WILD/WEED BETA POPULATIONS IN THE IMPERIAL VALLEY, CALIFORNIA. Washington State University, Pullman, WA 99164
|
|
|
- Evelyn Parsons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WILD/WEED BETA POPULATIONS IN THE IMPERIAL VALLEY, CALIFORNIA Kelley L. Richardson 1 * and Barbara C. Hellier 2 1 USDA-ARS, 1636 East Alisal Street, Salinas, CA and 2 USDA-ARS, 59 Johnson Hall, Washington State University, Pullman, WA INTRODUCTION In North America, wild populations of Beta vulgaris subsp. maritima, Beta macrocarpa, and respective hybrids with cultivated beet are found in California. These likely originated from contaminated seed imported from Europe (Biancardi et al., 2012). Section Beta includes the wild species B. macrocarpa, and B. v. ssp. maritima, and the cultivated sugar beet, Beta vulgaris subsp. vulgaris (Frese, 2010). Successful hybridization amongst species of section Beta varies. Sugar beet will readily crossfertilize with B. v. ssp. maritima, but there is conflicting evidence for successful hybridization between sugar beet and B. macrocarpa (de Bock, 1986; Bartsch and Ellstrand, 1999; Jung et al., 1993; Frese, 2010). The relationships among the three species of section Beta have been investigated with PCR-based marker and DNA sequencing techniques. Previous research suggests a close relationship between B. v. ssp. vulgaris and B. v. ssp. maritima with a more distant position of B. macrocarpa in the phylogenetic tree (Letschert, 1993; Shen et al., 1998; Villain, 2007). When commercial production areas are adjacent to wild beet populations, gene flow from cultivated beets has the potential to alter the genetic composition of the nearby wild populations (Bartsch and Ellstrand, 1999). Carsner reported populations of B. v. ssp. maritima, B. macrocarpa, and respective hybrids with cultivated beet in the Imperial Valley, California in 1938 and they continue to be identified in California. Plant and root characteristics of Imperial Valley wild beets were compared with collections of B. v. ssp. maritima and B. macrocarpa from European coastlines. The wild beets found in the Imperial Valley differ from typical B. v. ssp. maritima and other wild beets found in California and are most similar to B. macrocarpa (McFarlane, 1975). In 2011, plants were collected from wild Beta populations adjacent to commercial sugar beet fields and while many samples had clear morphological characteristics of B. macrocarpa, several showed B. v. ssp. maritima-like characteristics. This distinction is critical because B. v. ssp. maritima will readily cross hybridize with cultivated sugar beet while B. macrocarpa hybrids occur less frequently and often result in infertile progeny. Further research is needed to evaluate wild beets in the Imperial Valley to understand the origin of populations, determine the species, and explore whether or not gene flow occurs between these wild beets and cultivated beet. Herbarium samples, leaf tissue and seed of weed beet in and around commercial sugar beet fields were collected with the objectives of assigning taxonomy based on morphology and determining genetic variation by genotyping. MATERIALS AND METHODS Locating and sampling wild beet populations Wild beet populations growing in and adjacent to commercial sugar beet fields in the Imperial Valley, CA were identified and located by the agriculture department of Spreckels Sugar (Brawley, CA) April 4-6, Collected populations were located in commercial sugar beet fields throughout the agricultural production area in the Imperial Valley and, when possible, were at least 3 km apart. GPS coordinates, elevation, and site description were recorded at each collection location. Irrigation canals and drainage ditches adjacent to sugar beet fields were checked for wild beet populations. The eastern edge of the Sonny Bono Salton Sea National Wild Life refuge and north along the eastern shore of the Salton Sea were checked for wild beet populations. Banks of the Alamo and New rivers from Brawley to the Salton Sea were also checked for wild beet populations.
2 Thousands of wild beet plants were present at each site and seed stage varied greatly. When ripe seed was present, the most mature seed was collected from 20 to 50 plants per site. An average of 43.2 g of seed was collected per site. Plants were randomly selected from within and along the edges of the sugar beet fields. Images of the wild beet plants and fields and one to three herbarium samples were collected at each site. Whole plants were collected for herbarium samples but because most plants were very large, some secondary stems were trimmed when the samples were pressed. At least 100 mg young leaf tissue was collected from between four to eight plants randomly located throughout each site. Herbarium sample characterization Morphology of seed and herbarium samples were compared to several B. v. ssp. maritima plants of National Plant Germplasm System accessions growing in the greenhouses at the Western Regional Plant Introduction Station (WRPIS), Pullman, WA and identification was made using the Letschert (1993) taxonomic key. Images and notes including general seed ball size, if there were seed balls low on the main stalk, if the upper bracts were large or small were recorded for each herbarium sample. Seven herbarium samples were not kept because of mold: IVCA11-01; -10;-11a,b,c;-13 a,b; and -15. Based on their morphology, the taxonomic identity of some herbarium samples was unclear. If a sample had more characteristics of B. macrocarpa but some confounding characteristics it was identified as "B. macrocarpa-like" and likewise with the samples with more B. v. ssp. maritima characteristics. To clarify taxonomic identification, collected seed from each population was planted and one to five seedlings each were grown in the WRPIS greenhouse. The number of plants, average number of nodes (leaf and secondary stems) from the soil line to first seed, average bract length (5 bracts per plant on the upper half of the flower stalk), average glomerule diameter (from the measured bracts), hypocotyl color, and presence or absence of leaf hairs were recorded. In addition, images and herbarium samples were collected for each accession. Molecular characterization DNA was extracted from mg of frozen leaf tissue harvested from wild beet plants using the Qiagen DNeasy 96 Plant Kit (Qiagen Inc, Valencia, CA). Supplied protocol was modified slightly. A Qiagen/Retsch MM300 mixer Mill was used for tissue disruption and centrifugation steps were run at 3500 x g. For DNA elution, incubation time was increased to three minutes prior to centrifugation. Sixty expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeat (EST-SSR) markers were used for genotyping, which were developed from the sugar beet GenBank EST database at NCBI (McGrath, 2007 and Imad Eujyl, personal communication). Known B. v. ssp. maritima and B. macrocarpa accessions were included as checks: five individuals from B. macrocarpa accessions PI , PI , and PI (collected in France, Spain, and California (Imperial County), respectively) and two individuals from B. v. ssp. maritima accessions PI , PI , and W (collected in England, England, and Morocco, respectively). PCR was performed with M-13 tailed forward primers labeled with FAM dye (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The PCR reaction mixture (10 l) consisted of approximately 20 ng template DNA, 1X PCR buffer (New England BioLabs Inc., Ipswich, MA), 0.2 mm of each dntp, 0.05 M of forward labeled primer, 0.2 M of M-13, 0.25 M of reverse primer, and 0.05 U of Taq DNA polymerase (New England BioLabs Inc., Ipswich, MA). Thermocycler conditions included an initial denaturing period of 5 min at 95 o C, followed by 35 cycles of 95 o C for 50 s, annealing at 58 o C or 60 o C for 50 s, extension at 72 o C for 90 s, and a final extension period for 10 min at 72 o C. PCR products were electrophoresed using ABI 3500 Genetic Analyzer following the manufacturer s protocol (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Electrophoresed product sizes were analyzed using GeneMapper v4.1 software (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). RESULTS
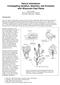
3 Throughout the Imperial Valley production area, 25 commercial sugar beet fields with wild beet populations were visited and locality data recorded (Figure 1). At the time of our collection, no wild beet populations were identified in irrigation canals or drainage ditches adjacent to sugar beet fields. Nor were wild beet populations identified along the eastern edge of the Sonny Bono Salton Sea National Wild Life refuge or north along the eastern shore of the Salton Sea. Banks of the Alamo and New rivers from Brawley to the Salton Sea were also free of wild beet populations. None of the wild Beta plants taken for herbarium samples had morphological characteristics of B. v. ssp. vulgaris. While many samples had clear morphological characteristics of B. macrocarpa (14 samples), several did not. Many samples were collected from plants growing amongst sugar beet plants, resulting in abnormal stem elongation. If a sample had more characteristics of B. macrocarpa but some confounding characteristics it was identified as "B. macrocarpa-like" (7 samples) and likewise with the samples with more B. v. ssp. maritima characteristics (7 samples). Stem elongation due to growing location was factored into the identifications. The collected seed was incorporated into the National Plant Germplasm System Beta collection (IVCA11-01 to IVCA11-27). To clarify taxonomic identification, collected seed from each population was planted and between one and five plants per accession were grown in individual pots in the greenhouse. The average number of nodes from the soil line to first seed ranged from three to nine nodes. Average bract length ranged from 14.9 to 41.3mm. Average glomerule diameter (from the measured bracts) ranged from 5.6 to 9.6mm. All samples had red hypocotyl color and glabrous leaves. All plants grown from the collected seed in the WRPIS greenhouses had clearer B. macrocarpa morphology. Of the 60 EST-SSRs used for genotyping, 20 did not amplify a product and 18 amplified monomorphic products. There was great variability amongst the 22 markers in the number of individuals from which product was amplified. The number of individuals successfully amplifying a product ranged from across all markers. The total number of alleles amplified per marker ranged from Thirteen markers had alleles that amplified in only one individual. Too few marker data were available for accurate genetic diversity analyses. DISCUSSION It is likely that when wild beets were reported in the Imperial Valley in 1928, Carsner incorrectly identified them as B. v. ssp. maritima descendents. This is plausible as, at the time, wild beets in other California sugar beet areas had been identified as B. v. ssp. maritima and that original identification was based on morphology of plants at time of collection. In 1975, McFarlane grew Imperial Valley wild beets under greenhouse conditions and, based on morphology, the wild beets were determined to be B. macrocarpa. This type of characterization has limitations in species identification as trait expression is strongly influenced by the environment (Laurentin, 2009). Our herbarium and seed sample results agree with this and suggest it is critical to grow out collected seed under non-competitive, greenhouse conditions to clarify taxonomy. In 1999, Bartsch and Ellstrand used allozyme biochemical markers and not morphology to compare genetic diversity of CA wild beets with that of cultivated beet and wild relatives. These markers avoid environmental influence, but are unable to detect low levels of variation. In this study, we used simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. As DNA-based markers, they are not influenced by the environment, but are also found throughout the genome and able to identify low levels of variation. Our results indicate particularly low levels of polymorphism amongst wild beets in Imperial Valley and that few of the available SSRs developed for sugar beet will successfully transfer to B. macrocarpa. McFarlane identified plants with morphology intermediate of sugar beet and B. macrocarpa suggesting hybridization. Bartsch and Ellstrand identified otherwise sugar beet-specific allozyme banding patterns in wild populations. To accurately identify the wild beet species in Imperial Valley, determine levels of hybridization, and potentially trace its origin we must develop tools capable of characterizing genetic variation present in populations. New technologies of sequencing and marker genotyping are needed and will enable new approaches towards improvement, such as clarifying relationships within the
4 species Beta and the accurate identification of hybrids between wild and cultivated beet (Morrell et al., 2012). ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The 2011 collecting trip was funded by the California Beet Growers Association. LITERATURE CITED Bartsch,D., and Ellstrand, N.C Genetic evidence for the origin of Californian wild beets (genus Beta). Theor Appl Genet 99: Biancardi, E., Panella, L.W., and Lewellen, R.T.(Editors) Range of distribution. In Beta maritima the origin of beets. Springer, New York, NY. p Carsner,E The wild beet in California. Facts About Sugar 23: De Bock, Tb.S.M., The genus Beta: Domestication, taxonomy and interspecific hybridization for plant breeding. Acta Horticult.183: Frese, L Conservation and access to sugarbeet germplasm. Sugar Tech 12(3-4): Jung, C., Pillen, K., Frese, L., Fahr, S., and Melchinger, A.E Phylogenetic relationships between cultivated and wild species of the genus Beta revealed by DNA fingerprinting. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 86: Laurentin, H Data analysis for molecular characterization of plant genetic resources. Genet Resour Crop Evol 56: Letschert, J.P.W Beta section Beta: Biogeographical patterns of variation and taxonomy. Wageningen Agricultural University Papers McFarlane, J.S Naturally occurring hybrids between sugarbeet and Beta macrocarpa in the Imperial Valley of California. J Am Soc Sugar Beet Technol 18: McGrath, J. M., Trebbi, D., Fenwick, A., Panella, L., Schulz, B., Laurent, V., Barnes, S., and Murray, S. C An open-source first-generation molecular genetic map from a sugarbeet x table beet cross and its extension to physical mapping. The Plant Genome 1:S27-S44. Morrell, P.L., Buckler, E. S., and Ross-Ibarra, J Crop genomics: advances and applications. Nature Reviews Genetics 13: Shen, Y., B.V. Ford-Lloyd, and H.J. Newbury Genetic relationships within the genus Beta determined using both PCR-based marker and DNA sequencing techniques. Heredity 80: Villain, S Histoire evolutive de la section Beta. Mise en e vidence des phe nome`nes d hybridation et de spe ciation au sein de la section dans le bassin me diterrane en. These pour obtenir le grade de docteur en sciences de l Universite de Lille 1. Spe cialite : sciences de la vie. Pre sente e par Sarah Villain le 13 de cembre 2007.
5 Figure 1. Locations of the 25 commercial sugar beet fields with wild beet populations throughout the Imperial Valley, CA production area visited during the 2011 collecting trip.
2 Numbers in parentheses refer to literature cited.
 A Genetic Study of Monogerm and Multigerm Characters in Beets V. F. SAVITSKY 1 Introduction Monogerm beets were found in the variety Michigan Hybrid 18 in Oregon in 1948. Two of these monogerm plants,
A Genetic Study of Monogerm and Multigerm Characters in Beets V. F. SAVITSKY 1 Introduction Monogerm beets were found in the variety Michigan Hybrid 18 in Oregon in 1948. Two of these monogerm plants,
Assessment of Genetic Diversity of Pawpaw Cultivars with Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat Markers
 Assessment of Genetic Diversity of Pawpaw Cultivars with Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat Markers Kirk W. Pomper*, Sheri B. Crabtree, and Snake C. Jones Kentucky State University What is Pawpaw? Asimina triloba
Assessment of Genetic Diversity of Pawpaw Cultivars with Inter-Simple Sequence Repeat Markers Kirk W. Pomper*, Sheri B. Crabtree, and Snake C. Jones Kentucky State University What is Pawpaw? Asimina triloba
Other funding Sources Agency Name: MSU Agricultural Experiment Station /Project GREEEN Amount requested or awarded: 30,000
 FINAL PROJECT REPORT Project Title: Functional genomics of flowering in apple PI: Herb Aldwinckle Co-PI(2): Steve VanNocker Organization: Cornell University Organization: Michigan State University Telephone/email:
FINAL PROJECT REPORT Project Title: Functional genomics of flowering in apple PI: Herb Aldwinckle Co-PI(2): Steve VanNocker Organization: Cornell University Organization: Michigan State University Telephone/email:
GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL
 GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL Kelsey Hoth 1 Dr. Maria Ivanchenko 2 Bioresourse Research 1, Department of Botany and Plant Physiology 2, Oregon State University, Corvallis,
GENETIC ANALYSES OF ROOT SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT IN THE TOMATO CROP MODEL Kelsey Hoth 1 Dr. Maria Ivanchenko 2 Bioresourse Research 1, Department of Botany and Plant Physiology 2, Oregon State University, Corvallis,
Managing segregating populations
 Managing segregating populations Aim of the module At the end of the module, we should be able to: Apply the general principles of managing segregating populations generated from parental crossing; Describe
Managing segregating populations Aim of the module At the end of the module, we should be able to: Apply the general principles of managing segregating populations generated from parental crossing; Describe
MARKER ASSISTED SELECTION (MAS) FOR DROUGHT TOLERANCE IN WHEAT USING MARKERS ASSOCIATED WITH MEMBRANE STABILITY
 AN. I.N.C.D.A. FUNDULEA, VOL. LXXVII, 2009 GENETICA ŞI AMELIORAREA PLANTELOR MARKER ASSISTED SELECTION (MAS) FOR DROUGHT TOLERANCE IN WHEAT USING MARKERS ASSOCIATED WITH MEMBRANE STABILITY SELECŢIA ASISTATĂ
AN. I.N.C.D.A. FUNDULEA, VOL. LXXVII, 2009 GENETICA ŞI AMELIORAREA PLANTELOR MARKER ASSISTED SELECTION (MAS) FOR DROUGHT TOLERANCE IN WHEAT USING MARKERS ASSOCIATED WITH MEMBRANE STABILITY SELECŢIA ASISTATĂ
Qualities of monogerm male-sterile sugar beet lines
 RESEARCH PAPER International Journal of Agronomy and Agricultural Research (IJAAR) ISSN: 2223-7054 (Print) 2225-3610 (Online) http://www.innspub.net Vol. 8, No. 4, p. 81-86, 2016 Qualities of monogerm
RESEARCH PAPER International Journal of Agronomy and Agricultural Research (IJAAR) ISSN: 2223-7054 (Print) 2225-3610 (Online) http://www.innspub.net Vol. 8, No. 4, p. 81-86, 2016 Qualities of monogerm
Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants
 Introduction Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants Daniel Lauffer Wisconsin Fast Plants Program University of Wisconsin - Madison Since the dawn
Introduction Hairy s Inheritance: Investigating Variation, Selection, and Evolution with Wisconsin Fast Plants Daniel Lauffer Wisconsin Fast Plants Program University of Wisconsin - Madison Since the dawn
BREEDING AND GENETICS
 The Journal of Cotton Science 6:97-103 (2002) http://journal.cotton.org, The Cotton Foundation 2002 97 BREEDING AND GENETICS Assessment of Day-Neutral Backcross Populations of Cotton Using AFLP Markers
The Journal of Cotton Science 6:97-103 (2002) http://journal.cotton.org, The Cotton Foundation 2002 97 BREEDING AND GENETICS Assessment of Day-Neutral Backcross Populations of Cotton Using AFLP Markers
Complementary Ex Situ Conservation. Nigel Maxted
 Complementary Ex Situ Conservation Nigel Maxted SADC Crop Wild Relatives Regional training workshop In situ conservation of CWR including diversity assessment techniques Le Meridien Ile Maurice, Mauritius
Complementary Ex Situ Conservation Nigel Maxted SADC Crop Wild Relatives Regional training workshop In situ conservation of CWR including diversity assessment techniques Le Meridien Ile Maurice, Mauritius
Molecular characterisation of a population derived from microspores of Brassica napus B. carinata hybrids
 Molecular characterisation of a population derived from microspores of Brassica napus B. carinata hybrids Annaliese Mason 1, Matthew Nelson 1,2, Guijun Yan 1 and Wallace Cowling 1,2 1 School of Plant Biology,
Molecular characterisation of a population derived from microspores of Brassica napus B. carinata hybrids Annaliese Mason 1, Matthew Nelson 1,2, Guijun Yan 1 and Wallace Cowling 1,2 1 School of Plant Biology,
Combining Ability in Diploid andtriploid Sugarbeet Hybrids From Diverse Parents*
 10 Journal of Sugar Beet Research Vol 26 No 1 Combining Ability in Diploid andtriploid Sugarbeet Hybrids From Diverse Parents* J. M. Lasal, I. Romagosa 2, R. J. Hecke~, and J. M. Sanz 1 laula Dei Exp.
10 Journal of Sugar Beet Research Vol 26 No 1 Combining Ability in Diploid andtriploid Sugarbeet Hybrids From Diverse Parents* J. M. Lasal, I. Romagosa 2, R. J. Hecke~, and J. M. Sanz 1 laula Dei Exp.
belonging to the Genus Pantoea
 Emerging diseases of maize and onion caused by bacteria belonging to the Genus Pantoea by Teresa Goszczynska Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree Philosophiae Doctoriae in
Emerging diseases of maize and onion caused by bacteria belonging to the Genus Pantoea by Teresa Goszczynska Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree Philosophiae Doctoriae in
PEST MANAGEMENT: WEEDS
 PEST MANAGEMENT: WEEDS Outcrossing Frequency and Phenotypes of Outcrosses Based on Flowering of Red Rice Accessions and Clearfield Cultivars in the Grand Prairie V.K. Shivrain, N.R. Burgos, J.A. Bullington,
PEST MANAGEMENT: WEEDS Outcrossing Frequency and Phenotypes of Outcrosses Based on Flowering of Red Rice Accessions and Clearfield Cultivars in the Grand Prairie V.K. Shivrain, N.R. Burgos, J.A. Bullington,
Inheritance of plant and tuber traits in diploid potatoes
 Inheritance of plant and tuber traits in diploid potatoes Mosquera, V. 1, Mendoza, H. A. 1, Villagómez. V. 1 and Tay, D. 1 National Agrarian University Peru; International Potato Center (CIP) E-mail: roni_atenea@yahoo.com
Inheritance of plant and tuber traits in diploid potatoes Mosquera, V. 1, Mendoza, H. A. 1, Villagómez. V. 1 and Tay, D. 1 National Agrarian University Peru; International Potato Center (CIP) E-mail: roni_atenea@yahoo.com
Genetic controls of apple fruit-specific auxin metabolism. PI: Yanmin Zhu Co-PI(2): James Mattheis
 FINAL PROJECT REPORT Project Title: Genetic controls of apple fruit-specific auxin metabolism PI: Yanmin Zhu Co-PI(2): James Mattheis Organization: TFRL-ARS-USDA Organization: TFRL-ARS-USDA Telephone:
FINAL PROJECT REPORT Project Title: Genetic controls of apple fruit-specific auxin metabolism PI: Yanmin Zhu Co-PI(2): James Mattheis Organization: TFRL-ARS-USDA Organization: TFRL-ARS-USDA Telephone:
Introduction to Plant Breeding. Master Gardener Training
 Introduction to Plant Breeding Master Gardener Training Start with a seed Germplasm Germplasm The greatest service which can be rendered to any country is to add a useful plant to its culture -Thomas Jefferson
Introduction to Plant Breeding Master Gardener Training Start with a seed Germplasm Germplasm The greatest service which can be rendered to any country is to add a useful plant to its culture -Thomas Jefferson
Germplasm. Introduction to Plant Breeding. Germplasm 2/12/2013. Master Gardener Training. Start with a seed
 Introduction to Plant Breeding Master Gardener Training Start with a seed Germplasm Germplasm The greatest service which can be rendered to any country is to add a useful plant to its culture -Thomas Jefferson
Introduction to Plant Breeding Master Gardener Training Start with a seed Germplasm Germplasm The greatest service which can be rendered to any country is to add a useful plant to its culture -Thomas Jefferson
An Alternaria Leaf Spot of the Sugar Beet
 An Alternaria Leaf Spot of the Sugar Beet J. S. MCFARLANE, ROY BARDIN AND WILLIAM C. SNYDER 1 A hitherto unreported disease of the sugar beet, Beta vulgaris L., incited by a parasitic species of Alternaria
An Alternaria Leaf Spot of the Sugar Beet J. S. MCFARLANE, ROY BARDIN AND WILLIAM C. SNYDER 1 A hitherto unreported disease of the sugar beet, Beta vulgaris L., incited by a parasitic species of Alternaria
COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR CURED LEAF YIELD AND ITS COMPONENT TRAITS IN BIDI TOBACCO (NicotianatabacumL.)
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 1373 1380 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR CURED LEAF YIELD AND ITS COMPONENT TRAITS IN
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 3, 2016, 1373 1380 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMBINING ABILITY ANALYSIS FOR CURED LEAF YIELD AND ITS COMPONENT TRAITS IN
Gene-flow in Beta (beet) complex and its consequences for growing of HT sugar beet
 Gene-flow in Beta (beet) complex and its consequences for growing of HT sugar beet Josef Soukup, Josef Holec and Kateřina Hamouzová Department of Agroecology and Biometeorology Faculty of Agrobiology,
Gene-flow in Beta (beet) complex and its consequences for growing of HT sugar beet Josef Soukup, Josef Holec and Kateřina Hamouzová Department of Agroecology and Biometeorology Faculty of Agrobiology,
Genetic diversity of beech in Greece
 Genetic diversity of beech in Greece A.C. Papageorgiou (1), I. Tsiripidis (2), S. Hatziskakis (1) Democritus University of Thrace Forest Genetics Laboratory Orestiada, Greece (2) Aristotle University of
Genetic diversity of beech in Greece A.C. Papageorgiou (1), I. Tsiripidis (2), S. Hatziskakis (1) Democritus University of Thrace Forest Genetics Laboratory Orestiada, Greece (2) Aristotle University of
4/26/18. Domesticated plants vs. their wild relatives. Lettuce leaf size/shape, fewer secondary compounds
 The final exam: Tuesday, May 8 at 4:05-6:05pm in Ruttan Hall B35. 75 multiple choice questions for 150 points 50 questions from Lecture 20 27 25 questions directly from the first two exams. Key for exam
The final exam: Tuesday, May 8 at 4:05-6:05pm in Ruttan Hall B35. 75 multiple choice questions for 150 points 50 questions from Lecture 20 27 25 questions directly from the first two exams. Key for exam
You are encouraged to answer/comment on other people s questions. Domestication conversion of plants or animals to domestic uses
 The final exam: Tuesday, May 8 at 4:05-6:05pm in Ruttan Hall B35. 75 multiple choice questions for 150 points 50 questions from Lecture 20 27 25 questions directly from the first two exams. Key for exam
The final exam: Tuesday, May 8 at 4:05-6:05pm in Ruttan Hall B35. 75 multiple choice questions for 150 points 50 questions from Lecture 20 27 25 questions directly from the first two exams. Key for exam
Beta vulgaris L. ssp. vulgaris var. altissima Döll
 PROTOCOL FOR TESTS ON DISTINCTNESS, UNIFORMITY AND STABILITY Beta vulgaris L. ssp. vulgaris var. altissima Döll SUGARBEET COMPONENTS UPOV Code: BETAA_VUL Adopted on 21/03/2018 Entry into force on 01/02/2018
PROTOCOL FOR TESTS ON DISTINCTNESS, UNIFORMITY AND STABILITY Beta vulgaris L. ssp. vulgaris var. altissima Döll SUGARBEET COMPONENTS UPOV Code: BETAA_VUL Adopted on 21/03/2018 Entry into force on 01/02/2018
Unit 2 Lesson 4 - Heredity. 7 th Grade Cells and Heredity (Mod A) Unit 2 Lesson 4 - Heredity
 Unit 2 Lesson 4 - Heredity 7 th Grade Cells and Heredity (Mod A) Unit 2 Lesson 4 - Heredity Give Peas a Chance What is heredity? Traits, such as hair color, result from the information stored in genetic
Unit 2 Lesson 4 - Heredity 7 th Grade Cells and Heredity (Mod A) Unit 2 Lesson 4 - Heredity Give Peas a Chance What is heredity? Traits, such as hair color, result from the information stored in genetic
I to the renewed scientific interest in the introduction of cotton stocks from
 THE GENETICS OF FLOWERING RESPONSE IN COTTON. 11. INHERITANCE OF FLOWERING RESPONSE IN A GOSSYPIUM BARBADENSE CROSS1 C. F. LEWIS' AND T. R. RICHMOND Plant Industry Station, Beltsville, Maryland, and Dept.
THE GENETICS OF FLOWERING RESPONSE IN COTTON. 11. INHERITANCE OF FLOWERING RESPONSE IN A GOSSYPIUM BARBADENSE CROSS1 C. F. LEWIS' AND T. R. RICHMOND Plant Industry Station, Beltsville, Maryland, and Dept.
The Wheat Plant and Its Life Cycle
 The Wheat Plant and Its Life Cycle Week 1 Day 4 Lesson Overview The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to the specific structures and functions of a wheat plant as well as to the wheat life
The Wheat Plant and Its Life Cycle Week 1 Day 4 Lesson Overview The purpose of this lesson is to introduce students to the specific structures and functions of a wheat plant as well as to the wheat life
Mitochondrial DNA Variation in Maintainer Lines (O-type) ofsugarbeet
 Mitochondrial DNA Variation 153 Mitochondrial DNA Variation in Maintainer Lines (O-type) ofsugarbeet Zbigniew Sadoch, Rafal Wierzchoslawski and Tadeusz Panczyk Plant Breeding and Acclimatization Institute,
Mitochondrial DNA Variation 153 Mitochondrial DNA Variation in Maintainer Lines (O-type) ofsugarbeet Zbigniew Sadoch, Rafal Wierzchoslawski and Tadeusz Panczyk Plant Breeding and Acclimatization Institute,
H. Paul, B. Henken, O. E. Scholten, Th. S. M. De Bock and W. Lange
 January.June 1994 Resistance in Beta Species of the Section Corollinae Resistance to Po/ymyxa betae and Beet Necrotic Yellow Vein Virus in Beta Species of the Section Coro/linae H. Paul, B. Henken, O.
January.June 1994 Resistance in Beta Species of the Section Corollinae Resistance to Po/ymyxa betae and Beet Necrotic Yellow Vein Virus in Beta Species of the Section Coro/linae H. Paul, B. Henken, O.
EVALUATION OF WILD JUGLANS SPECIES FOR CROWN GALL RESISTANCE
 EVALUATION OF WILD JUGLANS SPECIES FOR CROWN GALL RESISTANCE Ed Stover, Malendia Maccree, Malli Aradhya, Ali E. McClean, and Daniel A. Kluepfel INTRODUCTION Crown Gall disease of walnut is caused by the
EVALUATION OF WILD JUGLANS SPECIES FOR CROWN GALL RESISTANCE Ed Stover, Malendia Maccree, Malli Aradhya, Ali E. McClean, and Daniel A. Kluepfel INTRODUCTION Crown Gall disease of walnut is caused by the
Introduction to Biosystematics - Zool 575
 Introduction to Biosystematics Lecture 8 - Modern Taxonomy Outline - 1. Tools - digital imaging, databases 2. Dissemination - WWW 3. Tools - Molecular data, species demarcation, phylogeography 1 2 Prognosis
Introduction to Biosystematics Lecture 8 - Modern Taxonomy Outline - 1. Tools - digital imaging, databases 2. Dissemination - WWW 3. Tools - Molecular data, species demarcation, phylogeography 1 2 Prognosis
7.2: Natural Selection and Artificial Selection pg
 7.2: Natural Selection and Artificial Selection pg. 305-311 Key Terms: natural selection, selective pressure, fitness, artificial selection, biotechnology, and monoculture. Natural Selection is the process
7.2: Natural Selection and Artificial Selection pg. 305-311 Key Terms: natural selection, selective pressure, fitness, artificial selection, biotechnology, and monoculture. Natural Selection is the process
Apomixis in Plants. Authors. Sven E. Asker, Ph.D. Department of Genetics University of Lund Lund, Sweden
 Apomixis in Plants I (0 ') r,\ q f Authors Sven E. Asker, Ph.D. Department of Genetics University of Lund Lund, Sweden Lenn Jerling, Ph.D. Botany Department University of Stockholm Stockholm, Sweden CRC
Apomixis in Plants I (0 ') r,\ q f Authors Sven E. Asker, Ph.D. Department of Genetics University of Lund Lund, Sweden Lenn Jerling, Ph.D. Botany Department University of Stockholm Stockholm, Sweden CRC
PHYLOGENETIC GROUPING BY PCR ANALYSES OF Sinorhizobium meliloti STRAINS ISOLATED FROM EUTROPHIC SOIL. Abstract
 ID # 15-01 PHYLOGENETIC GROUPING BY PCR ANALYSES OF Sinorhizobium meliloti STRAINS ISOLATED FROM EUTROPHIC SOIL. W.S. Oliveira 1, P.P.A. Oliveira 2, C.M. Bellato 1, F.R.S. Duarte 1, S.M. Tsai 1 1 Universidade
ID # 15-01 PHYLOGENETIC GROUPING BY PCR ANALYSES OF Sinorhizobium meliloti STRAINS ISOLATED FROM EUTROPHIC SOIL. W.S. Oliveira 1, P.P.A. Oliveira 2, C.M. Bellato 1, F.R.S. Duarte 1, S.M. Tsai 1 1 Universidade
Plant Systematics and Plant/Pollinator Interactions. Jacob Landis
 Plant Systematics and Plant/Pollinator Interactions Jacob Landis Why study plants Important for food Clothing Drugs Bryophytes Lycophytes,Monilophytes Gymnosperms Angiosperms Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts
Plant Systematics and Plant/Pollinator Interactions Jacob Landis Why study plants Important for food Clothing Drugs Bryophytes Lycophytes,Monilophytes Gymnosperms Angiosperms Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts
Principles of QTL Mapping. M.Imtiaz
 Principles of QTL Mapping M.Imtiaz Introduction Definitions of terminology Reasons for QTL mapping Principles of QTL mapping Requirements For QTL Mapping Demonstration with experimental data Merit of QTL
Principles of QTL Mapping M.Imtiaz Introduction Definitions of terminology Reasons for QTL mapping Principles of QTL mapping Requirements For QTL Mapping Demonstration with experimental data Merit of QTL
Studies on Fertility Restoration Using Newly Derived Restorers in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.)
 Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.ci (218) 7(1): 2131-2135 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied ciences IN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 1 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.ci (218) 7(1): 2131-2135 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied ciences IN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 1 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original
Family Trees for all grades. Learning Objectives. Materials, Resources, and Preparation
 page 2 Page 2 2 Introduction Family Trees for all grades Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including this one, are available
page 2 Page 2 2 Introduction Family Trees for all grades Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including this one, are available
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
 Chapter Test A CHAPTER 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term, number, or phrase that best answers each question. 1. How many
Chapter Test A CHAPTER 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term, number, or phrase that best answers each question. 1. How many
Lodging-Resistance Breeding of Platycodon grandiflorus Using Distant Hybridization
 American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2015, 6, 2844-2849 Published Online November 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajps http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2015.618281 Lodging-Resistance Breeding
American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2015, 6, 2844-2849 Published Online November 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajps http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2015.618281 Lodging-Resistance Breeding
Mendel and the Gene Idea. Biology Exploring Life Section Modern Biology Section 9-1
 Mendel and the Gene Idea Biology Exploring Life Section 10.0-10.2 Modern Biology Section 9-1 Objectives Summarize the Blending Hypothesis and the problems associated with it. Describe the methods used
Mendel and the Gene Idea Biology Exploring Life Section 10.0-10.2 Modern Biology Section 9-1 Objectives Summarize the Blending Hypothesis and the problems associated with it. Describe the methods used
Biparental Plastid Inheritance in Zantedeschia albomaculata (Araceae)
 Biparental Plastid Inheritance in Zantedeschia albomaculata (Araceae) F. Santiago Brown, R.C. Snijder and J.M. van Tuyl Plant Research International, Wageningen University and Research Centre P.O. Box
Biparental Plastid Inheritance in Zantedeschia albomaculata (Araceae) F. Santiago Brown, R.C. Snijder and J.M. van Tuyl Plant Research International, Wageningen University and Research Centre P.O. Box
HEREDITY: Objective: I can describe what heredity is because I can identify traits and characteristics
 Mendel and Heredity HEREDITY: SC.7.L.16.1 Understand and explain that every organism requires a set of instructions that specifies its traits, that this hereditary information. Objective: I can describe
Mendel and Heredity HEREDITY: SC.7.L.16.1 Understand and explain that every organism requires a set of instructions that specifies its traits, that this hereditary information. Objective: I can describe
Daucus pusillus Michx. l Sarah Schumann Hort 5051 May 5, 2008
 Daucus pusillus Michx. http://www.fireflyforest.com/flowers/whites/white33.htm l Sarah Schumann Hort 5051 May 5, 2008 Taxonomy Scientific Name: Daucus pusillus Michx. Synonyms: D. montevidensis and D.
Daucus pusillus Michx. http://www.fireflyforest.com/flowers/whites/white33.htm l Sarah Schumann Hort 5051 May 5, 2008 Taxonomy Scientific Name: Daucus pusillus Michx. Synonyms: D. montevidensis and D.
Genetic diversity and population structure in rice. S. Kresovich 1,2 and T. Tai 3,5. Plant Breeding Dept, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY
 Genetic diversity and population structure in rice S. McCouch 1, A. Garris 1,2, J. Edwards 1, H. Lu 1,3 M Redus 4, J. Coburn 1, N. Rutger 4, S. Kresovich 1,2 and T. Tai 3,5 1 Plant Breeding Dept, Cornell
Genetic diversity and population structure in rice S. McCouch 1, A. Garris 1,2, J. Edwards 1, H. Lu 1,3 M Redus 4, J. Coburn 1, N. Rutger 4, S. Kresovich 1,2 and T. Tai 3,5 1 Plant Breeding Dept, Cornell
Model plants and their Role in genetic manipulation. Mitesh Shrestha
 Model plants and their Role in genetic manipulation Mitesh Shrestha Definition of Model Organism Specific species or organism Extensively studied in research laboratories Advance our understanding of Cellular
Model plants and their Role in genetic manipulation Mitesh Shrestha Definition of Model Organism Specific species or organism Extensively studied in research laboratories Advance our understanding of Cellular
Teacher s Discussion Notes Part 1
 Teacher s Discussion Notes Part 1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Vocabulary: Chlorophyll--A green substance which gives leaves their color. Chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight, which a plant uses to make food. Chloroplast--A
Teacher s Discussion Notes Part 1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Vocabulary: Chlorophyll--A green substance which gives leaves their color. Chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight, which a plant uses to make food. Chloroplast--A
BREEDING, GENETICS, AND PHYSIOLOGY. Phenotypic Analysis of the 2006 MY2 Mapping Population in Arkansas
 BREEDING, GENETICS, AND PHYSIOLOGY Phenotypic Analysis of the 2006 MY2 Mapping Population in Arkansas E.J. Boza, K.A.K. Moldenhauer, R.D. Cartwright, S. Linscombe, J.H. Oard, and M.M. Blocker ABSTRACT
BREEDING, GENETICS, AND PHYSIOLOGY Phenotypic Analysis of the 2006 MY2 Mapping Population in Arkansas E.J. Boza, K.A.K. Moldenhauer, R.D. Cartwright, S. Linscombe, J.H. Oard, and M.M. Blocker ABSTRACT
Minor Research Project
 Executive Summary Minor Research Project DNA BARCODING OF MURDANNIA (COMMELINACEAE) IN WESTERN GHATS MRP (S)-1409/11-12/KLMG002/UGC-SWRO By Rogimon P. Thomas Assistant Professor Department of Botany CMS
Executive Summary Minor Research Project DNA BARCODING OF MURDANNIA (COMMELINACEAE) IN WESTERN GHATS MRP (S)-1409/11-12/KLMG002/UGC-SWRO By Rogimon P. Thomas Assistant Professor Department of Botany CMS
Curriculum Links. AQA GCE Biology. AS level
 Curriculum Links AQA GCE Biology Unit 2 BIOL2 The variety of living organisms 3.2.1 Living organisms vary and this variation is influenced by genetic and environmental factors Causes of variation 3.2.2
Curriculum Links AQA GCE Biology Unit 2 BIOL2 The variety of living organisms 3.2.1 Living organisms vary and this variation is influenced by genetic and environmental factors Causes of variation 3.2.2
Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies:
 Chapter 3- Human Manipulation of Plants Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies: -a diploid, spore-producing sporophyte -a haploid, gamete-producing gametophyte Sexual Reproduction in
Chapter 3- Human Manipulation of Plants Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies: -a diploid, spore-producing sporophyte -a haploid, gamete-producing gametophyte Sexual Reproduction in
Seed Genetic Purity Assessment of Hybrid Maize Using Microsatellite Markers (SSR)
 Seed Genetic Purity Assessment of Hybrid Maize Using Microsatellite Markers (SSR) Awaludin Hipi 1, Memen Surahman 2, Satriyas Ilyas 2, Giyanto 3 1 West Nusa Tenggara Assesment Institute of Agricultural
Seed Genetic Purity Assessment of Hybrid Maize Using Microsatellite Markers (SSR) Awaludin Hipi 1, Memen Surahman 2, Satriyas Ilyas 2, Giyanto 3 1 West Nusa Tenggara Assesment Institute of Agricultural
Plant Genetic Resources: Effective Utilization
 Plant Genetic Resources: Effective Utilization AU: Please check if the affiliation has been identified correctly. Hikmet Budak Faculty of Engineering and Natural Science, Biological Science and Bioengineering
Plant Genetic Resources: Effective Utilization AU: Please check if the affiliation has been identified correctly. Hikmet Budak Faculty of Engineering and Natural Science, Biological Science and Bioengineering
Taxonomy. Content. How to determine & classify a species. Phylogeny and evolution
 Taxonomy Content Why Taxonomy? How to determine & classify a species Domains versus Kingdoms Phylogeny and evolution Why Taxonomy? Classification Arrangement in groups or taxa (taxon = group) Nomenclature
Taxonomy Content Why Taxonomy? How to determine & classify a species Domains versus Kingdoms Phylogeny and evolution Why Taxonomy? Classification Arrangement in groups or taxa (taxon = group) Nomenclature
Family Trees for all grades. Learning Objectives. Materials, Resources, and Preparation
 page 2 Page 2 2 Introduction Family Trees for all grades Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including this one, are available
page 2 Page 2 2 Introduction Family Trees for all grades Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including this one, are available
Genetic variation between Spanish and American versions of sweet corn. P. Revilla, M. C. Abuín, R. A. Malvar, P. Soengas, B. Ordás, and A.
 Genetic variation between Spanish and American versions of sweet corn inbred lines P. Revilla, M. C. Abuín, R. A. Malvar, P. Soengas, B. Ordás, and A. Ordás Misión Biológica de Galicia, Spanish Council
Genetic variation between Spanish and American versions of sweet corn inbred lines P. Revilla, M. C. Abuín, R. A. Malvar, P. Soengas, B. Ordás, and A. Ordás Misión Biológica de Galicia, Spanish Council
DEVELOPMENTAL GENETICS OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA
 DEVELOPMENTAL GENETICS OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA CHASE BALLARD LINDA EAN HECTOR LOPEZ DR. JOANNA WERNER-FRACZEK IN COLLABORATION WITH DR. PATRICIA SPRINGER S LAB AT UCR AND ROBERT KOBLE PURPOSE OF RESEARCH
DEVELOPMENTAL GENETICS OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA CHASE BALLARD LINDA EAN HECTOR LOPEZ DR. JOANNA WERNER-FRACZEK IN COLLABORATION WITH DR. PATRICIA SPRINGER S LAB AT UCR AND ROBERT KOBLE PURPOSE OF RESEARCH
C.v. Dr. Mohammed Ali Hussein
 C.v. Dr. Mohammed Ali Hussein - Dr Mohammed Ali Hussien Al- Falahe Email: dr.mohammed1953@yahoo.com Tele : 07507718671. - Was born in Baghdad Iraq 1953. - Graduated from Al-Nasar primary school in 1966.
C.v. Dr. Mohammed Ali Hussein - Dr Mohammed Ali Hussien Al- Falahe Email: dr.mohammed1953@yahoo.com Tele : 07507718671. - Was born in Baghdad Iraq 1953. - Graduated from Al-Nasar primary school in 1966.
Class Copy! Return to teacher at the end of class! Mendel's Genetics
 Class Copy! Return to teacher at the end of class! Mendel's Genetics For thousands of years farmers and herders have been selectively breeding their plants and animals to produce more useful hybrids. It
Class Copy! Return to teacher at the end of class! Mendel's Genetics For thousands of years farmers and herders have been selectively breeding their plants and animals to produce more useful hybrids. It
Passiflora coriacea (bat-leafed passion flower)
 Australia/New Zealand Weed Risk Assessment adapted for Florida. Data used for analysis published in: Gordon, D.R., D.A. Onderdonk, A.M. Fox, R.K. Stocker, and C. Gantz. 28. Predicting Invasive Plants in
Australia/New Zealand Weed Risk Assessment adapted for Florida. Data used for analysis published in: Gordon, D.R., D.A. Onderdonk, A.M. Fox, R.K. Stocker, and C. Gantz. 28. Predicting Invasive Plants in
Increasing Processing Tomato Fruit Soluble Solids
 Increasing Processing Tomato Fruit Soluble Solids Diane M Beckles Department of Plant Sciences dmbeckles@ucdavis.edu Processing Tomato Conference @ UC Davis December 13 th 2018 Soil Micronutrients Cultivar
Increasing Processing Tomato Fruit Soluble Solids Diane M Beckles Department of Plant Sciences dmbeckles@ucdavis.edu Processing Tomato Conference @ UC Davis December 13 th 2018 Soil Micronutrients Cultivar
GFP GAL bp 3964 bp
 Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Supplemental Data. Møller et al. (2009) Shoot Na + exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na + transport in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figure 1. Salt-sensitive
Systematics - BIO 615
 ICZN UPDATE Several issues now confronting the zoological community make desirable the development of a 5th edition of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (Code). Prime among them are: 1)
ICZN UPDATE Several issues now confronting the zoological community make desirable the development of a 5th edition of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (Code). Prime among them are: 1)
2013 Breeding Progress for Rust Resistance in Confection Sunflower
 2013 Breeding Progress for Rust Resistance in Confection Sunflower Guojia Ma 1,2, Yunming Long 1,3, Sam Markell 2, Tom Gulya 1 and Lili Qi 1 1 USDA, ARS, NCSL, Fargo, ND 2 NDSU Plant Pathology, Fargo,
2013 Breeding Progress for Rust Resistance in Confection Sunflower Guojia Ma 1,2, Yunming Long 1,3, Sam Markell 2, Tom Gulya 1 and Lili Qi 1 1 USDA, ARS, NCSL, Fargo, ND 2 NDSU Plant Pathology, Fargo,
I. GREGOR MENDEL - father of heredity
 GENETICS: Mendel Background: Students know that Meiosis produces 4 haploid sex cells that are not identical, allowing for genetic variation. Essential Question: What are two characteristics about Mendel's
GENETICS: Mendel Background: Students know that Meiosis produces 4 haploid sex cells that are not identical, allowing for genetic variation. Essential Question: What are two characteristics about Mendel's
Identification of Rhizosphere Abiotic Stress Tolerance and Related Root Traits in Soybean [ Glycine max ( L. ) Merr. ]
![Identification of Rhizosphere Abiotic Stress Tolerance and Related Root Traits in Soybean [ Glycine max ( L. ) Merr. ] Identification of Rhizosphere Abiotic Stress Tolerance and Related Root Traits in Soybean [ Glycine max ( L. ) Merr. ]](/thumbs/91/105886481.jpg) 31 9 2005 9 1132 1137 ACTA AGRONOMICA SINICA Vol131, No19 pp1 1132-1137 Sept1, 2005 1,2 1, 3 1 Ξ ( 1,, 210095 2, 056038) : 301 62,,, P 1 4 6 2, 7 3 3, : : S565 Identification of Rhizosphere Abiotic Stress
31 9 2005 9 1132 1137 ACTA AGRONOMICA SINICA Vol131, No19 pp1 1132-1137 Sept1, 2005 1,2 1, 3 1 Ξ ( 1,, 210095 2, 056038) : 301 62,,, P 1 4 6 2, 7 3 3, : : S565 Identification of Rhizosphere Abiotic Stress
Fei Lu. Post doctoral Associate Cornell University
 Fei Lu Post doctoral Associate Cornell University http://www.maizegenetics.net Genotyping by sequencing (GBS) is simple and cost effective 1. Digest DNA 2. Ligate adapters with barcodes 3. Pool DNAs 4.
Fei Lu Post doctoral Associate Cornell University http://www.maizegenetics.net Genotyping by sequencing (GBS) is simple and cost effective 1. Digest DNA 2. Ligate adapters with barcodes 3. Pool DNAs 4.
Essential Questions. Meiosis. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education
 Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of meiosis? What is the importance of meiosis in providing genetic variation? Meiosis Vocabulary
Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of meiosis? What is the importance of meiosis in providing genetic variation? Meiosis Vocabulary
Biodiversity and sustainability of grasslands
 Biodiversity and sustainability of grasslands Ruaraidh Sackville Hamilton and Ann Cresswell Biodiversity and response to environment 36 Tools to explore genetic diversity within natural populations 37
Biodiversity and sustainability of grasslands Ruaraidh Sackville Hamilton and Ann Cresswell Biodiversity and response to environment 36 Tools to explore genetic diversity within natural populations 37
Transferring Powdery Mildew Resistance Genes from Wild Helianthus into Cultivated Sunflower. Pilar Rojas-Barros, Chao-Chien Jan, and Thomas J.
 Transferring Powdery Mildew Resistance Genes from Wild Helianthus into Cultivated Sunflower Pilar Rojas-Barros, Chao-Chien Jan, and Thomas J. Gulya USDA-ARS, Northern Crop Science Laboratory, Fargo, ND
Transferring Powdery Mildew Resistance Genes from Wild Helianthus into Cultivated Sunflower Pilar Rojas-Barros, Chao-Chien Jan, and Thomas J. Gulya USDA-ARS, Northern Crop Science Laboratory, Fargo, ND
wild tomato tomato teosinte corn, maize
 2 wild tomato tomato teosinte corn, maize 4 Crop Wild Relatives Traditional landraces Modern cultivars Genetic bottlenecks during crop domestication and during modern plant breeding. The circles represent
2 wild tomato tomato teosinte corn, maize 4 Crop Wild Relatives Traditional landraces Modern cultivars Genetic bottlenecks during crop domestication and during modern plant breeding. The circles represent
Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis: Bt Corn, Lignin, and ANOVAs
 Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis: Bt Corn, Lignin, and ANOVAs Part I "Abstract" This case is based on a recent publication Saxena and Stotzky entitled "Bt Corn Has a Higher Lignin Content Than
Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis: Bt Corn, Lignin, and ANOVAs Part I "Abstract" This case is based on a recent publication Saxena and Stotzky entitled "Bt Corn Has a Higher Lignin Content Than
RFLP facilitated analysis of tiller and leaf angles in rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 Euphytica 109: 79 84, 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 79 RFLP facilitated analysis of tiller and leaf angles in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Zhikang Li 1,2,3, Andrew H. Paterson
Euphytica 109: 79 84, 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 79 RFLP facilitated analysis of tiller and leaf angles in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Zhikang Li 1,2,3, Andrew H. Paterson
ESTIMATION OF GERMINATION POSSIBILITIES OF SOME PEAS STORAGES ACCESSIONS AND THE EVALUATION OF SOME QUALITATIVE INDICATORS ON ALBANIAN PLANT GENE BANK
 ESTIMATION OF GERMINATION POSSIBILITIES OF SOME PEAS STORAGES ACCESSIONS AND THE EVALUATION OF SOME QUALITATIVE INDICATORS ON ALBANIAN PLANT GENE BANK Conference on Biotechnological Developments 21 November
ESTIMATION OF GERMINATION POSSIBILITIES OF SOME PEAS STORAGES ACCESSIONS AND THE EVALUATION OF SOME QUALITATIVE INDICATORS ON ALBANIAN PLANT GENE BANK Conference on Biotechnological Developments 21 November
MiGA: The Microbial Genome Atlas
 December 12 th 2017 MiGA: The Microbial Genome Atlas Jim Cole Center for Microbial Ecology Dept. of Plant, Soil & Microbial Sciences Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan U.S.A. Where I m From
December 12 th 2017 MiGA: The Microbial Genome Atlas Jim Cole Center for Microbial Ecology Dept. of Plant, Soil & Microbial Sciences Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan U.S.A. Where I m From
Genetic proof of chromatin diminution under mitotic agamospermy
 Genetic proof of chromatin diminution under mitotic agamospermy Evgenii V. Levites Institute of Cytology and Genetics, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Novosibirsk, Russia Email: levites@bionet.nsc.ru
Genetic proof of chromatin diminution under mitotic agamospermy Evgenii V. Levites Institute of Cytology and Genetics, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Novosibirsk, Russia Email: levites@bionet.nsc.ru
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Haploid plant produced by centromere-mediated genome elimination Chromosomes containing altered CENH3 in their centromeres (green dots) are eliminated after fertilization in a cross to wild
Figure S1. Haploid plant produced by centromere-mediated genome elimination Chromosomes containing altered CENH3 in their centromeres (green dots) are eliminated after fertilization in a cross to wild
Invasion genomics and adaptation in Australian fireweed. Andrew Lowe Peter Prentis, Elly Dormontt University of Adelaide, Australia
 Invasion genomics and adaptation in Australian fireweed Andrew Lowe Peter Prentis, Elly Dormontt University of Adelaide, Australia S. vulgaris var. vulgaris S. squalidus S. eboracensis Oliver Payne & Nick
Invasion genomics and adaptation in Australian fireweed Andrew Lowe Peter Prentis, Elly Dormontt University of Adelaide, Australia S. vulgaris var. vulgaris S. squalidus S. eboracensis Oliver Payne & Nick
, Waxy : A : (2003)
 2003, 26 (3) : 1 6 Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University ( T1 ae stivum L1) Waxy 3, (, 210095) : SDS2PAGE 293 ( ) Waxy, Wx2A1 2 ; Wx2B1 15, 14 ; Wx2D1 2 ; Wx2A1 Wx2B1 2 ; 3 Waxy, Wx2A1 STS : ; Waxy
2003, 26 (3) : 1 6 Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University ( T1 ae stivum L1) Waxy 3, (, 210095) : SDS2PAGE 293 ( ) Waxy, Wx2A1 2 ; Wx2B1 15, 14 ; Wx2D1 2 ; Wx2A1 Wx2B1 2 ; 3 Waxy, Wx2A1 STS : ; Waxy
Lentils biodiversity: the characterization of two local landraces
 Nimis P. L., Vignes Lebbe R. (eds.) Tools for Identifying Biodiversity: Progress and Problems pp. 327-331. ISBN 978-88-8303-295-0. EUT, 2010. Lentils biodiversity: the characterization of two local landraces
Nimis P. L., Vignes Lebbe R. (eds.) Tools for Identifying Biodiversity: Progress and Problems pp. 327-331. ISBN 978-88-8303-295-0. EUT, 2010. Lentils biodiversity: the characterization of two local landraces
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The phenotypes of PI , BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype of the HI strain. (A) Phenotype of the HI and wild type plant after flowering (~1month). Wild type plant is tall with well elongated inflorescence. All four HI plants
Keywords: CGMS, combining ability, fertility restoration, heterosis, pigeonpea. Introduction
 Sri Lanka Journal of Food and Agriculture (2015) Byregowda et al. 1(2): 1-8 ISSN 2424-6913 Research Paper Identification of fertility restorers, stable combiners and heterotic combinations across environments
Sri Lanka Journal of Food and Agriculture (2015) Byregowda et al. 1(2): 1-8 ISSN 2424-6913 Research Paper Identification of fertility restorers, stable combiners and heterotic combinations across environments
3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of selective breeding?
 UNIT VI - PLANT TECHNOLOGIES Lesson 1: Traditional Plant Breeding Competency/Objective: Describe traditional plant breeding processes. Study Questions References: 1. What is natural crossbreeding? 2. What
UNIT VI - PLANT TECHNOLOGIES Lesson 1: Traditional Plant Breeding Competency/Objective: Describe traditional plant breeding processes. Study Questions References: 1. What is natural crossbreeding? 2. What
Kentucky Seed Certification Standards. I. Explanation of General Standards as Applied to Corn Hybrids
 Kentucky Seed Certification Standards H Y B R I D C O R N I. Explanation of General Standards as Applied to Corn Hybrids A. The General Seed Certification Standards as adopted are basic and, together with
Kentucky Seed Certification Standards H Y B R I D C O R N I. Explanation of General Standards as Applied to Corn Hybrids A. The General Seed Certification Standards as adopted are basic and, together with
Studies on the Bulb Development and Its Physiological Mechanisms in Lilium Oriental Hybrids
 Studies on the Bulb Development and Its Physiological Mechanisms in Lilium Oriental Hybrids Y.P. Xia, H.J. Zheng and C.H. Huang Department of Horticulture College of Agriculture and Biotechnology Zhejiang
Studies on the Bulb Development and Its Physiological Mechanisms in Lilium Oriental Hybrids Y.P. Xia, H.J. Zheng and C.H. Huang Department of Horticulture College of Agriculture and Biotechnology Zhejiang
Benefits of Insect Pollination to Confection Sunflowers: Comparisons across three states and multiple hybrids
 Benefits of Insect Pollination to Confection Sunflowers: Comparisons across three states and multiple hybrids Rachel Mallinger, Jarrad Prasifka, USDA-ARS Fargo ND Adam Varenhorst SDSU Jeff Bradshaw, University
Benefits of Insect Pollination to Confection Sunflowers: Comparisons across three states and multiple hybrids Rachel Mallinger, Jarrad Prasifka, USDA-ARS Fargo ND Adam Varenhorst SDSU Jeff Bradshaw, University
Introduction. Populus trichocarpa TORR. and GRAY. By M. G. R. CANNELL and S. C. WILLETT
 Shoot Growth Phenology, Dry Matter Distribution and Root: Shoot Ratios of Provenances of Populus trichocarpa, Picea sitchensis and Pinus contorta growing in Scotland By M. G. R. CANNELL and S. C. WILLETT
Shoot Growth Phenology, Dry Matter Distribution and Root: Shoot Ratios of Provenances of Populus trichocarpa, Picea sitchensis and Pinus contorta growing in Scotland By M. G. R. CANNELL and S. C. WILLETT
Conceptually, we define species as evolutionary units :
 Bio 1M: Speciation 1 How are species defined? S24.1 (2ndEd S26.1) Conceptually, we define species as evolutionary units : Individuals within a species are evolving together Individuals of different species
Bio 1M: Speciation 1 How are species defined? S24.1 (2ndEd S26.1) Conceptually, we define species as evolutionary units : Individuals within a species are evolving together Individuals of different species
unique aspect of pollen competition. A pollen mixture may Petunia hybrida
 Acta 801. Neerl. 31(1/2), February 1982, p. 97-103, The effect of delayed pollination in Petunia hybrida Gabriella+Bergamini Mulcahy* D.L. Mulcahy*, and P.L. Pfahler ** * Departmentof Botany, University
Acta 801. Neerl. 31(1/2), February 1982, p. 97-103, The effect of delayed pollination in Petunia hybrida Gabriella+Bergamini Mulcahy* D.L. Mulcahy*, and P.L. Pfahler ** * Departmentof Botany, University
Microbiome: 16S rrna Sequencing 3/30/2018
 Microbiome: 16S rrna Sequencing 3/30/2018 Skills from Previous Lectures Central Dogma of Biology Lecture 3: Genetics and Genomics Lecture 4: Microarrays Lecture 12: ChIP-Seq Phylogenetics Lecture 13: Phylogenetics
Microbiome: 16S rrna Sequencing 3/30/2018 Skills from Previous Lectures Central Dogma of Biology Lecture 3: Genetics and Genomics Lecture 4: Microarrays Lecture 12: ChIP-Seq Phylogenetics Lecture 13: Phylogenetics
GENETIC DIVERGENCE IN PEA (PISUM SATIVUM L.)
 Plant Archives Vol. 14 No. 2, 2014 pp. 887-891 ISSN 0972-5210 GENETIC DIVERGENCE IN PEA (PISUM SATIVUM L.) B. Senthamizh Selvi*, J. Rajangam and R. Muthuselvi Horticultural Research Station, Tamil Nadu
Plant Archives Vol. 14 No. 2, 2014 pp. 887-891 ISSN 0972-5210 GENETIC DIVERGENCE IN PEA (PISUM SATIVUM L.) B. Senthamizh Selvi*, J. Rajangam and R. Muthuselvi Horticultural Research Station, Tamil Nadu
Biological Evolution
 Biological Evolution What is Evolution Evolution is descent with modification Microevolution = changes in gene (allele) frequency in a population from one generation to the next Macroevolution = descent
Biological Evolution What is Evolution Evolution is descent with modification Microevolution = changes in gene (allele) frequency in a population from one generation to the next Macroevolution = descent
Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials
 Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials Margaret Worthington Graduate Group in Horticulture and Agronomy University of California, Davis April 14, 2009 http://www.judithbarathart.com
Cryotherapy: A New Method to Eliminate Pathogens from Sweetpotato Propagation Materials Margaret Worthington Graduate Group in Horticulture and Agronomy University of California, Davis April 14, 2009 http://www.judithbarathart.com
New Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii isolates: collection, identification and screening of efficiency in symbiosis with clover
 New Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii isolates: collection, identification and screening of efficiency in symbiosis with clover T. Šimon Research Institute of Crop Production, Prague-Ruzyne, Czech Republic
New Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii isolates: collection, identification and screening of efficiency in symbiosis with clover T. Šimon Research Institute of Crop Production, Prague-Ruzyne, Czech Republic
Washington Grain Commission Wheat and Barley Research Annual Progress Reports and Final Reports
 Washington Grain Commission Wheat and Barley Research Annual Progress Reports and Final Reports PROJECT #: 30109-5345 Progress report year: 3 of 3 Title: Evaluation And Selection For Cold Tolerance In
Washington Grain Commission Wheat and Barley Research Annual Progress Reports and Final Reports PROJECT #: 30109-5345 Progress report year: 3 of 3 Title: Evaluation And Selection For Cold Tolerance In
TAXONOMY GENERAL INFORMATION
 Plant Propagation Protocol for Pteryxia terebinthina ESRM 412 Native Plant Production Protocol URL: https://courses.washington.edu/esrm412/protocols/ptte.pdf Plant Family Scientific Name Common Name Species
Plant Propagation Protocol for Pteryxia terebinthina ESRM 412 Native Plant Production Protocol URL: https://courses.washington.edu/esrm412/protocols/ptte.pdf Plant Family Scientific Name Common Name Species
Shaw Nature Reserve. Preserving and documenting diversity By Garrett Billings
 Shaw Nature Reserve Preserving and documenting diversity By Garrett Billings History of Shaw Nature Reserve Burned frequently Native Americans Natural fire regimes Used almost exclusively as agriculture
Shaw Nature Reserve Preserving and documenting diversity By Garrett Billings History of Shaw Nature Reserve Burned frequently Native Americans Natural fire regimes Used almost exclusively as agriculture
Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit. M preps M preps M preps
 Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit M5635-00 5 preps M5635-01 50 preps M5635-02 200 preps January 2013 Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Preparing
Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit M5635-00 5 preps M5635-01 50 preps M5635-02 200 preps January 2013 Mag-Bind Soil DNA Kit Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Preparing
