MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
- Francis Burke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ch 5 Molecules & Compounds STUDY SHEET Accelerated Chemistry /100 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When elements combine to form compounds, 1) A) their properties do not change. B) their properties change completely. C) their properties are completely random. D) their properties are an average of all elements in the compound. 2) The first chemist to formally state the law of constant composition was. 2) A) Dalton B) Rutherford C) Mendeleev D) Proust 3) The law of constant composition states: 3) A) All samples of a given compound have the same proportions of their constituent elements. B) The nucleus is a dense region of positive charge that always contains protons and neutrons. C) All atoms of a given element have a constant composition and are different than atoms of any other element. D) Matter cannot be either created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. 4) The oxygen-to-hydrogen mass ratio of water is always 8.0 is an example of what fundamental law? A) Law of Constant Whole Number Ratio B) Law of Constant Composition C) Law of Conservation of Mass D) Law of Constant Mass Ratio 4) 5) What is the oxygen-to-hydrogen mass ratio for H 2 O 2? 5) A) B) 4 C) 8 D) 16 6) The phosphorous-to-hydrogen mass ratio is 10.2 for a compound. This ratio could correspond to the compound A) PH6. B) PH3. C) PH2. D) PH. 6) 7) What is the oxygen-to-sulfur mass ratio of sulfur dioxide? 7) A) 0.5 B) 1.0 C) 2.0 D) 16 8) Which of the following statements about chemical formulas is FALSE? 8) A) The subscripts represent the relative mass of each type of atom in the compound. B) Different compounds made of the same elements have different subscripts. C) The subscripts do not change for a given compound. D) The subscripts represent the relative number of each type of atom in the compound. 9) How many total atoms are in the formula Al 2 (CO 3 ) 3? 9) A) 9 B) 14 C) 8 D) 12 1
2 10) How many carbon atoms are in the formula Al 2 (CO 3 ) 3? 10) A) 3 B) 9 C) 6 D) 1 11) How many oxygen atoms are in the formula Al 2 (CO 3 ) 3? 11) A) 6 B) 9 C) 3 D) 1 12) Which formula shows the proper use of parentheses? 12) A) Ca(SO4) B) (NH4)3(PO4) C) Ca(NO3)2 D) Ca(F)2 13) How many of each type of atoms are there in the formula NH 4 C 2 H 3 O 2? 13) A) N = 1, H = 4, C = 2, O = 2 B) N = 1, H = 3, C = 2, O = 2 C) N = 4, H = 7, C = 2, O = 2 D) N = 1, H = 7, C = 2, O = 2 14) How many of each type of atom are there in the formula Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2? 14) A) Ca = 3, P = 2, O = 4 B) Ca = 3, P = 2, O = 8 C) Ca = 3, P = 1, O = 4 D) Ca = 3, P = 1, O = 8 15) How many of each type of atom are there in the formula (NH4)2HPO4? 15) A) N = 2, H = 9, P = 1, O = 4 B) N = 1, H = 5, P = 1, O = 4 C) N = 2, H = 8, P = 1, O = 4 D) N = 2, H = 5, P = 1, O = 4 16) What is the correct formula for a compound that has three oxygen atoms and one sulfur atom? 16) A) 3OS B) SO3 C) SO3 D) O3S 17) What is the correct formula of a compound that has ten oxygen atoms and four phosphorus atoms? A) 10OP 4 B) O 10 P 4 C) 4PO 10 D) P 4 O 10 17) 18) Carbon is considered which of the following? 18) A) molecular element B) atomic element C) molecular compound D) ionic compound 19) Which among the following elements does NOT exist as a diatomic molecule in nature? 19) A) nitrogen B) hydrogen C) fluorine D) neon 20) Carbon monoxide is considered which of the following? 20) A) molecular compound B) atomic element C) molecular element D) ionic compound 21) Fluorine is considered which of the following? 21) A) molecular element B) molecular compound C) atomic element D) ionic compound 22) Ammonium fluoride is considered which of the following? 22) A) molecular element B) molecular compound C) ionic compound D) atomic element 2
3 23) Which of the following species is a molecular element? 23) A) carbon dioxide B) neon C) chlorine D) sodium 24) Which of the following is a molecular compound? 24) A) potassium hydroxide B) nitrogen monoxide C) calcium acetate D) barium sulfide 25) What is the formula for an ionic compound made of barium and nitrogen? 25) A) Ba 2 N 3 B) BaN C) Ba 2 N 4 D) Ba 3 N 2 26) What is the formula for an ionic compound made of magnesium and sulfur? 26) A) MgS B) Mg 2 S C) Mg 2 S 3 D) MgS 2 27) What is the formula for an ionic compound made of carbon and oxygen? 27) A) CO B) CO 3 C) C 2 O D) CO 2 28) The ionic compound that forms between potassium and oxygen is 28) A) K2O. B) K2O2. C) KO. D) KO2. 29) What is the formula for an ionic compound made of aluminum and oxygen? 29) A) AlO B) Al 3 O 2 C) Al 2 O 3 D) AlO 2 30) What is the name of the ionic compound made of beryllium and chlorine? 30) A) beryllium chloride B) beryllium dichloride C) monoberyllium dichloride D) beryllium(ii) chloride 31) What is the name of the compound made from lithium and oxygen? 31) A) lithium(i) oxide B) lithium oxide C) lithium dioxide D) oxygen lithide 32) Which metal atom below would NOT be involved in formation of a Type II compound? 32) A) Mn B) Fe C) Ba D) Cr 33) What is the name of CoS? 33) A) cobalt monosulfide B) cobaltous sulfur C) cobalt(ii) sulfide D) cobalt sulfide 34) What is the name of Ca(NO3)2? 34) A) calcium nitride B) calcium nitrate C) calcium nitrite D) calcium dinitrite 35) Which formula shown is incorrect for the name given? 35) A) magnesium nitrite: Mg(NO 2 ) 3 B) potassium hydroxide: KOH C) aluminum sulfate: Al 2 (SO 4 )3 D) sodium hydrogen carbonate: NaHCO 3 3
4 36) Which formula shown is incorrect for the name given? 36) A) strontium carbonate: SrCO3 B) ammonium cyanide: NH4CN C) potassium acetate: KC2H3O2 D) lithium sulfate: LiSO4 37) What is the name of the compound whose formula is Na 2 O? 37) A) disodium oxide B) disodium monoxide C) sodium oxide D) sodium monoxide 38) What is the formula for the acetate polyatomic ion? 38) A) C 2 H 3 O- B) C 2 H 3 O 2 2- C) C 2 H 3 O 2 - D) C 3 H 2 O 3-39) What is the correct formula for potassium dichromate? 39) A) KCr2O7 B) K2Cr2O7 C) K2CrO4 D) K(CrO4)2 40) What is the correct formula for ammonium hydrogen sulfate? 40) A) (NH 4 ) 2 HSO 4 B) NH 4 HSO 4 C) Am 2 HSO 4 D) (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 41) The formula for potassium chlorate is KClO 3. The formula for magnesium chloride is MgCl 2. What is the formula for magnesium chlorate? A) Mg 2 ClO 3 B) Mg(ClO 3 )2 C) MgClO 3 D) Mg 2 (ClO 3 ) 3 41) 42) The charge of a vanadium ion in the compound V2O5 is: 42) A) 10- B) 5+ C) 2+ D) ) What is the correct formula for the hypochlorite polyatomic ion? 43) A) ClO 2 - B) ClO 3 - C) ClO- D) ClO 4-44) What is the correct name for the BrO4 1- ion? 44) A) perbromate B) bromate C) hypobromite D) bromite 45) Choose the pair of names and formulas that do NOT match. 45) A) copper(ii) nitride: Cu3N2 B) copper(i) nitrate: CuNO3 C) copper(ii) nitrite: Cu(NO2)2 D) all of these are correct 46) The name trisodium phosphate is incorrect for the compound Na3PO4 because 46) A) you cannot use a prefix for the first element of an ionic compound. B) this compound should be called trisodium monophosphate. C) you cannot use a prefix for the first element in a molecular compound. D) none of the above 47) What is the name of the molecular compound SF5? 47) A) sulfur pentafluoride B) sulfur heptafluoride C) sulfur hexafluoride D) none of the above 4
5 48) What is the name of the molecular compound SO 3? 48) A) sulfur(iv) oxide B) sulfur tetraoxide C) sulfur trioxide D) none of the above 49) What is correct name of the compound whose formula is N 2 O 4? 49) A) dinitrogen oxide B) nitrogen dioxide C) nitrogen tetroxide D) dinitrogen tetroxide 50) What is correct name of the compound whose formula is BF3? 50) A) boron(iii) fluoride B) boron fluoride C) boron trifluoride D) monoboron trifluorine 51) What would the formula of diiodine pentasulfide be? 51) A) I 2 S 5 B) I 2 S 7 C) I 4 S 9 D) I 5 S 2 52) What is the correct formula for the molecular compound heptaphosphorus octafluoride? 52) A) P 6 F 7 B) P 7 F 6 C) P 5 F 8 D) P 7 F 8 53) What is the proper name for HBr (aq)? 53) A) bromous acid B) hydrobromous acid C) hydrobromic acid D) hydrousbromic acid 54) What is the name of HI (aq)? 54) A) hydroiodous acid B) iodic acid C) iodous acid D) hydroiodic acid 55) What is the name of HIO 3 (aq)? 55) A) hydrogen iodate B) iodic acid C) hydroioidic acid D) iodous acid 56) What is the name of HNO 2 (aq)? 56) A) Nitric acid B) hydronitric acid C) Nitrous acid D) hydronitrous acid 57) A certain oxyacid is derived from the oxyanion SO3 2-. The formula for the oxyacid is 57) A) H2SO3. B) HSO3. C) H2SO4. D) H3SO3. 58) What is the formula mass of sulfurous acid? 58) A) amu B) amu C) amu D) amu 59) What is the formula mass for potassium nitrate? 59) A) amu B) amu C) amu D) amu 60) What is the formula mass for diboron tetrachloride? 60) A) amu B) amu C) amu D) amu 5
6 61) What is the formula mass of copper(ii) fluoride? 61) A) B) C) D) ) Which of the following has the largest formula mass? 62) A) NO 2 B) SiO 2 C) CO 2 D) SO 2 E) H 2 O 63) Which of the following compounds have the smallest formula mass? 63) A) CO 2 B) NO 2 C) SiO 2 D) SO 2 E) H 2 O 64) A compound has a formula mass of amu and is comprised of atoms of sodium and oxygen in a definite ratio. The name of the compound described here is A) sodium monoxide. B) sodium dioxide. C) disodium oxide. D) sodium oxide. 64) 65) If the mass ratio of K to F in a compound is 2.06:1, how many grams of F are needed to react with 97.5 g of K? A) B) 2.11 C) 4.73 D) ) 66) What is the mass ratio of Na to S in sodium sulfide? 66) A) B) 1.43 C) 7.17 D) ) How many O atoms are present in sodium chlorite? 67) A) 4 B) 1 C) 2 D) 6 68) How many C atoms are in ammonium acetate? 68) A) 3 B) 2 C) 1 D) 5 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' (A) if the statement is true and 'F' (B) if the statement is false. Correct the FALSE statements by changing the underlined word. 69) When elements combine to form compounds, their properties only change slightly. 69) 70) The properties of a compound are an average of the properties of the individual elements. 70) 71) Life could not exist with just 91 elements if they did not combine to form compounds. 71) 72) Although some substances we encounter in our routine lives are elements, most occur in the combined state. 72) 73) The law of constant composition states: All samples of a given compound have the same proportions of their constituent elements. 73) 74) The fact that water has an oxygen-to-hydrogen mass ratio of 8.0 illustrates the law of conservation of mass. 74) 75) The subscripts in a chemical formula represent the relative mass of each atom in a chemical compound. 75) 6
7 76) The subscripts in a chemical formula do not change for a given compound. 76) 77) Chemical formulas normally list the most metallic elements first. 77) 78) The formula of a compound comprised of two nitrogen atoms and one oxygen atom should be written properly as ON2. 78) 79) Molecular elements do not exist in nature. 79) 80) The element nitrogen normally exists in nature as a diatomic molecule. 80) 81) Carbon dioxide is an example of a molecular compound. 81) 82) The basic unit of an ionic compound is called the formula unit. 82) 83) SO2 is an ionic compound. 83) 84) Ionic compounds have a net charge of zero. 84) 85) Ionic compounds always contain positive and negative ions. 85) 86) In ionic compounds the net positive charge always equals the net negative charge. 86) 87) The ionic compound that forms between aluminum and oxygen is AlO. 87) 88) The ionic compound that forms between Mg and O is MgO. 88) 89) The correct formula for calcium fluoride is CaF 3. 89) 90) Ionic compounds are usually made up of a metal and a nonmetal. 90) 91) The ionic compound MgO is named manganese oxide. 91) 92) The name of KNO 3 is potassium nitratide. 92) 93) The correct formula for sodium permanganate is NaMgO4. 93) 94) Type II metal cations are usually found in the section of the periodic table known as the transition metals. 94) 95) If there are two ions in a series of oxoanions, the one with more oxygen is given the ending "-ite." 95) 96) The proper name for SF 6 is sulfur tetrafluoride. 96) 7
8 97) The proper name for the acid HF is hydrofluoric acid. 97) 98) The proper name for for HI is hydroiodic acid. 98) 99) The correct name for HNO 3 is hydronitric acid. 99) 100) The correct name for H 2 SO 3 is sulfurous acid. 100) 8
Test bank for Introductory Chemistry 5th Edition by Tro
 Test bank for Introductory Chemistry 5th Edition by Tro Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forintroductory-chemistry-5th-edition-by-tro/ Introductory Chemistry, 5e (Tro)
Test bank for Introductory Chemistry 5th Edition by Tro Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forintroductory-chemistry-5th-edition-by-tro/ Introductory Chemistry, 5e (Tro)
Honors Chemistry Semester 2 Final Exam MC Practice
 Honors Chemistry Semester 2 Final Exam MC Practice Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What do the alkali metals all have in common?
Honors Chemistry Semester 2 Final Exam MC Practice Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What do the alkali metals all have in common?
CH1410 Practice Exam #2 (Katz)
 CH1410 Practice Exam #2 (Katz) Section 1 - Multiple Choice - Write the letter of the BEST CHOICE in the space provided. 1. How are wavelength and frequency of light related? A) Wavelength is one-half of
CH1410 Practice Exam #2 (Katz) Section 1 - Multiple Choice - Write the letter of the BEST CHOICE in the space provided. 1. How are wavelength and frequency of light related? A) Wavelength is one-half of
4) A specific isotope of an element is known to have 15 protons and 16 neutrons. Which symbol would properly represent this isotope?
 CHM1025 Exam 2 Chapter 4 & 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements about different elements are true
CHM1025 Exam 2 Chapter 4 & 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements about different elements are true
Chemical Nomenclature
 Chemical Nomenclature! The first names for chemicals were common names: Sugar, quicklime, Epsom salts, milk of magnesia, gypsom, laughing gas Simple, but not practical, the tell us little about the chemicals
Chemical Nomenclature! The first names for chemicals were common names: Sugar, quicklime, Epsom salts, milk of magnesia, gypsom, laughing gas Simple, but not practical, the tell us little about the chemicals
Nomenclature of inorganic compounds. = naming non carbon (mostly) compounds. Some definitions:
 1 Chemistry 047 Inorganic Nomenclature Nomenclature of inorganic compounds = naming non carbon (mostly) compounds Some definitions: Nomenclature = system used by chemists to name and identify compounds
1 Chemistry 047 Inorganic Nomenclature Nomenclature of inorganic compounds = naming non carbon (mostly) compounds Some definitions: Nomenclature = system used by chemists to name and identify compounds
Topic 5: The Language of Chemistry
 Topic 5: The Language of Chemistry Chemical Formulas & Chemical Compounds (Chapter 7 in Modern Chemistry) A Chemical Formula Recall that a chemical formula indicates the relative number of atoms of each
Topic 5: The Language of Chemistry Chemical Formulas & Chemical Compounds (Chapter 7 in Modern Chemistry) A Chemical Formula Recall that a chemical formula indicates the relative number of atoms of each
Naming Chemical Compounds
 Naming Chemical Compounds Naming compounds is an important part of chemistry. Most compounds fall into one of four categories Ionic Compounds, Molecular Compounds, Acids and Bases, and Hydrates Part One:
Naming Chemical Compounds Naming compounds is an important part of chemistry. Most compounds fall into one of four categories Ionic Compounds, Molecular Compounds, Acids and Bases, and Hydrates Part One:
Chemistry--Unit 2: Chemical Names and Formulas Test Review
 vocab anion binary compound cation chemical formula formula unit ion ionic compound law of definite proportions law of multiple proportions molecular formula polyatomic ion representative particle ternary
vocab anion binary compound cation chemical formula formula unit ion ionic compound law of definite proportions law of multiple proportions molecular formula polyatomic ion representative particle ternary
Chemical Nomenclature Chapter 2.5-8
 Chemical Nomenclature Chapter 2.5-8 Octet Rule An octet is 8 valence electrons is associated with the stability of the noble gases does not occur with He, which is stable with two valence electrons (duet)
Chemical Nomenclature Chapter 2.5-8 Octet Rule An octet is 8 valence electrons is associated with the stability of the noble gases does not occur with He, which is stable with two valence electrons (duet)
Chapter 5. Molecules and Compounds. Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro 2/21/2011
 Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Chapter 5 Molecules and Compounds Based on notes of Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College 2006, Prentice Hall Molecules and Compounds Salt Sodium
Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Chapter 5 Molecules and Compounds Based on notes of Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College 2006, Prentice Hall Molecules and Compounds Salt Sodium
» Composed of more than one type of atom chemically bonded.» A pure substance, meaning its properties are the same throughout the substance.
 » Composed of more than one type of atom chemically bonded.» A pure substance, meaning its properties are the same throughout the substance.» Separated chemically not physically» No overall charge; they
» Composed of more than one type of atom chemically bonded.» A pure substance, meaning its properties are the same throughout the substance.» Separated chemically not physically» No overall charge; they
4. What is the law of constant composition (also known as the law of definite proportion)?
 Name: Exercises #1: 1. What is the law of conservation of mass? 2. Show that the results of the following experiments illustrate the law of conservation of mass. Experiment #1: a 5.00-g sample of pure
Name: Exercises #1: 1. What is the law of conservation of mass? 2. Show that the results of the following experiments illustrate the law of conservation of mass. Experiment #1: a 5.00-g sample of pure
Cations have a positive charge and anions have a negative charge. 3. Complete the following table.
 Name Pre-AP Chemistry: Ionic Bonding and Nomenclature Period Homework #1: Ionic Bonding 1. Use Lewis Dot Diagrams to predict the ionic compound formed between each of the following atoms. Use arrows to
Name Pre-AP Chemistry: Ionic Bonding and Nomenclature Period Homework #1: Ionic Bonding 1. Use Lewis Dot Diagrams to predict the ionic compound formed between each of the following atoms. Use arrows to
Chapter 6 and 7 Practice MC
 Chapter 6 and 7 Practice MC MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Ammonium fluoride is considered which of the following? 1) A) molecular
Chapter 6 and 7 Practice MC MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Ammonium fluoride is considered which of the following? 1) A) molecular
Chemical Formulas Types of chemical formulas [X m Y n ]
![Chemical Formulas Types of chemical formulas [X m Y n ] Chemical Formulas Types of chemical formulas [X m Y n ]](/thumbs/89/98748683.jpg) 1 Chemical Formulas Types of chemical formulas [X m Y n ] Molecular Actual # of atoms of each element Empirical Structural Relative # of atoms of each element Actual # of atoms and the bonds between them
1 Chemical Formulas Types of chemical formulas [X m Y n ] Molecular Actual # of atoms of each element Empirical Structural Relative # of atoms of each element Actual # of atoms and the bonds between them
Experiment #3: When 2.0 g of sodium hydroxide reacts with 2.2 g carbon dioxide, 4.2 g of baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) is produced.
 Name: Dalton s Atomic Theory: (1) Matter is composed of very small units called atoms. Atom is the smallest unit that possesses the chemical property of an element. (2) An element contains only one type
Name: Dalton s Atomic Theory: (1) Matter is composed of very small units called atoms. Atom is the smallest unit that possesses the chemical property of an element. (2) An element contains only one type
Naming Compounds. Part One: Naming Ionic Compounds. Identifying Ionic Compounds
 Naming Compounds Naming compounds is an important part of chemistry. Most compounds fall in to one of three categories ionic compounds, molecular compounds, or acids. Part One: Naming Ionic Compounds Identifying
Naming Compounds Naming compounds is an important part of chemistry. Most compounds fall in to one of three categories ionic compounds, molecular compounds, or acids. Part One: Naming Ionic Compounds Identifying
The chemical formulas of most of the elements are simply their elemental symbol:
 Chemical Formulas A chemical formula gives the numbers and types of atoms that are found in a substance. When the substance is a discrete molecule, then the chemical formula is also its molecular formula.
Chemical Formulas A chemical formula gives the numbers and types of atoms that are found in a substance. When the substance is a discrete molecule, then the chemical formula is also its molecular formula.
Chapter Six Chemical Names and Formulas WS C U1C6
 Chapter Six Chemical Names and Formulas WS C U1C6 Name Period Section 6.1 Part I: Matching. Match the definition with the term that best correlates to it. No definition will be used more than once. 1.
Chapter Six Chemical Names and Formulas WS C U1C6 Name Period Section 6.1 Part I: Matching. Match the definition with the term that best correlates to it. No definition will be used more than once. 1.
- Some MOLECULES can gain or lose electrons to form CATIONS or ANIONS. These are called POLYATOMIC IONS
 63 POLYATOMIC IONS - Some MOLECULES can gain or lose electrons to form CATIONS or ANIONS. These are called POLYATOMIC IONS - Polyatomic ions form ionic compounds in the same way that single-element ions
63 POLYATOMIC IONS - Some MOLECULES can gain or lose electrons to form CATIONS or ANIONS. These are called POLYATOMIC IONS - Polyatomic ions form ionic compounds in the same way that single-element ions
Ternary Compounds. , to give the compound, NaNO 3, sodium nitrate.
 Ternary Compounds Ternary Compounds Ternary compounds are those containing three different elements. (NaNO 3, NH 4 Cl, etc.). The naming of ternary compounds involves the memorization of several positive
Ternary Compounds Ternary Compounds Ternary compounds are those containing three different elements. (NaNO 3, NH 4 Cl, etc.). The naming of ternary compounds involves the memorization of several positive
Chemical Nomenclature
 Chemical Nomenclature IUPAC International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. This is a group of chemists that determines, among other things, how chemicals will be named. IONIC COMPOUNDS 1. Binary Ionic
Chemical Nomenclature IUPAC International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. This is a group of chemists that determines, among other things, how chemicals will be named. IONIC COMPOUNDS 1. Binary Ionic
Chemical Formulas and Chemical Nomenclature. Mr. Matthew Totaro Legacy High School Honors Chemistry
 Chemical Formulas and Chemical Nomenclature Mr. Matthew Totaro Legacy High School Honors Chemistry 1 Molecular View of Elements and Compounds 2 Atomic Elements Atomic Elements = elements whose smallest
Chemical Formulas and Chemical Nomenclature Mr. Matthew Totaro Legacy High School Honors Chemistry 1 Molecular View of Elements and Compounds 2 Atomic Elements Atomic Elements = elements whose smallest
+ #n; Z = atomic number = #p + C isotopes: 12 6
 CHEMISTRY 103 Help Sheet #2 Chapter 2 (Part I); Sections 2.1.8 Do topics appropriate for your lecture Prepared by Dr. Tony Jacob http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Nuggets: Periodic Table;
CHEMISTRY 103 Help Sheet #2 Chapter 2 (Part I); Sections 2.1.8 Do topics appropriate for your lecture Prepared by Dr. Tony Jacob http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Nuggets: Periodic Table;
AP Chemistry (1 of 20) AP Chemistry (2 of 20) AP Chemistry (3 of 20) AP Chemistry (4 of 20) AP Chemistry (5 of 20) AP Chemistry (6 of 20)
 Ions Ionic Charges of Representative Elements (1 of 20) (2 of 20) Formulas and Names of Common Metal Ions with More than One Common Ionic Charge Some Common Polyatomic Ions (3 of 20) (4 of 20) Naming Monatomic
Ions Ionic Charges of Representative Elements (1 of 20) (2 of 20) Formulas and Names of Common Metal Ions with More than One Common Ionic Charge Some Common Polyatomic Ions (3 of 20) (4 of 20) Naming Monatomic
Name: Hour: Unit 2 Periodic Table Nomenclature. Notepack Chapters 5 and 6
 Name: Hour: Unit 2 Periodic Table Nomenclature Notepack Chapters 5 and 6 1 Periodic Table & Nomenclature Chapter 5 Part One: Review of Atomic Structure (Pages 107-121) A. Define atom 1. proton - 2. neutron-
Name: Hour: Unit 2 Periodic Table Nomenclature Notepack Chapters 5 and 6 1 Periodic Table & Nomenclature Chapter 5 Part One: Review of Atomic Structure (Pages 107-121) A. Define atom 1. proton - 2. neutron-
CHEMISTRY 103 Help Sheet #2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions (Text: Ch 2: )
 CHEMISTRY 103 Help Sheet #2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions (Text: Ch 2: 2.1-2.8) Do the topics appropriate for your lecture Prepared by Dr. Tony Jacob http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Nuggets:
CHEMISTRY 103 Help Sheet #2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions (Text: Ch 2: 2.1-2.8) Do the topics appropriate for your lecture Prepared by Dr. Tony Jacob http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Nuggets:
Due Friday, August 18 th, 2017 Mrs. Hockstok - AP Chemistry Class Olentangy Orange High School Summer Assignment
 Due Friday, August 18 th, 2017 Mrs. Hockstok - AP Chemistry Class Olentangy Orange High School Summer Assignment 2017-2018 You will have a quiz on the first day of school (August 16 th, 2017) on the polyatomic
Due Friday, August 18 th, 2017 Mrs. Hockstok - AP Chemistry Class Olentangy Orange High School Summer Assignment 2017-2018 You will have a quiz on the first day of school (August 16 th, 2017) on the polyatomic
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions (Chapter 2) 1. a. Give the name and symbol for one alkaline earth metal.
 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions (Chapter 2) 1. a. Give the name and symbol for one alkaline earth metal. b. Give the name and symbol for one transition metal. c. Give the name and symbol for one noble gas.
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions (Chapter 2) 1. a. Give the name and symbol for one alkaline earth metal. b. Give the name and symbol for one transition metal. c. Give the name and symbol for one noble gas.
Chapter 6 Inorganic and Organic Compounds: Names and Formulas
 Chapter 6 Inorganic and Organic Compounds: Names and Formulas 6.1 Octet Rule and Ions 1 Octet Rule An octet is 8 valence electrons is associated with the stability of the noble gases does not occur with
Chapter 6 Inorganic and Organic Compounds: Names and Formulas 6.1 Octet Rule and Ions 1 Octet Rule An octet is 8 valence electrons is associated with the stability of the noble gases does not occur with
Ch.2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
 Ch.2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Naming Recall Ionic Bond = electrostatic attraction due to the transfer of vse - s between a metal and nonmetal Covalent Bond = sharing of valence electrons between nonmetals
Ch.2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Naming Recall Ionic Bond = electrostatic attraction due to the transfer of vse - s between a metal and nonmetal Covalent Bond = sharing of valence electrons between nonmetals
Unit 5: Bonding Part 2 (Covalent Bonds/Bond & Molecular Polarity/IMF)
 Unit 5: Bonding Part 2 (Covalent Bonds/Bond & Molecular ity/imf) The following pages are practice questions for this unit, and will be submitted for homework! You must complete: Ionic vs. Covalent Properties
Unit 5: Bonding Part 2 (Covalent Bonds/Bond & Molecular ity/imf) The following pages are practice questions for this unit, and will be submitted for homework! You must complete: Ionic vs. Covalent Properties
Big Idea: Matter & Atoms
 Big Idea: Matter & Atoms Naming Ionic Compounds Naming Covalent Compounds Naming Acids Naming Hydrates The cation (positive ion) is written first Takes the same name as the element if only forms one charge
Big Idea: Matter & Atoms Naming Ionic Compounds Naming Covalent Compounds Naming Acids Naming Hydrates The cation (positive ion) is written first Takes the same name as the element if only forms one charge
Nomenclature Hint Sheet
 Nomenclature Hint Sheet The nomenclature for four different classes of compounds is covered in CH101: ionic, covalent, acid/base, and organic compounds. This document will cover ionic (chapter 4) and covalent
Nomenclature Hint Sheet The nomenclature for four different classes of compounds is covered in CH101: ionic, covalent, acid/base, and organic compounds. This document will cover ionic (chapter 4) and covalent
Chapter 9 Naming Simple Compounds
 Chapter 9 Naming Simple Compounds Monatomic Ions Ionic compounds consists of a positive metal ion and a negative nonmetal ion combined in a proportion such that their charges add up to a net charge of
Chapter 9 Naming Simple Compounds Monatomic Ions Ionic compounds consists of a positive metal ion and a negative nonmetal ion combined in a proportion such that their charges add up to a net charge of
Ionic Compounds. And Acids
 CHAPTER 7 LANGUAGE OF CHEMISTRY CLASSIFICATION OF COMPOUNDS Inorganic compounds does not contain the element carbon, but there are exception to this rule, CO 2 (carbon dioxide), CO 3 2 (carbonate), and
CHAPTER 7 LANGUAGE OF CHEMISTRY CLASSIFICATION OF COMPOUNDS Inorganic compounds does not contain the element carbon, but there are exception to this rule, CO 2 (carbon dioxide), CO 3 2 (carbonate), and
CH1410 Practice Exam #2 (Katz) Sp2015
 H1410 Practice Eam #2 (Katz) Sp2015 Section 1 - Multiple hoice - Write the letter of the EST HOIE in the space provided. 1. The energy sublevel for the highest energy electrons added to the elements U,
H1410 Practice Eam #2 (Katz) Sp2015 Section 1 - Multiple hoice - Write the letter of the EST HOIE in the space provided. 1. The energy sublevel for the highest energy electrons added to the elements U,
DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE NAME
 DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE NAME - The name of an ionic compound is made of the names of the CATION and ANION in the compound. - To get the FORMULA, you must figure out the SMALLEST
DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE NAME - The name of an ionic compound is made of the names of the CATION and ANION in the compound. - To get the FORMULA, you must figure out the SMALLEST
Nomenclature. A Systematic Approach to Naming Chemical Compounds
 Nomenclature A Systematic Approach to Naming Chemical Compounds Nomenclature Ternary Ionic Compounds Binary and Ternary Acids Ternary Ionic Compounds >2 elements cation with an anion Metal cation with
Nomenclature A Systematic Approach to Naming Chemical Compounds Nomenclature Ternary Ionic Compounds Binary and Ternary Acids Ternary Ionic Compounds >2 elements cation with an anion Metal cation with
CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 6 - Nomenclature Practice Problems
 Name Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 6 - Nomenclature Practice Problems Due Date Assignment On-Time (100) Late (70) 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Warm-Up EC Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located
Name Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 6 - Nomenclature Practice Problems Due Date Assignment On-Time (100) Late (70) 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Warm-Up EC Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located
Polyatomic Ions. Why? Model 1 Types of Ions. Can a group of atoms have a charge?
 Why? Polyatomic Ions Can a group of atoms have a charge? Do you know you eat a lot of -ates? Next time you look at a food label, read the ingredients and you will likely find a number of ingredients that
Why? Polyatomic Ions Can a group of atoms have a charge? Do you know you eat a lot of -ates? Next time you look at a food label, read the ingredients and you will likely find a number of ingredients that
- Use the STEM NAME of the element, then add "-ide" suffix
 65 ANIONS 2 kinds Main-group nonmetals - Use the STEM NAME of the element, then add "-ide" suffix N : "nitride" ion P : "phosphide ion" O : "oxide ion" F : "fluoride ion" Polyatomic ions - Memorize list.(see
65 ANIONS 2 kinds Main-group nonmetals - Use the STEM NAME of the element, then add "-ide" suffix N : "nitride" ion P : "phosphide ion" O : "oxide ion" F : "fluoride ion" Polyatomic ions - Memorize list.(see
H 2 O. Chapter 9 Chemical Names and Formulas
 H 2 O Chapter 9 Chemical Names and Formulas Section 9.1 Naming Ions OBJECTIVES: Identify the charges on monatomic ions by using the periodic table, and name the ions. Section 9.1 Naming Ions OBJECTIVES:
H 2 O Chapter 9 Chemical Names and Formulas Section 9.1 Naming Ions OBJECTIVES: Identify the charges on monatomic ions by using the periodic table, and name the ions. Section 9.1 Naming Ions OBJECTIVES:
Naming Ionic Compounds with Two Elements
 Chapter 6 Lecture Chapter 6 Ionic and Molecular Compounds 6.3 Naming and Writing Ionic Compounds Fifth Edition Naming of Ionic Compounds In the name of an ionic compound, the positive ion (first ion) is
Chapter 6 Lecture Chapter 6 Ionic and Molecular Compounds 6.3 Naming and Writing Ionic Compounds Fifth Edition Naming of Ionic Compounds In the name of an ionic compound, the positive ion (first ion) is
#5 Nomenclature Quantitative Chemistry
 Name #5 Nomenclature Quantitative Chemistry Student Learning Map Unit EQ: How do I name and write formulas for chemical compounds? Key Learning: Naming and writing formulas for compounds is a systematic
Name #5 Nomenclature Quantitative Chemistry Student Learning Map Unit EQ: How do I name and write formulas for chemical compounds? Key Learning: Naming and writing formulas for compounds is a systematic
CHEM 1305: Introductory Chemistry
 CHEM 1305: Introductory Chemistry Naming Inorganic Compounds From Chapter 6 Textbook Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Language of Chemistry By
CHEM 1305: Introductory Chemistry Naming Inorganic Compounds From Chapter 6 Textbook Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Language of Chemistry By
CHEMICAL BONDING - CH 2 -
 CHEMICAL BONDING - CH 2 - Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Electron dot diagrams are used to represent the Lewis model of
CHEMICAL BONDING - CH 2 - Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Electron dot diagrams are used to represent the Lewis model of
CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND BONDING
 Name Date Period CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND BONDING IONIC COMPOUNDS 1. What are the two types of bonds that will be discussed in this chapter? 2. How do ionic bonds form? 3. What do you call the positive
Name Date Period CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND BONDING IONIC COMPOUNDS 1. What are the two types of bonds that will be discussed in this chapter? 2. How do ionic bonds form? 3. What do you call the positive
How to Use This Presentation
 How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
Chapter 8 Nomenclature
 8.1 Names of Atoms Chapter 8 Nomenclature Simple neutral atoms with no charge are named as is: Na is sodium atom, Ne is neon atom Know the names and symbols for elements #1-20 and Ba, Co, I, Cu, Fe, Pb,
8.1 Names of Atoms Chapter 8 Nomenclature Simple neutral atoms with no charge are named as is: Na is sodium atom, Ne is neon atom Know the names and symbols for elements #1-20 and Ba, Co, I, Cu, Fe, Pb,
Chemical Names and Formulas
 Chemical Names and Formulas ELECTRONS AND THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS BONDING AND INTERACTIONS 91 Naming Ions For students using the Foundation edition, assign problems 4, 8 15 Essential Understanding Ions
Chemical Names and Formulas ELECTRONS AND THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS BONDING AND INTERACTIONS 91 Naming Ions For students using the Foundation edition, assign problems 4, 8 15 Essential Understanding Ions
Compound Names and Formulas Activity
 Name: KEY Class Period: Compound Names and Formulas Activity Part 1 Instructions: Study the following compound formulas and their corresponding names. Then answer the questions below. Questions: 1. What
Name: KEY Class Period: Compound Names and Formulas Activity Part 1 Instructions: Study the following compound formulas and their corresponding names. Then answer the questions below. Questions: 1. What
629 CER Modular Laboratory Program in Chemistry
 M I S C 629 CER Modular Laboratory Program in Chemistry editor: M. L. Gillette Naming Inorganic Chemical Substances prepared by M. L. Gillette, Indiana University Kokomo, and H. A. Neidig, Lebanon Valley
M I S C 629 CER Modular Laboratory Program in Chemistry editor: M. L. Gillette Naming Inorganic Chemical Substances prepared by M. L. Gillette, Indiana University Kokomo, and H. A. Neidig, Lebanon Valley
Chemical Bonding. Chemical Bonds. Metals, Ions, or Molecules. All Matter Exists as Atoms,
 Chemical Bonding Valence electrons (the outer most electrons) are responsible for the interaction between atoms when forming chemical compounds. Another way to say that is that valence electrons are the
Chemical Bonding Valence electrons (the outer most electrons) are responsible for the interaction between atoms when forming chemical compounds. Another way to say that is that valence electrons are the
Nomenclature PO 4. phosphate ion. HC 2 H 3 O 2 Acetic Acid C 2 H 3 O 2. acetate ion. Chemistry 1 Honors: Chapter 7: pp
 Chemistry 1 Honors: Chapter 7: pp218-258 PO 4 3- phosphate ion Nomenclature HC 2 H 3 O 2 Acetic Acid C 2 H 3 O 2 - acetate ion SAVE PAPER AND INK!!! When you print out the notes on PowerPoint, print "Handouts"
Chemistry 1 Honors: Chapter 7: pp218-258 PO 4 3- phosphate ion Nomenclature HC 2 H 3 O 2 Acetic Acid C 2 H 3 O 2 - acetate ion SAVE PAPER AND INK!!! When you print out the notes on PowerPoint, print "Handouts"
Can a group of atoms have a charge?
 Why? Polyatomic Ions Can a group of atoms have a charge? Do you know you eat a lot of -ates? Next time you look at a food label, read the ingredients and you will likely find a number of ingredients that
Why? Polyatomic Ions Can a group of atoms have a charge? Do you know you eat a lot of -ates? Next time you look at a food label, read the ingredients and you will likely find a number of ingredients that
Section 1 Chemical Names and Formulas. Lesson Starter
 Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Significance of a Chemical Formula Monatomic Ions Binary Ionic Compounds Writing the Formula of an Ionic Compound Naming Binary Ionic Compounds Naming Binary Molecular
Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Significance of a Chemical Formula Monatomic Ions Binary Ionic Compounds Writing the Formula of an Ionic Compound Naming Binary Ionic Compounds Naming Binary Molecular
U N I T T E S T P R A C T I C E
 South Pasadena Honors Chemistry Name 6 Compounds Period Date U N I T T E S T P R A C T I C E Section 1: Multiple Choice. Select the best answer choice for each question. (1 point each) 1. Bonds between
South Pasadena Honors Chemistry Name 6 Compounds Period Date U N I T T E S T P R A C T I C E Section 1: Multiple Choice. Select the best answer choice for each question. (1 point each) 1. Bonds between
NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS. ammonium sulfide. iron(ii) carbonate. barium phosphate. titanium(iv) sulfide. Spelling matters!
 67 NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS ammonium sulfide iron(ii) carbonate titanium(iv) sulfide barium phosphate Spelling matters! barium phosphide 68 DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE NAME - The
67 NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS ammonium sulfide iron(ii) carbonate titanium(iv) sulfide barium phosphate Spelling matters! barium phosphide 68 DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE NAME - The
Summer Assignment 2014
 Summer Assignment 2014 The summer assignment is to help prepare you for the beginning of AP chemistry. The assignment is not graded, but the test on the second day of school covering the material will
Summer Assignment 2014 The summer assignment is to help prepare you for the beginning of AP chemistry. The assignment is not graded, but the test on the second day of school covering the material will
Naming Inorganic Compounds. common names systematic names
 Naming Inorganic Compounds common names systematic names Molecular Common Systematic Formula name name AgCl Lunar caustic Silver chloride H 2 SO 4 Oil of vitriol Sulfuric acid MgSO 4 Epsom salts Magnesium
Naming Inorganic Compounds common names systematic names Molecular Common Systematic Formula name name AgCl Lunar caustic Silver chloride H 2 SO 4 Oil of vitriol Sulfuric acid MgSO 4 Epsom salts Magnesium
Naming Simple Compounds
 Naming Simple Compounds Ionic Compounds Ionic compounds consist of positive and negative ions. have attractions called ionic bonds between positively and negatively charged ions. have high melting and
Naming Simple Compounds Ionic Compounds Ionic compounds consist of positive and negative ions. have attractions called ionic bonds between positively and negatively charged ions. have high melting and
WRITING FORMULAS: MOLAR MASS, %COMPOSITION, EMPIRICAL AND MOLECULAR FORMULAS
 WRITING FORMULAS: MOLAR MASS, %COMPOSITION, EMPIRICAL AND MOLECULAR FORMULAS REVIEW: Polyatomic ions, writing names from formulas, oxidation number rules I. WRITING FORMULAS FROM NAMES: A. Rules: 1. Know
WRITING FORMULAS: MOLAR MASS, %COMPOSITION, EMPIRICAL AND MOLECULAR FORMULAS REVIEW: Polyatomic ions, writing names from formulas, oxidation number rules I. WRITING FORMULAS FROM NAMES: A. Rules: 1. Know
26. N 2 + H 2 NH N 2 + O 2 N 2 O 28. CO 2 + H 2 O C 6 H 12 O 6 + O SiCl 4 + H 2 O H 4 SiO 4 + HCl 30. H 3 PO 4 H 4 P 2 O 7 + H 2 O
 Balance the following chemical equations: (Some may already be balanced.) 1. H 2 + O 2 H 2 O 2. S 8 + O 2 SO 3 3. HgO Hg + O 2 4. Zn + HCl ZnCl 2 + H 2 5. Na + H 2 O NaOH + H 2 6. C 10 H 16 + Cl 2 C +
Balance the following chemical equations: (Some may already be balanced.) 1. H 2 + O 2 H 2 O 2. S 8 + O 2 SO 3 3. HgO Hg + O 2 4. Zn + HCl ZnCl 2 + H 2 5. Na + H 2 O NaOH + H 2 6. C 10 H 16 + Cl 2 C +
Systematic Naming. Chapter 9. Two Types of Compounds. Two Types of Compounds 2 Ionic Compounds. Two Types of Compounds.
 Chapter 9 Naming Compounds Writing Formulas Systematic Naming There are too many compounds to remember the names of them all. Compound is made of two or more elements. Put together atoms. Name should tell
Chapter 9 Naming Compounds Writing Formulas Systematic Naming There are too many compounds to remember the names of them all. Compound is made of two or more elements. Put together atoms. Name should tell
Personal Guided Inquiry: Naming Chemical Compounds and Writing Formulas
 Personal Guided Inquiry: Naming Chemical Compounds and Writing Formulas As you work through the online videos, make notes of important ideas and practice what you are learning. These skills are some of
Personal Guided Inquiry: Naming Chemical Compounds and Writing Formulas As you work through the online videos, make notes of important ideas and practice what you are learning. These skills are some of
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Chapter 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Dalton s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. Elements are composed of extremely small
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Chapter 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Dalton s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. Elements are composed of extremely small
Chapter 6 Chemical Names and Formulas
 Chemistry/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 6 Chemical Names and Formulas Chapter 6: 1 9, 12, 14 24, 26 28, 31 36, 40, 42, 49, 52, 53, 56, 58, 62, 67 (37 total) 1. Provide the name and symbol of the ion formed
Chemistry/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 6 Chemical Names and Formulas Chapter 6: 1 9, 12, 14 24, 26 28, 31 36, 40, 42, 49, 52, 53, 56, 58, 62, 67 (37 total) 1. Provide the name and symbol of the ion formed
Nomenclature. Naming Compounds
 Nomenclature Naming Compounds Ionic Compounds Metal bonding with non-metal One atom gains electrons, one atom loses electrons Exist as ions with full highest energy levels. Are held together in a giant
Nomenclature Naming Compounds Ionic Compounds Metal bonding with non-metal One atom gains electrons, one atom loses electrons Exist as ions with full highest energy levels. Are held together in a giant
nomenclature nomen name + clatura calling Download the naming reference charts today!
 nomenclature nomen name + clatura calling Download the naming reference charts today! first we learn about binary cmpds, cmpds made of two elements there are two classes of binaries: metal/nonmetal & nonmetal/nonmetal
nomenclature nomen name + clatura calling Download the naming reference charts today! first we learn about binary cmpds, cmpds made of two elements there are two classes of binaries: metal/nonmetal & nonmetal/nonmetal
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
 Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1. According to the law of definite proportions, A) the ratio of the masses of the elements in a compound is always the same. B) it is not possible for the same two
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1. According to the law of definite proportions, A) the ratio of the masses of the elements in a compound is always the same. B) it is not possible for the same two
How to become a formulation hero
 How to become a formulation hero Basics you will need to know these and a couple more! Write the symbols and oxidation numbers for these elements (hint: these only have one ox. number): 1. Lithium, sodium
How to become a formulation hero Basics you will need to know these and a couple more! Write the symbols and oxidation numbers for these elements (hint: these only have one ox. number): 1. Lithium, sodium
Particle Relative Mass Charge
 ADVANCED CHEMISTRY REVISION THE FIRST 5 WEEKS 1. Define each of the following words so that you can differentiate between them:- ELEMENT and COMPOUND, ATOM and MOLECULE An element is comprised of one type
ADVANCED CHEMISTRY REVISION THE FIRST 5 WEEKS 1. Define each of the following words so that you can differentiate between them:- ELEMENT and COMPOUND, ATOM and MOLECULE An element is comprised of one type
Chapter 6. Naming Compounds Writing Formulas
 Chapter 6 Naming Compounds Writing Formulas Systematic Naming There are too many compounds to remember the names of them all. Compound is made of two or more elements. Put together atoms. Name should tell
Chapter 6 Naming Compounds Writing Formulas Systematic Naming There are too many compounds to remember the names of them all. Compound is made of two or more elements. Put together atoms. Name should tell
Chapter 9 Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Chapter 9 Study Guide Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. monatomic ion f. cation b. acid g. binary compound c. base h. anion d. law of definite proportions
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 9 Study Guide Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. monatomic ion f. cation b. acid g. binary compound c. base h. anion d. law of definite proportions
AP Chemistry - Summer Assignment
 AP Chemistry - Summer Assignment NOTE: a. MUST SHOW ALL WORK FOR CREDIT!! b. Where work is required, do on a separate sheet of paper c. These are the foundational things you should be able to do when you
AP Chemistry - Summer Assignment NOTE: a. MUST SHOW ALL WORK FOR CREDIT!! b. Where work is required, do on a separate sheet of paper c. These are the foundational things you should be able to do when you
AP Chemistry Unit 1 Review Guide: IUPAC Naming, Stoichiometry, Solution Chemistry
 I. IUPAC Naming AP Chemistry Unit 1 Review Guide: IUPAC Naming, Stoichiometry, Solution Chemistry For Ionic Compounds: Formula to Name: 1. Identify the cation (positive ion) by name, then identify the
I. IUPAC Naming AP Chemistry Unit 1 Review Guide: IUPAC Naming, Stoichiometry, Solution Chemistry For Ionic Compounds: Formula to Name: 1. Identify the cation (positive ion) by name, then identify the
NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS
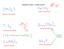 NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS iron(ii) carbonate ammonium sulfide titanium (IV) sulfide barium phosphate Spelling matters! calcium nitrate sodium phosphide DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE
NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS iron(ii) carbonate ammonium sulfide titanium (IV) sulfide barium phosphate Spelling matters! calcium nitrate sodium phosphide DETERMINING THE FORMULA OF AN IONIC COMPOUND FROM THE
2H 2 (g) + O 2 (g) 2H 2 O (g)
 Mass A AP Chemistry Stoichiometry Review Pages Mass to Mass Stoichiometry Problem (Review) Moles A Moles B Mass B Mass of given Amount of given Amount of unknown Mass of unknown in grams in Moles in moles
Mass A AP Chemistry Stoichiometry Review Pages Mass to Mass Stoichiometry Problem (Review) Moles A Moles B Mass B Mass of given Amount of given Amount of unknown Mass of unknown in grams in Moles in moles
Ions and Ionic Compounds
 Ions and Ionic Compounds Elements combine in a specific ratio to form compounds. Compounds can be categorized as ionic or covalent depending on the type of bond present within the compound. Ionic compounds
Ions and Ionic Compounds Elements combine in a specific ratio to form compounds. Compounds can be categorized as ionic or covalent depending on the type of bond present within the compound. Ionic compounds
Honors Chemistry - Unit 5 Chapter 7 - Nomenclature
 Honors Chemistry - Unit 5 Chapter 7 - Nomenclature Unit 5 Packet - Page 1 of 16 Vocab Due: Quiz(zes): 1) Test Date: UT Quest: 2) VOCABULARY: 1) monatomic ion 2) cation 3) anion 4) binary compound 4) ionic
Honors Chemistry - Unit 5 Chapter 7 - Nomenclature Unit 5 Packet - Page 1 of 16 Vocab Due: Quiz(zes): 1) Test Date: UT Quest: 2) VOCABULARY: 1) monatomic ion 2) cation 3) anion 4) binary compound 4) ionic
2. Covalent bonds result from the sharing of valence electrons between two atoms.
 CHAPTER 2.8 NAMING AND WRITING FORMULAS FOR IONIC AND COVALENT COMPOUNDS, ACIDS, AND HYDRATES Alpharetta High School Dr. Sonha Payne Elements combine to form compounds by the interaction of their valence
CHAPTER 2.8 NAMING AND WRITING FORMULAS FOR IONIC AND COVALENT COMPOUNDS, ACIDS, AND HYDRATES Alpharetta High School Dr. Sonha Payne Elements combine to form compounds by the interaction of their valence
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A molecule of water contains hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:8 ratio by mass. This is a statement
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A molecule of water contains hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:8 ratio by mass. This is a statement
Chemistry Chapter 7 Test
 Chemistry Chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A chemical formula includes the symbols of the elements in the compound and subscripts
Chemistry Chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A chemical formula includes the symbols of the elements in the compound and subscripts
2. The reaction of carbon monoxide and diiodine pentoxide as represented by the equation
 1. The complete combustion of phenylhydrazine, C 6 H 5 NHNH 2, with the oxidizer dinitrogen tetraoxide is shown in the equation C 6 H 5 NHNH 2 + N 2 O 4 CO 2 + H 2 O + N 2 When balanced, the sum of all
1. The complete combustion of phenylhydrazine, C 6 H 5 NHNH 2, with the oxidizer dinitrogen tetraoxide is shown in the equation C 6 H 5 NHNH 2 + N 2 O 4 CO 2 + H 2 O + N 2 When balanced, the sum of all
Extra Credit Directions
 Extra Credit Directions 1. Everything must be correct in order to receive extra credit. There is no partial extra credit. 2. Using the provided charts, you will end in one of the outlined boxes that have
Extra Credit Directions 1. Everything must be correct in order to receive extra credit. There is no partial extra credit. 2. Using the provided charts, you will end in one of the outlined boxes that have
Why does an element want to bond?
 Why does an element want to bond? State 3 differences between ionic vs. covalent compounds What is a chemical formula? It indicates the relative number of atoms of each kind in an ionic compound. Ex Al
Why does an element want to bond? State 3 differences between ionic vs. covalent compounds What is a chemical formula? It indicates the relative number of atoms of each kind in an ionic compound. Ex Al
Write the name or formula for:
 Do Now Date: Tuesday, November 2, 2015 Objective: Name and write formulas for ionic and molecular (covalent) compounds. Write the name or formula for: K 2 SO 4 NaNO 3 Calcium Hydroxide Tuesday, November
Do Now Date: Tuesday, November 2, 2015 Objective: Name and write formulas for ionic and molecular (covalent) compounds. Write the name or formula for: K 2 SO 4 NaNO 3 Calcium Hydroxide Tuesday, November
Nomenclature (Naming Compounds) and Chemical Formulas
 Nomenclature (Naming Compounds) and Chemical Formulas 1 Ions formed from a single atom Monatomic Ions Charges are determined by whether ion has lost electrons (+) or gained electrons (-) Symbols are written
Nomenclature (Naming Compounds) and Chemical Formulas 1 Ions formed from a single atom Monatomic Ions Charges are determined by whether ion has lost electrons (+) or gained electrons (-) Symbols are written
CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 6 - Nomenclature Practice Problems
 Name Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 6 - Nomenclature Practice Problems Due Date Assignment On-Time (100) Late (70) 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Warm-Up EC Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located
Name Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 6 - Nomenclature Practice Problems Due Date Assignment On-Time (100) Late (70) 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Warm-Up EC Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located
DETERMINING IONIC FORMULAS strontium oxide
 69 sodium sulfate DETERMINING IONIC FORMULAS strontium oxide tin(ii) phosphate chromium(iii) nitrate barium hydroxide titanium(iv) chloride Note: Be careful when adding subscripts to HYDROXIDE, CYANIDE,
69 sodium sulfate DETERMINING IONIC FORMULAS strontium oxide tin(ii) phosphate chromium(iii) nitrate barium hydroxide titanium(iv) chloride Note: Be careful when adding subscripts to HYDROXIDE, CYANIDE,
 Name Date Class 9 CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS SECTION 9.1 NAMING IONS (pages 253 258) This section explains the use of the periodic table to determine the charge of an ion. It also defines polyatomic ion
Name Date Class 9 CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS SECTION 9.1 NAMING IONS (pages 253 258) This section explains the use of the periodic table to determine the charge of an ion. It also defines polyatomic ion
Summary for Naming Compounds
 Summary for Naming Compounds 1. Group 1, 2, 3 metal with Group 15, 16, 17 nonmetals 2. Group 1, 2, 3, metal with polyatomic ions 3. Transition/other metal with Group 15, 16, 17 nonmetal 4. Transition/other
Summary for Naming Compounds 1. Group 1, 2, 3 metal with Group 15, 16, 17 nonmetals 2. Group 1, 2, 3, metal with polyatomic ions 3. Transition/other metal with Group 15, 16, 17 nonmetal 4. Transition/other
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
 Download full Download Chemical Principles 7th Edition by Zumdahl Test Bank https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/download-chemical-principles-7th-edition-by-zumdahl-te st-bank Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules,
Download full Download Chemical Principles 7th Edition by Zumdahl Test Bank https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/download-chemical-principles-7th-edition-by-zumdahl-te st-bank Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules,
Experiment #4. Chemical Nomenclature
 Experiment #4. Chemical Nomenclature Many everyday and historically important chemical compounds have common names. For example, water is the common name for H 2 O, baking soda is the common name for NaHCO
Experiment #4. Chemical Nomenclature Many everyday and historically important chemical compounds have common names. For example, water is the common name for H 2 O, baking soda is the common name for NaHCO
Welcome to AP Chemistry!
 Welcome to AP Chemistry! You will quickly notice that things will be different than they were in Honors Chemistry. For one, you must memorize a lot of the information that was given to you on the Chemistry
Welcome to AP Chemistry! You will quickly notice that things will be different than they were in Honors Chemistry. For one, you must memorize a lot of the information that was given to you on the Chemistry
Chapter 3 - Molecules, Compounds and Chemical Equations
 Chapter 3 - Molecules, Compounds and Chemical Equations Section 3.2 two general types of bonding between atoms found in compounds, ionic and covalent ionic bonds result when electrons have been transferred
Chapter 3 - Molecules, Compounds and Chemical Equations Section 3.2 two general types of bonding between atoms found in compounds, ionic and covalent ionic bonds result when electrons have been transferred
Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations
 Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations Molecular View of Elements and Compounds 2 How do atom join together to form a compound? compounds are made of atoms held together by chemical bonds
Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations Molecular View of Elements and Compounds 2 How do atom join together to form a compound? compounds are made of atoms held together by chemical bonds
Inorganic Nomenclature
 Inorganic Nomenclature A. The Chemical Elements 1. The term INORGANIC NOMENCLATURE refers to the naming of elements and inorganic compounds. Recall that ELEMENTS are the simplest form of matter that cannot
Inorganic Nomenclature A. The Chemical Elements 1. The term INORGANIC NOMENCLATURE refers to the naming of elements and inorganic compounds. Recall that ELEMENTS are the simplest form of matter that cannot
