Computational models: Reaction Diffusion. Matthias Vigelius Week 6
|
|
|
- Roxanne Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computational models: Reaction Diffusion Matthias Vigelius Week 6
2 Reactions
3 (Chemical) reactions Reaction is a transformation from reactants into products: A + 2B D + 3E + k k [ ] Reactions occur with a certain rate Elementary reactions are: s 1 (per second). Equation Type Rate A A B A + B C zeroth order first order second order k ka kab
4 Examples Birth reaction: Radioactive decay: Predator-Prey interaction: +
5 Simplistic model of gene expression The central dogma of molecular biology describes the way genetic information is expressed in all organisms: DNA mrna mrna Protein Exercise: Model this simple dogma in Insight Maker! Alberts et al.: Molecular Biology of the Cell (2002)
6 Simplistic model of gene regulation SIMPLISTIC GENE EXPRESSION MODEL I: NO REGULATION Loading Insight Maker... (This may take a few moments)
7 Gene regulation Proteins can switch genes on or off, which allows the cell to adapt to changing environmental conditions. What if a protein regulates its own production (feedback)?
8 Simplistic model of gene regulation GENE EXPRESSION MODEL II: REGULATION Loading Insight Maker... (This may take a few moments)
9 Feedback Feedback is associated with closed loops in the dynamic description (feedback loops) Negative feedback tends to stabilize systems (Exception: lecture feedback) Positive feedback destabilizes. If unchecked, things get out of control. Feedback is a central concept in nature and engineering. Group discussion: Find more feedback examples (positive/negative)!
10 Nuclear fission from: A. Zabludoff, Nuclear reactions in the sun Positive feedback: Neutrons induce fission step Fission produces more neutrons Can get out of control.. We can write the fission step as an autocatalytic reaction: n U 3n + 90 Kr Ba
11 Structure formation in the early universe
12 Diffusion
13 Microscopic model of diffusion Wiki Diffusion is caused by randomly moving entities Movement may be active (animals) or passive (solute in solvent, Brownian motion) Diffusion tends to smooth out concentration differences (gradients) If particles can interact: reaction-diffusion. Many applications in nature!
14 Hierarchy of models Microscopic level Describe motion of individual particles Mesoscopic level Count number of particles in cell Macroscopic level Let cell size become small (concentration!) Adapt the scale of your model to the problem! Question: How many molecules in your pencil?
15 Reaction diffusion: Pattern formation CDF plugin not found! Please download it here. The brusselator applet is here.
16 Reaction-diffusion: Pattern formation Further reading: Turing patterns activator species stimulates its own production (autocatalysis) and the production of the inhibitor inhibitor inhibits production of activator Inhibitor diffuses fast (away from peak) Activator diffuses slowly (stays at peak) This is where the zebra gets its stripes from.
17 Belousov Zhabotinsky (BZ) reaction Source: YouTube
18 Reaction scheme I: FKN model HOBr + Br + H + Br 2 + H 2 O HBr O 2 + Br + H + 2HOBr Br O + Br + 2H + HBr O + HOBr 3 2 2HBrO 2 Br O + HOBr + 3 H + Br O + HBr O + 2Br + O 3 2 H + O 2 H 2 Br O 3 + Ce 3+ + H + HBr O 2 + Ce 4+ Br O 2 + Ce 4+ + H 2 O Br O + Ce H + 3 Br 2 + CH 2 (COOH) 2 BrCH(COOH) 2 + Br + H + 6 Ce 4+ + CH 2 (COOH) 2 + 2H 2 O 6 Ce 3+ + HCOOH + 2 CO 2 + 6H + 4 Ce 4+ + BrCH(COOH) 2 + 2H 2 O Br + 4 Ce 3+ + HCOOH + 2C O 2 + 5H + Richard J. Field, Endre Koros, and Richard M. Noyes (1972): J. Am. Chem. Soc. 94
19 Separation of Time Scales Imagine catalytic reaction with intermediate: S + E X P + E fast Standard example: Enzyme kinetics Keener and Sneyd: Mathematical Physiology I [Question: Why is this hard to simulate?] The intermediate product is always in quasi steady-state equilibrium with the substrate. So we can simplify: S + E P + E slow
20 Reaction Scheme II: Oregonator model Using separation of time scales we can reduce the system to five equations: Scholarpedia: Oregonator A + Y X + P X + Y 2P A + X 2X + 2Z X + X A + P 1 B + Z Y 2 XZ We have three dynamic species:, and. Question: Where are the positive and negative feedback reactions? Y
21 Oregonator model Source: Vigelius/Meyer (2012)
Oregonator model of the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction Richard K. Herz,
 Oregonator model of the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction Richard K. Herz, rherz@ucsd.edu Boris Belousov in the 1950's discovered that a mixture of malonic acid, potassium bromate, and cerium sulfate an acidic
Oregonator model of the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction Richard K. Herz, rherz@ucsd.edu Boris Belousov in the 1950's discovered that a mixture of malonic acid, potassium bromate, and cerium sulfate an acidic
Festival of the Mind Chaotic Chemical Waves: Oscillations and waves in chemical systems. Dr. Jonathan Howse Dr.
 Festival of the Mind 2014 Chaotic Chemical Waves: Oscillations and waves in chemical systems Dr. Jonathan Howse Dr. Annette Taylor Mark Fell www.markfell.com Some history The BZ reaction In 1951, Belousov,
Festival of the Mind 2014 Chaotic Chemical Waves: Oscillations and waves in chemical systems Dr. Jonathan Howse Dr. Annette Taylor Mark Fell www.markfell.com Some history The BZ reaction In 1951, Belousov,
SPATIO-TEMPORAL MODELLING IN BIOLOGY
 SPATIO-TEMPORAL MODELLING IN BIOLOGY Prof Dagmar Iber, PhD DPhil ((Vorname Nachname)) 04/10/16 1 Challenge: Integration across scales Butcher et al (2004) Nat Biotech, 22, 1253-1259 INTERDISCIPLINARY WORK
SPATIO-TEMPORAL MODELLING IN BIOLOGY Prof Dagmar Iber, PhD DPhil ((Vorname Nachname)) 04/10/16 1 Challenge: Integration across scales Butcher et al (2004) Nat Biotech, 22, 1253-1259 INTERDISCIPLINARY WORK
7. Well-Stirred Reactors IV
 7. Well-Stirred Reactors IV The Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction: Models and Experiments Oregonator [based on the FKN mechanism; Field, R. J. & Noyes, R. M.: Oscillations in chemical systems. IV. Limit cycle
7. Well-Stirred Reactors IV The Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction: Models and Experiments Oregonator [based on the FKN mechanism; Field, R. J. & Noyes, R. M.: Oscillations in chemical systems. IV. Limit cycle
Basic Synthetic Biology circuits
 Basic Synthetic Biology circuits Note: these practices were obtained from the Computer Modelling Practicals lecture by Vincent Rouilly and Geoff Baldwin at Imperial College s course of Introduction to
Basic Synthetic Biology circuits Note: these practices were obtained from the Computer Modelling Practicals lecture by Vincent Rouilly and Geoff Baldwin at Imperial College s course of Introduction to
After lectures by. disappearance of reactants or appearance of. measure a reaction rate we monitor the. Reaction Rates (reaction velocities): To
 Revised 3/21/2017 After lectures by Dr. Loren Williams (GeorgiaTech) Protein Folding: 1 st order reaction DNA annealing: 2 nd order reaction Reaction Rates (reaction velocities): To measure a reaction
Revised 3/21/2017 After lectures by Dr. Loren Williams (GeorgiaTech) Protein Folding: 1 st order reaction DNA annealing: 2 nd order reaction Reaction Rates (reaction velocities): To measure a reaction
Reactions. John Vincent Department of Chemistry University of Alabama
 Oscillating Chemical Reactions John Vincent Department of Chemistry University of Alabama Kinetics In kinetics we study the rate at which a chemical process occurs. Besides information about the speed
Oscillating Chemical Reactions John Vincent Department of Chemistry University of Alabama Kinetics In kinetics we study the rate at which a chemical process occurs. Besides information about the speed
Biology Slide 1 of 34
 Biology 1 of 34 2 4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes 2 of 34 2 4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is a process that changes one set of chemicals into
Biology 1 of 34 2 4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes 2 of 34 2 4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is a process that changes one set of chemicals into
CHEM-UA 652: Thermodynamics and Kinetics
 CHEM-UA 65: Thermodynamics and Kinetics Notes for Lecture I. THE COMPLEXITY OF MULTI-STEP CHEMICAL REACTIONS It should be clear by now that chemical kinetics is governed by the mathematics of systems of
CHEM-UA 65: Thermodynamics and Kinetics Notes for Lecture I. THE COMPLEXITY OF MULTI-STEP CHEMICAL REACTIONS It should be clear by now that chemical kinetics is governed by the mathematics of systems of
Unit 1: Chemistry of Life Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 1 Exploring Life Unit 1: Chemistry of Life Guided Reading Questions
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 1 Exploring Life Unit 1: Chemistry of Life Guided Reading Questions
k 1 HBrO 2 + HOBr (2) k 2 2HOBr (3) 3 2 BrO 2 + 2H 2 O (4) Ce 4+ + HBrO 2 (5)
 Waldemar Nowici EXPERIMENT 2 The Belousov-Żabotyńsi reaction Basic notion: oscillating reaction Introduction Oscillating reactions are those in which the concentrations of reagents undergo periodical changes
Waldemar Nowici EXPERIMENT 2 The Belousov-Żabotyńsi reaction Basic notion: oscillating reaction Introduction Oscillating reactions are those in which the concentrations of reagents undergo periodical changes
1. Introduction to Chemical Kinetics
 1. Introduction to Chemical Kinetics objectives of chemical kinetics 1) Determine empirical rate laws H 2 + I 2 2HI How does the concentration of H 2, I 2, and HI change with time? 2) Determine the mechanism
1. Introduction to Chemical Kinetics objectives of chemical kinetics 1) Determine empirical rate laws H 2 + I 2 2HI How does the concentration of H 2, I 2, and HI change with time? 2) Determine the mechanism
Lecture 7: Simple genetic circuits I
 Lecture 7: Simple genetic circuits I Paul C Bressloff (Fall 2018) 7.1 Transcription and translation In Fig. 20 we show the two main stages in the expression of a single gene according to the central dogma.
Lecture 7: Simple genetic circuits I Paul C Bressloff (Fall 2018) 7.1 Transcription and translation In Fig. 20 we show the two main stages in the expression of a single gene according to the central dogma.
2 4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 2 4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes THINK ABOUT IT Living things are made up of chemical compounds, but chemistry isn t just what life is made of chemistry is also what life does. Everything that happens
2 4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes THINK ABOUT IT Living things are made up of chemical compounds, but chemistry isn t just what life is made of chemistry is also what life does. Everything that happens
Systems Biology in Photosynthesis INTRODUCTION
 1 / 26 Systems Biology in Photosynthesis INTRODUCTION Rainer Machné Institute for Theoretical Chemistry, University of Vienna, Austria PSI - Photon System Instruments, Czech Republic Brno, April, 2011
1 / 26 Systems Biology in Photosynthesis INTRODUCTION Rainer Machné Institute for Theoretical Chemistry, University of Vienna, Austria PSI - Photon System Instruments, Czech Republic Brno, April, 2011
Bioinformatics 3. V18 Kinetic Motifs. Fri, Jan 8, 2016
 Bioinformatics 3 V18 Kinetic Motifs Fri, Jan 8, 2016 Modelling of Signalling Pathways Curr. Op. Cell Biol. 15 (2003) 221 1) How do the magnitudes of signal output and signal duration depend on the kinetic
Bioinformatics 3 V18 Kinetic Motifs Fri, Jan 8, 2016 Modelling of Signalling Pathways Curr. Op. Cell Biol. 15 (2003) 221 1) How do the magnitudes of signal output and signal duration depend on the kinetic
Bioinformatics 3! V20 Kinetic Motifs" Mon, Jan 13, 2014"
 Bioinformatics 3! V20 Kinetic Motifs" Mon, Jan 13, 2014" Modelling of Signalling Pathways" Curr. Op. Cell Biol. 15 (2003) 221" 1) How do the magnitudes of signal output and signal duration depend on the
Bioinformatics 3! V20 Kinetic Motifs" Mon, Jan 13, 2014" Modelling of Signalling Pathways" Curr. Op. Cell Biol. 15 (2003) 221" 1) How do the magnitudes of signal output and signal duration depend on the
CH302 Unit7 Day 8 Activity Unit 7 Readiness Assessment Activity
 CH302 Unit7 Day 8 Activity Unit 7 Readiness Assessment Activity Spring 2013 VandenBout/LaBrake Name: KEY UT EID: Please work in small groups and be prepared to answer via clicker. Discussion Point I: Thinking
CH302 Unit7 Day 8 Activity Unit 7 Readiness Assessment Activity Spring 2013 VandenBout/LaBrake Name: KEY UT EID: Please work in small groups and be prepared to answer via clicker. Discussion Point I: Thinking
Chemistry 112 Name Exam I Form A Section January 29,
 Chemistry 112 Name Exam I Form A Section January 29, 2013 email IMPORTANT: On the scantron (answer sheet), you MUST clearly fill your name, your student number, section number, and test form (white cover
Chemistry 112 Name Exam I Form A Section January 29, 2013 email IMPORTANT: On the scantron (answer sheet), you MUST clearly fill your name, your student number, section number, and test form (white cover
2015 FALL FINAL REVIEW
 2015 FALL FINAL REVIEW Biomolecules & Enzymes Illustrate table and fill in parts missing 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
2015 FALL FINAL REVIEW Biomolecules & Enzymes Illustrate table and fill in parts missing 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics II. Chem 102 Dr. Eloranta
 Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics II Chem 102 Dr. Eloranta Rate Laws If you are familiar with calculus Experiments would allow you to determine the reaction order and rate constant, but what if you wanted
Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics II Chem 102 Dr. Eloranta Rate Laws If you are familiar with calculus Experiments would allow you to determine the reaction order and rate constant, but what if you wanted
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Metabolism*
 Chapter 6- An Introduction to Metabolism* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. The Energy of Life
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Metabolism* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. The Energy of Life
Previous Class. Today. Cosubstrates (cofactors)
 Previous Class Cosubstrates (cofactors) Today Proximity effect Basic equations of Kinetics Steady state kinetics Michaelis Menten equations and parameters Enzyme Kinetics Enzyme kinetics implies characterizing
Previous Class Cosubstrates (cofactors) Today Proximity effect Basic equations of Kinetics Steady state kinetics Michaelis Menten equations and parameters Enzyme Kinetics Enzyme kinetics implies characterizing
Fundamentals of Bio-architecture SUMMARY
 Fundamentals of Bio-architecture SUMMARY Melik Demirel, PhD *Pictures and tables in this lecture notes are copied from Internet sources for educational use only. Can order increase without breaking 2 nd
Fundamentals of Bio-architecture SUMMARY Melik Demirel, PhD *Pictures and tables in this lecture notes are copied from Internet sources for educational use only. Can order increase without breaking 2 nd
Rui Dilão NonLinear Dynamics Group, IST
 1st Conference on Computational Interdisciplinary Sciences (CCIS 2010) 23-27 August 2010, INPE, São José dos Campos, Brasil Modeling, Simulating and Calibrating Genetic Regulatory Networks: An Application
1st Conference on Computational Interdisciplinary Sciences (CCIS 2010) 23-27 August 2010, INPE, São José dos Campos, Brasil Modeling, Simulating and Calibrating Genetic Regulatory Networks: An Application
Theoretical Models for Chemical Kinetics
 Theoretical Models for Chemical Kinetics Thus far we have calculated rate laws, rate constants, reaction orders, etc. based on observations of macroscopic properties, but what is happening at the molecular
Theoretical Models for Chemical Kinetics Thus far we have calculated rate laws, rate constants, reaction orders, etc. based on observations of macroscopic properties, but what is happening at the molecular
Math 345 Intro to Math Biology Lecture 19: Models of Molecular Events and Biochemistry
 Math 345 Intro to Math Biology Lecture 19: Models of Molecular Events and Biochemistry Junping Shi College of William and Mary, USA Molecular biology and Biochemical kinetics Molecular biology is one of
Math 345 Intro to Math Biology Lecture 19: Models of Molecular Events and Biochemistry Junping Shi College of William and Mary, USA Molecular biology and Biochemical kinetics Molecular biology is one of
Chaos in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction
 Chaos in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction David Connolly Brad Nelson December 2, 2011 Abstract In this project, we investigate two different models of the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction, the Oregonator
Chaos in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction David Connolly Brad Nelson December 2, 2011 Abstract In this project, we investigate two different models of the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction, the Oregonator
Network Dynamics and Cell Physiology. John J. Tyson Dept. Biological Sciences Virginia Tech
 Network Dynamics and Cell hysiology John J. Tyson Dept. Biological Sciences Virginia Tech Collaborators Budapest Univ. Techn.. & Econ. Bela Novak Attila Csikasz-Nagy Andrea Ciliberto Virginia Tech Kathy
Network Dynamics and Cell hysiology John J. Tyson Dept. Biological Sciences Virginia Tech Collaborators Budapest Univ. Techn.. & Econ. Bela Novak Attila Csikasz-Nagy Andrea Ciliberto Virginia Tech Kathy
Study Guide: Fall Final Exam H O N O R S B I O L O G Y : U N I T S 1-5
 Study Guide: Fall Final Exam H O N O R S B I O L O G Y : U N I T S 1-5 Directions: The list below identifies topics, terms, and concepts that will be addressed on your Fall Final Exam. This list should
Study Guide: Fall Final Exam H O N O R S B I O L O G Y : U N I T S 1-5 Directions: The list below identifies topics, terms, and concepts that will be addressed on your Fall Final Exam. This list should
Kinetics. Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 14 Yonsei University In kinetics we study the rate at which a chemical process occurs. Besides information about the speed at which reactions occur, kinetics also sheds light
Lecture Presentation Chapter 14 Yonsei University In kinetics we study the rate at which a chemical process occurs. Besides information about the speed at which reactions occur, kinetics also sheds light
7.32/7.81J/8.591J. Rm Rm (under construction) Alexander van Oudenaarden Jialing Li. Bernardo Pando. Rm.
 Introducing... 7.32/7.81J/8.591J Systems Biology modeling biological networks Lectures: Recitations: ti TR 1:00-2:30 PM W 4:00-5:00 PM Rm. 6-120 Rm. 26-204 (under construction) Alexander van Oudenaarden
Introducing... 7.32/7.81J/8.591J Systems Biology modeling biological networks Lectures: Recitations: ti TR 1:00-2:30 PM W 4:00-5:00 PM Rm. 6-120 Rm. 26-204 (under construction) Alexander van Oudenaarden
Rate Mechanism Example reaction: 4HBr + O 2 2H 2 O + 2Br 2 all gases rate = k[hbr] [O 2 ]
![Rate Mechanism Example reaction: 4HBr + O 2 2H 2 O + 2Br 2 all gases rate = k[hbr] [O 2 ] Rate Mechanism Example reaction: 4HBr + O 2 2H 2 O + 2Br 2 all gases rate = k[hbr] [O 2 ]](/thumbs/95/126257756.jpg) Name Date Rate Mechanism Example reaction: 4HBr + O 2 2H 2 O + 2Br 2 all gases rate = k[hbr] [O 2 ] What is the likelihood that all 5 of those molecules will collide simultaneously? Balanced chemical equations
Name Date Rate Mechanism Example reaction: 4HBr + O 2 2H 2 O + 2Br 2 all gases rate = k[hbr] [O 2 ] What is the likelihood that all 5 of those molecules will collide simultaneously? Balanced chemical equations
Problem Set 2. 1 Competitive and uncompetitive inhibition (12 points) Systems Biology (7.32/7.81J/8.591J)
 Problem Set 2 1 Competitive and uncompetitive inhibition (12 points) a. Reversible enzyme inhibitors can bind enzymes reversibly, and slowing down or halting enzymatic reactions. If an inhibitor occupies
Problem Set 2 1 Competitive and uncompetitive inhibition (12 points) a. Reversible enzyme inhibitors can bind enzymes reversibly, and slowing down or halting enzymatic reactions. If an inhibitor occupies
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism. 1. Energy & Chemical Reactions 2. ATP 3. Enzymes & Metabolic Pathways
 Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism 1. Energy & Chemical Reactions 2. ATP 3. Enzymes & Metabolic Pathways 1. Energy & Chemical Reactions 2 Basic Forms of Energy Kinetic Energy (KE) energy in motion
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism 1. Energy & Chemical Reactions 2. ATP 3. Enzymes & Metabolic Pathways 1. Energy & Chemical Reactions 2 Basic Forms of Energy Kinetic Energy (KE) energy in motion
Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics
 Sample Exercise 14.1 (p. 578) For the reaction pictured at the bottom of the previous page, calculate the average rate at which A disappears over the time interval from 20 s to 40 s. (1.2 x 10-2 M/s) Practice
Sample Exercise 14.1 (p. 578) For the reaction pictured at the bottom of the previous page, calculate the average rate at which A disappears over the time interval from 20 s to 40 s. (1.2 x 10-2 M/s) Practice
An Introduction to Metabolism
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 8 An Introduction to Metabolism
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 8 An Introduction to Metabolism
From cell biology to Petri nets. Rainer Breitling, Groningen, NL David Gilbert, London, UK Monika Heiner, Cottbus, DE
 From cell biology to Petri nets Rainer Breitling, Groningen, NL David Gilbert, London, UK Monika Heiner, Cottbus, DE Biology = Concentrations Breitling / 2 The simplest chemical reaction A B irreversible,
From cell biology to Petri nets Rainer Breitling, Groningen, NL David Gilbert, London, UK Monika Heiner, Cottbus, DE Biology = Concentrations Breitling / 2 The simplest chemical reaction A B irreversible,
Organisms: We will need to have some examples in mind for our spherical cows.
 Lecture 4: Structure and Composition (Sept. 15) 4.1 Reading Assignment for Lectures 3-4: Phillips, Kondev, Theriot (PKT), Chapter 2 Problem Set 1 (due Sept. 24) now posted on the website. Cellular materials:
Lecture 4: Structure and Composition (Sept. 15) 4.1 Reading Assignment for Lectures 3-4: Phillips, Kondev, Theriot (PKT), Chapter 2 Problem Set 1 (due Sept. 24) now posted on the website. Cellular materials:
CS-E5880 Modeling biological networks Gene regulatory networks
 CS-E5880 Modeling biological networks Gene regulatory networks Jukka Intosalmi (based on slides by Harri Lähdesmäki) Department of Computer Science Aalto University January 12, 2018 Outline Modeling gene
CS-E5880 Modeling biological networks Gene regulatory networks Jukka Intosalmi (based on slides by Harri Lähdesmäki) Department of Computer Science Aalto University January 12, 2018 Outline Modeling gene
An Introduction to Metabolism
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 6 An Introduction to Metabolism Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Energy of Life The
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 6 An Introduction to Metabolism Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Energy of Life The
BIOLOGY 10/11/2014. An Introduction to Metabolism. Outline. Overview: The Energy of Life
 8 An Introduction to Metabolism CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Forms of Energy II. Laws of Thermodynamics III. Energy and metabolism IV. ATP V. Enzymes
8 An Introduction to Metabolism CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Forms of Energy II. Laws of Thermodynamics III. Energy and metabolism IV. ATP V. Enzymes
Chem 6 sample exam 1 (100 points total)
 Chem 6 sample exam 1 (100 points total) @ This is a closed book exam to which the Honor Principle applies. @ The last page contains several equations which may be useful; you can detach it for easy reference.
Chem 6 sample exam 1 (100 points total) @ This is a closed book exam to which the Honor Principle applies. @ The last page contains several equations which may be useful; you can detach it for easy reference.
Metabolism and enzymes
 Metabolism and enzymes 4-11-16 What is a chemical reaction? A chemical reaction is a process that forms or breaks the chemical bonds that hold atoms together Chemical reactions convert one set of chemical
Metabolism and enzymes 4-11-16 What is a chemical reaction? A chemical reaction is a process that forms or breaks the chemical bonds that hold atoms together Chemical reactions convert one set of chemical
Cell Organelles Tutorial
 1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
Basic modeling approaches for biological systems. Mahesh Bule
 Basic modeling approaches for biological systems Mahesh Bule The hierarchy of life from atoms to living organisms Modeling biological processes often requires accounting for action and feedback involving
Basic modeling approaches for biological systems Mahesh Bule The hierarchy of life from atoms to living organisms Modeling biological processes often requires accounting for action and feedback involving
Module 6 : Reaction Kinetics and Dynamics Lecture 30 : Complex Reactions
 Module 6 : Reaction Kinetics and Dynamics Lecture 30 : Complex Reactions Objectives After studying this Lecture you will learn to do the following. Analyze the kinetics of chain reactions Analyses the
Module 6 : Reaction Kinetics and Dynamics Lecture 30 : Complex Reactions Objectives After studying this Lecture you will learn to do the following. Analyze the kinetics of chain reactions Analyses the
2 4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Slide 1 of 34
 2 4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes 1 of 34 Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is a process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals. Some chemical reactions
2 4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes 1 of 34 Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is a process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals. Some chemical reactions
Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide
 Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Information: Exam has 100 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencils and a four-function calculator on the day of the test. Review ALL vocabulary,
Honors Biology Fall Final Exam Study Guide Helpful Information: Exam has 100 multiple choice questions. Be ready with pencils and a four-function calculator on the day of the test. Review ALL vocabulary,
Biology regimented study plan
 For each topic, write down notes, make it organized, always have a pencil and paper while studying. At the end of each section, test yourself (Answer past exam questions, practice Quizlet, watch Crash
For each topic, write down notes, make it organized, always have a pencil and paper while studying. At the end of each section, test yourself (Answer past exam questions, practice Quizlet, watch Crash
CHEMISTRY - CLUTCH CH.13 - CHEMICAL KINETICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: RATES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS is the study of reaction rates, and tells us the change in concentrations of reactants or products over a period of time. Although a chemical
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: RATES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS is the study of reaction rates, and tells us the change in concentrations of reactants or products over a period of time. Although a chemical
Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics
 Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics Common Student Misconceptions It is possible for mathematics to get in the way of some students understanding of the chemistry of this chapter. Students often assume that
Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics Common Student Misconceptions It is possible for mathematics to get in the way of some students understanding of the chemistry of this chapter. Students often assume that
Module 6 : Reaction Kinetics and Dynamics Lecture 28 : Elementary Reactions and Reaction Mechanisms
 Module 6 : Reaction Kinetics and Dynamics Lecture 28 : Elementary Reactions and Reaction Mechanisms Objectives In this Lecture you will learn to do the following Define what is an elementary reaction.
Module 6 : Reaction Kinetics and Dynamics Lecture 28 : Elementary Reactions and Reaction Mechanisms Objectives In this Lecture you will learn to do the following Define what is an elementary reaction.
Chapter 5. Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell
 Chapter 5 Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell Including some materials from lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Ammended by John Crocker Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.. Review
Chapter 5 Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell Including some materials from lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Ammended by John Crocker Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.. Review
An Introduction to Metabolism
 Chapter 8 An Introduction to Metabolism oweroint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Concept 8.1: An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws
Chapter 8 An Introduction to Metabolism oweroint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Concept 8.1: An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws
An Introduction to Metabolism
 Chapter 8 An Introduction to Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 8 An Introduction to Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Ground Rules of Metabolism CHAPTER 6
 Ground Rules of Metabolism CHAPTER 6 Antioxidants You ve heard the term. What s the big deal? Found naturally in many fruits and vegetables Added to many products What do they actually do? Antioxidants
Ground Rules of Metabolism CHAPTER 6 Antioxidants You ve heard the term. What s the big deal? Found naturally in many fruits and vegetables Added to many products What do they actually do? Antioxidants
1 The nuclear binding energy is the amount of energy consumed during. 2 An unstable isotope of Ga-73 undergoes radioactive decay to Ga-73
 version: master Exam 3 - REVIEW This exam should have 27 questions. The point values are given with each question. Bubble in your answer choices on the bubblehseet provided. Your score is based on what
version: master Exam 3 - REVIEW This exam should have 27 questions. The point values are given with each question. Bubble in your answer choices on the bubblehseet provided. Your score is based on what
CHEM 341 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM. Name
 CHEM 341 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM Name Do not open this exam until told to do so. The exam consists of 6 pages, including this one. Count them to insure that they are all there. Constants: R = 8.31
CHEM 341 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM Name Do not open this exam until told to do so. The exam consists of 6 pages, including this one. Count them to insure that they are all there. Constants: R = 8.31
Computer Simulation and Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Biophysics
 Victor Bloomfield Computer Simulation and Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Biophysics An Introduction Using R Springer Contents Part I The Basics of R 1 Calculating with R 3 1.1 Installing R 3 1.1.1
Victor Bloomfield Computer Simulation and Data Analysis in Molecular Biology and Biophysics An Introduction Using R Springer Contents Part I The Basics of R 1 Calculating with R 3 1.1 Installing R 3 1.1.1
Judith Herzfeld 1997,1999. These exercises are provided here for classroom and study use only. All other uses are copyright protected.
 Judith Herzfeld 1997,1999 These exercises are provided here for classroom and study use only. All other uses are copyright protected. 5.5-010 Which of the following statements is not valid concerning a
Judith Herzfeld 1997,1999 These exercises are provided here for classroom and study use only. All other uses are copyright protected. 5.5-010 Which of the following statements is not valid concerning a
Chapter 6: Energy and Metabolism
 Chapter 6: Energy and Metabolism Student: 1. Oxidation and reduction reactions are chemical processes that result in a gain or loss in A) atoms. B) neutrons. C) electrons. D) molecules. E) protons. 2.
Chapter 6: Energy and Metabolism Student: 1. Oxidation and reduction reactions are chemical processes that result in a gain or loss in A) atoms. B) neutrons. C) electrons. D) molecules. E) protons. 2.
9/25/2011. Outline. Overview: The Energy of Life. I. Forms of Energy II. Laws of Thermodynamics III. Energy and metabolism IV. ATP V.
 Chapter 8 Introduction to Metabolism Outline I. Forms of Energy II. Laws of Thermodynamics III. Energy and metabolism IV. ATP V. Enzymes Overview: The Energy of Life Figure 8.1 The living cell is a miniature
Chapter 8 Introduction to Metabolism Outline I. Forms of Energy II. Laws of Thermodynamics III. Energy and metabolism IV. ATP V. Enzymes Overview: The Energy of Life Figure 8.1 The living cell is a miniature
CHAPTER 8. An Introduction to Metabolism
 CHAPTER 8 An Introduction to Metabolism WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW: Examples of endergonic and exergonic reactions. The key role of ATP in energy coupling. That enzymes work by lowering the energy of activation.
CHAPTER 8 An Introduction to Metabolism WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW: Examples of endergonic and exergonic reactions. The key role of ATP in energy coupling. That enzymes work by lowering the energy of activation.
CHEM 116 Collision Theory and Reaction Mechanisms
 CHEM 116 Collision Theory and Reaction Mechanisms Lecture 13 Prof. Sevian Note: If there is anything we do not finish about reaction mechanisms today, that is where we will start on Tuesday with Lecture
CHEM 116 Collision Theory and Reaction Mechanisms Lecture 13 Prof. Sevian Note: If there is anything we do not finish about reaction mechanisms today, that is where we will start on Tuesday with Lecture
Pattern Formation and Wave Propagation in the Belousov-Zhabotinskii Reaction
 Pattern Formation and Wave Propagation in the Belousov-Zhabotinskii Reaction Dan Hill and Timothy Morgan University of California, San Diego Physics Department INTRODUCTION The Belousov-Zhabotinskii (BZ)
Pattern Formation and Wave Propagation in the Belousov-Zhabotinskii Reaction Dan Hill and Timothy Morgan University of California, San Diego Physics Department INTRODUCTION The Belousov-Zhabotinskii (BZ)
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Description
 CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
Biological Pathways Representation by Petri Nets and extension
 Biological Pathways Representation by and extensions December 6, 2006 Biological Pathways Representation by and extension 1 The cell Pathways 2 Definitions 3 4 Biological Pathways Representation by and
Biological Pathways Representation by and extensions December 6, 2006 Biological Pathways Representation by and extension 1 The cell Pathways 2 Definitions 3 4 Biological Pathways Representation by and
Objectives INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM. Metabolism. Catabolic Pathways. Anabolic Pathways 3/6/2011. How to Read a Chemical Equation
 Objectives INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM. Chapter 8 Metabolism, Energy, and Life Explain the role of catabolic and anabolic pathways in cell metabolism Distinguish between kinetic and potential energy Distinguish
Objectives INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM. Chapter 8 Metabolism, Energy, and Life Explain the role of catabolic and anabolic pathways in cell metabolism Distinguish between kinetic and potential energy Distinguish
BioControl - Week 6, Lecture 1
 BioControl - Week 6, Lecture 1 Goals of this lecture Large metabolic networks organization Design principles for small genetic modules - Rules based on gene demand - Rules based on error minimization Suggested
BioControl - Week 6, Lecture 1 Goals of this lecture Large metabolic networks organization Design principles for small genetic modules - Rules based on gene demand - Rules based on error minimization Suggested
Enzyme Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of
 Enzyme Enzyme Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme
Enzyme Enzyme Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control
 BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control Lecture 24 Unregulated Gene Expression Model Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 The genetic material inside a cell, encoded in its DNA, governs the response of a cell to various
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control Lecture 24 Unregulated Gene Expression Model Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 The genetic material inside a cell, encoded in its DNA, governs the response of a cell to various
CHAPTER : Prokaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
Identify stages of plant life cycle Botany Oral/written pres, exams
 DPI Standards Biology Education (for students) 1. Characteristics of organisms Know Properties of living organisms, including: Acquire and use energy and materials Sense and respond to stimuli Reproduce
DPI Standards Biology Education (for students) 1. Characteristics of organisms Know Properties of living organisms, including: Acquire and use energy and materials Sense and respond to stimuli Reproduce
Crosscutting Concepts
 Crosscutting Concepts Patterns Observed patterns of forms and events guide organization and classification, and they prompt questions about relationships and the factors that influence them. Patterns exist
Crosscutting Concepts Patterns Observed patterns of forms and events guide organization and classification, and they prompt questions about relationships and the factors that influence them. Patterns exist
Final exam. Please write your name on the exam and keep an ID card ready. You may use a calculator (but no computer or smart phone) and a dictionary.
 Biophysics of Macromolecules Prof. D. Braun and Prof. J. Lipfert SS 2015 Final exam Final exam Name: Student number ( Matrikelnummer ): Please write your name on the exam and keep an ID card ready. You
Biophysics of Macromolecules Prof. D. Braun and Prof. J. Lipfert SS 2015 Final exam Final exam Name: Student number ( Matrikelnummer ): Please write your name on the exam and keep an ID card ready. You
Biol2174 Cell Physiology in Health & Disease
 Biol2174 Cell Physiology in Health & Disease Lecture 4: Membrane Transport Proteins Kiaran Kirk Research School of Biology Learning objectives To understand: The need for membrane transport proteins in
Biol2174 Cell Physiology in Health & Disease Lecture 4: Membrane Transport Proteins Kiaran Kirk Research School of Biology Learning objectives To understand: The need for membrane transport proteins in
Ch 13 Rates of Reaction (Chemical Kinetics)
 Ch 13 Rates of Reaction (Chemical Kinetics) Reaction Rates and Kinetics - The reaction rate is how fast reactants are converted to products. - Chemical kinetics is the study of reaction rates. Kinetics
Ch 13 Rates of Reaction (Chemical Kinetics) Reaction Rates and Kinetics - The reaction rate is how fast reactants are converted to products. - Chemical kinetics is the study of reaction rates. Kinetics
Computational Biology 1
 Computational Biology 1 Protein Function & nzyme inetics Guna Rajagopal, Bioinformatics Institute, guna@bii.a-star.edu.sg References : Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4 th d. Alberts et. al. Pg. 129 190
Computational Biology 1 Protein Function & nzyme inetics Guna Rajagopal, Bioinformatics Institute, guna@bii.a-star.edu.sg References : Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4 th d. Alberts et. al. Pg. 129 190
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism
 Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism Key Concepts 8.1 An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics 8.2 The free-energy change of a reaction tells us
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism Key Concepts 8.1 An organism s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the laws of thermodynamics 8.2 The free-energy change of a reaction tells us
Analyze the roles of enzymes in biochemical reactions
 ENZYMES and METABOLISM Elements: Cell Biology (Enzymes) Estimated Time: 6 7 hours By the end of this course, students will have an understanding of the role of enzymes in biochemical reactions. Vocabulary
ENZYMES and METABOLISM Elements: Cell Biology (Enzymes) Estimated Time: 6 7 hours By the end of this course, students will have an understanding of the role of enzymes in biochemical reactions. Vocabulary
Leader: Deborah Course: CHEM 178 Instructor: Bonaccorsi/Vela Date: 2/6/18 + H 2 CHF 3. a. Express the rate law in terms of m, n, and k.
 EXAM I REVIEW KEY Leader: Deborah Course: CHEM 178 Instructor: Bonaccorsi/Vela Date: 2/6/18 1. Given the following reaction: CF 4 + H 2 CHF 3 + HF a. Express the rate law in terms of m, n, and k. Rate
EXAM I REVIEW KEY Leader: Deborah Course: CHEM 178 Instructor: Bonaccorsi/Vela Date: 2/6/18 1. Given the following reaction: CF 4 + H 2 CHF 3 + HF a. Express the rate law in terms of m, n, and k. Rate
Lecture 15 (10/20/17) Lecture 15 (10/20/17)
 Reading: Ch6; 98-203 Ch6; Box 6- Lecture 5 (0/20/7) Problems: Ch6 (text); 8, 9, 0,, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 Ch6 (study guide-facts); 6, 7, 8, 9, 20, 2 8, 0, 2 Ch6 (study guide-applying); NEXT Reading: Ch6; 207-20
Reading: Ch6; 98-203 Ch6; Box 6- Lecture 5 (0/20/7) Problems: Ch6 (text); 8, 9, 0,, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 Ch6 (study guide-facts); 6, 7, 8, 9, 20, 2 8, 0, 2 Ch6 (study guide-applying); NEXT Reading: Ch6; 207-20
How fast reactants turn into products. Usually measured in Molarity per second units. Kinetics
 How fast reactants turn into products. Usually measured in Molarity per second units. Kinetics Reaction rated are fractions of a second for fireworks to explode. Reaction Rates takes years for a metal
How fast reactants turn into products. Usually measured in Molarity per second units. Kinetics Reaction rated are fractions of a second for fireworks to explode. Reaction Rates takes years for a metal
Dependence of Wave Speed on Acidity and Initial Bromate Concentration in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction-Diffusion System
 Subscriber access provided by BRANDEIS UNIV Dependence of Wave Speed on Acidity and Initial Bromate Concentration in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction-Diffusion System Matthew D. Eager, Marianne Santos,
Subscriber access provided by BRANDEIS UNIV Dependence of Wave Speed on Acidity and Initial Bromate Concentration in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction-Diffusion System Matthew D. Eager, Marianne Santos,
+ regulation. ribosomes
 central dogma + regulation rpl DNA tsx rrna trna mrna ribosomes tsl ribosomal proteins structural proteins transporters enzymes srna regulators RNAp DNAp tsx initiation control by transcription factors
central dogma + regulation rpl DNA tsx rrna trna mrna ribosomes tsl ribosomal proteins structural proteins transporters enzymes srna regulators RNAp DNAp tsx initiation control by transcription factors
CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry
 CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zakarian/armen/courses.html Chapter 5 Alkene: Introduction Thermodynamics and Kinetics Midterm 2... Grades will be posted on Tuesday, Feb. 27 th.
CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zakarian/armen/courses.html Chapter 5 Alkene: Introduction Thermodynamics and Kinetics Midterm 2... Grades will be posted on Tuesday, Feb. 27 th.
Diffusion, Reaction, and Biological pattern formation
 Diffusion, Reaction, and Biological pattern formation Morphogenesis and positional information How do cells know what to do? Fundamental questions How do proteins in a cell segregate to front or back?
Diffusion, Reaction, and Biological pattern formation Morphogenesis and positional information How do cells know what to do? Fundamental questions How do proteins in a cell segregate to front or back?
Chapter 16. Rate Laws. The rate law describes the way in which reactant concentration affects reaction rate.
 Rate Laws The rate law describes the way in which reactant concentration affects reaction rate. A rate law is the expression that shows how the rate of formation of product depends on the concentration
Rate Laws The rate law describes the way in which reactant concentration affects reaction rate. A rate law is the expression that shows how the rate of formation of product depends on the concentration
Equilibrium, Positive and Negative Feedback
 Equilibrium, Positive and Negative Feedback Most ecosystems are very complex. There are many flows and storages. A high level of complexity makes for a more stable system which can withstand stress and
Equilibrium, Positive and Negative Feedback Most ecosystems are very complex. There are many flows and storages. A high level of complexity makes for a more stable system which can withstand stress and
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 6 Kinetics - Concluded
 Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 6 Kinetics - Concluded Why? The half-life idea is most useful in conjunction with first-order kinetics, which include many chemical reactions and all nuclear decay processes.
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 6 Kinetics - Concluded Why? The half-life idea is most useful in conjunction with first-order kinetics, which include many chemical reactions and all nuclear decay processes.
2 Dilution of Proteins Due to Cell Growth
 Problem Set 1 1 Transcription and Translation Consider the following set of reactions describing the process of maing a protein out of a gene: G β g G + M M α m M β m M + X X + S 1+ 1 X S 2+ X S X S 2
Problem Set 1 1 Transcription and Translation Consider the following set of reactions describing the process of maing a protein out of a gene: G β g G + M M α m M β m M + X X + S 1+ 1 X S 2+ X S X S 2
2 4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chemical Reactions
 Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction occurs when chemical bonds are broken and reformed. Rust forms very slowly, while rocket fuel combustion is explosive! The significance of this comparison is that
Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction occurs when chemical bonds are broken and reformed. Rust forms very slowly, while rocket fuel combustion is explosive! The significance of this comparison is that
An Introduction to Metabolism
 Chapter 8 1 An Introduction to Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 8 1 An Introduction to Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
02/02/ Living things are organized. Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures. Learning Outcome B1
 Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Biology Midterm Review
 Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic
Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic
From Friday s material
 5.111 Lecture 35 35.1 Kinetics Topic: Catalysis Chapter 13 (Section 13.14-13.15) From Friday s material Le Chatelier's Principle - when a stress is applied to a system in equilibrium, the equilibrium tends
5.111 Lecture 35 35.1 Kinetics Topic: Catalysis Chapter 13 (Section 13.14-13.15) From Friday s material Le Chatelier's Principle - when a stress is applied to a system in equilibrium, the equilibrium tends
Principles of Synthetic Biology: Midterm Exam
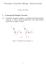 Principles of Synthetic Biology: Midterm Exam October 28, 2010 1 Conceptual Simple Circuits 1.1 Consider the plots in figure 1. Identify all critical points with an x. Put a circle around the x for each
Principles of Synthetic Biology: Midterm Exam October 28, 2010 1 Conceptual Simple Circuits 1.1 Consider the plots in figure 1. Identify all critical points with an x. Put a circle around the x for each
Chapter 12. Chemical Kinetics
 Chapter 12 Chemical Kinetics Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Reaction Rate Change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time. Rate = concentration of A at time t t 2 1 2 1 concentration of A at
Chapter 12 Chemical Kinetics Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Reaction Rate Change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time. Rate = concentration of A at time t t 2 1 2 1 concentration of A at
Elements and Isotopes
 Section 2-1 Notes Atoms Life depends on chemistry. The basic unit of matter is the atom. Atoms are incredibly small The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Parts
Section 2-1 Notes Atoms Life depends on chemistry. The basic unit of matter is the atom. Atoms are incredibly small The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Parts
