CS54701 Information Retrieval. Link Analysis. Luo Si. Department of Computer Science Purdue University. Borrowed Slides from Prof.
|
|
|
- Brianne Hood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS54701 Information Retrieval Link Analysis Luo Si Department of Computer Science Purdue University Borrowed Slides from Prof. Rong Jin (MSU)
2 Citation Analysis
3 Web Structure Web is a graph Each web site correspond to a node A link from one site to another site forms a directed edge What does it look likes? Web is small world The diameter of the web is 19 e.g. the average number of clicks from one web site to another is 19
4 Bowtie Structure Strongly Connected Component Broder et al., 2001
5 Bowtie Structure Sites that link towards the center of the web Broder et al., 2001
6 Bowtie Structure Sites that link from the center of the web Broder et al., 2001
7 Inlinks and Outlinks Both degrees of incoming and outgoing links follow power law Broder et al., 2001
8 Early Approaches Basic Assumptions Hyperlinks contain information about the human judgment of a site The more incoming links to a site, the more it is judged important Bray 1996 The visibility of a site is measured by the number of other sites pointing to it The luminosity of a site is measured by the number of other sites to which it points Limitation: failure to capture the relative importance of different parents (children) sites
9 HITS - Kleinberg s Algorithm HITS Hypertext Induced Topic Selection For each vertex v Є V in a subgraph of interest: a(v) - the authority of v h(v) - the hubness of v A site is very authoritative if it receives many citations. Citation from important sites weight more than citations from less-important sites Hubness shows the importance of a site. A good hub is a site that links to many authoritative sites
10 Authority and Hubness a(1) = h(2) + h(3) + h(4) h(1) = a(5) + a(6) + a(7)
11 Authority and Hubness: Version 1 R e c u rs iv e d e p e n d e n c y a ( v ) h ( w ) w p a [ v ] h ( v ) a ( w ) w c h [ v ] HubsAuthorities(G) 1 1 [1,,1] Є R 2 a h t 1 4 repeat 5 for each v in V 6 do a (v) Σ h (w) t 7 h (v) Σ a (w) t w Є pa[v] 8 t t + 1 t -1 9 until a a + h h < ε t t -1 t t return (a, h ) t t V w Є pa[v] t -1
12 Authority and Hubness: Version 1 R e c u rs iv e d e p e n d e n c y a ( v ) h ( w ) w p a [ v ] h ( v ) a ( w ) w c h [ v ] HubsAuthorities(G) 1 1 [1,,1] Є R 2 a h t 1 4 repeat 5 for each v in V 6 do a (v) Σ h (w) t 7 h (v) Σ a (w) t w Є pa[v] 8 t t + 1 t -1 9 until a a + h h < ε t t -1 t t return (a, h ) t t V w Є pa[v] t -1 Problems?
13 Authority and Hubness: Version 2 R e c u rs iv e d e p e n d e n c y a ( v ) h ( w ) w p a [ v ] h ( v ) a ( w ) a( v) h( v) w c h [ v ] + Normalization a( v) w a( w) h( v) w h( w) HubsAuthorities(G) 1 1 [1,,1] Є R 2 a 0 h t 1 4 repeat 5 for each v in V 6 do a (v) Σ h (w) t 7 h t (v) Σ w Є pa[v] a (w) t -1 8 a t a t / a 9 h t h t / h 10 t t until a t a t -1 + h t h t -1 < ε 12 return (a, h ) t t V w Є pa[v] t -1
14 HITS Example Results Authority Hubness Authority and hubness weights
15 Authority and Hubness Authority score Not only depends on the number of incoming links But also the quality (e.g., hubness) of the incoming links Hubness score Not only depends on the number of outgoing links But also the quality (e.g., hubness) of the outgoing links
16 Authority and Hub Column vector a: a i is the authority score for the i-th site Column vector h: h i is the hub score for the i-th site Matrix M: M i, j 1 th e ith site p o in ts to th e jth site 0 o th e rw ise M =
17 Authority and Hub Vector a: a i is the authority score for the i-th site Vector h: h i is the hub score for the i-th site Matrix M: M i, j 1 th e ith site p o in ts to th e jth site 0 o th e rw ise Recursive dependency: a(v) Σ h(w) w Є pa[v] h(v) Σ a(w) w Є ch[v]
18 Authority and Hub Column vector a: a i is the authority score for the i-th site Column vector h: h i is the hub score for the i-th site Matrix M: M i, j 1 th e ith site p o in ts to th e jth site 0 o th e rw ise Recursive dependency: a(v) Σ h(w) w Є pa[v] h(v) Σ a(w) w Є ch[v] a M T h h M a
19 Authority and Hub Column vector a: a i is the authority score for the i-th site Column vector h: h i is the hub score for the i-th site M i, j Recursive dependency: Matrix M: 1 th e ith site p o in ts to th e jth site 0 o th e rw ise Normalization Procedure a(v) Σ h(w) w Є pa[v] h(v) Σ a(w) w Є ch[v] T t t t a M h h M a t t t
20 Authority and Hub T t t t Apply SVD to matrix M T t t t t a M h a M M a h M a h M M h T t t t t t t t T i T i i i M UΣ V u v a u 1, h v 1
21 PageRank Introduced by Page et al (1998) The weight is assigned by the rank of parents Difference with HITS HITS takes Hubness & Authority weights The page rank is proportional to its parents rank, but inversely proportional to its parents outdegree
22 Matrix Notation M i, j 1 th e ith site p o in ts to th e jth site 0 o th e rw ise B i, j j 1 M i, j i, j 0 0 o th e rw is e j M M = B =
23 Matrix Notation : rep resen ts th e ran k sco re fo r th e i-th w eb p ag e r r i Finding Pagerank to find principle eigenvector of B r = α B T r α : eigenvalue r : eigenvector of B
24 Matrix Notation
25 Random Walk Model Consider a random walk through the Web graph?? B =???
26 Random Walk Model Consider a random walk through the Web graph B =
27 Random Walk Model Consider a random walk through the Web graph B =
28 Random Walk Model Consider a random walk through the Web graph B = T, what is portion of time that the surfer will spend time on each site?
29 Random Walk Model Consider a random walk through the Web graph B = p( k) : p e rc e n ta g e o f tim e th a t th e su rfe r w ill sta y a t th e i-th site p k ( ) p ( i ) B i, k i T p B p
30 Adding Self Loop Allow surfer to decide to stay on the same place B = B ' B (1 ) I
31 Problem Rank Sink Problem In general, many Web pages have no inlinks/outlinks It results in dangling edges in the graph B = r(new page) = 0
32 Problem Rank Sink Problem In general, many Web pages have no inlinks/outlinks It results in dangling edges in the graph B = r(new page) = 1
33 Distribution of the Mixture Model H i, j 1/ n B ' H (1 ) B r B r ' T Prevent the page ranks to be either zeros or one.
34 Stability Whether the link analysis algorithms based on eigenvectors are stable in the sense that results don t change significantly? The connectivity of a portion of the graph is changed arbitrary How will it affect the results of algorithms?
35 Stability of HITS Ng et al (2001) A bound on the number of hyperlinks k that can be added or deleted from one page without affecting the authority or hubness weights It is possible to perturb a symmetric matrix by a quantity that grows as δ that produces a constant perturbation of the dominant eigenvector δ: eigengap λ1 λ2 d: maximum outdegree of G
36 Stability of PageRank r r 2 r ( j ) jv Ng et al (2001) V: the set of vertices touched by the perturbation The parameter ε of the mixture model has a stabilization role If the set of pages affected by the perturbation have a small rank, the overall change will also be small
CS47300: Web Information Search and Management
 CS473: Web Information Search and Management Using Graph Structure for Retrieval Prof. Chris Clifton 24 September 218 Material adapted from slides created by Dr. Rong Jin (formerly Michigan State, now
CS473: Web Information Search and Management Using Graph Structure for Retrieval Prof. Chris Clifton 24 September 218 Material adapted from slides created by Dr. Rong Jin (formerly Michigan State, now
CS 277: Data Mining. Mining Web Link Structure. CS 277: Data Mining Lectures Analyzing Web Link Structure Padhraic Smyth, UC Irvine
 CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
LINK ANALYSIS. Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS
 LINK ANALYSIS Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS 2012-13 1 Outline Intro Basics of probability and information theory Retrieval models Retrieval evaluation Link analysis Models
LINK ANALYSIS Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS 2012-13 1 Outline Intro Basics of probability and information theory Retrieval models Retrieval evaluation Link analysis Models
Link Analysis. Leonid E. Zhukov
 Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies. authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page
![Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies. authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies. authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page](/thumbs/95/125556981.jpg) IV.3 HITS Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) hubs as good link sources (~high outdegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page a
IV.3 HITS Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) hubs as good link sources (~high outdegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page a
Web Ranking. Classification (manual, automatic) Link Analysis (today s lesson)
 Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis. Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa
 Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
A Note on Google s PageRank
 A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
Link Analysis Ranking
 Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Node Centrality and Ranking on Networks
 Node Centrality and Ranking on Networks Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Social
Node Centrality and Ranking on Networks Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Social
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining. Prof. Matteo Matteucci
 Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining Prof. Matteo Matteucci Hyperlinks for Indexing and Ranking 2 Page A Hyperlink Page B Intuitions The anchor text might describe the target page B Anchor
Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining Prof. Matteo Matteucci Hyperlinks for Indexing and Ranking 2 Page A Hyperlink Page B Intuitions The anchor text might describe the target page B Anchor
Information Retrieval and Search. Web Linkage Mining. Miłosz Kadziński
 Web Linkage Analysis D24 D4 : Web Linkage Mining Miłosz Kadziński Institute of Computing Science Poznan University of Technology, Poland www.cs.put.poznan.pl/mkadzinski/wpi Web mining: Web Mining Discovery
Web Linkage Analysis D24 D4 : Web Linkage Mining Miłosz Kadziński Institute of Computing Science Poznan University of Technology, Poland www.cs.put.poznan.pl/mkadzinski/wpi Web mining: Web Mining Discovery
As it is not necessarily possible to satisfy this equation, we just ask for a solution to the more general equation
 Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
DATA MINING LECTURE 13. Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS
 DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Web Ranking. Classification (manual, automatic) Link Analysis (today s lesson)
 Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Data Mining and Matrices
 Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors
 MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics
MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics
0.1 Naive formulation of PageRank
 PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
PageRank. Ryan Tibshirani /36-662: Data Mining. January Optional reading: ESL 14.10
 PageRank Ryan Tibshirani 36-462/36-662: Data Mining January 24 2012 Optional reading: ESL 14.10 1 Information retrieval with the web Last time we learned about information retrieval. We learned how to
PageRank Ryan Tibshirani 36-462/36-662: Data Mining January 24 2012 Optional reading: ESL 14.10 1 Information retrieval with the web Last time we learned about information retrieval. We learned how to
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides
 Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Complex Social System, Elections. Introduction to Network Analysis 1
 Complex Social System, Elections Introduction to Network Analysis 1 Complex Social System, Network I person A voted for B A is more central than B if more people voted for A In-degree centrality index
Complex Social System, Elections Introduction to Network Analysis 1 Complex Social System, Network I person A voted for B A is more central than B if more people voted for A In-degree centrality index
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides
 Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Intelligent Data Analysis. PageRank. School of Computer Science University of Birmingham
 Intelligent Data Analysis PageRank Peter Tiňo School of Computer Science University of Birmingham Information Retrieval on the Web Most scoring methods on the Web have been derived in the context of Information
Intelligent Data Analysis PageRank Peter Tiňo School of Computer Science University of Birmingham Information Retrieval on the Web Most scoring methods on the Web have been derived in the context of Information
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University.
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu What is the structure of the Web? How is it organized? 2/7/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu What is the structure of the Web? How is it organized? 2/7/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive
How does Google rank webpages?
 Linear Algebra Spring 016 How does Google rank webpages? Dept. of Internet and Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University leehw@konkuk.ac.kr 1 Background on search engines Outline HITS algorithm (Jon Kleinberg)
Linear Algebra Spring 016 How does Google rank webpages? Dept. of Internet and Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University leehw@konkuk.ac.kr 1 Background on search engines Outline HITS algorithm (Jon Kleinberg)
Data and Algorithms of the Web
 Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK. Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech. Lecture for CS 6505
 INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
Applications to network analysis: Eigenvector centrality indices Lecture notes
 Applications to network analysis: Eigenvector centrality indices Lecture notes Dario Fasino, University of Udine (Italy) Lecture notes for the second part of the course Nonnegative and spectral matrix
Applications to network analysis: Eigenvector centrality indices Lecture notes Dario Fasino, University of Udine (Italy) Lecture notes for the second part of the course Nonnegative and spectral matrix
1998: enter Link Analysis
 1998: enter Link Analysis uses hyperlink structure to focus the relevant set combine traditional IR score with popularity score Page and Brin 1998 Kleinberg Web Information Retrieval IR before the Web
1998: enter Link Analysis uses hyperlink structure to focus the relevant set combine traditional IR score with popularity score Page and Brin 1998 Kleinberg Web Information Retrieval IR before the Web
Google PageRank. Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano
 Google PageRank Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano fricci@unibz.it 1 Content p Linear Algebra p Matrices p Eigenvalues and eigenvectors p Markov chains p Google
Google PageRank Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano fricci@unibz.it 1 Content p Linear Algebra p Matrices p Eigenvalues and eigenvectors p Markov chains p Google
IR: Information Retrieval
 / 44 IR: Information Retrieval FIB, Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Slides by Marta Arias, José Luis Balcázar, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ricard Gavaldá Department of Computer Science, UPC
/ 44 IR: Information Retrieval FIB, Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Slides by Marta Arias, José Luis Balcázar, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ricard Gavaldá Department of Computer Science, UPC
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank. Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018
 Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Inf 2B: Ranking Queries on the WWW
 Inf B: Ranking Queries on the WWW Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Queries Suppose we have an Inverted Index for a set of webpages. Disclaimer Not really the scenario of
Inf B: Ranking Queries on the WWW Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Queries Suppose we have an Inverted Index for a set of webpages. Disclaimer Not really the scenario of
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK. Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech. Lecture for CS 6505
 INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012
 Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Cross-lingual and temporal Wikipedia analysis
 MTA SZTAKI Data Mining and Search Group June 14, 2013 Supported by the EC FET Open project New tools and algorithms for directed network analysis (NADINE No 288956) Table of Contents 1 Link prediction
MTA SZTAKI Data Mining and Search Group June 14, 2013 Supported by the EC FET Open project New tools and algorithms for directed network analysis (NADINE No 288956) Table of Contents 1 Link prediction
Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University.
 Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University http://www.mmds.org #1: C4.5 Decision Tree - Classification (61 votes) #2: K-Means - Clustering
Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University http://www.mmds.org #1: C4.5 Decision Tree - Classification (61 votes) #2: K-Means - Clustering
Slides based on those in:
 Spyros Kontogiannis & Christos Zaroliagis Slides based on those in: http://www.mmds.org High dim. data Graph data Infinite data Machine learning Apps Locality sensitive hashing PageRank, SimRank Filtering
Spyros Kontogiannis & Christos Zaroliagis Slides based on those in: http://www.mmds.org High dim. data Graph data Infinite data Machine learning Apps Locality sensitive hashing PageRank, SimRank Filtering
Link Mining PageRank. From Stanford C246
 Link Mining PageRank From Stanford C246 Broad Question: How to organize the Web? First try: Human curated Web dictionaries Yahoo, DMOZ LookSmart Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates
Link Mining PageRank From Stanford C246 Broad Question: How to organize the Web? First try: Human curated Web dictionaries Yahoo, DMOZ LookSmart Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates
Multiple Relational Ranking in Tensor: Theory, Algorithms and Applications
 Multiple Relational Ranking in Tensor: Theory, Algorithms and Applications Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University Email: mng@math.hkbu.edu.hk
Multiple Relational Ranking in Tensor: Theory, Algorithms and Applications Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University Email: mng@math.hkbu.edu.hk
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval
 Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence
 Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
Introduction to Data Mining
 Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
Ranking on Large-Scale Graphs with Rich Metadata
 Ranking on Large-Scale Graphs with Rich Metadata Bin Gao, Taifeng Wang, and Tie-Yan Liu Microsoft Research Asia 1 Presenters Bin Gao Researcher, MSR Asia http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/people/bingao/
Ranking on Large-Scale Graphs with Rich Metadata Bin Gao, Taifeng Wang, and Tie-Yan Liu Microsoft Research Asia 1 Presenters Bin Gao Researcher, MSR Asia http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/people/bingao/
Wiki Definition. Reputation Systems I. Outline. Introduction to Reputations. Yury Lifshits. HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte
 Reputation Systems I HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte Yury Lifshits Wiki Definition Reputation is the opinion (more technically, a social evaluation) of the public toward a person, a
Reputation Systems I HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte Yury Lifshits Wiki Definition Reputation is the opinion (more technically, a social evaluation) of the public toward a person, a
Link Analysis. Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016
 Link Analysis Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 Match keywords, language (information retrieval) Explore directory The Web, circa 1998
Link Analysis Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 Match keywords, language (information retrieval) Explore directory The Web, circa 1998
The Second Eigenvalue of the Google Matrix
 The Second Eigenvalue of the Google Matrix Taher H. Haveliwala and Sepandar D. Kamvar Stanford University {taherh,sdkamvar}@cs.stanford.edu Abstract. We determine analytically the modulus of the second
The Second Eigenvalue of the Google Matrix Taher H. Haveliwala and Sepandar D. Kamvar Stanford University {taherh,sdkamvar}@cs.stanford.edu Abstract. We determine analytically the modulus of the second
1 Searching the World Wide Web
 Hubs and Authorities in a Hyperlinked Environment 1 Searching the World Wide Web Because diverse users each modify the link structure of the WWW within a relatively small scope by creating web-pages on
Hubs and Authorities in a Hyperlinked Environment 1 Searching the World Wide Web Because diverse users each modify the link structure of the WWW within a relatively small scope by creating web-pages on
Spectral Graph Theory and You: Matrix Tree Theorem and Centrality Metrics
 Spectral Graph Theory and You: and Centrality Metrics Jonathan Gootenberg March 11, 2013 1 / 19 Outline of Topics 1 Motivation Basics of Spectral Graph Theory Understanding the characteristic polynomial
Spectral Graph Theory and You: and Centrality Metrics Jonathan Gootenberg March 11, 2013 1 / 19 Outline of Topics 1 Motivation Basics of Spectral Graph Theory Understanding the characteristic polynomial
Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3
 Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3 Jack Rae January 28, 2013 1 Information Retrieval Given a set of documents, pull the (k) most similar document(s) to a given query. 1.1 Setup Say we have D documents
Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3 Jack Rae January 28, 2013 1 Information Retrieval Given a set of documents, pull the (k) most similar document(s) to a given query. 1.1 Setup Say we have D documents
Uncertainty and Randomization
 Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method
 eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method Slides by Olson. Some taken loosely from Jeff Jauregui, Some from Semeraro L. Olson Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method Slides by Olson. Some taken loosely from Jeff Jauregui, Some from Semeraro L. Olson Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search
 6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search Daron Acemoglu and Asu Ozdaglar MIT September 30, 2009 1 Networks: Lecture 7 Outline Navigation (or decentralized search)
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search Daron Acemoglu and Asu Ozdaglar MIT September 30, 2009 1 Networks: Lecture 7 Outline Navigation (or decentralized search)
Link Analysis. Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze
 Link Analysis Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze 1 The Web as a Directed Graph Page A Anchor hyperlink Page B Assumption 1: A hyperlink between pages
Link Analysis Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze 1 The Web as a Directed Graph Page A Anchor hyperlink Page B Assumption 1: A hyperlink between pages
CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68
 CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68 References 1 L. Freeman, Centrality in Social Networks: Conceptual Clarification, Social Networks, Vol. 1, 1978/1979, pp. 215 239. 2 S. Wasserman
CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68 References 1 L. Freeman, Centrality in Social Networks: Conceptual Clarification, Social Networks, Vol. 1, 1978/1979, pp. 215 239. 2 S. Wasserman
PROBABILISTIC LATENT SEMANTIC ANALYSIS
 PROBABILISTIC LATENT SEMANTIC ANALYSIS Lingjia Deng Revised from slides of Shuguang Wang Outline Review of previous notes PCA/SVD HITS Latent Semantic Analysis Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis Applications
PROBABILISTIC LATENT SEMANTIC ANALYSIS Lingjia Deng Revised from slides of Shuguang Wang Outline Review of previous notes PCA/SVD HITS Latent Semantic Analysis Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis Applications
Computing PageRank using Power Extrapolation
 Computing PageRank using Power Extrapolation Taher Haveliwala, Sepandar Kamvar, Dan Klein, Chris Manning, and Gene Golub Stanford University Abstract. We present a novel technique for speeding up the computation
Computing PageRank using Power Extrapolation Taher Haveliwala, Sepandar Kamvar, Dan Klein, Chris Manning, and Gene Golub Stanford University Abstract. We present a novel technique for speeding up the computation
The Static Absorbing Model for the Web a
 Journal of Web Engineering, Vol. 0, No. 0 (2003) 000 000 c Rinton Press The Static Absorbing Model for the Web a Vassilis Plachouras University of Glasgow Glasgow G12 8QQ UK vassilis@dcs.gla.ac.uk Iadh
Journal of Web Engineering, Vol. 0, No. 0 (2003) 000 000 c Rinton Press The Static Absorbing Model for the Web a Vassilis Plachouras University of Glasgow Glasgow G12 8QQ UK vassilis@dcs.gla.ac.uk Iadh
CS47300: Web Information Search and Management
 CS47300: Web Information Search and Management Prof. Chris Clifton 6 September 2017 Material adapted from course created by Dr. Luo Si, now leading Alibaba research group 1 Vector Space Model Disadvantages:
CS47300: Web Information Search and Management Prof. Chris Clifton 6 September 2017 Material adapted from course created by Dr. Luo Si, now leading Alibaba research group 1 Vector Space Model Disadvantages:
Hub, Authority and Relevance Scores in Multi-Relational Data for Query Search
 Hub, Authority and Relevance Scores in Multi-Relational Data for Query Search Xutao Li 1 Michael Ng 2 Yunming Ye 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Shenzhen Graduate School, Harbin Institute of Technology,
Hub, Authority and Relevance Scores in Multi-Relational Data for Query Search Xutao Li 1 Michael Ng 2 Yunming Ye 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Shenzhen Graduate School, Harbin Institute of Technology,
Index. Copyright (c)2007 The Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics From: Matrix Methods in Data Mining and Pattern Recgonition By: Lars Elden
 Index 1-norm, 15 matrix, 17 vector, 15 2-norm, 15, 59 matrix, 17 vector, 15 3-mode array, 91 absolute error, 15 adjacency matrix, 158 Aitken extrapolation, 157 algebra, multi-linear, 91 all-orthogonality,
Index 1-norm, 15 matrix, 17 vector, 15 2-norm, 15, 59 matrix, 17 vector, 15 3-mode array, 91 absolute error, 15 adjacency matrix, 158 Aitken extrapolation, 157 algebra, multi-linear, 91 all-orthogonality,
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing
 STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
DOMINANT VECTORS APPLICATION TO INFORMATION EXTRACTION IN LARGE GRAPHS. Laure NINOVE OF NONNEGATIVE MATRICES
 UNIVERSITÉ CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE DE LOUVAIN DÉPARTEMENT D INGÉNIERIE MATHÉMATIQUE DOMINANT VECTORS OF NONNEGATIVE MATRICES APPLICATION TO INFORMATION EXTRACTION IN LARGE GRAPHS Laure
UNIVERSITÉ CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE DE LOUVAIN DÉPARTEMENT D INGÉNIERIE MATHÉMATIQUE DOMINANT VECTORS OF NONNEGATIVE MATRICES APPLICATION TO INFORMATION EXTRACTION IN LARGE GRAPHS Laure
Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm
 Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 The PageRank Algorithm I Invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin around 1998 and
Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 The PageRank Algorithm I Invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin around 1998 and
PageRank algorithm Hubs and Authorities. Data mining. Web Data Mining PageRank, Hubs and Authorities. University of Szeged.
 Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
CS 3750 Advanced Machine Learning. Applications of SVD and PCA (LSA and Link analysis) Cem Akkaya
 CS 375 Advanced Machine Learning Applications of SVD and PCA (LSA and Link analysis) Cem Akkaya Outline SVD and LSI Kleinberg s Algorithm PageRank Algorithm Vector Space Model Vector space model represents
CS 375 Advanced Machine Learning Applications of SVD and PCA (LSA and Link analysis) Cem Akkaya Outline SVD and LSI Kleinberg s Algorithm PageRank Algorithm Vector Space Model Vector space model represents
Faloutsos, Tong ICDE, 2009
 Large Graph Mining: Patterns, Tools and Case Studies Christos Faloutsos Hanghang Tong CMU Copyright: Faloutsos, Tong (29) 2-1 Outline Part 1: Patterns Part 2: Matrix and Tensor Tools Part 3: Proximity
Large Graph Mining: Patterns, Tools and Case Studies Christos Faloutsos Hanghang Tong CMU Copyright: Faloutsos, Tong (29) 2-1 Outline Part 1: Patterns Part 2: Matrix and Tensor Tools Part 3: Proximity
Analysis of Google s PageRank
 Analysis of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University Joint work with Rebecca M. Wills AN05 p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance of a web page [Brin & Page 1998]
Analysis of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University Joint work with Rebecca M. Wills AN05 p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance of a web page [Brin & Page 1998]
Data Mining and Analysis: Fundamental Concepts and Algorithms
 Data Mining and Analysis: Fundamental Concepts and Algorithms dataminingbook.info Mohammed J. Zaki 1 Wagner Meira Jr. 2 1 Department of Computer Science Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY, USA
Data Mining and Analysis: Fundamental Concepts and Algorithms dataminingbook.info Mohammed J. Zaki 1 Wagner Meira Jr. 2 1 Department of Computer Science Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY, USA
Node and Link Analysis
 Node and Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Applied Mathematics and Information Science National Research University Higher School of Economics 10.02.2014 Leonid E. Zhukov (HSE) Lecture 5 10.02.2014
Node and Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Applied Mathematics and Information Science National Research University Higher School of Economics 10.02.2014 Leonid E. Zhukov (HSE) Lecture 5 10.02.2014
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
Pr[positive test virus] Pr[virus] Pr[positive test] = Pr[positive test] = Pr[positive test]
![Pr[positive test virus] Pr[virus] Pr[positive test] = Pr[positive test] = Pr[positive test] Pr[positive test virus] Pr[virus] Pr[positive test] = Pr[positive test] = Pr[positive test]](/thumbs/77/74699650.jpg) 146 Probability Pr[virus] = 0.00001 Pr[no virus] = 0.99999 Pr[positive test virus] = 0.99 Pr[positive test no virus] = 0.01 Pr[virus positive test] = Pr[positive test virus] Pr[virus] = 0.99 0.00001 =
146 Probability Pr[virus] = 0.00001 Pr[no virus] = 0.99999 Pr[positive test virus] = 0.99 Pr[positive test no virus] = 0.01 Pr[virus positive test] = Pr[positive test virus] Pr[virus] = 0.99 0.00001 =
Link Analysis and Web Search
 Link Analysis and Web Search Episode 11 Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Link Analysis and Web Search (Chapter 13, 14) Information networks and
Link Analysis and Web Search Episode 11 Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Link Analysis and Web Search (Chapter 13, 14) Information networks and
Models and Algorithms for Complex Networks. Link Analysis Ranking
 Models and Algorithms for Complex Networks Link Analysis Ranking Why Link Analysis? First generation search engines view documents as flat text files could not cope with size, spamming, user needs Second
Models and Algorithms for Complex Networks Link Analysis Ranking Why Link Analysis? First generation search engines view documents as flat text files could not cope with size, spamming, user needs Second
The PageRank Problem, Multi-Agent. Consensus and Web Aggregation
 The PageRank Problem, Multi-Agent Consensus and Web Aggregation A Systems and Control Viewpoint arxiv:32.904v [cs.sy] 6 Dec 203 Hideaki Ishii and Roberto Tempo PageRank is an algorithm introduced in 998
The PageRank Problem, Multi-Agent Consensus and Web Aggregation A Systems and Control Viewpoint arxiv:32.904v [cs.sy] 6 Dec 203 Hideaki Ishii and Roberto Tempo PageRank is an algorithm introduced in 998
Mathematical Properties & Analysis of Google s PageRank
 Mathematical Properties & Analysis of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University, USA Joint work with Rebecca M. Wills Cedya p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance
Mathematical Properties & Analysis of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University, USA Joint work with Rebecca M. Wills Cedya p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance
Chapter 10. Finite-State Markov Chains. Introductory Example: Googling Markov Chains
 Chapter 0 Finite-State Markov Chains Introductory Example: Googling Markov Chains Google means many things: it is an Internet search engine, the company that produces the search engine, and a verb meaning
Chapter 0 Finite-State Markov Chains Introductory Example: Googling Markov Chains Google means many things: it is an Internet search engine, the company that produces the search engine, and a verb meaning
The Dynamic Absorbing Model for the Web
 The Dynamic Absorbing Model for the Web Gianni Amati, Iadh Ounis, Vassilis Plachouras Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow Glasgow G12 8QQ, U.K. Abstract In this paper we propose a new
The Dynamic Absorbing Model for the Web Gianni Amati, Iadh Ounis, Vassilis Plachouras Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow Glasgow G12 8QQ, U.K. Abstract In this paper we propose a new
Idea: Select and rank nodes w.r.t. their relevance or interestingness in large networks.
 Graph Databases and Linked Data So far: Obects are considered as iid (independent and identical diributed) the meaning of obects depends exclusively on the description obects do not influence each other
Graph Databases and Linked Data So far: Obects are considered as iid (independent and identical diributed) the meaning of obects depends exclusively on the description obects do not influence each other
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu March 16, 2016 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu March 16, 2016 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
How works. or How linear algebra powers the search engine. M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University
 How works or How linear algebra powers the search engine M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University From: gomath.com/geometry/ellipse.php Metric mishap causes loss of Mars orbiter
How works or How linear algebra powers the search engine M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University From: gomath.com/geometry/ellipse.php Metric mishap causes loss of Mars orbiter
6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities
 6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities 1 Outline Outline Dynamical systems. Linear and Non-linear. Convergence. Linear algebra and Lyapunov functions. Markov
6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities 1 Outline Outline Dynamical systems. Linear and Non-linear. Convergence. Linear algebra and Lyapunov functions. Markov
Data Mining Techniques
 Data Mining Techniques CS 622 - Section 2 - Spring 27 Pre-final Review Jan-Willem van de Meent Feedback Feedback https://goo.gl/er7eo8 (also posted on Piazza) Also, please fill out your TRACE evaluations!
Data Mining Techniques CS 622 - Section 2 - Spring 27 Pre-final Review Jan-Willem van de Meent Feedback Feedback https://goo.gl/er7eo8 (also posted on Piazza) Also, please fill out your TRACE evaluations!
Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search
 CCST907 Hidden Order in Daily Life: A Mathematical Perspective Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search Dr. S. P. Yung (907A) Dr. Z. Hua (907B) Department of Mathematics, HKU Outline Google is the
CCST907 Hidden Order in Daily Life: A Mathematical Perspective Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search Dr. S. P. Yung (907A) Dr. Z. Hua (907B) Department of Mathematics, HKU Outline Google is the
CS249: ADVANCED DATA MINING
 CS249: ADVANCED DATA MINING Graph and Network Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu May 31, 2017 Methods Learnt Classification Clustering Vector Data Text Data Recommender System Decision Tree; Naïve
CS249: ADVANCED DATA MINING Graph and Network Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu May 31, 2017 Methods Learnt Classification Clustering Vector Data Text Data Recommender System Decision Tree; Naïve
Page rank computation HPC course project a.y
 Page rank computation HPC course project a.y. 2015-16 Compute efficient and scalable Pagerank MPI, Multithreading, SSE 1 PageRank PageRank is a link analysis algorithm, named after Brin & Page [1], and
Page rank computation HPC course project a.y. 2015-16 Compute efficient and scalable Pagerank MPI, Multithreading, SSE 1 PageRank PageRank is a link analysis algorithm, named after Brin & Page [1], and
Calculating Web Page Authority Using the PageRank Algorithm
 Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 5: Graphs as matrices, spectral graph theory, and PageRank
 Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 5: Graphs as matrices, spectral graph theory, and PageRank David Glickenstein November 3, 4 Representing graphs as matrices It will sometimes be useful to represent graphs
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 5: Graphs as matrices, spectral graph theory, and PageRank David Glickenstein November 3, 4 Representing graphs as matrices It will sometimes be useful to represent graphs
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper)
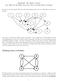 PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
Conditioning of the Entries in the Stationary Vector of a Google-Type Matrix. Steve Kirkland University of Regina
 Conditioning of the Entries in the Stationary Vector of a Google-Type Matrix Steve Kirkland University of Regina June 5, 2006 Motivation: Google s PageRank algorithm finds the stationary vector of a stochastic
Conditioning of the Entries in the Stationary Vector of a Google-Type Matrix Steve Kirkland University of Regina June 5, 2006 Motivation: Google s PageRank algorithm finds the stationary vector of a stochastic
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University
 Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University We ve had our first HC cases. Please, please, please, before you do anything that might violate the HC, talk to me or a TA to make sure it is legitimate. It is much
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University We ve had our first HC cases. Please, please, please, before you do anything that might violate the HC, talk to me or a TA to make sure it is legitimate. It is much
Finding central nodes in large networks
 Finding central nodes in large networks Nelly Litvak University of Twente Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands Woudschoten Conference 2017 Complex networks Networks: Internet, WWW, social
Finding central nodes in large networks Nelly Litvak University of Twente Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands Woudschoten Conference 2017 Complex networks Networks: Internet, WWW, social
Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks
 Network Analysis Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks Papers (in almost all fields) refer to works done earlier on same/related topics Citations A network can be defined as Each node is
Network Analysis Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks Papers (in almost all fields) refer to works done earlier on same/related topics Citations A network can be defined as Each node is
Lecture 10. Lecturer: Aleksander Mądry Scribes: Mani Bastani Parizi and Christos Kalaitzis
 CS-621 Theory Gems October 18, 2012 Lecture 10 Lecturer: Aleksander Mądry Scribes: Mani Bastani Parizi and Christos Kalaitzis 1 Introduction In this lecture, we will see how one can use random walks to
CS-621 Theory Gems October 18, 2012 Lecture 10 Lecturer: Aleksander Mądry Scribes: Mani Bastani Parizi and Christos Kalaitzis 1 Introduction In this lecture, we will see how one can use random walks to
c 2016 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics
 SIAM J. MATRIX ANAL. APPL. Vol. 37, No., pp. 443 468 c 06 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics EDGE MODIFIATION RITERIA FOR ENHANING THE OMMUNIABILITY OF DIGRAPHS FRANESA ARRIGO AND MIHELE BENZI
SIAM J. MATRIX ANAL. APPL. Vol. 37, No., pp. 443 468 c 06 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics EDGE MODIFIATION RITERIA FOR ENHANING THE OMMUNIABILITY OF DIGRAPHS FRANESA ARRIGO AND MIHELE BENZI
Perturbation of the hyper-linked environment
 Perturbation of the hyper-linked environment Hyun Chul Lee and Allan Borodin Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Toronto, Ontario, M5S3G4 {leehyun,bor}@cs.toronto.edu Abstract. After the
Perturbation of the hyper-linked environment Hyun Chul Lee and Allan Borodin Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Toronto, Ontario, M5S3G4 {leehyun,bor}@cs.toronto.edu Abstract. After the
