Link Analysis and Web Search
|
|
|
- Jessie Ford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Link Analysis and Web Search Episode 11 Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto
2 Link Analysis and Web Search (Chapter 13, 14)
3 Information networks and the Web Logical relationships among pieces of information Best example: the Web 1991: Tim Berners-Lee at CERN (Switzerland) created the Web provided an easy way to make documents web pages for the world to see view these pages using browsers it is based on the idea of connecting these pages using links 3
4 The idea of links is both inspired and non-obvious There are many ways of organizing information: classification (library), series of folders (files), or just alphabetically (phone book) 4
5 Modeling the web as a directed graph Objective: create a map of the web But how? 5
6 Strongly Connected Components Strongly connected component: a subset of nodes such that (1) every node in the subset has a path to every other; and (2) the subset is not part of some larger set in which every node can reach every other. 6
7
8 Now we can build a global map of the Web, using strongly connected components (Broder et al. [1999])
9 A giant strongly connected component
10 Can there be a second giant strongly connected component? 10
11 Not really it s too fragile 11
12 The bow-tie structure of the web 12
13 Tendrils 44 Million nodes IN SCC OUT 44 Million nodes 56 Million nodes 44 Million nodes Tubes Disconnected components
14 How do we find web pages using search? Up through the 1980s, very few people cared about information retrieval (search) librarians patent attorneys They are trained to formulate effective queries, and the documents they were searching for were written by professionals research articles court documents U.S. patents 14
15 The Web is entirely different Both search users and web page authors are amateurs Scale is really large Highly dynamic nature of the content to be searched Some of the authors may even optimize their content for a search engine An industry called Search Engine Optimization Millions of dollars on the line 15
16 When I search for a key phrase, what do I need? University of Washington University of Waterloo University of Wisconsin University of Windsor University of Winnipeg University of Wyoming? 16
17 Basic idea: let the links vote 17
18 Using links as more than simple votes 18
19 Searching for good museum 19
20 Link-based ranking with hubs and authorities Key idea: voting again and again 20
21 Link-based ranking with hubs and authorities Key idea: principle of repeated improvement 21
22 But why stop here? 22
23 Let s make it more formal Two kinds of quality measures for web pages Authority score Auth(p): level of endorsement Hub score Hub(p) : quality as a list Authority update rule: Auth(p) = sum of hub scores of all pages that link to p. Hub update rule: Hub(p) = sum of authority scores of all pages that p points to. Divide all scores so that they add to 1. 23
24 Using adjacency matrices to represent a graph view a set of n pages, 1, 2, n, as a set of nodes in a directed graph n x n matrix M: Mij is equal to 1 if thee is a link from node i to node j node node node 3 node
25 Hub update rule as matrix multiplication h i M i1 a 1 + M i2 a 2 + +M in a n h Ma. node node = node 3 node 4 25
26 The authority update rule as matrix multiplication a i M 1i h 1 + M 2i h 2 + +M ni h n. a M T h. 26
27 Unwinding the k-step hub-authority updates a 1 = M T h 0 h 1 = Ma 1 = MM T h 0 a 2 = M T h 1 = M T MM T h 0 h 2 = Ma 2 = MM T MM T h 0 = (MM T ) 2 h 0. a k = (M T M) k 1 M T h 0 h k = (MM T ) k h 0 27
28 Thinking about multiplication in terms of eigenvectors We wish to show that there are constants, c and d, such that the sequences of vectors, h <k> /c k and a <k> /d k converge to limits as k goes to infinity Let s consider hub vectors first After convergence: h k c k = (MMT ) k h 0 c k,whatpropertiesdo (MM T )h = ch In other words, h <*> is the eigenvector of the matrix MM T, and c is the corresponding eigenvalue. 28
29 The convergence of hub vector updates Any symmetric matrix A with n rows and n columns has a set of n eigenvectors, that are all unit vectors and all mutually orthogonal they form the basis for the space R n. Since MM T is symmetric, it has n orthogonal eigenvectors z1, z2,, zn, and their corresponding eigenvalues c1, c2,, cn (let c1 > c2 >= cn ) Given + vector + + x: (MM T )x = (MM T )(p 1 z 1 + p 2 z 2 + +p n z n ) = p 1 MM T z 1 + p 2 MM T z 2 + +p n MM T z n = p 1 c 1 z 1 + p 2 c 2 z 2 + +p n c n z n, (MM T ) k x = c k 1 p 1z 1 + c k 2 p 2z 2 + +c k n p nz n. 29
30 The convergence of hub vector updates = + + h k = (MM T ) k h 0 = c1 k q 1z 1 + c2 k q 2z 2 + +cn k q nz n, and if we divide both sides by c1 k,thenweget h k c k 1 = q 1 z 1 + ( c2 c 1 ) k q 2 z ( cn c 1 ) k q n z n. 30
31 PageRank: the core of Google search 31
32 Basic PageRank update rule 32
33
34
35 Basic PageRank update rule Assign each page p a PageRank value start with 1/n, n is the number of pages Basic PageRank update rule Each node divides its current PageRank into equal shares, and then pass them across outbound links And then use the principle of repeated improvement Fact: If the network is strongly connected, then there are unique equilibrium PageRank values. 35
36 Equilibrium PageRank values 36
37 Basic PageRank updates as matrix multiplication Each entry in the adjacency matrix Nij specifies the portion of i s PageRank that should be passed to j in one single step start with 1/Li, where Li is the number of links out of i node 1 0 1/2 0 1/ /2 1/2 node node 3 node
38 Basic PageRank updates as matrix multiplication Vector r: the PageRanks of all the nodes r i N 1i r 1 + N 2i r 2 + +N ni r n. r N T r. 38
39 One major problem with the basic update rule 39
40 One major problem with the basic update rule 40
41
42 Scaled PageRank update rule First apply the basic PageRank Update rule Then scale down all PageRank values by a factor of s The total PageRank in the network has shrunk from 1 to s We then divide the residual 1-s units of PageRank equally over all nodes, given (1 - s)/n to each 42
43 Scaled PageRank update rule Fact: Repeatedly applying the scaled PageRank update rule converges to a unique equilibrium set of PageRank values for all networks. node node node 3 node 4 here Ñ ij sn ij + (1 s)/n, r i Ñ 1i r 1 + Ñ 2i r 2 + +Ñ ni r n r Ñ T r. r k = (Ñ T ) k r 0. 43
44 Convergence to r <*> We wish to show that r <k> converges to r <*>, so that: Ñ T r = r ; ding eigenvalue Unfortunately, we cannot use the fact that the matrix (e.g. MM T ) is symmetric, since it is not But fortunately, there is a Perron s theorem stating that there is a unique vector y that remains fixed under the application of the scaled PageRank update rule, and that the update rule converges to y from any starting point. 44
45 Chapter , , 14.6
Link Analysis. Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze
 Link Analysis Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze 1 The Web as a Directed Graph Page A Anchor hyperlink Page B Assumption 1: A hyperlink between pages
Link Analysis Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze 1 The Web as a Directed Graph Page A Anchor hyperlink Page B Assumption 1: A hyperlink between pages
A Note on Google s PageRank
 A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
Link Analysis. Leonid E. Zhukov
 Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank. Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018
 Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
PageRank algorithm Hubs and Authorities. Data mining. Web Data Mining PageRank, Hubs and Authorities. University of Szeged.
 Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
As it is not necessarily possible to satisfy this equation, we just ask for a solution to the more general equation
 Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
Link Mining PageRank. From Stanford C246
 Link Mining PageRank From Stanford C246 Broad Question: How to organize the Web? First try: Human curated Web dictionaries Yahoo, DMOZ LookSmart Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates
Link Mining PageRank From Stanford C246 Broad Question: How to organize the Web? First try: Human curated Web dictionaries Yahoo, DMOZ LookSmart Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates
Math 304 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks.
 Math 30 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks. December, 006. GRAPHS AND ADJACENCY MATRICES. Definition. A graph is a collection of vertices connected by edges. A directed graph is a graph all
Math 30 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks. December, 006. GRAPHS AND ADJACENCY MATRICES. Definition. A graph is a collection of vertices connected by edges. A directed graph is a graph all
IR: Information Retrieval
 / 44 IR: Information Retrieval FIB, Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Slides by Marta Arias, José Luis Balcázar, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ricard Gavaldá Department of Computer Science, UPC
/ 44 IR: Information Retrieval FIB, Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Slides by Marta Arias, José Luis Balcázar, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ricard Gavaldá Department of Computer Science, UPC
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012
 Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity. Due July 18, 2014
 Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University.
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu What is the structure of the Web? How is it organized? 2/7/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu What is the structure of the Web? How is it organized? 2/7/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
DATA MINING LECTURE 13. Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS
 DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Applications to network analysis: Eigenvector centrality indices Lecture notes
 Applications to network analysis: Eigenvector centrality indices Lecture notes Dario Fasino, University of Udine (Italy) Lecture notes for the second part of the course Nonnegative and spectral matrix
Applications to network analysis: Eigenvector centrality indices Lecture notes Dario Fasino, University of Udine (Italy) Lecture notes for the second part of the course Nonnegative and spectral matrix
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3
 Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3 Jack Rae January 28, 2013 1 Information Retrieval Given a set of documents, pull the (k) most similar document(s) to a given query. 1.1 Setup Say we have D documents
Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3 Jack Rae January 28, 2013 1 Information Retrieval Given a set of documents, pull the (k) most similar document(s) to a given query. 1.1 Setup Say we have D documents
1 Searching the World Wide Web
 Hubs and Authorities in a Hyperlinked Environment 1 Searching the World Wide Web Because diverse users each modify the link structure of the WWW within a relatively small scope by creating web-pages on
Hubs and Authorities in a Hyperlinked Environment 1 Searching the World Wide Web Because diverse users each modify the link structure of the WWW within a relatively small scope by creating web-pages on
MAE 298, Lecture 8 Feb 4, Web search and decentralized search on small-worlds
 MAE 298, Lecture 8 Feb 4, 2008 Web search and decentralized search on small-worlds Search for information Assume some resource of interest is stored at the vertices of a network: Web pages Files in a file-sharing
MAE 298, Lecture 8 Feb 4, 2008 Web search and decentralized search on small-worlds Search for information Assume some resource of interest is stored at the vertices of a network: Web pages Files in a file-sharing
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval
 Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis. Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa
 Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Eigenvalues of Exponentiated Adjacency Matrices
 Eigenvalues of Exponentiated Adjacency Matrices Tracy Powell Lesley A Ward, Advisor Estelle Basor, Reader November 21, 25 Department of Mathematics 2 Chapter Problem A graph G is made up of vertices, or
Eigenvalues of Exponentiated Adjacency Matrices Tracy Powell Lesley A Ward, Advisor Estelle Basor, Reader November 21, 25 Department of Mathematics 2 Chapter Problem A graph G is made up of vertices, or
1998: enter Link Analysis
 1998: enter Link Analysis uses hyperlink structure to focus the relevant set combine traditional IR score with popularity score Page and Brin 1998 Kleinberg Web Information Retrieval IR before the Web
1998: enter Link Analysis uses hyperlink structure to focus the relevant set combine traditional IR score with popularity score Page and Brin 1998 Kleinberg Web Information Retrieval IR before the Web
0.1 Naive formulation of PageRank
 PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm
 Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 The PageRank Algorithm I Invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin around 1998 and
Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 The PageRank Algorithm I Invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin around 1998 and
Link Analysis Ranking
 Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Node and Link Analysis
 Node and Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Applied Mathematics and Information Science National Research University Higher School of Economics 10.02.2014 Leonid E. Zhukov (HSE) Lecture 5 10.02.2014
Node and Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Applied Mathematics and Information Science National Research University Higher School of Economics 10.02.2014 Leonid E. Zhukov (HSE) Lecture 5 10.02.2014
How works. or How linear algebra powers the search engine. M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University
 How works or How linear algebra powers the search engine M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University From: gomath.com/geometry/ellipse.php Metric mishap causes loss of Mars orbiter
How works or How linear algebra powers the search engine M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University From: gomath.com/geometry/ellipse.php Metric mishap causes loss of Mars orbiter
Intelligent Data Analysis. PageRank. School of Computer Science University of Birmingham
 Intelligent Data Analysis PageRank Peter Tiňo School of Computer Science University of Birmingham Information Retrieval on the Web Most scoring methods on the Web have been derived in the context of Information
Intelligent Data Analysis PageRank Peter Tiňo School of Computer Science University of Birmingham Information Retrieval on the Web Most scoring methods on the Web have been derived in the context of Information
CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68
 CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68 References 1 L. Freeman, Centrality in Social Networks: Conceptual Clarification, Social Networks, Vol. 1, 1978/1979, pp. 215 239. 2 S. Wasserman
CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68 References 1 L. Freeman, Centrality in Social Networks: Conceptual Clarification, Social Networks, Vol. 1, 1978/1979, pp. 215 239. 2 S. Wasserman
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks
 ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
CS 277: Data Mining. Mining Web Link Structure. CS 277: Data Mining Lectures Analyzing Web Link Structure Padhraic Smyth, UC Irvine
 CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University.
 Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University http://www.mmds.org #1: C4.5 Decision Tree - Classification (61 votes) #2: K-Means - Clustering
Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University http://www.mmds.org #1: C4.5 Decision Tree - Classification (61 votes) #2: K-Means - Clustering
eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method
 eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method Slides by Olson. Some taken loosely from Jeff Jauregui, Some from Semeraro L. Olson Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method Slides by Olson. Some taken loosely from Jeff Jauregui, Some from Semeraro L. Olson Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Lecture 10. Lecturer: Aleksander Mądry Scribes: Mani Bastani Parizi and Christos Kalaitzis
 CS-621 Theory Gems October 18, 2012 Lecture 10 Lecturer: Aleksander Mądry Scribes: Mani Bastani Parizi and Christos Kalaitzis 1 Introduction In this lecture, we will see how one can use random walks to
CS-621 Theory Gems October 18, 2012 Lecture 10 Lecturer: Aleksander Mądry Scribes: Mani Bastani Parizi and Christos Kalaitzis 1 Introduction In this lecture, we will see how one can use random walks to
Spectral Graph Theory and You: Matrix Tree Theorem and Centrality Metrics
 Spectral Graph Theory and You: and Centrality Metrics Jonathan Gootenberg March 11, 2013 1 / 19 Outline of Topics 1 Motivation Basics of Spectral Graph Theory Understanding the characteristic polynomial
Spectral Graph Theory and You: and Centrality Metrics Jonathan Gootenberg March 11, 2013 1 / 19 Outline of Topics 1 Motivation Basics of Spectral Graph Theory Understanding the characteristic polynomial
Pseudocode for calculating Eigenfactor TM Score and Article Influence TM Score using data from Thomson-Reuters Journal Citations Reports
 Pseudocode for calculating Eigenfactor TM Score and Article Influence TM Score using data from Thomson-Reuters Journal Citations Reports Jevin West and Carl T. Bergstrom November 25, 2008 1 Overview There
Pseudocode for calculating Eigenfactor TM Score and Article Influence TM Score using data from Thomson-Reuters Journal Citations Reports Jevin West and Carl T. Bergstrom November 25, 2008 1 Overview There
PageRank. Ryan Tibshirani /36-662: Data Mining. January Optional reading: ESL 14.10
 PageRank Ryan Tibshirani 36-462/36-662: Data Mining January 24 2012 Optional reading: ESL 14.10 1 Information retrieval with the web Last time we learned about information retrieval. We learned how to
PageRank Ryan Tibshirani 36-462/36-662: Data Mining January 24 2012 Optional reading: ESL 14.10 1 Information retrieval with the web Last time we learned about information retrieval. We learned how to
Web Ranking. Classification (manual, automatic) Link Analysis (today s lesson)
 Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
LINK ANALYSIS. Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS
 LINK ANALYSIS Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS 2012-13 1 Outline Intro Basics of probability and information theory Retrieval models Retrieval evaluation Link analysis Models
LINK ANALYSIS Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS 2012-13 1 Outline Intro Basics of probability and information theory Retrieval models Retrieval evaluation Link analysis Models
Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies. authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page
![Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies. authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies. authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page](/thumbs/95/125556981.jpg) IV.3 HITS Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) hubs as good link sources (~high outdegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page a
IV.3 HITS Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) hubs as good link sources (~high outdegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page a
Machine Learning CPSC 340. Tutorial 12
 Machine Learning CPSC 340 Tutorial 12 Random Walk on Graph Page Rank Algorithm Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected graph G = (V, A) Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected
Machine Learning CPSC 340 Tutorial 12 Random Walk on Graph Page Rank Algorithm Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected graph G = (V, A) Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper)
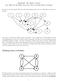 PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu March 16, 2016 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu March 16, 2016 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence
 Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
A New Method to Find the Eigenvalues of Convex. Matrices with Application in Web Page Rating
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 4, 200, no. 9, 905-9 A New Method to Find the Eigenvalues of Convex Matrices with Application in Web Page Rating F. Soleymani Department of Mathematics, Islamic Azad
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 4, 200, no. 9, 905-9 A New Method to Find the Eigenvalues of Convex Matrices with Application in Web Page Rating F. Soleymani Department of Mathematics, Islamic Azad
Introduction to Data Mining
 Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides
 Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides
 Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
Uncertainty and Randomization
 Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
COMPSCI 514: Algorithms for Data Science
 COMPSCI 514: Algorithms for Data Science Arya Mazumdar University of Massachusetts at Amherst Fall 2018 Lecture 4 Markov Chain & Pagerank Homework Announcement Show your work in the homework Write the
COMPSCI 514: Algorithms for Data Science Arya Mazumdar University of Massachusetts at Amherst Fall 2018 Lecture 4 Markov Chain & Pagerank Homework Announcement Show your work in the homework Write the
Application. Stochastic Matrices and PageRank
 Application Stochastic Matrices and PageRank Stochastic Matrices Definition A square matrix A is stochastic if all of its entries are nonnegative, and the sum of the entries of each column is. We say A
Application Stochastic Matrices and PageRank Stochastic Matrices Definition A square matrix A is stochastic if all of its entries are nonnegative, and the sum of the entries of each column is. We say A
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing
 STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
Calculating Web Page Authority Using the PageRank Algorithm
 Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search
 6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search Daron Acemoglu and Asu Ozdaglar MIT September 30, 2009 1 Networks: Lecture 7 Outline Navigation (or decentralized search)
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search Daron Acemoglu and Asu Ozdaglar MIT September 30, 2009 1 Networks: Lecture 7 Outline Navigation (or decentralized search)
How does Google rank webpages?
 Linear Algebra Spring 016 How does Google rank webpages? Dept. of Internet and Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University leehw@konkuk.ac.kr 1 Background on search engines Outline HITS algorithm (Jon Kleinberg)
Linear Algebra Spring 016 How does Google rank webpages? Dept. of Internet and Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University leehw@konkuk.ac.kr 1 Background on search engines Outline HITS algorithm (Jon Kleinberg)
Today. Next lecture. (Ch 14) Markov chains and hidden Markov models
 Today (Ch 14) Markov chains and hidden Markov models Graphical representation Transition probability matrix Propagating state distributions The stationary distribution Next lecture (Ch 14) Markov chains
Today (Ch 14) Markov chains and hidden Markov models Graphical representation Transition probability matrix Propagating state distributions The stationary distribution Next lecture (Ch 14) Markov chains
Data and Algorithms of the Web
 Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University
 Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University 2 Web pages are important if people visit them a lot. But we can t watch everybody using the Web. A good surrogate for visiting pages is to assume people follow links
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University 2 Web pages are important if people visit them a lot. But we can t watch everybody using the Web. A good surrogate for visiting pages is to assume people follow links
Kristina Lerman USC Information Sciences Institute
 Rethinking Network Structure Kristina Lerman USC Information Sciences Institute Università della Svizzera Italiana, December 16, 2011 Measuring network structure Central nodes Community structure Strength
Rethinking Network Structure Kristina Lerman USC Information Sciences Institute Università della Svizzera Italiana, December 16, 2011 Measuring network structure Central nodes Community structure Strength
Fiedler s Theorems on Nodal Domains
 Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 7 Fiedler s Theorems on Nodal Domains Daniel A Spielman September 9, 202 7 About these notes These notes are not necessarily an accurate representation of what happened in
Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 7 Fiedler s Theorems on Nodal Domains Daniel A Spielman September 9, 202 7 About these notes These notes are not necessarily an accurate representation of what happened in
ELEC6910Q Analytics and Systems for Social Media and Big Data Applications Lecture 3 Centrality, Similarity, and Strength Ties
 ELEC6910Q Analytics and Systems for Social Media and Big Data Applications Lecture 3 Centrality, Similarity, and Strength Ties Prof. James She james.she@ust.hk 1 Last lecture 2 Selected works from Tutorial
ELEC6910Q Analytics and Systems for Social Media and Big Data Applications Lecture 3 Centrality, Similarity, and Strength Ties Prof. James She james.she@ust.hk 1 Last lecture 2 Selected works from Tutorial
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
Data Mining and Matrices
 Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University
 Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University We ve had our first HC cases. Please, please, please, before you do anything that might violate the HC, talk to me or a TA to make sure it is legitimate. It is much
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University We ve had our first HC cases. Please, please, please, before you do anything that might violate the HC, talk to me or a TA to make sure it is legitimate. It is much
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 5: Graphs as matrices, spectral graph theory, and PageRank
 Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 5: Graphs as matrices, spectral graph theory, and PageRank David Glickenstein November 3, 4 Representing graphs as matrices It will sometimes be useful to represent graphs
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 5: Graphs as matrices, spectral graph theory, and PageRank David Glickenstein November 3, 4 Representing graphs as matrices It will sometimes be useful to represent graphs
Why matrices matter. Paul Van Dooren, UCL, CESAME
 Why matrices matter Paul Van Dooren, UCL, CESAME Where are matrices coming from? ma trix (mā'trĭks) n., pl., ma tri ces (mā'trĭ-sēz') Anatomy. The womb (uterus).... Geology. The solid matter in which a
Why matrices matter Paul Van Dooren, UCL, CESAME Where are matrices coming from? ma trix (mā'trĭks) n., pl., ma tri ces (mā'trĭ-sēz') Anatomy. The womb (uterus).... Geology. The solid matter in which a
MAS275 Probability Modelling Exercises
 MAS75 Probability Modelling Exercises Note: these questions are intended to be of variable difficulty. In particular: Questions or part questions labelled (*) are intended to be a bit more challenging.
MAS75 Probability Modelling Exercises Note: these questions are intended to be of variable difficulty. In particular: Questions or part questions labelled (*) are intended to be a bit more challenging.
Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining. Prof. Matteo Matteucci
 Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining Prof. Matteo Matteucci Hyperlinks for Indexing and Ranking 2 Page A Hyperlink Page B Intuitions The anchor text might describe the target page B Anchor
Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining Prof. Matteo Matteucci Hyperlinks for Indexing and Ranking 2 Page A Hyperlink Page B Intuitions The anchor text might describe the target page B Anchor
SVD, Power method, and Planted Graph problems (+ eigenvalues of random matrices)
 Chapter 14 SVD, Power method, and Planted Graph problems (+ eigenvalues of random matrices) Today we continue the topic of low-dimensional approximation to datasets and matrices. Last time we saw the singular
Chapter 14 SVD, Power method, and Planted Graph problems (+ eigenvalues of random matrices) Today we continue the topic of low-dimensional approximation to datasets and matrices. Last time we saw the singular
CS47300: Web Information Search and Management
 CS473: Web Information Search and Management Using Graph Structure for Retrieval Prof. Chris Clifton 24 September 218 Material adapted from slides created by Dr. Rong Jin (formerly Michigan State, now
CS473: Web Information Search and Management Using Graph Structure for Retrieval Prof. Chris Clifton 24 September 218 Material adapted from slides created by Dr. Rong Jin (formerly Michigan State, now
Linear Algebra Practice Problems
 Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Math 19620 Outline of Course Linear Equations and Matrices Linear Transformations, Inverses Bases, Linear Independence, Subspaces Abstract Vector Spaces
Lecture 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Math 19620 Outline of Course Linear Equations and Matrices Linear Transformations, Inverses Bases, Linear Independence, Subspaces Abstract Vector Spaces
Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Enviroment
 Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Enviroment Dimitris Sakavalas June 15, 2010 Outline Introduction Problem description Authorities and Broad-topic queries Algorithm outline Construction of a Focused
Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Enviroment Dimitris Sakavalas June 15, 2010 Outline Introduction Problem description Authorities and Broad-topic queries Algorithm outline Construction of a Focused
13 Searching the Web with the SVD
 13 Searching the Web with the SVD 13.1 Information retrieval Over the last 20 years the number of internet users has grown exponentially with time; see Figure 1. Trying to extract information from this
13 Searching the Web with the SVD 13.1 Information retrieval Over the last 20 years the number of internet users has grown exponentially with time; see Figure 1. Trying to extract information from this
9 Searching the Internet with the SVD
 9 Searching the Internet with the SVD 9.1 Information retrieval Over the last 20 years the number of internet users has grown exponentially with time; see Figure 1. Trying to extract information from this
9 Searching the Internet with the SVD 9.1 Information retrieval Over the last 20 years the number of internet users has grown exponentially with time; see Figure 1. Trying to extract information from this
This section is an introduction to the basic themes of the course.
 Chapter 1 Matrices and Graphs 1.1 The Adjacency Matrix This section is an introduction to the basic themes of the course. Definition 1.1.1. A simple undirected graph G = (V, E) consists of a non-empty
Chapter 1 Matrices and Graphs 1.1 The Adjacency Matrix This section is an introduction to the basic themes of the course. Definition 1.1.1. A simple undirected graph G = (V, E) consists of a non-empty
Singular Value Decompsition
 Singular Value Decompsition Massoud Malek One of the most useful results from linear algebra, is a matrix decomposition known as the singular value decomposition It has many useful applications in almost
Singular Value Decompsition Massoud Malek One of the most useful results from linear algebra, is a matrix decomposition known as the singular value decomposition It has many useful applications in almost
MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors
 MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics
MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics
MTH 2032 Semester II
 MTH 232 Semester II 2-2 Linear Algebra Reference Notes Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education December 28, 2 ii Contents Table of Contents
MTH 232 Semester II 2-2 Linear Algebra Reference Notes Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education December 28, 2 ii Contents Table of Contents
Node Centrality and Ranking on Networks
 Node Centrality and Ranking on Networks Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Social
Node Centrality and Ranking on Networks Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Social
Section 5.4 (Systems of Linear Differential Equation); 9.5 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors, cont d
 Section 5.4 (Systems of Linear Differential Equation); 9.5 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors, cont d July 6, 2009 Today s Session Today s Session A Summary of This Session: Today s Session A Summary of This
Section 5.4 (Systems of Linear Differential Equation); 9.5 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors, cont d July 6, 2009 Today s Session Today s Session A Summary of This Session: Today s Session A Summary of This
CSE 494/598 Lecture-4: Correlation Analysis. **Content adapted from last year s slides
 CSE 494/598 Lecture-4: Correlation Analysis LYDIA MANIKONDA HT TP://WWW.PUBLIC.ASU.EDU/~LMANIKON / **Content adapted from last year s slides Announcements Project-1 Due: February 12 th 2016 Analysis report:
CSE 494/598 Lecture-4: Correlation Analysis LYDIA MANIKONDA HT TP://WWW.PUBLIC.ASU.EDU/~LMANIKON / **Content adapted from last year s slides Announcements Project-1 Due: February 12 th 2016 Analysis report:
Faloutsos, Tong ICDE, 2009
 Large Graph Mining: Patterns, Tools and Case Studies Christos Faloutsos Hanghang Tong CMU Copyright: Faloutsos, Tong (29) 2-1 Outline Part 1: Patterns Part 2: Matrix and Tensor Tools Part 3: Proximity
Large Graph Mining: Patterns, Tools and Case Studies Christos Faloutsos Hanghang Tong CMU Copyright: Faloutsos, Tong (29) 2-1 Outline Part 1: Patterns Part 2: Matrix and Tensor Tools Part 3: Proximity
CS54701 Information Retrieval. Link Analysis. Luo Si. Department of Computer Science Purdue University. Borrowed Slides from Prof.
 CS54701 Information Retrieval Link Analysis Luo Si Department of Computer Science Purdue University Borrowed Slides from Prof. Rong Jin (MSU) Citation Analysis Web Structure Web is a graph Each web site
CS54701 Information Retrieval Link Analysis Luo Si Department of Computer Science Purdue University Borrowed Slides from Prof. Rong Jin (MSU) Citation Analysis Web Structure Web is a graph Each web site
Justification and Application of Eigenvector Centrality
 Justification and Application of Eigenvector Centrality Leo Spizzirri With great debt to P. D. Straffin, Jr Algebra in Geography: Eigenvectors of Networks[7] 3/6/2 Introduction Mathematics is only a hobby
Justification and Application of Eigenvector Centrality Leo Spizzirri With great debt to P. D. Straffin, Jr Algebra in Geography: Eigenvectors of Networks[7] 3/6/2 Introduction Mathematics is only a hobby
A physical model for efficient rankings in networks
 A physical model for efficient rankings in networks Daniel Larremore Assistant Professor Dept. of Computer Science & BioFrontiers Institute March 5, 2018 CompleNet danlarremore.com @danlarremore The idea
A physical model for efficient rankings in networks Daniel Larremore Assistant Professor Dept. of Computer Science & BioFrontiers Institute March 5, 2018 CompleNet danlarremore.com @danlarremore The idea
Google PageRank. Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano
 Google PageRank Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano fricci@unibz.it 1 Content p Linear Algebra p Matrices p Eigenvalues and eigenvectors p Markov chains p Google
Google PageRank Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano fricci@unibz.it 1 Content p Linear Algebra p Matrices p Eigenvalues and eigenvectors p Markov chains p Google
Fiedler s Theorems on Nodal Domains
 Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 7 Fiedler s Theorems on Nodal Domains Daniel A. Spielman September 19, 2018 7.1 Overview In today s lecture we will justify some of the behavior we observed when using eigenvectors
Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 7 Fiedler s Theorems on Nodal Domains Daniel A. Spielman September 19, 2018 7.1 Overview In today s lecture we will justify some of the behavior we observed when using eigenvectors
Slides based on those in:
 Spyros Kontogiannis & Christos Zaroliagis Slides based on those in: http://www.mmds.org High dim. data Graph data Infinite data Machine learning Apps Locality sensitive hashing PageRank, SimRank Filtering
Spyros Kontogiannis & Christos Zaroliagis Slides based on those in: http://www.mmds.org High dim. data Graph data Infinite data Machine learning Apps Locality sensitive hashing PageRank, SimRank Filtering
Data science with multilayer networks: Mathematical foundations and applications
 Data science with multilayer networks: Mathematical foundations and applications CDSE Days University at Buffalo, State University of New York Monday April 9, 2018 Dane Taylor Assistant Professor of Mathematics
Data science with multilayer networks: Mathematical foundations and applications CDSE Days University at Buffalo, State University of New York Monday April 9, 2018 Dane Taylor Assistant Professor of Mathematics
The Miracles of Tropical Spectral Theory
 The Miracles of Tropical Spectral Theory Emmanuel Tsukerman University of California, Berkeley e.tsukerman@berkeley.edu July 31, 2015 1 / 110 Motivation One of the most important results in max-algebra
The Miracles of Tropical Spectral Theory Emmanuel Tsukerman University of California, Berkeley e.tsukerman@berkeley.edu July 31, 2015 1 / 110 Motivation One of the most important results in max-algebra
IS4200/CS6200 Informa0on Retrieval. PageRank Con+nued. with slides from Hinrich Schütze and Chris6na Lioma
 IS4200/CS6200 Informa0on Retrieval PageRank Con+nued with slides from Hinrich Schütze and Chris6na Lioma Exercise: Assump0ons underlying PageRank Assump0on 1: A link on the web is a quality signal the
IS4200/CS6200 Informa0on Retrieval PageRank Con+nued with slides from Hinrich Schütze and Chris6na Lioma Exercise: Assump0ons underlying PageRank Assump0on 1: A link on the web is a quality signal the
Introduction to Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 18: Latent Semantic Indexing Hinrich Schütze Center for Information and Language Processing, University of Munich 2013-07-10 1/43
Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 18: Latent Semantic Indexing Hinrich Schütze Center for Information and Language Processing, University of Munich 2013-07-10 1/43
No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1.
 Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, 2015 2:02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly
Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, 2015 2:02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly
Distributed Randomized Algorithms for the PageRank Computation Hideaki Ishii, Member, IEEE, and Roberto Tempo, Fellow, IEEE
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 55, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2010 1987 Distributed Randomized Algorithms for the PageRank Computation Hideaki Ishii, Member, IEEE, and Roberto Tempo, Fellow, IEEE Abstract
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 55, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2010 1987 Distributed Randomized Algorithms for the PageRank Computation Hideaki Ishii, Member, IEEE, and Roberto Tempo, Fellow, IEEE Abstract
PV211: Introduction to Information Retrieval https://www.fi.muni.cz/~sojka/pv211
 PV211: Introduction to Information Retrieval https://www.fi.muni.cz/~sojka/pv211 IIR 18: Latent Semantic Indexing Handout version Petr Sojka, Hinrich Schütze et al. Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University,
PV211: Introduction to Information Retrieval https://www.fi.muni.cz/~sojka/pv211 IIR 18: Latent Semantic Indexing Handout version Petr Sojka, Hinrich Schütze et al. Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University,
Piecewise Functions In the toolkit functions we introduced the absolute value function f( x)
 8 Chapter 1 Piecewise Functions In the toolkit functions we introduced the absolute value function f( x) x. With a domain of all real numbers and a range of values greater than or equal to 0, the absolute
8 Chapter 1 Piecewise Functions In the toolkit functions we introduced the absolute value function f( x) x. With a domain of all real numbers and a range of values greater than or equal to 0, the absolute
