Supplementary Information
|
|
|
- Luke Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Information Direct observation of crystal defects in an organic molecular crystals of copper hexachlorophthalocyanine by STEM-EELS Mitsutaka Haruta*, Hiroki Kurata Institute for hemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto , Japan correspondence to: 1
2 1. Materials The crystal structure of 16 -upc is illustrated schematically in Fig. S1(a). The molecules are packed in a base-centered monoclinic structure, with unit-cell dimensions of a = 1.96 nm, b = 2.61 nm, c = nm, and = The molecules are arranged in a herringbone structure where the molecular plane in every second column is parallel to the substrate surface, while the molecular plane in the other columns is tilted 26.5 away from the substrate as shown in Fig. S1(b) 1. High-resolution images were observed along the c-axis by inclining the specimen with respect to the incident electron beam. Therefore, the molecular plane is not perpendicular to the electron beam but tilted at an angle of On the other hand, for molecules observed at the grain boundary, the molecular plane, as indicated by the blue lines, lies parallel to the electron beam. 2
3 N N N N N N N u N N N u N N N N N N N N N N u N a N N N N N N N N N N u N N u N N N N N N N b a Electron beam c Substrate b 26.5 a Figure S1. Schematic illustrations showing (a) molecular arrangement in the a b plane of the monoclinic structure and (b) incident electron direction at the monoclinic 16 -upc crystallite. The plane of the green molecules is parallel to the substrate surface, while that of the blue molecules is parallel to the electron beam direction. The molecular images are obtained with the beam transmitting along the c-axis. 3
4 2. Advantage of LAADF-STEM for organic crystals Figure S2(a) shows schematic ray diagrams of ADF-STEM. Generally, the inner detection angle (θ min ) for HAADF imaging is selected to be more than 50 mrad for inorganic crystal to avoid the elastic scattering electrons. The elastic scattering intensity I BS and thermal diffuse scattering (TDS) I TDS can be expressed respectively as I BS 2 TDS 2 f ( s) exp 2M ( s) and I f ( s) 1 exp 2M ( s) x x x x 25, where s = sin( )/, and f x (s) and exp[-2m x (s)] are the atomic structure factor for the electron and the Debye-Waller factor of each element x, respectively. When the atoms vibrate independently (Einstein model), the temperature factor can be expressed as 2 M x ( s) Bs, where the constant B is related to the lattice vibration amplitude. Figure S2(b) shows the intensity profiles of the elastic scattering and TDS for isolated, N,, u, and Si atoms assuming the Einstein model. The values of constant B for, N, u, and were assumed to be the same as those used in the multislice image simulation for halogenated upc 7 and that for Si was taken as the value for a Si crystal at room temperature 26. Generally, in the case of an atom in an inorganic crystal, the crossover point between the elastic and TDS profiles is found at a scattering angle of around 50 mrad. Therefore, the inner detection angle (θ min ) is usually set to more than 50 mrad in 4
5 order to detect mainly the TDS electrons which are scattered incoherently. On the other hand, since the temperature factor in organic materials is large compared to that in inorganic materials, the crossover point between elastic and TDS profiles is found at a scattering angle of under 20 mrad for each atom. Therefore, because of the large temperature factor in the case of organic materials, the LAADF-STEM method can be used to detect electrons scattered above 30 mrad and almost guarantee collection of only TDS signals, leading to incoherent high-resolution Z-contrast imaging. Figs. S2(c) and (d) show the microdiffraction patterns of Si [110] and 16 upc along the c-axis with a convergence semi-angle of 3.4 mrad. As the lattice constants of 16 -upc are comparatively large, elastically diffracted beams are confined to the lower angular region. Since the high-resolution LAADF-STEM experiments were performed using an electron probe with a convergence semi-angle of 23 mrad to form a fine probe, the inner detection angle was set to 39 mrad in order to avoid the contribution from first-order diffraction. The elastic component was considered to be low in the LAADF images of the 16 -upc crystal under the present experimental conditions. 5
6 Intensity a Objective lens Specimen θ min θ max ADF detector α b 4 TDS Elastic N TDS Elastic 3 TDS Elastic u TDS Elastic 2 Si TDS Elastic 1 LAADF HAADF Scattering angle (mrad) c d Diffracted disk Figure S2. (a) Schematic diagram of ADF-STEM. (b) Intensity profiles of elastic and thermal diffuse scattering (TDS) from isolated, N,, u, and Si atoms under the Einstein model. The Debye-Waller factors for, N, u, and were assumed to be the same as those used in the multislice image simulation for halogenated-upc 1 and that for Si was that for a Si crystal at room temperature 26. The microdiffraction patterns of (c) Si [110] and (d) 16 upc along the c-axis projection with a convergence semi-angle of 3.4 mrad. The inner detection angle (39 mrad) for LAADF imaging is indicated by the white circles. 6
7 3. Effect of spherical aberration corrector in STEM imaging for organic crystals In our previous research 7, only the copper atomic column in each molecular unit was observed directly in the raw image while chlorine atomic columns were visible after noise filtering. This was a critical problem in the high-resolution analysis of non-periodical structures. Increasing the signal-to-noise ratio in the LAADF image by incorporating a spherical aberration (s) corrector, however, not only allowed observation in the raw image of chlorine but also lighter elements. As discussed in our previous research, radiation damage of the specimen has also been an issue. In a previous study using STEM without a s-corrector, the clearest images were observed at 6M-fold magnification with a pixel size of 0.05 nm and a dwell time of 60 s per pixel. The probe current was set to about 5 pa, corresponding to an average electron dose of ca. 12 cm 2, which is smaller than the end-point dose (ca. 35 cm 2 ) for the 16 -upc crystal 24. At magnifications higher than 6 M, the molecular crystal was completely destroyed by electron bombardment. This was because the broad electron probe, with a full-width at half-maximum of about 0.18 nm, leads to unnecessary irradiation when the pixel size in the image was decreased at a higher magnification. In order to achieve a higher resolution in ADF-STEM imaging of organic crystals, any unnecessary irradiation should be minimized by using a finer 7
8 electron probe. The s corrector has improved the size of the electron probe so that it is 1 Å or less in diameter. This improvement in probe size enables observation of an image at a low probe current of about 1 pa, which provides a low-dose observation of about 1.1 cm -2 at 6M-fold magnification with a dwell time of 26.7 s per pixel, leading to a decrease in the unnecessary irradiation and an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio of the STEM image. Therefore, high magnification imaging could be performed even at 25M-fold magnification, corresponding to an average electron dose of ca cm 2, as shown in Figs. 1(d)-(g). The pixel size in 25M-fold magnification images was nm, i.e. the images were over-sampled with 15 pixels per the horizontal u-n atomic distance (0.18 nm) and with 11 pixel per the horizontal - atomic distance (0.14 nm) in the projected plane, which was enough to directly resolve the atomic columns in the molecular unit. In case of the high resolution LAADF image (Fig. 1 (e)), the light elements ( and N) were visible together with the heavier elements ( and u) but not atomically resolved. Fast Fourier transformation (FFT) of the LAADF image indicates that the spatial resolution of the image is 0.18 nm. On the other hands, - columns of the benzene as well as u-n columns of the porphyrin rings were clearly resolved in ABF image, which indicates a spatial resolution better than 0.14 nm. Therefore, we concluded that spatial resolutions of better than 0.18 nm 8
9 for LAADF and 0.14 nm for ABF were attained in imaging of organic crystals in the present experiment. References 1. Uyeda, N. Kobayashi, T. Ishizuka, K. & Fujiyoshi, Y. High voltage electron microscopy for image discrimination of constituent atoms in crystals and molecules. hem. Scripta. 14, ( ). 2. Kobayashi, T. in: N. Karl (Ed.), Epitaxial growth of organic thin films and characterization of their defect structures by high-resolution electron microscopy. rystal, Growth, Properties and Application, vol. 13, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1991, p Uyeda, N. Kobayashi, T. Ishizuka, K. & Fujiyoshi, Y. rystal structure of Ag TNQ. Nature. 285, (1980). 4. Maeda, T. Isoda, S. & Kobayashi, T. Epitaxial growth and defect Structure of quaterrylene studied using high resolution electron microscopy. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 191, (2002). 5. Koshino, M. Kurata, H. & Isoda, S. Study of structures at the boundary and defects in 9
10 organic thin films of perchlorocoronene by high-resolution and analytical transmission electron microscopy. Ultramicroscopy. 110, (2010). 6. Pennycook, S. J. & Jesson, D. E. High-resolution incoherent imaging of crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, (1990). 7. Haruta, M. Yoshida, K. Kurata, H. & Isoda, S. Atomic resolution ADF-STEM imaging of organic molecular crystal of halogenated copper phthalocyanine. Ultramicroscopy. 108, (2008). 8. Haruta, M. Yoshida, K. Kurata, H. & Isoda, S. High resolution ADF-STEM imaging application for organic crystals. Mol. ryst. Liq. ryst. 492, (2008). 9. Batson, P. E. Delby, N. & Krivanek, O. L. Sub-ångstrom resolution using aberration corrected electron optics. Nature. 418, (2002). 10. Krivanek, O. L. et al., Atom-by-atom structural and chemical analysis by annular dark-field electron microscopy. Nature. 464, (2010). 11. Suenaga, K. & Koshino, M. Atom-by-atom spectroscopy at graphene edge. Nature. 468, (2010). 12. Findlay, S. D. et al., Direct imaging of hydrogen within a crystalline environment. Appl. Phys. Express. 3, (2010). 10
11 13. Ishikawa, R. et al., Direct imaging of hydrogen-atom columns in a crystal by annular bright-field electron microscopy. Nature mater. 10, (2011). 14. Smith, D. J. Fryer, J. R. & amps, R. A. Radiation damage and structural studies: halogenated phthalocyanines. Ultramicroscopy. 19, (1986). 15. Pennycook, S. J. & Nellist, P. D. Scanning transmission electron microscopy : imaging and analysis (2011) (Springer, New York). 16. Hashimoto, S. Isoda, S. Kurata, H. Lieser, G. & Kobayashi, T. Molecular orientation of perfluoro-vanadyl-phthalocyanine examined by electron energy loss spectroscopy. J. Porphyrins and Phthalocyanines, 3, (1999) 17. Kurata, H. Ishizuka, K. Kobayashi, T. & Uyeda, N. Orientation dependence of the carbon K-edge in the electron energy loss spectra of a potassium-benzene-graphite intercalation compound. Synthetic Metals. 22, (1988). 18. Browning, N. D. Yuan, J. & Brown, L. M. Real-space determination of anisotropic electronic structure by electron energy loss spectroscopy. Ultramicroscopy. 38, (1991). 19. Batson, P. E. & hisholm, M. F. Anisotropy in the near-edge absorption fine structure of YBa 2 u 3 O 7-σ. Phys. Rev. B37, (1988). 11
12 20. Batson, P. E. arbon 1s near-edge-absorption fine structure in Graphite. Phys. Rev. B48, (1993). 21. Tokito, S. Sakata, J. & Taga, Y. The molecular orientation in copper phthalocyanine thin films deposited on metal film surfaces. Thin Solid Films. 256, (1995). 22. Ling, M. M. Bao, Z. & Erk, P. Air-stable n-channel copper hexachlorophthalocyanine for field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, (2006). 23 Kurata, H. Isoda S. & Tomita, T. Proc. of the 16th International Microscopy ongress (IM16), Sapporo, Japan, p (2006). 24. Kurata, H. Isoda S. & Kobayashi, T. EELS study of radiation damage in chlorinated u-phthalocyanine and poly GeO-phthalocyanine. Ultramicroscopy, 41, (1992). 25. Hall,. R. & Hirsch, P. B. Effect of thermal diffuse scattering on propagation of high energy electron through crystals. Proc. Roy. Soc. A286, (1965). 26. Xu, P. Loane, R. F. & Silcox, J. Energy-filtered convergent-beam electron diffraction in STEM. Ultramicroscopy 38, (1991). 12
Elastic and Inelastic Scattering in Electron Diffraction and Imaging
 Elastic and Inelastic Scattering in Electron Diffraction and Imaging Contents Introduction Symbols and definitions Part A Diffraction and imaging of elastically scattered electrons Chapter 1. Basic kinematical
Elastic and Inelastic Scattering in Electron Diffraction and Imaging Contents Introduction Symbols and definitions Part A Diffraction and imaging of elastically scattered electrons Chapter 1. Basic kinematical
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Transmission Electron Microscopy
 L. Reimer H. Kohl Transmission Electron Microscopy Physics of Image Formation Fifth Edition el Springer Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Transmission Electron Microscopy... 1 1.1.1 Conventional Transmission
L. Reimer H. Kohl Transmission Electron Microscopy Physics of Image Formation Fifth Edition el Springer Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Transmission Electron Microscopy... 1 1.1.1 Conventional Transmission
Supplementary Figure 1: ADF images and profiles for several types of atomic chains encapsulated in DWNTs. (a d) ADF images of NaI, CsF, CsCl, and CsI
 Supplementary Figure 1: ADF images and profiles for several types of atomic chains encapsulated in DWNTs. (a d) ADF images of NaI, CsF, CsCl, and CsI atomic chains encapsulated in DWNTs, respectively.
Supplementary Figure 1: ADF images and profiles for several types of atomic chains encapsulated in DWNTs. (a d) ADF images of NaI, CsF, CsCl, and CsI atomic chains encapsulated in DWNTs, respectively.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary figure S1: Characterisation of the electron beam intensity profile. (a) A 3D plot of beam intensity (grey value) with position, (b) the beam
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary figure S1: Characterisation of the electron beam intensity profile. (a) A 3D plot of beam intensity (grey value) with position, (b) the beam
Detecting strain in scanning transmission electron microscope images. Part II Thesis
 Detecting strain in scanning transmission electron microscope images Part II Thesis Ina M. Sørensen Mansfield College, Oxford 10th of June, 2015 1 Abstract Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopes (STEM)
Detecting strain in scanning transmission electron microscope images Part II Thesis Ina M. Sørensen Mansfield College, Oxford 10th of June, 2015 1 Abstract Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopes (STEM)
High-Resolution. Transmission. Electron Microscopy
 Part 4 High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy 186 Significance high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM): resolve object details smaller than 1nm (10 9 m) image the interior of
Part 4 High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy 186 Significance high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM): resolve object details smaller than 1nm (10 9 m) image the interior of
Controllable Atomic Scale Patterning of Freestanding Monolayer. Graphene at Elevated Temperature
 Controllable Atomic Scale Patterning of Freestanding Monolayer Graphene at Elevated Temperature AUTHOR NAMES Qiang Xu 1, Meng-Yue Wu 1, Grégory F. Schneider 1, Lothar Houben 2, Sairam K. Malladi 1, Cees
Controllable Atomic Scale Patterning of Freestanding Monolayer Graphene at Elevated Temperature AUTHOR NAMES Qiang Xu 1, Meng-Yue Wu 1, Grégory F. Schneider 1, Lothar Houben 2, Sairam K. Malladi 1, Cees
Atomic Resolved HAADF-STEM for Composition Analysis
 Volume 38 Number 2 November 10, 2003 Atomic Resolved HAADF-STEM for Composition Analysis Makoto Shiojiri,, and Takashi. Yamazaki Kanazawa Medical University, Ishikawa 920-0293, Japan Kyoto Institute of
Volume 38 Number 2 November 10, 2003 Atomic Resolved HAADF-STEM for Composition Analysis Makoto Shiojiri,, and Takashi. Yamazaki Kanazawa Medical University, Ishikawa 920-0293, Japan Kyoto Institute of
a b c Supplementary Figure S1
 a b c Supplementary Figure S1 AFM measurements of MoS 2 nanosheets prepared from the electrochemical Liintercalation and exfoliation. (a) AFM measurement of a typical MoS 2 nanosheet, deposited on Si/SiO
a b c Supplementary Figure S1 AFM measurements of MoS 2 nanosheets prepared from the electrochemical Liintercalation and exfoliation. (a) AFM measurement of a typical MoS 2 nanosheet, deposited on Si/SiO
Imaging of built-in electric field at a p-n junction by scanning transmission electron microscopy
 Imaging of built-in electric field at a p-n junction by scanning transmission electron microscopy N. Shibata, S.D. Findlay, H. Sasaki, T. Matsumoto, H. Sawada, Y. Kohno, S. Otomo, R. Minato and Y. Ikuhara
Imaging of built-in electric field at a p-n junction by scanning transmission electron microscopy N. Shibata, S.D. Findlay, H. Sasaki, T. Matsumoto, H. Sawada, Y. Kohno, S. Otomo, R. Minato and Y. Ikuhara
(Supporting Information)
 Atomic and Electronic Structure of Graphene-Oxide (Supporting Information) K. Andre Mkhoyan, 1,2 * Alexander W. Contryman, 1 John Silcox, 1 Derek A. Stewart, 3 Goki Eda, 4 Cecilia Mattevi, 4 Steve Miller,
Atomic and Electronic Structure of Graphene-Oxide (Supporting Information) K. Andre Mkhoyan, 1,2 * Alexander W. Contryman, 1 John Silcox, 1 Derek A. Stewart, 3 Goki Eda, 4 Cecilia Mattevi, 4 Steve Miller,
SIMULATION OF TRANSMISSION AND SCANNING TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC IMAGES CONSIDERING ELASTIC AND THERMAL DIFFUSE SCATTERING
 Scanning Microscopy Vol. 11, 1997 (Pages 277-286) 0891-7035/97$5.00+.25 Scanning Microscopy International, Chicago (AMF Simulation O Hare), of TEM IL 60666 and STEM USA images SIMULATION OF TRANSMISSION
Scanning Microscopy Vol. 11, 1997 (Pages 277-286) 0891-7035/97$5.00+.25 Scanning Microscopy International, Chicago (AMF Simulation O Hare), of TEM IL 60666 and STEM USA images SIMULATION OF TRANSMISSION
Supporting Information for. Revealing Surface Elemental Composition and Dynamic Processes
 Supporting Information for Revealing Surface Elemental Composition and Dynamic Processes Involved in Facet-dependent Oxidation of Pt 3 Co Nanoparticles via in-situ Transmission Electron Microscopy Sheng
Supporting Information for Revealing Surface Elemental Composition and Dynamic Processes Involved in Facet-dependent Oxidation of Pt 3 Co Nanoparticles via in-situ Transmission Electron Microscopy Sheng
Simultaneous visualization of oxygen vacancies and the accompanying cation shifts in a perovskite oxide by combining annular imaging techniques
 Simultaneous visualization of oxygen vacancies and the accompanying cation shifts in a perovskite oxide by combining annular imaging techniques Shunsuke Kobayashi 1, Scott D. Findlay 2, Naoya Shibata 3,
Simultaneous visualization of oxygen vacancies and the accompanying cation shifts in a perovskite oxide by combining annular imaging techniques Shunsuke Kobayashi 1, Scott D. Findlay 2, Naoya Shibata 3,
Nanoelectronics 09. Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics. Quick Review over the Last Lecture
 Nanoelectronics 09 Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics 13:00 Monday, 12/February/2018 (P/T 006) Quick Review over the Last Lecture ( Field effect transistor (FET) ): ( Drain ) current increases
Nanoelectronics 09 Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics 13:00 Monday, 12/February/2018 (P/T 006) Quick Review over the Last Lecture ( Field effect transistor (FET) ): ( Drain ) current increases
A practical approach for STEM image simulation based on the FFT multislice method
 Ultramicroscopy 90 (00) 71 83 A practical approach for STEM image simulation based on the FFT multislice method Kazuo Ishizuka n HREM Research Inc., 14-48 Matsukazedai, Higashimatsuyama, Saitama 355-0055,
Ultramicroscopy 90 (00) 71 83 A practical approach for STEM image simulation based on the FFT multislice method Kazuo Ishizuka n HREM Research Inc., 14-48 Matsukazedai, Higashimatsuyama, Saitama 355-0055,
Aberration-corrected TEM studies on interface of multilayered-perovskite systems
 Aberration-corrected TEM studies on interface of multilayered-perovskite systems By Lina Gunawan (0326114) Supervisor: Dr. Gianluigi Botton November 1, 2006 MSE 702(1) Presentation Outline Literature Review
Aberration-corrected TEM studies on interface of multilayered-perovskite systems By Lina Gunawan (0326114) Supervisor: Dr. Gianluigi Botton November 1, 2006 MSE 702(1) Presentation Outline Literature Review
Structure analysis: Electron diffraction LEED TEM RHEED
 Structure analysis: Electron diffraction LEED: Low Energy Electron Diffraction SPA-LEED: Spot Profile Analysis Low Energy Electron diffraction RHEED: Reflection High Energy Electron Diffraction TEM: Transmission
Structure analysis: Electron diffraction LEED: Low Energy Electron Diffraction SPA-LEED: Spot Profile Analysis Low Energy Electron diffraction RHEED: Reflection High Energy Electron Diffraction TEM: Transmission
CHEM 681 Seminar Mingqi Zhao April 20, 1998 Room 2104, 4:00 p.m. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy: theories and applications
 CHEM 681 Seminar Mingqi Zhao April 20, 1998 Room 2104, 4:00 p.m. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy: theories and applications In materials science, people are always interested in viewing
CHEM 681 Seminar Mingqi Zhao April 20, 1998 Room 2104, 4:00 p.m. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy: theories and applications In materials science, people are always interested in viewing
PROBE AND OBJECT FUNCTION RECONSTRUCTION IN INCOHERENT SCANNING TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPE IMAGING
 Scanning Microscopy Vol. 11, 1997 (Pages 81-90) 0891-7035/97$5.00+.25 Scanning Microscopy International, Chicago Probe (AMF and O Hare), object IL function 60666 reconstruction USA PROBE AND OBJECT FUNCTION
Scanning Microscopy Vol. 11, 1997 (Pages 81-90) 0891-7035/97$5.00+.25 Scanning Microscopy International, Chicago Probe (AMF and O Hare), object IL function 60666 reconstruction USA PROBE AND OBJECT FUNCTION
Supplementary Figure S1. The detailed procedure for TEM imaging of graphene torn edge. (a) TEM image of a graphene torn edge before the tear
 Supplementary Figure S1. The detailed procedure for TEM imaging of graphene torn edge. (a) TEM image of a graphene torn edge before the tear propagation. Once a tear is identified at low magnification,
Supplementary Figure S1. The detailed procedure for TEM imaging of graphene torn edge. (a) TEM image of a graphene torn edge before the tear propagation. Once a tear is identified at low magnification,
Characterization of crystallographic defects in LaNiO 3 through TEM image simulations
 Characterization of crystallographic defects in LaNiO 3 through TEM image simulations Author: Joan Carles Bastons Garcia. Departament d Electrònica, Universitat de Barcelona Advisors: Sònia Estradé Albiol
Characterization of crystallographic defects in LaNiO 3 through TEM image simulations Author: Joan Carles Bastons Garcia. Departament d Electrònica, Universitat de Barcelona Advisors: Sònia Estradé Albiol
AP5301/ Name the major parts of an optical microscope and state their functions.
 Review Problems on Optical Microscopy AP5301/8301-2015 1. Name the major parts of an optical microscope and state their functions. 2. Compare the focal lengths of two glass converging lenses, one with
Review Problems on Optical Microscopy AP5301/8301-2015 1. Name the major parts of an optical microscope and state their functions. 2. Compare the focal lengths of two glass converging lenses, one with
Effect of Spiral Microwave Antenna Configuration on the Production of Nano-crystalline Film by Chemical Sputtering in ECR Plasma
 THE HARRIS SCIENCE REVIEW OF DOSHISHA UNIVERSITY, VOL. 56, No. 1 April 2015 Effect of Spiral Microwave Antenna Configuration on the Production of Nano-crystalline Film by Chemical Sputtering in ECR Plasma
THE HARRIS SCIENCE REVIEW OF DOSHISHA UNIVERSITY, VOL. 56, No. 1 April 2015 Effect of Spiral Microwave Antenna Configuration on the Production of Nano-crystalline Film by Chemical Sputtering in ECR Plasma
Overview of scattering, diffraction & imaging in the TEM
 Overview of scattering, diffraction & imaging in the TEM Eric A. Stach Purdue University Scattering Electrons, photons, neutrons Radiation Elastic Mean Free Path (Å)( Absorption Length (Å)( Minimum Probe
Overview of scattering, diffraction & imaging in the TEM Eric A. Stach Purdue University Scattering Electrons, photons, neutrons Radiation Elastic Mean Free Path (Å)( Absorption Length (Å)( Minimum Probe
Chapter 9. Electron mean free path Microscopy principles of SEM, TEM, LEEM
 Chapter 9 Electron mean free path Microscopy principles of SEM, TEM, LEEM 9.1 Electron Mean Free Path 9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) -SEM design; Secondary electron imaging; Backscattered electron
Chapter 9 Electron mean free path Microscopy principles of SEM, TEM, LEEM 9.1 Electron Mean Free Path 9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) -SEM design; Secondary electron imaging; Backscattered electron
Atomic Bonding Effects in Annular Dark Field Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy I: Computational Predictions
 Atomic Bonding Effects in Annular Dark Field Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy I: Computational Predictions Michael L. Odlyzko 1, Burak Himmetoglu 1,2, Matteo Cococcioni 1,3, K. Andre Mkhoyan 1
Atomic Bonding Effects in Annular Dark Field Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy I: Computational Predictions Michael L. Odlyzko 1, Burak Himmetoglu 1,2, Matteo Cococcioni 1,3, K. Andre Mkhoyan 1
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1. SEM images of perovskite single-crystal patterned thin film with
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1. SEM images of perovskite single-crystal patterned thin film with
Praktikum zur. Materialanalytik
 Praktikum zur Materialanalytik Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy B513 Stand: 19.10.2016 Contents 1 Introduction... 2 2. Fundamental Physics and Notation... 3 2.1. Alignments of the microscope... 3 2.2.
Praktikum zur Materialanalytik Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy B513 Stand: 19.10.2016 Contents 1 Introduction... 2 2. Fundamental Physics and Notation... 3 2.1. Alignments of the microscope... 3 2.2.
Supporting information for. Direct imaging of kinetic pathways of atomic diffusion in. monolayer molybdenum disulfide
 Supporting information for Direct imaging of kinetic pathways of atomic diffusion in monolayer molybdenum disulfide Jinhua Hong,, Yuhao Pan,, Zhixin Hu, Danhui Lv, Chuanhong Jin, *, Wei Ji, *, Jun Yuan,,*,
Supporting information for Direct imaging of kinetic pathways of atomic diffusion in monolayer molybdenum disulfide Jinhua Hong,, Yuhao Pan,, Zhixin Hu, Danhui Lv, Chuanhong Jin, *, Wei Ji, *, Jun Yuan,,*,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
Transmission Electron Microscopy for metrology and characterization of semiconductor devices
 Transmission Electron Microscopy for metrology and characterization of semiconductor devices Bert Freitag, Laurens Kwakman, Ivan Lazic and Frank de Jong FEI / ThermoFisher Scientific, Achtseweg Noord 5,
Transmission Electron Microscopy for metrology and characterization of semiconductor devices Bert Freitag, Laurens Kwakman, Ivan Lazic and Frank de Jong FEI / ThermoFisher Scientific, Achtseweg Noord 5,
IMAGING DIFFRACTION SPECTROSCOPY
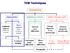 TEM Techniques TEM/STEM IMAGING DIFFRACTION SPECTROSCOPY Amplitude contrast (diffracion contrast) Phase contrast (highresolution imaging) Selected area diffraction Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy
TEM Techniques TEM/STEM IMAGING DIFFRACTION SPECTROSCOPY Amplitude contrast (diffracion contrast) Phase contrast (highresolution imaging) Selected area diffraction Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy
Energy-Filtering. Transmission. Electron Microscopy
 Part 3 Energy-Filtering Transmission Electron Microscopy 92 Energy-Filtering TEM Principle of EFTEM expose specimen to mono-energetic electron radiation inelastic scattering in the specimen poly-energetic
Part 3 Energy-Filtering Transmission Electron Microscopy 92 Energy-Filtering TEM Principle of EFTEM expose specimen to mono-energetic electron radiation inelastic scattering in the specimen poly-energetic
Dislocation networks in graphite
 Dislocation networks in graphite High Resolution Microscop With Reference to Lattice Fringe Imaging in a TEM f f r Real space Specimen Reciprocal space hr Point spread function Diffraction pattern Back
Dislocation networks in graphite High Resolution Microscop With Reference to Lattice Fringe Imaging in a TEM f f r Real space Specimen Reciprocal space hr Point spread function Diffraction pattern Back
Atomic Resolution Interfacial Structure of Lead-free Ferroelectric
 Atomic Resolution Interfacial Structure of Lead-free Ferroelectric K 0.5 Na 0.5 NbO 3 Thin films Deposited on SrTiO 3 Chao Li 1, Lingyan Wang 1*, Zhao Wang 2, Yaodong Yang 2, Wei Ren 1 and Guang Yang 1
Atomic Resolution Interfacial Structure of Lead-free Ferroelectric K 0.5 Na 0.5 NbO 3 Thin films Deposited on SrTiO 3 Chao Li 1, Lingyan Wang 1*, Zhao Wang 2, Yaodong Yang 2, Wei Ren 1 and Guang Yang 1
Weak-Beam Dark-Field Technique
 Basic Idea recall bright-field contrast of dislocations: specimen close to Bragg condition, s î 0 Weak-Beam Dark-Field Technique near the dislocation core, some planes curved to s = 0 ) strong Bragg reflection
Basic Idea recall bright-field contrast of dislocations: specimen close to Bragg condition, s î 0 Weak-Beam Dark-Field Technique near the dislocation core, some planes curved to s = 0 ) strong Bragg reflection
Supplementary Figure 1. Crystal packing of pentacene.
 t 3 t 4 t 1 t 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Crystal packing of pentacene. The largestholecharge transfer integrals are shown in red:t 1 = 75 mev, t 2 = 32 mev, t 3 = 20 mev, t 4 = 6 mev. Note that IRactive
t 3 t 4 t 1 t 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Crystal packing of pentacene. The largestholecharge transfer integrals are shown in red:t 1 = 75 mev, t 2 = 32 mev, t 3 = 20 mev, t 4 = 6 mev. Note that IRactive
Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials
 Brent Fultz James Howe Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials Fourth Edition ~Springer 1 1 Diffraction and the X-Ray Powder Diffractometer 1 1.1 Diffraction... 1 1.1.1 Introduction
Brent Fultz James Howe Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials Fourth Edition ~Springer 1 1 Diffraction and the X-Ray Powder Diffractometer 1 1.1 Diffraction... 1 1.1.1 Introduction
Phonon scattering: how does it a ect the image contrast in high-resolution transmission electron microscopy?
 PHILOSOPHICAL MAGAZINE B, 1999, VOL. 79, NO. 1, 37± 48 Phonon scattering: how does it a ect the image contrast in high-resolution transmission electron microscopy? Z. L. Wang² School of Materials Science
PHILOSOPHICAL MAGAZINE B, 1999, VOL. 79, NO. 1, 37± 48 Phonon scattering: how does it a ect the image contrast in high-resolution transmission electron microscopy? Z. L. Wang² School of Materials Science
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure. X-ray diffraction pattern of CH 3 NH 3 PbI 3 film. Strong reflections of the () family of planes is characteristics of the preferred orientation of the perovskite
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure. X-ray diffraction pattern of CH 3 NH 3 PbI 3 film. Strong reflections of the () family of planes is characteristics of the preferred orientation of the perovskite
M any functional properties observed in perovskite oxides, ABO3, exhibit close couplings to slight structural
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPY CERAMICS CHARACTERIZATION AND ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Atomic level observation of octahedral distortions at the perovskite oxide
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPY CERAMICS CHARACTERIZATION AND ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Atomic level observation of octahedral distortions at the perovskite oxide
Characterisation of Nanoparticle Structure by High Resolution Electron Microscopy
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Characterisation of Nanoparticle Structure by High Resolution Electron Microscopy To cite this article: Robert D Boyd et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 522
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Characterisation of Nanoparticle Structure by High Resolution Electron Microscopy To cite this article: Robert D Boyd et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 522
Conventional Transmission Electron Microscopy. Introduction. Text Books. Text Books. EMSE-509 CWRU Frank Ernst
 Text Books Conventional Transmission Electron Microscopy EMSE-509 CWRU Frank Ernst D. B. Williams and C. B. Carter: Transmission Electron Microscopy, New York: Plenum Press (1996). L. Reimer: Transmission
Text Books Conventional Transmission Electron Microscopy EMSE-509 CWRU Frank Ernst D. B. Williams and C. B. Carter: Transmission Electron Microscopy, New York: Plenum Press (1996). L. Reimer: Transmission
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Atomic structure and dynamic behaviour of truly one-dimensional ionic chains inside carbon nanotubes Ryosuke Senga 1, Hannu-Pekka Komsa 2, Zheng Liu 1, Kaori Hirose-Takai 1, Arkady V. Krasheninnikov 2
Atomic structure and dynamic behaviour of truly one-dimensional ionic chains inside carbon nanotubes Ryosuke Senga 1, Hannu-Pekka Komsa 2, Zheng Liu 1, Kaori Hirose-Takai 1, Arkady V. Krasheninnikov 2
Lithium Atom Microscopy at Sub-50pm Resolution by R005
 Volume 45 Number 1 July, 2010 Lithium Atom Microscopy at Sub-50pm Resolution by R005 Contents Lithium Atom Microscopy at Sub-50pm Resolution by R005............... 2 Atomic-Resolution Elemental Mapping
Volume 45 Number 1 July, 2010 Lithium Atom Microscopy at Sub-50pm Resolution by R005 Contents Lithium Atom Microscopy at Sub-50pm Resolution by R005............... 2 Atomic-Resolution Elemental Mapping
ABNORMAL X-RAY EMISSION FROM INSULATORS BOMBARDED WITH LOW ENERGY IONS
 302 ABNORMAL X-RAY EMISSION FROM INSULATORS BOMBARDED WITH LOW ENERGY IONS M. Song 1, K. Mitsuishi 1, M. Takeguchi 1, K. Furuya 1, R. C. Birtcher 2 1 High Voltage Electron Microscopy Station, National
302 ABNORMAL X-RAY EMISSION FROM INSULATORS BOMBARDED WITH LOW ENERGY IONS M. Song 1, K. Mitsuishi 1, M. Takeguchi 1, K. Furuya 1, R. C. Birtcher 2 1 High Voltage Electron Microscopy Station, National
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Characterization of pure CaO and Zr-TiO 2 /CaO nanocomposite
 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1. Characterization of pure CaO and Zr-TiO 2 /CaO nanocomposite 4.1.1. Scanning electron microscopy analysis (SEM) SEM images of prepared CaO are shown in Fig. 4.1 (a and b). CaO
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1. Characterization of pure CaO and Zr-TiO 2 /CaO nanocomposite 4.1.1. Scanning electron microscopy analysis (SEM) SEM images of prepared CaO are shown in Fig. 4.1 (a and b). CaO
Supplementary Figure 1: Example non-overlapping, binary probe functions P1 (~q) and P2 (~q), that add to form a top hat function A(~q).
 Supplementary Figures P(q) A(q) + Function Value P(q) qmax = Supplementary Figure : Example non-overlapping, binary probe functions P (~q) and P (~q), that add to form a top hat function A(~q). qprobe
Supplementary Figures P(q) A(q) + Function Value P(q) qmax = Supplementary Figure : Example non-overlapping, binary probe functions P (~q) and P (~q), that add to form a top hat function A(~q). qprobe
Raman spectroscopy study of rotated double-layer graphene: misorientation angle dependence of electronic structure
 Supplementary Material for Raman spectroscopy study of rotated double-layer graphene: misorientation angle dependence of electronic structure Kwanpyo Kim 1,2,3, Sinisa Coh 1,3, Liang Z. Tan 1,3, William
Supplementary Material for Raman spectroscopy study of rotated double-layer graphene: misorientation angle dependence of electronic structure Kwanpyo Kim 1,2,3, Sinisa Coh 1,3, Liang Z. Tan 1,3, William
Single Emitter Detection with Fluorescence and Extinction Spectroscopy
 Single Emitter Detection with Fluorescence and Extinction Spectroscopy Michael Krall Elements of Nanophotonics Associated Seminar Recent Progress in Nanooptics & Photonics May 07, 2009 Outline Single molecule
Single Emitter Detection with Fluorescence and Extinction Spectroscopy Michael Krall Elements of Nanophotonics Associated Seminar Recent Progress in Nanooptics & Photonics May 07, 2009 Outline Single molecule
Spin-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy
 Spin-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy Application Notes Spin-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy experiments were performed in an experimental station consisting of an analysis and a preparation chamber.
Spin-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy Application Notes Spin-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy experiments were performed in an experimental station consisting of an analysis and a preparation chamber.
Resolution of coherent and incoherent imaging systems reconsidered - Classical criteria and a statistical alternative
 Resolution of coherent and incoherent imaging systems reconsidered - Classical criteria and a statistical alternative Sandra Van Aert and Dirk Van Dyck University of Antwerp, Department of Physics, Groenenborgerlaan
Resolution of coherent and incoherent imaging systems reconsidered - Classical criteria and a statistical alternative Sandra Van Aert and Dirk Van Dyck University of Antwerp, Department of Physics, Groenenborgerlaan
These authors contributed equally to this work. 1. Structural analysis of as-deposited PbS quantum dots by Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD)
 Supporting information for: Atomic Layer Deposition of Lead Sulfide Quantum Dots on Nanowire Surfaces Neil P. Dasgupta 1,*,, Hee Joon Jung 2,, Orlando Trejo 1, Matthew T. McDowell 2, Aaron Hryciw 3, Mark
Supporting information for: Atomic Layer Deposition of Lead Sulfide Quantum Dots on Nanowire Surfaces Neil P. Dasgupta 1,*,, Hee Joon Jung 2,, Orlando Trejo 1, Matthew T. McDowell 2, Aaron Hryciw 3, Mark
Supporting Information. Polar Second-Harmonic Imaging to Resolve Pure. and Mixed Crystal Phases along GaAs Nanowires.
 Supporting Information Polar Second-Harmonic Imaging to Resolve Pure and Mixed Crystal Phases along GaAs Nanowires. Maria Timofeeva,,*, Alexei Bouravleuv,, George Cirlin,,, Igor Shtrom,, Ilya Soshnikov,
Supporting Information Polar Second-Harmonic Imaging to Resolve Pure and Mixed Crystal Phases along GaAs Nanowires. Maria Timofeeva,,*, Alexei Bouravleuv,, George Cirlin,,, Igor Shtrom,, Ilya Soshnikov,
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Identification of Active Zr-WO x Clusters on a ZrO 2 Support for Solid Acid Catalysts Wu Zhou 1, Elizabeth I. Ross-Medgaarden 2, William V. Knowles 3, Michael S. Wong 3, Israel
Supplementary information Identification of Active Zr-WO x Clusters on a ZrO 2 Support for Solid Acid Catalysts Wu Zhou 1, Elizabeth I. Ross-Medgaarden 2, William V. Knowles 3, Michael S. Wong 3, Israel
Surface Sensitivity & Surface Specificity
 Surface Sensitivity & Surface Specificity The problems of sensitivity and detection limits are common to all forms of spectroscopy. In its simplest form, the question of sensitivity boils down to whether
Surface Sensitivity & Surface Specificity The problems of sensitivity and detection limits are common to all forms of spectroscopy. In its simplest form, the question of sensitivity boils down to whether
3D and Atomic-resolution Imaging with Coherent Electron Nanobeams - Opportunities and Challenges for X-rays
 3D and Atomic-resolution Imaging with Coherent Electron Nanobeams - Opportunities and Challenges for X-rays David A. Muller Lena Fitting Kourkoutis, Megan Holtz, Robert Hovden, Qingyun Mao, Julia Mundy,
3D and Atomic-resolution Imaging with Coherent Electron Nanobeams - Opportunities and Challenges for X-rays David A. Muller Lena Fitting Kourkoutis, Megan Holtz, Robert Hovden, Qingyun Mao, Julia Mundy,
The ideal fiber pattern exhibits 4-quadrant symmetry. In the ideal pattern the fiber axis is called the meridian, the perpendicular direction is
 Fiber diffraction is a method used to determine the structural information of a molecule by using scattering data from X-rays. Rosalind Franklin used this technique in discovering structural information
Fiber diffraction is a method used to determine the structural information of a molecule by using scattering data from X-rays. Rosalind Franklin used this technique in discovering structural information
A menu of electron probes for optimising information from Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy
 This is the preprint. The Published Journal Article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultramic.2017.08.020 2018. This manuscript version is made available under the CC-BY-NCND 4.0 license https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0
This is the preprint. The Published Journal Article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultramic.2017.08.020 2018. This manuscript version is made available under the CC-BY-NCND 4.0 license https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0
Microscopy: Principles
 Low Voltage Electron Microscopy: Principles and Applications Edited by David C. Bell Harvard University, USA and Natasha Erdman JEOL USA Inc., USA Published in association with the Royal Microscopical
Low Voltage Electron Microscopy: Principles and Applications Edited by David C. Bell Harvard University, USA and Natasha Erdman JEOL USA Inc., USA Published in association with the Royal Microscopical
Everhart-Thornley detector
 SEI Detector Everhart-Thornley detector Microscope chamber wall Faraday cage Scintillator Electrons in Light pipe Photomultiplier Electrical signal out Screen Quartz window +200 V +10 kv Always contains
SEI Detector Everhart-Thornley detector Microscope chamber wall Faraday cage Scintillator Electrons in Light pipe Photomultiplier Electrical signal out Screen Quartz window +200 V +10 kv Always contains
Chapter 4 Imaging Lecture 24
 Chapter 4 Imaging Lecture 4 d (110) Final Exam Notice Time and Date: :30 4:30 PM, Wednesday, Dec. 10, 08. Place: Classroom CHEM-10 Coverage: All contents after midterm Open note Term project is due today
Chapter 4 Imaging Lecture 4 d (110) Final Exam Notice Time and Date: :30 4:30 PM, Wednesday, Dec. 10, 08. Place: Classroom CHEM-10 Coverage: All contents after midterm Open note Term project is due today
Supporting Information for. Structural and Chemical Dynamics of Pyridinic Nitrogen. Defects in Graphene
 Supporting Information for Structural and Chemical Dynamics of Pyridinic Nitrogen Defects in Graphene Yung-Chang Lin, 1* Po-Yuan Teng, 2 Chao-Hui Yeh, 2 Masanori Koshino, 1 Po-Wen Chiu, 2 Kazu Suenaga
Supporting Information for Structural and Chemical Dynamics of Pyridinic Nitrogen Defects in Graphene Yung-Chang Lin, 1* Po-Yuan Teng, 2 Chao-Hui Yeh, 2 Masanori Koshino, 1 Po-Wen Chiu, 2 Kazu Suenaga
Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies.
 PY482 Lecture. February 28 th, 2013 Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies. Kevin E. Smith Department of Physics Department of Chemistry Division
PY482 Lecture. February 28 th, 2013 Studying Metal to Insulator Transitions in Solids using Synchrotron Radiation-based Spectroscopies. Kevin E. Smith Department of Physics Department of Chemistry Division
Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of SE spectra from annealed and unannealed P3HT samples. See Supplementary Note 1 for discussion.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of SE spectra from annealed and unannealed P3HT samples. See Supplementary Note 1 for discussion. Supplementary Figure 2: SE spectra from blend films. a) and b) compare
Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of SE spectra from annealed and unannealed P3HT samples. See Supplementary Note 1 for discussion. Supplementary Figure 2: SE spectra from blend films. a) and b) compare
SOLID STATE 18. Reciprocal Space
 SOLID STATE 8 Reciprocal Space Wave vectors and the concept of K-space can simplify the explanation of several properties of the solid state. They will be introduced to provide more information on diffraction
SOLID STATE 8 Reciprocal Space Wave vectors and the concept of K-space can simplify the explanation of several properties of the solid state. They will be introduced to provide more information on diffraction
Development of 2-Dimentional Imaging XAFS System at BL-4
 Development of 2-Dimentional Imaging XAFS System at BL-4 Koichi Sumiwaka 1, Misaki Katayama 2, Yasuhiro Inada 2 1) Department of Applied Chemistry, College of Science and Engineering, Ritsumeikan, University,
Development of 2-Dimentional Imaging XAFS System at BL-4 Koichi Sumiwaka 1, Misaki Katayama 2, Yasuhiro Inada 2 1) Department of Applied Chemistry, College of Science and Engineering, Ritsumeikan, University,
Setting The motor that rotates the sample about an axis normal to the diffraction plane is called (or ).
 X-Ray Diffraction X-ray diffraction geometry A simple X-ray diffraction (XRD) experiment might be set up as shown below. We need a parallel X-ray source, which is usually an X-ray tube in a fixed position
X-Ray Diffraction X-ray diffraction geometry A simple X-ray diffraction (XRD) experiment might be set up as shown below. We need a parallel X-ray source, which is usually an X-ray tube in a fixed position
Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental setup for crystal growth. Schematic drawing of the experimental setup for C 8 -BTBT crystal growth.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental setup for crystal growth. Schematic drawing of the experimental setup for C 8 -BTBT crystal growth. Supplementary Figure 2 AFM study of the C 8 -BTBT crystal growth
Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental setup for crystal growth. Schematic drawing of the experimental setup for C 8 -BTBT crystal growth. Supplementary Figure 2 AFM study of the C 8 -BTBT crystal growth
High-Resolution Electron Microscopy: From Imaging Toward Measuring
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 51, NO. 4, AUGUST 2002 611 High-Resolution Electron Microscopy: From Imaging Toward Measuring Sandra Van Aert, Arnold J. den Dekker, Adriaan van
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 51, NO. 4, AUGUST 2002 611 High-Resolution Electron Microscopy: From Imaging Toward Measuring Sandra Van Aert, Arnold J. den Dekker, Adriaan van
Ma5: Auger- and Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy
 Ma5: Auger- and Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy 1 Introduction Electron spectroscopies, namely Auger electron- and electron energy loss spectroscopy are utilized to determine the KLL spectrum and the
Ma5: Auger- and Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy 1 Introduction Electron spectroscopies, namely Auger electron- and electron energy loss spectroscopy are utilized to determine the KLL spectrum and the
Chemical Analysis in TEM: XEDS, EELS and EFTEM. HRTEM PhD course Lecture 5
 Chemical Analysis in TEM: XEDS, EELS and EFTEM HRTEM PhD course Lecture 5 1 Part IV Subject Chapter Prio x-ray spectrometry 32 1 Spectra and mapping 33 2 Qualitative XEDS 34 1 Quantitative XEDS 35.1-35.4
Chemical Analysis in TEM: XEDS, EELS and EFTEM HRTEM PhD course Lecture 5 1 Part IV Subject Chapter Prio x-ray spectrometry 32 1 Spectra and mapping 33 2 Qualitative XEDS 34 1 Quantitative XEDS 35.1-35.4
SYNCHROTRON X-RAY MICROBEAM CHARACTERIZATION OF SMECTIC A LIQUID CRYSTALS UNDER ELECTRIC FIELD
 73 SYNCHROTRON X-RAY MICROBEAM CHARACTERIZATION OF SMECTIC A LIQUID CRYSTALS UNDER ELECTRIC FIELD Atsuo Iida 1), Yoichi Takanishi 2) 1)Photon Factory, Institute of Materials Structure Science, High Energy
73 SYNCHROTRON X-RAY MICROBEAM CHARACTERIZATION OF SMECTIC A LIQUID CRYSTALS UNDER ELECTRIC FIELD Atsuo Iida 1), Yoichi Takanishi 2) 1)Photon Factory, Institute of Materials Structure Science, High Energy
DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY. Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University
 DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University 1995 ELSEVIER Amsterdam Lausanne New York Oxford Shannon Tokyo CONTENTS Preface to the first
DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University 1995 ELSEVIER Amsterdam Lausanne New York Oxford Shannon Tokyo CONTENTS Preface to the first
Imaging Methods: Scanning Force Microscopy (SFM / AFM)
 Imaging Methods: Scanning Force Microscopy (SFM / AFM) The atomic force microscope (AFM) probes the surface of a sample with a sharp tip, a couple of microns long and often less than 100 Å in diameter.
Imaging Methods: Scanning Force Microscopy (SFM / AFM) The atomic force microscope (AFM) probes the surface of a sample with a sharp tip, a couple of microns long and often less than 100 Å in diameter.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Lateral heterojunctions within monolayer MoSe 2 -WSe 2 semiconductors Chunming Huang 1,#,*, Sanfeng Wu 1,#,*, Ana M. Sanchez 2,#,*, Jonathan J. P. Peters 2, Richard Beanland 2, Jason S. Ross 3, Pasqual
Lateral heterojunctions within monolayer MoSe 2 -WSe 2 semiconductors Chunming Huang 1,#,*, Sanfeng Wu 1,#,*, Ana M. Sanchez 2,#,*, Jonathan J. P. Peters 2, Richard Beanland 2, Jason S. Ross 3, Pasqual
Unusual Molecular Material formed through Irreversible Transformation and Revealed by 4D Electron Microscopy
 26 March 2013 Unusual Molecular Material formed through Irreversible Transformation and Revealed by 4D Electron Microscopy Renske M. van der Veen, Antoine Tissot, Andreas Hauser, Ahmed H. Zewail Physical
26 March 2013 Unusual Molecular Material formed through Irreversible Transformation and Revealed by 4D Electron Microscopy Renske M. van der Veen, Antoine Tissot, Andreas Hauser, Ahmed H. Zewail Physical
CHEM-E5225 :Electron Microscopy Imaging
 CHEM-E5225 :Electron Microscopy Imaging 2016.10 Yanling Ge Outline Planar Defects Image strain field WBDF microscopy HRTEM information theory Discuss of question homework? Planar Defects - Internal Interface
CHEM-E5225 :Electron Microscopy Imaging 2016.10 Yanling Ge Outline Planar Defects Image strain field WBDF microscopy HRTEM information theory Discuss of question homework? Planar Defects - Internal Interface
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 3, March-2014 ISSN
 156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
Elastic Constants and Microstructure of Amorphous SiO 2 Thin Films Studied by Brillouin Oscillations
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Elastic Constants and Microstructure of Amorphous SiO 2 Thin Films Studied by Brillouin
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Elastic Constants and Microstructure of Amorphous SiO 2 Thin Films Studied by Brillouin
Structural Characterization of Nanoparticles
 Structural Characterization of Nanoparticles Nicola Pinna Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces e-mail: pinna@mpikg-golm.mpg.de - http://www.pinna.cx Plan 1. Transmission Electron Microscopy
Structural Characterization of Nanoparticles Nicola Pinna Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces e-mail: pinna@mpikg-golm.mpg.de - http://www.pinna.cx Plan 1. Transmission Electron Microscopy
An Introduction to Diffraction and Scattering. School of Chemistry The University of Sydney
 An Introduction to Diffraction and Scattering Brendan J. Kennedy School of Chemistry The University of Sydney 1) Strong forces 2) Weak forces Types of Forces 3) Electromagnetic forces 4) Gravity Types
An Introduction to Diffraction and Scattering Brendan J. Kennedy School of Chemistry The University of Sydney 1) Strong forces 2) Weak forces Types of Forces 3) Electromagnetic forces 4) Gravity Types
Scanning transmission electron microscopy
 Scanning transmission electron microscopy L. Brown To cite this version: L. Brown. Scanning transmission electron microscopy. Journal de Physique IV Colloque, 1993, 03 (C7), pp.c7-2073-c7-2080. .
Scanning transmission electron microscopy L. Brown To cite this version: L. Brown. Scanning transmission electron microscopy. Journal de Physique IV Colloque, 1993, 03 (C7), pp.c7-2073-c7-2080. .
Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)/X-ray Absorption Near Edge Spectroscopy (XANES).
 S1 Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)/X-ray Absorption Near Edge Spectroscopy (XANES). The combined SAXS/XANES measurements were carried out at the µspot beamline at BESSY II (Berlin, Germany). The beamline
S1 Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)/X-ray Absorption Near Edge Spectroscopy (XANES). The combined SAXS/XANES measurements were carried out at the µspot beamline at BESSY II (Berlin, Germany). The beamline
Electron Microscopy I
 Characterization of Catalysts and Surfaces Characterization Techniques in Heterogeneous Catalysis Electron Microscopy I Introduction Properties of electrons Electron-matter interactions and their applications
Characterization of Catalysts and Surfaces Characterization Techniques in Heterogeneous Catalysis Electron Microscopy I Introduction Properties of electrons Electron-matter interactions and their applications
MICROSTRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON FIBERS USING ABERRATION CORRECTED SCANNING TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPY.
 MICROSTRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON FIBERS USING ABERRATION CORRECTED SCANNING TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPY Klaus van Benthem, Cristian I. Contescu, Nidia C. Gallego, Stephen J. Pennycook,
MICROSTRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON FIBERS USING ABERRATION CORRECTED SCANNING TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPY Klaus van Benthem, Cristian I. Contescu, Nidia C. Gallego, Stephen J. Pennycook,
Experimental Section
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Modification of Ga 2 O 3 by Ag Cr Core
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Modification of Ga 2 O 3 by Ag Cr Core
Lecture 10: Surface Plasmon Excitation. 5 nm
 Excitation Lecture 10: Surface Plasmon Excitation 5 nm Summary The dispersion relation for surface plasmons Useful for describing plasmon excitation & propagation This lecture: p sp Coupling light to surface
Excitation Lecture 10: Surface Plasmon Excitation 5 nm Summary The dispersion relation for surface plasmons Useful for describing plasmon excitation & propagation This lecture: p sp Coupling light to surface
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Methods and supplementary materials Materials and sample preparation Bulk hexagonal boron nitride (h-bn) powders were provided by Saint-Gobain Advanced Ceramics Lauf GmbH. The stated chemical composition
Methods and supplementary materials Materials and sample preparation Bulk hexagonal boron nitride (h-bn) powders were provided by Saint-Gobain Advanced Ceramics Lauf GmbH. The stated chemical composition
Energy-Filtered High-Resolution Electron Microscopy for Quantitative Solid State Structure Determination
 [J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 102, 1 (1997)] Energy-Filtered High-Resolution Electron Microscopy for Quantitative Solid State Structure Determination Volume 102 Number 1 January February 1997 Z.
[J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 102, 1 (1997)] Energy-Filtered High-Resolution Electron Microscopy for Quantitative Solid State Structure Determination Volume 102 Number 1 January February 1997 Z.
April 10th-12th, 2017
 Thomas LaGrange, Ph.D. Faculty Lecturer and Senior Staff Scientist Introduction: Basics of Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) TEM Doctoral Course MS-637 April 10th-12th, 2017 Outline 1. What is microcopy?
Thomas LaGrange, Ph.D. Faculty Lecturer and Senior Staff Scientist Introduction: Basics of Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) TEM Doctoral Course MS-637 April 10th-12th, 2017 Outline 1. What is microcopy?
EELS Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy
 EELS Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy (Thanks to Steve Pennycook, Quan Li, Charlie Lyman, Ondre Krivenak, David Muller, David Bell, Natasha Erdman, Nestor Zaluzec and many others) Nestor Zaluzec,
EELS Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy (Thanks to Steve Pennycook, Quan Li, Charlie Lyman, Ondre Krivenak, David Muller, David Bell, Natasha Erdman, Nestor Zaluzec and many others) Nestor Zaluzec,
Exploring the Formation of Symmetric Gold Nanostars by Liquid-Cell Transmission Electron Microscopy
 Supplementary information Exploring the Formation of Symmetric Gold Nanostars by Liquid-Cell Transmission Electron Microscopy Nabeel Ahmad, 1,2 Guillaume Wang, 1 Jaysen Nelayah, 1 Christian Ricolleau,
Supplementary information Exploring the Formation of Symmetric Gold Nanostars by Liquid-Cell Transmission Electron Microscopy Nabeel Ahmad, 1,2 Guillaume Wang, 1 Jaysen Nelayah, 1 Christian Ricolleau,
The Principles of STEM Imaging
 2 The Principles of STEM Imaging Peter D. Nellist 2.1 Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to review the principles underlying imaging in the scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM). Consideration
2 The Principles of STEM Imaging Peter D. Nellist 2.1 Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to review the principles underlying imaging in the scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM). Consideration
Supporting information:
 Epitaxially Integrating Ferromagnetic Fe 1.3 Ge Nanowire Arrays on Few-Layer Graphene Hana Yoon, Taejoon Kang, Jung Min Lee, Si-in Kim, Kwanyong Seo, Jaemyung Kim, Won Il Park, and Bongsoo Kim,* Department
Epitaxially Integrating Ferromagnetic Fe 1.3 Ge Nanowire Arrays on Few-Layer Graphene Hana Yoon, Taejoon Kang, Jung Min Lee, Si-in Kim, Kwanyong Seo, Jaemyung Kim, Won Il Park, and Bongsoo Kim,* Department
Determining Carbon Nanotube Properties from Raman. Scattering Measurements
 Determining Carbon Nanotube Properties from Raman Scattering Measurements Ying Geng 1, David Fang 2, and Lei Sun 3 1 2 3 The Institute of Optics, Electrical and Computer Engineering, Laboratory for Laser
Determining Carbon Nanotube Properties from Raman Scattering Measurements Ying Geng 1, David Fang 2, and Lei Sun 3 1 2 3 The Institute of Optics, Electrical and Computer Engineering, Laboratory for Laser
Atomic and Nuclear Physics
 Atomic and Nuclear Physics Introductory experiments ualism of wave and particle L Physics Leaflets P6.1.5.1 iffraction of electrons in a polycrystalline lattice (ebye-scherrer diffraction) Objects of the
Atomic and Nuclear Physics Introductory experiments ualism of wave and particle L Physics Leaflets P6.1.5.1 iffraction of electrons in a polycrystalline lattice (ebye-scherrer diffraction) Objects of the
6.5 mm. ε = 1%, r = 9.4 mm. ε = 3%, r = 3.1 mm
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Gold wires Substrate Compression holder 6.5 mm Supplementary Figure 1 Picture of the compression holder. 6.5 mm ε = 0% ε = 1%, r = 9.4 mm ε = 2%, r = 4.7
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Gold wires Substrate Compression holder 6.5 mm Supplementary Figure 1 Picture of the compression holder. 6.5 mm ε = 0% ε = 1%, r = 9.4 mm ε = 2%, r = 4.7
