b g 6. P 2 4 π b g b g of the way from A to B. LATE AND ABSENT HOMEWORK IS ACCEPTED UP TO THE TIME OF THE CHAPTER TEST ON ASSIGNMENT DUE
|
|
|
- Timothy Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Trig/Math Anal Name No LATE AND ABSENT HOMEWORK IS ACCEPTED UP TO THE TIME OF THE CHAPTER TEST ON HW NO. SECTIONS (Brown Book) ASSIGNMENT DUE V 1 1 1/1 Practice Set A V 1 3 Practice Set B #1 1 V B 1 3 Practice Set G V Practice Set C V 3B 1 4 Practice Set K V Practice Set D V Practice Set E V Practice Set F #1 3 V 7 Review Practice Set F #4 17 Practice Set A: Vectors 1. UNavigation: U ship travels 00 km west from port and then 40 km due south before it is disabled. Illustrate this in a vector diagram. Use trigonometry to find the course that a rescue ship must take from port in order to reach the disabled ship.. UAviation:U On graph paper, make a diagram that illustrates the velocity of an airplane heading east at 400 knots. Illustrate a wind velocity of 50 knots blowing toward the northeast. If the airplane encounters this wind, illustrate its resultant velocity. Estimate the resultant speed and direction of the airplane. (The direction is the angle the resultant makes with due north measured clockwise from north.) Plot points A and B. Give the component form of AB and find AB b g b g 4. Ab 3, 5 g, Bb 5, 1g 3. A 1,, B 3, Polar coordinates of point P are given and O is the origin. Draw vector OP and give its component form. 5. P 6, 7 b g 6. P 4 π b, 3 g = b3, 1 g, = b 8, 4 g, and = b 6, g. Calculate each expression. 7. Let u v w a. u + v b. u v c. 3u+ w d. 3u+ w Find the coordinates of the point P described A 0, 0, B 6, 3 ; 4 9. A 7,, B, 8 ; 5 b g b g of the way from A to B. b g b g of the way from A to B. TMA Assignment List - Vectors Page 1
2 10. UPhysics:U Suppose that you pull a child in a wagon by pulling a rope that makes a 60 angle with the ground. a. If the pulling force F is 40 lb in the direction of the rope, give the horizontal and vertical components of the force. b. Which component, horizontal or vertical, moves the wagon along the ground? c. If the rope made a50 angle with the ground rather than a 60 angle, would the wagon move more easily or less easily? Why? Practice Set B: Vectors and Parametric Equations Find vector and parametric equations for each specified line. 1. The line through (1, 5) with direction vector. The line through (1, 0) and (3, 4) (, 1) 3. The line through (, 3) and (5, 1) 4. The horizontal line through π, e 5. A point moves in the plane so that its position Pxy, b g b g b xy, = 14, + t3, g b g b g at time t is given by the equation a. Graph the point s position at the times t = 0, 1,, 3, -1, -, and - 3 b. Find the velocity and speed of the moving point. c. Find the parametric equations of the moving point. 6. Find the vector and parametric equations of the moving object with velocity (3, 1) and position vector at time t = 0 is (, 3). 7. A line has vector equationbxy, g = b3, g + tb4, g. Give a pair of parametric equations and a Cartesian equation of the line. 8. A line has parametric equations x = 5 t and y = 4+ t. Give a vector equation and a Cartesian equation of the line. 9. a. Describe the line having parametric equations x = and y = t. b. Give a direction vector of the line. c. What can you say about the slope of the line? 10. a. A line has direction vector (, 3). What is the slope of the line? b. A line has direction vector (4, 6). What is the slope of the line? c. Explain why the following lines are parallel: d. Find a vector equation of the line through (7, 9) and parallel to these lines. 11. At time t, the position of an object moving with constant velocity is given by the parametric equations x = 3 t and y = 1+ t. a. What are the velocity and speed of the object? b. When and where does it cross the line x + y =. b g b g b 1 b g + y = 5? Illustrate with a sketch. 1. An object moves with constant velocity so that its position at time t is xy, = 1, 1 + t 1, 1. When and where does the object cross the circle x 13. Without graphing, describe the curve with parametric equations x = r cos t and y = rsin t. (Hint: What is the value of x + y?) g TMA Assignment List - Vectors Page
3 14. a. Before graphing, describe what you think the curve with parametric equations x = cos t and y = 5sin t looks like. Then graph the equations. b. Find a Cartesian equation for the parametric equations given in part (a) c. An ellipse has Cartesian equation 4x + y = 36. What do you think the parametric equations of the ellipse are? Check your answer by graphing. Practice Set C: Parallel and Perpendicular Vectors; Dot Products, 3 4, 5 3, 5 7, 4 1. Find: a. ( ) ( ) b. ( ) ( ). Find the value of a if the vectors (4, 6) and (a, 3) are a. parallel b. perpendicular 3. If u =, 3 TMA Assignment List - Vectors Page 3 g, find: a. u u b. u b5, 3g and b3, 7g, verify that a. u v = v u b. bu vg = bug v b g b g b g if u= b, 5 g, v = b1, 3 g, and w= b 1, g b g and v = b, 1g is 45. b3, 4g and v = b3, 4g. 4. If u= v = 5. Verify that u v+ w = u v + u w 6. Verify that the angle between u = 1, 3 7. Find the measure of the angle between u = 8. Given A(1, 5), B(4, 6), and C(, 8), find the measure of A. 9. Given P(0, 3), Q(, 4), and R(3, 7), verify that cos P = a. Given A(1, 3), B( 1, 3) and C(6, ), find cos C and sin C. b. Use the formula Area = 1 ab sin C to find the area of ΔABC Practice Set D: Vectors in Three Dimensions 1. Find the length and midpoint of AB : A=(, 5, 3) and B=(0, 3, 1). Simplify 3,8, 4, 1, 1, 8, 6 5,,1 a. ( ) + ( ) b. ( ) ( ) c. ( 3,5,1 ) 3. Find the value of k if (, k, 3) and ( 4,,6 ) are perpendicular. 4. Find an equation of the sphere with radius 7 and center (1, 5, 3). Show that point ( 7,7,6 ) is on the sphere. 5. Find the center and radius of the sphere with equation x + y + z + x 4y 6z = Find the angle between (8, 6, 0) and (, 1, ) to the nearest tenth of a degree. 7. Let A = ( 1, 3, 4), B = ( 3, 1, 0), and C = ( 3,, 6). a. Show that AB and AC are perpendicular. b. Find the area of right triangle ABC 8. Line L has vector equation ( xyz,, ) = (, 0,1) + t( 4, 1,1) a. Find three parametric equations of L. b. Name two points on L. c. Write a vector equation of the line containing (1,, 3) and parallel to L 4,, 1 B 6,3,. 9. Write vector and parametric equations for the line containing A( ) and ( ) 10. Where does the line ( xyz,, ) = ( 6, 5,4) + t( 3,,4) intersect a. the xy plane b. the yz plane c. the xz plane
4 11. Describe the set of points S in the xy plane that are also on the sphere whose equation x 1 + y + z 3 = 5. Give an equation of S. is( ) ( ) ( ) 1. Show that the lines with equations ( xyz,, ) ( 1,5,0) t( 1,, 1) ( xyz,, ) ( 0,1,3) s( 1, 1,1) = + and = + intersect. Find the coordinates of their point of intersection. Practice Set E: Vectors and Planes 1. Sketch the plane: a. x+ 3y+ 6z = 1 b. 3x+ y+ z = 6. Find a vector perpendicular to the plane whose equation is 3x+ 4y+ 6z = 1 3. Find a Cartesian equation of the plane: a. Vector (, 3, 5) is perpendicular to the plane that contains point A(3, 1, 7) b. Vector (1, 4, ) is perpendicular to the plane that contains point A(3, 0, ) 4. Consider the points A(,, ) and B(4, 6, 8) a. Find a Cartesian equation of the plane that is perpendicular to AB at its midpoint M. b. Show that the point P(,0,8) satisfies your answer to part (a) 5. Find an equation of the plane tangent to the sphere ( x 1) + ( y 1) + ( z 1) = 49 at the point (7, 1, 4). 6. The plane z = 3 intersects the sphere x + y + z = 5 in a circle. Find the area of the circle. 7. To the nearest tenth of a degree, find the measure of the angle between the planes x + y z = 3 and x+ y+ z = Are the planes 3x+ 4y+ z = 5 and x y z = 3 perpendicular? 9. Which of the following planes are perpendicular and which are parallel? M :3x+ y z = 6 M :6x+ 4y z = 8 1 M3 = 4x y+ 8z = 7 Practice Set F: Determinants and Vectors 1. Let u = ( 4,0,1 ), v= ( 5, 1,0 ), and w= ( 3,1, ) a. Calculate v u and u v. Do your results agree with property? b. Verify that u vis perpendicular to u and to v. c. Find the area of the parallelogram determined by u and v.. Let P(1,1,0), Q( 1,0,), and R(,1,1) a. Find a vector perpendicular to the plane determined by P, Q, and R. b. Find a Cartesian equation of the plane determined by P, Q, and R. 3. Angle θ is between vectors u = (1,,) and v = (4,3,0) a. Find sinθ by using property 3 of the cross product b. Find cosθ by using the dot product property c. Verify that sin θ + cos θ = 1 Review Section: 4. An object is pulled due south by a force F 1 of 5 N, and due east by a force F of 1 N. Find the direction and magnitude of F3 = F1+ F 5. Find the component form of AB and find AB if A(7, ) and B(3,4) 6. Given polar coordinates P (8,140 ) draw OP and find its component form. TMA Assignment List - Vectors Page 4
5 7. Find the coordinates of the point P, 1 4 of the way from A(1, 4) to B (5, 4) 8a. Find the velocity and speed of an object that moves with constant velocity so that its position at time t is ( xy, ) = (, ) + t( 1,4) 8b. Find a pair of parametric equations of the path of the object. 8c. When and where does it intersect the parabola y = 4x 6x? 9. Find vector and parametric equations for the line through A(3,1) and B( 4, 4) 10. Find a Cartesian equation for the vector equation ( xy, ) = (, 3) + t( 5,4) 11. Find the value of a if vectors (4, ) and ( a,8) are a. parallel b. perpendicular 1. If u = (,3 ) and v= ( 4,1) a. find u v b. find the angle between u and v 13. Given A(4,3), B(5, ), and C(8,1), find m B. 14. Given the points A(4,0, 5), and B( 6,,7) a. find the length of AB b. find the midpoint of AB 15. Line L has equation ( xyz,, ) = ( 0, 1,6) + t( 4, 1, 3) a. Write a vector equation for the line through (,1,7) parallel to L. b. Where does L intersect the xz plane? 16. Find an equation of the plane that is tangent to the sphere with equation ( ) ( ) x y z = 33 at the point (, 3, ). 17. A(0,1, 3), B( 6,1,1) and C(4,5,) determine a plane. a. find a vector perpendicular to the plane b. find the area of triangle ABC Practice Set G: Vectors and Parametric Equations Find AB and AB : A 3,, B 4,3 1. ( ) ( ). A( 4,1 ) B( 7, ) Draw vector OP and give its component form: 3. P ( 4, 11 ) 4. P ( 6,13 ) 5. Let u = ( 4,5 ), v = ( 4, 6 ) and w = (,8). Calculate each expression. a. 4u+ w b. u 3v c. 5v d. 4u+ w 6. Find the coordinates of the point P 3 7. Find the coordinates of the point P 3 4 of the way from A(, 4) to B(7, ) of the way from A( 6, 5) to B(, 9) Find vector and parametric equations for each specified line. 8. The line through ( 1, 4) and (5, 8) 9. The vertical line through (, 3) TMA Assignment List - Vectors Page 5
6 10. A point moves in the plane so that its position Pxy, ( xy), = ( 4,3) + t(, 5) b g at time t is given by the equation d. Graph e. Find the velocity and speed of the moving point. f. Find the parametric equations of the moving point. 11. A line has vector equation ( xy, ) = ( 1,3) + t( 4,). Give a pair of parametric equations and a Cartesian equation of the line. x = 5+ 3t 1. A line has parametric equations. Write a vector and Cartesian equation for the y = 4t line. 13. Line L has equation ( xy, ) = ( 4, ) + t( 3,8). a. Write a vector equation for the line through (,1) parallel to L. b. Write a vector equation for the line through (4, 3) perpendicular to L. 14. The velocity of a plane heading west is 55 knots. It encounters a wind heading north east with a velocity of 5 knots. Calculate the resultant speed and direction of the plane. Practice Set K: Vectors and Parametric Equations 1. Find AB and AB : A( 4, 3 ), B( 1,6 ). Draw vector OP and give its component form: P ( 6, 3 ) 3. Let u = ( 3,6 ), v = (, 1 ) and w = ( 4,5). Calculate each expression. a. u + w b. 4u v c. 3v d. 4u v e. uv i 4. Find the coordinates of the point P 5 6 of the way from A( 4, 3) to B(, 15) Find vector and parametric equations for each specified line. 5. The line through ( 5, 7) and (3, ) 6. The horizontal line through (5, 3) 7. A point moves in the plane so that its position Pxy, ( xy) b g at time t is given by the equation, = (, 5) + t(3, 1) a. Graph b. Find the velocity and speed of the moving point. 8. A line has vector equation ( xy, ) = ( 4, 3) + t( 7,5). Give a pair of parametric equations and a Cartesian equation of the line. 9. An object moves with constant velocity so that its position at time t is ( xy, ) = (,1) + t( 1,1). When and where does the object cross the line3x+ 4y = 15? 10. Find the value of a if the vectors (3a, 4) and (5, 7) are a. parallel b. perpendicular u = ( 4, 7 ) and v = (,8) 3( uv i ) 11. If find u = ( 5, ) v = ( 3,1) 1. Find the measure of the angle between and. 13. Given A(, 7), B( 3, 6), and C(5, 1), find the measure of ABC. 14. Given P(5, ), Q( 3, 4), and R(6, 1), find the measure of QPR. TMA Assignment List - Vectors Page 6
7 = +. a. Write a vector equation for the line through (3, 5) parallel to L. b. Write a vector equation for the line through (, 3) perpendicular to L. 16. The velocity of a plane heading south is 340 knots. It encounters a wind heading south west with a velocity of 65 knots. Calculate the resultant speed and direction of the plane. 15. Line L has equation ( xy, ) ( 5,) t( 4,8) ANSWERS Practice Set A knots; (, 0); 4. (, 6); (1.85, 5.71) 6. ( 1, 1.73) 7a. ( 5, 5) 7b. (11, 3) 7c. (3, 1) 7d , 3 b g 9. (3, 6) d i 10b. horizontal 10c. easier 10a. 0, 0 3 Practice Set B 1. xy, = 15, + t, 1; x= 1+ t, y= 5 t. xy, = 10, + t, 4 ; x= 1+ t, y= 4 t g b g b g b g b g b, g = b, g + b, g; = +, = b g bπ g b10 g = b3, g ; = 13 5c. x = t; y = 4 t, =, +, ; = +, =, ; b, g = b54, g + b 1, g; + = 14 9a. vertical line thru (, 0) b, g = b 79, g + b 3, g v= 3, ; v = 13 11b. t = 1; b5, 3g 3. xy 3 t7 x 7t y 3 t 4. xy, =, e+ t, ; x= π + t, y= e 5b. v v 6. xy 3 t3 1 x 3t y 3 t 7. x = 3+ t y = + 4t x y = 4 8. xy t x y 9b. (0, 1) 9c. slope is undefined 10a b c. slopes are equal 10d. xy t 11a. ( ) b g b g 13. circle; radius=r; center (0,0) 1. t = 1, 0, ; t =, 3, 1 14a. ellipse; vertices 0,± 5 b g 14b. 5x + 4y = c. x = 3cos t, y = 6sin t Practice Set C 1a. 7 1b. 1. ; ; a. cos C = 06. ; sin C = b. 0 Practice Set D 1. 6; (1, 4, 1) a. (11, 6, ) b. 5 c. 35 x+ 1 + y + z 3 = b k=5 5. ( ) ( ) ( ) 8a. x = + 4t ; y= t; z = 1+ t 8b. ex: t = 1, (, 1, ) ; t =, ( 6,,3) 8c. ( xyz,, ) = ( 1,,3) + t( 4, 1,1) 9. Vector: ( xyz,, ) = ( 4,, 1) + t(,1,3 ); Parametric: x = 4+ t; y = + t; z = 1+ 3t 10a. (3, 3,0) 10b. (0, 1, 4) 10c. ( 3,0, 6 ) 11. ( x 1) ( y ) 16 + = 1. (, 3, 1) Practice Set E. (3, 4, 6) 3a. x+ 3y+ 5z = 44 3b. 1x 4y+ z = 7 4a. x+ 4y+ 6z = x y+ 3z = x + y = 16; A= 16π M1 M ; M1 M3; M M3 TMA Assignment List - Vectors Page 7
8 Practice Set F 1c. 4a. ( 1,4,1) b. x + 4y+ z = 3 3a AB = 4,6 ; AB = ( 6.14,5.14) 3b , 13N 5. ( ) 7. (,) 8a. v= (1, 4); v = ( ) 8b. x = + t; y = + 4t 8c. t = 3 :( 1,4); t = 5: ( 3,18) 4 3 x, y = (3,1) + t( 7, 5); x= 3 7 t; y = 1 5t 10. y = x 11a b. 4 1a. 5 1b xyz,, =,1,7 + t4, 1, 3 14a b. ( 1, 1,1) 15a. ( ) ( ) ( ) 15b. ( 4,0,9) 16. x y 5z = 0 17a. ( 16,46, 4) 17b. 7.1 Practice Set G AB = 7,5 ; AB = 74 ; AB = ( ). AB = ( 11, 3) 3. ( 1.5,3.71) 4. ( 4.01,4.46) 5a. ( 18,8) 5b. ( 16,3) 5c d ( 4,0 ) 7. (0, 8) 8. ( xy, ) = ( 1,4) + t( 6,4) ; x = 1+ 6 t; y = 4+ 4t 9. ( xy, ) = (, 3) + t( 0,1) ; x = ; y = 3 + t 10b. velocity = (, 5) ; speed = 9 10c. x = 4+ t; y = 3 5t 11. x = 1+ 4 t; y = 3+ t; x 4y = ( ) ( ) ( ) 13a. ( xy, ) = (,1) + t( 3,8) 13b. ( xy, ) = ( 4, 3) + t( 8,3) ; Practice Set K AB = 5,9 ; AB = ( ) xy, = 5, + t3, 4 ; 4x+ 3y= 14. ( 3.69, 4.73) 3a. ( 11,16) 3b. ( 16,6) 3c. 45 3d. 93 3e ( 1, 1) 5. ( xy, ) = ( 5,7) + t( 8, 9) ; x = 5+ 8 t; y = 7 9t 6. ( xy, ) = ( 5, 3) + t( 1,0) ; x= 5 + t; y = 3 7b. velocity = ( 3, 1) 9. when t = 5 ; where ( 3, 6) ; speed = x = 4+ 7 t; y = 3+ 5t; 5x 7y = a. 10b xy, 3, 5 t 4,8 xy, =, 3 + t8,4 15a. ( ) = ( ) + ( ) 15b. ( ) ( ) ( ) ; TMA Assignment List - Vectors Page 8
DATE: MATH ANALYSIS 2 CHAPTER 12: VECTORS & DETERMINANTS
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: MATH ANALYSIS 2 MR. MELLINA CHAPTER 12: VECTORS & DETERMINANTS Sections: v 12.1 Geometric Representation of Vectors v 12.2 Algebraic Representation of Vectors v 12.3 Vector and Parametric
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: MATH ANALYSIS 2 MR. MELLINA CHAPTER 12: VECTORS & DETERMINANTS Sections: v 12.1 Geometric Representation of Vectors v 12.2 Algebraic Representation of Vectors v 12.3 Vector and Parametric
5. A triangle has sides represented by the vectors (1, 2) and (5, 6). Determine the vector representing the third side.
 Vectors EXAM review Problem 1 = 8 and = 1 a) Find the net force, assume that points North, and points East b) Find the equilibrant force 2 = 15, = 7, and the angle between and is 60 What is the magnitude
Vectors EXAM review Problem 1 = 8 and = 1 a) Find the net force, assume that points North, and points East b) Find the equilibrant force 2 = 15, = 7, and the angle between and is 60 What is the magnitude
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
BC VECTOR PROBLEMS. 13. Find the area of the parallelogram having AB and AC as adjacent sides: A(2,1,3), B(1,4,2), C( 3,2,7) 14.
 For problems 9 use: u (,3) v (3, 4) s (, 7). w =. 3u v = 3. t = 4. 7u = u w (,3,5) 5. wt = t (,, 4) 6. Find the measure of the angle between w and t to the nearest degree. 7. Find the unit vector having
For problems 9 use: u (,3) v (3, 4) s (, 7). w =. 3u v = 3. t = 4. 7u = u w (,3,5) 5. wt = t (,, 4) 6. Find the measure of the angle between w and t to the nearest degree. 7. Find the unit vector having
Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations.
 1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 3 2, 5 2 C) - 5 2
 Test Review (chap 0) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. ) Find the point on the curve x = sin t, y = cos t, -
Test Review (chap 0) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. ) Find the point on the curve x = sin t, y = cos t, -
Exercise. Exercise 1.1. MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 1
 MA112 Section 750001: Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 1 Exercise Exercise 1.1 1 8 Find the vertex, focus, and directrix of the parabola and sketch its graph. 1. x = 2y 2 2. 4y +x 2 = 0 3. 4x 2 =
MA112 Section 750001: Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 1 Exercise Exercise 1.1 1 8 Find the vertex, focus, and directrix of the parabola and sketch its graph. 1. x = 2y 2 2. 4y +x 2 = 0 3. 4x 2 =
11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System
 11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System In three dimensions, a point has three coordinates: (x,y,z). The normal orientation of the x, y, and z-axes is shown below. The three axes divide the region into
11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System In three dimensions, a point has three coordinates: (x,y,z). The normal orientation of the x, y, and z-axes is shown below. The three axes divide the region into
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #2, Math 253
 SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #, Math 5. Find the equation of a sphere if one of its diameters has end points (, 0, 5) and (5, 4, 7). The length of the diameter is (5 ) + ( 4 0) + (7 5) = =, so the
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #, Math 5. Find the equation of a sphere if one of its diameters has end points (, 0, 5) and (5, 4, 7). The length of the diameter is (5 ) + ( 4 0) + (7 5) = =, so the
(arrows denote positive direction)
 12 Chapter 12 12.1 3-dimensional Coordinate System The 3-dimensional coordinate system we use are coordinates on R 3. The coordinate is presented as a triple of numbers: (a,b,c). In the Cartesian coordinate
12 Chapter 12 12.1 3-dimensional Coordinate System The 3-dimensional coordinate system we use are coordinates on R 3. The coordinate is presented as a triple of numbers: (a,b,c). In the Cartesian coordinate
Example 2.1. Draw the points with polar coordinates: (i) (3, π) (ii) (2, π/4) (iii) (6, 2π/4) We illustrate all on the following graph:
 Section 10.3: Polar Coordinates The polar coordinate system is another way to coordinatize the Cartesian plane. It is particularly useful when examining regions which are circular. 1. Cartesian Coordinates
Section 10.3: Polar Coordinates The polar coordinate system is another way to coordinatize the Cartesian plane. It is particularly useful when examining regions which are circular. 1. Cartesian Coordinates
3. Interpret the graph of x = 1 in the contexts of (a) a number line (b) 2-space (c) 3-space
 MA2: Prepared by Dr. Archara Pacheenburawana Exercise Chapter 3 Exercise 3.. A cube of side 4 has its geometric center at the origin and its faces parallel to the coordinate planes. Sketch the cube and
MA2: Prepared by Dr. Archara Pacheenburawana Exercise Chapter 3 Exercise 3.. A cube of side 4 has its geometric center at the origin and its faces parallel to the coordinate planes. Sketch the cube and
8. Find r a! r b. a) r a = [3, 2, 7], r b = [ 1, 4, 5] b) r a = [ 5, 6, 7], r b = [2, 7, 4]
![8. Find r a! r b. a) r a = [3, 2, 7], r b = [ 1, 4, 5] b) r a = [ 5, 6, 7], r b = [2, 7, 4] 8. Find r a! r b. a) r a = [3, 2, 7], r b = [ 1, 4, 5] b) r a = [ 5, 6, 7], r b = [2, 7, 4]](/thumbs/95/122742655.jpg) Chapter 8 Prerequisite Skills BLM 8-1.. Linear Relations 1. Make a table of values and graph each linear function a) y = 2x b) y = x + 5 c) 2x + 6y = 12 d) x + 7y = 21 2. Find the x- and y-intercepts of
Chapter 8 Prerequisite Skills BLM 8-1.. Linear Relations 1. Make a table of values and graph each linear function a) y = 2x b) y = x + 5 c) 2x + 6y = 12 d) x + 7y = 21 2. Find the x- and y-intercepts of
Created by T. Madas LINE INTEGRALS. Created by T. Madas
 LINE INTEGRALS LINE INTEGRALS IN 2 DIMENSIONAL CARTESIAN COORDINATES Question 1 Evaluate the integral ( x + 2y) dx, C where C is the path along the curve with equation y 2 = x + 1, from ( ) 0,1 to ( )
LINE INTEGRALS LINE INTEGRALS IN 2 DIMENSIONAL CARTESIAN COORDINATES Question 1 Evaluate the integral ( x + 2y) dx, C where C is the path along the curve with equation y 2 = x + 1, from ( ) 0,1 to ( )
8.3 GRAPH AND WRITE EQUATIONS OF CIRCLES
 8.3 GRAPH AND WRITE EQUATIONS OF CIRCLES What is the standard form equation for a circle? Why do you use the distance formula when writing the equation of a circle? What general equation of a circle is
8.3 GRAPH AND WRITE EQUATIONS OF CIRCLES What is the standard form equation for a circle? Why do you use the distance formula when writing the equation of a circle? What general equation of a circle is
10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products
 Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
BELLWORK feet
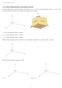
 BELLWORK 1 A hot air balloon is being held in place by two people holding ropes and standing 35 feet apart. The angle formed between the ground and the rope held by each person is 40. Determine the length
BELLWORK 1 A hot air balloon is being held in place by two people holding ropes and standing 35 feet apart. The angle formed between the ground and the rope held by each person is 40. Determine the length
Pre-Calc Vectors ~1~ NJCTL.org
 Intro to Vectors Class Work Draw vectors to represent the scenarios. 1. A plane flies east at 300 mph. 2. A ship sails northwest at 20 knots. 3. A river flows south at 4 mph. Draw the following vector.
Intro to Vectors Class Work Draw vectors to represent the scenarios. 1. A plane flies east at 300 mph. 2. A ship sails northwest at 20 knots. 3. A river flows south at 4 mph. Draw the following vector.
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter Midterm 1 Review Solutions
 MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 11 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 11.1: #19 Particle starts at point ( 1,, traces out a semicircle in the counterclockwise direction, ending at the point (1,. 11.1:
MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 11 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 11.1: #19 Particle starts at point ( 1,, traces out a semicircle in the counterclockwise direction, ending at the point (1,. 11.1:
MATH 1020 WORKSHEET 12.1 & 12.2 Vectors in the Plane
 MATH 100 WORKSHEET 1.1 & 1. Vectors in the Plane Find the vector v where u =, 1 and w = 1, given the equation v = u w. Solution. v = u w =, 1 1, =, 1 +, 4 =, 1 4 = 0, 5 Find the magnitude of v = 4, 3 Solution.
MATH 100 WORKSHEET 1.1 & 1. Vectors in the Plane Find the vector v where u =, 1 and w = 1, given the equation v = u w. Solution. v = u w =, 1 1, =, 1 +, 4 =, 1 4 = 0, 5 Find the magnitude of v = 4, 3 Solution.
10.1 Curves Defined by Parametric Equation
 10.1 Curves Defined by Parametric Equation 1. Imagine that a particle moves along the curve C shown below. It is impossible to describe C by an equation of the form y = f (x) because C fails the Vertical
10.1 Curves Defined by Parametric Equation 1. Imagine that a particle moves along the curve C shown below. It is impossible to describe C by an equation of the form y = f (x) because C fails the Vertical
CHAPTER 10 TRIGONOMETRY
 CHAPTER 10 TRIGONOMETRY EXERCISE 39, Page 87 1. Find the length of side x in the diagram below. By Pythagoras, from which, 2 25 x 7 2 x 25 7 and x = 25 7 = 24 m 2. Find the length of side x in the diagram
CHAPTER 10 TRIGONOMETRY EXERCISE 39, Page 87 1. Find the length of side x in the diagram below. By Pythagoras, from which, 2 25 x 7 2 x 25 7 and x = 25 7 = 24 m 2. Find the length of side x in the diagram
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1
 OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
ALGEBRA 2 X. Final Exam. Review Packet
 ALGEBRA X Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Match: 1) x + y = r a) equation of a line ) x = 5y 4y+ b) equation of a hyperbola ) 4) x y + = 1 64 9 c) equation of a parabola x y = 1 4 49 d) equation
ALGEBRA X Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Match: 1) x + y = r a) equation of a line ) x = 5y 4y+ b) equation of a hyperbola ) 4) x y + = 1 64 9 c) equation of a parabola x y = 1 4 49 d) equation
1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus Rectangular Coordinate Systems... 4
 MATH2202 Notebook 1 Fall 2015/2016 prepared by Professor Jenny Baglivo Contents 1 MATH2202 Notebook 1 3 1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus................... 3 1.2 Rectangular Coordinate
MATH2202 Notebook 1 Fall 2015/2016 prepared by Professor Jenny Baglivo Contents 1 MATH2202 Notebook 1 3 1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus................... 3 1.2 Rectangular Coordinate
Pre-Calculus Vectors
 Slide 1 / 159 Slide 2 / 159 Pre-Calculus Vectors 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 159 Table of Contents Intro to Vectors Converting Rectangular and Polar Forms Operations with Vectors Scalar Multiples
Slide 1 / 159 Slide 2 / 159 Pre-Calculus Vectors 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 159 Table of Contents Intro to Vectors Converting Rectangular and Polar Forms Operations with Vectors Scalar Multiples
Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
 Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Parametrizations of Plane Curves In previous chapters, we have studied curves as the graphs of functions or equations involving the two variables x and y. Another
Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Parametrizations of Plane Curves In previous chapters, we have studied curves as the graphs of functions or equations involving the two variables x and y. Another
Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars.
 1 Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars. Scalars: have magnitude (magnitude means size) only Examples of scalar quantities include time, mass, volume, area,
1 Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars. Scalars: have magnitude (magnitude means size) only Examples of scalar quantities include time, mass, volume, area,
A unit vector in the same direction as a vector a would be a and a unit vector in the
 In the previous lesson we discussed unit vectors on the positive x-axis (i) and on the positive y- axis (j). What is we wanted to find other unit vectors? There are an infinite number of unit vectors in
In the previous lesson we discussed unit vectors on the positive x-axis (i) and on the positive y- axis (j). What is we wanted to find other unit vectors? There are an infinite number of unit vectors in
8-2 Vectors in the Coordinate Plane
 37. ROWING Nadia is rowing across a river at a speed of 5 miles per hour perpendicular to the shore. The river has a current of 3 miles per hour heading downstream. a. At what speed is she traveling? b.
37. ROWING Nadia is rowing across a river at a speed of 5 miles per hour perpendicular to the shore. The river has a current of 3 miles per hour heading downstream. a. At what speed is she traveling? b.
Math 323 Exam 1 Practice Problem Solutions
 Math Exam Practice Problem Solutions. For each of the following curves, first find an equation in x and y whose graph contains the points on the curve. Then sketch the graph of C, indicating its orientation.
Math Exam Practice Problem Solutions. For each of the following curves, first find an equation in x and y whose graph contains the points on the curve. Then sketch the graph of C, indicating its orientation.
11.4 Dot Product Contemporary Calculus 1
 11.4 Dot Product Contemporary Calculus 1 11.4 DOT PRODUCT In the previous sections we looked at the meaning of vectors in two and three dimensions, but the only operations we used were addition and subtraction
11.4 Dot Product Contemporary Calculus 1 11.4 DOT PRODUCT In the previous sections we looked at the meaning of vectors in two and three dimensions, but the only operations we used were addition and subtraction
9.4 Polar Coordinates
 9.4 Polar Coordinates Polar coordinates uses distance and direction to specify a location in a plane. The origin in a polar system is a fixed point from which a ray, O, is drawn and we call the ray the
9.4 Polar Coordinates Polar coordinates uses distance and direction to specify a location in a plane. The origin in a polar system is a fixed point from which a ray, O, is drawn and we call the ray the
9.1 VECTORS. A Geometric View of Vectors LEARNING OBJECTIVES. = a, b
 vectors and POLAR COORDINATES LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, ou will: View vectors geometricall. Find magnitude and direction. Perform vector addition and scalar multiplication. Find the component
vectors and POLAR COORDINATES LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, ou will: View vectors geometricall. Find magnitude and direction. Perform vector addition and scalar multiplication. Find the component
SB Ch 6 May 15, 2014
 Warm Up 1 Chapter 6: Applications of Trig: Vectors Section 6.1 Vectors in a Plane Vector: directed line segment Magnitude is the length of the vector Direction is the angle in which the vector is pointing
Warm Up 1 Chapter 6: Applications of Trig: Vectors Section 6.1 Vectors in a Plane Vector: directed line segment Magnitude is the length of the vector Direction is the angle in which the vector is pointing
Precalculus Notes: Unit 6 Vectors, Parametrics, Polars, & Complex Numbers. A: Initial Point (start); B: Terminal Point (end) : ( ) ( )
 Syllabus Objectives: 5.1 The student will explore methods of vector addition and subtraction. 5. The student will develop strategies for computing a vector s direction angle and magnitude given its coordinates.
Syllabus Objectives: 5.1 The student will explore methods of vector addition and subtraction. 5. The student will develop strategies for computing a vector s direction angle and magnitude given its coordinates.
MATH 32A: MIDTERM 1 REVIEW. 1. Vectors. v v = 1 22
 MATH 3A: MIDTERM 1 REVIEW JOE HUGHES 1. Let v = 3,, 3. a. Find e v. Solution: v = 9 + 4 + 9 =, so 1. Vectors e v = 1 v v = 1 3,, 3 b. Find the vectors parallel to v which lie on the sphere of radius two
MATH 3A: MIDTERM 1 REVIEW JOE HUGHES 1. Let v = 3,, 3. a. Find e v. Solution: v = 9 + 4 + 9 =, so 1. Vectors e v = 1 v v = 1 3,, 3 b. Find the vectors parallel to v which lie on the sphere of radius two
Detailed objectives are given in each of the sections listed below. 1. Cartesian Space Coordinates. 2. Displacements, Forces, Velocities and Vectors
 Unit 1 Vectors In this unit, we introduce vectors, vector operations, and equations of lines and planes. Note: Unit 1 is based on Chapter 12 of the textbook, Salas and Hille s Calculus: Several Variables,
Unit 1 Vectors In this unit, we introduce vectors, vector operations, and equations of lines and planes. Note: Unit 1 is based on Chapter 12 of the textbook, Salas and Hille s Calculus: Several Variables,
Exam 1 Review SOLUTIONS
 1. True or False (and give a short reason): Exam 1 Review SOLUTIONS (a) If the parametric curve x = f(t), y = g(t) satisfies g (1) = 0, then it has a horizontal tangent line when t = 1. FALSE: To make
1. True or False (and give a short reason): Exam 1 Review SOLUTIONS (a) If the parametric curve x = f(t), y = g(t) satisfies g (1) = 0, then it has a horizontal tangent line when t = 1. FALSE: To make
Precalculus Summer Assignment 2015
 Precalculus Summer Assignment 2015 The following packet contains topics and definitions that you will be required to know in order to succeed in CP Pre-calculus this year. You are advised to be familiar
Precalculus Summer Assignment 2015 The following packet contains topics and definitions that you will be required to know in order to succeed in CP Pre-calculus this year. You are advised to be familiar
Congruence Axioms. Data Required for Solving Oblique Triangles
 Math 335 Trigonometry Sec 7.1: Oblique Triangles and the Law of Sines In section 2.4, we solved right triangles. We now extend the concept to all triangles. Congruence Axioms Side-Angle-Side SAS Angle-Side-Angle
Math 335 Trigonometry Sec 7.1: Oblique Triangles and the Law of Sines In section 2.4, we solved right triangles. We now extend the concept to all triangles. Congruence Axioms Side-Angle-Side SAS Angle-Side-Angle
AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 10 Test No Calculator Section. Name: Date: Period:
 AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 10 Test No Calculator Section Name: Date: Period: Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.) 1. The graph in the xy-plane represented
AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 10 Test No Calculator Section Name: Date: Period: Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.) 1. The graph in the xy-plane represented
College Prep Math Final Exam Review Packet
 College Prep Math Final Exam Review Packet Name: Date of Exam: In Class 1 Directions: Complete each assignment using the due dates given by the calendar below. If you are absent from school, you are still
College Prep Math Final Exam Review Packet Name: Date of Exam: In Class 1 Directions: Complete each assignment using the due dates given by the calendar below. If you are absent from school, you are still
Applications of Trigonometry and Vectors. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 7 Applications of Trigonometry and Vectors Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 7.4 Geometrically Defined Vectors and Applications Basic Terminology The Equilibrant Incline Applications
7 Applications of Trigonometry and Vectors Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 7.4 Geometrically Defined Vectors and Applications Basic Terminology The Equilibrant Incline Applications
Vectors, dot product, and cross product
 MTH 201 Multivariable calculus and differential equations Practice problems Vectors, dot product, and cross product 1. Find the component form and length of vector P Q with the following initial point
MTH 201 Multivariable calculus and differential equations Practice problems Vectors, dot product, and cross product 1. Find the component form and length of vector P Q with the following initial point
MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I
 MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I Spring 2018, WEEK 1 JoungDong Kim Week 1 Vectors, The Dot Product, Vector Functions and Parametric Curves. Section 1.1 Vectors Definition. A Vector is a quantity that
MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I Spring 2018, WEEK 1 JoungDong Kim Week 1 Vectors, The Dot Product, Vector Functions and Parametric Curves. Section 1.1 Vectors Definition. A Vector is a quantity that
Find graphically, using scaled diagram, following vectors (both magnitude and direction):
 1 HOMEWORK 1 on VECTORS: use ruler and protractor, please!!! 1. v 1 = 3m/s, E and v = 4m/s, 3 Find graphically, using scaled diagram, following vectors (both magnitude and direction): a. v = v 1 + v b.
1 HOMEWORK 1 on VECTORS: use ruler and protractor, please!!! 1. v 1 = 3m/s, E and v = 4m/s, 3 Find graphically, using scaled diagram, following vectors (both magnitude and direction): a. v = v 1 + v b.
Notes: Vectors and Scalars
 A particle moving along a straight line can move in only two directions and we can specify which directions with a plus or negative sign. For a particle moving in three dimensions; however, a plus sign
A particle moving along a straight line can move in only two directions and we can specify which directions with a plus or negative sign. For a particle moving in three dimensions; however, a plus sign
North Seattle Community College Computer Based Mathematics Instruction Math 102 Test Reviews
 North Seattle Community College Computer Based Mathematics Instruction Math 10 Test Reviews Click on a bookmarked heading on the left to access individual reviews. To print a review, choose print and the
North Seattle Community College Computer Based Mathematics Instruction Math 10 Test Reviews Click on a bookmarked heading on the left to access individual reviews. To print a review, choose print and the
chapter 1 vector geometry solutions V Consider the parallelogram shown alongside. Which of the following statements are true?
 chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Mathematics Trigonometry: Unit Circle
 a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta
 MATH 214 (R1) Winter 2008 Intermediate Calculus I Solutions to Problem Set #8 Completion Date: Friday March 14, 2008 Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta Question 1.
MATH 214 (R1) Winter 2008 Intermediate Calculus I Solutions to Problem Set #8 Completion Date: Friday March 14, 2008 Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta Question 1.
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE The Final Exam takes place on Wednesday, June 13, 2018, from 10:30 AM to 12:30 PM in 1100 Donald Bren Hall (not the usual lecture room!!!) NO books/notes/calculators/cheat sheets
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE The Final Exam takes place on Wednesday, June 13, 2018, from 10:30 AM to 12:30 PM in 1100 Donald Bren Hall (not the usual lecture room!!!) NO books/notes/calculators/cheat sheets
Chapter 1: Trigonometric Functions 1. Find (a) the complement and (b) the supplement of 61. Show all work and / or support your answer.
 Trig Exam Review F07 O Brien Trigonometry Exam Review: Chapters,, To adequately prepare for the exam, try to work these review problems using only the trigonometry knowledge which you have internalized
Trig Exam Review F07 O Brien Trigonometry Exam Review: Chapters,, To adequately prepare for the exam, try to work these review problems using only the trigonometry knowledge which you have internalized
Review exercise 2. 1 The equation of the line is: = 5 a The gradient of l1 is 3. y y x x. So the gradient of l2 is. The equation of line l2 is: y =
 Review exercise The equation of the line is: y y x x y y x x y 8 x+ 6 8 + y 8 x+ 6 y x x + y 0 y ( ) ( x 9) y+ ( x 9) y+ x 9 x y 0 a, b, c Using points A and B: y y x x y y x x y x 0 k 0 y x k ky k x a
Review exercise The equation of the line is: y y x x y y x x y 8 x+ 6 8 + y 8 x+ 6 y x x + y 0 y ( ) ( x 9) y+ ( x 9) y+ x 9 x y 0 a, b, c Using points A and B: y y x x y y x x y x 0 k 0 y x k ky k x a
Solutions to old Exam 3 problems
 Solutions to old Exam 3 problems Hi students! I am putting this version of my review for the Final exam review here on the web site, place and time to be announced. Enjoy!! Best, Bill Meeks PS. There are
Solutions to old Exam 3 problems Hi students! I am putting this version of my review for the Final exam review here on the web site, place and time to be announced. Enjoy!! Best, Bill Meeks PS. There are
LB 220 Homework 2 (due Tuesday, 01/22/13)
 LB 220 Homework 2 (due Tuesday, 01/22/13) Directions. Please solve the problems below. Your solutions must begin with a clear statement (or re-statement in your own words) of the problem. You solutions
LB 220 Homework 2 (due Tuesday, 01/22/13) Directions. Please solve the problems below. Your solutions must begin with a clear statement (or re-statement in your own words) of the problem. You solutions
Math 263 Final. (b) The cross product is. i j k c. =< c 1, 1, 1 >
 Math 63 Final Problem 1: [ points, 5 points to each part] Given the points P : (1, 1, 1), Q : (1,, ), R : (,, c 1), where c is a parameter, find (a) the vector equation of the line through P and Q. (b)
Math 63 Final Problem 1: [ points, 5 points to each part] Given the points P : (1, 1, 1), Q : (1,, ), R : (,, c 1), where c is a parameter, find (a) the vector equation of the line through P and Q. (b)
Worksheet 1.7: Introduction to Vector Functions - Position
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.7: Introduction to Vector Functions - Position From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Cartesian Coordinates: Coordinates of points in general,
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.7: Introduction to Vector Functions - Position From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Cartesian Coordinates: Coordinates of points in general,
Math 20C Homework 2 Partial Solutions
 Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
Math 2C Homework 2 Partial Solutions Problem 1 (12.4.14). Calculate (j k) (j + k). Solution. The basic properties of the cross product are found in Theorem 2 of Section 12.4. From these properties, we
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 14.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 1.1 Name Date By Air and By Sea Introduction to Vectors Vocabulary Match each term to its corresponding definition. 1. column vector notation a. a quantity that
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 1.1 Name Date By Air and By Sea Introduction to Vectors Vocabulary Match each term to its corresponding definition. 1. column vector notation a. a quantity that
Directional Derivatives and Gradient Vectors. Suppose we want to find the rate of change of a function z = f x, y at the point in the
 14.6 Directional Derivatives and Gradient Vectors 1. Partial Derivates are nice, but they only tell us the rate of change of a function z = f x, y in the i and j direction. What if we are interested in
14.6 Directional Derivatives and Gradient Vectors 1. Partial Derivates are nice, but they only tell us the rate of change of a function z = f x, y in the i and j direction. What if we are interested in
Find c. Show that. is an equation of a sphere, and find its center and radius. This n That. 3D Space is like, far out
 D Space is like, far out Introspective Intersections Inverses Gone wild Transcendental Computations This n That 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 c Find
D Space is like, far out Introspective Intersections Inverses Gone wild Transcendental Computations This n That 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 c Find
Physics 12. Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions
 Physics 12 Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions 1. Definitions When studying mechanics in Physics 11, we have realized that there are two major types of quantities that we can measure for the systems
Physics 12 Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions 1. Definitions When studying mechanics in Physics 11, we have realized that there are two major types of quantities that we can measure for the systems
2 and v! = 3 i! + 5 j! are given.
 1. ABCD is a rectangle and O is the midpoint of [AB]. D C 2. The vectors i!, j! are unit vectors along the x-axis and y-axis respectively. The vectors u! = i! + j! 2 and v! = 3 i! + 5 j! are given. (a)
1. ABCD is a rectangle and O is the midpoint of [AB]. D C 2. The vectors i!, j! are unit vectors along the x-axis and y-axis respectively. The vectors u! = i! + j! 2 and v! = 3 i! + 5 j! are given. (a)
Student Content Brief Advanced Level
 Student Content Brief Advanced Level Vectors Background Information Physics and Engineering deal with quantities that have both size and direction. These physical quantities have a special math language
Student Content Brief Advanced Level Vectors Background Information Physics and Engineering deal with quantities that have both size and direction. These physical quantities have a special math language
Math 370 Exam 3 Review Name
 Math 370 Exam 3 Review Name The following problems will give you an idea of the concepts covered on the exam. Note that the review questions may not be formatted like those on the exam. You should complete
Math 370 Exam 3 Review Name The following problems will give you an idea of the concepts covered on the exam. Note that the review questions may not be formatted like those on the exam. You should complete
CALCULUS 3 February 6, st TEST
 MATH 400 (CALCULUS 3) Spring 008 1st TEST 1 CALCULUS 3 February, 008 1st TEST YOUR NAME: 001 A. Spina...(9am) 00 E. Wittenbn... (10am) 003 T. Dent...(11am) 004 J. Wiscons... (1pm) 005 A. Spina...(1pm)
MATH 400 (CALCULUS 3) Spring 008 1st TEST 1 CALCULUS 3 February, 008 1st TEST YOUR NAME: 001 A. Spina...(9am) 00 E. Wittenbn... (10am) 003 T. Dent...(11am) 004 J. Wiscons... (1pm) 005 A. Spina...(1pm)
3. A( 2,0) and B(6, -2), find M 4. A( 3, 7) and M(4,-3), find B. 5. M(4, -9) and B( -10, 11) find A 6. B(4, 8) and M(-2, 5), find A
 Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(4, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -9), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(4, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -9), find M 3. A( 2,0)
(6, 4, 0) = (3, 2, 0). Find the equation of the sphere that has the line segment from P to Q as a diameter.
 Solutions Review for Eam #1 Math 1260 1. Consider the points P = (2, 5, 1) and Q = (4, 1, 1). (a) Find the distance from P to Q. Solution. dist(p, Q) = (4 2) 2 + (1 + 5) 2 + (1 + 1) 2 = 4 + 36 + 4 = 44
Solutions Review for Eam #1 Math 1260 1. Consider the points P = (2, 5, 1) and Q = (4, 1, 1). (a) Find the distance from P to Q. Solution. dist(p, Q) = (4 2) 2 + (1 + 5) 2 + (1 + 1) 2 = 4 + 36 + 4 = 44
LB 220 Homework 4 Solutions
 LB 220 Homework 4 Solutions Section 11.4, # 40: This problem was solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 42: This problem was also solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 43: Also solved in class
LB 220 Homework 4 Solutions Section 11.4, # 40: This problem was solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 42: This problem was also solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 43: Also solved in class
mathematical objects can be described via equations, functions, graphs, parameterization in R, R, and R.
 Multivariable Calculus Lecture # Notes This lecture completes the discussion of the cross product in R and addresses the variety of different ways that n mathematical objects can be described via equations,
Multivariable Calculus Lecture # Notes This lecture completes the discussion of the cross product in R and addresses the variety of different ways that n mathematical objects can be described via equations,
MAC2313 Final A. (5 pts) 1. How many of the following are necessarily true? i. The vector field F = 2x + 3y, 3x 5y is conservative.
 MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. How many of the following are necessarily true? i. The vector field F = 2x + 3y, 3x 5y is conservative. ii. The vector field F = 5(x 2 + y 2 ) 3/2 x, y is radial. iii. All constant
MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. How many of the following are necessarily true? i. The vector field F = 2x + 3y, 3x 5y is conservative. ii. The vector field F = 5(x 2 + y 2 ) 3/2 x, y is radial. iii. All constant
Math 233 Calculus 3 - Fall 2016
 Math 233 Calculus 3 - Fall 2016 2 12.1 - Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems 12.1 - THREE-DIMENSIONAL COORDINATE SYSTEMS Definition. R 3 means By convention, we graph points in R 3 using a right-handed
Math 233 Calculus 3 - Fall 2016 2 12.1 - Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems 12.1 - THREE-DIMENSIONAL COORDINATE SYSTEMS Definition. R 3 means By convention, we graph points in R 3 using a right-handed
Things to Know and Be Able to Do Understand the meaning of equations given in parametric and polar forms, and develop a sketch of the appropriate
 AP Calculus BC Review Chapter (Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates) Things to Know and Be Able to Do Understand the meaning of equations given in parametric and polar forms, and develop a sketch
AP Calculus BC Review Chapter (Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates) Things to Know and Be Able to Do Understand the meaning of equations given in parametric and polar forms, and develop a sketch
LB 220 Homework 1 (due Monday, 01/14/13)
 LB 220 Homework 1 (due Monday, 01/14/13) Directions. Please solve the problems below. Your solutions must begin with a clear statement (or re-statement in your own words) of the problem. You solutions
LB 220 Homework 1 (due Monday, 01/14/13) Directions. Please solve the problems below. Your solutions must begin with a clear statement (or re-statement in your own words) of the problem. You solutions
Time : 3 hours 02 - Mathematics - July 2006 Marks : 100 Pg - 1 Instructions : S E CT I O N - A
 Time : 3 hours 0 Mathematics July 006 Marks : 00 Pg Instructions :. Answer all questions.. Write your answers according to the instructions given below with the questions. 3. Begin each section on a new
Time : 3 hours 0 Mathematics July 006 Marks : 00 Pg Instructions :. Answer all questions.. Write your answers according to the instructions given below with the questions. 3. Begin each section on a new
Math 241: Multivariable calculus
 Math 241: Multivariable calculus Professor Leininger Fall 2014 Calculus of 1 variable In Calculus I and II you study real valued functions of a single real variable. Examples: f (x) = x 2, r(x) = 2x2 +x
Math 241: Multivariable calculus Professor Leininger Fall 2014 Calculus of 1 variable In Calculus I and II you study real valued functions of a single real variable. Examples: f (x) = x 2, r(x) = 2x2 +x
New concepts: scalars, vectors, unit vectors, vector components, vector equations, scalar product. reading assignment read chap 3
 New concepts: scalars, vectors, unit vectors, vector components, vector equations, scalar product reading assignment read chap 3 Most physical quantities are described by a single number or variable examples:
New concepts: scalars, vectors, unit vectors, vector components, vector equations, scalar product reading assignment read chap 3 Most physical quantities are described by a single number or variable examples:
LATE AND ABSENT HOMEWORK IS ACCEPTED UP TO THE TIME OF THE CHAPTER TEST ON
 Trig/Math Anal Name No LATE AND ABSENT HOMEWORK IS ACCEPTED UP TO THE TIME OF THE CHAPTER TEST ON HW NO. SECTIONS ASSIGNMENT DUE FS-1 4-4 Practice Set A #1-57 eoo 4-5 Practice Set B #1-45 eoo, 57, 59 FS-
Trig/Math Anal Name No LATE AND ABSENT HOMEWORK IS ACCEPTED UP TO THE TIME OF THE CHAPTER TEST ON HW NO. SECTIONS ASSIGNMENT DUE FS-1 4-4 Practice Set A #1-57 eoo 4-5 Practice Set B #1-45 eoo, 57, 59 FS-
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today The Dot Product Equations of Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/29 Direction angles and Direction cosines Projections Definitions: 1. a : a 1, a 2, a 3, b : b 1, b 2, b 3, a
What you will learn today The Dot Product Equations of Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/29 Direction angles and Direction cosines Projections Definitions: 1. a : a 1, a 2, a 3, b : b 1, b 2, b 3, a
Name: ID: Math 233 Exam 1. Page 1
 Page 1 Name: ID: This exam has 20 multiple choice questions, worth 5 points each. You are allowed to use a scientific calculator and a 3 5 inch note card. 1. Which of the following pairs of vectors are
Page 1 Name: ID: This exam has 20 multiple choice questions, worth 5 points each. You are allowed to use a scientific calculator and a 3 5 inch note card. 1. Which of the following pairs of vectors are
( )( ) Algebra 136 Semester 2 Review. ( ) 6. g( h( x) ( ) Name. In 1-6, use the functions below to find the solutions.
 Algebra 136 Semester Review In 1-6, use the functions below to find the solutions. Name f ( x) = 3x x + g( x) = x 3 h( x) = x + 3 1. ( f + h) ( x). ( h g) ( x) 3. h x g ( ) 4. ( gh) ( x). f g( x) ( ) 6.
Algebra 136 Semester Review In 1-6, use the functions below to find the solutions. Name f ( x) = 3x x + g( x) = x 3 h( x) = x + 3 1. ( f + h) ( x). ( h g) ( x) 3. h x g ( ) 4. ( gh) ( x). f g( x) ( ) 6.
Unit 1 Representing and Operations with Vectors. Over the years you have come to accept various mathematical concepts or properties:
 Lesson1.notebook November 27, 2012 Algebra Unit 1 Representing and Operations with Vectors Over the years you have come to accept various mathematical concepts or properties: Communative Property Associative
Lesson1.notebook November 27, 2012 Algebra Unit 1 Representing and Operations with Vectors Over the years you have come to accept various mathematical concepts or properties: Communative Property Associative
Worksheet 1.4: Geometry of the Dot and Cross Products
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.4: Geometry of the Dot and Cross Products From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Basic algebra and trigonometry: be able to solve quadratic equations,
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.4: Geometry of the Dot and Cross Products From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Basic algebra and trigonometry: be able to solve quadratic equations,
The Distance Formula. The Midpoint Formula
 Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Distance Midpoint Formulas The Distance Formula The distance between two points P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ) P 2 = (x 1, y 1 ), denoted by d(p 1, P 2 ), is d(p 1, P 2 ) = (x
Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Distance Midpoint Formulas The Distance Formula The distance between two points P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ) P 2 = (x 1, y 1 ), denoted by d(p 1, P 2 ), is d(p 1, P 2 ) = (x
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations
 4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate System Graphs of Equations in Two Variables x-intercepts and y-intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate System Graphs of Equations in Two Variables x-intercepts and y-intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the
Math Level 2. Mathematics Level 2
 Math Reference Information THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS FOR YOUR REFERENCE IN ANSWERING SOME OF THE SAMPLE QUESTIONS. THIS INFORMATION IS ALSO PROVIDED ON THE ACTUAL SUBJECT TEST IN MATHEMATICS LEVEL.
Math Reference Information THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS FOR YOUR REFERENCE IN ANSWERING SOME OF THE SAMPLE QUESTIONS. THIS INFORMATION IS ALSO PROVIDED ON THE ACTUAL SUBJECT TEST IN MATHEMATICS LEVEL.
Vector Supplement Part 1: Vectors
 Vector Supplement Part 1: Vectors A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Vectors are drawn as directed line segments and are denoted by boldface letters a or by a. The magnitude
Vector Supplement Part 1: Vectors A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Vectors are drawn as directed line segments and are denoted by boldface letters a or by a. The magnitude
Vectors (Trigonometry Explanation)
 Vectors (Trigonometry Explanation) CK12 Editor Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive
Vectors (Trigonometry Explanation) CK12 Editor Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive
MATH 52 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MAH 5 FINAL EXAM OLUION. (a) ketch the region R of integration in the following double integral. x xe y5 dy dx R = {(x, y) x, x y }. (b) Express the region R as an x-simple region. R = {(x, y) y, x y }
MAH 5 FINAL EXAM OLUION. (a) ketch the region R of integration in the following double integral. x xe y5 dy dx R = {(x, y) x, x y }. (b) Express the region R as an x-simple region. R = {(x, y) y, x y }
MATH 100 REVIEW PACKAGE
 SCHOOL OF UNIVERSITY ARTS AND SCIENCES MATH 00 REVIEW PACKAGE Gearing up for calculus and preparing for the Assessment Test that everybody writes on at. You are strongly encouraged not to use a calculator
SCHOOL OF UNIVERSITY ARTS AND SCIENCES MATH 00 REVIEW PACKAGE Gearing up for calculus and preparing for the Assessment Test that everybody writes on at. You are strongly encouraged not to use a calculator
e x3 dx dy. 0 y x 2, 0 x 1.
 Problem 1. Evaluate by changing the order of integration y e x3 dx dy. Solution:We change the order of integration over the region y x 1. We find and x e x3 dy dx = y x, x 1. x e x3 dx = 1 x=1 3 ex3 x=
Problem 1. Evaluate by changing the order of integration y e x3 dx dy. Solution:We change the order of integration over the region y x 1. We find and x e x3 dy dx = y x, x 1. x e x3 dx = 1 x=1 3 ex3 x=
Analytic Geometry MAT 1035
 Analytic Geometry MAT 035 5.09.04 WEEKLY PROGRAM - The first week of the semester, we will introduce the course and given a brief outline. We continue with vectors in R n and some operations including
Analytic Geometry MAT 035 5.09.04 WEEKLY PROGRAM - The first week of the semester, we will introduce the course and given a brief outline. We continue with vectors in R n and some operations including
Culminating Review for Vectors
 Culminating Review for Vectors 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 An Introduction to Vectors Applications of Vectors Equations of Lines and Planes 4 12 Relationships between Points, Lines and Planes An
Culminating Review for Vectors 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 An Introduction to Vectors Applications of Vectors Equations of Lines and Planes 4 12 Relationships between Points, Lines and Planes An
OpenStax-CNX module: m Vectors. OpenStax College. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49412 1 Vectors OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section you will: Abstract View vectors
OpenStax-CNX module: m49412 1 Vectors OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section you will: Abstract View vectors
Graphing Review Part 1: Circles, Ellipses and Lines
 Graphing Review Part : Circles, Ellipses and Lines Definition The graph of an equation is the set of ordered pairs, (, y), that satisfy the equation We can represent the graph of a function by sketching
Graphing Review Part : Circles, Ellipses and Lines Definition The graph of an equation is the set of ordered pairs, (, y), that satisfy the equation We can represent the graph of a function by sketching
Precalculus Notes: Unit 6 Vectors, Parametrics, Polars, & Complex Numbers
 Syllabus Objectives: 5.1 The student will eplore methods of vector addition and subtraction. 5. The student will develop strategies for computing a vector s direction angle and magnitude given its coordinates.
Syllabus Objectives: 5.1 The student will eplore methods of vector addition and subtraction. 5. The student will develop strategies for computing a vector s direction angle and magnitude given its coordinates.
