4906,789 Grzywa et al. Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 1990 54 METHODS-FORBISPHENOLA 56 References Cited PRODUCTION U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS Marai 3,049,569 8/1962 Apel
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E.
 MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - I-SET -A 008 Sulphuric acid, Ammonia, Analytical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry HCl, Nitric acid, Metallurgy Chemistry SCIENCE
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - I-SET -A 008 Sulphuric acid, Ammonia, Analytical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry HCl, Nitric acid, Metallurgy Chemistry SCIENCE
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
Working with Hazardous Chemicals
 A Publication of Reliable Methods for the Preparation of Organic Compounds Working with Hazardous Chemicals The procedures in Organic Syntheses are intended for use only by persons with proper training
A Publication of Reliable Methods for the Preparation of Organic Compounds Working with Hazardous Chemicals The procedures in Organic Syntheses are intended for use only by persons with proper training
MSWI Flue Gas Two-Stage Dry Treatment: Modeling and Simulation
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 26, 2012 Guest Editors: Valerio Cozzani, Eddy De Rademaeker Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-17-4; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 26, 2012 Guest Editors: Valerio Cozzani, Eddy De Rademaeker Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-17-4; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
INDUSTRIAL EXPERIENCE WITH HYBRID DISTILLATION PERVAPORATION OR VAPOR PERMEATION APPLICATIONS
 INDUSTRIAL EXPERIENCE WITH HYBRID DISTILLATION PERVAPORATION OR VAPOR PERMEATION APPLICATIONS Mario Roza, Eva Maus Sulzer Chemtech AG, Winterthur, Switzerland; E-mails: mario.roza@sulzer.com, eva.maus@sulzer.com
INDUSTRIAL EXPERIENCE WITH HYBRID DISTILLATION PERVAPORATION OR VAPOR PERMEATION APPLICATIONS Mario Roza, Eva Maus Sulzer Chemtech AG, Winterthur, Switzerland; E-mails: mario.roza@sulzer.com, eva.maus@sulzer.com
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
SSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSS 22. 8a 1. United States Patent (19) Maru et al. 11 4,365,007 45) Dec. 21, 1982
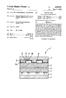 United States Patent (19) Maru et al. (54) FUEL CELL WITH INTERNAL REFORMING (75) Inventors: Hansraj C. Maru, Brookfield Center; Pinakin S. Patel, Danbury, both of Conn. 73 Assignee: Energy Research Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Maru et al. (54) FUEL CELL WITH INTERNAL REFORMING (75) Inventors: Hansraj C. Maru, Brookfield Center; Pinakin S. Patel, Danbury, both of Conn. 73 Assignee: Energy Research Corporation,
(10) Patent No.: US 7820,053 B2
 US007820053B2 (12) United States Patent Cort (54) (76) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) MAGNETIC SEPARATION AND SEEDING TO IMPROVE BALLASTED CLARIFICATION OF WATER Inventor: Notice: Steven L.
US007820053B2 (12) United States Patent Cort (54) (76) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) MAGNETIC SEPARATION AND SEEDING TO IMPROVE BALLASTED CLARIFICATION OF WATER Inventor: Notice: Steven L.
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2004/22
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP0014222A1* (11) EP 1 422 2 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.0.04 Bulletin 04/22 (1) Int
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP0014222A1* (11) EP 1 422 2 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.0.04 Bulletin 04/22 (1) Int
IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date...
 IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date... 1 Winston Churchill, a British Prime Minister, had his false teeth electroplated with gold. The teeth were coated with a thin layer of carbon and were then placed
IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date... 1 Winston Churchill, a British Prime Minister, had his false teeth electroplated with gold. The teeth were coated with a thin layer of carbon and were then placed
United States Patent (19) Amiet
 United States Patent (19) Amiet 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,879,407 Nov. 7, 1989 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF ETHYL TRFLUOROACETATE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Louis Amiet, Lyons, France
United States Patent (19) Amiet 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,879,407 Nov. 7, 1989 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF ETHYL TRFLUOROACETATE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Louis Amiet, Lyons, France
Which row correctly describes the type of reaction and the energy of the reactants and products? energy of the reactants and products
 1 The energy level diagram for the reaction between sodium hydrogen carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid is shown. sodium chloride + water + carbon dioxide energy sodium hydrogen carbonate + dilute hydrochloric
1 The energy level diagram for the reaction between sodium hydrogen carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid is shown. sodium chloride + water + carbon dioxide energy sodium hydrogen carbonate + dilute hydrochloric
Process Classification
 Process Classification Before writing a material balance (MB) you must first identify the type of process in question. Batch no material (mass) is transferred into or out of the system over the time period
Process Classification Before writing a material balance (MB) you must first identify the type of process in question. Batch no material (mass) is transferred into or out of the system over the time period
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,693,586 Nicolau et al. 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 1997
 III USOO56986A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Nicolau et al. Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 1997 54. PALLADIUM-GOLD CATALYST FOR WINYL 4,087,622 5/1978 Nakamura et al....... 560/2 ACETATE PRODUCTION
III USOO56986A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Nicolau et al. Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 1997 54. PALLADIUM-GOLD CATALYST FOR WINYL 4,087,622 5/1978 Nakamura et al....... 560/2 ACETATE PRODUCTION
Unit OperatiOn. Table 1: List of some unit operations
 Unit OperatiOn What is chemical engineering? Chemical Engineering is a group of industrial processes in which row materials are changed or separated into useful products What are "Unit Operations"? Every
Unit OperatiOn What is chemical engineering? Chemical Engineering is a group of industrial processes in which row materials are changed or separated into useful products What are "Unit Operations"? Every
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent NO.: US 6,371,384 ~1 Garcia (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16,2002
 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent NO.: US 6,371,384 ~1 Garcia (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16,2002 (54) AQUEOUS FOAM GENERATING SYSTEM 4,802,630 A * 211989 Kromrey... 2391428 AND METHOD FOR GENERATING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent NO.: US 6,371,384 ~1 Garcia (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16,2002 (54) AQUEOUS FOAM GENERATING SYSTEM 4,802,630 A * 211989 Kromrey... 2391428 AND METHOD FOR GENERATING
Method of modifying weather
 Page 1 of 8 Method of modifying weather Abstract ( 6 of 42 ) United States Patent 6,315,213 Cordani November 13, 2001 A method for artificially modifying the weather by seeding rain clouds of a storm with
Page 1 of 8 Method of modifying weather Abstract ( 6 of 42 ) United States Patent 6,315,213 Cordani November 13, 2001 A method for artificially modifying the weather by seeding rain clouds of a storm with
United States Patent (19) 11) 3,970,625
 United States Patent (19) 11) 3,970,6 Moore et al. () July, 1976 4 PRODUCTION OF UREA-FORMALDEHYDE 6 References Cited CONCENTRATES UNITED STATES PATENTS (7) Inventors: William Percy Moore, Hopewell; 2,,027
United States Patent (19) 11) 3,970,6 Moore et al. () July, 1976 4 PRODUCTION OF UREA-FORMALDEHYDE 6 References Cited CONCENTRATES UNITED STATES PATENTS (7) Inventors: William Percy Moore, Hopewell; 2,,027
EXPERIMENT #4 Separation of a Three-Component Mixture
 OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #4 Separation of a Three-Component Mixture Define chemical and physical properties, mixture, solubility, filtration, sublimation, and percent Separate a mixture of sodium chloride
OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #4 Separation of a Three-Component Mixture Define chemical and physical properties, mixture, solubility, filtration, sublimation, and percent Separate a mixture of sodium chloride
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
Process Design Decisions and Project Economics Prof. Dr. V. S. Moholkar Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Process Design Decisions and Project Economics Prof. Dr. V. S. Moholkar Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 2 Flowsheet Synthesis (Conceptual Design of
Process Design Decisions and Project Economics Prof. Dr. V. S. Moholkar Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 2 Flowsheet Synthesis (Conceptual Design of
2. Review on Material Balances
 2. Review on Material Balances Objectives After completing this chapter, students should be able to recall the principle of the conservation of mass recall the principle of the stoichiometry of chemical
2. Review on Material Balances Objectives After completing this chapter, students should be able to recall the principle of the conservation of mass recall the principle of the stoichiometry of chemical
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 200402369A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/023.6009 A1 Mafoti et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LW DENSITY ADHESIVES AND SEALANTS Publication Classification
US 200402369A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/023.6009 A1 Mafoti et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LW DENSITY ADHESIVES AND SEALANTS Publication Classification
5.4 Chemical changes Reactivity of metals Metal oxides The reactivity series. Key opportunities for skills development
 5.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
5.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
Methods of purification
 Methods of purification Question Paper 1 Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620/0971) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic Experimental techniques Sub-Topic Methods of purification ooklet
Methods of purification Question Paper 1 Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620/0971) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic Experimental techniques Sub-Topic Methods of purification ooklet
CHLORINE PROCESS ECONOMICS PROGRAM. Report No. 61A. Supplement A. by YEN CHEN YEN. May A private report by the STANFORD RESEARCH INSTITUTE
 Report No. 61A CHLORINE Supplement A by YEN CHEN YEN May 1074 A private report by the PROCESS ECONOMICS PROGRAM STANFORD RESEARCH INSTITUTE I I MENLO PARK, CALIFORNIA CONTENTS 1 2 3 INTRODUCTION... 1 SUMMARY...
Report No. 61A CHLORINE Supplement A by YEN CHEN YEN May 1074 A private report by the PROCESS ECONOMICS PROGRAM STANFORD RESEARCH INSTITUTE I I MENLO PARK, CALIFORNIA CONTENTS 1 2 3 INTRODUCTION... 1 SUMMARY...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 200700.9861 OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0098610 A1 Ingram et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF RETARDING QUICKLIME Publication Classification FOR
US 200700.9861 OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0098610 A1 Ingram et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF RETARDING QUICKLIME Publication Classification FOR
CHEMISTRY PAPER 1999
 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1999 (One and a half hours) Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will NOT be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent
CHEMISTRY PAPER 1999 (One and a half hours) Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will NOT be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent
: Y. ti- sk 22N. Sir S. United States Patent (19) Uhri 4,687,061. Aug. 18, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4 g
 i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
Review Topic 8: Phases of Matter and Mixtures
 Name: Score: 24 / 24 points (100%) Review Topic 8: Phases of Matter and Mixtures Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. C 1. Soda water is a solution
Name: Score: 24 / 24 points (100%) Review Topic 8: Phases of Matter and Mixtures Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. C 1. Soda water is a solution
IMADUDDIN SCHOOL Second Term Examination 2017
 Index Register Class number number Name IMADUDDIN SCHOOL Second Term Examination 2017 GRADE 9 CHEMISTRY 5070/02 Paper 2 Theory Nov 2017 TIME 1 hour 30 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Write your name,
Index Register Class number number Name IMADUDDIN SCHOOL Second Term Examination 2017 GRADE 9 CHEMISTRY 5070/02 Paper 2 Theory Nov 2017 TIME 1 hour 30 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Write your name,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2. Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007
 USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
United States Patent (19) Micinski
 United States Patent (19) Micinski (54) PREPARATION OF ALKYL TRFLUOROACETOACETATE 75) Inventor: Edward Micinski, Maryland Heights, Mo. 73 Assignee: Monsanto Company, St. Louis, Mo. (21) Appl. No.: 403,754
United States Patent (19) Micinski (54) PREPARATION OF ALKYL TRFLUOROACETOACETATE 75) Inventor: Edward Micinski, Maryland Heights, Mo. 73 Assignee: Monsanto Company, St. Louis, Mo. (21) Appl. No.: 403,754
1. (25 points) C 6 H O 2 6CO 2 + 7H 2 O C 6 H O 2 6CO + 7H 2 O
 MEEBAL Exam 2 November 2013 Show all work in your blue book. Points will be deducted if steps leading to answers are not shown. No work outside blue books (such as writing on the flow sheets) will be considered.
MEEBAL Exam 2 November 2013 Show all work in your blue book. Points will be deducted if steps leading to answers are not shown. No work outside blue books (such as writing on the flow sheets) will be considered.
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/06
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 281 809 A1 (43) Date of publication: 09.02.2011 Bulletin 2011/06 (21) Application number: 09178846.3 (1) Int Cl.: C07C 231/24 (2006.01) C07C 237/46 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 281 809 A1 (43) Date of publication: 09.02.2011 Bulletin 2011/06 (21) Application number: 09178846.3 (1) Int Cl.: C07C 231/24 (2006.01) C07C 237/46 (2006.01)
? Ns 54 F2 44. al-f2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Sartori et al. 54) 75 73) 21 22) (51) (52) 58 56) PROCESS FOR REMOVING ACD GASES USING A BASIC SALT ACTIVATED WITH A NONSTERICALLY HINDERED DAMINE Inventors: Guido Sartori, Linden;
United States Patent (19) Sartori et al. 54) 75 73) 21 22) (51) (52) 58 56) PROCESS FOR REMOVING ACD GASES USING A BASIC SALT ACTIVATED WITH A NONSTERICALLY HINDERED DAMINE Inventors: Guido Sartori, Linden;
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND HUMAN RESOURCES, TERTIARY EDUCATION AND SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH MAURITIUS EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE. CHEMISTRY OCTOBER hour
 MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND HUMAN RESOURCES, TERTIARY EDUCATION AND SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH MAURITIUS EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE NATIONAL ASSESSMENT AT FORM III NAME SCHOOL NAME CLASS/SECTION CHEMISTRY OCTOBER 2016
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION AND HUMAN RESOURCES, TERTIARY EDUCATION AND SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH MAURITIUS EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE NATIONAL ASSESSMENT AT FORM III NAME SCHOOL NAME CLASS/SECTION CHEMISTRY OCTOBER 2016
The Solution Process. Section 2. Increasing the Surface Area of the Solute
 The Solution Process Key Terms solution equilibrium solubility Henry s Law saturated solution hydration effervescence unsaturated solution immiscible solvated supersaturated solution miscible enthalpy
The Solution Process Key Terms solution equilibrium solubility Henry s Law saturated solution hydration effervescence unsaturated solution immiscible solvated supersaturated solution miscible enthalpy
Questions Maximum Score Candidate s Score
 Name:...Index Number Date... Candidate s Signature:... 233/1 CHEMISTRY Theory PAPER 1 July 2013 2 Hours STAREHE GIRLS CENTRE FORM 4 MOCK EXAMS, JULY 2013 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 2 Hours Instructions to candidates:
Name:...Index Number Date... Candidate s Signature:... 233/1 CHEMISTRY Theory PAPER 1 July 2013 2 Hours STAREHE GIRLS CENTRE FORM 4 MOCK EXAMS, JULY 2013 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 2 Hours Instructions to candidates:
Systems Engineering Spring Group Project #1: Process Flowsheeting Calculations for Acetic Anhydride Plant. Date: 2/25/00 Due: 3/3/00
 10.551 Systems Engineering Spring 2000 Group Project #1: Process Flowsheeting Calculations for Acetic Anhydride Plant Date: 2/25/00 Due: 3/3/00 c Paul I. Barton, 14th February 2000 At our Nowhere City
10.551 Systems Engineering Spring 2000 Group Project #1: Process Flowsheeting Calculations for Acetic Anhydride Plant Date: 2/25/00 Due: 3/3/00 c Paul I. Barton, 14th February 2000 At our Nowhere City
Universal Indicator turns green. Which method is used to obtain pure solid X from an aqueous solution? A. mixture
 1 The results of some tests on a colourless liquid X are shown. oiling point = 102 Universal Indicator turns green What is X? ethanol hydrochloric acid pure water sodium chloride (salt) solution 2 blue
1 The results of some tests on a colourless liquid X are shown. oiling point = 102 Universal Indicator turns green What is X? ethanol hydrochloric acid pure water sodium chloride (salt) solution 2 blue
4 aerie Ae/e/ Me7hy/ Aora fe
 Oct. 1, 1957 F. H. MAY PROCESS FOR THE MANUFACTURE OF METHYL BORATE Filed June 22, 1955 a/co/o/ //7 As 22 57// Aso'7ors 4 aerie Ae/e/ Me7hy/ Aora fe INVENTOR. Az/7A /7. May A6Aadora 2 savaa 4772 remay-1s
Oct. 1, 1957 F. H. MAY PROCESS FOR THE MANUFACTURE OF METHYL BORATE Filed June 22, 1955 a/co/o/ //7 As 22 57// Aso'7ors 4 aerie Ae/e/ Me7hy/ Aora fe INVENTOR. Az/7A /7. May A6Aadora 2 savaa 4772 remay-1s
4.4.1 Reactivity of metals Metal oxides The reactivity series. Key opportunities for skills development.
 4.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
4.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
Methods of Separation. Vacuum Filtration. Distillation. The Physical Separation of Matter Chemistry 11 2/17/2014
 The Physical Separation of Matter Chemistry 11 Methods of Separation n Depending upon the physical properties of the substances involved, various methods of separation can be used. n Hand separation: A
The Physical Separation of Matter Chemistry 11 Methods of Separation n Depending upon the physical properties of the substances involved, various methods of separation can be used. n Hand separation: A
EVAPORATION YUSRON SUGIARTO
 EVAPORATION YUSRON SUGIARTO Evaporation: - Factors affecting evaporation - Evaporators - Film evaporators - Single effect and multiple effect evaporators - Mathematical problems on evaporation Principal
EVAPORATION YUSRON SUGIARTO Evaporation: - Factors affecting evaporation - Evaporators - Film evaporators - Single effect and multiple effect evaporators - Mathematical problems on evaporation Principal
