Reading. 3. Image processing. Pixel movement. Image processing Y R I G Q
|
|
|
- Gerard Watts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reading Jain, Kasturi, Schunck, Machine Vision. McGraw-Hill, Sections , 4.5(intro), 4.5.5, 4.5.6, Image processing 1 Image processing An image processing operation typically defines a new image g in terms of an existing image f. The simplest operations are those that transform each pixel in isolation. These pixel-to-pixel operations can be written: Pixel movement Some operations preserve intensities, but move pixels around in the image gxy (, ) f( xxy (, ), yxy (, )) Examples: many amusing warps of images g( x, y) t( f( x, y)) Examples: threshold, RGB grayscale Note: a typical choice for mapping to grayscale is to apply the YIQ television matrix and keep the Y. Y R I G Q B [Show image sequence.] 3 4
2 Noise Ideal noise reduction Image processing is also useful for noise reduction and edge enhancement. We will focus on these applications for the remainder of the lecture Common types of noise: Salt and pepper noise: contains random occurrences of black and white pixels Impulse noise: contains random occurrences of white pixels Gaussian noise: variations in intensity drawn from a Gaussian normal distribution 5 6 Ideal noise reduction Practical noise reduction How can we smooth away noise in a single image? Is there a more abstract way to represent this sort of operation? Of course there is! 7 8
3 Discrete convolution Discrete convolution in D For a digital signal, we define discrete convolution as: where hi [ ] h[ i]. gi [] f[] i hi [] f['][ i h ii'] i ' i ' f['][' i h ii] Similarly, discrete convolution in D becomes: gi [, j] f[, i j] hi [, j] f[ i', j'] h[ ii', j j'] j' i' f[', i j'][' h ii, j' j] j' i' where hi [, j] h[ i, j] Convolution representation Mean filters Since f and h are defined over finite regions, we can write them out in two-dimensional arrays: How can we represent our noise-reducing averaging filter as a convolution diagram (know as a mean filter)? X. X 0 X. X 0 X. X 0 X. X 0 X. Note: This is not matrix multiplication! Q: What happens at the edges? 11 1
4 Effect of mean filters Gaussian filters Gaussian filters weigh pixels based on their distance from the center of the convolution filter. In particular: h[i, j ] e (i j ) /(V ) C This does a decent job of blurring noise while preserving features of the image. What parameter controls the width of the Gaussian? What happens to the image as the Gaussian filter kernel gets wider? What is the constant C? What should we set it to? 13 Effect of Gaussian filters 14 Median filters A median filter operates over an mxm region by selecting the median intensity in the region. What advantage does a median filter have over a mean filter? Is a median filter a kind of convolution? 15 16
5 Effect of median filters Comparison: Gaussian noise 17 Comparison: salt and pepper noise 18 Edge detection One of the most important uses of image processing is edge detection: Really easy for humans Really difficult for computers Fundamental in computer vision Important in many graphics applications 19 0
6 What is an edge? Gradients The gradient is the D equivalent of the derivative: Properties of the gradient f f f( x, y), x y It s a vector Points in the direction of maximum increase of f Magnitude is rate of increase How can we approximate the gradient in a discrete image? Q: How might you detect an edge in 1D? 1 Less than ideal edges Steps in edge detection Edge detection algorithms typically proceed in three or four steps: Filtering: cut down on noise Enhancement: amplify the difference between edges and non-edges Detection: use a threshold operation Localization (optional): estimate geometry of edges beyond pixels 3 4
7 Edge enhancement Results of Sobel edge detection A popular gradient magnitude computation is the Sobel operator: sx s y We can then compute the magnitude of the vector (s x, s y ). 5 6 Second derivative operators Localization with the Laplacian An equivalent measure of the second derivative in D is the Laplacian: f x f y f( x, y) Using the same arguments we used to compute the gradient filters, we can derive a Laplacian filter to be: The Sobel operator can produce thick edges. Ideally, we re looking for infinitely thin boundaries. An alternative approach is to look for local extrema in the first derivative: places where the change in the gradient is highest. Q: A peak in the first derivative corresponds to what in the second derivative? Zero crossings of this filter correspond to positions of maximum gradient. These zero crossings can be used to localize edges. Q: How might we write this as a convolution filter? 7 8
8 Localization with the Laplacian Marching squares We can convert these signed values into edge contours using a marching squares technique: Original Smoothed Laplacian (+18) 9 30 Sharpening with the Laplacian Spectral impact of sharpening We can look at the impact of sharpening on the Fourier spectrum: Spatial domain Frequency domain Original Laplacian (+18) Original + Laplacian Original - Laplacian Why does the sign make a difference? How can you write each filter that makes each bottom image? 31 3
9 Summary What you should take away from this lecture: The meanings of all the boldfaced terms. How noise reduction is done How discrete convolution filtering works The effect of mean, Gaussian, and median filters What an image gradient is and how it can be computed How edge detection is done What the Laplacian image is and how it is used in either edge detection or image sharpening 33
Lecture 04 Image Filtering
 Institute of Informatics Institute of Neuroinformatics Lecture 04 Image Filtering Davide Scaramuzza 1 Lab Exercise 2 - Today afternoon Room ETH HG E 1.1 from 13:15 to 15:00 Work description: your first
Institute of Informatics Institute of Neuroinformatics Lecture 04 Image Filtering Davide Scaramuzza 1 Lab Exercise 2 - Today afternoon Room ETH HG E 1.1 from 13:15 to 15:00 Work description: your first
Review Smoothing Spatial Filters Sharpening Spatial Filters. Spatial Filtering. Dr. Praveen Sankaran. Department of ECE NIT Calicut.
 Spatial Filtering Dr. Praveen Sankaran Department of ECE NIT Calicut January 7, 203 Outline 2 Linear Nonlinear 3 Spatial Domain Refers to the image plane itself. Direct manipulation of image pixels. Figure:
Spatial Filtering Dr. Praveen Sankaran Department of ECE NIT Calicut January 7, 203 Outline 2 Linear Nonlinear 3 Spatial Domain Refers to the image plane itself. Direct manipulation of image pixels. Figure:
Today s lecture. Local neighbourhood processing. The convolution. Removing uncorrelated noise from an image The Fourier transform
 Cris Luengo TD396 fall 4 cris@cbuuse Today s lecture Local neighbourhood processing smoothing an image sharpening an image The convolution What is it? What is it useful for? How can I compute it? Removing
Cris Luengo TD396 fall 4 cris@cbuuse Today s lecture Local neighbourhood processing smoothing an image sharpening an image The convolution What is it? What is it useful for? How can I compute it? Removing
Edge Detection. CS 650: Computer Vision
 CS 650: Computer Vision Edges and Gradients Edge: local indication of an object transition Edge detection: local operators that find edges (usually involves convolution) Local intensity transitions are
CS 650: Computer Vision Edges and Gradients Edge: local indication of an object transition Edge detection: local operators that find edges (usually involves convolution) Local intensity transitions are
Laplacian Filters. Sobel Filters. Laplacian Filters. Laplacian Filters. Laplacian Filters. Laplacian Filters
 Sobel Filters Note that smoothing the image before applying a Sobel filter typically gives better results. Even thresholding the Sobel filtered image cannot usually create precise, i.e., -pixel wide, edges.
Sobel Filters Note that smoothing the image before applying a Sobel filter typically gives better results. Even thresholding the Sobel filtered image cannot usually create precise, i.e., -pixel wide, edges.
Digital Image Processing. Lecture 6 (Enhancement) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 2009
 Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 009 Outline Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain Spatial Filtering Smoothing Filters Median Filter
Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 009 Outline Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain Spatial Filtering Smoothing Filters Median Filter
Local enhancement. Local Enhancement. Local histogram equalized. Histogram equalized. Local Contrast Enhancement. Fig 3.23: Another example
 Local enhancement Local Enhancement Median filtering Local Enhancement Sometimes Local Enhancement is Preferred. Malab: BlkProc operation for block processing. Left: original tire image. 0/07/00 Local
Local enhancement Local Enhancement Median filtering Local Enhancement Sometimes Local Enhancement is Preferred. Malab: BlkProc operation for block processing. Left: original tire image. 0/07/00 Local
Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks
 Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks 09/9/ Computer Vision James Hays, Brown Slides: Hoiem and others Review. Match the spatial domain image to the Fourier magnitude image 2 3 4 5 B A C D E Slide:
Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks 09/9/ Computer Vision James Hays, Brown Slides: Hoiem and others Review. Match the spatial domain image to the Fourier magnitude image 2 3 4 5 B A C D E Slide:
TRACKING and DETECTION in COMPUTER VISION Filtering and edge detection
 Technischen Universität München Winter Semester 0/0 TRACKING and DETECTION in COMPUTER VISION Filtering and edge detection Slobodan Ilić Overview Image formation Convolution Non-liner filtering: Median
Technischen Universität München Winter Semester 0/0 TRACKING and DETECTION in COMPUTER VISION Filtering and edge detection Slobodan Ilić Overview Image formation Convolution Non-liner filtering: Median
Introduction to Computer Vision
 Introduction to Computer Vision Michael J. Black Sept 2009 Lecture 8: Pyramids and image derivatives Goals Images as functions Derivatives of images Edges and gradients Laplacian pyramids Code for lecture
Introduction to Computer Vision Michael J. Black Sept 2009 Lecture 8: Pyramids and image derivatives Goals Images as functions Derivatives of images Edges and gradients Laplacian pyramids Code for lecture
Computer Vision Lecture 3
 Computer Vision Lecture 3 Linear Filters 03.11.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Demo Haribo Classification Code available on the class website...
Computer Vision Lecture 3 Linear Filters 03.11.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Demo Haribo Classification Code available on the class website...
Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing
 Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing Image Restoration and Reconstruction I Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 11-1 Image restoration Restoration is an objective process that attempts to recover an image
Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing Image Restoration and Reconstruction I Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 11-1 Image restoration Restoration is an objective process that attempts to recover an image
ECE Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision. Outline
 2/9/7 ECE592-064 Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision Depart. of ECE, NC State University Instructor: Tianfu (Matt) Wu Spring 207. Recap Outline 2. Sharpening Filtering Illustration
2/9/7 ECE592-064 Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision Depart. of ECE, NC State University Instructor: Tianfu (Matt) Wu Spring 207. Recap Outline 2. Sharpening Filtering Illustration
Lecture 7: Edge Detection
 #1 Lecture 7: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Definition of an Edge First Order Derivative Approximation as Edge Detector #2 This Lecture Examples of Edge Detection
#1 Lecture 7: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Definition of an Edge First Order Derivative Approximation as Edge Detector #2 This Lecture Examples of Edge Detection
Machine vision. Summary # 4. The mask for Laplacian is given
 1 Machine vision Summary # 4 The mask for Laplacian is given L = 0 1 0 1 4 1 (6) 0 1 0 Another Laplacian mask that gives more importance to the center element is L = 1 1 1 1 8 1 (7) 1 1 1 Note that the
1 Machine vision Summary # 4 The mask for Laplacian is given L = 0 1 0 1 4 1 (6) 0 1 0 Another Laplacian mask that gives more importance to the center element is L = 1 1 1 1 8 1 (7) 1 1 1 Note that the
Machine vision, spring 2018 Summary 4
 Machine vision Summary # 4 The mask for Laplacian is given L = 4 (6) Another Laplacian mask that gives more importance to the center element is given by L = 8 (7) Note that the sum of the elements in the
Machine vision Summary # 4 The mask for Laplacian is given L = 4 (6) Another Laplacian mask that gives more importance to the center element is given by L = 8 (7) Note that the sum of the elements in the
Image as a signal. Luc Brun. January 25, 2018
 Image as a signal Luc Brun January 25, 2018 Introduction Smoothing Edge detection Fourier Transform 2 / 36 Different way to see an image A stochastic process, A random vector (I [0, 0], I [0, 1],..., I
Image as a signal Luc Brun January 25, 2018 Introduction Smoothing Edge detection Fourier Transform 2 / 36 Different way to see an image A stochastic process, A random vector (I [0, 0], I [0, 1],..., I
Local Enhancement. Local enhancement
 Local Enhancement Local Enhancement Median filtering (see notes/slides, 3.5.2) HW4 due next Wednesday Required Reading: Sections 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6, 3.7 Local Enhancement 1 Local enhancement Sometimes
Local Enhancement Local Enhancement Median filtering (see notes/slides, 3.5.2) HW4 due next Wednesday Required Reading: Sections 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6, 3.7 Local Enhancement 1 Local enhancement Sometimes
Spatial Enhancement Region operations: k'(x,y) = F( k(x-m, y-n), k(x,y), k(x+m,y+n) ]
![Spatial Enhancement Region operations: k'(x,y) = F( k(x-m, y-n), k(x,y), k(x+m,y+n) ] Spatial Enhancement Region operations: k'(x,y) = F( k(x-m, y-n), k(x,y), k(x+m,y+n) ]](/thumbs/77/75889528.jpg) CEE 615: Digital Image Processing Spatial Enhancements 1 Spatial Enhancement Region operations: k'(x,y) = F( k(x-m, y-n), k(x,y), k(x+m,y+n) ] Template (Windowing) Operations Template (window, box, kernel)
CEE 615: Digital Image Processing Spatial Enhancements 1 Spatial Enhancement Region operations: k'(x,y) = F( k(x-m, y-n), k(x,y), k(x+m,y+n) ] Template (Windowing) Operations Template (window, box, kernel)
Roadmap. Introduction to image analysis (computer vision) Theory of edge detection. Applications
 Edge Detection Roadmap Introduction to image analysis (computer vision) Its connection with psychology and neuroscience Why is image analysis difficult? Theory of edge detection Gradient operator Advanced
Edge Detection Roadmap Introduction to image analysis (computer vision) Its connection with psychology and neuroscience Why is image analysis difficult? Theory of edge detection Gradient operator Advanced
Filtering and Edge Detection
 Filtering and Edge Detection Local Neighborhoods Hard to tell anything from a single pixel Example: you see a reddish pixel. Is this the object s color? Illumination? Noise? The next step in order of complexity
Filtering and Edge Detection Local Neighborhoods Hard to tell anything from a single pixel Example: you see a reddish pixel. Is this the object s color? Illumination? Noise? The next step in order of complexity
Image Gradients and Gradient Filtering Computer Vision
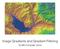 Image Gradients and Gradient Filtering 16-385 Computer Vision What is an image edge? Recall that an image is a 2D function f(x) edge edge How would you detect an edge? What kinds of filter would you use?
Image Gradients and Gradient Filtering 16-385 Computer Vision What is an image edge? Recall that an image is a 2D function f(x) edge edge How would you detect an edge? What kinds of filter would you use?
Introduction to Computer Vision. 2D Linear Systems
 Introduction to Computer Vision D Linear Systems Review: Linear Systems We define a system as a unit that converts an input function into an output function Independent variable System operator or Transfer
Introduction to Computer Vision D Linear Systems Review: Linear Systems We define a system as a unit that converts an input function into an output function Independent variable System operator or Transfer
Lecture Outline. Basics of Spatial Filtering Smoothing Spatial Filters. Sharpening Spatial Filters
 1 Lecture Outline Basics o Spatial Filtering Smoothing Spatial Filters Averaging ilters Order-Statistics ilters Sharpening Spatial Filters Laplacian ilters High-boost ilters Gradient Masks Combining Spatial
1 Lecture Outline Basics o Spatial Filtering Smoothing Spatial Filters Averaging ilters Order-Statistics ilters Sharpening Spatial Filters Laplacian ilters High-boost ilters Gradient Masks Combining Spatial
Edge Detection in Computer Vision Systems
 1 CS332 Visual Processing in Computer and Biological Vision Systems Edge Detection in Computer Vision Systems This handout summarizes much of the material on the detection and description of intensity
1 CS332 Visual Processing in Computer and Biological Vision Systems Edge Detection in Computer Vision Systems This handout summarizes much of the material on the detection and description of intensity
Edge Detection. Introduction to Computer Vision. Useful Mathematics Funcs. The bad news
 Edge Detection Introduction to Computer Vision CS / ECE 8B Thursday, April, 004 Edge detection (HO #5) Edge detection is a local area operator that seeks to find significant, meaningful changes in image
Edge Detection Introduction to Computer Vision CS / ECE 8B Thursday, April, 004 Edge detection (HO #5) Edge detection is a local area operator that seeks to find significant, meaningful changes in image
Image preprocessing in spatial domain
 Image preprocessing in spatial domain Sharpening, image derivatives, Laplacian, edges Revision: 1.2, dated: May 25, 2007 Tomáš Svoboda Czech Technical University, Faculty of Electrical Engineering Center
Image preprocessing in spatial domain Sharpening, image derivatives, Laplacian, edges Revision: 1.2, dated: May 25, 2007 Tomáš Svoboda Czech Technical University, Faculty of Electrical Engineering Center
Image Filtering. Slides, adapted from. Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski, U.Washington
 Image Filtering Slides, adapted from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski, U.Washington The power of blur All is Vanity by Charles Allen Gillbert (1873-1929) Harmon LD & JuleszB (1973) The recognition of faces.
Image Filtering Slides, adapted from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski, U.Washington The power of blur All is Vanity by Charles Allen Gillbert (1873-1929) Harmon LD & JuleszB (1973) The recognition of faces.
Histogram Processing
 Histogram Processing The histogram of a digital image with gray levels in the range [0,L-] is a discrete function h ( r k ) = n k where r k n k = k th gray level = number of pixels in the image having
Histogram Processing The histogram of a digital image with gray levels in the range [0,L-] is a discrete function h ( r k ) = n k where r k n k = k th gray level = number of pixels in the image having
Edge Detection. Computer Vision P. Schrater Spring 2003
 Edge Detection Computer Vision P. Schrater Spring 2003 Simplest Model: (Canny) Edge(x) = a U(x) + n(x) U(x)? x=0 Convolve image with U and find points with high magnitude. Choose value by comparing with
Edge Detection Computer Vision P. Schrater Spring 2003 Simplest Model: (Canny) Edge(x) = a U(x) + n(x) U(x)? x=0 Convolve image with U and find points with high magnitude. Choose value by comparing with
Edge Detection. Image Processing - Computer Vision
 Image Processing - Lesson 10 Edge Detection Image Processing - Computer Vision Low Level Edge detection masks Gradient Detectors Compass Detectors Second Derivative - Laplace detectors Edge Linking Image
Image Processing - Lesson 10 Edge Detection Image Processing - Computer Vision Low Level Edge detection masks Gradient Detectors Compass Detectors Second Derivative - Laplace detectors Edge Linking Image
Basics on 2-D 2 D Random Signal
 Basics on -D D Random Signal Spring 06 Instructor: K. J. Ray Liu ECE Department, Univ. of Maryland, College Park Overview Last Time: Fourier Analysis for -D signals Image enhancement via spatial filtering
Basics on -D D Random Signal Spring 06 Instructor: K. J. Ray Liu ECE Department, Univ. of Maryland, College Park Overview Last Time: Fourier Analysis for -D signals Image enhancement via spatial filtering
Empirical Mean and Variance!
 Global Image Properties! Global image properties refer to an image as a whole rather than components. Computation of global image properties is often required for image enhancement, preceding image analysis.!
Global Image Properties! Global image properties refer to an image as a whole rather than components. Computation of global image properties is often required for image enhancement, preceding image analysis.!
ITK Filters. Thresholding Edge Detection Gradients Second Order Derivatives Neighborhood Filters Smoothing Filters Distance Map Image Transforms
 ITK Filters Thresholding Edge Detection Gradients Second Order Derivatives Neighborhood Filters Smoothing Filters Distance Map Image Transforms ITCS 6010:Biomedical Imaging and Visualization 1 ITK Filters:
ITK Filters Thresholding Edge Detection Gradients Second Order Derivatives Neighborhood Filters Smoothing Filters Distance Map Image Transforms ITCS 6010:Biomedical Imaging and Visualization 1 ITK Filters:
Lecture 3: Linear Filters
 Lecture 3: Linear Filters Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Images as functions Linear systems (filters) Convolution and correlation Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
Lecture 3: Linear Filters Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Images as functions Linear systems (filters) Convolution and correlation Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
Edge Detection PSY 5018H: Math Models Hum Behavior, Prof. Paul Schrater, Spring 2005
 Edge Detection PSY 5018H: Math Models Hum Behavior, Prof. Paul Schrater, Spring 2005 Gradients and edges Points of sharp change in an image are interesting: change in reflectance change in object change
Edge Detection PSY 5018H: Math Models Hum Behavior, Prof. Paul Schrater, Spring 2005 Gradients and edges Points of sharp change in an image are interesting: change in reflectance change in object change
Image Enhancement: Methods. Digital Image Processing. No Explicit definition. Spatial Domain: Frequency Domain:
 Image Enhancement: No Explicit definition Methods Spatial Domain: Linear Nonlinear Frequency Domain: Linear Nonlinear 1 Spatial Domain Process,, g x y T f x y 2 For 1 1 neighborhood: Contrast Enhancement/Stretching/Point
Image Enhancement: No Explicit definition Methods Spatial Domain: Linear Nonlinear Frequency Domain: Linear Nonlinear 1 Spatial Domain Process,, g x y T f x y 2 For 1 1 neighborhood: Contrast Enhancement/Stretching/Point
Image Enhancement (Spatial Filtering 2)
 Image Enhancement (Spatial Filtering ) Dr. Samir H. Abdul-Jauwad Electrical Engineering Department College o Engineering Sciences King Fahd University o Petroleum & Minerals Dhahran Saudi Arabia samara@kupm.edu.sa
Image Enhancement (Spatial Filtering ) Dr. Samir H. Abdul-Jauwad Electrical Engineering Department College o Engineering Sciences King Fahd University o Petroleum & Minerals Dhahran Saudi Arabia samara@kupm.edu.sa
Lecture 3: Linear Filters
 Lecture 3: Linear Filters Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Images as functions Linear systems (filters) Convolution and correlation Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
Lecture 3: Linear Filters Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Images as functions Linear systems (filters) Convolution and correlation Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
Lecture 6: Edge Detection. CAP 5415: Computer Vision Fall 2008
 Lecture 6: Edge Detection CAP 5415: Computer Vision Fall 2008 Announcements PS 2 is available Please read it by Thursday During Thursday lecture, I will be going over it in some detail Monday - Computer
Lecture 6: Edge Detection CAP 5415: Computer Vision Fall 2008 Announcements PS 2 is available Please read it by Thursday During Thursday lecture, I will be going over it in some detail Monday - Computer
Announcements. Filtering. Image Filtering. Linear Filters. Example: Smoothing by Averaging. Homework 2 is due Apr 26, 11:59 PM Reading:
 Announcements Filtering Homework 2 is due Apr 26, :59 PM eading: Chapter 4: Linear Filters CSE 52 Lecture 6 mage Filtering nput Output Filter (From Bill Freeman) Example: Smoothing by Averaging Linear
Announcements Filtering Homework 2 is due Apr 26, :59 PM eading: Chapter 4: Linear Filters CSE 52 Lecture 6 mage Filtering nput Output Filter (From Bill Freeman) Example: Smoothing by Averaging Linear
Fourier Transforms 1D
 Fourier Transforms 1D 3D Image Processing Alireza Ghane 1 Overview Recap Intuitions Function representations shift-invariant spaces linear, time-invariant (LTI) systems complex numbers Fourier Transforms
Fourier Transforms 1D 3D Image Processing Alireza Ghane 1 Overview Recap Intuitions Function representations shift-invariant spaces linear, time-invariant (LTI) systems complex numbers Fourier Transforms
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 13 Oct 2 nd, 2018 Pranav Mantini Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, and Frank Liu Review f 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 w 1 2 3 2 8 Zero Padding 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 13 Oct 2 nd, 2018 Pranav Mantini Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, and Frank Liu Review f 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 w 1 2 3 2 8 Zero Padding 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
Additional Pointers. Introduction to Computer Vision. Convolution. Area operations: Linear filtering
 Additional Pointers Introduction to Computer Vision CS / ECE 181B andout #4 : Available this afternoon Midterm: May 6, 2004 W #2 due tomorrow Ack: Prof. Matthew Turk for the lecture slides. See my ECE
Additional Pointers Introduction to Computer Vision CS / ECE 181B andout #4 : Available this afternoon Midterm: May 6, 2004 W #2 due tomorrow Ack: Prof. Matthew Turk for the lecture slides. See my ECE
Digital Image Processing ERRATA. Wilhelm Burger Mark J. Burge. An algorithmic introduction using Java. Second Edition. Springer
 Wilhelm Burger Mark J. Burge Digital Image Processing An algorithmic introduction using Java Second Edition ERRATA Springer Berlin Heidelberg NewYork Hong Kong London Milano Paris Tokyo 5 Filters K K No
Wilhelm Burger Mark J. Burge Digital Image Processing An algorithmic introduction using Java Second Edition ERRATA Springer Berlin Heidelberg NewYork Hong Kong London Milano Paris Tokyo 5 Filters K K No
Colorado School of Mines Image and Multidimensional Signal Processing
 Image and Multidimensional Signal Processing Professor William Hoff Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spatial Filtering Main idea Spatial filtering Define a neighborhood of a pixel
Image and Multidimensional Signal Processing Professor William Hoff Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spatial Filtering Main idea Spatial filtering Define a neighborhood of a pixel
I Chen Lin, Assistant Professor Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung University. Computer Vision: 4. Filtering
 I Chen Lin, Assistant Professor Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung University Computer Vision: 4. Filtering Outline Impulse response and convolution. Linear filter and image pyramid. Textbook: David A. Forsyth
I Chen Lin, Assistant Professor Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung University Computer Vision: 4. Filtering Outline Impulse response and convolution. Linear filter and image pyramid. Textbook: David A. Forsyth
COMP344 Digital Image Processing Fall 2007 Final Examination
 COMP344 Digital Image Processing Fall 2007 Final Examination Time allowed: 2 hours Name Student ID Email Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Question 4 Question 5 Question 6 Total With model answer HK University
COMP344 Digital Image Processing Fall 2007 Final Examination Time allowed: 2 hours Name Student ID Email Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Question 4 Question 5 Question 6 Total With model answer HK University
Case Studies of Logical Computation on Stochastic Bit Streams
 Case Studies of Logical Computation on Stochastic Bit Streams Peng Li 1, Weikang Qian 2, David J. Lilja 1, Kia Bazargan 1, and Marc D. Riedel 1 1 Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Minnesota,
Case Studies of Logical Computation on Stochastic Bit Streams Peng Li 1, Weikang Qian 2, David J. Lilja 1, Kia Bazargan 1, and Marc D. Riedel 1 1 Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Minnesota,
Outline. Convolution. Filtering
 Filtering Outline Convolution Filtering Logistics HW1 HW2 - out tomorrow Recall: what is a digital (grayscale) image? Matrix of integer values Images as height fields Let s think of image as zero-padded
Filtering Outline Convolution Filtering Logistics HW1 HW2 - out tomorrow Recall: what is a digital (grayscale) image? Matrix of integer values Images as height fields Let s think of image as zero-padded
Prof. Mohd Zaid Abdullah Room No:
 EEE 52/4 Advnced Digital Signal and Image Processing Tuesday, 00-300 hrs, Data Com. Lab. Friday, 0800-000 hrs, Data Com. Lab Prof. Mohd Zaid Abdullah Room No: 5 Email: mza@usm.my www.eng.usm.my Electromagnetic
EEE 52/4 Advnced Digital Signal and Image Processing Tuesday, 00-300 hrs, Data Com. Lab. Friday, 0800-000 hrs, Data Com. Lab Prof. Mohd Zaid Abdullah Room No: 5 Email: mza@usm.my www.eng.usm.my Electromagnetic
Advanced Edge Detection 1
 Advanced Edge Detection 1 Lecture 4 See Sections 2.4 and 1.2.5 in Reinhard Klette: Concise Computer Vision Springer-Verlag, London, 2014 1 See last slide for copyright information. 1 / 27 Agenda 1 LoG
Advanced Edge Detection 1 Lecture 4 See Sections 2.4 and 1.2.5 in Reinhard Klette: Concise Computer Vision Springer-Verlag, London, 2014 1 See last slide for copyright information. 1 / 27 Agenda 1 LoG
FILTERING IN THE FREQUENCY DOMAIN
 1 FILTERING IN THE FREQUENCY DOMAIN Lecture 4 Spatial Vs Frequency domain 2 Spatial Domain (I) Normal image space Changes in pixel positions correspond to changes in the scene Distances in I correspond
1 FILTERING IN THE FREQUENCY DOMAIN Lecture 4 Spatial Vs Frequency domain 2 Spatial Domain (I) Normal image space Changes in pixel positions correspond to changes in the scene Distances in I correspond
Erkut Erdem. Hacettepe University February 24 th, Linear Diffusion 1. 2 Appendix - The Calculus of Variations 5.
 LINEAR DIFFUSION Erkut Erdem Hacettepe University February 24 th, 2012 CONTENTS 1 Linear Diffusion 1 2 Appendix - The Calculus of Variations 5 References 6 1 LINEAR DIFFUSION The linear diffusion (heat)
LINEAR DIFFUSION Erkut Erdem Hacettepe University February 24 th, 2012 CONTENTS 1 Linear Diffusion 1 2 Appendix - The Calculus of Variations 5 References 6 1 LINEAR DIFFUSION The linear diffusion (heat)
Medical Image Analysis
 Medical Image Analysis CS 593 / 791 Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Dept. West Virginia University 23rd January 2006 Outline 1 Recap 2 Edge Enhancement 3 Experimental Results 4 The rest of
Medical Image Analysis CS 593 / 791 Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Dept. West Virginia University 23rd January 2006 Outline 1 Recap 2 Edge Enhancement 3 Experimental Results 4 The rest of
Digital Image Processing: Sharpening Filtering in Spatial Domain CSC Biomedical Imaging and Analysis Dr. Kazunori Okada
 Homework Exercise Start project coding work according to the project plan Adjust project plans according to my comments (reply ilearn threads) New Exercise: Install VTK & FLTK. Find a simple hello world
Homework Exercise Start project coding work according to the project plan Adjust project plans according to my comments (reply ilearn threads) New Exercise: Install VTK & FLTK. Find a simple hello world
Edges and Scale. Image Features. Detecting edges. Origin of Edges. Solution: smooth first. Effects of noise
 Edges and Scale Image Features From Sandlot Science Slides revised from S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, S. Lazebnik, etc. Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity
Edges and Scale Image Features From Sandlot Science Slides revised from S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, S. Lazebnik, etc. Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity
CS 3710: Visual Recognition Describing Images with Features. Adriana Kovashka Department of Computer Science January 8, 2015
 CS 3710: Visual Recognition Describing Images with Features Adriana Kovashka Department of Computer Science January 8, 2015 Plan for Today Presentation assignments + schedule changes Image filtering Feature
CS 3710: Visual Recognition Describing Images with Features Adriana Kovashka Department of Computer Science January 8, 2015 Plan for Today Presentation assignments + schedule changes Image filtering Feature
CITS 4402 Computer Vision
 CITS 4402 Computer Vision Prof Ajmal Mian Adj/A/Prof Mehdi Ravanbakhsh, CEO at Mapizy (www.mapizy.com) and InFarm (www.infarm.io) Lecture 04 Greyscale Image Analysis Lecture 03 Summary Images as 2-D signals
CITS 4402 Computer Vision Prof Ajmal Mian Adj/A/Prof Mehdi Ravanbakhsh, CEO at Mapizy (www.mapizy.com) and InFarm (www.infarm.io) Lecture 04 Greyscale Image Analysis Lecture 03 Summary Images as 2-D signals
Medical Image Analysis
 Medical Image Analysis CS 593 / 791 Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Dept. West Virginia University 20th January 2006 Outline 1 Discretizing the heat equation 2 Outline 1 Discretizing the heat
Medical Image Analysis CS 593 / 791 Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Dept. West Virginia University 20th January 2006 Outline 1 Discretizing the heat equation 2 Outline 1 Discretizing the heat
Image enhancement. Why image enhancement? Why image enhancement? Why image enhancement? Example of artifacts caused by image encoding
 13 Why image enhancement? Image enhancement Example of artifacts caused by image encoding Computer Vision, Lecture 14 Michael Felsberg Computer Vision Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering 12
13 Why image enhancement? Image enhancement Example of artifacts caused by image encoding Computer Vision, Lecture 14 Michael Felsberg Computer Vision Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering 12
Chapter 16. Local Operations
 Chapter 16 Local Operations g[x, y] =O{f[x ± x, y ± y]} In many common image processing operations, the output pixel is a weighted combination of the gray values of pixels in the neighborhood of the input
Chapter 16 Local Operations g[x, y] =O{f[x ± x, y ± y]} In many common image processing operations, the output pixel is a weighted combination of the gray values of pixels in the neighborhood of the input
CAP 5415 Computer Vision Fall 2011
 CAP 545 Computer Vision Fall 2 Dr. Mubarak Sa Univ. o Central Florida www.cs.uc.edu/~vision/courses/cap545/all22 Oice 247-F HEC Filtering Lecture-2 General Binary Gray Scale Color Binary Images Y Row X
CAP 545 Computer Vision Fall 2 Dr. Mubarak Sa Univ. o Central Florida www.cs.uc.edu/~vision/courses/cap545/all22 Oice 247-F HEC Filtering Lecture-2 General Binary Gray Scale Color Binary Images Y Row X
Chapter 4: Filtering in the Frequency Domain. Fourier Analysis R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods
 Fourier Analysis 1992 2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Properties of δ (t) and (x) δ : f t) δ ( t t ) dt = f ( ) f x) δ ( x x ) = f ( ) ( 0 t0 x= ( 0 x0 1992 2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Sampling
Fourier Analysis 1992 2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Properties of δ (t) and (x) δ : f t) δ ( t t ) dt = f ( ) f x) δ ( x x ) = f ( ) ( 0 t0 x= ( 0 x0 1992 2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Sampling
CAP 5415 Computer Vision
 CAP 545 Computer Vision Dr. Mubarak Sa Univ. o Central Florida Filtering Lecture-2 Contents Filtering/Smooting/Removing Noise Convolution/Correlation Image Derivatives Histogram Some Matlab Functions General
CAP 545 Computer Vision Dr. Mubarak Sa Univ. o Central Florida Filtering Lecture-2 Contents Filtering/Smooting/Removing Noise Convolution/Correlation Image Derivatives Histogram Some Matlab Functions General
CS4670: Computer Vision Kavita Bala. Lecture 7: Harris Corner Detec=on
 CS4670: Computer Vision Kavita Bala Lecture 7: Harris Corner Detec=on Announcements HW 1 will be out soon Sign up for demo slots for PA 1 Remember that both partners have to be there We will ask you to
CS4670: Computer Vision Kavita Bala Lecture 7: Harris Corner Detec=on Announcements HW 1 will be out soon Sign up for demo slots for PA 1 Remember that both partners have to be there We will ask you to
Intensity Transformations and Spatial Filtering: WHICH ONE LOOKS BETTER? Intensity Transformations and Spatial Filtering: WHICH ONE LOOKS BETTER?
 : WHICH ONE LOOKS BETTER? 3.1 : WHICH ONE LOOKS BETTER? 3.2 1 Goal: Image enhancement seeks to improve the visual appearance of an image, or convert it to a form suited for analysis by a human or a machine.
: WHICH ONE LOOKS BETTER? 3.1 : WHICH ONE LOOKS BETTER? 3.2 1 Goal: Image enhancement seeks to improve the visual appearance of an image, or convert it to a form suited for analysis by a human or a machine.
Taking derivative by convolution
 Taking derivative by convolution Partial derivatives with convolution For 2D function f(x,y), the partial derivative is: For discrete data, we can approximate using finite differences: To implement above
Taking derivative by convolution Partial derivatives with convolution For 2D function f(x,y), the partial derivative is: For discrete data, we can approximate using finite differences: To implement above
Image Enhancement in the frequency domain. GZ Chapter 4
 Image Enhancement in the frequency domain GZ Chapter 4 Contents In this lecture we will look at image enhancement in the frequency domain The Fourier series & the Fourier transform Image Processing in
Image Enhancement in the frequency domain GZ Chapter 4 Contents In this lecture we will look at image enhancement in the frequency domain The Fourier series & the Fourier transform Image Processing in
Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing. Periodicity of the Fourier transform
 Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing Fourier Transform Properties, the Laplacian, Convolution and Correlation Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 9- Periodicity of the Fourier transform The discrete Fourier
Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing Fourier Transform Properties, the Laplacian, Convolution and Correlation Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 9- Periodicity of the Fourier transform The discrete Fourier
Lecture 8: Interest Point Detection. Saad J Bedros
 #1 Lecture 8: Interest Point Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review of Edge Detectors #2 Today s Lecture Interest Points Detection What do we mean with Interest Point Detection in an Image Goal:
#1 Lecture 8: Interest Point Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review of Edge Detectors #2 Today s Lecture Interest Points Detection What do we mean with Interest Point Detection in an Image Goal:
Vlad Estivill-Castro (2016) Robots for People --- A project for intelligent integrated systems
 1 Vlad Estivill-Castro (2016) Robots for People --- A project for intelligent integrated systems V. Estivill-Castro 2 Perception Concepts Vision Chapter 4 (textbook) Sections 4.3 to 4.5 What is the course
1 Vlad Estivill-Castro (2016) Robots for People --- A project for intelligent integrated systems V. Estivill-Castro 2 Perception Concepts Vision Chapter 4 (textbook) Sections 4.3 to 4.5 What is the course
CSE 473/573 Computer Vision and Image Processing (CVIP)
 CSE 473/573 Computer Vision and Image Processing (CVIP) Ifeoma Nwogu inwogu@buffalo.edu Lecture 11 Local Features 1 Schedule Last class We started local features Today More on local features Readings for
CSE 473/573 Computer Vision and Image Processing (CVIP) Ifeoma Nwogu inwogu@buffalo.edu Lecture 11 Local Features 1 Schedule Last class We started local features Today More on local features Readings for
Introduction to Image Processing #5/7
 Outline Introduction to Image Processing #5/7 Thierry Géraud EPITA Research and Development Laboratory (LRDE) 2006 Outline Outline 1 Introduction 2 About the Dirac Delta Function Some Useful Functions
Outline Introduction to Image Processing #5/7 Thierry Géraud EPITA Research and Development Laboratory (LRDE) 2006 Outline Outline 1 Introduction 2 About the Dirac Delta Function Some Useful Functions
PSET 0 Due Today by 11:59pm Any issues with submissions, post on Piazza. Fall 2018: T-R: Lopata 101. Median Filter / Order Statistics
 CSE 559A: Computer Vision OFFICE HOURS This Friday (and this Friday only): Zhihao's Office Hours in Jolley 43 instead of 309. Monday Office Hours: 5:30-6:30pm, Collaboration Space @ Jolley 27. PSET 0 Due
CSE 559A: Computer Vision OFFICE HOURS This Friday (and this Friday only): Zhihao's Office Hours in Jolley 43 instead of 309. Monday Office Hours: 5:30-6:30pm, Collaboration Space @ Jolley 27. PSET 0 Due
Gaussian derivatives
 Gaussian derivatives UCU Winter School 2017 James Pritts Czech Tecnical University January 16, 2017 1 Images taken from Noah Snavely s and Robert Collins s course notes Definition An image (grayscale)
Gaussian derivatives UCU Winter School 2017 James Pritts Czech Tecnical University January 16, 2017 1 Images taken from Noah Snavely s and Robert Collins s course notes Definition An image (grayscale)
CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation III Statistical Nonparametric Methods for Segmentation
 CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation III Statistical Nonparametric Methods for Segmentation Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science CS 534 Segmentation III- Nonparametric Methods - - 1 Outlines Density
CS 534: Computer Vision Segmentation III Statistical Nonparametric Methods for Segmentation Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science CS 534 Segmentation III- Nonparametric Methods - - 1 Outlines Density
Detectors part II Descriptors
 EECS 442 Computer vision Detectors part II Descriptors Blob detectors Invariance Descriptors Some slides of this lectures are courtesy of prof F. Li, prof S. Lazebnik, and various other lecturers Goal:
EECS 442 Computer vision Detectors part II Descriptors Blob detectors Invariance Descriptors Some slides of this lectures are courtesy of prof F. Li, prof S. Lazebnik, and various other lecturers Goal:
ECE Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision
 ECE592-064 Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision Depart. of ECE, NC State University Instructor: Tianfu (Matt) Wu Spring 2017 Outline Recap, image degradation / restoration Template
ECE592-064 Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision Depart. of ECE, NC State University Instructor: Tianfu (Matt) Wu Spring 2017 Outline Recap, image degradation / restoration Template
3.8 Combining Spatial Enhancement Methods 137
 3.8 Combining Spatial Enhancement Methods 137 a b FIGURE 3.45 Optical image of contact lens (note defects on the boundary at 4 and 5 o clock). (b) Sobel gradient. (Original image courtesy of Mr. Pete Sites,
3.8 Combining Spatial Enhancement Methods 137 a b FIGURE 3.45 Optical image of contact lens (note defects on the boundary at 4 and 5 o clock). (b) Sobel gradient. (Original image courtesy of Mr. Pete Sites,
Computational Photography
 Computational Photography Si Lu Spring 208 http://web.cecs.pdx.edu/~lusi/cs50/cs50_computati onal_photography.htm 04/0/208 Last Time o Digital Camera History of Camera Controlling Camera o Photography
Computational Photography Si Lu Spring 208 http://web.cecs.pdx.edu/~lusi/cs50/cs50_computati onal_photography.htm 04/0/208 Last Time o Digital Camera History of Camera Controlling Camera o Photography
Recursive Gaussian filters
 CWP-546 Recursive Gaussian filters Dave Hale Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines, Golden CO 80401, USA ABSTRACT Gaussian or Gaussian derivative filtering is in several ways optimal for
CWP-546 Recursive Gaussian filters Dave Hale Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines, Golden CO 80401, USA ABSTRACT Gaussian or Gaussian derivative filtering is in several ways optimal for
Locality function LOC(.) and loss function LOSS (.) and a priori knowledge on images inp
 L. Yaroslavsky. Course 0510.7211 Digital Image Processing: Applications Lecture 12. Nonlinear filters for image restoration and enhancement Local criteria of image quality: AVLOSS( k, l) = AV LOC( m, n;
L. Yaroslavsky. Course 0510.7211 Digital Image Processing: Applications Lecture 12. Nonlinear filters for image restoration and enhancement Local criteria of image quality: AVLOSS( k, l) = AV LOC( m, n;
CS4495/6495 Introduction to Computer Vision. 2A-L6 Edge detection: 2D operators
 CS4495/6495 Introduction to Computer Vision 2A-L6 Edge detection: 2D operators Derivative theorem of convolution - 1D This saves us one operation: ( ) ( ) x h f h f x f h h x h x ( ) f Derivative of Gaussian
CS4495/6495 Introduction to Computer Vision 2A-L6 Edge detection: 2D operators Derivative theorem of convolution - 1D This saves us one operation: ( ) ( ) x h f h f x f h h x h x ( ) f Derivative of Gaussian
Computer Vision Lecture 3
 Demo Haribo Classification Computer Vision Lecture 3 Linear Filters 23..24 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Code available on the class website...
Demo Haribo Classification Computer Vision Lecture 3 Linear Filters 23..24 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Code available on the class website...
Convolution Spatial Aliasing Frequency domain filtering fundamentals Applications Image smoothing Image sharpening
 Frequency Domain Filtering Correspondence between Spatial and Frequency Filtering Fourier Transform Brief Introduction Sampling Theory 2 D Discrete Fourier Transform Convolution Spatial Aliasing Frequency
Frequency Domain Filtering Correspondence between Spatial and Frequency Filtering Fourier Transform Brief Introduction Sampling Theory 2 D Discrete Fourier Transform Convolution Spatial Aliasing Frequency
Theory of signals and images I. Dr. Victor Castaneda
 Theory of signals and images I Dr. Victor Castaneda Image as a function Think of an image as a function, f, f: R 2 R I=f(x, y) gives the intensity at position (x, y) The image only is defined over a rectangle,
Theory of signals and images I Dr. Victor Castaneda Image as a function Think of an image as a function, f, f: R 2 R I=f(x, y) gives the intensity at position (x, y) The image only is defined over a rectangle,
Lecture 4 Filtering in the Frequency Domain. Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Spring 2016
 Lecture 4 Filtering in the Frequency Domain Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Spring 2016 Outline Background From Fourier series to Fourier transform Properties of the Fourier
Lecture 4 Filtering in the Frequency Domain Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Spring 2016 Outline Background From Fourier series to Fourier transform Properties of the Fourier
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 11 Oct 3 rd, 2017 Pranav Mantini Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, and Frank Liu Review: 2D Discrete Fourier Transform If I is an image of size N then Sin
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 11 Oct 3 rd, 2017 Pranav Mantini Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, and Frank Liu Review: 2D Discrete Fourier Transform If I is an image of size N then Sin
The Frequency Domain, without tears. Many slides borrowed from Steve Seitz
 The Frequency Domain, without tears Many slides borrowed from Steve Seitz Somewhere in Cinque Terre, May 2005 CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2016
The Frequency Domain, without tears Many slides borrowed from Steve Seitz Somewhere in Cinque Terre, May 2005 CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2016
Fourier transforms and convolution
 Fourier transforms and convolution (without the agonizing pain) CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 26, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline Why do we care? Fourier transforms Writing functions as sums of sinusoids The
Fourier transforms and convolution (without the agonizing pain) CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 26, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline Why do we care? Fourier transforms Writing functions as sums of sinusoids The
FIR APPROXIMATION OF ND LOG FILTER IN FOURIER DOMAIN
 FIR APPROXIMATION OF ND LOG FILTER IN FOURIER DOMAIN P. Brabec, J. Kukal Institute of Chemical Technology, Prague Abstract The Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filter is a kind of linear and infinite impulse
FIR APPROXIMATION OF ND LOG FILTER IN FOURIER DOMAIN P. Brabec, J. Kukal Institute of Chemical Technology, Prague Abstract The Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filter is a kind of linear and infinite impulse
SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM BY DAVID LOWE
 SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM BY DAVID LOWE Overview Motivation of Work Overview of Algorithm Scale Space and Difference of Gaussian Keypoint Localization Orientation Assignment Descriptor Building
SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM BY DAVID LOWE Overview Motivation of Work Overview of Algorithm Scale Space and Difference of Gaussian Keypoint Localization Orientation Assignment Descriptor Building
EECS490: Digital Image Processing. Lecture #11
 Lecture #11 Filtering Applications: OCR, scanning Highpass filters Laplacian in the frequency domain Image enhancement using highpass filters Homomorphic filters Bandreject/bandpass/notch filters Correlation
Lecture #11 Filtering Applications: OCR, scanning Highpass filters Laplacian in the frequency domain Image enhancement using highpass filters Homomorphic filters Bandreject/bandpass/notch filters Correlation
CSCI 250: Intro to Robotics. Spring Term 2017 Prof. Levy. Computer Vision: A Brief Survey
 CSCI 25: Intro to Robotics Spring Term 27 Prof. Levy Computer Vision: A Brief Survey What Is Computer Vision? Higher-order tasks Face recognition Object recognition (Deep Learning) What Is Computer Vision?
CSCI 25: Intro to Robotics Spring Term 27 Prof. Levy Computer Vision: A Brief Survey What Is Computer Vision? Higher-order tasks Face recognition Object recognition (Deep Learning) What Is Computer Vision?
Using Entropy and 2-D Correlation Coefficient as Measuring Indices for Impulsive Noise Reduction Techniques
 Using Entropy and 2-D Correlation Coefficient as Measuring Indices for Impulsive Noise Reduction Techniques Zayed M. Ramadan Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
Using Entropy and 2-D Correlation Coefficient as Measuring Indices for Impulsive Noise Reduction Techniques Zayed M. Ramadan Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
Advanced Features. Advanced Features: Topics. Jana Kosecka. Slides from: S. Thurn, D. Lowe, Forsyth and Ponce. Advanced features and feature matching
 Advanced Features Jana Kosecka Slides from: S. Thurn, D. Lowe, Forsyth and Ponce Advanced Features: Topics Advanced features and feature matching Template matching SIFT features Haar features 2 1 Features
Advanced Features Jana Kosecka Slides from: S. Thurn, D. Lowe, Forsyth and Ponce Advanced Features: Topics Advanced features and feature matching Template matching SIFT features Haar features 2 1 Features
Linear Operators and Fourier Transform
 Linear Operators and Fourier Transform DD2423 Image Analysis and Computer Vision Mårten Björkman Computational Vision and Active Perception School of Computer Science and Communication November 13, 2013
Linear Operators and Fourier Transform DD2423 Image Analysis and Computer Vision Mårten Björkman Computational Vision and Active Perception School of Computer Science and Communication November 13, 2013
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing 2D SYSTEMS & PRELIMINARIES Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 Two Dimensional Fourier & Z-transform Toeplitz & Circulant Matrices Orthogonal & Unitary Matrices Block Matrices
Digital Image Processing 2D SYSTEMS & PRELIMINARIES Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 Two Dimensional Fourier & Z-transform Toeplitz & Circulant Matrices Orthogonal & Unitary Matrices Block Matrices
Detection of signal transitions by order statistics filtering
 Detection of signal transitions by order statistics filtering A. Raji Images, Signals and Intelligent Systems Laboratory Paris-Est Creteil University, France Abstract In this article, we present a non
Detection of signal transitions by order statistics filtering A. Raji Images, Signals and Intelligent Systems Laboratory Paris-Est Creteil University, France Abstract In this article, we present a non
