What is pollination? How you can help
|
|
|
- Solomon Esmond Dalton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3 What is pollination? Bees Birds Bats Butterflies How you can help
4 What is pollination? Pollination is a very important part of a plant s life cycle. During pollination, pollen from the anther, the male part of the flower, is moved to the stigma, the female part of the flower, to form seeds that later grow into new plants. Some plants, such as wheat, rice, corn, rye, barley and oats, use the wind for pollination. The male plants make dry, lightweight pollen. When the wind blows, the pollen travels with it to the female plants. Other plants need a little help from insects and animals called pollinators. Some examples are bees, birds, bats and butterflies. Plants and pollinators form special relationships with one another. The plants provide food, called nectar, to the pollinators. When a pollinator eats from a flower, it ends up getting some of the plant s pollen on it. When it flies to other flowers, it takes that pollen with it and spreads it to other plants. 2 Pollinators at Mizzou
5 Pollen is found on the anther of the flower and can be all sorts of different colors. When pollen reaches the stigma, it is fertilized and turns into a seed for a new plant! Stigma Style Pollen grain Pollen tube Pistil Stamens Ovary Ovules Petals Pollen Anther Sepals Filament Pollinators at Mizzou 3
6 Did you know? Bees, birds and other pollinators work hard to help make some of your favorite foods. Here s a look at just a few foods that wouldn t be possible without pollinators. Apples: honey bees and blue mason orchard bees Bananas: birds and fruit bats Blueberries: more than 115 kinds of bees, including bumblebees, mason bees, mining bees and leafcutter bees Cherries: honey bees, bumblebees, solitary bees and flies Chocolate: midges (tiny flies) and stingless bees Milk, cheese and ice cream: Dairy cows eat alfalfa, which is pollinated by leafcutter and honey bees Grapes: bees Strawberries: bees Tea plants: flies, bees and other insects Tomatoes: bumblebees Vanilla: bees How many of these foods have YOU eaten this month? Hey you! Because plants need pollinators to help them produce fruit and seeds, they have developed some clever ways to get the pollinators attention. Color: Colors and markings on flowers help attract certain birds and insects. For example, bees like bright blue and violet flowers. Hummingbirds like red, pink, fuchsia and purple flowers. Butterflies like bright colors such as yellow, orange, pink and red. Fragrance: Sweet-smelling flowers are a good way to get attention from a pollinator that doesn t see color. Moths and bats, which come out at night, are attracted to fragrant flowers. Shape: A flower s shape also attracts pollinators. Butterflies like flowers with flat petals, which they use like a landing strip. Hummingbirds like long, tubular flowers that are easy for them to fit their long, thin beaks into to gather nectar. Look around you. What kinds of pollinators do you think are attracted to the flowers you see? Who cares? You should! Pollinators are responsible for producing one out of every three bites of food we take. Pollinators are so important that some farmers make a point to make homes for them in and near their fields. Pollinators also play an important role in their natural ecosystems. They help 95 percent of all flowering plants reproduce, and they are an important food source for many larger animals. A bird, for example, can eat more than 700 caterpillars in one day! But pollinator populations have declined over the years because of habitat loss, pollution, chemicals, diseases and changing climates. Today we will learn about some of the most common pollinators in our area and how we can help save them. 4 Pollinators at Mizzou
7 Did you know one out of every three bites of food is thanks to a pollinator? Without bees, butterflies, bats and birds, our diets wouldn t be as healthy or delicious. Let s take a look at what the lunchroom would look like without them. School Lunch: What s on the menu with pollinators? Chips with seasoning Burger with sesame seed bun, cheese, lettuce, tomato, pickle, onion, ketchup, mustard Milk Apple What if we didn t have pollinators? Your lunch would be a really boring if we didn t have pollinators! A burger bun with lettuce doesn t match up to a burger and its toppings. Even if you were excited about your chips, some of the seasonings that make them tasty would be gone. Chips Bun with lettuce Pollinators at Mizzou 5
8 Native Bees Bees are one of the hardest-working pollinators around. There are more than 4,000 native bee species in the United States. Of these, about 452 live in Missouri. Here are some of the most common native bees you ll find around here. Carpenter Bees Carpenter bees get their name because they make their nests in wood. The males hover around the nests to scare away predators, but don t worry they can t sting. Carpenter bees are big. Some can grow almost the size of an adult s thumb! Leafcutter Bees Leafcutter bees get their name because they cut leaves to make their nests. Most bees carry pollen on their legs, but leafcutter bees carry it on their bellies. If you like ice cream, then the alfalfa leafcutter bee is your hero. Almost 100 years ago, farmers started noticing that it was harder to grow alfalfa, a legume like beans we feed dairy cows. But the alfalfa leafcutter bee saved the alfalfa crop and in turn saved delicious ice cream! Bumblebees Bumblebees get their name from Middle English bombeln, which means to boom or buzz. To bumble also means to move in a clumsy manner, a lot like the way bumblebees fly. Bumblebees live underground in colonies with other bees. Bumblebees are such good pollinators that some farmers and plant growers release them in their fields and greenhouses. Buck s Ice Cream Did you know that the University of Missouri has been studying ice cream since the 1920s? Buck s Ice Cream is famous for its favorite flavor, Tiger Stripe Ice Cream which is swirled to look like Truman the Tiger s coat! Sweat Bees On hot days, you might get a visit from a sweat bee. Sweat bees are attracted to salt in sweat. Sweat bees nest in the ground or in rotten wood. Some live alone and some live with other sweat bees. We think of bees as being black and yellow, but sweat bees also can be metallic green. 6 Pollinators at Mizzou
9 Honey bees are responsible for more than just pollination they make delicious honey! In the wild, honey bees make their homes in old tree trunks. But most of the honey we eat is harvested by beekeepers who manage the hives. Hive Structure: Outer cover Inner cover Super Hive body Bottom board Hive stand 3. Honey bees fill the frames combs so they can store honey and baby bees Pollinators at Mizzou 7
10 Worker Bees Smaller than drones and the queen, workers bees are all female and make up the majority of the bees in a hive. Sometimes they wear pollen pants, which is what beekeepers call it when a bee carries bundles of pollen on its legs. Worker bees also help with cleaning and guarding the hive, looking for food and caring for baby bees and the queen. Drones Each hive has a small population of male drones. They mate with queens from other hives and then die. Sometimes they are mistaken for the queen because of their size, but they have much bigger, bulgier eyes. Queen The queen has a long, slender, pointy body. She lays eggs all day and is fed and cleaned by her royal court of worker bees. There is only one queen per hive. Brood The brood is the egg, larva and pupa are stages for bees when they grow from babies to adult worker bees. The bees cover or cap the brood to protect it while the baby bee gets ready to hatch. Eggs are very hard to see because they are smaller than a grain of rice. The larvae look like little white worms that curl up into a circle. Pupae eventually hatch from the capped brood and wiggle their way out. Honey Everyone knows what honey looks like! After bees have finished making it, they seal or cap it. Honey is syrupy and sweet and can have different flavors depending on the flower the nectar came from. Bees feed themselves with honey over the winter when there are no flowers blooming. Did you know honey can be used to treat wounds and allergies? The best thing about honey is that it is the only food in the world that stays fresh forever if it is properly stored. Scientists have even found honey in the Egyptian pyramids! Pollen Pollen looks dusty and helps feed bees. Honeybees carry pollen on their legs. It comes in all sorts of different colors depending on the plant. Bees store pollen in their comb so they can feed themselves while in the hive. When it is stored in the hive, it looks clumpy. Wax Wax is the structure bees make their comb with. It is shaped like a hexagon and filled with the brood, pollen and honey. Bees are very particular when they build their homes, and even have a universal spacing in between the wax combs called bee space. Humans use beeswax for things like candles and lip balm. Propolis Propolis is a dark, glue-like substance bees use to seal cracks in the hive. Bees make it by mixing their spit with tree sap. 8 Pollinators at Mizzou
11 What s the buzz? Honey bee fun facts Honey bees were first brought from Europe to the United States in the 17th century. Honey bees pollinate 80 percent of flowering crops in the United States. Missourians love honey bees so much they made the honey bee the official state insect! Many bees live in social colonies, which are a lot like tiny towns. The queen bee is the boss of all the other bees, and she is the only bee that can have babies. The worker bees make honey, clean the hive and feed baby bees. The males leave the nest to mate and then die. As many as 60,000 bees live in one hive. Can you imagine living with that many people in such a small space? Did you know? They like to move it, move it Honey bees might make a lot of noise, but they talk to each other by dancing. They use a round dance to tell each other how to get to nearby food sources and a waggle dance to tell each other how to get to food located farther away. Nobody likes getting stung by a bee, but it hurts the bee more than it hurts you. In fact, honey bees die after they sting people, so do not scare them! Bees can nest in the wild, but they are easily managed by humans. Round Dance A beekeeper at Mizzou Botanic Garden shows off a frame from a hive. Waggle Dance Pollinators at Mizzou 9
12 Birds There are between 350 and 400 bird species in Missouri. Although birds do not pollinate food crops, some species play an important role in pollinating wildflowers. Hummingbirds are especially important pollinators. All about Bluebirds Pollinators make food for us, and they are food for many of our favorite songbirds, including the Eastern bluebird, which is Missouri s state bird. Here are some fun facts about bluebirds: Bluebirds live in open areas and edges of woodlands with assorted trees and shrubs. They live in tree cavities and make their nests out of twigs, loose grasses and pine needles. Bluebirds love to eat wild fruit and insects. If you want to attract them to your yard, you should put out feeders filled with mealworms, dried fruit, suet, peanut butter and cornmeal. Male bluebirds are a beautiful bright blue, while females are pale blue and brown, which allows them to hide from predators while they sit on their eggs. Since 1996, almost 2,500 have hatched and fledged in the birdhouses at Mizzou s A.L. Gustin Golf Course. In addition to bluebirds, more than 80 bird species have been seen by golfers and bird enthusiasts. Many have been common Missouri birds such as blue jays and robins, but there also have been some unusual visitors you might not expect on a golf course. These include: Turkey vultures Mallards Barred owls Yellow-bellied sapsuckers Eastern wood pewees Bald eagles Snow geese Bluebirds don t just have blue feathers. They also lay small, pale blue eggs. At Mizzou s A.L. Gustin Golf Course, staff have helped restore bluebird populations by putting out birdhouses for them. 10 Pollinators at Mizzou
13 How to: Make hummingbird food Combine 4 cups water and 1 cup sugar in a pot and stir until sugar is dissolved. Sugar Water Stir regularly as you bring water to a boil, then remove from heat. What s the buzz? Hummingbird fun facts The ruby-throated hummingbird is the most common hummingbird in Missouri. These migratory birds are seen in Missouri from May to September, then they fly to Mexico and South America for the winter. These tiny birds don t take up much space their nests are half the size of ping-pong balls! But don t be fooled by their small size. Hummingbirds have huge appetites. They drink eight times their bodyweight in nectar each day. Cover pot and allow to cool, then pour into hummingbird feeder. Hummingbirds can t smell, so they rely on their sight to find food. Bright red and orange flowers like Indian Pink, Columbine and Butterfly Milkweed are good for attracting hummingbirds. Hummingbirds are amazing flyers! They flap their wings an average of 53 times per second, which allows them to hover over the flowers they feed from. They also can fly backward and even upside down! Hang your hummingbird feeder in a quiet spot where the hummingbirds won t be disturbed. If you want to attract hummingbirds to your yard, you should fill a red feeder with sugar water. Pollinators at Mizzou 11
14 Bats They might be easy to overlook because they come out at night, but bats also play a big role in pollination of tropical and desert plants and in their ecosystems! There are 14 bat species in Missouri. Here are some you might see flying around Columbia: Big Brown Bat If you encounter a bat in Columbia, it s very likely to be a big brown bat. This species eats beetles, so it has large teeth that allow it to crunch through hard beetle shells. These are the largest bats you ll find living in Missouri caves, but they ve also learned to live in people s barns, attics and porches. Despite the name, they are not really very big the largest are about the size of an iphone. Eastern Red Bat Eastern red bats are a hibernating species, meaning they fly south for the winter so they can keep hunting their favorite food moths. In the summer, this species roosts in the tops of oak and maple trees, where it hangs on to the ends of leaves, which means they are pretty light. Most weigh as much as two nickels. These clever animals have learned to use human inventions to help them hunt. Moths are attracted to street lights, and so the eastern red bat often can be found in neighborhoods or city parks. 12 Pollinators at Mizzou
15 Eastern Pipistrelle Also called the tri-colored bat, the eastern pipistrelle usually is yellowish or pale reddish brown in color. They have small ears and are 3 3 ½ inches long with an additional tail length of 1 ½ to 1 ¾ inches. In the summer, they roost in trees and in crannies in cliffs or buildings. They primarily eat insects. Fact or Fiction: Bat Edition There are a lot of myths about bats. Here s a look at what s true and false. Bats are flying mice. Actually, they aren t even related to mice. Bats have much more in common with primates including humans! and lemurs. Bats are the only flying mammal in the world, and baby bats called pups can start flying as soon as five weeks after they are born. Bats are vampires. Gray Bat Gray bats are the largest of the myotis, or mouseeared bats. Their bodies are only about 3 inches long, but they have a wing span of inches. Gray bats are insectavores, and they mostly eat on the wing, or while flying. Gray bats once flourished in Missouri s limestone caves, but today they are an endangered species. Other bat populations in the United States are declining, too. Some causes include habitat loss; white-nose syndrome, a fungal disease brought over by humans traveling from Eurasia; and deaths caused by wind turbines. Well, that s partially true. There are three species of vampire bats, but they do not attack humans or drink our blood. Instead, they suck the blood of sleeping animals, such as cattle or sheep in a pasture. The rest of the world s bat species live on insects, fruit, nectar and pollen. Many of the insects bats eat are harmful to Missouri crops such as cotton and corn. In addition to helping protect the food we eat, bats provide food to other animals bat poop, also called guano, helps feed many of the other animals found in caves. Bats are blind. Not true at all. Most bats see at least as well as humans. However, because they fly at night, they have to use their other senses. Bats navigate and find their food through echolocation. They make a high-pitched noise and then listen to hear how long it takes for the sound to bounce back to them. Pollinators at Mizzou 13
16 Butterflies Butterflies are another pretty pollinator. In Missouri, there are about 200 butterfly species. Here are a few common types: Viceroys, which have black and orange wings, look very similar to monarchs. You can tell them apart by looking for a line that crosses the black hindwing and a row of white spots in the black wing margins. Sulphurs are medium-sized butterflies that can be yellow, orange, white or neon green. Monarchs are large butterflies with black and orange wings. They eat only milkweed, and many Missourians have started planting milkweed to encourage monarch population growth. Swallowtails are recognizable by the long tails on their bottom wings. The Eastern Tiger Swallowtail is a large butterfly. They often are yellow with black tiger stripes, but can also be black and blue. 14 Pollinators at Mizzou
17 How to: Build a butterfly garden First, choose a spot that gets plenty of sun but isn t too windy. Trees or shrubs will provide butterflies with a place to get out of the wind, which makes it easier for them to explore. You ll also get more butterflies if you provide some sort of water feature such as a puddling station. Next, choose an assortment of plants that butterflies like. Butterflies love bright colors and flowers with plenty of pollen and nectar. Some of their favorites are: Butterfly Life Cycle 1. Egg Butterfly Weed Blazing Star Purple Coneflower Asters Joe Pye Weed You also should choose some plants for butterflies to lay their eggs. We refer to plants butterflies lay their eggs on as host plants, and some butterflies will only use certain plants. Some good choices are: Milkweed Hackberry Parsley Spicebush Pawpaw While we tend to think of gardening as a summer activity, a butterfly garden should have plants that bloom in the spring and fall as well. Monarchs lay their eggs in the spring and migrate in the fall, and they need fuel! Other species do not migrate and so will need cover to hibernate. If you re just starting your butterfly garden, it might be a while before you have enough flowers to feed a kaleidoscope of butterflies, but you can use over-ripe fruit from your kitchen as a food and nectar source for them. If you re just starting your butterfly garden, it might be a while before you have enough flowers to feed a kaleidoscope of butterflies, but you can use over-ripe fruit as a food and nectar source for them. Just cut it up to allow the butterflies easy access to the fruit s juices. 2. Larva (Caterpillar) 3. Pupa (Chrysalis) 4. Adult (Butterfly) Pollinators at Mizzou 15
18 Now that you know how important pollinators are to our day-today lives, you might be wondering what you can do to help them. Fortunately, there are a number of things to do to help. Here are a few ideas: Plant pollinator gardens. Choose flowering plants pollinators like, such as blue wild indigo, wild hydrangea, blazing star, bee balm, foxglove beardtongue and showy goldenrod. Trees also are important for pollinators. Oak, blueberry, maple and elm tree leaves are favorite foods for many butterfly and moths. Don t forget a water source! Provide nesting areas for pollinators. Butterfly gardens, bird houses, bat houses and bee hotels all make great homes for pollinators. Buy local food especially honey at the farmers market. Many local farmers know how important pollinators are, so they make efforts to use fewer chemicals if any at all and plant pollinator-friendly plants in their fields. Tell your friends and family how important pollinators are! 16 Pollinators at Mizzou
19 Notes: Pollinators at Mizzou 17
20 Notes: 18 Pollinators at Mizzou
21 Notes: Pollinators at Mizzou 19
22 Notes: 20 Pollinators at Mizzou
23 Notes: Pollinators at Mizzou 21
24
How Does Pollination Work?
 How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service. Attracting Pollinators to Your Garden
 U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Attracting Pollinators to Your Garden Why are Pollinators Important? Pollinators are nearly as important as sunlight, soil and water to the reproductive success of over 75%
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Attracting Pollinators to Your Garden Why are Pollinators Important? Pollinators are nearly as important as sunlight, soil and water to the reproductive success of over 75%
Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People
 Theme: Spring in the Garden Grade Level: K- 5 th Time Required: 45 minutes Number of Students: 15-25 Buzzy Buzzy Bee! Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People Description Students learn about pollination
Theme: Spring in the Garden Grade Level: K- 5 th Time Required: 45 minutes Number of Students: 15-25 Buzzy Buzzy Bee! Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People Description Students learn about pollination
Pollinator Slide Show Notes DIRECTIONS IN ALL CAPS 1
 Pollinator Slide Show Notes DIRECTIONS IN ALL CAPS 1 THIS PRESENTATION IS INTENDED TO BE USED IN SECTIONS TO SUPPORT TEACHING ON THE TOPICS PRESENTED. ANY OF THE SLIDES CAN BE USED AS HANDOUTS. YOU CAN
Pollinator Slide Show Notes DIRECTIONS IN ALL CAPS 1 THIS PRESENTATION IS INTENDED TO BE USED IN SECTIONS TO SUPPORT TEACHING ON THE TOPICS PRESENTED. ANY OF THE SLIDES CAN BE USED AS HANDOUTS. YOU CAN
o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee?
 o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee? *NOTE: The queen in Observation Hive #1 has a yellow mark on her. Put the wooden panels
o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee? *NOTE: The queen in Observation Hive #1 has a yellow mark on her. Put the wooden panels
Elementary Science: Pollination
 Elementary Science: Pollination A collection of hands-on lessons and activities for the elementary classroom that explore the process and importance of pollination and pollinators. Table of Contents A
Elementary Science: Pollination A collection of hands-on lessons and activities for the elementary classroom that explore the process and importance of pollination and pollinators. Table of Contents A
Dedicated to bees, and My dad who loved reading to the kids on his lap, My children who spent plenty of time on his lap and mine, And Melvin, who
 Dedicated to bees, and My dad who loved reading to the kids on his lap, My children who spent plenty of time on his lap and mine, And Melvin, who thinks all laps belong to him. Published by Melvin TC PO
Dedicated to bees, and My dad who loved reading to the kids on his lap, My children who spent plenty of time on his lap and mine, And Melvin, who thinks all laps belong to him. Published by Melvin TC PO
 Honeybees There are more than 22,000 types of bees in the world. Do you know which bees make honey? Without honeybees, you wouldn t have any honey to spread on your toast in the morning. You may have seen
Honeybees There are more than 22,000 types of bees in the world. Do you know which bees make honey? Without honeybees, you wouldn t have any honey to spread on your toast in the morning. You may have seen
Where in the world does your food come from?
 Pollinators come in all species, sizes, shapes and shades Where in the world does your food come from? Do you eat fruits? vegetables? nuts? seeds? grains? Where do you get them? Usually Mom or Dad go to
Pollinators come in all species, sizes, shapes and shades Where in the world does your food come from? Do you eat fruits? vegetables? nuts? seeds? grains? Where do you get them? Usually Mom or Dad go to
Bee Colony Activities Throughout The Year
 Bee Colony Activities Throughout The Year Written by Khalil Hamdan Apeldoorn The Netherlands A honeybee gathering nectar from a flower. Photo source: forestwander.com Bee collecting pollen. Photo source:
Bee Colony Activities Throughout The Year Written by Khalil Hamdan Apeldoorn The Netherlands A honeybee gathering nectar from a flower. Photo source: forestwander.com Bee collecting pollen. Photo source:
Pollinator Activity Guide
 Pollinator Activity Guide Two-tailed tiger swallowtail on western serviceberry Learn about pollinators and native plants and why we need them. What are pollinators and why should we care? Have you ever
Pollinator Activity Guide Two-tailed tiger swallowtail on western serviceberry Learn about pollinators and native plants and why we need them. What are pollinators and why should we care? Have you ever
Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program
 Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Pollination is a sticky situation. In this active lesson, students learn
Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Pollination is a sticky situation. In this active lesson, students learn
Pollinator Adaptations
 Adapted from: Life Lab Garden Pollinators unit Pollinator Adaptations Overview: Students will learn about pollinators and their adaptations, and match flowers to the kinds of pollinators they attract.
Adapted from: Life Lab Garden Pollinators unit Pollinator Adaptations Overview: Students will learn about pollinators and their adaptations, and match flowers to the kinds of pollinators they attract.
NATURE S. Insect Pollinators, Plants, and. The pedigree of honey Does not concern the bee; A clover, anytime, to her Is aristocracy.
 NATURE S Insect Pollinators, Plants, and The pedigree of honey Does not concern the bee; A clover, anytime, to her Is aristocracy. Emily Dickenson The basics of cross-pollination 1. The petals attract
NATURE S Insect Pollinators, Plants, and The pedigree of honey Does not concern the bee; A clover, anytime, to her Is aristocracy. Emily Dickenson The basics of cross-pollination 1. The petals attract
Lesson: Honeybees and Trees
 Camp Woodlands/Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Revised 2016 Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten
Camp Woodlands/Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Revised 2016 Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten
The All-Ireland Pollinator Plan
 The All-Ireland Pollinator Plan Pollen is the fine powder inside a flower. Flowers use pollen to make new seeds. To make a seed, plants need to move pollen from one flower to another flower of the same
The All-Ireland Pollinator Plan Pollen is the fine powder inside a flower. Flowers use pollen to make new seeds. To make a seed, plants need to move pollen from one flower to another flower of the same
Pollinator Activity #1: How to Raise a Butterfly
 How to Raise a Butterfly How to Raise a Butterfly A Conversation Where do you most often see butterflies? What are they doing when you see them? Have you ever seen a butterfly in another form? They have
How to Raise a Butterfly How to Raise a Butterfly A Conversation Where do you most often see butterflies? What are they doing when you see them? Have you ever seen a butterfly in another form? They have
A Gallery of Important Insect Pollinators
 A Gallery of Important Insect Pollinators Bees Beetles Flies Wasps Butterflies Moths Who Are the Pollinators and What Do They Need to be Effective? Bees Attracted to bright white, yellow, orange, blue
A Gallery of Important Insect Pollinators Bees Beetles Flies Wasps Butterflies Moths Who Are the Pollinators and What Do They Need to be Effective? Bees Attracted to bright white, yellow, orange, blue
Lesson: Why a Butterfly Garden? Seeking Pollinator Certification for a Butterfly Garden
 Lesson: Why a Butterfly Garden? Seeking Pollinator Certification for a Butterfly Garden What is the primary threat to most endangered species? Why is our butterfly and pollinator population declining?
Lesson: Why a Butterfly Garden? Seeking Pollinator Certification for a Butterfly Garden What is the primary threat to most endangered species? Why is our butterfly and pollinator population declining?
V Q \ = 7]Z 4IVL 126 Unit 5
![V Q \ = 7]Z 4IVL 126 Unit 5 V Q \ = 7]Z 4IVL 126 Unit 5](/thumbs/77/75709676.jpg) 126 Unit 5 Is it cold and windy? Or is it a sunny day? Is it raining cats and dogs? Or can we go out to play? I will learn to talk about seasons and weather plant life environments caring for the earth
126 Unit 5 Is it cold and windy? Or is it a sunny day? Is it raining cats and dogs? Or can we go out to play? I will learn to talk about seasons and weather plant life environments caring for the earth
Pollinator Conservation
 Pollinator Conservation By https://www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/evolution-and-the-origin-of-species-18/formation-of-new-species-125/reproductive-isolation-504-11730/ http://padena.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/pollinator-slider1.jpg
Pollinator Conservation By https://www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/evolution-and-the-origin-of-species-18/formation-of-new-species-125/reproductive-isolation-504-11730/ http://padena.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/pollinator-slider1.jpg
FLOWERS AND POLLINATION. This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination.
 FLOWERS AND POLLINATION This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination. Objectives for Exam #1 1. Identify flower structures and match those structures to specific
FLOWERS AND POLLINATION This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination. Objectives for Exam #1 1. Identify flower structures and match those structures to specific
Jody: Pollinators are the insects, birds, and other animals who carry pollen from one plant to
 Pollinators Webisode Narrative Description [Jenny and Connor eating outdoors at picnic bench] [Connor swats at a wasp] Connor: Get away! Get away! Jenny: Don t swat at it. Connor: Ow! [Hinterland Who s
Pollinators Webisode Narrative Description [Jenny and Connor eating outdoors at picnic bench] [Connor swats at a wasp] Connor: Get away! Get away! Jenny: Don t swat at it. Connor: Ow! [Hinterland Who s
Lesson: Honeybees and Trees
 Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Content Standards: NGSS K-LS1-1. Use
Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Content Standards: NGSS K-LS1-1. Use
Bees Are Cool. Bee First Aid
 Bees Are Cool Bees Sting Many people are afraid of bees, but that is because they don t understand them. Bees are pollinators and without pollinators a flower could not make a seed. So you think you could
Bees Are Cool Bees Sting Many people are afraid of bees, but that is because they don t understand them. Bees are pollinators and without pollinators a flower could not make a seed. So you think you could
Ch. 4- Plants. STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Taxonomy
 Ch. 4- Plants STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Taxonomy Plants belong to the kingdom: Plantae PLANTS AND PLANT REPRODUCTION STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Classification Two types of seed plants are gymnosperms
Ch. 4- Plants STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Taxonomy Plants belong to the kingdom: Plantae PLANTS AND PLANT REPRODUCTION STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION And Classification Two types of seed plants are gymnosperms
The Basics: Grade Level 5 th - 8th. Subject Areas Life sciences. Duration 95 minutes. Number of Docents Needed 2. Wetland Stewards Program Lesson 8 1
 Grade Level 5 th - 8th The Basics: POLLINATORS AND WILDFLOWERS Summary Students will understand that plants depend on pollinators to reproduce and maintain their populations. They learn about wetland plant
Grade Level 5 th - 8th The Basics: POLLINATORS AND WILDFLOWERS Summary Students will understand that plants depend on pollinators to reproduce and maintain their populations. They learn about wetland plant
Listening. The Air. Did you know? Did you know?
 Listening 1. Find a place to sit. 2. Close your eyes and listen carefully to all the sounds you can hear. Cup your hands around your ears and turn your head to help you listen in particular directions.
Listening 1. Find a place to sit. 2. Close your eyes and listen carefully to all the sounds you can hear. Cup your hands around your ears and turn your head to help you listen in particular directions.
Where Animals and Plants Are Found
 About Animals and Plants What I Need to Know Animals and plants are linked. They are connected. They make up an ecosystem. Not all the ecosystems are the same. Different ecosystems have different plants.
About Animals and Plants What I Need to Know Animals and plants are linked. They are connected. They make up an ecosystem. Not all the ecosystems are the same. Different ecosystems have different plants.
Learning about bees - Maths Questions
 Learning about bees - Maths Questions Preparation: Before beginning this activity, cut out each of the hexagons in the Learning about bees - maths questions resource. You may consider pre-assigning the
Learning about bees - Maths Questions Preparation: Before beginning this activity, cut out each of the hexagons in the Learning about bees - maths questions resource. You may consider pre-assigning the
There are approximately 25,000 species of Bee in the World There are almost 4000 species of Bee in North America There are approximately 1000
 There are approximately 25,000 species of Bee in the World There are almost 4000 species of Bee in North America There are approximately 1000 different species of Bee in Texas There are only 7-9 species
There are approximately 25,000 species of Bee in the World There are almost 4000 species of Bee in North America There are approximately 1000 different species of Bee in Texas There are only 7-9 species
13 November 2005 Volume XIII No. 11
 13 November 2005 Volume XIII No. 11 Can you believe we re still seeing butterflies in great abundance in butterfly gardens, even though we have had a couple of nights of light frost? The dry weather must
13 November 2005 Volume XIII No. 11 Can you believe we re still seeing butterflies in great abundance in butterfly gardens, even though we have had a couple of nights of light frost? The dry weather must
Amy Ant. Formica Mica Grant. Dr. Sheila Grant (Mica s mom)
 Dr. Sheila Grant (Mica s mom) Formica Mica Grant Amy Ant By Elisabeth Schlegel, Jessica Louton, Natasha Mehdiabadi, and Ted Schultz Illustrated by Katherine Arisumi At the Smithsonian Institution s National
Dr. Sheila Grant (Mica s mom) Formica Mica Grant Amy Ant By Elisabeth Schlegel, Jessica Louton, Natasha Mehdiabadi, and Ted Schultz Illustrated by Katherine Arisumi At the Smithsonian Institution s National
The Importance of Bees
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: The Importance of Bees Imagine a world without bees. Some might rejoice at the thought of never being stung by one of those little yellow buzzers, and others might miss the
Name: Class Period: Due Date: The Importance of Bees Imagine a world without bees. Some might rejoice at the thought of never being stung by one of those little yellow buzzers, and others might miss the
Parts of a Flower. A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program
 Parts of a Flower A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program OVERVIEW: Students create a flower with craft materials in order to learn the parts of flowers and
Parts of a Flower A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program OVERVIEW: Students create a flower with craft materials in order to learn the parts of flowers and
Bees. Garden Classroom. 90 minutes. Grade 6 4/10. ESY Berkeley Teaching Staff Edible Schoolyard Project Berkeley, CA. Bees Safety Pollinators Honey
 LESSON: 4/10 SIXTH GRADE GARDEN ROTATION STANDARDS ALIGNED: YES Bees PLACE OF LEARNING: Garden Classroom DURATION: 90 minutes GRADE LEVEL: Grade 6 CONTRIBUTOR ESY Berkeley Teaching Staff Edible Schoolyard
LESSON: 4/10 SIXTH GRADE GARDEN ROTATION STANDARDS ALIGNED: YES Bees PLACE OF LEARNING: Garden Classroom DURATION: 90 minutes GRADE LEVEL: Grade 6 CONTRIBUTOR ESY Berkeley Teaching Staff Edible Schoolyard
Introducing the Read-Aloud
 Introducing the Read-Aloud The Life Cycle of a Plant 4A 10 minutes What Have We Already Learned? 5 minutes Remind students that during the last few lessons they learned about the seasonal cycle. Have students
Introducing the Read-Aloud The Life Cycle of a Plant 4A 10 minutes What Have We Already Learned? 5 minutes Remind students that during the last few lessons they learned about the seasonal cycle. Have students
2nd Grade. Slide 1 / 106. Slide 2 / 106. Slide 3 / 106. Plants. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 2nd Grade Plants 2015-11-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 106 Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal Slide
Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 2nd Grade Plants 2015-11-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 106 Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal Slide
What are the different stages of the life cycle of living things? life cycle stage
 Manny is at his family reunion. First he catches up with his grandparents. People always tell him how much he looks like his grandfather, but Manny doesn t agree. His grandfather is so much taller, and
Manny is at his family reunion. First he catches up with his grandparents. People always tell him how much he looks like his grandfather, but Manny doesn t agree. His grandfather is so much taller, and
7. Where do most crustaceans live? A. in the air B. in water C. on the land D. underground. 10. Which of the following is true about all mammals?
 1 A flounder is a type of fish The flounder can change its color to match the surroundings If a shark approaches, the flounder lays still, blending into the sandy ocean bottom This is known as 2 Which
1 A flounder is a type of fish The flounder can change its color to match the surroundings If a shark approaches, the flounder lays still, blending into the sandy ocean bottom This is known as 2 Which
Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life
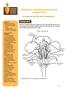 Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life Pollination and the Next Generation Objectives Students will be able to: list the parts to a flower; show how to pollinate flowers explain the best pollination
Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life Pollination and the Next Generation Objectives Students will be able to: list the parts to a flower; show how to pollinate flowers explain the best pollination
Andy Norris. Dario Sanches
 Andy Norris Hardy fuchsia Dario Sanches Hummingbird Comet orchid Morgan s sphinx moth Dan Mullen Common blue violet Dan Mullen Common blue violet Wild celery Water Sumatran corpse flower Carrion beetle
Andy Norris Hardy fuchsia Dario Sanches Hummingbird Comet orchid Morgan s sphinx moth Dan Mullen Common blue violet Dan Mullen Common blue violet Wild celery Water Sumatran corpse flower Carrion beetle
Coevolution and Pollination
 Coevolution and Pollination Coevolution is the the mutual evolutionary influence between two species (the evolution of two species totally dependent on each other). Each of the species involved exerts
Coevolution and Pollination Coevolution is the the mutual evolutionary influence between two species (the evolution of two species totally dependent on each other). Each of the species involved exerts
2nd Grade. Plants.
 1 2nd Grade Plants 2015 11 24 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal 3 Lab: What do plants need? What do plants
1 2nd Grade Plants 2015 11 24 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section What are plants? Photosynthesis Pollination Dispersal 3 Lab: What do plants need? What do plants
BENEFICIAL INSECTS GOING BUGGY
 BENEFICIAL INSECTS GOING BUGGY GOALS FOR THIS STATION Understand the importance of beneficial insects Understand the importance of native bees Understand the importance of conserving insect habitats ROLES
BENEFICIAL INSECTS GOING BUGGY GOALS FOR THIS STATION Understand the importance of beneficial insects Understand the importance of native bees Understand the importance of conserving insect habitats ROLES
Pollinators. Pam Brown University of Florida/IFAS Extension, Retired
 Pollinators Pam Brown University of Florida/IFAS Extension, Retired What is Pollination Pollination is the transfer of pollen from male anther to female stigma resulting in fertilization. Pollination results
Pollinators Pam Brown University of Florida/IFAS Extension, Retired What is Pollination Pollination is the transfer of pollen from male anther to female stigma resulting in fertilization. Pollination results
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: The gametophyte grows as an independent plant.
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION 3 Introduction to Plants Seed Plants 7.2.a, 7.5.f California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are seed
CHAPTER 12 SECTION 3 Introduction to Plants Seed Plants 7.2.a, 7.5.f California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are seed
Name Date Block. Plant Structures
 Name Date Block What are the Functions of Roots, Stems, and Leaves? Plant Structures Each part of a plant plays an important role in its structure and function. Roots, stems, and leaves are just three
Name Date Block What are the Functions of Roots, Stems, and Leaves? Plant Structures Each part of a plant plays an important role in its structure and function. Roots, stems, and leaves are just three
Cal and Tramp Camp. His dog Tramp ran up to him. Cal and Tramp set up. camp. They put up a tent in back of Cal s house. Cal and
 Cal and Tramp Camp Cal and Tramp Camp Cal said, Let s camp. His dog Tramp ran up to him. Cal and Tramp set up camp. They put up a tent in back of Cal s house. Cal and Tramp got in the tent. Then they heard,
Cal and Tramp Camp Cal and Tramp Camp Cal said, Let s camp. His dog Tramp ran up to him. Cal and Tramp set up camp. They put up a tent in back of Cal s house. Cal and Tramp got in the tent. Then they heard,
Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Major Emphasis: Major Curriculum Area: Related Curriculum Areas: Program Indicator: Student Outcomes:
 Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Grade 5 Major Emphasis: Invertebrates and Their Environments Major Curriculum Area: Science Related Curriculum Areas: Refer to Outdoor Education Curriculum Matrix
Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Grade 5 Major Emphasis: Invertebrates and Their Environments Major Curriculum Area: Science Related Curriculum Areas: Refer to Outdoor Education Curriculum Matrix
Leave That Willow Bee: Pollinators Need Trees and Shrubs too! Debbie Fluegel, Illinois Program Manager
 Leave That Willow Bee: Pollinators Need Trees and Shrubs too! Debbie Fluegel, Illinois Program Manager About Trees Forever Presentation Overview How we learned about importance of trees & forests for pollinators
Leave That Willow Bee: Pollinators Need Trees and Shrubs too! Debbie Fluegel, Illinois Program Manager About Trees Forever Presentation Overview How we learned about importance of trees & forests for pollinators
FISKE KINDERGARTEN SPRING NATURE WALK Plants, Animals, and Seasonal Changes
 1 FISKE KINDERGARTEN SPRING NATURE WALK Plants, Animals, and Seasonal Changes OBJECTIVES: Using touch, smell, sight, and sound, observe, describe and compare seasonal changes in the weather and the schoolyard
1 FISKE KINDERGARTEN SPRING NATURE WALK Plants, Animals, and Seasonal Changes OBJECTIVES: Using touch, smell, sight, and sound, observe, describe and compare seasonal changes in the weather and the schoolyard
Plant Growth & Reproduction
 Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) 4/24/2014 Plant Growth & Reproduction BI 103 Plant-Animal Systems Turn in Homework #1 Lab Wed! (schedule change) 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 no wind
Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) Water loss (ml) 4/24/2014 Plant Growth & Reproduction BI 103 Plant-Animal Systems Turn in Homework #1 Lab Wed! (schedule change) 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 no wind
Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution
 Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution coevolutionary plant-animal associations alliances that have influenced the evoluton of both partners. These examples show that plants have acquired traits
Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution coevolutionary plant-animal associations alliances that have influenced the evoluton of both partners. These examples show that plants have acquired traits
Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation
 Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation Grade Level(s) 3-5 Estimated Time 2 hours Purpose Students will identify the parts of a honey bee, the stages of its life cycle, and its role in pollination. Materials
Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation Grade Level(s) 3-5 Estimated Time 2 hours Purpose Students will identify the parts of a honey bee, the stages of its life cycle, and its role in pollination. Materials
Peter Dutton. 28 August Halesworth& District
 Peter Dutton 28 August 2014 Halesworth& District Bees Hymenoptera - 150,000+ species Sawflies, Wasps, Bees, Ants, Bees - 20,000+ species Most solitary, a few social Honey Bee - The only one which produces
Peter Dutton 28 August 2014 Halesworth& District Bees Hymenoptera - 150,000+ species Sawflies, Wasps, Bees, Ants, Bees - 20,000+ species Most solitary, a few social Honey Bee - The only one which produces
Celebrate Spring! Vernal Equinox
 Celebrate Spring! Vernal Equinox In temperate climates that is, climates which have varying temperatures and seasons spring brings lots of changes to our world. The official first day of spring is called
Celebrate Spring! Vernal Equinox In temperate climates that is, climates which have varying temperatures and seasons spring brings lots of changes to our world. The official first day of spring is called
Part 2: Adaptations and Reproduction
 Part 2: Adaptations and Reproduction Review: Plants need 6 things to grow 1. Air (Carbon Dioxide) 2. Water 3. Light 4. Nutrients 5. Proper Temperature 6. Space Adaptations Adaptations are characteristics
Part 2: Adaptations and Reproduction Review: Plants need 6 things to grow 1. Air (Carbon Dioxide) 2. Water 3. Light 4. Nutrients 5. Proper Temperature 6. Space Adaptations Adaptations are characteristics
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees
 Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Beekeeping in Urban Areas. Where to put your bees!
 Beekeeping in Urban Areas Where to put your bees! Check the laws in your area Go online Regulations such as distance from property lines Neighbors signatures Considerations Neighbors Pools Fences Dogs
Beekeeping in Urban Areas Where to put your bees! Check the laws in your area Go online Regulations such as distance from property lines Neighbors signatures Considerations Neighbors Pools Fences Dogs
Funding for the duplication of this publication is provided by the St. Lucie County Board of County Commissioners.
 This booklet was adapted by Kate O Neill, Program Specialist from Africanized Honey Bees on the Move, University of Arizona. Reviewed by: Anita Neal, St. Lucie County Extension Director 8400 Picos Road,
This booklet was adapted by Kate O Neill, Program Specialist from Africanized Honey Bees on the Move, University of Arizona. Reviewed by: Anita Neal, St. Lucie County Extension Director 8400 Picos Road,
Summer Walk. Summer Walk. Ramble through the woods as you VIRGINIA BRIMHALL SNOW
 VIRGINIA BRIMHALL SNOW, author of Fall Walk, Winter Walk, and Spring Walk, lives in a wooded area bordering a national forest in northern Utah. For more than twenty-six years, she has expressed herself
VIRGINIA BRIMHALL SNOW, author of Fall Walk, Winter Walk, and Spring Walk, lives in a wooded area bordering a national forest in northern Utah. For more than twenty-six years, she has expressed herself
Flower Power!! Background knowledge material and dissection directions.
 Flower Power!! Background knowledge material and dissection directions. 96 Plant Dissection 3.2 Plants Essential Question: Why do plants have flowers? Questions: As you read the lab background, complete
Flower Power!! Background knowledge material and dissection directions. 96 Plant Dissection 3.2 Plants Essential Question: Why do plants have flowers? Questions: As you read the lab background, complete
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees
 Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
2. Which of the following is an organism that is made of only one cell? A. a larva B. an oyster C. an amoeba D. a mold
 1. I am the barrier between the inside and the outside of the cell. I allow food, oxygen, and other needed materials to enter the cell. I am a part of animal and plant cells. A. cell membrane B. cell wall
1. I am the barrier between the inside and the outside of the cell. I allow food, oxygen, and other needed materials to enter the cell. I am a part of animal and plant cells. A. cell membrane B. cell wall
The Birds and Bees of Wildflowers! Pollination Strategies of Plants All text and photos by Kris H. Light 2005
 The Birds and Bees of Wildflowers! Pollination Strategies of Plants All text and photos by Kris H. Light 2005 The Parts of Flowers Petals Stamens Sepals Pistils Strawberry Hedgehog Cactus Boy parts and
The Birds and Bees of Wildflowers! Pollination Strategies of Plants All text and photos by Kris H. Light 2005 The Parts of Flowers Petals Stamens Sepals Pistils Strawberry Hedgehog Cactus Boy parts and
Community Involvement in Research Monitoring Pollinator Populations using Public Participation in Scientific Research
 Overview Community Involvement in Research Monitoring Pollinator Populations using Public Participation in Scientific Research Public Participation in Scientific Research (PPSR) is a concept adopted by
Overview Community Involvement in Research Monitoring Pollinator Populations using Public Participation in Scientific Research Public Participation in Scientific Research (PPSR) is a concept adopted by
Midwestern native plants for pollinators
 Midwestern native plants for pollinators Prairie plants 500 plant species at Neal Smith National Wildlife Refuge, about 250 prairie plant species Native plants are adapted to our soils Prairie species
Midwestern native plants for pollinators Prairie plants 500 plant species at Neal Smith National Wildlife Refuge, about 250 prairie plant species Native plants are adapted to our soils Prairie species
Creating a Pollinator Paradise: Part 1. Debbie Roos North Carolina Cooperative Extension
 Creating a Pollinator Paradise: Part 1 Debbie Roos North Carolina Cooperative Extension www.protectpollinators.org Photos by Debbie Roos 95% of photos taken in Chatham Mills Pollinator Garden Outline Primary
Creating a Pollinator Paradise: Part 1 Debbie Roos North Carolina Cooperative Extension www.protectpollinators.org Photos by Debbie Roos 95% of photos taken in Chatham Mills Pollinator Garden Outline Primary
Plants can be either herbaceous or woody.
 Plant Structure Plants can be either herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous plants are plants with growth which dies back to the ground each year, in contrast with woody plants Most herbaceous plants have stems
Plant Structure Plants can be either herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous plants are plants with growth which dies back to the ground each year, in contrast with woody plants Most herbaceous plants have stems
POLLINATION STATION. Wild Discover Zone
 Wild Discover Zone POLLINATION STATION This activity is designed to engage all ages of Zoo visitors. Your duty as an excellent educator and interpreter is to adjust your approach to fit each group you
Wild Discover Zone POLLINATION STATION This activity is designed to engage all ages of Zoo visitors. Your duty as an excellent educator and interpreter is to adjust your approach to fit each group you
Structures of Seed Plants
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
The Green Queens jericho.s_r Jericho High School DAY 12 GREENER BIO DIVERSITY
 The Green Queens jericho.s_r rachelle.lee@jerichoapps.org Jericho High School DAY 12 GREENER BIO DIVERSITY Our Dream Garden Our 12 Native Plants False White Indigo- These are beneficial because not only
The Green Queens jericho.s_r rachelle.lee@jerichoapps.org Jericho High School DAY 12 GREENER BIO DIVERSITY Our Dream Garden Our 12 Native Plants False White Indigo- These are beneficial because not only
Transcription of Science Time video Spring and Flowers
 Transcription of Science Time video Spring and Flowers The video for this transcript can be found on the Questacon website at: http://canberra.questacon.edu.au/sciencetime/ Transcription from video: Hi,
Transcription of Science Time video Spring and Flowers The video for this transcript can be found on the Questacon website at: http://canberra.questacon.edu.au/sciencetime/ Transcription from video: Hi,
Second grade summer work:
 Second grade summer work: Reading - In order to be prepared for second grade, rising second graders need to read at least two chapter books during the summer and write a book report on each one. One book
Second grade summer work: Reading - In order to be prepared for second grade, rising second graders need to read at least two chapter books during the summer and write a book report on each one. One book
Objective Students will construct bee puppets and use them to act out some behaviors.
 Bee Dance Objective Students will construct bee puppets and use them to act out some behaviors. Background Honeybees are social insects. They depend on one another for survival. Bees live in groups called
Bee Dance Objective Students will construct bee puppets and use them to act out some behaviors. Background Honeybees are social insects. They depend on one another for survival. Bees live in groups called
Ladybug- 7A-2. By the end of today, you will know a lot about these amazingly diverse insects. They come in all shapes, sizes, and colors.
 Ladybug- 7A-2 My grasshopper friend tells me that he asked you to guess the largest group of insects on Earth. Did anyone guess flies? Perhaps you guessed ants. Both ants and flies are good guesses. You
Ladybug- 7A-2 My grasshopper friend tells me that he asked you to guess the largest group of insects on Earth. Did anyone guess flies? Perhaps you guessed ants. Both ants and flies are good guesses. You
Bio Ch Plants.notebook. April 09, 2015
 1 Plants are vitally important to all life on Earth, especially humans Form the base of the food chain Medicines Clothing Building Materials 2 Plants for Food Cereals - The grass family - Rich in carbohydrates
1 Plants are vitally important to all life on Earth, especially humans Form the base of the food chain Medicines Clothing Building Materials 2 Plants for Food Cereals - The grass family - Rich in carbohydrates
BASIC BEE BIOLOGY. Tammy Horn, KY State Apiarist
 BASIC BEE BIOLOGY Tammy Horn, KY State Apiarist THE HONEY BEE COLONY Regardless of the race of bees, the colony will have three castes: One Queen (female) Workers (female), numbers depend upon season Drones
BASIC BEE BIOLOGY Tammy Horn, KY State Apiarist THE HONEY BEE COLONY Regardless of the race of bees, the colony will have three castes: One Queen (female) Workers (female), numbers depend upon season Drones
Vocabulary: New Context
 9. The Tunguska is an isolated area in central Siberia. 10. Others that it was an exploding spaceship. 11., some of the trees at the center of the explosion weren t burned. b Vocabulary: New Context Put
9. The Tunguska is an isolated area in central Siberia. 10. Others that it was an exploding spaceship. 11., some of the trees at the center of the explosion weren t burned. b Vocabulary: New Context Put
SAMPLE PAGE. Flowers Express Lapbook. Any Age. A Journey Through Learning
 A J T L Any Age Flowers Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guides, Activities, and Coloring Sheets A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning
A J T L Any Age Flowers Express Lapbook Mini Lapbook, Study Guides, Activities, and Coloring Sheets A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2013 A Journey Through Learning
28 3 Insects Slide 1 of 44
 1 of 44 Class Insecta contains more species than any other group of animals. 2 of 44 What Is an Insect? What Is an Insect? Insects have a body divided into three parts head, thorax, and abdomen. Three
1 of 44 Class Insecta contains more species than any other group of animals. 2 of 44 What Is an Insect? What Is an Insect? Insects have a body divided into three parts head, thorax, and abdomen. Three
My Journal By: Copyright 2015 A Dab of Glue Will Do
 My Journal By: My Journal By: My Journal By: My Journal By: Science Notebook Contract This is my Science Notebook for the 20 school year: I promise to take care of my notebook. use one page at a time.
My Journal By: My Journal By: My Journal By: My Journal By: Science Notebook Contract This is my Science Notebook for the 20 school year: I promise to take care of my notebook. use one page at a time.
Next Generation Science Standards
 Flower Functions Students learn the basic structure of a plant and how each part works together as a system to obtain essential resources needed for the plant s survival. Grade Level: 1st Phenomena: How
Flower Functions Students learn the basic structure of a plant and how each part works together as a system to obtain essential resources needed for the plant s survival. Grade Level: 1st Phenomena: How
Bees. By: Jourdan Wu, Olakunle Olawonyi, Adina Gibson, Elizabeth Peterson. Image drawn by Adina Gibson using Sketchpad 5.1
 Bees By: Jourdan Wu, Olakunle Olawonyi, Adina Gibson, Elizabeth Peterson Image drawn by Adina Gibson using Sketchpad 5.1 According to an Article by NRDC (Natural Resources Defense Council) titled Why We
Bees By: Jourdan Wu, Olakunle Olawonyi, Adina Gibson, Elizabeth Peterson Image drawn by Adina Gibson using Sketchpad 5.1 According to an Article by NRDC (Natural Resources Defense Council) titled Why We
8/14 DRAFT Grade Two Fall 1. GRADE TWO FALL NATURE WALK A Place for Butterflies
 8/14 DRAFT Grade Two Fall 1 GRADE TWO FALL NATURE WALK A Place for Butterflies OBJECTIVES Students will: compare habitats around the school yard that support different types of insects observe that a variety
8/14 DRAFT Grade Two Fall 1 GRADE TWO FALL NATURE WALK A Place for Butterflies OBJECTIVES Students will: compare habitats around the school yard that support different types of insects observe that a variety
The Pollinators Journey
 The Pollinators Journey Summary Students perform a short play about threatened migratory pollinators. Grade Level: K-4; 5-8 Time: 2 to 3 class periods (90 minutes or more) Subjects: Science, Language Arts,
The Pollinators Journey Summary Students perform a short play about threatened migratory pollinators. Grade Level: K-4; 5-8 Time: 2 to 3 class periods (90 minutes or more) Subjects: Science, Language Arts,
United States Department of Agriculture. Farm Service Agency. Natural Resources Conservation Service. April Helping People Help the Land
 nited tates epartment of griculture arm ervice gency atural esources onservation ervice pril 2009 elping eople elp the and ee ollen opular he ee and the lower ollen is a fine to coarse powder made by plants.
nited tates epartment of griculture arm ervice gency atural esources onservation ervice pril 2009 elping eople elp the and ee ollen opular he ee and the lower ollen is a fine to coarse powder made by plants.
National Pollinator week, June 20-26, 2016
 FOR THE POLLINATORS National Pollinator week, June 20-26, 2016 Why the focus on pollinators? 75% of all plants on earth require pollination by animals. For humans: fruits, vegetables, seeds/nuts, fibers,
FOR THE POLLINATORS National Pollinator week, June 20-26, 2016 Why the focus on pollinators? 75% of all plants on earth require pollination by animals. For humans: fruits, vegetables, seeds/nuts, fibers,
3 Types of Interactions
 CHAPTER 18 3 Types of Interactions SECTION Interactions of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What determines an area s carrying capacity?
CHAPTER 18 3 Types of Interactions SECTION Interactions of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What determines an area s carrying capacity?
All species evolve characteristics, features or behaviours that allow them to survive in a certain habitat (or environment)
 What is adaptation? All species evolve characteristics, features or behaviours that allow them to survive in a certain habitat (or environment) o Animals and plants living in different habitats need different
What is adaptation? All species evolve characteristics, features or behaviours that allow them to survive in a certain habitat (or environment) o Animals and plants living in different habitats need different
University of Kentucky Department of Entomology Insects in the Classroom: Lesson Plan No. 105
 University of Kentucky Department of Entomology Insects in the Classroom: Lesson Plan No. 105 BENEFICIAL BUG SCAVENGER HUNT Prepared by Blake Newton, Extension Specialist Developed from an activity designed
University of Kentucky Department of Entomology Insects in the Classroom: Lesson Plan No. 105 BENEFICIAL BUG SCAVENGER HUNT Prepared by Blake Newton, Extension Specialist Developed from an activity designed
Lesson Plan: Vectors and Venn Diagrams
 Prep Time: Minimal Lesson Plan: Vectors and Venn Diagrams Age Level: Can be modified for any grade Materials Needed: Blank Venn diagrams can be printed for students to complete (included in this document),
Prep Time: Minimal Lesson Plan: Vectors and Venn Diagrams Age Level: Can be modified for any grade Materials Needed: Blank Venn diagrams can be printed for students to complete (included in this document),
For Creative Minds. Grassland Habitat
 For Creative Minds The For Creative Minds educational section may be photocopied or printed from our website by the owner of this book for educational, non-commercial uses. Cross-curricular teaching activities,
For Creative Minds The For Creative Minds educational section may be photocopied or printed from our website by the owner of this book for educational, non-commercial uses. Cross-curricular teaching activities,
adaptations: structures or behaviors in organisms that help them survive in their environment
 Giraffes are unique animals because they have such long necks. The neck of a modern day giraffe is much longer than the neck of an ancient giraffe that lived long ago. How and why did the giraffe change
Giraffes are unique animals because they have such long necks. The neck of a modern day giraffe is much longer than the neck of an ancient giraffe that lived long ago. How and why did the giraffe change
Ecology Student Edition. A. Sparrows breathe air. B. Sparrows drink water. C. Sparrows use the sun for food. D. Sparrows use plants for shelter.
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following does not give an example of how sparrows use resources in their environment to survive? A. Sparrows breathe air. B. Sparrows drink water. C. Sparrows use the sun for
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following does not give an example of how sparrows use resources in their environment to survive? A. Sparrows breathe air. B. Sparrows drink water. C. Sparrows use the sun for
All About Plants. What are plants?
 All About Plants What are plants? Plants are living things that are made up of cells. They need air, water, soil, and sunlight to live. They cannot move from place to place, but their leaves move to catch
All About Plants What are plants? Plants are living things that are made up of cells. They need air, water, soil, and sunlight to live. They cannot move from place to place, but their leaves move to catch
Henbury Millennium Green
 Henbury Millennium Green Insects Just a small selection! The most obvious are illustrated there are many more including small day-flying moths that move so fast you (well, I) can t identify them. Photo
Henbury Millennium Green Insects Just a small selection! The most obvious are illustrated there are many more including small day-flying moths that move so fast you (well, I) can t identify them. Photo
Upskilling community leaders for Australian Pollinator Week
 Upskilling community leaders for Australian Pollinator Week Classroom or other educational activities DISCLAIMER Hello and thank you for being part of this project. This presentation is designed to be
Upskilling community leaders for Australian Pollinator Week Classroom or other educational activities DISCLAIMER Hello and thank you for being part of this project. This presentation is designed to be
