Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation
|
|
|
- Randall Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Honey Bees: A Pollination Simulation Grade Level(s) 3-5 Estimated Time 2 hours Purpose Students will identify the parts of a honey bee, the stages of its life cycle, and its role in pollination. Materials Activity 1: Preserved honey bee, 1 per group Hand lenses, 1 per group Honey Bee PowerPoint Anatomy of a Worker Bee activity sheets, 1 per student Activity 2: 32 black chenille stems 8 containers of 100 mini (5mm) pompoms 8 small containers* of water 16 medium-sized (1") pompoms* 16 jewel bags (1.5" x 2") with yarn tied as a necklace* 16 drinking straws* Construction paper, 25 pieces *These items are included in the Pollination Simulation Kit, which is available for purchase from agclassroomstore.com. Activity 3: Beeswax Modeling Clay Recipe A Beeswax Modeling Clay Kit is available for purchase from agclassroomstore.com. Cardstock or construction paper Honeycomb, optional Essential Files (maps, charts, pictures, or documents) Honey Bee PowerPoint Beeswax Modeling Clay Recipe Anatomy of a Worker Bee KEY Anatomy of a Worker Bee Activity Sheet Vocabulary beeswax: a substance secreted from glands located on the underside of a worker bee s abdomen brood: the offspring produced by the colony (eggs and larvae) cell: a hexagonal wax chamber built from beeswax for brood rearing and storage of honey and pollen colony: a group living together hive: a home to a colony of bees honeycomb: six-sided wax cells in a beehive
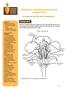
2 metamorphosis: the process of change in the form and habits of an organism during transformation from an immature stage to an adult stage nectar: a sweet liquid secreted by flowers pollen: a fine, powder-like material produced by flowering plants pollination: the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a plant propolis: a resin-like material used by bees to construct and seal parts of the beehive royal jelly: a milky, yellow syrup secreted from a gland in a young worker bee s head; used to feed larvae Did you know? (Ag Facts) Bees pollinate 95 different crops, helping to create nearly one-third of the world's food supply. Honey is the only food produced by insects that is eaten by humans on a wide scale. A queen bee can lay over one million eggs in her lifetime. Worker bees' wings can beat 250 times per second allowing the bee to fly at speeds of up to 15 miles per hour. Background Agricultural Connections Honey bees are extremely important to humans. Bees are pollinators. They collect pollen and nectar from flowering trees and plants and transfer pollen from flower to flower. Bees pollinate 95 different crops, helping to create nearly one-third of the world s food supply. Honey bees use the nectar they gather from flowers to make honey, which is the only commercial food produced by insects that is eaten by humans on a wide scale. Honey bees also produce beeswax, which is used to make candles, artists materials, lubricants, polishes, and cosmetics. Bee venom, pollen, royal jelly, and propolis are other bee-made products used in manufacturing, and for nutritional and medical purposes. Honey bees live in large groups called colonies. There are three types, or castes, of honey bees queen, worker, and drone. The queen bee is a female that lays eggs. Each colony has only one queen bee. The queen can live up to four years and can lay over one million eggs in her lifetime. She can lay close to one egg per minute and between 1,000-2,000 eggs a day. Worker bees are female bees who perform many of the jobs for the colony, including feeding the larvae; cleaning the hive; creating wax and using it to make new cells; grooming and feeding the queen; guarding and protecting the hive; and leaving the hive to collect pollen, nectar, and water. Worker bees live for about six weeks in the summer and longer in the winter months when they are less active. Drones are male bees responsible only for mating with the queen. They do not work. There are about 100 drones in each colony. They live for about eight weeks in the summer, and are then expelled from the colony and die in the fall. The size of a honey bee s body depends on its caste and the task it performs. The queen bee is the largest, and the worker bee is the smallest. Honey bees, like all insects, have three main body regions head, thorax, and abdomen. The head contains two compound eyes, three simple eyes, two antennae, mandibles, and the proboscis. The compound eyes are made up of thousands of tiny lenses that allow the bee to see ultraviolet light (invisible to the human eye) and all colors of visible light except red.
3 The simple eyes each have a thick lens that can sense changes in brightness. The honey bee s antennae are movable feelers that detect smells and movement. The proboscis is a straw-like tongue used to suck nectar or honey. Mandibles are jaw-like structures used to knead wax and to chew honey and pollen. The thorax is the honey bee s middle region containing the flight muscles, four wings, and six legs. Honey bees have two hind wings and two forewings that can beat 250 times per second allowing the bee to fly at speeds of up to 15 miles per hour. They have three pairs of segmented legs used for walking, dusting their antennae, brushing pollen off body hairs, and storing pollen. The hind legs of worker bees contain a pollen basket a collection of hairs where pollen is stored for transport. The abdomen is the rear region that contains organs for digestion, reproduction, and respiration as well as the stinger and wax glands. The stinger is only found in female honey bees. A worker bee s barbed stinger is used for defense. When stinging, the barb anchors the stinger in the victim while the stinger s pouch pumps venom. After stinging, the bee dies of an abdominal rupture. When stinging insects, the bee s stinger remains attached while the barb tears through the target s exoskeleton. The honey sac is a stomach-like organ connected to the digestive tract. The sac stores the nectar until the bee returns to the hive. Wax glands are located on the underside of the bee s abdomen. These glands form and excrete wax. Honey bees have four distinct life stages egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Complete metamorphosis takes between 16 and 24 days. The queen lays each egg into a different cell of the honeycomb. It is her job to determine whether the egg will grow into a male or female bee. Fertilized eggs will become female workers, and unfertilized eggs will become male drones. After three days, the egg hatches and a worm-like creature, called larva, is unveiled. Worker bees feed the larva royal jelly a milky, yellow syrup secreted from a gland in the worker bee s head. As it grows, the larva sheds its skin four to five times. On about day nine, the larva spins itself a cocoon. A worker bee seals the cocoon into the cell with wax. Inside the cocoon, the larva transforms into a pupa developing eyes, legs, and wings. When the bee is fully grown, it chews its way out of the cell and emerges as an adult. It takes 16 days for a queen bee to develop from an egg to an adult; worker bees take days, and drones need 24 days. Interest Approach Engagement Ask students, "Why are honey bees important to humans?"
4 Procedures Activity 1: Bee Anatomy 1. Create groups of 4-5 students. Provide each group with hand lenses and preserved honey bees. Ask the students to examine the bees and, as a group, make a chart listing the details they observed. Provide time for each group to present their observations to the class. 2. Explain to the students that honey bees have three main body regions the head, thorax, and abdomen. Use the Honey Bee PowerPoint to discuss the main parts of a worker bee. 3. Ask students to label the parts of a worker bee on the Anatomy of a Worker Bee activity sheet.
5 Activity 2: Pollination Simulation 1. Using the background information as a guide, discuss the roles of each of the three castes of honey bees the queen, workers, and drones. Simulate the role worker bees play in pollination by conducting a pollination simulation. Choose 8 students to represent flowers, 16 students to represent worker bees, and 1 student to represent the queen bee. Numbers of flowers and worker bees may vary according to class sizes. Extra students can represent the worker bees and drones that remain in the hive. 2. Have students create construction paper headbands to differentiate flowers, worker bees, and the queen bee. Draw and cut out flowers to glue onto the flower headbands. Create antennae using chenille stems to staple onto the worker bee headbands. Cut out a crownshaped headband for the queen bee. 3. Choose a large area, preferably outdoors, to serve as the garden and a smaller area to the side of the garden to serve as the beehive. 4. Each flower will hold one container of mini pompoms to represent pollen and one container of water to represent nectar. The flowers will choose a location inside the garden in which to stand. 5. Each worker bee will carry one medium-sized pompom to represent the bee s hairy body, one jewel bag tied with yarn and worn as a necklace to represent the honey sac, and one straw to represent the proboscis. 6. The worker bees will begin at the beehive with the queen, drones, and other workers whose duties require them to work inside the hive. When the queen bee gives the command, the worker bees will leave the hive in search of nectar from flowers. 7. When a worker finds a flower, they will land their medium-sized pompom into the container of mini pompoms. The worker will then simulate gathering nectar with their proboscis by filling a straw with water using their finger to create a vacuum. The water will be deposited into the jewel bag. When the worker removes the medium-sized pompom from the container, the tiny pompoms will stick to the larger pompom much the same way pollen sticks to the hairs of a bee when it visits a flower. 8. After collecting nectar and pollen from the flower, the worker will find a new flower to visit. Here, the worker will brush off some of the pollen collected from the previous flower into the new flower s container. They will then collect more nectar and pollen before visiting another flower. 9. Once the worker bee has filled their honey sac with nectar, they will return to the hive. 10. For the purpose of this simulation, the worker bee must collect nectar and pollen from each flower before visiting a flower for a second time, and only two bees may visit the same flower at once. 11. Trade roles and repeat the simulation as many times as desired.
6 Activity 3: Beeswax Life Cycle Models 1. Ask the students if humans use any items made by honey bees. 2. Talk about how honey bees make beeswax. Explain that beeswax is secreted from the wax glands of worker bees to create and cap cells inside the hive. Beeswax is used in the production of candles, cosmetics, artists materials, electronics, lubricants, polishes, inks, and paints. Bees require the protein from pollen and the carbohydrates from honey to create beeswax. It takes 6-10 pounds of honey to make one pound of wax, which is enough to construct 35,000 cells within a hive. A beekeeper will harvest two pounds of wax cappings for every 100 pounds of honey. 3. If possible, obtain honeycomb so students can observe the wax cells and cappings. Honey in the comb can be obtained from beekeepers, specialty stores, online stores, and farmers markets. 4. Use the Honey Bee PowerPoint to discuss the life cycle of a honey bee. 5. Make beeswax modeling clay (recipe found in essential files). Instruct students to use the clay to create a honey bee life cycle model by creating an egg, larva, pupa, and adult honeybee. Refer to the Honey Bee PowerPoint for photographs of each life stage. Students can work in groups or individually to create their life cycle model. 6. A cell for each life stage can be created out of paper folded into the shape of a hexagon. Concept Elaboration and Evaluation After conducting these activities, review and summarize the following key concepts: Bees are important to pollinate crops that produce our food. If the plant is not pollinated it will not produce food. A colony of bees is very organized with specific workers for individual jobs. In addition to pollination, honey bees also make honey.
7 Enriching Activities Use the following videos to further explore the world of honey bees: In Flight of the Honey Bee (2:15) a commercial beekeeper illustrates how honey bees play an essential role in the crop production process. Give your students a close-up look at a honey bee covered in pollen and hives traveling across the country to pollinate different crops.
Learning about bees - Maths Questions
 Learning about bees - Maths Questions Preparation: Before beginning this activity, cut out each of the hexagons in the Learning about bees - maths questions resource. You may consider pre-assigning the
Learning about bees - Maths Questions Preparation: Before beginning this activity, cut out each of the hexagons in the Learning about bees - maths questions resource. You may consider pre-assigning the
Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Major Emphasis: Major Curriculum Area: Related Curriculum Areas: Program Indicator: Student Outcomes:
 Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Grade 5 Major Emphasis: Invertebrates and Their Environments Major Curriculum Area: Science Related Curriculum Areas: Refer to Outdoor Education Curriculum Matrix
Activity: Honey Bee Adaptation Grade Level: Grade 5 Major Emphasis: Invertebrates and Their Environments Major Curriculum Area: Science Related Curriculum Areas: Refer to Outdoor Education Curriculum Matrix
BASIC BEE BIOLOGY. Tammy Horn, KY State Apiarist
 BASIC BEE BIOLOGY Tammy Horn, KY State Apiarist THE HONEY BEE COLONY Regardless of the race of bees, the colony will have three castes: One Queen (female) Workers (female), numbers depend upon season Drones
BASIC BEE BIOLOGY Tammy Horn, KY State Apiarist THE HONEY BEE COLONY Regardless of the race of bees, the colony will have three castes: One Queen (female) Workers (female), numbers depend upon season Drones
 Honeybees There are more than 22,000 types of bees in the world. Do you know which bees make honey? Without honeybees, you wouldn t have any honey to spread on your toast in the morning. You may have seen
Honeybees There are more than 22,000 types of bees in the world. Do you know which bees make honey? Without honeybees, you wouldn t have any honey to spread on your toast in the morning. You may have seen
Bee Colony Activities Throughout The Year
 Bee Colony Activities Throughout The Year Written by Khalil Hamdan Apeldoorn The Netherlands A honeybee gathering nectar from a flower. Photo source: forestwander.com Bee collecting pollen. Photo source:
Bee Colony Activities Throughout The Year Written by Khalil Hamdan Apeldoorn The Netherlands A honeybee gathering nectar from a flower. Photo source: forestwander.com Bee collecting pollen. Photo source:
Funding for the duplication of this publication is provided by the St. Lucie County Board of County Commissioners.
 This booklet was adapted by Kate O Neill, Program Specialist from Africanized Honey Bees on the Move, University of Arizona. Reviewed by: Anita Neal, St. Lucie County Extension Director 8400 Picos Road,
This booklet was adapted by Kate O Neill, Program Specialist from Africanized Honey Bees on the Move, University of Arizona. Reviewed by: Anita Neal, St. Lucie County Extension Director 8400 Picos Road,
BEE BODIES HONEY BEE ANATOMY. Essential Question: MATERIALS. Chart Paper Markers Journals, Paper, or Digital Notebooks
 BEE BODIES HONEY BEE ANATOMY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essential Question: HOW DOES A HONEY BEE S STRUCTURE SUPPORT ITS FUNCTION IN THE ECOSYSTEM? n n n Distinguish between the structural and behavioral adaptations
BEE BODIES HONEY BEE ANATOMY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essential Question: HOW DOES A HONEY BEE S STRUCTURE SUPPORT ITS FUNCTION IN THE ECOSYSTEM? n n n Distinguish between the structural and behavioral adaptations
Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program
 Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Pollination is a sticky situation. In this active lesson, students learn
Pollination A Sticky Situation! A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Pollination is a sticky situation. In this active lesson, students learn
How Does Pollination Work?
 How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
28 3 Insects Slide 1 of 44
 1 of 44 Class Insecta contains more species than any other group of animals. 2 of 44 What Is an Insect? What Is an Insect? Insects have a body divided into three parts head, thorax, and abdomen. Three
1 of 44 Class Insecta contains more species than any other group of animals. 2 of 44 What Is an Insect? What Is an Insect? Insects have a body divided into three parts head, thorax, and abdomen. Three
Lesson: Honeybees and Trees
 Camp Woodlands/Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Revised 2016 Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten
Camp Woodlands/Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Revised 2016 Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten
Lesson: Honeybees and Trees
 Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Content Standards: NGSS K-LS1-1. Use
Lesson: Honeybees and Trees Topic/Essential Question: How do honeybees and trees help each other? Unit: Why Are Trees Terrific? Kindergarten Environmental Literacy Content Standards: NGSS K-LS1-1. Use
INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS. Bee Life Grade 2 Science and Technology Unit
 INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS Bee Life Grade 2 Science and Technology Unit ONTARIO TEACHER-FOCUSED TOOLKIT INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS Bee Life Instructions to Teachers This unit is a Science and Technology lesson
INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS Bee Life Grade 2 Science and Technology Unit ONTARIO TEACHER-FOCUSED TOOLKIT INSTRUCTIONS TO TEACHERS Bee Life Instructions to Teachers This unit is a Science and Technology lesson
The Importance of Bees
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: The Importance of Bees Imagine a world without bees. Some might rejoice at the thought of never being stung by one of those little yellow buzzers, and others might miss the
Name: Class Period: Due Date: The Importance of Bees Imagine a world without bees. Some might rejoice at the thought of never being stung by one of those little yellow buzzers, and others might miss the
The Biology of the Honeybee, Apis Mellifera
 The Biology of the Honeybee, Apis Mellifera NOTE: The images found in this document have been redrawn from Mark L. Winston. 1987. The Biology of the Honey Bee. Harvard University Press. Cambridge, MA.
The Biology of the Honeybee, Apis Mellifera NOTE: The images found in this document have been redrawn from Mark L. Winston. 1987. The Biology of the Honey Bee. Harvard University Press. Cambridge, MA.
Objective Students will construct bee puppets and use them to act out some behaviors.
 Bee Dance Objective Students will construct bee puppets and use them to act out some behaviors. Background Honeybees are social insects. They depend on one another for survival. Bees live in groups called
Bee Dance Objective Students will construct bee puppets and use them to act out some behaviors. Background Honeybees are social insects. They depend on one another for survival. Bees live in groups called
Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People
 Theme: Spring in the Garden Grade Level: K- 5 th Time Required: 45 minutes Number of Students: 15-25 Buzzy Buzzy Bee! Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People Description Students learn about pollination
Theme: Spring in the Garden Grade Level: K- 5 th Time Required: 45 minutes Number of Students: 15-25 Buzzy Buzzy Bee! Lesson Adapted from Food, Land, People Description Students learn about pollination
EXTERNAL ANATOMY OF INSECTS
 External Anatomy of Insects 1 The insect s exoskeleton is made up of a series of plates EXTERNAL ANATOMY OF INSECTS These plates make up the insect s exoskeleton. These plates are connected by joints or
External Anatomy of Insects 1 The insect s exoskeleton is made up of a series of plates EXTERNAL ANATOMY OF INSECTS These plates make up the insect s exoskeleton. These plates are connected by joints or
Bees. Garden Classroom. 90 minutes. Grade 6 4/10. ESY Berkeley Teaching Staff Edible Schoolyard Project Berkeley, CA. Bees Safety Pollinators Honey
 LESSON: 4/10 SIXTH GRADE GARDEN ROTATION STANDARDS ALIGNED: YES Bees PLACE OF LEARNING: Garden Classroom DURATION: 90 minutes GRADE LEVEL: Grade 6 CONTRIBUTOR ESY Berkeley Teaching Staff Edible Schoolyard
LESSON: 4/10 SIXTH GRADE GARDEN ROTATION STANDARDS ALIGNED: YES Bees PLACE OF LEARNING: Garden Classroom DURATION: 90 minutes GRADE LEVEL: Grade 6 CONTRIBUTOR ESY Berkeley Teaching Staff Edible Schoolyard
There are approximately 25,000 species of Bee in the World There are almost 4000 species of Bee in North America There are approximately 1000
 There are approximately 25,000 species of Bee in the World There are almost 4000 species of Bee in North America There are approximately 1000 different species of Bee in Texas There are only 7-9 species
There are approximately 25,000 species of Bee in the World There are almost 4000 species of Bee in North America There are approximately 1000 different species of Bee in Texas There are only 7-9 species
SOBA Bee School April, 2015
 SOBA Bee School April, 2015 Bee Girl - University of Montana, Missoula - Iridovirus and Microsporidian Linked to CCD - Sonagraphic analysis of hive health - Pesticide effects - Bomb sniffing bees - OLLI
SOBA Bee School April, 2015 Bee Girl - University of Montana, Missoula - Iridovirus and Microsporidian Linked to CCD - Sonagraphic analysis of hive health - Pesticide effects - Bomb sniffing bees - OLLI
BUTTERFLY SCIENCE. 9 Science Activities for PreK, K & EarthsBirthday.org
 BUTTERFLY SCIENCE 9 Science Activities for PreK, K & 1-3 1 800 698 4438 EarthsBirthday.org CONTENTS Butterfly Life Cycle Song 4 Changing Butterfly Dance 5 What Is a Caterpillar? 6 Caterpillar & Pupa Timelines
BUTTERFLY SCIENCE 9 Science Activities for PreK, K & 1-3 1 800 698 4438 EarthsBirthday.org CONTENTS Butterfly Life Cycle Song 4 Changing Butterfly Dance 5 What Is a Caterpillar? 6 Caterpillar & Pupa Timelines
Bees Are Cool. Bee First Aid
 Bees Are Cool Bees Sting Many people are afraid of bees, but that is because they don t understand them. Bees are pollinators and without pollinators a flower could not make a seed. So you think you could
Bees Are Cool Bees Sting Many people are afraid of bees, but that is because they don t understand them. Bees are pollinators and without pollinators a flower could not make a seed. So you think you could
Glossary of Terms used in Beekeeping
 Glossary of Terms used in Beekeeping A Abscond The action of bees leave the hive suddenly with few or no remainders. This should not be confused with swarming; it is often due to problems such as poor
Glossary of Terms used in Beekeeping A Abscond The action of bees leave the hive suddenly with few or no remainders. This should not be confused with swarming; it is often due to problems such as poor
Word Match Match the vocabulary words with the defi nitions below.
 LESSON A: Word Match Match the vocabulary words with the defi nitions below. Name: Date: a. honey bee b. insects c. thorax d. abdomen e. pollination f. colony g. solitary h. hive i. queen bee j. worker
LESSON A: Word Match Match the vocabulary words with the defi nitions below. Name: Date: a. honey bee b. insects c. thorax d. abdomen e. pollination f. colony g. solitary h. hive i. queen bee j. worker
the European Honeybee
 the European Honeybee Queen 1 queen in every hive the only fertile female in the hive lives 2 to 10 years longer than other bees perform every task in and out of the hive sterile females live for 28 to
the European Honeybee Queen 1 queen in every hive the only fertile female in the hive lives 2 to 10 years longer than other bees perform every task in and out of the hive sterile females live for 28 to
Arthropods. Ch. 13, pg
 Arthropods Ch. 13, pg. 374-382 382 Arthropods Insects Arachnids Centipedes and Millipedes Crustaceans Characteristics of Arthropods Arthropods have jointed appendages and include legs, antennae, claws,
Arthropods Ch. 13, pg. 374-382 382 Arthropods Insects Arachnids Centipedes and Millipedes Crustaceans Characteristics of Arthropods Arthropods have jointed appendages and include legs, antennae, claws,
*Add to Science Notebook Name 1
 *Add to Science Notebook Name 1 Arthropods, Ch. 13, pg. 374-382 Characteristics of Arthropods *Arthropods are the largest group of animals. *Arthropods have jointed and include,,, and. *Arthropod appendages
*Add to Science Notebook Name 1 Arthropods, Ch. 13, pg. 374-382 Characteristics of Arthropods *Arthropods are the largest group of animals. *Arthropods have jointed and include,,, and. *Arthropod appendages
Teacher s Guide. Bees. PA G E S 2 3 Bee Happy Structure and life cycle of bees. 4 5 To Bee or Not to Bee Bees and their look-alikes
 Teacher s Guide Bees Dear Educator, Your students will stay as busy as bees as they buzz through this issue of KIDS DISCOVER. Your young scientists will explore the topics at the right in Bees. This Teacher
Teacher s Guide Bees Dear Educator, Your students will stay as busy as bees as they buzz through this issue of KIDS DISCOVER. Your young scientists will explore the topics at the right in Bees. This Teacher
o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee?
 o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee? *NOTE: The queen in Observation Hive #1 has a yellow mark on her. Put the wooden panels
o Can you find any nectar? Brood? Honey? o Can you find any drones and drone cells? o Can you find the queen bee? *NOTE: The queen in Observation Hive #1 has a yellow mark on her. Put the wooden panels
Teacher Resource Materials for 5th Apiary Program GROWING IDEAS: CULTIVATING CONNECTIONS
 The Rotch-Jones-Duff House & Garden Museum Teacher Resource Materials for 5th Apiary Program GROWING IDEAS: CULTIVATING CONNECTIONS This program utilizes the property s unique urban garden setting to introduce
The Rotch-Jones-Duff House & Garden Museum Teacher Resource Materials for 5th Apiary Program GROWING IDEAS: CULTIVATING CONNECTIONS This program utilizes the property s unique urban garden setting to introduce
Bee Behavior. Summary of an article by. Stephen Taber III from Beekeeping in the United States
 Bee Behavior Summary of an article by Stephen Taber III from Beekeeping in the United States Bees Sense Organs: Vision Each compound eye is spherical in shape and comprised of some 6,300 cone-shaped facets
Bee Behavior Summary of an article by Stephen Taber III from Beekeeping in the United States Bees Sense Organs: Vision Each compound eye is spherical in shape and comprised of some 6,300 cone-shaped facets
The Biology of the Honeybee, Apis Mellifera
 Page 1 of 13 The Biology of the Honeybee, Apis Mellifera NOTE: The images found in this document have been redrawn from Mark L. Winston. 1987. The Biology of the Honey Bee. Harvard University Press. Cambridge,
Page 1 of 13 The Biology of the Honeybee, Apis Mellifera NOTE: The images found in this document have been redrawn from Mark L. Winston. 1987. The Biology of the Honey Bee. Harvard University Press. Cambridge,
Peter Dutton. 28 August Halesworth& District
 Peter Dutton 28 August 2014 Halesworth& District Bees Hymenoptera - 150,000+ species Sawflies, Wasps, Bees, Ants, Bees - 20,000+ species Most solitary, a few social Honey Bee - The only one which produces
Peter Dutton 28 August 2014 Halesworth& District Bees Hymenoptera - 150,000+ species Sawflies, Wasps, Bees, Ants, Bees - 20,000+ species Most solitary, a few social Honey Bee - The only one which produces
Creepy, Crawly Critters
 Creepy, Crawly Critters Objective Students will identify different insects as well as the body parts of insects. Background There are over 1.5 million kinds of insects. They come in all shapes and sizes.
Creepy, Crawly Critters Objective Students will identify different insects as well as the body parts of insects. Background There are over 1.5 million kinds of insects. They come in all shapes and sizes.
by Claire Tan HOUGHTON MIFFLIN
 by Claire Tan HOUGHTON MIFFLIN by Claire Tan PHOTOGRAPHY CREDITS: Cover Kim Taylor/npl/Minden Pictures. 1 Don Farrall/Getty Images. 2 Roger De La Harpe/ABPL/ Animals Animals - Earth Scenes. 3 Steve Hopkin/Getty
by Claire Tan HOUGHTON MIFFLIN by Claire Tan PHOTOGRAPHY CREDITS: Cover Kim Taylor/npl/Minden Pictures. 1 Don Farrall/Getty Images. 2 Roger De La Harpe/ABPL/ Animals Animals - Earth Scenes. 3 Steve Hopkin/Getty
Lesson Plan: Vectors and Venn Diagrams
 Prep Time: Minimal Lesson Plan: Vectors and Venn Diagrams Age Level: Can be modified for any grade Materials Needed: Blank Venn diagrams can be printed for students to complete (included in this document),
Prep Time: Minimal Lesson Plan: Vectors and Venn Diagrams Age Level: Can be modified for any grade Materials Needed: Blank Venn diagrams can be printed for students to complete (included in this document),
Elementary Science: Pollination
 Elementary Science: Pollination A collection of hands-on lessons and activities for the elementary classroom that explore the process and importance of pollination and pollinators. Table of Contents A
Elementary Science: Pollination A collection of hands-on lessons and activities for the elementary classroom that explore the process and importance of pollination and pollinators. Table of Contents A
Pollinator Activity #1: How to Raise a Butterfly
 How to Raise a Butterfly How to Raise a Butterfly A Conversation Where do you most often see butterflies? What are they doing when you see them? Have you ever seen a butterfly in another form? They have
How to Raise a Butterfly How to Raise a Butterfly A Conversation Where do you most often see butterflies? What are they doing when you see them? Have you ever seen a butterfly in another form? They have
Honey Bee. Bite-size Science
 Bite-size Science Trying new things can be hard. When you play a new sport, you have to learn and remember a whole new set of rules. When you try new food, you may end up not liking it (and you may even
Bite-size Science Trying new things can be hard. When you play a new sport, you have to learn and remember a whole new set of rules. When you try new food, you may end up not liking it (and you may even
Parts of a Flower. A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program
 Parts of a Flower A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program OVERVIEW: Students create a flower with craft materials in order to learn the parts of flowers and
Parts of a Flower A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society Learning Through Gardening Program OVERVIEW: Students create a flower with craft materials in order to learn the parts of flowers and
SOCIAL INSECT PROGRAM (grade 2 to 3)
 SOCIAL INSECT PROGRAM (grade 2 to 3) This one and a half hour program is delivered on site at Swan Lake Christmas Hill Nature Sanctuary. BEFORE YOU ARRIVE: 1. Provide each student with an easily read name
SOCIAL INSECT PROGRAM (grade 2 to 3) This one and a half hour program is delivered on site at Swan Lake Christmas Hill Nature Sanctuary. BEFORE YOU ARRIVE: 1. Provide each student with an easily read name
Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport
 Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport food, water and minerals throughout the plant. Water and
Nonvascular Plants mosses, liverworts and hornworts are nonvascular plants. These lack vascular tissue which is a system of tubes that transport food, water and minerals throughout the plant. Water and
Apis mellifera scuttelata. Common names: African honeybee also nicknamed the killer bee
 Apis mellifera scuttelata Common names: African honeybee also nicknamed the killer bee Description Compared to other Apis mellifera species, the most distinguishing trait of Apis mellifera scutellata is
Apis mellifera scuttelata Common names: African honeybee also nicknamed the killer bee Description Compared to other Apis mellifera species, the most distinguishing trait of Apis mellifera scutellata is
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees
 Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Module 1: Darwin s Bees
 Enquire with Darwin KS3 Module 1: Darwin s Bees Small links in the chain of evolution 01 Circus: link 1 Fossil bees and comb (slides 2-4) Look at the fossil evidence What do you notice about the packing
Enquire with Darwin KS3 Module 1: Darwin s Bees Small links in the chain of evolution 01 Circus: link 1 Fossil bees and comb (slides 2-4) Look at the fossil evidence What do you notice about the packing
Honey Bee Biology Workshop. The Queen. The Drone
 Honey Bee Biology Workshop 1. The bee colony 2. Behavioral sequence of workers 3. Worker-queen differentiation 4. Honey bee dances 5. Chemical communications The Queen Longevity: 1-3 years 1. The mother
Honey Bee Biology Workshop 1. The bee colony 2. Behavioral sequence of workers 3. Worker-queen differentiation 4. Honey bee dances 5. Chemical communications The Queen Longevity: 1-3 years 1. The mother
Enrichment Lesson 1: Making a Bee line
 Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Focus Areas: Animal Lifestyles; Science, Physical Education Focus Skills: understanding patterns, conducting an experiment, role playing, cooperating to achieve a goal
Dedicated to Reducing Pesticides Focus Areas: Animal Lifestyles; Science, Physical Education Focus Skills: understanding patterns, conducting an experiment, role playing, cooperating to achieve a goal
Honeybee Factsheet The Hive Queen Bee Worker Bee
 Honeybee Factsheet The Hive A honey bee colony can contain up to 60,000 bees at its peak (20,000-30,000 bees in the winter, and over 60,000-80,000 bees in the summer) Honey bees maintain a constant temperature
Honeybee Factsheet The Hive A honey bee colony can contain up to 60,000 bees at its peak (20,000-30,000 bees in the winter, and over 60,000-80,000 bees in the summer) Honey bees maintain a constant temperature
Honey Bees QUB Green Champions 9 th April
 Honey Bees QUB Green Champions 9 th April 2014 http://www.qub.ac.uk/staff/area/bees/ http://belfastbees.wordpress.com/ Contents The Beekeeping Year Inside the hive Outside the hive Swarming Discussion
Honey Bees QUB Green Champions 9 th April 2014 http://www.qub.ac.uk/staff/area/bees/ http://belfastbees.wordpress.com/ Contents The Beekeeping Year Inside the hive Outside the hive Swarming Discussion
Honey Bees. QUB CCRCB 11 th January
 Honey Bees QUB CCRCB 11 th January 2018 http://www.qub.ac.uk/staff/area/bees/ http://belfastbees.wordpress.com/ http://belfastbees.wordpress.com/ Contents The Beekeeping Year Inside the hive Outside the
Honey Bees QUB CCRCB 11 th January 2018 http://www.qub.ac.uk/staff/area/bees/ http://belfastbees.wordpress.com/ http://belfastbees.wordpress.com/ Contents The Beekeeping Year Inside the hive Outside the
Introduction. Description. Bumble bee:
 Introduction Bumble bee: There are roughly 800 bee species in Canada. Bees are considered the most important group of pollinators. The bumble bee (genus Bombus) is native to North America. Description
Introduction Bumble bee: There are roughly 800 bee species in Canada. Bees are considered the most important group of pollinators. The bumble bee (genus Bombus) is native to North America. Description
Dedicated to bees, and My dad who loved reading to the kids on his lap, My children who spent plenty of time on his lap and mine, And Melvin, who
 Dedicated to bees, and My dad who loved reading to the kids on his lap, My children who spent plenty of time on his lap and mine, And Melvin, who thinks all laps belong to him. Published by Melvin TC PO
Dedicated to bees, and My dad who loved reading to the kids on his lap, My children who spent plenty of time on his lap and mine, And Melvin, who thinks all laps belong to him. Published by Melvin TC PO
a British scientist who left his fortune to the United States Congress had trouble getting the Smithsonian project off the ground.
 ReadWorks.org Teacher Guide & Answers a British scientist who left his fortune to the United States Congress had trouble getting the Smithsonian project off the ground. The Smithsonian Institution is the
ReadWorks.org Teacher Guide & Answers a British scientist who left his fortune to the United States Congress had trouble getting the Smithsonian project off the ground. The Smithsonian Institution is the
The Honey Bee Pollinators Charlie Vanden Heuvel BG BEES
 The Honey Bee Pollinators Charlie Vanden Heuvel BG BEES Homework Identify 10 plants that require pollination Identify 5 pollinator species Pollinators Pollinators Honey Bee Biology Behavior Communication
The Honey Bee Pollinators Charlie Vanden Heuvel BG BEES Homework Identify 10 plants that require pollination Identify 5 pollinator species Pollinators Pollinators Honey Bee Biology Behavior Communication
Name Class Date. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 14 3 Invertebrates SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What structures and systems perform basic life functions
CHAPTER 14 3 Invertebrates SECTION Introduction to Animals BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What structures and systems perform basic life functions
Pheromones by Ellen Miller November 2015
 Pheromones by Ellen Miller November 2015 Greek word pherein to carry Greek word hormone to stimulate A released chemical that triggers a social response in members of the same species The chemical is transmitted
Pheromones by Ellen Miller November 2015 Greek word pherein to carry Greek word hormone to stimulate A released chemical that triggers a social response in members of the same species The chemical is transmitted
Approximate Pacing for First Grade Insects and Plants Unit
 Approximate Pacing for First Grade Insects and Plants Unit p.1 = Part 1 p.2 = Part 2 p.3 = Part 3 The schedule for this unit is almost COMPLETELY dependent on what the living organisms are doing and where
Approximate Pacing for First Grade Insects and Plants Unit p.1 = Part 1 p.2 = Part 2 p.3 = Part 3 The schedule for this unit is almost COMPLETELY dependent on what the living organisms are doing and where
Structures of Seed Plants
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
CHAPTER 12 SECTION 4 Introduction to Plants Structures of Seed Plants BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the functions of roots and stems?
FLOWERS AND POLLINATION. This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination.
 FLOWERS AND POLLINATION This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination. Objectives for Exam #1 1. Identify flower structures and match those structures to specific
FLOWERS AND POLLINATION This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination. Objectives for Exam #1 1. Identify flower structures and match those structures to specific
BEES AND FORESTS. Activity 1 After the clip. 1. On which coast of Tasmania north, east or west does the annual Leatherwood flowering take place?
 BEES AND FORESTS Activity 1 After the clip 1. On which coast of Tasmania north, east or west does the annual Leatherwood flowering take place? 2. Julian Wolfhagen is the president of which association
BEES AND FORESTS Activity 1 After the clip 1. On which coast of Tasmania north, east or west does the annual Leatherwood flowering take place? 2. Julian Wolfhagen is the president of which association
Lesson 4: Insect Life Cycles
 Life Cycles -> 4: Insect Life Cycles Lesson 4: Insect Life Cycles Getting Started? Big Ideas P P P How are the life cycles of plants and animals similar and different? Where can cycles be found in nature?
Life Cycles -> 4: Insect Life Cycles Lesson 4: Insect Life Cycles Getting Started? Big Ideas P P P How are the life cycles of plants and animals similar and different? Where can cycles be found in nature?
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees
 Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
Lesson: The Buzz on Bees Environmental Literacy Question: How have humans affected the Chesapeake Bay and its watershed? Topic/Essential Questions: How do the structures of plants help them survive in
The FIRST BOOK of. By ALBERT B.TIBBETS HELENE CARTER GREYSTONE PRESS NEW YORK. Pictures by. Copyright 1952 by Franklin Watts, Inc.
 The FIRST BOOK of By ALBERT B.TIBBETS Pictures by HELENE CARTER GREYSTONE PRESS NEW YORK Copyright 1952 by Franklin Watts, Inc. \ BEES ARE ALWAYS WORKING Almost any day in summer, you can find a bee buzzing
The FIRST BOOK of By ALBERT B.TIBBETS Pictures by HELENE CARTER GREYSTONE PRESS NEW YORK Copyright 1952 by Franklin Watts, Inc. \ BEES ARE ALWAYS WORKING Almost any day in summer, you can find a bee buzzing
Name Class Date. Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the description that best matches each term on the left. 1.
 Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Chapter Vocabulary Review Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the description that best matches each term on the left. 1. thorax a. shedding of the
Chapter 28 Arthropods and Echinoderms Chapter Vocabulary Review Matching On the lines provided, write the letter of the description that best matches each term on the left. 1. thorax a. shedding of the
The Bee, Part I: Dance of the Bees Gioietta Kuo
 January 9, 2018 Busy Bees by Sharon Sperry Flickr CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 The Bee, Part I: Dance of the Bees Gioietta Kuo Bees are not ordinary wildlife. They have a special relationship with human society. For
January 9, 2018 Busy Bees by Sharon Sperry Flickr CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 The Bee, Part I: Dance of the Bees Gioietta Kuo Bees are not ordinary wildlife. They have a special relationship with human society. For
13 November 2005 Volume XIII No. 11
 13 November 2005 Volume XIII No. 11 Can you believe we re still seeing butterflies in great abundance in butterfly gardens, even though we have had a couple of nights of light frost? The dry weather must
13 November 2005 Volume XIII No. 11 Can you believe we re still seeing butterflies in great abundance in butterfly gardens, even though we have had a couple of nights of light frost? The dry weather must
Beekeeping Jargon and Terms
 Beekeeping Jargon and Terms Abdomen the posterior region of the body of the bee that contains the crop, digestive tract, sting and reproductive tract Absconding swarm an entire colony of bees that abandons
Beekeeping Jargon and Terms Abdomen the posterior region of the body of the bee that contains the crop, digestive tract, sting and reproductive tract Absconding swarm an entire colony of bees that abandons
Pollinator Slide Show Notes DIRECTIONS IN ALL CAPS 1
 Pollinator Slide Show Notes DIRECTIONS IN ALL CAPS 1 THIS PRESENTATION IS INTENDED TO BE USED IN SECTIONS TO SUPPORT TEACHING ON THE TOPICS PRESENTED. ANY OF THE SLIDES CAN BE USED AS HANDOUTS. YOU CAN
Pollinator Slide Show Notes DIRECTIONS IN ALL CAPS 1 THIS PRESENTATION IS INTENDED TO BE USED IN SECTIONS TO SUPPORT TEACHING ON THE TOPICS PRESENTED. ANY OF THE SLIDES CAN BE USED AS HANDOUTS. YOU CAN
Bees! Communication. Sustainability. Nourishment. Life Skills. Academics. Garden Lesson G6-13
 Garden Lesson G6-13 Bees! Communication Students interpret visual aids, take part in group discussion, make an inference and share it with others. Sustainability Bees are a significant pollinator and are
Garden Lesson G6-13 Bees! Communication Students interpret visual aids, take part in group discussion, make an inference and share it with others. Sustainability Bees are a significant pollinator and are
Objectives. Bee Basics. Apis mellifera. Honey bees 3/13/2019. All about bees Pheromones in the hive Obtaining bees Foraging and nutrition Bee diseases
 OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Bee Basics Amanda Bennett Extension Educator, ANR Objectives All about bees Pheromones in the hive Obtaining bees Foraging and nutrition Bee diseases March 23, 2019 Southwestern
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Bee Basics Amanda Bennett Extension Educator, ANR Objectives All about bees Pheromones in the hive Obtaining bees Foraging and nutrition Bee diseases March 23, 2019 Southwestern
Soroptimist BeePlus Project for Schools
 Soroptimist BeePlus Project for Schools S o r o p t i m i s t I n t e r n at i o n a l R e p u b l i c o f I r e l a n d Contents Forward Bill Turnbull 1 BeePlus project overview i2 Quiz 23 Overview Day
Soroptimist BeePlus Project for Schools S o r o p t i m i s t I n t e r n at i o n a l R e p u b l i c o f I r e l a n d Contents Forward Bill Turnbull 1 BeePlus project overview i2 Quiz 23 Overview Day
Biology of the Colony. Dr. Deborah Delaney
 Biology of the Colony Dr. Deborah Delaney Eusociality Photograph Alex Wild 2004 Photograph Alex Wild 2003 Eusocial: True Sociality Found mainly in two orders: Hymenoptera (some bees and wasps, all ants)
Biology of the Colony Dr. Deborah Delaney Eusociality Photograph Alex Wild 2004 Photograph Alex Wild 2003 Eusocial: True Sociality Found mainly in two orders: Hymenoptera (some bees and wasps, all ants)
World of Insects. Characteristics, Orders, and Collecting
 World of Insects Characteristics, Orders, and Collecting What You Should Know About Insects Taxonomy Kingdom Animalia Phylum Arthropoda Class - Insecta Insects Are Arthropods Insects are the largest group
World of Insects Characteristics, Orders, and Collecting What You Should Know About Insects Taxonomy Kingdom Animalia Phylum Arthropoda Class - Insecta Insects Are Arthropods Insects are the largest group
GENERAL CURRICULUM MULTI-SUBJECT SUBTEST
 GENERAL CURRICULUM MULTI-SUBJECT SUBTEST SUPPLEMENTAL SAMPLE OPEN-RESPONSE ITEM WITH SAMPLE RESPONSES AND ANALYSES NOTE: This sample open-response item is provided as a supplement to the Test Information
GENERAL CURRICULUM MULTI-SUBJECT SUBTEST SUPPLEMENTAL SAMPLE OPEN-RESPONSE ITEM WITH SAMPLE RESPONSES AND ANALYSES NOTE: This sample open-response item is provided as a supplement to the Test Information
Insects. Name. Date Comp Ed, Inc.
 Name Date Copyright@ 2013 Comp Ed, Inc. www.schoolexpress.com All animals with six legs are called insects. Insects were on the Earth millions of years before people. Insects live all over the world. There
Name Date Copyright@ 2013 Comp Ed, Inc. www.schoolexpress.com All animals with six legs are called insects. Insects were on the Earth millions of years before people. Insects live all over the world. There
Next Generation Science Standards
 Flower Functions Students learn the basic structure of a plant and how each part works together as a system to obtain essential resources needed for the plant s survival. Grade Level: 1st Phenomena: How
Flower Functions Students learn the basic structure of a plant and how each part works together as a system to obtain essential resources needed for the plant s survival. Grade Level: 1st Phenomena: How
Musk thistle and Canada thistle
 Musk thistle and Canada thistle Musk thistle, Carduus nutans Identification & origins Eurasian origin Sometimes called the nodding thistle : long slender stems bear heavy flowers Flowers are broader at
Musk thistle and Canada thistle Musk thistle, Carduus nutans Identification & origins Eurasian origin Sometimes called the nodding thistle : long slender stems bear heavy flowers Flowers are broader at
Bee Basics. Objectives. Honey bees 3/15/2018. All about bees Pheromones in the hive Obtaining bees Foraging and nutrition Protecting pollinators
 OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Bee Basics Amanda Bennett Extension Educator, ANR March 24, 2018 Southwestern Ohio Beekeeper School Loveland, Ohio Objectives All about bees Pheromones in the hive Obtaining
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Bee Basics Amanda Bennett Extension Educator, ANR March 24, 2018 Southwestern Ohio Beekeeper School Loveland, Ohio Objectives All about bees Pheromones in the hive Obtaining
Grade 7 Lesson Instructions Friend or Foe? Preparation: Background information: Activity:
 Instructions Friend or Foe? You can use monarchs to teach about many things! Stone Mountain Memorial Association (SMMA) uses the monarch butterfly to help students apply their knowledge in other contexts
Instructions Friend or Foe? You can use monarchs to teach about many things! Stone Mountain Memorial Association (SMMA) uses the monarch butterfly to help students apply their knowledge in other contexts
Click Teacher Guide: May/June 2018
 Flower Power Flowers are more than meet the eye and nose! Students learn all about and how they are pollinated to make seeds that grow into new young plants. CONVERSATION QUESTION How do plants use? TEACHING
Flower Power Flowers are more than meet the eye and nose! Students learn all about and how they are pollinated to make seeds that grow into new young plants. CONVERSATION QUESTION How do plants use? TEACHING
Bees and Pollination: An Educator s Guide. Sponsored by the West Seattle Bee Garden and Puget Sound Beekeepers Association
 Bees and Pollination: An Educator s Guide Sponsored by the West Seattle Bee Garden and Puget Sound Beekeepers Association Content: - Introduction - Goals and Objectives - Vocabulary Words - Questions/Discussion
Bees and Pollination: An Educator s Guide Sponsored by the West Seattle Bee Garden and Puget Sound Beekeepers Association Content: - Introduction - Goals and Objectives - Vocabulary Words - Questions/Discussion
Biology: Get out your packet from yesterday! If you would like to use gloves on Mon and Tues for Dissection PLEASE BRING THEM!!!
 Biology: Get out your packet from yesterday! Today: 5/15/2014 Learning Objectives: *Discuss answers from yesterday Describe the characteristics of animals that belong to the Phylum Arthropoda *Arthropod
Biology: Get out your packet from yesterday! Today: 5/15/2014 Learning Objectives: *Discuss answers from yesterday Describe the characteristics of animals that belong to the Phylum Arthropoda *Arthropod
LEARN 10 Insect Orders of the Wenatchee Watershed
 LEARN 10 Insect Orders of the Wenatchee Watershed Text and photos by Susan Ballinger. Photos of specimens from the collection of Dr. Robert Gillespie, Wenatchee Valley College Order Odonata dragonflies
LEARN 10 Insect Orders of the Wenatchee Watershed Text and photos by Susan Ballinger. Photos of specimens from the collection of Dr. Robert Gillespie, Wenatchee Valley College Order Odonata dragonflies
Bees. By: Jourdan Wu, Olakunle Olawonyi, Adina Gibson, Elizabeth Peterson. Image drawn by Adina Gibson using Sketchpad 5.1
 Bees By: Jourdan Wu, Olakunle Olawonyi, Adina Gibson, Elizabeth Peterson Image drawn by Adina Gibson using Sketchpad 5.1 According to an Article by NRDC (Natural Resources Defense Council) titled Why We
Bees By: Jourdan Wu, Olakunle Olawonyi, Adina Gibson, Elizabeth Peterson Image drawn by Adina Gibson using Sketchpad 5.1 According to an Article by NRDC (Natural Resources Defense Council) titled Why We
Bee Communica,on A Hive Mind
 Bee Communica,on A Hive Mind Hive Mind Hive Mind One for all and all for one Kill self to protect the hive Fatal S,ng WHY? Kin Selec)on: So closely related The hive occupants: One queen a fer,le female
Bee Communica,on A Hive Mind Hive Mind Hive Mind One for all and all for one Kill self to protect the hive Fatal S,ng WHY? Kin Selec)on: So closely related The hive occupants: One queen a fer,le female
RHS Invisible Garden
 Mushroom Spore Prints (Agaricus bisporus) Mushrooms or fungi produce millions of spores. Can you see the tiny spores in this spore print? Each spore can develop into a new mushroom. Most plants rely on
Mushroom Spore Prints (Agaricus bisporus) Mushrooms or fungi produce millions of spores. Can you see the tiny spores in this spore print? Each spore can develop into a new mushroom. Most plants rely on
Insect Investigations
 Investigative Questions What are some adaptations that insects have that help them to feed on different foods and from different parts of plants, especially flowers? Goal: Students explore the ways that
Investigative Questions What are some adaptations that insects have that help them to feed on different foods and from different parts of plants, especially flowers? Goal: Students explore the ways that
Exploring Matthaei s Ecosystems
 Name: Exploring Matthaei s Ecosystems As you walk on the trails, look for evidence of each of the following components of an ecosystem. Draw and describe what you observed and where you found it. Component
Name: Exploring Matthaei s Ecosystems As you walk on the trails, look for evidence of each of the following components of an ecosystem. Draw and describe what you observed and where you found it. Component
Arthropoda ARTHRO JOINTED PODA FEET
 Arthropoda ARTHRO JOINTED PODA FEET The arthropods are a group of animals which has attained the greatest biological success largest number of species and individuals and occupy the greatest number of
Arthropoda ARTHRO JOINTED PODA FEET The arthropods are a group of animals which has attained the greatest biological success largest number of species and individuals and occupy the greatest number of
Ode-to-nata (Aeshna canadensis) productions presents
 Ode-to-nata (Aeshna canadensis) productions presents Taxonomy and Anatomy of Apis millefera What s in a (Latin)name? Apis= bee Melli= honey Ferre= to bear honey bearing bee A quick overview of classification.
Ode-to-nata (Aeshna canadensis) productions presents Taxonomy and Anatomy of Apis millefera What s in a (Latin)name? Apis= bee Melli= honey Ferre= to bear honey bearing bee A quick overview of classification.
Upskilling community leaders for Australian Pollinator Week
 Upskilling community leaders for Australian Pollinator Week Build an insect hotel DISCLAIMER Hello and thank you for being part of this project. This presentation is designed to be shared with the broader
Upskilling community leaders for Australian Pollinator Week Build an insect hotel DISCLAIMER Hello and thank you for being part of this project. This presentation is designed to be shared with the broader
National Tropical Botanic Garden Kampong Science Teacher Enrichment Program
 National Tropical Botanic Garden Kampong Science Teacher Enrichment Program Author: Susy Chu Affiliation: Carrollton School of the Sacred Heart Target Grade: 7 Lesson Length: 8 block sessions Title of
National Tropical Botanic Garden Kampong Science Teacher Enrichment Program Author: Susy Chu Affiliation: Carrollton School of the Sacred Heart Target Grade: 7 Lesson Length: 8 block sessions Title of
Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life
 Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life Pollination and the Next Generation Objectives Students will be able to: list the parts to a flower; show how to pollinate flowers explain the best pollination
Module 6: Interdependence and Garden Life Pollination and the Next Generation Objectives Students will be able to: list the parts to a flower; show how to pollinate flowers explain the best pollination
Upskilling community leaders for Australian Pollinator Week
 Upskilling community leaders for Australian Pollinator Week Science activities DISCLAIMER Hello and thank you for being part of this project. This presentation is designed to be shared with the broader
Upskilling community leaders for Australian Pollinator Week Science activities DISCLAIMER Hello and thank you for being part of this project. This presentation is designed to be shared with the broader
Abuzz for Honey Bees
 Objective: Students will explore the honey bee s life cycle, anatomy, social life, and its art of honey production. The purpose of honey bee education is to evoke feelings of appreciation for the honey
Objective: Students will explore the honey bee s life cycle, anatomy, social life, and its art of honey production. The purpose of honey bee education is to evoke feelings of appreciation for the honey
Love Food? Love Bees! Beeing Curious Year 5 & 6
 Love Food? Love Bees! Beeing Curious Year 5 & 6 Teacher preparation Overarching learning goal: Students discover the pivotal role bees play in food production and the health of our ecosystems. They build
Love Food? Love Bees! Beeing Curious Year 5 & 6 Teacher preparation Overarching learning goal: Students discover the pivotal role bees play in food production and the health of our ecosystems. They build
Language Supportive Teaching and Textbooks in Tanzania. Course for textbook writers, editors and illustrators John Clegg, July 2013
 LSTT Language Supportive Teaching and Textbooks in Tanzania Course for textbook writers, editors and illustrators John Clegg, July 2013 Parts 1-3 are in separate document Part 4: Biology book lesson structure
LSTT Language Supportive Teaching and Textbooks in Tanzania Course for textbook writers, editors and illustrators John Clegg, July 2013 Parts 1-3 are in separate document Part 4: Biology book lesson structure
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: The gametophyte grows as an independent plant.
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION 3 Introduction to Plants Seed Plants 7.2.a, 7.5.f California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are seed
CHAPTER 12 SECTION 3 Introduction to Plants Seed Plants 7.2.a, 7.5.f California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are seed
INVERTEBRATES. The Earth and Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 1
 INVERTEBRATES Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 1 How many animals can you see? ant rose coral snake anemone fish grass bee Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 2 Invertebrates There are animals without
INVERTEBRATES Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 1 How many animals can you see? ant rose coral snake anemone fish grass bee Living Things. Carme Font Casanovas 2 Invertebrates There are animals without
