Outline. Convolution. Filtering
|
|
|
- Buddy Rose
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Filtering
2 Outline Convolution Filtering
3 Logistics HW1 HW2 - out tomorrow
4 Recall: what is a digital (grayscale) image? Matrix of integer values
5 Images as height fields Let s think of image as zero-padded functions
6 How do we characterize image processing operations? Properties of nice functional transformations Additivity Scaling Shift Invariance
7 How do we characterize image processing operations? Properties of nice transformations Additivity Scaling Shift invariance G[i] =T (F [i]) T ( F 1 + F 2 )= G 1 + G 2 G[i j] =T (x[i j])
8 Convolution = F [i] =F [] [i]+f [1] [i 1] +... F [i] = X u F [u] [i u] T (F [i]) = X u F [u]t ( [i u]) impulse response, filter, kernel G[i] = X u F [u]h[i u] where h[i] =T ( [i]),g[i] =T (F [i]) G = F H
9 Example G[i] =F [i] H[i] = X u F [u]h[i u] * 1 2 X
10 Example * G[] = 5x1 = 5 G[1] = 5x2+ 4x1 = 14 G[2] = 5x3 + 4x2 + 2x1 = 25
11 Properties of convolution F H = H F F (H G) =(F H) G (F G)+(H G) =(F + H) G Commutative Associative Distributive Implies that we can efficiently implement complex operations
12 Proof: commutativity H F = X u H[u]F [i u] = X u H[i u]f [u ] where u = i u = X u F [u]h[i u] =F H
13 Size Given F of length N and H of length M, what s size of G = F * H?
14 Size Given F of length N and H of length M, what s size of G = F * H? >>conv(f,h, full ) >>conv(f,h, valid ) >>conv(f,h, same ) N+M-1 N-M+1 N
15 A simpler approach F H Scan original F instead of flipped version. What s the math?
16 (Cross) correlation F H Scan original F instead of flipped version. What s the math? F [i] H[i] = u=k X u= k H[u]F [i + u]
17 Properties Associativity, Commutative poperties do not hold but correlation is easier to think about
18 Convolution vs correlation (1-d) X G[i] =F [i] H[i] = X u F [u]h[i u] (convolution) X = H[i] F [i] = X u H[u]F [i u] (commutative property) G[i] =F [i] H[i] = X H[u]F [i + u] u (cross-correlation) = F [i] H[ i] (exercise for reader!) X
19 2D correlation G[i, j] =F H = kx u= k kx v= k H[u, v]f [i + u, j + v]
20 Convolution vs correlation X X (2-d) Convolution: G[i, j] =F H = H F = X u X v H[u, v]f [i u, j v] h f Correlation: X X X X G[i, j] =F H = H[u, v]f [i + u, j + v] u v X X >> conv2(h,f) convolution >> filter2(h,f) correlation h f Can we compute correlation with convolution?
21 Border effects g full same valid g g g g g f f f g g g g g g
22 Border padding
23 Examples of correlation = Original Blur (with a mean filter)
24 Examples of correlation 1? Original
25 Examples of correlation 1 Original Filtered (no change)
26 Examples of correlation 1 1? Original
27 Examples of correlation 1 Original Shifted left By 1 pixel What would this look like for convolution?
28 Examples of correlation 1 1? Original
29 Examples of correlation 1 1? Original Shifted left By 1 pixel
30 Examples of correlation /16 Original What would this look like for convolution?
31 Examples of correlation ? Original Original
32 Examples of correlation Original 1 ( - /16 ) scaled impulse Unsharp filter
33 Examples????????? Can rotations be represented with a convolution? Are they linear operations G[i,j] = T(F[i,j])?
34 Derivative filters (correlation) apple
35 Derivative filters: motivation rf = rf = apple fx f y q fx 2 + fy 2 s = tan 1 f y f x
36 Gradient magnitude Common approach for discrete filter design: start with continuous operation (like derivative), and discretize to make a filter
37 Question: what happens as we repeatedly convolve an image F with filter H? F F*H
38
39 Gaussian
40 = 1 pixel = 5 pixels = 1 pixels = 3 pixels
41 Implementation Matlab: >> G = FSPECIAL('gaussian',HSIZE,SIGMA) We usually do not need to use larger Gaussians - why? * = 2 a b = a 2 + b 2
42 Finite-support filters What should HSIZE be?
43 Rule-of-thumb Set radius of filter to be 3 sigma
44 Useful representation: Gaussian pyramid Filter + subsample (to exploit redundancy in output) Burt & Adelson 83
45 Smoothing vs edge filters How should filters behave on a flat region with value v?
46 Smoothing vs edge filters How should filters behave on a flat region with value v? Output v Output X X H[i, j] =1 H[i, j] = ij ij
47 Revisiting gradients (let s plot a single row of image as a function)
48 Solution: smooth first Where is the edge? Look for peaks in
49 Combine smoothing and derivative operation into a single filter Derivative of Gaussian We can think of this as an improved gradient filter (Lots of other edge filters) 49
50 Template matching with filters Can we use filtering to build detectors? 5
51 Attempt 1: correlate with eye patch G[i, j] = kx u= k kx v= k H[u, v]f [i + u, j + v] = H T F ij = H F ij cos, H,F ij 2 R (2K+1)2 Useful to think about correlation and convolution Input Filtered Image If we look for high responses, we d find the shirt. What s wrong?
52 Attempt 2: correlate with zero-mean eye patch G[i, j] =(H H) T F ij k,l True detections False detections Input Filtered Image (scaled) Thresholded Image 52
53 Attempt 3: SSD SSD[i, j] = H F ij 2 =(H F ij ) T (H F ij ) Can this be implemented with filtering? k,l True detections Input 1- sqrt(ssd) Thresholded Image 53
54 What will SSD find here? k,l Input 1- sqrt(ssd) 54
55 Normalized cross correlation NCC[i, j] = = HT F H F H T F p HT H p F T F = cos True detections Input Normalized X-Correlation Thresholded Image 55
56 Modern filter banks Convolutional Neural Nets (CNNs) Lecun et al 98 Learn filters from training data to look for low, mid, and high-level features 56
57 Any linear shift-invariant operation can be characterized by a convolution (Convolution) correlation intuitively corresponds to (flipped) matched-filters Derive filters by continuous operations (derivative, Gaussian, ) Contemporary application: convolutional neural networks 57
ECE Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision
 ECE592-064 Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision Depart. of ECE, NC State University Instructor: Tianfu (Matt) Wu Spring 2017 Outline Recap, image degradation / restoration Template
ECE592-064 Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision Depart. of ECE, NC State University Instructor: Tianfu (Matt) Wu Spring 2017 Outline Recap, image degradation / restoration Template
Lecture 04 Image Filtering
 Institute of Informatics Institute of Neuroinformatics Lecture 04 Image Filtering Davide Scaramuzza 1 Lab Exercise 2 - Today afternoon Room ETH HG E 1.1 from 13:15 to 15:00 Work description: your first
Institute of Informatics Institute of Neuroinformatics Lecture 04 Image Filtering Davide Scaramuzza 1 Lab Exercise 2 - Today afternoon Room ETH HG E 1.1 from 13:15 to 15:00 Work description: your first
Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks
 Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks 09/9/ Computer Vision James Hays, Brown Slides: Hoiem and others Review. Match the spatial domain image to the Fourier magnitude image 2 3 4 5 B A C D E Slide:
Templates, Image Pyramids, and Filter Banks 09/9/ Computer Vision James Hays, Brown Slides: Hoiem and others Review. Match the spatial domain image to the Fourier magnitude image 2 3 4 5 B A C D E Slide:
Convolution and Linear Systems
 CS 450: Introduction to Digital Signal and Image Processing Bryan Morse BYU Computer Science Introduction Analyzing Systems Goal: analyze a device that turns one signal into another. Notation: f (t) g(t)
CS 450: Introduction to Digital Signal and Image Processing Bryan Morse BYU Computer Science Introduction Analyzing Systems Goal: analyze a device that turns one signal into another. Notation: f (t) g(t)
Edges and Scale. Image Features. Detecting edges. Origin of Edges. Solution: smooth first. Effects of noise
 Edges and Scale Image Features From Sandlot Science Slides revised from S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, S. Lazebnik, etc. Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity
Edges and Scale Image Features From Sandlot Science Slides revised from S. Seitz, R. Szeliski, S. Lazebnik, etc. Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity
Taking derivative by convolution
 Taking derivative by convolution Partial derivatives with convolution For 2D function f(x,y), the partial derivative is: For discrete data, we can approximate using finite differences: To implement above
Taking derivative by convolution Partial derivatives with convolution For 2D function f(x,y), the partial derivative is: For discrete data, we can approximate using finite differences: To implement above
I Chen Lin, Assistant Professor Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung University. Computer Vision: 4. Filtering
 I Chen Lin, Assistant Professor Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung University Computer Vision: 4. Filtering Outline Impulse response and convolution. Linear filter and image pyramid. Textbook: David A. Forsyth
I Chen Lin, Assistant Professor Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung University Computer Vision: 4. Filtering Outline Impulse response and convolution. Linear filter and image pyramid. Textbook: David A. Forsyth
CS 179: LECTURE 16 MODEL COMPLEXITY, REGULARIZATION, AND CONVOLUTIONAL NETS
 CS 179: LECTURE 16 MODEL COMPLEXITY, REGULARIZATION, AND CONVOLUTIONAL NETS LAST TIME Intro to cudnn Deep neural nets using cublas and cudnn TODAY Building a better model for image classification Overfitting
CS 179: LECTURE 16 MODEL COMPLEXITY, REGULARIZATION, AND CONVOLUTIONAL NETS LAST TIME Intro to cudnn Deep neural nets using cublas and cudnn TODAY Building a better model for image classification Overfitting
CITS 4402 Computer Vision
 CITS 4402 Computer Vision Prof Ajmal Mian Adj/A/Prof Mehdi Ravanbakhsh, CEO at Mapizy (www.mapizy.com) and InFarm (www.infarm.io) Lecture 04 Greyscale Image Analysis Lecture 03 Summary Images as 2-D signals
CITS 4402 Computer Vision Prof Ajmal Mian Adj/A/Prof Mehdi Ravanbakhsh, CEO at Mapizy (www.mapizy.com) and InFarm (www.infarm.io) Lecture 04 Greyscale Image Analysis Lecture 03 Summary Images as 2-D signals
Edge Detection. Introduction to Computer Vision. Useful Mathematics Funcs. The bad news
 Edge Detection Introduction to Computer Vision CS / ECE 8B Thursday, April, 004 Edge detection (HO #5) Edge detection is a local area operator that seeks to find significant, meaningful changes in image
Edge Detection Introduction to Computer Vision CS / ECE 8B Thursday, April, 004 Edge detection (HO #5) Edge detection is a local area operator that seeks to find significant, meaningful changes in image
Computer Vision Lecture 3
 Computer Vision Lecture 3 Linear Filters 03.11.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Demo Haribo Classification Code available on the class website...
Computer Vision Lecture 3 Linear Filters 03.11.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Demo Haribo Classification Code available on the class website...
Today s lecture. Local neighbourhood processing. The convolution. Removing uncorrelated noise from an image The Fourier transform
 Cris Luengo TD396 fall 4 cris@cbuuse Today s lecture Local neighbourhood processing smoothing an image sharpening an image The convolution What is it? What is it useful for? How can I compute it? Removing
Cris Luengo TD396 fall 4 cris@cbuuse Today s lecture Local neighbourhood processing smoothing an image sharpening an image The convolution What is it? What is it useful for? How can I compute it? Removing
CS4670: Computer Vision Kavita Bala. Lecture 7: Harris Corner Detec=on
 CS4670: Computer Vision Kavita Bala Lecture 7: Harris Corner Detec=on Announcements HW 1 will be out soon Sign up for demo slots for PA 1 Remember that both partners have to be there We will ask you to
CS4670: Computer Vision Kavita Bala Lecture 7: Harris Corner Detec=on Announcements HW 1 will be out soon Sign up for demo slots for PA 1 Remember that both partners have to be there We will ask you to
Lecture 3: Linear Filters
 Lecture 3: Linear Filters Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Images as functions Linear systems (filters) Convolution and correlation Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
Lecture 3: Linear Filters Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Images as functions Linear systems (filters) Convolution and correlation Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
Comments. Assignment 3 code released. Thought questions 3 due this week. Mini-project: hopefully you have started. implement classification algorithms
 Neural networks Comments Assignment 3 code released implement classification algorithms use kernels for census dataset Thought questions 3 due this week Mini-project: hopefully you have started 2 Example:
Neural networks Comments Assignment 3 code released implement classification algorithms use kernels for census dataset Thought questions 3 due this week Mini-project: hopefully you have started 2 Example:
Laplacian Filters. Sobel Filters. Laplacian Filters. Laplacian Filters. Laplacian Filters. Laplacian Filters
 Sobel Filters Note that smoothing the image before applying a Sobel filter typically gives better results. Even thresholding the Sobel filtered image cannot usually create precise, i.e., -pixel wide, edges.
Sobel Filters Note that smoothing the image before applying a Sobel filter typically gives better results. Even thresholding the Sobel filtered image cannot usually create precise, i.e., -pixel wide, edges.
Achieving scale covariance
 Achieving scale covariance Goal: independently detect corresponding regions in scaled versions of the same image Need scale selection mechanism for finding characteristic region size that is covariant
Achieving scale covariance Goal: independently detect corresponding regions in scaled versions of the same image Need scale selection mechanism for finding characteristic region size that is covariant
Roadmap. Introduction to image analysis (computer vision) Theory of edge detection. Applications
 Edge Detection Roadmap Introduction to image analysis (computer vision) Its connection with psychology and neuroscience Why is image analysis difficult? Theory of edge detection Gradient operator Advanced
Edge Detection Roadmap Introduction to image analysis (computer vision) Its connection with psychology and neuroscience Why is image analysis difficult? Theory of edge detection Gradient operator Advanced
CSCI 315: Artificial Intelligence through Deep Learning
 CSCI 35: Artificial Intelligence through Deep Learning W&L Fall Term 27 Prof. Levy Convolutional Networks http://wernerstudio.typepad.com/.a/6ad83549adb53ef53629ccf97c-5wi Convolution: Convolution is
CSCI 35: Artificial Intelligence through Deep Learning W&L Fall Term 27 Prof. Levy Convolutional Networks http://wernerstudio.typepad.com/.a/6ad83549adb53ef53629ccf97c-5wi Convolution: Convolution is
Review for Exam 1. Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA
 Review for Exam Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA 0003 March 26, 204 Abstract Here are some things you need to know for the in-class
Review for Exam Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA 0003 March 26, 204 Abstract Here are some things you need to know for the in-class
LoG Blob Finding and Scale. Scale Selection. Blobs (and scale selection) Achieving scale covariance. Blob detection in 2D. Blob detection in 2D
 Achieving scale covariance Blobs (and scale selection) Goal: independently detect corresponding regions in scaled versions of the same image Need scale selection mechanism for finding characteristic region
Achieving scale covariance Blobs (and scale selection) Goal: independently detect corresponding regions in scaled versions of the same image Need scale selection mechanism for finding characteristic region
Lecture 3: Linear Filters
 Lecture 3: Linear Filters Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Images as functions Linear systems (filters) Convolution and correlation Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
Lecture 3: Linear Filters Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Images as functions Linear systems (filters) Convolution and correlation Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
Vlad Estivill-Castro (2016) Robots for People --- A project for intelligent integrated systems
 1 Vlad Estivill-Castro (2016) Robots for People --- A project for intelligent integrated systems V. Estivill-Castro 2 Perception Concepts Vision Chapter 4 (textbook) Sections 4.3 to 4.5 What is the course
1 Vlad Estivill-Castro (2016) Robots for People --- A project for intelligent integrated systems V. Estivill-Castro 2 Perception Concepts Vision Chapter 4 (textbook) Sections 4.3 to 4.5 What is the course
Reading. 3. Image processing. Pixel movement. Image processing Y R I G Q
 Reading Jain, Kasturi, Schunck, Machine Vision. McGraw-Hill, 1995. Sections 4.-4.4, 4.5(intro), 4.5.5, 4.5.6, 5.1-5.4. 3. Image processing 1 Image processing An image processing operation typically defines
Reading Jain, Kasturi, Schunck, Machine Vision. McGraw-Hill, 1995. Sections 4.-4.4, 4.5(intro), 4.5.5, 4.5.6, 5.1-5.4. 3. Image processing 1 Image processing An image processing operation typically defines
Filtering in Frequency Domain
 Dr. Praveen Sankaran Department of ECE NIT Calicut February 4, 2013 Outline 1 2D DFT - Review 2 2D Sampling 2D DFT - Review 2D Impulse Train s [t, z] = m= n= δ [t m T, z n Z] (1) f (t, z) s [t, z] sampled
Dr. Praveen Sankaran Department of ECE NIT Calicut February 4, 2013 Outline 1 2D DFT - Review 2 2D Sampling 2D DFT - Review 2D Impulse Train s [t, z] = m= n= δ [t m T, z n Z] (1) f (t, z) s [t, z] sampled
Spatial Enhancement Region operations: k'(x,y) = F( k(x-m, y-n), k(x,y), k(x+m,y+n) ]
![Spatial Enhancement Region operations: k'(x,y) = F( k(x-m, y-n), k(x,y), k(x+m,y+n) ] Spatial Enhancement Region operations: k'(x,y) = F( k(x-m, y-n), k(x,y), k(x+m,y+n) ]](/thumbs/77/75889528.jpg) CEE 615: Digital Image Processing Spatial Enhancements 1 Spatial Enhancement Region operations: k'(x,y) = F( k(x-m, y-n), k(x,y), k(x+m,y+n) ] Template (Windowing) Operations Template (window, box, kernel)
CEE 615: Digital Image Processing Spatial Enhancements 1 Spatial Enhancement Region operations: k'(x,y) = F( k(x-m, y-n), k(x,y), k(x+m,y+n) ] Template (Windowing) Operations Template (window, box, kernel)
Edge Detection PSY 5018H: Math Models Hum Behavior, Prof. Paul Schrater, Spring 2005
 Edge Detection PSY 5018H: Math Models Hum Behavior, Prof. Paul Schrater, Spring 2005 Gradients and edges Points of sharp change in an image are interesting: change in reflectance change in object change
Edge Detection PSY 5018H: Math Models Hum Behavior, Prof. Paul Schrater, Spring 2005 Gradients and edges Points of sharp change in an image are interesting: change in reflectance change in object change
Neural Networks 2. 2 Receptive fields and dealing with image inputs
 CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 04, 2016 Neural Networks 2 Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng, C. Cervantes Overview Convolutional Neural Networks Recurrent Neural Networks 1 Introduction There
CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 04, 2016 Neural Networks 2 Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng, C. Cervantes Overview Convolutional Neural Networks Recurrent Neural Networks 1 Introduction There
Signal Processing and Linear Systems1 Lecture 4: Characterizing Systems
 Signal Processing and Linear Systems Lecture : Characterizing Systems Nicholas Dwork www.stanford.edu/~ndwork Our goal will be to develop a way to learn how the system behaves. In general, this is a very
Signal Processing and Linear Systems Lecture : Characterizing Systems Nicholas Dwork www.stanford.edu/~ndwork Our goal will be to develop a way to learn how the system behaves. In general, this is a very
Properties of the Autocorrelation Function
 Properties of the Autocorrelation Function I The autocorrelation function of a (real-valued) random process satisfies the following properties: 1. R X (t, t) 0 2. R X (t, u) =R X (u, t) (symmetry) 3. R
Properties of the Autocorrelation Function I The autocorrelation function of a (real-valued) random process satisfies the following properties: 1. R X (t, t) 0 2. R X (t, u) =R X (u, t) (symmetry) 3. R
Additional Pointers. Introduction to Computer Vision. Convolution. Area operations: Linear filtering
 Additional Pointers Introduction to Computer Vision CS / ECE 181B andout #4 : Available this afternoon Midterm: May 6, 2004 W #2 due tomorrow Ack: Prof. Matthew Turk for the lecture slides. See my ECE
Additional Pointers Introduction to Computer Vision CS / ECE 181B andout #4 : Available this afternoon Midterm: May 6, 2004 W #2 due tomorrow Ack: Prof. Matthew Turk for the lecture slides. See my ECE
ECE Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision. Outline
 2/9/7 ECE592-064 Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision Depart. of ECE, NC State University Instructor: Tianfu (Matt) Wu Spring 207. Recap Outline 2. Sharpening Filtering Illustration
2/9/7 ECE592-064 Digital Image Processing and Introduction to Computer Vision Depart. of ECE, NC State University Instructor: Tianfu (Matt) Wu Spring 207. Recap Outline 2. Sharpening Filtering Illustration
Overview. Harris interest points. Comparing interest points (SSD, ZNCC, SIFT) Scale & affine invariant interest points
 Overview Harris interest points Comparing interest points (SSD, ZNCC, SIFT) Scale & affine invariant interest points Evaluation and comparison of different detectors Region descriptors and their performance
Overview Harris interest points Comparing interest points (SSD, ZNCC, SIFT) Scale & affine invariant interest points Evaluation and comparison of different detectors Region descriptors and their performance
Homework 5 Solutions
 18-290 Signals and Systems Profs. Byron Yu and Pulkit Grover Fall 2017 Homework 5 Solutions Part One 1. (18 points) For each of the following impulse responses, determine whether the corresponding LTI
18-290 Signals and Systems Profs. Byron Yu and Pulkit Grover Fall 2017 Homework 5 Solutions Part One 1. (18 points) For each of the following impulse responses, determine whether the corresponding LTI
Gaussian derivatives
 Gaussian derivatives UCU Winter School 2017 James Pritts Czech Tecnical University January 16, 2017 1 Images taken from Noah Snavely s and Robert Collins s course notes Definition An image (grayscale)
Gaussian derivatives UCU Winter School 2017 James Pritts Czech Tecnical University January 16, 2017 1 Images taken from Noah Snavely s and Robert Collins s course notes Definition An image (grayscale)
Image Filtering. Slides, adapted from. Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski, U.Washington
 Image Filtering Slides, adapted from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski, U.Washington The power of blur All is Vanity by Charles Allen Gillbert (1873-1929) Harmon LD & JuleszB (1973) The recognition of faces.
Image Filtering Slides, adapted from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski, U.Washington The power of blur All is Vanity by Charles Allen Gillbert (1873-1929) Harmon LD & JuleszB (1973) The recognition of faces.
Deep Learning. Convolutional Neural Network (CNNs) Ali Ghodsi. October 30, Slides are partially based on Book in preparation, Deep Learning
 Convolutional Neural Network (CNNs) University of Waterloo October 30, 2015 Slides are partially based on Book in preparation, by Bengio, Goodfellow, and Aaron Courville, 2015 Convolutional Networks Convolutional
Convolutional Neural Network (CNNs) University of Waterloo October 30, 2015 Slides are partially based on Book in preparation, by Bengio, Goodfellow, and Aaron Courville, 2015 Convolutional Networks Convolutional
Filtering and Edge Detection
 Filtering and Edge Detection Local Neighborhoods Hard to tell anything from a single pixel Example: you see a reddish pixel. Is this the object s color? Illumination? Noise? The next step in order of complexity
Filtering and Edge Detection Local Neighborhoods Hard to tell anything from a single pixel Example: you see a reddish pixel. Is this the object s color? Illumination? Noise? The next step in order of complexity
INTEREST POINTS AT DIFFERENT SCALES
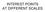 INTEREST POINTS AT DIFFERENT SCALES Thank you for the slides. They come mostly from the following sources. Dan Huttenlocher Cornell U David Lowe U. of British Columbia Martial Hebert CMU Intuitively, junctions
INTEREST POINTS AT DIFFERENT SCALES Thank you for the slides. They come mostly from the following sources. Dan Huttenlocher Cornell U David Lowe U. of British Columbia Martial Hebert CMU Intuitively, junctions
CS4495/6495 Introduction to Computer Vision. 2A-L6 Edge detection: 2D operators
 CS4495/6495 Introduction to Computer Vision 2A-L6 Edge detection: 2D operators Derivative theorem of convolution - 1D This saves us one operation: ( ) ( ) x h f h f x f h h x h x ( ) f Derivative of Gaussian
CS4495/6495 Introduction to Computer Vision 2A-L6 Edge detection: 2D operators Derivative theorem of convolution - 1D This saves us one operation: ( ) ( ) x h f h f x f h h x h x ( ) f Derivative of Gaussian
CSE 473/573 Computer Vision and Image Processing (CVIP)
 CSE 473/573 Computer Vision and Image Processing (CVIP) Ifeoma Nwogu inwogu@buffalo.edu Lecture 11 Local Features 1 Schedule Last class We started local features Today More on local features Readings for
CSE 473/573 Computer Vision and Image Processing (CVIP) Ifeoma Nwogu inwogu@buffalo.edu Lecture 11 Local Features 1 Schedule Last class We started local features Today More on local features Readings for
Homework 5 Solutions
 18-290 Signals and Systems Profs. Byron Yu and Pulkit Grover Fall 2018 Homework 5 Solutions. Part One 1. (12 points) Calculate the following convolutions: (a) x[n] δ[n n 0 ] (b) 2 n u[n] u[n] (c) 2 n u[n]
18-290 Signals and Systems Profs. Byron Yu and Pulkit Grover Fall 2018 Homework 5 Solutions. Part One 1. (12 points) Calculate the following convolutions: (a) x[n] δ[n n 0 ] (b) 2 n u[n] u[n] (c) 2 n u[n]
Edge Detection. Computer Vision P. Schrater Spring 2003
 Edge Detection Computer Vision P. Schrater Spring 2003 Simplest Model: (Canny) Edge(x) = a U(x) + n(x) U(x)? x=0 Convolve image with U and find points with high magnitude. Choose value by comparing with
Edge Detection Computer Vision P. Schrater Spring 2003 Simplest Model: (Canny) Edge(x) = a U(x) + n(x) U(x)? x=0 Convolve image with U and find points with high magnitude. Choose value by comparing with
Colorado School of Mines Image and Multidimensional Signal Processing
 Image and Multidimensional Signal Processing Professor William Hoff Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spatial Filtering Main idea Spatial filtering Define a neighborhood of a pixel
Image and Multidimensional Signal Processing Professor William Hoff Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spatial Filtering Main idea Spatial filtering Define a neighborhood of a pixel
Lecture 6: Edge Detection. CAP 5415: Computer Vision Fall 2008
 Lecture 6: Edge Detection CAP 5415: Computer Vision Fall 2008 Announcements PS 2 is available Please read it by Thursday During Thursday lecture, I will be going over it in some detail Monday - Computer
Lecture 6: Edge Detection CAP 5415: Computer Vision Fall 2008 Announcements PS 2 is available Please read it by Thursday During Thursday lecture, I will be going over it in some detail Monday - Computer
Introduction to Computer Vision. 2D Linear Systems
 Introduction to Computer Vision D Linear Systems Review: Linear Systems We define a system as a unit that converts an input function into an output function Independent variable System operator or Transfer
Introduction to Computer Vision D Linear Systems Review: Linear Systems We define a system as a unit that converts an input function into an output function Independent variable System operator or Transfer
Convolution and Pooling as an Infinitely Strong Prior
 Convolution and Pooling as an Infinitely Strong Prior Sargur Srihari srihari@buffalo.edu This is part of lecture slides on Deep Learning: http://www.cedar.buffalo.edu/~srihari/cse676 1 Topics in Convolutional
Convolution and Pooling as an Infinitely Strong Prior Sargur Srihari srihari@buffalo.edu This is part of lecture slides on Deep Learning: http://www.cedar.buffalo.edu/~srihari/cse676 1 Topics in Convolutional
Gaussian Basics Random Processes Filtering of Random Processes Signal Space Concepts
 White Gaussian Noise I Definition: A (real-valued) random process X t is called white Gaussian Noise if I X t is Gaussian for each time instance t I Mean: m X (t) =0 for all t I Autocorrelation function:
White Gaussian Noise I Definition: A (real-valued) random process X t is called white Gaussian Noise if I X t is Gaussian for each time instance t I Mean: m X (t) =0 for all t I Autocorrelation function:
Statistical Machine Learning
 Statistical Machine Learning Lecture 9 Numerical optimization and deep learning Niklas Wahlström Division of Systems and Control Department of Information Technology Uppsala University niklas.wahlstrom@it.uu.se
Statistical Machine Learning Lecture 9 Numerical optimization and deep learning Niklas Wahlström Division of Systems and Control Department of Information Technology Uppsala University niklas.wahlstrom@it.uu.se
Overview. Introduction to local features. Harris interest points + SSD, ZNCC, SIFT. Evaluation and comparison of different detectors
 Overview Introduction to local features Harris interest points + SSD, ZNCC, SIFT Scale & affine invariant interest point detectors Evaluation and comparison of different detectors Region descriptors and
Overview Introduction to local features Harris interest points + SSD, ZNCC, SIFT Scale & affine invariant interest point detectors Evaluation and comparison of different detectors Region descriptors and
Lecture 7 Convolutional Neural Networks
 Lecture 7 Convolutional Neural Networks CMSC 35246: Deep Learning Shubhendu Trivedi & Risi Kondor University of Chicago April 17, 2017 We saw before: ŷ x 1 x 2 x 3 x 4 A series of matrix multiplications:
Lecture 7 Convolutional Neural Networks CMSC 35246: Deep Learning Shubhendu Trivedi & Risi Kondor University of Chicago April 17, 2017 We saw before: ŷ x 1 x 2 x 3 x 4 A series of matrix multiplications:
Robert Collins CSE598G Mean-Shift Blob Tracking through Scale Space
 Mean-Shift Blob Tracking through Scale Space Robert Collins, CVPR 03 Abstract Mean-shift tracking Choosing scale of kernel is an issue Scale-space feature selection provides inspiration Perform mean-shift
Mean-Shift Blob Tracking through Scale Space Robert Collins, CVPR 03 Abstract Mean-shift tracking Choosing scale of kernel is an issue Scale-space feature selection provides inspiration Perform mean-shift
ITK Filters. Thresholding Edge Detection Gradients Second Order Derivatives Neighborhood Filters Smoothing Filters Distance Map Image Transforms
 ITK Filters Thresholding Edge Detection Gradients Second Order Derivatives Neighborhood Filters Smoothing Filters Distance Map Image Transforms ITCS 6010:Biomedical Imaging and Visualization 1 ITK Filters:
ITK Filters Thresholding Edge Detection Gradients Second Order Derivatives Neighborhood Filters Smoothing Filters Distance Map Image Transforms ITCS 6010:Biomedical Imaging and Visualization 1 ITK Filters:
Image Gradients and Gradient Filtering Computer Vision
 Image Gradients and Gradient Filtering 16-385 Computer Vision What is an image edge? Recall that an image is a 2D function f(x) edge edge How would you detect an edge? What kinds of filter would you use?
Image Gradients and Gradient Filtering 16-385 Computer Vision What is an image edge? Recall that an image is a 2D function f(x) edge edge How would you detect an edge? What kinds of filter would you use?
Group Equivariant Convolutional Networks. Taco Cohen
 Group Equivariant Convolutional Networks Taco Cohen Outline 1. Symmetry & Deep Learning: Statistical Power from Symmetry Invariance vs Equivariance Equivariance in Deep Learning 2.Group Theory Symmetry,
Group Equivariant Convolutional Networks Taco Cohen Outline 1. Symmetry & Deep Learning: Statistical Power from Symmetry Invariance vs Equivariance Equivariance in Deep Learning 2.Group Theory Symmetry,
Digital Image Processing. Filtering in the Frequency Domain
 2D Linear Systems 2D Fourier Transform and its Properties The Basics of Filtering in Frequency Domain Image Smoothing Image Sharpening Selective Filtering Implementation Tips 1 General Definition: System
2D Linear Systems 2D Fourier Transform and its Properties The Basics of Filtering in Frequency Domain Image Smoothing Image Sharpening Selective Filtering Implementation Tips 1 General Definition: System
Thinking in Frequency
 09/05/17 Thinking in Frequency Computational Photography University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Administrative Matlab/linear algebra tutorial tomorrow, planned for 6:30pm Probably 1214 DCL (will send confirmation
09/05/17 Thinking in Frequency Computational Photography University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Administrative Matlab/linear algebra tutorial tomorrow, planned for 6:30pm Probably 1214 DCL (will send confirmation
Convolutional networks. Sebastian Seung
 Convolutional networks Sebastian Seung Convolutional network Neural network with spatial organization every neuron has a location usually on a grid Translation invariance synaptic strength depends on locations
Convolutional networks Sebastian Seung Convolutional network Neural network with spatial organization every neuron has a location usually on a grid Translation invariance synaptic strength depends on locations
Reminders. Thought questions should be submitted on eclass. Please list the section related to the thought question
 Linear regression Reminders Thought questions should be submitted on eclass Please list the section related to the thought question If it is a more general, open-ended question not exactly related to a
Linear regression Reminders Thought questions should be submitted on eclass Please list the section related to the thought question If it is a more general, open-ended question not exactly related to a
CENG 783. Special topics in. Deep Learning. AlchemyAPI. Week 8. Sinan Kalkan
 CENG 783 Special topics in Deep Learning AlchemyAPI Week 8 Sinan Kalkan Loss functions Many correct labels case: Binary prediction for each label, independently: L i = σ j max 0, 1 y ij f j y ij = +1 if
CENG 783 Special topics in Deep Learning AlchemyAPI Week 8 Sinan Kalkan Loss functions Many correct labels case: Binary prediction for each label, independently: L i = σ j max 0, 1 y ij f j y ij = +1 if
Empirical Mean and Variance!
 Global Image Properties! Global image properties refer to an image as a whole rather than components. Computation of global image properties is often required for image enhancement, preceding image analysis.!
Global Image Properties! Global image properties refer to an image as a whole rather than components. Computation of global image properties is often required for image enhancement, preceding image analysis.!
Corner detection: the basic idea
 Corner detection: the basic idea At a corner, shifting a window in any direction should give a large change in intensity flat region: no change in all directions edge : no change along the edge direction
Corner detection: the basic idea At a corner, shifting a window in any direction should give a large change in intensity flat region: no change in all directions edge : no change along the edge direction
The Kernel Trick, Gram Matrices, and Feature Extraction. CS6787 Lecture 4 Fall 2017
 The Kernel Trick, Gram Matrices, and Feature Extraction CS6787 Lecture 4 Fall 2017 Momentum for Principle Component Analysis CS6787 Lecture 3.1 Fall 2017 Principle Component Analysis Setting: find the
The Kernel Trick, Gram Matrices, and Feature Extraction CS6787 Lecture 4 Fall 2017 Momentum for Principle Component Analysis CS6787 Lecture 3.1 Fall 2017 Principle Component Analysis Setting: find the
Introduction to Linear Systems
 cfl David J Fleet, 998 Introduction to Linear Systems David Fleet For operator T, input I, and response R = T [I], T satisfies: ffl homogeniety: iff T [ai] = at[i] 8a 2 C ffl additivity: iff T [I + I 2
cfl David J Fleet, 998 Introduction to Linear Systems David Fleet For operator T, input I, and response R = T [I], T satisfies: ffl homogeniety: iff T [ai] = at[i] 8a 2 C ffl additivity: iff T [I + I 2
Convolutional Neural Networks
 Convolutional Neural Networks Books» http://www.deeplearningbook.org/ Books http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/.org/ reviews» http://www.deeplearningbook.org/contents/linear_algebra.html» http://www.deeplearningbook.org/contents/prob.html»
Convolutional Neural Networks Books» http://www.deeplearningbook.org/ Books http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/.org/ reviews» http://www.deeplearningbook.org/contents/linear_algebra.html» http://www.deeplearningbook.org/contents/prob.html»
Computational Photography
 Computational Photography Si Lu Spring 208 http://web.cecs.pdx.edu/~lusi/cs50/cs50_computati onal_photography.htm 04/0/208 Last Time o Digital Camera History of Camera Controlling Camera o Photography
Computational Photography Si Lu Spring 208 http://web.cecs.pdx.edu/~lusi/cs50/cs50_computati onal_photography.htm 04/0/208 Last Time o Digital Camera History of Camera Controlling Camera o Photography
Edge Detection. CS 650: Computer Vision
 CS 650: Computer Vision Edges and Gradients Edge: local indication of an object transition Edge detection: local operators that find edges (usually involves convolution) Local intensity transitions are
CS 650: Computer Vision Edges and Gradients Edge: local indication of an object transition Edge detection: local operators that find edges (usually involves convolution) Local intensity transitions are
Lecture 1 January 5, 2016
 MATH 262/CME 372: Applied Fourier Analysis and Winter 26 Elements of Modern Signal Processing Lecture January 5, 26 Prof. Emmanuel Candes Scribe: Carlos A. Sing-Long; Edited by E. Candes & E. Bates Outline
MATH 262/CME 372: Applied Fourier Analysis and Winter 26 Elements of Modern Signal Processing Lecture January 5, 26 Prof. Emmanuel Candes Scribe: Carlos A. Sing-Long; Edited by E. Candes & E. Bates Outline
Lecture 8: Interest Point Detection. Saad J Bedros
 #1 Lecture 8: Interest Point Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review of Edge Detectors #2 Today s Lecture Interest Points Detection What do we mean with Interest Point Detection in an Image Goal:
#1 Lecture 8: Interest Point Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review of Edge Detectors #2 Today s Lecture Interest Points Detection What do we mean with Interest Point Detection in an Image Goal:
Image Filtering, Edges and Image Representation
 Image Filtering, Edges and Image Representation Capturing what s important Req reading: Chapter 7, 9 F&P Adelson, Simoncelli and Freeman (handout online) Opt reading: Horn 7 & 8 FP 8 February 19, 8 A nice
Image Filtering, Edges and Image Representation Capturing what s important Req reading: Chapter 7, 9 F&P Adelson, Simoncelli and Freeman (handout online) Opt reading: Horn 7 & 8 FP 8 February 19, 8 A nice
CEE598 - Visual Sensing for Civil Infrastructure Eng. & Mgmt.
 CEE598 - Visual Sensing for Civil Infrastructure Eng. & Mgmt. Session 8- Linear Filters From Spatial Domain to Frequency Domain Mani Golparvar-Fard Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 329D,
CEE598 - Visual Sensing for Civil Infrastructure Eng. & Mgmt. Session 8- Linear Filters From Spatial Domain to Frequency Domain Mani Golparvar-Fard Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 329D,
printing Three areas: solid calculus, particularly calculus of several
 Math 5610 printing 5600 5610 Notes of 8/21/18 Quick Review of some Prerequisites Three areas: solid calculus, particularly calculus of several variables. linear algebra Programming (Coding) The term project
Math 5610 printing 5600 5610 Notes of 8/21/18 Quick Review of some Prerequisites Three areas: solid calculus, particularly calculus of several variables. linear algebra Programming (Coding) The term project
Histogram Processing
 Histogram Processing The histogram of a digital image with gray levels in the range [0,L-] is a discrete function h ( r k ) = n k where r k n k = k th gray level = number of pixels in the image having
Histogram Processing The histogram of a digital image with gray levels in the range [0,L-] is a discrete function h ( r k ) = n k where r k n k = k th gray level = number of pixels in the image having
Machine vision, spring 2018 Summary 4
 Machine vision Summary # 4 The mask for Laplacian is given L = 4 (6) Another Laplacian mask that gives more importance to the center element is given by L = 8 (7) Note that the sum of the elements in the
Machine vision Summary # 4 The mask for Laplacian is given L = 4 (6) Another Laplacian mask that gives more importance to the center element is given by L = 8 (7) Note that the sum of the elements in the
RegML 2018 Class 8 Deep learning
 RegML 2018 Class 8 Deep learning Lorenzo Rosasco UNIGE-MIT-IIT June 18, 2018 Supervised vs unsupervised learning? So far we have been thinking of learning schemes made in two steps f(x) = w, Φ(x) F, x
RegML 2018 Class 8 Deep learning Lorenzo Rosasco UNIGE-MIT-IIT June 18, 2018 Supervised vs unsupervised learning? So far we have been thinking of learning schemes made in two steps f(x) = w, Φ(x) F, x
Reconnaissance d objetsd et vision artificielle
 Reconnaissance d objetsd et vision artificielle http://www.di.ens.fr/willow/teaching/recvis09 Lecture 6 Face recognition Face detection Neural nets Attention! Troisième exercice de programmation du le
Reconnaissance d objetsd et vision artificielle http://www.di.ens.fr/willow/teaching/recvis09 Lecture 6 Face recognition Face detection Neural nets Attention! Troisième exercice de programmation du le
Lesson 04. KAZE, Non-linear diffusion filtering, ORB, MSER. Ing. Marek Hrúz, Ph.D.
 Lesson 04 KAZE, Non-linear diffusion filtering, ORB, MSER Ing. Marek Hrúz, Ph.D. Katedra Kybernetiky Fakulta aplikovaných věd Západočeská univerzita v Plzni Lesson 04 KAZE ORB: an efficient alternative
Lesson 04 KAZE, Non-linear diffusion filtering, ORB, MSER Ing. Marek Hrúz, Ph.D. Katedra Kybernetiky Fakulta aplikovaných věd Západočeská univerzita v Plzni Lesson 04 KAZE ORB: an efficient alternative
Local Enhancement. Local enhancement
 Local Enhancement Local Enhancement Median filtering (see notes/slides, 3.5.2) HW4 due next Wednesday Required Reading: Sections 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6, 3.7 Local Enhancement 1 Local enhancement Sometimes
Local Enhancement Local Enhancement Median filtering (see notes/slides, 3.5.2) HW4 due next Wednesday Required Reading: Sections 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6, 3.7 Local Enhancement 1 Local enhancement Sometimes
Introduction to gradient descent
 6-1: Introduction to gradient descent Prof. J.C. Kao, UCLA Introduction to gradient descent Derivation and intuitions Hessian 6-2: Introduction to gradient descent Prof. J.C. Kao, UCLA Introduction Our
6-1: Introduction to gradient descent Prof. J.C. Kao, UCLA Introduction to gradient descent Derivation and intuitions Hessian 6-2: Introduction to gradient descent Prof. J.C. Kao, UCLA Introduction Our
Deep Learning (CNNs)
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Deep Learning (CNNs) Deep Learning Readings: Murphy 28 Bishop - - HTF - - Mitchell
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Deep Learning (CNNs) Deep Learning Readings: Murphy 28 Bishop - - HTF - - Mitchell
9 Classification. 9.1 Linear Classifiers
 9 Classification This topic returns to prediction. Unlike linear regression where we were predicting a numeric value, in this case we are predicting a class: winner or loser, yes or no, rich or poor, positive
9 Classification This topic returns to prediction. Unlike linear regression where we were predicting a numeric value, in this case we are predicting a class: winner or loser, yes or no, rich or poor, positive
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 10a. Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 10a. Markov Chain Monte Carlo Markov Chain Monte Carlo In high-dimensional spaces, rejection sampling and importance sampling are very inefficient An alternative is Markov Chain
Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 10a. Markov Chain Monte Carlo Markov Chain Monte Carlo In high-dimensional spaces, rejection sampling and importance sampling are very inefficient An alternative is Markov Chain
Digital Image Processing. Lecture 6 (Enhancement) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 2009
 Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 009 Outline Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain Spatial Filtering Smoothing Filters Median Filter
Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 009 Outline Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain Spatial Filtering Smoothing Filters Median Filter
CS5540: Computational Techniques for Analyzing Clinical Data. Prof. Ramin Zabih (CS) Prof. Ashish Raj (Radiology)
 CS5540: Computational Techniques for Analyzing Clinical Data Prof. Ramin Zabih (CS) Prof. Ashish Raj (Radiology) Administrivia We re going to try to end class by 2:25 Like the registrar believes Sign up
CS5540: Computational Techniques for Analyzing Clinical Data Prof. Ramin Zabih (CS) Prof. Ashish Raj (Radiology) Administrivia We re going to try to end class by 2:25 Like the registrar believes Sign up
Corners, Blobs & Descriptors. With slides from S. Lazebnik & S. Seitz, D. Lowe, A. Efros
 Corners, Blobs & Descriptors With slides from S. Lazebnik & S. Seitz, D. Lowe, A. Efros Motivation: Build a Panorama M. Brown and D. G. Lowe. Recognising Panoramas. ICCV 2003 How do we build panorama?
Corners, Blobs & Descriptors With slides from S. Lazebnik & S. Seitz, D. Lowe, A. Efros Motivation: Build a Panorama M. Brown and D. G. Lowe. Recognising Panoramas. ICCV 2003 How do we build panorama?
The Convolution Sum for Discrete-Time LTI Systems
 The Convolution Sum for Discrete-Time LTI Systems Andrew W. H. House 01 June 004 1 The Basics of the Convolution Sum Consider a DT LTI system, L. x(n) L y(n) DT convolution is based on an earlier result
The Convolution Sum for Discrete-Time LTI Systems Andrew W. H. House 01 June 004 1 The Basics of the Convolution Sum Consider a DT LTI system, L. x(n) L y(n) DT convolution is based on an earlier result
Convolutional neural networks
 11-1: Convolutional neural networks Prof. J.C. Kao, UCLA Convolutional neural networks Motivation Biological inspiration Convolution operation Convolutional layer Padding and stride CNN architecture 11-2:
11-1: Convolutional neural networks Prof. J.C. Kao, UCLA Convolutional neural networks Motivation Biological inspiration Convolution operation Convolutional layer Padding and stride CNN architecture 11-2:
Frequency2: Sampling and Aliasing
 CS 4495 Computer Vision Frequency2: Sampling and Aliasing Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia Project 1 is due tonight. Submit what you have at the deadline. Next problem set stereo
CS 4495 Computer Vision Frequency2: Sampling and Aliasing Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia Project 1 is due tonight. Submit what you have at the deadline. Next problem set stereo
Review Smoothing Spatial Filters Sharpening Spatial Filters. Spatial Filtering. Dr. Praveen Sankaran. Department of ECE NIT Calicut.
 Spatial Filtering Dr. Praveen Sankaran Department of ECE NIT Calicut January 7, 203 Outline 2 Linear Nonlinear 3 Spatial Domain Refers to the image plane itself. Direct manipulation of image pixels. Figure:
Spatial Filtering Dr. Praveen Sankaran Department of ECE NIT Calicut January 7, 203 Outline 2 Linear Nonlinear 3 Spatial Domain Refers to the image plane itself. Direct manipulation of image pixels. Figure:
Multiresolution schemes
 Multiresolution schemes Fondamenti di elaborazione del segnale multi-dimensionale Multi-dimensional signal processing Stefano Ferrari Università degli Studi di Milano stefano.ferrari@unimi.it Elaborazione
Multiresolution schemes Fondamenti di elaborazione del segnale multi-dimensionale Multi-dimensional signal processing Stefano Ferrari Università degli Studi di Milano stefano.ferrari@unimi.it Elaborazione
Fourier Transforms 1D
 Fourier Transforms 1D 3D Image Processing Alireza Ghane 1 Overview Recap Intuitions Function representations shift-invariant spaces linear, time-invariant (LTI) systems complex numbers Fourier Transforms
Fourier Transforms 1D 3D Image Processing Alireza Ghane 1 Overview Recap Intuitions Function representations shift-invariant spaces linear, time-invariant (LTI) systems complex numbers Fourier Transforms
Blobs & Scale Invariance
 Blobs & Scale Invariance Prof. Didier Stricker Doz. Gabriele Bleser Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking With slides from Bebis, S. Lazebnik & S. Seitz, D. Lowe, A. Efros 1 Apertizer: some videos
Blobs & Scale Invariance Prof. Didier Stricker Doz. Gabriele Bleser Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking With slides from Bebis, S. Lazebnik & S. Seitz, D. Lowe, A. Efros 1 Apertizer: some videos
Neural networks and optimization
 Neural networks and optimization Nicolas Le Roux Criteo 18/05/15 Nicolas Le Roux (Criteo) Neural networks and optimization 18/05/15 1 / 85 1 Introduction 2 Deep networks 3 Optimization 4 Convolutional
Neural networks and optimization Nicolas Le Roux Criteo 18/05/15 Nicolas Le Roux (Criteo) Neural networks and optimization 18/05/15 1 / 85 1 Introduction 2 Deep networks 3 Optimization 4 Convolutional
Convolutional Neural Networks. Srikumar Ramalingam
 Convolutional Neural Networks Srikumar Ramalingam Reference Many of the slides are prepared using the following resources: neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com (mainly Chapter 6) http://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/
Convolutional Neural Networks Srikumar Ramalingam Reference Many of the slides are prepared using the following resources: neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com (mainly Chapter 6) http://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/
Νεςπο-Ασαυήρ Υπολογιστική Neuro-Fuzzy Computing
 Νεςπο-Ασαυήρ Υπολογιστική Neuro-Fuzzy Computing ΗΥ418 Διδάσκων Δημήτριος Κατσαρός @ Τμ. ΗΜΜΥ Πανεπιστήμιο Θεσσαλίαρ Διάλεξη 21η BackProp for CNNs: Do I need to understand it? Why do we have to write the
Νεςπο-Ασαυήρ Υπολογιστική Neuro-Fuzzy Computing ΗΥ418 Διδάσκων Δημήτριος Κατσαρός @ Τμ. ΗΜΜΥ Πανεπιστήμιο Θεσσαλίαρ Διάλεξη 21η BackProp for CNNs: Do I need to understand it? Why do we have to write the
MAT Mathematics in Today's World
 MAT 1000 Mathematics in Today's World Last Time We discussed the four rules that govern probabilities: 1. Probabilities are numbers between 0 and 1 2. The probability an event does not occur is 1 minus
MAT 1000 Mathematics in Today's World Last Time We discussed the four rules that govern probabilities: 1. Probabilities are numbers between 0 and 1 2. The probability an event does not occur is 1 minus
Multiresolution schemes
 Multiresolution schemes Fondamenti di elaborazione del segnale multi-dimensionale Stefano Ferrari Università degli Studi di Milano stefano.ferrari@unimi.it Elaborazione dei Segnali Multi-dimensionali e
Multiresolution schemes Fondamenti di elaborazione del segnale multi-dimensionale Stefano Ferrari Università degli Studi di Milano stefano.ferrari@unimi.it Elaborazione dei Segnali Multi-dimensionali e
CSC321 Lecture 4: Learning a Classifier
 CSC321 Lecture 4: Learning a Classifier Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 4: Learning a Classifier 1 / 28 Overview Last time: binary classification, perceptron algorithm Limitations of the perceptron
CSC321 Lecture 4: Learning a Classifier Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 4: Learning a Classifier 1 / 28 Overview Last time: binary classification, perceptron algorithm Limitations of the perceptron
Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
 Convolutional Neural Network Architecture Zhisheng Zhong Feburary 2nd, 2018 Zhisheng Zhong Convolutional Neural Network Architecture Feburary 2nd, 2018 1 / 55 Outline 1 Introduction of Convolution Motivation
Convolutional Neural Network Architecture Zhisheng Zhong Feburary 2nd, 2018 Zhisheng Zhong Convolutional Neural Network Architecture Feburary 2nd, 2018 1 / 55 Outline 1 Introduction of Convolution Motivation
Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients
 Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients Roger Grosse 1 Introduction Last lecture, we introduced RNNs and saw how to derive the gradients using backprop through time. In principle, this lets us train
Lecture 15: Exploding and Vanishing Gradients Roger Grosse 1 Introduction Last lecture, we introduced RNNs and saw how to derive the gradients using backprop through time. In principle, this lets us train
