MATH 223A NOTES 2011 LIE ALGEBRAS 35
|
|
|
- Deborah Young
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MATH 3A NOTES 011 LIE ALGEBRAS Abstract root systems We now attempt to reconstruct the Lie algebra based only on the information given by the set of roots Φ which is embedded in Euclidean space E Definition. Any finite subset Φ of Euclidean space E satisfying the conditions of Theorem 8.5. will be called a root system. To repeat: Definition A root system is defined to be a subset Φ of standard Euclidean space E (i.e., finite dimensional real vector space with a positive definite inner product (, )) satisfying the following. (1) Φ is finite, spans E and 0 / Φ. () If Φ then Φ and not other real multiple of is in Φ. (3) If, β Φ then β, := (β,) (, ) Z (4) If, β Φ then β β, Φ Note that, =. Proposition Let σ : E E be the linear mapping given by σ (x) =x x, Then σ is reflection through the hyperplane perpendicular to. Proof. σ sends to and leaves fixed every vector perpendicular to. Condition (4) says that σ (Φ) = Φ for all Φ. Definition The Weyl group W is defined to be the subgroup of GL(E) generated by the reflections σ for all Φ. β σ (β) =β ( 3) Figure 1. In this example, β, = 3 and σ (β) =β +3 Φ. We will prove later that the vectors in the middle: β +, β + are also in Φ. Example (1) A n 1 = {± i 1 i n} E = R n is a root system. σ i sends i to i and leaves the other unit vectors j fixed. The matrix of this reflection map is the diagonal matrix with 1 in the ith position with other diagonal entries equal to 1. Therefore, the Weyl group is the group of diagonal matrices with ±1 on the diagonal: W = Z n = Z Z Z. (Z = Z/Z)
2 36 MATH 3A NOTES 011 LIE ALGEBRAS () A n 1 = {±( i j ) 1 i<j n} (3) is a root system in E = {x R n x i =0}. For = i j, the reflection σ switches i and j and leaves the other k fixed. This clearly sends the set A n 1 to itself. The reflections are transpositions. So, the Weyl group is the symmetric group S n. D n = {±( i ± j ) 1 i<j n} is a root system. For = i + j, the reflection σ switches i and j (and i j ) and leaves the other k fixed. This clearly sends the set D n to itself. One can show that the Weyl group is the group of signed permutations with an even number of negative signs. Exercise Find an explicit isomorphism D 3 = A Two roots. Lemma Suppose that, β Φ and β = ±. Then, ββ, =0, 1, or 3. Proof. This follows from the Schwartz inequality:, ββ, = where equality holds iff, β are collinear. 4(, β)(β,) (β,β)(, ) = 4(, β) β 4 This is also equal to 4 cos θ where θ is the angle between, β. cos θ = ± cos θ = θ or π θ = π π π π If the product, ββ, is 0 then, β are perpendicular and σ (β) =β. This is illustrated in the first example above. If the product of, β, β, is nonzero, one of them must be ±1. By symmetry assume, β = ±1. Then β, = ±1, ±, ±3. β, = β,, β = (β,)/ (β,)/ β = β =1,, 3 This looks like 6 cases, but this reduces to 3 cases with the following observation. Let γ = σ (β) =β β, Then γ, = β, β, = β, So, by replacing β with γ if necessary, we may assume that β, is negative.
3 MATH 3A NOTES 011 LIE ALGEBRAS root system A. Suppose that β, = 1. Then = β and θ =π/3. Also σ (β) =β β, = β + β β β + β This is the root system of sl(3,f). Also, it is a special case of example above with n = 3. The correspondence is with = β = and = 1, β = 3 ( + β = 1 3 ) β, = (β,) (, ) = = 1 In terms of H, the Cartan subalgebra of L = sl(3,f), i H is defined by i (h) =h i. So, which agrees with the earlier terminology. (h) = 1 (h) (h) =h 1 h Exercise 9... Generalize this correspondenc to show that Example is the root system for sl(n, F ). An animation of A 3 = D 3, the root system of sl(4,f) is on the webpage. In that rotating figure, the green arrow is = 1, the red arrow is β = 3 and the blue arrow is γ = 3 4. The angles are:, β =, β,γ =, θ =π/3 θ =π/3, γ =0, θ = π/ The white arrow is the sum of these three roots: + β + γ = 1 4. Note that all roots have the same length:.
4 38 MATH 3A NOTES 011 LIE ALGEBRAS 9... root system B = C. Suppose that β, =. Then β = and θ = 3π/4. Also σ (β) =β β, = β + β β + β + β β β This root system has short roots of length 1 and long roots of length. Exercise Show that the 6 vectors in R 3 given by ± i (6vectors), ± i ± j (1vectors), ± 1 ± ± 3 (8vectors) do not form a root system. (These vectors form a cube just as the figure above forms a square.) Definition The root system B n in R n is defined to be the union of the set of n short roots ± i and the 4 n long roots ±i ± j. The long roots of B n form a subsystem D n as in Example (3) and the short roots form A n 1 as in Example (1). For example, for n = 3, there are 6 short roots and 1 long roots and these long roots form D 3 = A 3. Definition The root system C n in R n is defined to be the union of the set of n long roots ± i and the 4 n short roots ±i ± j. The short roots of C n form a subsystem D n.forn = 3 there are 1 short roots and 6 long roots. The case B 3,C 3 can be seen in these animations: B 3, C 3. The short roots are red and the long roots are blue in both root system G. Suppose that β, = 3. Then β = 3 and θ =5π/6. Also σ (β) =β β, = β +3
5 MATH 3A NOTES 011 LIE ALGEBRAS 39 β +3 β β + β + β +3 β 3 β β β β root system A 1 A 1. When β, = 0 the two roots are perpendicular. They could have any length. β This is the root system of sl(,f) sl(,f) Irreducible root systems. β Definition We say that a root system Φ decomposes if it is a disjoint union Φ 1 Φ of two nonempty subsets so that every root in Φ 1 is perpendicular to every root of Φ. We say that Φ is irreducible if there is no such decomposition. If Φ decomposes, then E also decomposes as an orthogonal direct sum E = E 1 E where E i is the span of Φ i.eachφ i E i is a root system. Exercise Show that the root system of a product L = L 1 L of two semisimple Lie algebras decomposes as the union of the root systems of L 1,L. Conversely, any decomposition of the root system of L comes from such a factorization of L. Proposition The decomposition of a root system Φ into irreducible components is unique. Proof. If Φ = Φ i and Φ = Ψ j are any two decompositions then so is Φ = Φ i Ψ j.
6 40 MATH 3A NOTES 011 LIE ALGEBRAS 9.4. Bases for root systems. Definition A subset = { 1,,, n } of Φ is called a base for the root system if (1) is a basis for E () Every element β Φ can be written as β = k i i where all k i are integers with the same sign (or zero). Given a choice of base, the root in are called simple roots, roots which are positive linear combinations of simple roots are called positive roots the set of positive roots is denoted Φ +. The set of negative roots (negatives of positive roots) is Φ. Thus Φ=Φ + Φ Example In the root systems A,B,G,A 1 A 1 above, the roots, β were chosen to form a base for the root system. Example In the root system A n 1 = { i j R n } the roots i := i i+1, i =1,,n 1 form a base. In the A 3 -animation, the simple roots are green, red and blue. Example In the second set of animations for the root systems B 3 and C 3 the simple roots have green tips, and the positive roots are in the foreground (with negative roots behind a semitransparent plane). Lemma If, β Φ and (, β) < 0 then + β is a root. Similarly, if (, β) > 0 then β is a root. Proof. By symmetry we may assume, β = ±1 and this has the same sign as (, β). Then + β if (, β) < 0 σ β () = β if (, β) > 0 and σ β () Φ by definition of root system. Theorem Every root system has a base. Proof. First choose a vector x which is not perpendicular to any root. Since there are only finitely many roots and their perpendicular hyperplane have zero measure, their union also has zero measure. Take any point in the complement. Define a root β Φtobepositive if (β,x) > 0. Let S be the set of all real numbers (β,x) > 0forβ Φ. Then S is finite. Define a positive root to be indecomposable if it cannot be written as a sum of other positive roots. Claim 1 Every positive root β can be written as a sum of indecomposable positive roots. Pf: This holds by induction on the number of elements in the set S which are less than (β,x). If this number is zero then β is indecomposable. If β decomposes into a sum β = β 1 +β, we have (β i,x) < (β,x). So, by induction, each β i is a sum of indecomposable positive roots.
7 MATH 3A NOTES 011 LIE ALGEBRAS 41 Claim If, β are indecomposable positive roots then (, β) 0. Pf: If (, β) > 0 then γ = β is a root and therefore either γ or γ is a positive room. In the first case, = β +γ is not indecomposable. In the second case, β = +( γ) is not indecomposable. Claim 3 Let be the set of indecomposable positive roots. Then is a base for Φ. Pf: Since the second condition in the definition of a base is satisfied by construction, it suffices to show that is a basis for E. Since spans Φ it also spans E. So, it suffices to show is linearly independent. Suppose not. Then there is a linear dependence k i i = 0 where i. Separate the positive and negative coefficients κ i to obtain a relation: si i = t j j where s i,t j are all 0 and i = j. Let z denote this sum. Then (z,z) = s i t j ( i, j ) 0 by Claim. So, z = 0 proving Claim 3 and the theorem.
Lecture Notes Introduction to Cluster Algebra
 Lecture Notes Introduction to Cluster Algebra Ivan C.H. Ip Update: May 16, 2017 5 Review of Root Systems In this section, let us have a brief introduction to root system and finite Lie type classification
Lecture Notes Introduction to Cluster Algebra Ivan C.H. Ip Update: May 16, 2017 5 Review of Root Systems In this section, let us have a brief introduction to root system and finite Lie type classification
Classification of semisimple Lie algebras
 Chapter 6 Classification of semisimple Lie algebras When we studied sl 2 (C), we discovered that it is spanned by elements e, f and h fulfilling the relations: [e, h] = 2e, [ f, h] = 2 f and [e, f ] =
Chapter 6 Classification of semisimple Lie algebras When we studied sl 2 (C), we discovered that it is spanned by elements e, f and h fulfilling the relations: [e, h] = 2e, [ f, h] = 2 f and [e, f ] =
Root systems. S. Viswanath
 Root systems S. Viswanath 1. (05/07/011) 1.1. Root systems. Let V be a finite dimensional R-vector space. A reflection is a linear map s α,h on V satisfying s α,h (x) = x for all x H and s α,h (α) = α,
Root systems S. Viswanath 1. (05/07/011) 1.1. Root systems. Let V be a finite dimensional R-vector space. A reflection is a linear map s α,h on V satisfying s α,h (x) = x for all x H and s α,h (α) = α,
ROOT SYSTEMS AND DYNKIN DIAGRAMS
 ROOT SYSTEMS AND DYNKIN DIAGRAMS DAVID MEHRLE In 1969, Murray Gell-Mann won the nobel prize in physics for his contributions and discoveries concerning the classification of elementary particles and their
ROOT SYSTEMS AND DYNKIN DIAGRAMS DAVID MEHRLE In 1969, Murray Gell-Mann won the nobel prize in physics for his contributions and discoveries concerning the classification of elementary particles and their
Classification of root systems
 Classification of root systems September 8, 2017 1 Introduction These notes are an approximate outline of some of the material to be covered on Thursday, April 9; Tuesday, April 14; and Thursday, April
Classification of root systems September 8, 2017 1 Introduction These notes are an approximate outline of some of the material to be covered on Thursday, April 9; Tuesday, April 14; and Thursday, April
PROPERTIES OF SIMPLE ROOTS
 PROPERTIES OF SIMPLE ROOTS ERIC BRODER Let V be a Euclidean space, that is a finite dimensional real linear space with a symmetric positive definite inner product,. Recall that for a root system Δ in V,
PROPERTIES OF SIMPLE ROOTS ERIC BRODER Let V be a Euclidean space, that is a finite dimensional real linear space with a symmetric positive definite inner product,. Recall that for a root system Δ in V,
A 2 G 2 A 1 A 1. (3) A double edge pointing from α i to α j if α i, α j are not perpendicular and α i 2 = 2 α j 2
 46 MATH 223A NOTES 2011 LIE ALGEBRAS 11. Classification of semisimple Lie algebras I will explain how the Cartan matrix and Dynkin diagrams describe root systems. Then I will go through the classification
46 MATH 223A NOTES 2011 LIE ALGEBRAS 11. Classification of semisimple Lie algebras I will explain how the Cartan matrix and Dynkin diagrams describe root systems. Then I will go through the classification
QUIVERS AND LATTICES.
 QUIVERS AND LATTICES. KEVIN MCGERTY We will discuss two classification results in quite different areas which turn out to have the same answer. This note is an slightly expanded version of the talk given
QUIVERS AND LATTICES. KEVIN MCGERTY We will discuss two classification results in quite different areas which turn out to have the same answer. This note is an slightly expanded version of the talk given
L(C G (x) 0 ) c g (x). Proof. Recall C G (x) = {g G xgx 1 = g} and c g (x) = {X g Ad xx = X}. In general, it is obvious that
 ALGEBRAIC GROUPS 61 5. Root systems and semisimple Lie algebras 5.1. Characteristic 0 theory. Assume in this subsection that chark = 0. Let me recall a couple of definitions made earlier: G is called reductive
ALGEBRAIC GROUPS 61 5. Root systems and semisimple Lie algebras 5.1. Characteristic 0 theory. Assume in this subsection that chark = 0. Let me recall a couple of definitions made earlier: G is called reductive
Background on Chevalley Groups Constructed from a Root System
 Background on Chevalley Groups Constructed from a Root System Paul Tokorcheck Department of Mathematics University of California, Santa Cruz 10 October 2011 Abstract In 1955, Claude Chevalley described
Background on Chevalley Groups Constructed from a Root System Paul Tokorcheck Department of Mathematics University of California, Santa Cruz 10 October 2011 Abstract In 1955, Claude Chevalley described
REPRESENTATION THEORY OF S n
 REPRESENTATION THEORY OF S n EVAN JENKINS Abstract. These are notes from three lectures given in MATH 26700, Introduction to Representation Theory of Finite Groups, at the University of Chicago in November
REPRESENTATION THEORY OF S n EVAN JENKINS Abstract. These are notes from three lectures given in MATH 26700, Introduction to Representation Theory of Finite Groups, at the University of Chicago in November
Classification of Root Systems
 U.U.D.M. Project Report 2018:30 Classification of Root Systems Filip Koerfer Examensarbete i matematik, 15 hp Handledare: Jakob Zimmermann Examinator: Martin Herschend Juni 2018 Department of Mathematics
U.U.D.M. Project Report 2018:30 Classification of Root Systems Filip Koerfer Examensarbete i matematik, 15 hp Handledare: Jakob Zimmermann Examinator: Martin Herschend Juni 2018 Department of Mathematics
REFLECTIONS IN A EUCLIDEAN SPACE
 REFLECTIONS IN A EUCLIDEAN SPACE PHILIP BROCOUM Let V be a finite dimensional real linear space. Definition 1. A function, : V V R is a bilinear form in V if for all x 1, x, x, y 1, y, y V and all k R,
REFLECTIONS IN A EUCLIDEAN SPACE PHILIP BROCOUM Let V be a finite dimensional real linear space. Definition 1. A function, : V V R is a bilinear form in V if for all x 1, x, x, y 1, y, y V and all k R,
Some notes on Coxeter groups
 Some notes on Coxeter groups Brooks Roberts November 28, 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Sources 2 2 Reflections 3 3 The orthogonal group 7 4 Finite subgroups in two dimensions 9 5 Finite subgroups in three
Some notes on Coxeter groups Brooks Roberts November 28, 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Sources 2 2 Reflections 3 3 The orthogonal group 7 4 Finite subgroups in two dimensions 9 5 Finite subgroups in three
The classification of root systems
 The classification of root systems Maris Ozols University of Waterloo Department of C&O November 28, 2007 Definition of the root system Definition Let E = R n be a real vector space. A finite subset R
The classification of root systems Maris Ozols University of Waterloo Department of C&O November 28, 2007 Definition of the root system Definition Let E = R n be a real vector space. A finite subset R
Weyl s Character Formula for Representations of Semisimple Lie Algebras
 Weyl s Character Formula for Representations of Semisimple Lie Algebras Ben Reason University of Toronto December 22, 2005 1 Introduction Weyl s character formula is a useful tool in understanding the
Weyl s Character Formula for Representations of Semisimple Lie Algebras Ben Reason University of Toronto December 22, 2005 1 Introduction Weyl s character formula is a useful tool in understanding the
LIE ALGEBRAS: LECTURE 7 11 May 2010
 LIE ALGEBRAS: LECTURE 7 11 May 2010 CRYSTAL HOYT 1. sl n (F) is simple Let F be an algebraically closed field with characteristic zero. Let V be a finite dimensional vector space. Recall, that f End(V
LIE ALGEBRAS: LECTURE 7 11 May 2010 CRYSTAL HOYT 1. sl n (F) is simple Let F be an algebraically closed field with characteristic zero. Let V be a finite dimensional vector space. Recall, that f End(V
Math 306 Topics in Algebra, Spring 2013 Homework 7 Solutions
 Math 306 Topics in Algebra, Spring 203 Homework 7 Solutions () (5 pts) Let G be a finite group. Show that the function defines an inner product on C[G]. We have Also Lastly, we have C[G] C[G] C c f + c
Math 306 Topics in Algebra, Spring 203 Homework 7 Solutions () (5 pts) Let G be a finite group. Show that the function defines an inner product on C[G]. We have Also Lastly, we have C[G] C[G] C c f + c
SIMPLE AND POSITIVE ROOTS
 SIMPLE AND POSITIVE ROOTS JUHA VALKAMA MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Let V be a Euclidean space, i.e. a real finite dimensional linear space with a symmetric positive definite inner product,. We
SIMPLE AND POSITIVE ROOTS JUHA VALKAMA MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Let V be a Euclidean space, i.e. a real finite dimensional linear space with a symmetric positive definite inner product,. We
We simply compute: for v = x i e i, bilinearity of B implies that Q B (v) = B(v, v) is given by xi x j B(e i, e j ) =
 Math 395. Quadratic spaces over R 1. Algebraic preliminaries Let V be a vector space over a field F. Recall that a quadratic form on V is a map Q : V F such that Q(cv) = c 2 Q(v) for all v V and c F, and
Math 395. Quadratic spaces over R 1. Algebraic preliminaries Let V be a vector space over a field F. Recall that a quadratic form on V is a map Q : V F such that Q(cv) = c 2 Q(v) for all v V and c F, and
Particles I, Tutorial notes Sessions I-III: Roots & Weights
 Particles I, Tutorial notes Sessions I-III: Roots & Weights Kfir Blum June, 008 Comments/corrections regarding these notes will be appreciated. My Email address is: kf ir.blum@weizmann.ac.il Contents 1
Particles I, Tutorial notes Sessions I-III: Roots & Weights Kfir Blum June, 008 Comments/corrections regarding these notes will be appreciated. My Email address is: kf ir.blum@weizmann.ac.il Contents 1
BLOCKS IN THE CATEGORY OF FINITE-DIMENSIONAL REPRESENTATIONS OF gl(m n)
 BLOCKS IN THE CATEGORY OF FINITE-DIMENSIONAL REPRESENTATIONS OF gl(m n) VERA SERGANOVA Abstract. We decompose the category of finite-dimensional gl (m n)- modules into the direct sum of blocks, show that
BLOCKS IN THE CATEGORY OF FINITE-DIMENSIONAL REPRESENTATIONS OF gl(m n) VERA SERGANOVA Abstract. We decompose the category of finite-dimensional gl (m n)- modules into the direct sum of blocks, show that
Longest element of a finite Coxeter group
 Longest element of a finite Coxeter group September 10, 2015 Here we draw together some well-known properties of the (unique) longest element w in a finite Coxeter group W, with reference to theorems and
Longest element of a finite Coxeter group September 10, 2015 Here we draw together some well-known properties of the (unique) longest element w in a finite Coxeter group W, with reference to theorems and
Enhanced Dynkin diagrams and Weyl orbits
 Enhanced Dynkin diagrams and Weyl orbits E. B. Dynkin and A. N. Minchenko February 3, 010 Abstract The root system Σ of a complex semisimple Lie algebra is uniquely determined by its basis (also called
Enhanced Dynkin diagrams and Weyl orbits E. B. Dynkin and A. N. Minchenko February 3, 010 Abstract The root system Σ of a complex semisimple Lie algebra is uniquely determined by its basis (also called
Lie Algebras. Shlomo Sternberg
 Lie Algebras Shlomo Sternberg March 8, 2004 2 Chapter 5 Conjugacy of Cartan subalgebras It is a standard theorem in linear algebra that any unitary matrix can be diagonalized (by conjugation by unitary
Lie Algebras Shlomo Sternberg March 8, 2004 2 Chapter 5 Conjugacy of Cartan subalgebras It is a standard theorem in linear algebra that any unitary matrix can be diagonalized (by conjugation by unitary
CHAPTER 6. Representations of compact groups
 CHAPTER 6 Representations of compact groups Throughout this chapter, denotes a compact group. 6.1. Examples of compact groups A standard theorem in elementary analysis says that a subset of C m (m a positive
CHAPTER 6 Representations of compact groups Throughout this chapter, denotes a compact group. 6.1. Examples of compact groups A standard theorem in elementary analysis says that a subset of C m (m a positive
NOTES ON POLYNOMIAL REPRESENTATIONS OF GENERAL LINEAR GROUPS
 NOTES ON POLYNOMIAL REPRESENTATIONS OF GENERAL LINEAR GROUPS MARK WILDON Contents 1. Definition of polynomial representations 1 2. Weight spaces 3 3. Definition of the Schur functor 7 4. Appendix: some
NOTES ON POLYNOMIAL REPRESENTATIONS OF GENERAL LINEAR GROUPS MARK WILDON Contents 1. Definition of polynomial representations 1 2. Weight spaces 3 3. Definition of the Schur functor 7 4. Appendix: some
THE EULER CHARACTERISTIC OF A LIE GROUP
 THE EULER CHARACTERISTIC OF A LIE GROUP JAY TAYLOR 1 Examples of Lie Groups The following is adapted from [2] We begin with the basic definition and some core examples Definition A Lie group is a smooth
THE EULER CHARACTERISTIC OF A LIE GROUP JAY TAYLOR 1 Examples of Lie Groups The following is adapted from [2] We begin with the basic definition and some core examples Definition A Lie group is a smooth
Typical Problem: Compute.
 Math 2040 Chapter 6 Orhtogonality and Least Squares 6.1 and some of 6.7: Inner Product, Length and Orthogonality. Definition: If x, y R n, then x y = x 1 y 1 +... + x n y n is the dot product of x and
Math 2040 Chapter 6 Orhtogonality and Least Squares 6.1 and some of 6.7: Inner Product, Length and Orthogonality. Definition: If x, y R n, then x y = x 1 y 1 +... + x n y n is the dot product of x and
Root systems and optimal block designs
 Root systems and optimal block designs Peter J. Cameron School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary, University of London Mile End Road London E1 4NS, UK p.j.cameron@qmul.ac.uk Abstract Motivated by a question
Root systems and optimal block designs Peter J. Cameron School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary, University of London Mile End Road London E1 4NS, UK p.j.cameron@qmul.ac.uk Abstract Motivated by a question
AN UPPER BOUND FOR SIGNATURES OF IRREDUCIBLE, SELF-DUAL gl(n, C)-REPRESENTATIONS
 AN UPPER BOUND FOR SIGNATURES OF IRREDUCIBLE, SELF-DUAL gl(n, C)-REPRESENTATIONS CHRISTOPHER XU UROP+ Summer 2018 Mentor: Daniil Kalinov Project suggested by David Vogan Abstract. For every irreducible,
AN UPPER BOUND FOR SIGNATURES OF IRREDUCIBLE, SELF-DUAL gl(n, C)-REPRESENTATIONS CHRISTOPHER XU UROP+ Summer 2018 Mentor: Daniil Kalinov Project suggested by David Vogan Abstract. For every irreducible,
Section II.1. Free Abelian Groups
 II.1. Free Abelian Groups 1 Section II.1. Free Abelian Groups Note. This section and the next, are independent of the rest of this chapter. The primary use of the results of this chapter is in the proof
II.1. Free Abelian Groups 1 Section II.1. Free Abelian Groups Note. This section and the next, are independent of the rest of this chapter. The primary use of the results of this chapter is in the proof
Since G is a compact Lie group, we can apply Schur orthogonality to see that G χ π (g) 2 dg =
 Problem 1 Show that if π is an irreducible representation of a compact lie group G then π is also irreducible. Give an example of a G and π such that π = π, and another for which π π. Is this true for
Problem 1 Show that if π is an irreducible representation of a compact lie group G then π is also irreducible. Give an example of a G and π such that π = π, and another for which π π. Is this true for
Schur s Triangularization Theorem. Math 422
 Schur s Triangularization Theorem Math 4 The characteristic polynomial p (t) of a square complex matrix A splits as a product of linear factors of the form (t λ) m Of course, finding these factors is a
Schur s Triangularization Theorem Math 4 The characteristic polynomial p (t) of a square complex matrix A splits as a product of linear factors of the form (t λ) m Of course, finding these factors is a
Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra)
 Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra) I.0 : Background Note. There is no corresponding section in the course notes, but as noted at the beginning of Unit I these are a few exercises which involve
Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra) I.0 : Background Note. There is no corresponding section in the course notes, but as noted at the beginning of Unit I these are a few exercises which involve
The Cartan Decomposition of a Complex Semisimple Lie Algebra
 The Cartan Decomposition of a Complex Semisimple Lie Algebra Shawn Baland University of Colorado, Boulder November 29, 2007 Definition Let k be a field. A k-algebra is a k-vector space A equipped with
The Cartan Decomposition of a Complex Semisimple Lie Algebra Shawn Baland University of Colorado, Boulder November 29, 2007 Definition Let k be a field. A k-algebra is a k-vector space A equipped with
Welsh s problem on the number of bases of matroids
 Welsh s problem on the number of bases of matroids Edward S. T. Fan 1 and Tony W. H. Wong 2 1 Department of Mathematics, California Institute of Technology 2 Department of Mathematics, Kutztown University
Welsh s problem on the number of bases of matroids Edward S. T. Fan 1 and Tony W. H. Wong 2 1 Department of Mathematics, California Institute of Technology 2 Department of Mathematics, Kutztown University
Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra)
 Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra) I.0 : Background This does not correspond to a section in the course notes, but as noted at the beginning of Unit I it contains some exercises which involve
Exercises for Unit I (Topics from linear algebra) I.0 : Background This does not correspond to a section in the course notes, but as noted at the beginning of Unit I it contains some exercises which involve
MATH Linear Algebra
 MATH 304 - Linear Algebra In the previous note we learned an important algorithm to produce orthogonal sequences of vectors called the Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization process. Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization
MATH 304 - Linear Algebra In the previous note we learned an important algorithm to produce orthogonal sequences of vectors called the Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization process. Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization
Math Linear Algebra
 Math 220 - Linear Algebra (Summer 208) Solutions to Homework #7 Exercise 6..20 (a) TRUE. u v v u = 0 is equivalent to u v = v u. The latter identity is true due to the commutative property of the inner
Math 220 - Linear Algebra (Summer 208) Solutions to Homework #7 Exercise 6..20 (a) TRUE. u v v u = 0 is equivalent to u v = v u. The latter identity is true due to the commutative property of the inner
FILTRATIONS IN SEMISIMPLE LIE ALGEBRAS, I
 TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 00, Number 0, Pages 000 000 S 0002-9947(XX)0000-0 FILTRATIONS IN SEMISIMPLE LIE ALGEBRAS, I Y. BARNEA AND D. S. PASSMAN Abstract. In this paper,
TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 00, Number 0, Pages 000 000 S 0002-9947(XX)0000-0 FILTRATIONS IN SEMISIMPLE LIE ALGEBRAS, I Y. BARNEA AND D. S. PASSMAN Abstract. In this paper,
Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality
 Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Linear Algebra MATH 2076 Linear Algebra,, Chapter 6, Section 1 1 / 13 Algebraic Definition for Dot Product u 1 v 1 u 2 Let u =., v = v 2. be vectors in Rn. The
Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Linear Algebra MATH 2076 Linear Algebra,, Chapter 6, Section 1 1 / 13 Algebraic Definition for Dot Product u 1 v 1 u 2 Let u =., v = v 2. be vectors in Rn. The
5 Quiver Representations
 5 Quiver Representations 5. Problems Problem 5.. Field embeddings. Recall that k(y,..., y m ) denotes the field of rational functions of y,..., y m over a field k. Let f : k[x,..., x n ] k(y,..., y m )
5 Quiver Representations 5. Problems Problem 5.. Field embeddings. Recall that k(y,..., y m ) denotes the field of rational functions of y,..., y m over a field k. Let f : k[x,..., x n ] k(y,..., y m )
Highest-weight Theory: Verma Modules
 Highest-weight Theory: Verma Modules Math G4344, Spring 2012 We will now turn to the problem of classifying and constructing all finitedimensional representations of a complex semi-simple Lie algebra (or,
Highest-weight Theory: Verma Modules Math G4344, Spring 2012 We will now turn to the problem of classifying and constructing all finitedimensional representations of a complex semi-simple Lie algebra (or,
Review of Linear Algebra
 Review of Linear Algebra Definitions An m n (read "m by n") matrix, is a rectangular array of entries, where m is the number of rows and n the number of columns. 2 Definitions (Con t) A is square if m=
Review of Linear Algebra Definitions An m n (read "m by n") matrix, is a rectangular array of entries, where m is the number of rows and n the number of columns. 2 Definitions (Con t) A is square if m=
Math 396. An application of Gram-Schmidt to prove connectedness
 Math 396. An application of Gram-Schmidt to prove connectedness 1. Motivation and background Let V be an n-dimensional vector space over R, and define GL(V ) to be the set of invertible linear maps V V
Math 396. An application of Gram-Schmidt to prove connectedness 1. Motivation and background Let V be an n-dimensional vector space over R, and define GL(V ) to be the set of invertible linear maps V V
The Geometry of Root Systems. Brian C. Hall
 The Geometry of Root Systems A E Z S Brian C. Hall T G R S T G R S 1 1. I Root systems arise in the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebras, but can also be studied as mathematical objects in their own right.
The Geometry of Root Systems A E Z S Brian C. Hall T G R S T G R S 1 1. I Root systems arise in the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebras, but can also be studied as mathematical objects in their own right.
Solutions of exercise sheet 8
 D-MATH Algebra I HS 14 Prof. Emmanuel Kowalski Solutions of exercise sheet 8 1. In this exercise, we will give a characterization for solvable groups using commutator subgroups. See last semester s (Algebra
D-MATH Algebra I HS 14 Prof. Emmanuel Kowalski Solutions of exercise sheet 8 1. In this exercise, we will give a characterization for solvable groups using commutator subgroups. See last semester s (Algebra
Solutions of exercise sheet 6
 D-MATH Algebra I HS 14 Prof. Emmanuel Kowalski Solutions of exercise sheet 6 1. (Irreducibility of the cyclotomic polynomial) Let n be a positive integer, and P Z[X] a monic irreducible factor of X n 1
D-MATH Algebra I HS 14 Prof. Emmanuel Kowalski Solutions of exercise sheet 6 1. (Irreducibility of the cyclotomic polynomial) Let n be a positive integer, and P Z[X] a monic irreducible factor of X n 1
Category O and its basic properties
 Category O and its basic properties Daniil Kalinov 1 Definitions Let g denote a semisimple Lie algebra over C with fixed Cartan and Borel subalgebras h b g. Define n = α>0 g α, n = α
Category O and its basic properties Daniil Kalinov 1 Definitions Let g denote a semisimple Lie algebra over C with fixed Cartan and Borel subalgebras h b g. Define n = α>0 g α, n = α
The Symmetric Space for SL n (R)
 The Symmetric Space for SL n (R) Rich Schwartz November 27, 2013 The purpose of these notes is to discuss the symmetric space X on which SL n (R) acts. Here, as usual, SL n (R) denotes the group of n n
The Symmetric Space for SL n (R) Rich Schwartz November 27, 2013 The purpose of these notes is to discuss the symmetric space X on which SL n (R) acts. Here, as usual, SL n (R) denotes the group of n n
ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY I - FINAL PROJECT
 ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY I - FINAL PROJECT ADAM KAYE Abstract This paper begins with a description of the Schubert varieties of a Grassmannian variety Gr(k, n) over C Following the technique of Ryan [3] for
ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY I - FINAL PROJECT ADAM KAYE Abstract This paper begins with a description of the Schubert varieties of a Grassmannian variety Gr(k, n) over C Following the technique of Ryan [3] for
4.4 Noetherian Rings
 4.4 Noetherian Rings Recall that a ring A is Noetherian if it satisfies the following three equivalent conditions: (1) Every nonempty set of ideals of A has a maximal element (the maximal condition); (2)
4.4 Noetherian Rings Recall that a ring A is Noetherian if it satisfies the following three equivalent conditions: (1) Every nonempty set of ideals of A has a maximal element (the maximal condition); (2)
Chapter 2 Linear Transformations
 Chapter 2 Linear Transformations Linear Transformations Loosely speaking, a linear transformation is a function from one vector space to another that preserves the vector space operations. Let us be more
Chapter 2 Linear Transformations Linear Transformations Loosely speaking, a linear transformation is a function from one vector space to another that preserves the vector space operations. Let us be more
Introduction to Association Schemes
 Introduction to Association Schemes Akihiro Munemasa Tohoku University June 5 6, 24 Algebraic Combinatorics Summer School, Sendai Assumed results (i) Vandermonde determinant: a a m =. a m a m m i
Introduction to Association Schemes Akihiro Munemasa Tohoku University June 5 6, 24 Algebraic Combinatorics Summer School, Sendai Assumed results (i) Vandermonde determinant: a a m =. a m a m m i
Cartan s Criteria. Math 649, Dan Barbasch. February 26
 Cartan s Criteria Math 649, 2013 Dan Barbasch February 26 Cartan s Criteria REFERENCES: Humphreys, I.2 and I.3. Definition The Cartan-Killing form of a Lie algebra is the bilinear form B(x, y) := Tr(ad
Cartan s Criteria Math 649, 2013 Dan Barbasch February 26 Cartan s Criteria REFERENCES: Humphreys, I.2 and I.3. Definition The Cartan-Killing form of a Lie algebra is the bilinear form B(x, y) := Tr(ad
Matrices and Matrix Algebra.
 Matrices and Matrix Algebra 3.1. Operations on Matrices Matrix Notation and Terminology Matrix: a rectangular array of numbers, called entries. A matrix with m rows and n columns m n A n n matrix : a square
Matrices and Matrix Algebra 3.1. Operations on Matrices Matrix Notation and Terminology Matrix: a rectangular array of numbers, called entries. A matrix with m rows and n columns m n A n n matrix : a square
LECTURE 25-26: CARTAN S THEOREM OF MAXIMAL TORI. 1. Maximal Tori
 LECTURE 25-26: CARTAN S THEOREM OF MAXIMAL TORI 1. Maximal Tori By a torus we mean a compact connected abelian Lie group, so a torus is a Lie group that is isomorphic to T n = R n /Z n. Definition 1.1.
LECTURE 25-26: CARTAN S THEOREM OF MAXIMAL TORI 1. Maximal Tori By a torus we mean a compact connected abelian Lie group, so a torus is a Lie group that is isomorphic to T n = R n /Z n. Definition 1.1.
Math 210C. The representation ring
 Math 210C. The representation ring 1. Introduction Let G be a nontrivial connected compact Lie group that is semisimple and simply connected (e.g., SU(n) for n 2, Sp(n) for n 1, or Spin(n) for n 3). Let
Math 210C. The representation ring 1. Introduction Let G be a nontrivial connected compact Lie group that is semisimple and simply connected (e.g., SU(n) for n 2, Sp(n) for n 1, or Spin(n) for n 3). Let
THE THEOREM OF THE HIGHEST WEIGHT
 THE THEOREM OF THE HIGHEST WEIGHT ANKE D. POHL Abstract. Incomplete notes of the talk in the IRTG Student Seminar 07.06.06. This is a draft version and thought for internal use only. The Theorem of the
THE THEOREM OF THE HIGHEST WEIGHT ANKE D. POHL Abstract. Incomplete notes of the talk in the IRTG Student Seminar 07.06.06. This is a draft version and thought for internal use only. The Theorem of the
Lattice Theory Lecture 4. Non-distributive lattices
 Lattice Theory Lecture 4 Non-distributive lattices John Harding New Mexico State University www.math.nmsu.edu/ JohnHarding.html jharding@nmsu.edu Toulouse, July 2017 Introduction Here we mostly consider
Lattice Theory Lecture 4 Non-distributive lattices John Harding New Mexico State University www.math.nmsu.edu/ JohnHarding.html jharding@nmsu.edu Toulouse, July 2017 Introduction Here we mostly consider
Elementary linear algebra
 Chapter 1 Elementary linear algebra 1.1 Vector spaces Vector spaces owe their importance to the fact that so many models arising in the solutions of specific problems turn out to be vector spaces. The
Chapter 1 Elementary linear algebra 1.1 Vector spaces Vector spaces owe their importance to the fact that so many models arising in the solutions of specific problems turn out to be vector spaces. The
UC Berkeley Summer Undergraduate Research Program 2015 July 9 Lecture
 UC Berkeley Summer Undergraduate Research Program 205 July 9 Lecture We will introduce the basic structure and representation theory of the symplectic group Sp(V ). Basics Fix a nondegenerate, alternating
UC Berkeley Summer Undergraduate Research Program 205 July 9 Lecture We will introduce the basic structure and representation theory of the symplectic group Sp(V ). Basics Fix a nondegenerate, alternating
ALGEBRAIC GROUPS J. WARNER
 ALGEBRAIC GROUPS J. WARNER Let k be an algebraically closed field. varieties unless otherwise stated. 1. Definitions and Examples For simplicity we will work strictly with affine Definition 1.1. An algebraic
ALGEBRAIC GROUPS J. WARNER Let k be an algebraically closed field. varieties unless otherwise stated. 1. Definitions and Examples For simplicity we will work strictly with affine Definition 1.1. An algebraic
Math 2070BC Term 2 Weeks 1 13 Lecture Notes
 Math 2070BC 2017 18 Term 2 Weeks 1 13 Lecture Notes Keywords: group operation multiplication associative identity element inverse commutative abelian group Special Linear Group order infinite order cyclic
Math 2070BC 2017 18 Term 2 Weeks 1 13 Lecture Notes Keywords: group operation multiplication associative identity element inverse commutative abelian group Special Linear Group order infinite order cyclic
Ir O D = D = ( ) Section 2.6 Example 1. (Bottom of page 119) dim(v ) = dim(l(v, W )) = dim(v ) dim(f ) = dim(v )
 Section 3.2 Theorem 3.6. Let A be an m n matrix of rank r. Then r m, r n, and, by means of a finite number of elementary row and column operations, A can be transformed into the matrix ( ) Ir O D = 1 O
Section 3.2 Theorem 3.6. Let A be an m n matrix of rank r. Then r m, r n, and, by means of a finite number of elementary row and column operations, A can be transformed into the matrix ( ) Ir O D = 1 O
The Real Grassmannian Gr(2, 4)
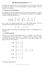 The Real Grassmannian Gr(2, 4) We discuss the topology of the real Grassmannian Gr(2, 4) of 2-planes in R 4 and its double cover Gr + (2, 4) by the Grassmannian of oriented 2-planes They are compact four-manifolds
The Real Grassmannian Gr(2, 4) We discuss the topology of the real Grassmannian Gr(2, 4) of 2-planes in R 4 and its double cover Gr + (2, 4) by the Grassmannian of oriented 2-planes They are compact four-manifolds
arxiv: v1 [math.rt] 15 Oct 2008
![arxiv: v1 [math.rt] 15 Oct 2008 arxiv: v1 [math.rt] 15 Oct 2008](/thumbs/72/66342658.jpg) CLASSIFICATION OF FINITE-GROWTH GENERAL KAC-MOODY SUPERALGEBRAS arxiv:0810.2637v1 [math.rt] 15 Oct 2008 CRYSTAL HOYT AND VERA SERGANOVA Abstract. A contragredient Lie superalgebra is a superalgebra defined
CLASSIFICATION OF FINITE-GROWTH GENERAL KAC-MOODY SUPERALGEBRAS arxiv:0810.2637v1 [math.rt] 15 Oct 2008 CRYSTAL HOYT AND VERA SERGANOVA Abstract. A contragredient Lie superalgebra is a superalgebra defined
Math 249B. Geometric Bruhat decomposition
 Math 249B. Geometric Bruhat decomposition 1. Introduction Let (G, T ) be a split connected reductive group over a field k, and Φ = Φ(G, T ). Fix a positive system of roots Φ Φ, and let B be the unique
Math 249B. Geometric Bruhat decomposition 1. Introduction Let (G, T ) be a split connected reductive group over a field k, and Φ = Φ(G, T ). Fix a positive system of roots Φ Φ, and let B be the unique
Math 396. Quotient spaces
 Math 396. Quotient spaces. Definition Let F be a field, V a vector space over F and W V a subspace of V. For v, v V, we say that v v mod W if and only if v v W. One can readily verify that with this definition
Math 396. Quotient spaces. Definition Let F be a field, V a vector space over F and W V a subspace of V. For v, v V, we say that v v mod W if and only if v v W. One can readily verify that with this definition
Definitions. Notations. Injective, Surjective and Bijective. Divides. Cartesian Product. Relations. Equivalence Relations
 Page 1 Definitions Tuesday, May 8, 2018 12:23 AM Notations " " means "equals, by definition" the set of all real numbers the set of integers Denote a function from a set to a set by Denote the image of
Page 1 Definitions Tuesday, May 8, 2018 12:23 AM Notations " " means "equals, by definition" the set of all real numbers the set of integers Denote a function from a set to a set by Denote the image of
Cambridge University Press The Mathematics of Signal Processing Steven B. Damelin and Willard Miller Excerpt More information
 Introduction Consider a linear system y = Φx where Φ can be taken as an m n matrix acting on Euclidean space or more generally, a linear operator on a Hilbert space. We call the vector x a signal or input,
Introduction Consider a linear system y = Φx where Φ can be taken as an m n matrix acting on Euclidean space or more generally, a linear operator on a Hilbert space. We call the vector x a signal or input,
Math 121 Homework 5: Notes on Selected Problems
 Math 121 Homework 5: Notes on Selected Problems 12.1.2. Let M be a module over the integral domain R. (a) Assume that M has rank n and that x 1,..., x n is any maximal set of linearly independent elements
Math 121 Homework 5: Notes on Selected Problems 12.1.2. Let M be a module over the integral domain R. (a) Assume that M has rank n and that x 1,..., x n is any maximal set of linearly independent elements
Math 21b: Linear Algebra Spring 2018
 Math b: Linear Algebra Spring 08 Homework 8: Basis This homework is due on Wednesday, February 4, respectively on Thursday, February 5, 08. Which of the following sets are linear spaces? Check in each
Math b: Linear Algebra Spring 08 Homework 8: Basis This homework is due on Wednesday, February 4, respectively on Thursday, February 5, 08. Which of the following sets are linear spaces? Check in each
GROUP THEORY PRIMER. New terms: so(2n), so(2n+1), symplectic algebra sp(2n)
 GROUP THEORY PRIMER New terms: so(2n), so(2n+1), symplectic algebra sp(2n) 1. Some examples of semi-simple Lie algebras In the previous chapter, we developed the idea of understanding semi-simple Lie algebras
GROUP THEORY PRIMER New terms: so(2n), so(2n+1), symplectic algebra sp(2n) 1. Some examples of semi-simple Lie algebras In the previous chapter, we developed the idea of understanding semi-simple Lie algebras
AND AFFINE ROOT SYSTEMS
 AFFINE LIE ALGEBRAS AND AFFINE ROOT SYSTEMS A Killing-Cartan type classification of affine Lie algebras, reduced irreducible affine root systems and affine Cartan matrices Jan S. Nauta MSc Thesis under
AFFINE LIE ALGEBRAS AND AFFINE ROOT SYSTEMS A Killing-Cartan type classification of affine Lie algebras, reduced irreducible affine root systems and affine Cartan matrices Jan S. Nauta MSc Thesis under
IRREDUCIBLE REPRESENTATIONS OF SEMISIMPLE LIE ALGEBRAS. Contents
 IRREDUCIBLE REPRESENTATIONS OF SEMISIMPLE LIE ALGEBRAS NEEL PATEL Abstract. The goal of this paper is to study the irreducible representations of semisimple Lie algebras. We will begin by considering two
IRREDUCIBLE REPRESENTATIONS OF SEMISIMPLE LIE ALGEBRAS NEEL PATEL Abstract. The goal of this paper is to study the irreducible representations of semisimple Lie algebras. We will begin by considering two
Homework #2 Solutions Due: September 5, for all n N n 3 = n2 (n + 1) 2 4
 Do the following exercises from the text: Chapter (Section 3):, 1, 17(a)-(b), 3 Prove that 1 3 + 3 + + n 3 n (n + 1) for all n N Proof The proof is by induction on n For n N, let S(n) be the statement
Do the following exercises from the text: Chapter (Section 3):, 1, 17(a)-(b), 3 Prove that 1 3 + 3 + + n 3 n (n + 1) for all n N Proof The proof is by induction on n For n N, let S(n) be the statement
Notes on Lie Algebras
 NEW MEXICO TECH (October 23, 2010) DRAFT Notes on Lie Algebras Ivan G. Avramidi Department of Mathematics New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology Socorro, NM 87801, USA E-mail: iavramid@nmt.edu 1
NEW MEXICO TECH (October 23, 2010) DRAFT Notes on Lie Algebras Ivan G. Avramidi Department of Mathematics New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology Socorro, NM 87801, USA E-mail: iavramid@nmt.edu 1
Weyl orbits of π-systems in Kac-Moody algebras
 Weyl orbits of π-systems in Kac-Moody algebras Krishanu Roy The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai, India (Joint with Lisa Carbone, K N Raghavan, Biswajit Ransingh and Sankaran Viswanath) June
Weyl orbits of π-systems in Kac-Moody algebras Krishanu Roy The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai, India (Joint with Lisa Carbone, K N Raghavan, Biswajit Ransingh and Sankaran Viswanath) June
Chapter 6: Orthogonality
 Chapter 6: Orthogonality (Last Updated: November 7, 7) These notes are derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed). A few theorems have been moved around.. Inner products
Chapter 6: Orthogonality (Last Updated: November 7, 7) These notes are derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed). A few theorems have been moved around.. Inner products
Notes on the Vershik-Okounkov approach to the representation theory of the symmetric groups
 Notes on the Vershik-Okounkov approach to the representation theory of the symmetric groups 1 Introduction These notes 1 contain an expository account of the beautiful new approach to the complex finite
Notes on the Vershik-Okounkov approach to the representation theory of the symmetric groups 1 Introduction These notes 1 contain an expository account of the beautiful new approach to the complex finite
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 0 Fall Linear Algebra. These notes provide a review of basic concepts in linear algebra.
 DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 0 Fall 2016 Linear Algebra These notes provide a review of basic concepts in linear algebra. 1 Vector spaces You are no doubt familiar with vectors in R 2 or R 3, i.e. [ ] 1.1
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 0 Fall 2016 Linear Algebra These notes provide a review of basic concepts in linear algebra. 1 Vector spaces You are no doubt familiar with vectors in R 2 or R 3, i.e. [ ] 1.1
= ϕ r cos θ. 0 cos ξ sin ξ and sin ξ cos ξ. sin ξ 0 cos ξ
 8. The Banach-Tarski paradox May, 2012 The Banach-Tarski paradox is that a unit ball in Euclidean -space can be decomposed into finitely many parts which can then be reassembled to form two unit balls
8. The Banach-Tarski paradox May, 2012 The Banach-Tarski paradox is that a unit ball in Euclidean -space can be decomposed into finitely many parts which can then be reassembled to form two unit balls
Lecture 10 - Representation Theory II: Heuristics
 Lecture 10 - Representation Theory II: Heuristics February 15, 2013 1 Weights 1.1 Weight space decomposition We switch notation from last time. We let Λ indicate a highest weight, and λ to be an arbitrary
Lecture 10 - Representation Theory II: Heuristics February 15, 2013 1 Weights 1.1 Weight space decomposition We switch notation from last time. We let Λ indicate a highest weight, and λ to be an arbitrary
Epilogue: Quivers. Gabriel s Theorem
 Epilogue: Quivers Gabriel s Theorem A figure consisting of several points connected by edges is called a graph. More precisely, a graph is a purely combinatorial object, which is considered given, if a
Epilogue: Quivers Gabriel s Theorem A figure consisting of several points connected by edges is called a graph. More precisely, a graph is a purely combinatorial object, which is considered given, if a
Citation Osaka Journal of Mathematics. 43(2)
 TitleIrreducible representations of the Author(s) Kosuda, Masashi Citation Osaka Journal of Mathematics. 43(2) Issue 2006-06 Date Text Version publisher URL http://hdl.handle.net/094/0396 DOI Rights Osaka
TitleIrreducible representations of the Author(s) Kosuda, Masashi Citation Osaka Journal of Mathematics. 43(2) Issue 2006-06 Date Text Version publisher URL http://hdl.handle.net/094/0396 DOI Rights Osaka
x i e i ) + Q(x n e n ) + ( i<n c ij x i x j
 Math 210A. Quadratic spaces over R 1. Algebraic preliminaries Let V be a finite free module over a nonzero commutative ring F. Recall that a quadratic form on V is a map Q : V F such that Q(cv) = c 2 Q(v)
Math 210A. Quadratic spaces over R 1. Algebraic preliminaries Let V be a finite free module over a nonzero commutative ring F. Recall that a quadratic form on V is a map Q : V F such that Q(cv) = c 2 Q(v)
MATH 101A: ALGEBRA I, PART D: GALOIS THEORY 11
 MATH 101A: ALGEBRA I, PART D: GALOIS THEORY 11 3. Examples I did some examples and explained the theory at the same time. 3.1. roots of unity. Let L = Q(ζ) where ζ = e 2πi/5 is a primitive 5th root of
MATH 101A: ALGEBRA I, PART D: GALOIS THEORY 11 3. Examples I did some examples and explained the theory at the same time. 3.1. roots of unity. Let L = Q(ζ) where ζ = e 2πi/5 is a primitive 5th root of
Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide
 Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide Phil R. Smith, Ph.D. February 28, 20 Homework Problem Sets Organized by Learning Outcomes Test I: Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Lesson. Give examples of
Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide Phil R. Smith, Ph.D. February 28, 20 Homework Problem Sets Organized by Learning Outcomes Test I: Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Lesson. Give examples of
On the Irreducibility of the Commuting Variety of the Symmetric Pair so p+2, so p so 2
 Journal of Lie Theory Volume 16 (2006) 57 65 c 2006 Heldermann Verlag On the Irreducibility of the Commuting Variety of the Symmetric Pair so p+2, so p so 2 Hervé Sabourin and Rupert W.T. Yu Communicated
Journal of Lie Theory Volume 16 (2006) 57 65 c 2006 Heldermann Verlag On the Irreducibility of the Commuting Variety of the Symmetric Pair so p+2, so p so 2 Hervé Sabourin and Rupert W.T. Yu Communicated
Irreducible Representations of symmetric group S n
 Irreducible Representations of symmetric group S n Yin Su 045 Good references: ulton Young tableaux with applications to representation theory and geometry ulton Harris Representation thoery a first course
Irreducible Representations of symmetric group S n Yin Su 045 Good references: ulton Young tableaux with applications to representation theory and geometry ulton Harris Representation thoery a first course
Mic ael Flohr Representation theory of semi-simple Lie algebras: Example su(3) 6. and 20. June 2003
 Handout V for the course GROUP THEORY IN PHYSICS Mic ael Flohr Representation theory of semi-simple Lie algebras: Example su(3) 6. and 20. June 2003 GENERALIZING THE HIGHEST WEIGHT PROCEDURE FROM su(2)
Handout V for the course GROUP THEORY IN PHYSICS Mic ael Flohr Representation theory of semi-simple Lie algebras: Example su(3) 6. and 20. June 2003 GENERALIZING THE HIGHEST WEIGHT PROCEDURE FROM su(2)
arxiv: v4 [math.rt] 9 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v4 [math.rt] 9 Jun 2017 arxiv: v4 [math.rt] 9 Jun 2017](/thumbs/79/79130807.jpg) ON TANGENT CONES OF SCHUBERT VARIETIES D FUCHS, A KIRILLOV, S MORIER-GENOUD, V OVSIENKO arxiv:1667846v4 [mathrt] 9 Jun 217 Abstract We consider tangent cones of Schubert varieties in the complete flag
ON TANGENT CONES OF SCHUBERT VARIETIES D FUCHS, A KIRILLOV, S MORIER-GENOUD, V OVSIENKO arxiv:1667846v4 [mathrt] 9 Jun 217 Abstract We consider tangent cones of Schubert varieties in the complete flag
REPRESENTATIONS OF U(N) CLASSIFICATION BY HIGHEST WEIGHTS NOTES FOR MATH 261, FALL 2001
 9 REPRESENTATIONS OF U(N) CLASSIFICATION BY HIGHEST WEIGHTS NOTES FOR MATH 261, FALL 21 ALLEN KNUTSON 1 WEIGHT DIAGRAMS OF -REPRESENTATIONS Let be an -dimensional torus, ie a group isomorphic to The we
9 REPRESENTATIONS OF U(N) CLASSIFICATION BY HIGHEST WEIGHTS NOTES FOR MATH 261, FALL 21 ALLEN KNUTSON 1 WEIGHT DIAGRAMS OF -REPRESENTATIONS Let be an -dimensional torus, ie a group isomorphic to The we
SIMPLE LIE ALGEBRAS AND THEIR CLASSIFICATION
 SIMPLE LIE ALGEBRAS AND THEIR CLASSIFICATION by DRAGOMIR MITKOV TSONEV A thesis submitted to The University of Birmingham for the degree of Master of Philosophy School of Mathematics The University of
SIMPLE LIE ALGEBRAS AND THEIR CLASSIFICATION by DRAGOMIR MITKOV TSONEV A thesis submitted to The University of Birmingham for the degree of Master of Philosophy School of Mathematics The University of
Math 250A, Fall 2004 Problems due October 5, 2004 The problems this week were from Lang s Algebra, Chapter I.
 Math 250A, Fall 2004 Problems due October 5, 2004 The problems this week were from Lang s Algebra, Chapter I. 24. We basically know already that groups of order p 2 are abelian. Indeed, p-groups have non-trivial
Math 250A, Fall 2004 Problems due October 5, 2004 The problems this week were from Lang s Algebra, Chapter I. 24. We basically know already that groups of order p 2 are abelian. Indeed, p-groups have non-trivial
Part III Symmetries, Fields and Particles
 Part III Symmetries, Fields and Particles Theorems Based on lectures by N. Dorey Notes taken by Dexter Chua Michaelmas 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often
Part III Symmetries, Fields and Particles Theorems Based on lectures by N. Dorey Notes taken by Dexter Chua Michaelmas 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often
Math 225B: Differential Geometry, Final
 Math 225B: Differential Geometry, Final Ian Coley March 5, 204 Problem Spring 20,. Show that if X is a smooth vector field on a (smooth) manifold of dimension n and if X p is nonzero for some point of
Math 225B: Differential Geometry, Final Ian Coley March 5, 204 Problem Spring 20,. Show that if X is a smooth vector field on a (smooth) manifold of dimension n and if X p is nonzero for some point of
Topics in Representation Theory: SU(n), Weyl Chambers and the Diagram of a Group
 Topics in Representation Theory: SU(n), Weyl hambers and the Diagram of a Group 1 Another Example: G = SU(n) Last time we began analyzing how the maximal torus T of G acts on the adjoint representation,
Topics in Representation Theory: SU(n), Weyl hambers and the Diagram of a Group 1 Another Example: G = SU(n) Last time we began analyzing how the maximal torus T of G acts on the adjoint representation,
