Announcements 5 Dec 2013
|
|
|
- Lawrence Lindsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Announcements 5 Dec Photo contest submissions due tomorrow night! 2. Online course evaluations due Sun, Dec Please take both the ratings and the comments seriously. I read every single comment, as does the Physics Department promotion/tenure committee. 3. TA-led final exam review doodle.com survey again Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 1
2 Reflections Clicker quiz: What happens when an upward pulse hits the end and turns around? a. the wave reflects back, upward b. the wave reflects back, downward c. it depends Demo: rubber tubing Web demo: Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 2
3 Boundaries Rope: Light rope meets heavy rope Light: Air meets glass In both cases: Part of wave r and part of wave t Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 3
4 Superposition/Interference From warmup: What happens when two pulses on a string (one coming from each end) meet in the middle? a. The pulses pass through each other b. The pulses reflect off of each other Demo: Shive wave machine Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 4
5 What about this case? Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 5
6 Review: What gets transported by the wave? What does the transporting? What was wrong with the Star Wars video? Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 6
7 Demo No sound in a vacuum Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 7
8 Sound Clicker quiz: What type of oscillation is a sound wave? a. Longitudinal b. Transverse c. Neither Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 8
9 What is Sound? Kind of like this: but not entirely. (What s different?) Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 9
10 Compressions & Rarefactions Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 10
11 Demo Hearing test! Frequency source & speaker Audible sound waves: ~20 Hz to ~20 khz (different for everyone) Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 11
12 How is sound produced? Speaker cutaway Demo: Tuning fork Demo: singing rod Demo: Air jet and spinning disk Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 12
13 Speed of sound Gases Air: v = 343 m/s at 20 C Other temps: v = 331 m/s T K To impress your date: ~1 km in 3 seconds 273 (You need that for HW 26-1) Helium: 972 m/s (at 0 C) Why so much faster? Solids Like the P (longitudinal) and S (transverse) waves in earthquakes Table in book: Aluminum 5100 m/s Copper 3560 m/s Almost certainly these speeds are for longitudinal waves Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 13
14 Speed of sound, cont. Liquids Only longitudinal. (Why are transverse waves not possible?) Table in book: Water 1490 m/s Methanol 1140 m/s Why would solids be the fastest? Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 14
15 Intensity How concentrated (or focused ) the wave is Definition I P A (not just for sound) Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 15
16 Intensity vs distance For a spherically emitting source: P I A I so I P 4 r r r1 2 i s l! True also for most sound waves, even if not spherical, since A ~ r 2 for other shapes as well. Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 16
17 From warmup If a loudspeaker emits spherical sound waves in all directions, what decreases as you go farther away from the loudspeaker? a. frequency b. intensity c. wavelength Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 17
18 Clicker quiz You measure the sound intensity produced by a spherically-emitting speaker to be 10 W/m 2 at a distance of 1.5 meters. What will be the intensity at 3 meters away? a. 2.5 W/m 2 b. 5 c. 10 d. 20 e. 40 W/m 2 Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 18
19 Worked Problem Same situation (spherically emitting speaker, 10 W/m 2 at 1.5 meters). What is the total sound power (watts) being produced by the speaker? Answer: W Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 19
20 Clicker quiz An earthquake that has a Richter scale magnitude of 8 is how much more powerful (in some sense) than one that has a magnitude of 7? Earthquake1 = Earthquake 2. a. 1.1 b c. 2 d. 8 e. 10 Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 20
21 Decibels We hear over a huge range of intensities So use a logarithmic scale (like earthquakes) multiplied by 10, for no apparent reason Decibel number I 10log where Io 10 W/m I o log = logarithm, base adding ten to db number = 10 to the intensity Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 21
22 From warmup You go to a rock concert where the sound level where you are standing is 110 db. How does the intensity (power/area) of sound waves compare to when you listen to the same music on your home stereo system, 90 db at the spot you sit? a. Concert intensity = Stereo intensity b. Concert intensity = 1.20 stereo intensity c. Concert intensity = 2 stereo intensity d. Concert intensity = 10 stereo intensity e. Concert intensity = 20 stereo intensity f. Concert intensity = 100 stereo intensity Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 22
23 Decibels, cont. From table in book: W/m 2 db Jet on a runway Instant pain, damage Machine gun damage Rock concert (best seats) pain, damage Power mower damage (if all day) Vacuum cleaner safe all day Conversation Whisper Rub fingers by ear Threshold Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 23
24 OSHA Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 24
25 From warmup Ralph is confused about Table 14.2 (8th edition), where the book lists different intensity levels for different sources. For example, the table says a vacuum cleaner has an intensity of 70 db. What confuses Ralph, is that it seems like a vacuum cleaner should sound louder to someone who is pushing the vacuum cleaner than to someone who is a little farther away. How can the intensity level be 70 db for both people? How should you answer Ralph's question? My answer: For once in Ralph s life, he got something right!! Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 25
26 Logarithm Review (base 10) Log 10 (x) is the inverse of 10 y if x = 10 y then y = log 10 (x) I.e. 10 to the what equals 22? answer: ( log(22) ) log 10 (100) =? Translation: 10 to what number equals 100? (2) Test: 10 2 = 100 ln(100) =? ( ln = log e = log ) Translation: e to what number equals 100? (4.605) Test with calculator: = If the problem just says log(100) could be either log 10 or ln For us: assume log 10 Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 26
27 Clicker quiz What is log 10 (1,000,000)? a. 1 b. 6 c. 7.5 d. 10 e. 93 Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 27
28 Laws of Logs Review 1. log(ab) = log(a) + log(b) 2. log(a n ) = n log(a) Worked problem: If log(3) = 0.477, what is log(300)? Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 28
29 Decibels, cont. 10log I I o = decibel number I 0 = W/m 2 Compare two intensities: If you increase I by a factor of 10, add to If you increase I by a factor of 100, add to If you increase I by a factor of 1000, add to each factor of ten added to db number = 10 to the intensity Worked problem: If you increase I by 2, what do you add to? (Given that log(2) = ) Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 29
30 You may need to know this for final each factor of ten added to db number = 10 to the intensity each 10 to the intensity means you add 10 dbs each factor of 3 added to db number = 2 to the intensity each 2 to the intensity means you add 3 dbs Clicker quiz: If you increase I by a factor of 8, add to the decibel level (Hint: do it with 2 s) a. 4 b. 6 c. 8 d. 9 e. 12 Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 30
31 Worked problem You hear an average of 82 db in your workshop as three printing presses run. The next day you come in and find the sound level to be 88 db. How many total printing presses are now running? Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 31
32 What if you need to solve for I? (this equation is not given on final) Answer: I I 10 0 /10 Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 32
33 Review quizzes Clicker quiz 1: The intensity of a wave is its a. power b. power/area c. power area Clicker quiz 2: T/F: If you double the sound intensity, the decibel number also gets doubled. a. true b. false Clicker quiz 3: 10-4 W/m 2 has a db level of db. (Eqn given on exam is: 10log I / I I 0 0 = W/m 2.) a. 4 b. 8 c. 60 d. 80 e. 90 Colton - Lecture 26 - pg 33
Announcements 2 Dec 2014
 Announcements 2 Dec 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 3 going on a. Covers Ch 9-12, HW 18-24 b. Late fee on Wed Dec 3, 3 pm c. Closes on Thursday Dec 4, 3 pm 3. Photo contest submissions due Friday Dec 5, midnight
Announcements 2 Dec 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 3 going on a. Covers Ch 9-12, HW 18-24 b. Late fee on Wed Dec 3, 3 pm c. Closes on Thursday Dec 4, 3 pm 3. Photo contest submissions due Friday Dec 5, midnight
PHYSICS 231 Sound PHY 231
 PHYSICS 231 Sound 1 Travelling (transverse) waves The wave moves to the right, but each point makes a simple harmonic vertical motion oscillation position y position x wave Since the oscillation is in
PHYSICS 231 Sound 1 Travelling (transverse) waves The wave moves to the right, but each point makes a simple harmonic vertical motion oscillation position y position x wave Since the oscillation is in
Sound. Speed of Sound
 Sound TUNING FORK CREATING SOUND WAVES GUITAR STRING CREATING SOUND WAVES Speed of Sound Sound travels at a speed that depends on the medium through which it propagates. The speed of sound depends: - directly
Sound TUNING FORK CREATING SOUND WAVES GUITAR STRING CREATING SOUND WAVES Speed of Sound Sound travels at a speed that depends on the medium through which it propagates. The speed of sound depends: - directly
Page # Physics 103: Lecture 26 Sound. Lecture 26, Preflight 2. Lecture 26, Preflight 1. Producing a Sound Wave. Sound from a Tuning Fork
 Physics 103: Lecture 6 Sound Producing a Sound Wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave A tuning fork will produce
Physics 103: Lecture 6 Sound Producing a Sound Wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave A tuning fork will produce
Sound Waves SOUND VIBRATIONS THAT TRAVEL THROUGH THE AIR OR OTHER MEDIA WHEN THESE VIBRATIONS REACH THE AIR NEAR YOUR EARS YOU HEAR THE SOUND.
 SOUND WAVES Objectives: 1. WHAT IS SOUND? 2. HOW DO SOUND WAVES TRAVEL? 3. HOW DO PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF A MEDIUM AFFECT THE SPEED OF SOUND WAVES? 4. WHAT PROPERTIES OF WAVES AFFECT WHAT WE HEAR? 5. WHAT
SOUND WAVES Objectives: 1. WHAT IS SOUND? 2. HOW DO SOUND WAVES TRAVEL? 3. HOW DO PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF A MEDIUM AFFECT THE SPEED OF SOUND WAVES? 4. WHAT PROPERTIES OF WAVES AFFECT WHAT WE HEAR? 5. WHAT
Producing a Sound Wave. Chapter 14. Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a Sound Wave. Using a Tuning Fork, cont.
 Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 13 Sound
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 13 Sound Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 13 Sound Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities
Chapter 8: Wave Motion. Homework #4 Reminder. But what moves? Wave properties. Waves can reflect. Waves can pass through each other
 Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating disturbance
Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating disturbance
Waves PY1054. Special Topics in Physics. Coláiste na hollscoile Corcaigh, Éire University College Cork, Ireland. ROINN NA FISICE Department of Physics
 Waves Special Topics in Physics 1 Waves Types of Waves: - longitudinal - transverse Longitudinal: Compression waves, e.g. sound Surface: Transverse: Attributes: Ocean Waves. Light, string etc. Speed, wavelength,
Waves Special Topics in Physics 1 Waves Types of Waves: - longitudinal - transverse Longitudinal: Compression waves, e.g. sound Surface: Transverse: Attributes: Ocean Waves. Light, string etc. Speed, wavelength,
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220. Final Exam. Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total)
 Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects.
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Announcements Oct 16, 2014
 Announcements Oct 16, 2014 1. Prayer 2. While waiting, see how many of these blanks you can fill out: Centripetal Accel.: Causes change in It points but not Magnitude: a c = How to use with N2: Always
Announcements Oct 16, 2014 1. Prayer 2. While waiting, see how many of these blanks you can fill out: Centripetal Accel.: Causes change in It points but not Magnitude: a c = How to use with N2: Always
Homework #4 Reminder Due Wed. 10/6
 Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Due Wed. 10/6 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating
Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Due Wed. 10/6 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating
due to striking, rubbing, Any vibration of matter spinning, plucking, etc. Find frequency first, then calculate period.
 Equilibrium Position Disturbance Period (T in sec) # sec T = # cycles Frequency (f in Hz) f = # cycles # sec Amplitude (A in cm, m or degrees [θ]) Other Harmonic Motion Basics Basic Definitions Pendulums
Equilibrium Position Disturbance Period (T in sec) # sec T = # cycles Frequency (f in Hz) f = # cycles # sec Amplitude (A in cm, m or degrees [θ]) Other Harmonic Motion Basics Basic Definitions Pendulums
Announcements Oct 17, 2013
 Announcements Oct 17, 2013 1. No announcements! Colton - Lecture 14 - pg 1 Real satellites: http://science.nasa.gov/realtime/jtrack/3d/jtrack3d.html International space station, 340.5 km above surface
Announcements Oct 17, 2013 1. No announcements! Colton - Lecture 14 - pg 1 Real satellites: http://science.nasa.gov/realtime/jtrack/3d/jtrack3d.html International space station, 340.5 km above surface
PHYSICS 231 Sound PHY 231
 PHYSICS 231 Sound 1 Sound: longitudinal waves A sound wave consist o longitudinal oscillations in the pressure o the medium that carries the sound wave. Thereore, in vacuum: there is no sound. 2 Relation
PHYSICS 231 Sound 1 Sound: longitudinal waves A sound wave consist o longitudinal oscillations in the pressure o the medium that carries the sound wave. Thereore, in vacuum: there is no sound. 2 Relation
What does the speed of a wave depend on?
 Today s experiment Goal answer the question What does the speed of a wave depend on? Materials: Wave on a String PHeT Simulation (link in schedule) and Wave Machine Write a CER in pairs. Think about the
Today s experiment Goal answer the question What does the speed of a wave depend on? Materials: Wave on a String PHeT Simulation (link in schedule) and Wave Machine Write a CER in pairs. Think about the
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES
 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string)
 1 Part 5: Waves 5.1: Harmonic Waves Wave a disturbance in a medium that propagates Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string) Longitudinal
1 Part 5: Waves 5.1: Harmonic Waves Wave a disturbance in a medium that propagates Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string) Longitudinal
Physics 207 Lecture 28
 Goals: Lecture 28 Chapter 20 Employ the wae model Visualize wae motion Analyze functions of two ariables Know the properties of sinusoidal waes, including waelength, wae number, phase, and frequency. Work
Goals: Lecture 28 Chapter 20 Employ the wae model Visualize wae motion Analyze functions of two ariables Know the properties of sinusoidal waes, including waelength, wae number, phase, and frequency. Work
1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place.
 v = fλ 1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place. Transverse Wave Longitudinal Wave How is a guitar made to create different notes/pitches/frequencies? A wave s
v = fλ 1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place. Transverse Wave Longitudinal Wave How is a guitar made to create different notes/pitches/frequencies? A wave s
Chapter 6. Wave Motion. Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
 Chapter 6 Waves We know that when matter is disturbed, energy emanates from the disturbance. This propagation of energy from the disturbance is know as a wave. We call this transfer of energy wave motion.
Chapter 6 Waves We know that when matter is disturbed, energy emanates from the disturbance. This propagation of energy from the disturbance is know as a wave. We call this transfer of energy wave motion.
Chapter 2 SOUND WAVES
 Chapter SOUND WAVES Introduction: A sound wave (or pressure or compression wave) results when a surface (layer of molecules) moves back and forth in a medium producing a sequence of compressions C and
Chapter SOUND WAVES Introduction: A sound wave (or pressure or compression wave) results when a surface (layer of molecules) moves back and forth in a medium producing a sequence of compressions C and
Origin of Sound. Those vibrations compress and decompress the air (or other medium) around the vibrating object
 Sound Each celestial body, in fact each and every atom, produces a particular sound on account of its movement, its rhythm or vibration. All these sounds and vibrations form a universal harmony in which
Sound Each celestial body, in fact each and every atom, produces a particular sound on account of its movement, its rhythm or vibration. All these sounds and vibrations form a universal harmony in which
Sound. Extra Practice: C14.1, 14.1, 14.3, 14.5, 14.9, 14.11, 14.13, 14.15, 14.17, 14.19
 Sound Extra Practice: C14.1, 14.1, 14.3, 14.5, 14.9, 14.11, 14.13, 14.15, 14.17, 14.19 Reminders! WebAssign: Better your grade by requesting manual extensions on old assignments (50% recovery). Last homework:
Sound Extra Practice: C14.1, 14.1, 14.3, 14.5, 14.9, 14.11, 14.13, 14.15, 14.17, 14.19 Reminders! WebAssign: Better your grade by requesting manual extensions on old assignments (50% recovery). Last homework:
SoundWaves. Lecture (2) Special topics Dr.khitam Y, Elwasife
 SoundWaves Lecture (2) Special topics Dr.khitam Y, Elwasife VGTU EF ESK stanislovas.staras@el.vgtu.lt 2 Mode Shapes and Boundary Conditions, VGTU EF ESK stanislovas.staras@el.vgtu.lt ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI
SoundWaves Lecture (2) Special topics Dr.khitam Y, Elwasife VGTU EF ESK stanislovas.staras@el.vgtu.lt 2 Mode Shapes and Boundary Conditions, VGTU EF ESK stanislovas.staras@el.vgtu.lt ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI
CLASS 2 CLASS 2. Section 13.5
 CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound
 EXAM III Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 12 Physics 101: Lecture 22, Pg 1 Standing Waves Fixed Endpoints Fundamental n=1 (2 nodes) l n = 2L/n f n = n v / (2L)
EXAM III Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 12 Physics 101: Lecture 22, Pg 1 Standing Waves Fixed Endpoints Fundamental n=1 (2 nodes) l n = 2L/n f n = n v / (2L)
Chapters 11 and 12. Sound and Standing Waves
 Chapters 11 and 12 Sound and Standing Waves The Nature of Sound Waves LONGITUDINAL SOUND WAVES Speaker making sound waves in a tube The Nature of Sound Waves The distance between adjacent condensations
Chapters 11 and 12 Sound and Standing Waves The Nature of Sound Waves LONGITUDINAL SOUND WAVES Speaker making sound waves in a tube The Nature of Sound Waves The distance between adjacent condensations
Lecture 18. Waves and Sound
 Lecture 18 Waves and Sound Today s Topics: Nature o Waves Periodic Waves Wave Speed The Nature o Sound Speed o Sound Sound ntensity The Doppler Eect Disturbance Wave Motion DEMO: Rope A wave is a traveling
Lecture 18 Waves and Sound Today s Topics: Nature o Waves Periodic Waves Wave Speed The Nature o Sound Speed o Sound Sound ntensity The Doppler Eect Disturbance Wave Motion DEMO: Rope A wave is a traveling
TYPES OF WAVES. 4. Waves and Sound 1
 TYPES OF WAVES Consider a set of playground swings attached by a rope from seat to seat If you sit in the first swing and begin oscillating, this disturbs the equilibrium The connecting ropes cause the
TYPES OF WAVES Consider a set of playground swings attached by a rope from seat to seat If you sit in the first swing and begin oscillating, this disturbs the equilibrium The connecting ropes cause the
Chapter 17: Waves II. Sound waves are one example of Longitudinal Waves. Sound waves are pressure waves: Oscillations in air pressure and air density
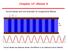 Sound waves are one example of Longitudinal Waves Sound waves are pressure waves: Oscillations in air pressure and air density Before we can understand pressure waves in detail, we need to understand what
Sound waves are one example of Longitudinal Waves Sound waves are pressure waves: Oscillations in air pressure and air density Before we can understand pressure waves in detail, we need to understand what
PHY132 Introduction to Physics II Class 2 Outline: i-clicker Discussion Question
 PHY132 Introduction to Physics II Class 2 Outline: Waves in 2-D and 3-D Spherical waves and plane waves Index of Refraction Power, Intensity and Decibels The Doppler Effect QuickCheck 20.6 i-clicker Discussion
PHY132 Introduction to Physics II Class 2 Outline: Waves in 2-D and 3-D Spherical waves and plane waves Index of Refraction Power, Intensity and Decibels The Doppler Effect QuickCheck 20.6 i-clicker Discussion
PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section VIII
 PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section VIII Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and
PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section VIII Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and
42 TRAVELING WAVES (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G)
 42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
Wave Motions and Sound
 EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
Announcements 12 Dec 2013
 Announcements 12 Dec 2013 1. Tutorial lab info: I think it will be open during reading days and finals, but the TAs have their own exams to worry about so staffing may vary significantly from normal. 2.
Announcements 12 Dec 2013 1. Tutorial lab info: I think it will be open during reading days and finals, but the TAs have their own exams to worry about so staffing may vary significantly from normal. 2.
Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound
 EXAM III Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 12 Physics 101: Lecture 22, Pg 1 Speed of Sound Recall for pulse on string: v = sqrt(t / m) For fluids: v = sqrt(b/r)
EXAM III Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 12 Physics 101: Lecture 22, Pg 1 Speed of Sound Recall for pulse on string: v = sqrt(t / m) For fluids: v = sqrt(b/r)
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
Physics General Physics. Lecture 25 Waves. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
Tute W3 : SOUND 1. n = 10 log 10 I 2
 Tute W3 : SOUND 1 Some phenomena in nature can vary over an extremely large range of intensities and so it is convenient to define a logarithmic scale to describe them. An example is earthquakes, that
Tute W3 : SOUND 1 Some phenomena in nature can vary over an extremely large range of intensities and so it is convenient to define a logarithmic scale to describe them. An example is earthquakes, that
Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section
 Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section Claudio Campagnari Lecture 3: 30 Sep. 2004 Web page: http://hep.ucsb.edu/people/claudio/ph3-04/ 1 Sound Sound = longitudinal wave in a medium. The medium can be anything:
Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section Claudio Campagnari Lecture 3: 30 Sep. 2004 Web page: http://hep.ucsb.edu/people/claudio/ph3-04/ 1 Sound Sound = longitudinal wave in a medium. The medium can be anything:
The Nature of Sound Waves
 The Nature of Sound Waves Read from Lesson 1 of the Sound and Music chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/sound/u11l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/sound/u11l1b.html
The Nature of Sound Waves Read from Lesson 1 of the Sound and Music chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/sound/u11l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/sound/u11l1b.html
Lecture 23 Sound Beats Sound Solids and Fluids
 Lecture 23 Sound Beats Sound Solids and Fluids To round out our discussion of interference and waves, we should talk about beats. When you combine two waves (sound is a good example), if the frequencies
Lecture 23 Sound Beats Sound Solids and Fluids To round out our discussion of interference and waves, we should talk about beats. When you combine two waves (sound is a good example), if the frequencies
Physics 231 Lecture 27
 Physics 31 Lecture 7 Concepts for today s lecture Wae speed for a string / μ : tension; μ m /L. Sound intensity I β 10log 10 I 0 IP/A, I 0 μ 1x10-1 W/m Spherical waes Here P is the string tension I and
Physics 31 Lecture 7 Concepts for today s lecture Wae speed for a string / μ : tension; μ m /L. Sound intensity I β 10log 10 I 0 IP/A, I 0 μ 1x10-1 W/m Spherical waes Here P is the string tension I and
What is a wave? Waves
 What is a wave? Waves Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance that carries energy from one place to another. Classifying waves 1. Mechanical Waves - e.g., water waves, sound waves, and waves on strings.
What is a wave? Waves Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance that carries energy from one place to another. Classifying waves 1. Mechanical Waves - e.g., water waves, sound waves, and waves on strings.
Announcements 9 Sep 2014
 Announcements 9 Sep 2014 1. Prayer 2. Course homepage via: physics.byu.edu Class web pages Physics 105 (Colton J) Colton - Lecture 3 - pg 1 Which of the problems from last night's HW assignment would you
Announcements 9 Sep 2014 1. Prayer 2. Course homepage via: physics.byu.edu Class web pages Physics 105 (Colton J) Colton - Lecture 3 - pg 1 Which of the problems from last night's HW assignment would you
Marketed and Distributed By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 WAVES GUPTA CLASSES For any help contact: 995368795, 968789880 Nishant Gupta, D-, Prashant vihar, Rohini, Delhi-85 Waves Wave motion A wave motion is a kind of disturbance which is transferred from one
WAVES GUPTA CLASSES For any help contact: 995368795, 968789880 Nishant Gupta, D-, Prashant vihar, Rohini, Delhi-85 Waves Wave motion A wave motion is a kind of disturbance which is transferred from one
v wave Here F is the tension and µ is the mass/length.
 Main points of today s lecture: Transverse and longitudinal waves traveling waves v wave = Wave speed for a string fλ v = F µ Here F is the tension Intensity of sound I = and µ is the mass/length. P =
Main points of today s lecture: Transverse and longitudinal waves traveling waves v wave = Wave speed for a string fλ v = F µ Here F is the tension Intensity of sound I = and µ is the mass/length. P =
Lecture 5 Notes: 07 / 05. Energy and intensity of sound waves
 Lecture 5 Notes: 07 / 05 Energy and intensity of sound waves Sound waves carry energy, just like waves on a string do. This energy comes in several types: potential energy due to the compression of the
Lecture 5 Notes: 07 / 05 Energy and intensity of sound waves Sound waves carry energy, just like waves on a string do. This energy comes in several types: potential energy due to the compression of the
LECTURE 7 ENERGY AND INTENSITY. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 7 ENERGY AND INTENSITY Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 7 2 15.5 Energy and intensity Circular, spherical, and plane waves Power, energy, and intensity 15.6 Loudness of sound The decibel scale
LECTURE 7 ENERGY AND INTENSITY Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 7 2 15.5 Energy and intensity Circular, spherical, and plane waves Power, energy, and intensity 15.6 Loudness of sound The decibel scale
Answer: 101 db. db = 10 * log( 1.16 x 10-2 W/m 2 / 1 x W/m 2 ) = 101 db
 54. A machine produces a sound with an intensity of 2.9 x 10-3 W/m 2. What would be the decibel rating if four of these machines occupy the same room? Answer: 101 db Four of these machines would be four
54. A machine produces a sound with an intensity of 2.9 x 10-3 W/m 2. What would be the decibel rating if four of these machines occupy the same room? Answer: 101 db Four of these machines would be four
Physics 140. Sound. Chapter 12
 Physics 140 Sound Chapter 12 Sound waves Sound is composed of longitudinal pressure waves. wave propagabon Compression Compression Compression è when parbcles come together RarefacBon RarefacBon RarefacBon
Physics 140 Sound Chapter 12 Sound waves Sound is composed of longitudinal pressure waves. wave propagabon Compression Compression Compression è when parbcles come together RarefacBon RarefacBon RarefacBon
Ch Guided Reading Sound and Light
 Name Date Hour Chapter 15 Answer Key Ch.15-18 Guided Reading Sound and Light 1. Compare the speed of sound as it travels within a liquid, a solid, and a gas. Why does the speed of sound differ? Sound travels
Name Date Hour Chapter 15 Answer Key Ch.15-18 Guided Reading Sound and Light 1. Compare the speed of sound as it travels within a liquid, a solid, and a gas. Why does the speed of sound differ? Sound travels
Announcements 13 Nov 2014
 Announcements 13 Nov 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 3 starts on Tues Nov 25 a. Covers Ch 9-12, HW 18-24 b. Late fee on Wed after Thanksgiving, 3 pm c. Closes on Thursday after Thanksgiving, 3 pm d. Jerika review
Announcements 13 Nov 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 3 starts on Tues Nov 25 a. Covers Ch 9-12, HW 18-24 b. Late fee on Wed after Thanksgiving, 3 pm c. Closes on Thursday after Thanksgiving, 3 pm d. Jerika review
Homework Book. Wave Properties. Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2. Name: Homeroom: Physics Class:
 Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Schedule for the remainder of class
 Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
Exercises The Origin of Sound (page 515) 26.2 Sound in Air (pages ) 26.3 Media That Transmit Sound (page 517)
 Exercises 26.1 The Origin of (page 515) Match each sound source with the part that vibrates. Source Vibrating Part 1. violin a. strings 2. your voice b. reed 3. saxophone c. column of air at the mouthpiece
Exercises 26.1 The Origin of (page 515) Match each sound source with the part that vibrates. Source Vibrating Part 1. violin a. strings 2. your voice b. reed 3. saxophone c. column of air at the mouthpiece
Physics 11. Unit 7 (Part 2) The Physics of Sound
 Physics 11 Unit 7 (Part 2) The Physics of Sound 1. Sound waves As introduced in the previous section, sound is one of the many types of waves we encounter in our daily lives. It possesses the properties
Physics 11 Unit 7 (Part 2) The Physics of Sound 1. Sound waves As introduced in the previous section, sound is one of the many types of waves we encounter in our daily lives. It possesses the properties
Review &The hardest MC questions in media, waves, A guide for the perplexed
 Review &The hardest MC questions in media, waves, A guide for the perplexed Grades online pp. I have been to the Grades online and A. Mine are up-to-date B. The quizzes are not up-to-date. C. My labs are
Review &The hardest MC questions in media, waves, A guide for the perplexed Grades online pp. I have been to the Grades online and A. Mine are up-to-date B. The quizzes are not up-to-date. C. My labs are
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
PHYSICS. Chapter 16 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
Learning Goal: By the end of today, I will be familiar with the following concepts: Demo Newton's Cradle Tuning Forks. Section 8.
 Section 8.1 Vibrations Learning Goal: By the end of today, I will be familiar with the following concepts: Vibrations and Mechanical waves The cyclical motion about an equilibrium point is called a vibration.
Section 8.1 Vibrations Learning Goal: By the end of today, I will be familiar with the following concepts: Vibrations and Mechanical waves The cyclical motion about an equilibrium point is called a vibration.
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Work. Work and Energy Examples. Energy. To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or:
 Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz. FINAL EXAM December 10, :00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS
 Seat # Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz FINAL EXAM December 10, 2001 8:00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS 1. Sit in SEAT # given above. 2. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. 3. Print your name (last
Seat # Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz FINAL EXAM December 10, 2001 8:00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS 1. Sit in SEAT # given above. 2. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. 3. Print your name (last
Physics 101. Hour Exam 3 Spring Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name:
 Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators may not be shared. Please keep yours on your own desk. This is
Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators may not be shared. Please keep yours on your own desk. This is
Can you hear me? 4. Have the second test subject order the sounds. 5. How do the two test subjects compare? 6. Do you think sound waves carry energy?
 HPP Activity A50v1 Can you hear me? Exploration Let's explore just how good your hearing is. Go to the web page "Sound Levels" in the course web. Turn the volume on your computer speakers up to the half
HPP Activity A50v1 Can you hear me? Exploration Let's explore just how good your hearing is. Go to the web page "Sound Levels" in the course web. Turn the volume on your computer speakers up to the half
Announcements 23 Sep 2014
 Announcements 23 Sep 2014 1. After today, just one more lecture of new material before Exam 1!! a. Exam 1: Oct 2 Oct 7 (2 pm) in the Testing Center, late fee after Oct 6 2 pm b. Exam review sessions by
Announcements 23 Sep 2014 1. After today, just one more lecture of new material before Exam 1!! a. Exam 1: Oct 2 Oct 7 (2 pm) in the Testing Center, late fee after Oct 6 2 pm b. Exam review sessions by
Logarithmic Scales 37
 37 When a physical quantity varies over a very large range, it is often convenient to take its logarithm in order to have a more manageable set of numbers. We discuss three such situations: the ph scale,
37 When a physical quantity varies over a very large range, it is often convenient to take its logarithm in order to have a more manageable set of numbers. We discuss three such situations: the ph scale,
Quiz on Chapters 13-15
 Quiz on Chapters 13-15 Final Exam, Thursday May 3, 8:00 10:00PM ANH 1281 (Anthony Hall). Seat assignments TBD RCPD students: Thursday May 3, 5:00 9:00PM, BPS 3239. Email will be sent. Alternate Final Exam,
Quiz on Chapters 13-15 Final Exam, Thursday May 3, 8:00 10:00PM ANH 1281 (Anthony Hall). Seat assignments TBD RCPD students: Thursday May 3, 5:00 9:00PM, BPS 3239. Email will be sent. Alternate Final Exam,
Sound, Decibels, Doppler Effect
 Phys101 Lectures 31, 32 Sound, Decibels, Doppler Effect Key points: Intensity of Sound: Decibels Doppler Effect Ref: 12-1,2,7. Page 1 Characteristics of Sound Sound can trael through any kind of matter,
Phys101 Lectures 31, 32 Sound, Decibels, Doppler Effect Key points: Intensity of Sound: Decibels Doppler Effect Ref: 12-1,2,7. Page 1 Characteristics of Sound Sound can trael through any kind of matter,
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal compression waves that propagate through a medium gas, liquid, or solid. Sound Waves in Air:
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal compression waves that propagate through a medium gas, liquid, or solid. Sound Waves in Air: Pressure and density vary sinusoidally. PheT The speed of sound in
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal compression waves that propagate through a medium gas, liquid, or solid. Sound Waves in Air: Pressure and density vary sinusoidally. PheT The speed of sound in
CS 1124Media computation. Oct 6, 2008 Steve Harrison
 CS 1124Media computation Oct 6, 2008 Steve Harrison Today Midterm Introduction to working with sound HW 5 - Faster and Faster Today Midterm Introduction to working with sound HW 5 - Faster and Faster Mid
CS 1124Media computation Oct 6, 2008 Steve Harrison Today Midterm Introduction to working with sound HW 5 - Faster and Faster Today Midterm Introduction to working with sound HW 5 - Faster and Faster Mid
Seminary 10 SOUND WAVES 2
 Seminary 10 SOUND WAVES 2 1/ Bird sings in a meadow Consider an idealized bird (treated as a point source) that emits constant sound power, with intensity obeying the inverse-square law. If you move twice
Seminary 10 SOUND WAVES 2 1/ Bird sings in a meadow Consider an idealized bird (treated as a point source) that emits constant sound power, with intensity obeying the inverse-square law. If you move twice
Music 170: Quantifying Sound
 Music 170: Quantifying Sound Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego UCSD) October 5, 2017 1 Sound as a Wave Sound is a longitudinal compression wave: The
Music 170: Quantifying Sound Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego UCSD) October 5, 2017 1 Sound as a Wave Sound is a longitudinal compression wave: The
Lecture 18. Sound Waves: Intensity, Interference, Beats and Doppler Effect.
 Lecture 18 Sound Waes: Intensity, Interference, Beats and Doppler Effect. Speed of sound Speed of soun in air, depends on temperature: = (331 + 0.60 T ) m/s where T in C Sound intensity leel β = 10log
Lecture 18 Sound Waes: Intensity, Interference, Beats and Doppler Effect. Speed of sound Speed of soun in air, depends on temperature: = (331 + 0.60 T ) m/s where T in C Sound intensity leel β = 10log
Physics Mechanics. Lecture 34 Waves and sound II
 1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 34 Waves and sound II 2 Sound Waves Sound waves are pressure waves in solids, liquids, and gases. They are longitudinal in liquids and gases, and may have transverse components
1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 34 Waves and sound II 2 Sound Waves Sound waves are pressure waves in solids, liquids, and gases. They are longitudinal in liquids and gases, and may have transverse components
Introduction to Audio and Music Engineering
 Introduction to Audio and Music Engineering Lecture 7 Sound waves Sound localization Sound pressure level Range of human hearing Sound intensity and power 3 Waves in Space and Time Period: T Seconds Frequency:
Introduction to Audio and Music Engineering Lecture 7 Sound waves Sound localization Sound pressure level Range of human hearing Sound intensity and power 3 Waves in Space and Time Period: T Seconds Frequency:
Chapter 1 Fundamentals of Sound Waves -1
 Chapter 1 Fundamentals of Sound Waves -1 Sound Sections What is Sound? Producing a Sound Wave Characteristics of Sound Waves The Speed of Sound Intensity of Sound Waves What is Sound? Sound is such a common
Chapter 1 Fundamentals of Sound Waves -1 Sound Sections What is Sound? Producing a Sound Wave Characteristics of Sound Waves The Speed of Sound Intensity of Sound Waves What is Sound? Sound is such a common
Forces and motion. Announcements. Force: A push or pull between pairs of objects. Newton s First Law: Inertia
 Announcements 1. Exam 1 still going on a. until Monday night b. My advice: take it sooner rather than later, because we re moving on now Forces and motion Aristotle: 384 322 BC, Greece Four elements, two
Announcements 1. Exam 1 still going on a. until Monday night b. My advice: take it sooner rather than later, because we re moving on now Forces and motion Aristotle: 384 322 BC, Greece Four elements, two
Final Exam Notes 8am WednesdayDecember 16, 2015 Physics 1320 Music & Physics Prof. Tunks & Olness
 Final Exam Notes 8am WednesdayDecember 16, 2015 Physics 1320 Music & Physics Prof. Tunks & Olness 1)This contains review material for the Final exam. It consists of review sheets for exams 1 and 2, as
Final Exam Notes 8am WednesdayDecember 16, 2015 Physics 1320 Music & Physics Prof. Tunks & Olness 1)This contains review material for the Final exam. It consists of review sheets for exams 1 and 2, as
Announcements - 9 Oct 2014
 Announcements - 9 Oct 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 2 results a. Median Score: b. Curve: c. Exams will be returned soon, our office assistant should put them in the boxes near N357 ESC sometime today. d. I'll
Announcements - 9 Oct 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 2 results a. Median Score: b. Curve: c. Exams will be returned soon, our office assistant should put them in the boxes near N357 ESC sometime today. d. I'll
Lecture 17. Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves.
 Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
Question 01. A. Incorrect! The speed of sound is not the same in all medium; it is dependent on the properties of the material.
 High School Physics - Problem Drill 15: Sound 1. Which of these is not a true statement about sound waves? Question 01 (A) Sound waves are travel at different speeds in different mediums. (B) Sound waves
High School Physics - Problem Drill 15: Sound 1. Which of these is not a true statement about sound waves? Question 01 (A) Sound waves are travel at different speeds in different mediums. (B) Sound waves
Thermodynamics continued
 Chapter 15 Thermodynamics continued 15 Work The area under a pressure-volume graph is the work for any kind of process. B Pressure A W AB W AB is positive here volume increases Volume Clicker Question
Chapter 15 Thermodynamics continued 15 Work The area under a pressure-volume graph is the work for any kind of process. B Pressure A W AB W AB is positive here volume increases Volume Clicker Question
3 THE P HYSICS PHYSICS OF SOUND
 Chapter 3 THE PHYSICS OF SOUND Contents What is sound? What is sound wave?» Wave motion» Source & Medium How do we analyze sound?» Classifications» Fourier Analysis How do we measure sound?» Amplitude,
Chapter 3 THE PHYSICS OF SOUND Contents What is sound? What is sound wave?» Wave motion» Source & Medium How do we analyze sound?» Classifications» Fourier Analysis How do we measure sound?» Amplitude,
SOUND. Representative Sample Physics: Sound. 1. Periodic Motion of Particles PLANCESS CONCEPTS
 Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
Sound Intensity and Sound Level *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42257 1 Sound Intensity and Sound Level * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Dene intensity, sound
OpenStax-CNX module: m42257 1 Sound Intensity and Sound Level * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Dene intensity, sound
Waves. 1. Types of waves. Mechanical Waves
 Waves 1. Types of waves 1. Mechanical Waves 2. Waves, a mathematical formulation 1. A basic wave 3. Speed of a traveling wave 1. Wave speed on a real string. 4. Energy 1. The wave equation 5. Sound waves
Waves 1. Types of waves 1. Mechanical Waves 2. Waves, a mathematical formulation 1. A basic wave 3. Speed of a traveling wave 1. Wave speed on a real string. 4. Energy 1. The wave equation 5. Sound waves
Announcements 24 Sep 2013
 Announcements 24 Sep 2013 1. If you have questions on exam 1 2. Newton s 2 nd Law Problems: F m a. Inclined planes b. Pulleys c. Ropes d. Friction e. Etc Remember N2 is a blueprint for obtaining a useful
Announcements 24 Sep 2013 1. If you have questions on exam 1 2. Newton s 2 nd Law Problems: F m a. Inclined planes b. Pulleys c. Ropes d. Friction e. Etc Remember N2 is a blueprint for obtaining a useful
4. What is the speed (in cm s - 1 ) of the tip of the minute hand?
 Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Decibels and Acoustical Engineering
 Decibels and Acoustical Engineering What is Sound? Sound is the movement of energy through substances in longitudinal (compression/rarefaction) waves. Sound is produced when a force causes an object or
Decibels and Acoustical Engineering What is Sound? Sound is the movement of energy through substances in longitudinal (compression/rarefaction) waves. Sound is produced when a force causes an object or
Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016
 Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016 Name: Circle the BEST Answer 1 Electromagnetic waves consist of A) compressions and rarefactions of electromagnetic pulses. B) oscillating electric and magnetic fields. C)
Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016 Name: Circle the BEST Answer 1 Electromagnetic waves consist of A) compressions and rarefactions of electromagnetic pulses. B) oscillating electric and magnetic fields. C)
PHYSICS 220. Lecture 21. Textbook Sections Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 220 1
 PHYSICS 220 Lecture 21 Sound Textbook Sections 13.1 13.7 Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Overview Last Lecture Interference and Diffraction Constructive, destructive Diffraction: bending of
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 21 Sound Textbook Sections 13.1 13.7 Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Overview Last Lecture Interference and Diffraction Constructive, destructive Diffraction: bending of
Contents. Lehman College Department of Physics and Astronomy. Lab manual for PHY 141 Sound, speech and music 1 PENDULUM EXPERIMENT 3
 Lehman College Department of Physics and Astronomy Lab manual for PHY 141 Sound, speech and music Contents 1 PENDULUM EXPERIMENT 3 2 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION 9 3 STANDING WAVES ON STRINGS 15 4 STANDING WAVES
Lehman College Department of Physics and Astronomy Lab manual for PHY 141 Sound, speech and music Contents 1 PENDULUM EXPERIMENT 3 2 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION 9 3 STANDING WAVES ON STRINGS 15 4 STANDING WAVES
17 SOUND. Introduction. Chapter Outline
 Chapter 17 Sound 867 17 SOUND Figure 17.1 Hearing is an important human sense that can detect frequencies of sound, ranging between 20 Hz and 20 khz. However, other species have very different ranges of
Chapter 17 Sound 867 17 SOUND Figure 17.1 Hearing is an important human sense that can detect frequencies of sound, ranging between 20 Hz and 20 khz. However, other species have very different ranges of
SAMPLE FINAL EXAM (Closed Book)
 PHYS 111-01 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM (Closed Book) 1. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO. NAME: (Given) (Family) 2. For the problems, write clearly and neatly and be sure to show your work. Answers without
PHYS 111-01 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM (Closed Book) 1. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO. NAME: (Given) (Family) 2. For the problems, write clearly and neatly and be sure to show your work. Answers without
MCAT Physics Problem Solving Drill 13: Sound
 MCAT Physics Problem Solving Drill 13: Sound Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The wave lengths of audible sounds are 17 m to 0.017 m. Find the range of audible frequencies assuming velocity of sound in
MCAT Physics Problem Solving Drill 13: Sound Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The wave lengths of audible sounds are 17 m to 0.017 m. Find the range of audible frequencies assuming velocity of sound in
