Thickness-induced anomalous angular-dependent magnetoresistance of La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 thin films grown on SrTiO 3
|
|
|
- Mae Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Received: 27 June 2017 Accepted: 15 December 2017 DOI: /jace ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thickness-induced anomalous angular-dependent magnetoresistance of La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 thin films grown on SrTiO 3 Xiaotian Li 1 Bin Liu 1 Yiqian Wang 1 Xuyan Xue 1 Guiju Liu 1 Huaiwen Yang 2 Jirong Sun 2 1 College of Physics, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China 2 Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China Correspondence Yiqian Wang, College of Physics, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China. yqwang@qdu.edu.cn Funding information National Key Basic Research Development Program of China, Grant/ Award Number: 2012CB722705; National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant/Award Number: ; Program for Foreign Cultural and Educational Experts, Grant/Award Number: GDW , GDW ; Top-notch Innovative Talent Program of Qingdao City, Grant/Award Number: 13-CX-8 In this paper the effect of thickness on angular-dependent magnetoresistance (MR) of La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 (LSMO) thin films grown on SrTiO 3 is systematically investigated. In films thinner than 8 nm, we observe an anomalous weak peak in the MR curves when the magnetic field is parallel to the film surface. In films thicker than 10 nm, however, the weak peak disappears and a novel MR valley appears when the magnetic field is perpendicular to the film surface. The weak peak is thought to be induced by the formation of two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) at the interface, which is confirmed by density functional theory calculations. The disappearance of the peak and appearance of the valley in the films thicker than 10 nm is associated with the formation of misfit dislocations near the interface between film and substrate, which are clearly visible in high-resolution transmission electron microscopy images. Our work could shed significant light on the influence of film thickness on 2DEG formation. KEYWORDS dislocations, magnetoresistance, thin films 1 INTRODUCTION Thin films of the doped perovskite manganites, La 1 x Sr x MnO 3, have attracted considerable great attention due to their fascinating physical properties. 1-5 The transport properties of La 1 x Sr x MnO 3 films are sensitive to the film thickness and the lattice strain. For example, it was reported that La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 films switched from metallic to insulating when the film thickness was reduced to 2.3 nm. 6 In addition, the effect of quantum interference on the electrical transport properties was observed in La 0.9 Sr 0.1 MnO 3 films thinner than 4 nm. 7 Ohtomo and Hwang 8 firstly discovered the conducting two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) at the interface of 2 Li and Liu contributed to this work equally. insulators, LaAlO 3 and SrTiO 3 (STO). Recently, the 2DEG has been found at the interface between La 0.3 Sr 0.7 MnO 3 films and SrTiO 3 substrate when the film is thinner than 5 nm, whereas it disappears in the 24-nm films. 9 It is obvious that the film thickness has a substantial effect on the 2DEG. However, the critical film thickness for 2DEG disappearance has not yet been reported. As is well known, the formation of misfit dislocations is closely related to the film thickness. The lattice misfit at the interface can be accommodated by elastic deformation when the epitaxial film is thinner than the critical thickness, while the strain is relaxed via the formation of misfit dislocations when the film thickness exceeds a critical value. 10 The physical properties of perovskite manganite films can be strongly influenced by the formation of misfit dislocations, which J Am Ceram Soc. 2018;101: wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/jace 2017 The American Ceramic Society 2339
2 2340 LI ET AL. play an important role in the performance of the films. 11,12 Chu et al 13 found that misfit dislocations greatly affect the stability of polarization in ferroelectric perovskites. The electrical transport in the 2DEG can also be influenced by the misfit dislocations since the 2DEG is located at the heterointerface. 14 Many investigations on 2DEG have been reported, both theoretical and experimental However, the reason for the disappearance of the 2DEG in the case of thick films is not unveiled. In addition, the direct connection between the misfit dislocations and the properties of LSMO films is still unclear even though the misfit dislocations have been extensively studied in the perovskite manganite films. In this work we investigate the angular-dependent magnetoresistance (MR) of La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 (LSMO/ STO) films with a thickness ranging from 6 to 20 nm. When the film is thinner than 8 nm, we find an unexpected weak MR peak with the magnetic field parallel to the film surface. However, when the film is thicker than 10 nm, this peak disappears and an anomalous MR valley is observed with the magnetic field perpendicular to the film surface. The weak MR peak is assigned to a 2DEG formed at the LSMO/STO interface resulting from the magnetic reconstruction, as confirmed by density functional theory calculations. The appearance of the MR valley in films thicker than 10 nm is associated with the formation of misfit dislocations near the interface between film and substrate, which are clearly visible in high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images. This work could shed light on understanding the influence of film thickness on the 2DEG, and more specifically the reason for the disappearance of the 2DEG in thicker films. 2 EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 films with a thickness of 6, 8, 10, 15, and 20 nm were epitaxially grown on (001) STO substrates (purchased from Hefei Kejing Materials Technology Company) using pulsed laser deposition (PLD) technique. The ceramic target was prepared by a solid-state reaction. During the deposition, the substrates were maintained at 750 C under an oxygen pressure of 50 Pa. The laser wavelength was 248 nm, the pulse fluency was 1.5 J/cm 2, and the ablation frequency was 1 Hz. After the deposition, all the films were maintained in an oxygen atmosphere of 30 Pa for 15 minutes and then naturally cooled down to room temperature at 30 Pa. The film thickness is determined from HRTEM images, and the measurement accuracy is about 0.4 nm. The angular-dependent magnetotransport (MR) measurements were carried out on the physical property measurement system (PPMS, Quantum Design) equipped with sample rotation system using Van Der Pauw method. The MR measurements were performed on the LSMO films with same thickness grown on different STO substrates to make sure that the MR results are reproducible. The silver paste was used as electrical contact in the measurement. During the measurement, the films were clockwise rotated in an applied magnetic field (H = 80 koe) and the rotation axis was parallel to the sample edge, as shown in Figure 1. The D R and h denoted the rotational direction and angle of the film, and the D M marked the direction of magnetic field. h = 0 and h = 90 refer to the magnetic field being perpendicular and parallel to the interface plane, respectively. Two possible current directions, [100] and [010], were considered. As no qualitative difference was found between the 2 in-plane current orientations, 9 the [010] direction was taken in our work. Specimens for TEM observations were prepared in cross-sectional orientations ([010] zone axis of the STO substrate) using conventional techniques of mechanical polishing and ion thinning. The ion milling was performed using a Gatan Model 691 precision ion polishing system. HRTEM examinations were carried out on a JEOL JEM2100F electron microscope operating at 200 kv. The film structure was analyzed by X-ray diffraction (Bruker X-ray diffractometer, k = A). The surface morphology of the films was examined by the atomic force microscope (Seiko SPI 3800N) at the ambient conditions. The density functional theory (DFT) calculations were implemented in the Cambridge Serial Total Energy Package (CASTEP), including a Hubbard U term accounting for the on-site Coulomb interaction. Exchange-correlation interaction was described by the local density approximation (LDA) with the Ceperley-Alder exchange-correlation potential (CA-PZ) in order to optimize the atomic structures. Spin polarization was taken into account in the FIGURE 1 The configuration of angular-dependent magnetotransport measurement [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
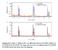
3 LI ET AL calculations. The calculation was performed using ultrasoft pseudopotential with a 10-eV cut-off energy, and a regular Γ-centered k-point mesh in the Brillouin zone. 3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Figure 2 shows the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the LSMO films with different thickness. In Figure 2, the (002) diffraction peaks of LSMO films and STO substrate can be clearly seen, indicating that all the films are single crystalline and epitaxially grown on the STO substrates. The (002) diffraction peak intensity of LSMO films increases with the thickness of LSMO films. The surface roughness of the LSMO films is examined by the atomic force microscope (AFM) (see Supporting Information). All the films show a step-featured morphology, indicating that their surfaces are relatively flat. Angular magnetoresistance (MR) is a common feature of ferromagnets due to the anisotropy of spin-dependent scattering. For the ferromagnetic, it is found that the MR depends on the angular h between the applied magnetic field and the electric current. To investigate the effect of thickness on angular MR, we perform the angular-dependent MR of La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 (LSMO/STO) films with a thickness ranging from 6 to 20 nm. The thickness of all the LSMO films is larger than that of the dead layer (3 5 nm) in LSMO. 22 Therefore, the influence of dead layers on the MR measurement is not considered in our work. Figure 3 shows the angular MR for LSMO/STO films. MR is defined as R H /R 0, where R H is the resistance at a magnetic field H and R 0 is R (H = 0). In the films thinner than 8 nm, 2 different MR peaks are observed. One is observed when the magnetic field is perpendicular to the FIGURE 2 XRD patterns of LSMO films with a thickness of 6, 8, 10, 15, and 20 nm. XRD, X-ray diffraction; LSMO, La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com] film surface, which is called out-of-plane MR peak. The out-of-plane peak is the standard resistivity maxima occurring for the ferromagnetic manganites. 23 The other one occurs when the magnetic field is parallel to the film surface, which is called in-plane MR peak (pmr). With the film thickness increasing from 6 to 8 nm, the height of the pmr decreases from to When the film thickness increases to 10 nm, the pmr disappears and an anomalous MR valley (vmr) is observed with the magnetic field perpendicular to the film surface. Nemes et al 9 believe that the pmr is produced by the 2DEG forming at the LSMO interface. Through DFT calculations, they revealed that the 2DEG arises from the antiferromagnetic coupling (A-type) between a ferromagnetic interfacial manganite layer and the rest LSMO. In their LSMO/STO model used for DFT calculations, La and Sr cations are arranged in order. As we all know, if La and Sr cations are arranged in order, it will be reflected as modulated stripes in the HRTEM images. 24,25 However, in the HRTEM images of LSMO film as shown in Figure 4, no modulated stripes are observed. In other words, the Sr and La cations should be arranged at random in the film. To reconfirm if A-type coupling still exists at the interface of the film when the cations are arranged at random, DFT calculations are also performed in our work. In our LSMO/ STO model for the DFT calculations, all the Sr and La cations are arranged at random and the calculated density of states (DOS) is shown in Figure 5. The LSMO is halfmetal because its spin-up and spin-down electrons have different nature around the Fermi level. The magnetic moments of Mn cations from the interface to the film surface are calculated to be 3.4, 3.7, and 4.0 l B, respectively. It is obvious that the spin polarization of Mn is inverted at the interface. In other words, a manganite layer exists at the interface antiferromagnetically coupling to the rest LSMO. Such a manganite layer would be electrically decoupled as hopping between sites with antiparallel spins is suppressed in half-metals by virtue of double-exchange mechanism, 26 which leads to the formation of 2DEG at the interface and finally gives rise to the appearance of pmr. In our work, the magnetic moments of Mn cations are a little higher than those obtained by Nemes et al as the La and Sr cations are arranged at random in our model. To explore the influence of different termination layers on the MR, we also carried out the angular-dependent MR measurement of the LSMO films on single-crystalline STO terminated by either SrO or TiO 2 (see Supporting Information). From the MR results, it can be seen that the pmr still exists. Therefore, it is believed that the termination layer type of STO substrates does not affect the formation of the 2DEG. In addition to the pmr, a novel phenomenon is found in our work. When the film is thicker than 10 nm, the
4 2342 LI ET AL. FIGURE 3 Angular MR for LSMO/STO films with a thickness of 6 nm (A), 8 nm (B), 10 nm (C), 15 nm (D), and 20 nm (E) at 2K, 80 koe. LSMO/STO, La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 pmr disappears and an anomalous vmr is observed with the magnetic field perpendicular to the film surface. In this case, the films are too thick to perform DFT calculations. Considering that the performance of materials depends on their microstructure, we carry out extensive HRTEM examinations of the LSMO/STO interface to clarify the possible reasons for this phenomenon. The typical crosssectional HRTEM images of 6- and 8-nm-thick LSMO/ STO films are shown in the Figures 4 and 6. The interface between film and substrate is marked by dashed lines. No
5 LI ET AL FIGURE 4 Typical cross-sectional HRTEM image of LSMO/ STO with a film thickness of 6 nm. HRTEM, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy; LSMO/STO, La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 dislocation can be found near the interface when the film is thinner than 8 nm. However, as the film thickness increases to 10 nm, a pure edge dislocation is observed near the LSMO/STO interface (shown in Figure 7A). To clearly show this dislocation, a magnified HRTEM image of the enclosed rectangle in Figure 7A is shown in Figure 7B. In this image, the extra half atomic plane is clear and the Burgers vector is determined to be <110>. Figure 7C shows the one dimensional Fourier-filtered lattice image of Figure 7B. It is obvious that an extra half plane is vertically inserted. The pure edge dislocation is also observed in the 20-nm-thick LSMO/STO film (shown in Figure 8). According to our HRTEM observations, no misfit dislocation is observed in the 6- and 8-nm-thick films, and no vmr appears. Whereas once the film exceeds 10 nm, the vmr emerged with the appearance of misfit dislocations. Thus, we predict that the disappearance of pmr and the emergence of vmr are associated with the formation of misfit dislocations. To further verify our prediction, the FIGURE 6 Typical cross-sectional HRTEM image of LSMO/ STO with a film thickness of 8 nm. HRTEM, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy; LSMO/STO, La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 critical thickness (t c ) where a pure edge dislocation existing in the film can be theoretically calculated using the following formula, b~ 6 B t c t c ¼ ln C 7 4pf ð1 þ vþ A þ 15 (1) b~ where b is the Burgers vector (b ~ 2.736), v is the Poisson ratio (v ~ 0.43), and f is the lattice mismatch. The lattice mismatch (f) can be calculated using the following formula, f ¼ a s a f 100% a s (2) where a s and a f refer to the lattice parameter of the substrate (3.905 A) and film (3.87 A), respectively. f is calculated to be 0.896%. The t c for the LSMO film is calculated FIGURE 5 LSMO/STO model (left) for calculation (O atoms are omitted for clarity) and density of states results (right). The dashed line indicates the position of the Fermi level. The upper (blue) and lower (red) lines represent the majority and minority spin densities, respectively. LSMO/STO, La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
6 2344 LI ET AL. (A) (B) (C) FIGURE 7 A, Cross-sectional HRTEM image of the LSMO/STO film with a thickness of 10 nm; B, Burgers circuit drawn in enlarged HRTEM image of the region enclosed by a rectangle in (A); C, Fourier filtered lattice image of (B). HRTEM, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy; LSMO/STO, La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 (A) (B) (C) FIGURE 8 A, Cross-section HRTEM image of the LSMO/STO film with a thickness of 20 nm; B, Burgers circuit drawn in enlarged HRTEM image of the region enclosed by a rectangle in (A); C, Fourier filtered lattice image of (B). HRTEM, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy; LSMO/STO, La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3
7 LI ET AL to be 7.27 nm. In other words, the misfit dislocations will form once the film thicker than 7.27 nm. In the Equation (1), the kinetics is ignored. So the actual t c should be larger than the calculated one and even larger than 8 nm. Thus, no misfit dislocation is formed in the 6- and 8-nmthick LSMO films. The 2DEG forming at the LSMO interface results in the appearance of pmr. However, when the film thickness exceeds 7.27 nm, the misfit dislocations begin to generate, which could affect the spin polarization at the interface and hinder the magnetic reconstruction. With the increase in the film thickness, the misfit dislocations continue to grow up and the 2DEG gradually disappear. Similar to the previous report, 9 the pmr peak is not prominent with increasing film thickness. When the film thickness increases from 10 to 15 nm, the dominant function in electronic transport at interface gradually changes from 2DEG into misfit dislocation. Consequently the pmr ultimately disappears and the vmr increases. The calculated critical thickness t c is consistent with our experimental results. Strangely, the vmr becomes indistinct when the film thickness reaches 20 nm. We deduce that the film will gradually possess the property of the bulk materials when it is thick enough. Under this condition, the misfit dislocations have very small impact on the electronic transport at interface and the vmr would become weak and eventually disappeared. That is why the vmr can only be observed in the films that just exceeds the critical thickness. 4 CONCLUSIONS In summary, we have investigated the effect of film thickness on the angular-dependent MR of thin films grown on STO. When the magnetic field is parallel to the film surface, an additional weak peak appears in the MR curves of the films thinner than 8 nm. As revealed by DFT calculations, this peak signals the formation of 2DEG at the interface which arises from a magnetic reconstruction. However, this 2DEG gradually disappears with increasing film thickness. When the film is thicker than 10 nm, the 2DEG completely disappears and an anomalous vmr simultaneously appears when the magnetic field is perpendicular to the films surface. Combining HRTEM observations and the calculation of critical thickness, we demonstrate that the appearance of this valley is associated with the formation of pure edge dislocations at the interface. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors thank the financial support from the National Key Basic Research Development Program of China (grant no.: 2012CB722705), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no.: ), and the Program for Foreign Cultural and Educational Experts (grant nos.: GDW , GDW ). Y.Q. Wang thank the financial support from the Top-notch Innovative Talent Program of Qingdao City (grant no.: 13-CX-8), the Taishan Scholar Program of Shandong Province, China, and Qingdao International Center for Semiconductor Photoelectric Nanomaterials. ORCID Yiqian Wang REFERENCES 1. Wang LM, Guo CC. Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 superlattices. Appl Phys Lett. 2005;87: Dey P, Nath TK, Taraphder A. Effect of substrate-induced strain on transport and magnetic properties of epitaxial La 0.66 Sr 0.33 MnO 3 thin films. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;91: Yoshimatsu K, Horiba K, Kumigashira H, Ikenaga E, Oshima M. Thickness dependent electronic structure of La 0.6 Sr 0.4 MnO 3 layer in SrTiO 3 /La 0.6 Sr 0.4 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 heterostructures studied by hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy. Appl Phys Lett. 2009;94: Majumdar S, Huhtinen H, Majumdar HS, Paturi P. Stress and defect induced enhanced low field magnetoresistance and dielectric constant in La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films. J Alloy Compd. 2012;512: Zhou JL, Tra VT, Dong S, et al. Thickness dependence of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 magnetoelectric interfaces. Appl Phys Lett. 2015;107: Dorr K, Walter T, Sahana M, et al. Magnetotransport of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /SrTiO 3 multilayers with ultrathin manganite layers. J Appl Phys. 2001;89: Wang C, Jin KJ, Gu L, et al. Magnetoelectric transport and quantum interference effect in ultrathin manganite films. Appl Phys Lett. 2014;104: Ohtomo A, Hwang HY. A high-mobility electron gas at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 heterointerface. Nature. 2004;427: Nemes NM, Calderon MJ, Beltran JI, et al. Signatures of a twodimensional ferromagnetic electron gas at the La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 interface arising from orbital reconstruction. Adv Mater. 2014;26: Van der Merwe JH. Crystal interfaces part I semi-infinite crystals. J Appl Phys. 1963;34: Gao GY, Jin SW, Wu WB. Lattice-mismatch-strain induced inhomogeneities in epitaxial La 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 films. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;90: Vailionis A, Boschker H, Liao Z, et al. Symmetry and lattice mismatch induced strain accommodation near and away from correlated perovskite interfaces. Appl Phys Lett. 2014;105: Chu MW, Szafraniak I, Scholz R, et al. Impact of misfit dislocations on the polarization instability of epitaxial nanostructured ferroelectric perovskites. Nat Mater. 2004;3: Liu B, Lu YW, Huang Y, Liu GP, Zhu QS, Wang ZG. Interfacial misfit dislocation scattering effect in two-dimensional electron
8 2346 LI ET AL. gas channel of GaN heterojunction. Phys Lett A. 2012;376: Popovic ZS, Satpathy S, Martin RM. Origin of the two-dimensional electron gas carrier density at the LaAlO 3 on SrTiO 3 interface. Phys Rev Lett. 2008;101: Li JC, Beltran JI, Munoz MC. Multiorbital structure of the two-dimensional electron gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 heterostructures: the formation ofad xy ferromagnetic sheet.physrevb.2013;87: Zhong ZC, Toth A, Held K. Theory of spin-orbit coupling at LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interfaces and SrTiO 3 surfaces. Phys Rev B. 2013;87: Ong PV, Lee J. Orbital-selective charge transfer at oxygen-deficient LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 (001) interface. Phys Rev B. 2013;87: Herranz G, Basletic M, Bibes M, et al. High mobility in LaAlO 3 / SrTiO 3 heterostructures: origin, dimensionality, and perspectives. Phys Rev Lett. 2007;9: Kalabukhov A, Gunnarsson R, Borjesson J, Olsson E, Claeson T, Winkler D. Effect of oxygen vacancies in the SrTiO 3 substrate on the electrical properties of the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface. Phys Rev B. 2007;75: Cen C, Thiel S, Mannhart J, Levy J. Oxide nanoelectronics on demand. Science. 2009;323: Angeloni M, Balestrino G, Boggio NG, Medaglia PG, Orgiani P, Tebano A. Suppression of the metal-insulator transition temperature in thin films. J Appl Phys. 2004;96: Ben Shalom M, Tai CW, Lereah Y, et al. Anisotropic magnetotransport at the SrTiO 3 /LaAlO 3 interface. Phys Rev B. 2009;80: Liu B, Liu GJ, Feng HL, Wang C, Yang HW, Wang YQ. Effect of oxygen vacancies on structural, electrical and magnetic properties of La 0.67 Sr 0.33 CoO 3 thin films. Mater Design. 2016;89: Liu B, Wang YQ, Liu GJ, et al. Tuning the magnetic properties of La 0.67 Sr 0.33 CoO 3 d films by oxygen pressure. Phys Rev B. 2016;93: Tokura Y. Critical features of colossal magnetoresistive manganites. Rep Prog Phys. 2006;69: People R, Bean JC. Calculation of critical layer thickness versus lattice mismatch for Ge x Si 1-x /Si strained-layer heterostructures. Appl Phys Lett. 1985;47: SUPPORTING INFORMATION Additional Supporting Information may be found online in the supporting information tab for this article. How to cite this article: Li X, Liu B, Wang Y, et al. Thickness-induced anomalous angulardependent magnetoresistance of La 2/3 Sr 1/3 MnO 3 thin films grown on SrTiO 3. J Am Ceram Soc. 2018;101: /jace.15402
Magnetoresistance of 2D and 3D Electron Gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3. Heterostructures: Influence of Magnetic Ordering, Interface Scattering and
 Magnetoresistance of 2D and 3D Electron Gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 Heterostructures: Influence of Magnetic Ordering, Interface Scattering and Dimensionality X. Wang 1,2, W.M Lü 1,2, A. Annadi 1,2, Z.Q. Liu
Magnetoresistance of 2D and 3D Electron Gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 Heterostructures: Influence of Magnetic Ordering, Interface Scattering and Dimensionality X. Wang 1,2, W.M Lü 1,2, A. Annadi 1,2, Z.Q. Liu
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007](/thumbs/93/118034102.jpg) Electrical transport properties of polar heterointerface between KTaO 3 and SrTiO 3 A. Kalabukhov, 1, R. Gunnarsson, 1 T. Claeson, 1 and D. Winkler 1 arxiv:0704.1050v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007 1
Electrical transport properties of polar heterointerface between KTaO 3 and SrTiO 3 A. Kalabukhov, 1, R. Gunnarsson, 1 T. Claeson, 1 and D. Winkler 1 arxiv:0704.1050v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 9 Apr 2007 1
Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional Oxide p-n Heterojunctions
 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface
 What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces
 Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces Y. Z. Chen *, Y. L. Gan, D. V. Christensen, Y. Zhang, and N. Pryds Department of Energy Conversion
Effect of Sr-doping of LaMnO3 spacer on modulation-doped two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces Y. Z. Chen *, Y. L. Gan, D. V. Christensen, Y. Zhang, and N. Pryds Department of Energy Conversion
Origin of Metallic States at Heterointerface between Band Insulators LaAlO 3 and SrTiO 3
 Origin of Metallic States at Heterointerface between Band Insulators LaAlO 3 and SrTiO 3 K. Yoshimatsu 1, R. Yasuhara 1, H. Kumigashira 1, 2, *, and M. Oshima 1, 2 1 Department of Applied Chemistry, University
Origin of Metallic States at Heterointerface between Band Insulators LaAlO 3 and SrTiO 3 K. Yoshimatsu 1, R. Yasuhara 1, H. Kumigashira 1, 2, *, and M. Oshima 1, 2 1 Department of Applied Chemistry, University
Nanoxide electronics
 Nanoxide electronics Alexey Kalabukhov Quantum Device Physics Laboratory MC2, room D515 Alexei.kalaboukhov@chalmers.se Playing Lego with oxide materials: G. Rijnders, D.H.A. Blank, Nature 433, 369 (2005)
Nanoxide electronics Alexey Kalabukhov Quantum Device Physics Laboratory MC2, room D515 Alexei.kalaboukhov@chalmers.se Playing Lego with oxide materials: G. Rijnders, D.H.A. Blank, Nature 433, 369 (2005)
Chris G. Van de Walle
 Complex oxide interfaces Chris G. Van de Walle Anderson Janotti, Lars Bjaalie, Luke Gordon, Burak Himmetoglu, K. Krishnaswamy Materials Department, University of California, Santa Barbara ES213 June 11-14,
Complex oxide interfaces Chris G. Van de Walle Anderson Janotti, Lars Bjaalie, Luke Gordon, Burak Himmetoglu, K. Krishnaswamy Materials Department, University of California, Santa Barbara ES213 June 11-14,
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film
 Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
with micrometer wide atomic terraces
 Epitaxial growth and properties of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films with micrometer wide atomic terraces Wei Yuan 1, Yuelei Zhao 1, Chi Tang 2, Tang Su 1, Qi Song 1, Jing Shi 2,a), and Wei Han 1,3,b) 1 International
Epitaxial growth and properties of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films with micrometer wide atomic terraces Wei Yuan 1, Yuelei Zhao 1, Chi Tang 2, Tang Su 1, Qi Song 1, Jing Shi 2,a), and Wei Han 1,3,b) 1 International
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study
 Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
Aberration-corrected TEM studies on interface of multilayered-perovskite systems
 Aberration-corrected TEM studies on interface of multilayered-perovskite systems By Lina Gunawan (0326114) Supervisor: Dr. Gianluigi Botton November 1, 2006 MSE 702(1) Presentation Outline Literature Review
Aberration-corrected TEM studies on interface of multilayered-perovskite systems By Lina Gunawan (0326114) Supervisor: Dr. Gianluigi Botton November 1, 2006 MSE 702(1) Presentation Outline Literature Review
Electrostatic charging and redox effects in oxide heterostructures
 Electrostatic charging and redox effects in oxide heterostructures Peter Littlewood 1,2,3 Nick Bristowe 3 & Emilio Artacho 3,6 Miguel Pruneda 4 and Massimiliano Stengel 5 1 Argonne National Laboratory
Electrostatic charging and redox effects in oxide heterostructures Peter Littlewood 1,2,3 Nick Bristowe 3 & Emilio Artacho 3,6 Miguel Pruneda 4 and Massimiliano Stengel 5 1 Argonne National Laboratory
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of
 Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The
Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films
 Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Supplementary Figure 1. Magneto-transport characteristics of topological semimetal Cd 3 As 2 microribbon. (a) Measured resistance (R) as a function
 Supplementary Figure 1. Magneto-transport characteristics of topological semimetal Cd 3 As 2 microribbon. (a) Measured resistance (R) as a function of temperature (T) at zero magnetic field. (b) Magnetoresistance
Supplementary Figure 1. Magneto-transport characteristics of topological semimetal Cd 3 As 2 microribbon. (a) Measured resistance (R) as a function of temperature (T) at zero magnetic field. (b) Magnetoresistance
S emiconductor heterostructures have brought about prominent advances in a variety of mainstream electronics
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: SURFACES, INTERFACES AND THIN FILMS ELECTRONIC PROPERTIES AND MATERIALS SPINTRONICS MAGNETIC PROPERTIES AND MATERIALS Tuning the entanglement between orbital reconstruction and charge
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: SURFACES, INTERFACES AND THIN FILMS ELECTRONIC PROPERTIES AND MATERIALS SPINTRONICS MAGNETIC PROPERTIES AND MATERIALS Tuning the entanglement between orbital reconstruction and charge
Holcomb Group Capabilities
 Holcomb Group Capabilities Synchrotron Radiation & Ultrafast Optics West Virginia University mikel.holcomb@mail.wvu.edu The Physicists New Playground The interface is the device. - Herbert Kroemer, beginning
Holcomb Group Capabilities Synchrotron Radiation & Ultrafast Optics West Virginia University mikel.holcomb@mail.wvu.edu The Physicists New Playground The interface is the device. - Herbert Kroemer, beginning
Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in
 Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in Thin Film Perovskites Xin CHEN,* Naijuan WU, Alex IGNATIEV Texas Center for Advanced Materials, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204,
Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in Thin Film Perovskites Xin CHEN,* Naijuan WU, Alex IGNATIEV Texas Center for Advanced Materials, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204,
Spin Lifetime Enhancement by Shear Strain in Thin Silicon-on-Insulator Films. Dmitry Osintsev, Viktor Sverdlov, and Siegfried Selberherr
 10.1149/05305.0203ecst The Electrochemical Society Spin Lifetime Enhancement by Shear Strain in Thin Silicon-on-Insulator Films Dmitry Osintsev, Viktor Sverdlov, and Siegfried Selberherr Institute for
10.1149/05305.0203ecst The Electrochemical Society Spin Lifetime Enhancement by Shear Strain in Thin Silicon-on-Insulator Films Dmitry Osintsev, Viktor Sverdlov, and Siegfried Selberherr Institute for
Ferromagnetism and Anomalous Hall Effect in Graphene
 Ferromagnetism and Anomalous Hall Effect in Graphene Jing Shi Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of California, Riverside Graphene/YIG Introduction Outline Proximity induced ferromagnetism Quantized
Ferromagnetism and Anomalous Hall Effect in Graphene Jing Shi Department of Physics & Astronomy, University of California, Riverside Graphene/YIG Introduction Outline Proximity induced ferromagnetism Quantized
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reversible Electric Control of Exchange Bias in a Multiferroic Field Effect Device S. M. Wu 1, 2, Shane A. Cybart 1, 2, P. Yu 1, 2, M. D. Abrodos 1, J. Zhang 1, R. Ramesh 1, 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reversible Electric Control of Exchange Bias in a Multiferroic Field Effect Device S. M. Wu 1, 2, Shane A. Cybart 1, 2, P. Yu 1, 2, M. D. Abrodos 1, J. Zhang 1, R. Ramesh 1, 2
Atomic Resolution Interfacial Structure of Lead-free Ferroelectric
 Atomic Resolution Interfacial Structure of Lead-free Ferroelectric K 0.5 Na 0.5 NbO 3 Thin films Deposited on SrTiO 3 Chao Li 1, Lingyan Wang 1*, Zhao Wang 2, Yaodong Yang 2, Wei Ren 1 and Guang Yang 1
Atomic Resolution Interfacial Structure of Lead-free Ferroelectric K 0.5 Na 0.5 NbO 3 Thin films Deposited on SrTiO 3 Chao Li 1, Lingyan Wang 1*, Zhao Wang 2, Yaodong Yang 2, Wei Ren 1 and Guang Yang 1
Nanoxide electronics
 Nanoxide electronics Alexey Kalabukhov Quantum Device Physics Laboratory MC2, room D515 Alexei.kalaboukhov@chalmers.se Playing Lego with oxide materials: G. Rijnders, D.H.A. Blank, Nature 433, 369 (2005)
Nanoxide electronics Alexey Kalabukhov Quantum Device Physics Laboratory MC2, room D515 Alexei.kalaboukhov@chalmers.se Playing Lego with oxide materials: G. Rijnders, D.H.A. Blank, Nature 433, 369 (2005)
Artificially layered structures
 http://accessscience.com/popup.ap x?id=053450&name=print Close Window ENCYCLOPEDIA ARTICLE Artificially layered structures Manufactured, reproducibly layered structures having layer thicknesses approaching
http://accessscience.com/popup.ap x?id=053450&name=print Close Window ENCYCLOPEDIA ARTICLE Artificially layered structures Manufactured, reproducibly layered structures having layer thicknesses approaching
Supplementary Information for Dimensionality-Driven. Insulator-Metal Transition in A-site Excess. Nonstoichiometric Perovskites
 Supplementary Information for Dimensionality-Driven Insulator-Metal Transition in A-site Excess Nonstoichiometric Perovskites Z. Wang, M. Okude, M. Saito, S. Tsukimoto, A. Ohtomo, M. Tsukada, M. Kawasaki,
Supplementary Information for Dimensionality-Driven Insulator-Metal Transition in A-site Excess Nonstoichiometric Perovskites Z. Wang, M. Okude, M. Saito, S. Tsukimoto, A. Ohtomo, M. Tsukada, M. Kawasaki,
MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES. J. M. De Teresa
 MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES J. M. De Teresa Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, Facultad de Ciencias, 50009 Zaragoza, Spain. E-mail:
MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES J. M. De Teresa Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, Facultad de Ciencias, 50009 Zaragoza, Spain. E-mail:
Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 11 1 DECEMBER 2002 Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films Y. Li, V. Nagarajan, S. Aggarwal, R. Ramesh, L. G. Salamanca-Riba, and L.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 11 1 DECEMBER 2002 Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films Y. Li, V. Nagarajan, S. Aggarwal, R. Ramesh, L. G. Salamanca-Riba, and L.
(a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1. (a) (b) (a) Supplementary Figure 2. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
 (a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1. (a) An AFM image of the device after the formation of the contact electrodes and the top gate dielectric Al 2 O 3. (b) A line scan performed along the white dashed line
(a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1. (a) An AFM image of the device after the formation of the contact electrodes and the top gate dielectric Al 2 O 3. (b) A line scan performed along the white dashed line
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface J.-S. Lee 1,*, Y. W. Xie 2, H. K. Sato 3, C. Bell 3, Y. Hikita 3, H. Y. Hwang 2,3, C.-C. Kao 1 1 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource,
Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface J.-S. Lee 1,*, Y. W. Xie 2, H. K. Sato 3, C. Bell 3, Y. Hikita 3, H. Y. Hwang 2,3, C.-C. Kao 1 1 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource,
Polar Discontinuity Doping of the LaVO 3 /SrTiO 3 Interface
 Polar Discontinuity Doping of the LaVO 3 /SrTiO 3 Interface Y. Hotta, 1,a T. Susaki, 1 and H. Y. Hwang 1,2,b 1 Department of Advanced Materials Science, University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8651, Japan
Polar Discontinuity Doping of the LaVO 3 /SrTiO 3 Interface Y. Hotta, 1,a T. Susaki, 1 and H. Y. Hwang 1,2,b 1 Department of Advanced Materials Science, University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8651, Japan
Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Te x MnO 3
 phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in. manganite multilayers
 Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials
 Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar
 Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport. Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR)
 Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
Topological edge states in a high-temperature superconductor FeSe/SrTiO 3 (001) film
 Topological edge states in a high-temperature superconductor FeSe/SrTiO 3 (001) film Z. F. Wang 1,2,3+, Huimin Zhang 2,4+, Defa Liu 5, Chong Liu 2, Chenjia Tang 2, Canli Song 2, Yong Zhong 2, Junping Peng
Topological edge states in a high-temperature superconductor FeSe/SrTiO 3 (001) film Z. F. Wang 1,2,3+, Huimin Zhang 2,4+, Defa Liu 5, Chong Liu 2, Chenjia Tang 2, Canli Song 2, Yong Zhong 2, Junping Peng
Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 -
 Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 - La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 heterostructures P. Yu 1, J. -S. Lee 2, S. Okamoto 3, M. D. Rossell 4, M. Huijben 1,5, C. -H. Yang 1, Q. He 1, J. -X.
Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 - La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 heterostructures P. Yu 1, J. -S. Lee 2, S. Okamoto 3, M. D. Rossell 4, M. Huijben 1,5, C. -H. Yang 1, Q. He 1, J. -X.
Stripes developed at the strong limit of nematicity in FeSe film
 Stripes developed at the strong limit of nematicity in FeSe film Wei Li ( ) Department of Physics, Tsinghua University IASTU Seminar, Sep. 19, 2017 Acknowledgements Tsinghua University Prof. Qi-Kun Xue,
Stripes developed at the strong limit of nematicity in FeSe film Wei Li ( ) Department of Physics, Tsinghua University IASTU Seminar, Sep. 19, 2017 Acknowledgements Tsinghua University Prof. Qi-Kun Xue,
An Advanced Anode Material for Sodium Ion. Batteries
 Layered-Structure SbPO 4 /Reduced Graphene Oxide: An Advanced Anode Material for Sodium Ion Batteries Jun Pan, Shulin Chen, # Qiang Fu, Yuanwei Sun, # Yuchen Zhang, Na Lin, Peng Gao,* # Jian Yang,* and
Layered-Structure SbPO 4 /Reduced Graphene Oxide: An Advanced Anode Material for Sodium Ion Batteries Jun Pan, Shulin Chen, # Qiang Fu, Yuanwei Sun, # Yuchen Zhang, Na Lin, Peng Gao,* # Jian Yang,* and
Thickness dependence of superconductivity and superconductor-insulator transition in ultrathin FeSe films on SrTiO 3 (001) substrate
 Thickness dependence of superconductivity and superconductor-insulator transition in ultrathin FeSe films on SrTiO 3 (001) substrate Qingyan Wang 1,2, Wenhao Zhang 3, Zuocheng Zhang 3, Yi Sun 1,2, Ying
Thickness dependence of superconductivity and superconductor-insulator transition in ultrathin FeSe films on SrTiO 3 (001) substrate Qingyan Wang 1,2, Wenhao Zhang 3, Zuocheng Zhang 3, Yi Sun 1,2, Ying
Oxide Interfaces: Perspectives & New Physics
 Oxide Interfaces: Perspectives & New Physics Seminar, University of Illinois September 24, 2007 Sashi Satpathy University of Missouri, Columbia Funding: DOE, AFOSR, PRF, MURB, DFG http://www.missouri.edu/~satpathys
Oxide Interfaces: Perspectives & New Physics Seminar, University of Illinois September 24, 2007 Sashi Satpathy University of Missouri, Columbia Funding: DOE, AFOSR, PRF, MURB, DFG http://www.missouri.edu/~satpathys
Solid Surfaces, Interfaces and Thin Films
 Hans Lüth Solid Surfaces, Interfaces and Thin Films Fifth Edition With 427 Figures.2e Springer Contents 1 Surface and Interface Physics: Its Definition and Importance... 1 Panel I: Ultrahigh Vacuum (UHV)
Hans Lüth Solid Surfaces, Interfaces and Thin Films Fifth Edition With 427 Figures.2e Springer Contents 1 Surface and Interface Physics: Its Definition and Importance... 1 Panel I: Ultrahigh Vacuum (UHV)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2491 Experimental Realization of Two-dimensional Boron Sheets Baojie Feng 1, Jin Zhang 1, Qing Zhong 1, Wenbin Li 1, Shuai Li 1, Hui Li 1, Peng Cheng 1, Sheng Meng 1,2, Lan Chen 1 and
DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2491 Experimental Realization of Two-dimensional Boron Sheets Baojie Feng 1, Jin Zhang 1, Qing Zhong 1, Wenbin Li 1, Shuai Li 1, Hui Li 1, Peng Cheng 1, Sheng Meng 1,2, Lan Chen 1 and
A new era in surface diffraction pulsed laser deposition of complex metal oxide thin films
 A new era in surface diffraction pulsed laser deposition of complex metal oxide thin films Phil Willmott, Christian Schlepütz tz,, Roger Herger, Oliver Bunk, and Bruce Patterson Beamline X04SA Materials
A new era in surface diffraction pulsed laser deposition of complex metal oxide thin films Phil Willmott, Christian Schlepütz tz,, Roger Herger, Oliver Bunk, and Bruce Patterson Beamline X04SA Materials
Colossal magnetoresistance:
 Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Osaka University, Toyonaka , Japan. University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba , Japan. Kawaguchi, Saitama , Japan
 SLAC-PUB-14503 Structural comparison of n-type and p-type LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 Interfaces Ryosuke Yamamoto 1,ChristopherBell 2, Yasuyuki Hikita 2,HaroldY.Hwang 2,3,4, Hiroyuki Nakamura 1, Tsuyoshi Kimura 1,
SLAC-PUB-14503 Structural comparison of n-type and p-type LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 Interfaces Ryosuke Yamamoto 1,ChristopherBell 2, Yasuyuki Hikita 2,HaroldY.Hwang 2,3,4, Hiroyuki Nakamura 1, Tsuyoshi Kimura 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/NMAT3449 Topological crystalline insulator states in Pb 1 x Sn x Se Content S1 Crystal growth, structural and chemical characterization. S2 Angle-resolved photoemission measurements at various
DOI: 1.138/NMAT3449 Topological crystalline insulator states in Pb 1 x Sn x Se Content S1 Crystal growth, structural and chemical characterization. S2 Angle-resolved photoemission measurements at various
Thin Film Bi-based Perovskites for High Energy Density Capacitor Applications
 ..SKELETON.. Thin Film Bi-based Perovskites for High Energy Density Capacitor Applications Colin Shear Advisor: Dr. Brady Gibbons 2010 Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Motivation and Objective...
..SKELETON.. Thin Film Bi-based Perovskites for High Energy Density Capacitor Applications Colin Shear Advisor: Dr. Brady Gibbons 2010 Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Motivation and Objective...
Efficient Hydrogen Evolution. University of Central Florida, 4000 Central Florida Blvd. Orlando, Florida, 32816,
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 MoS 2 /TiO 2 Heterostructures as Nonmetal Plasmonic Photocatalysts for Highly
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 MoS 2 /TiO 2 Heterostructures as Nonmetal Plasmonic Photocatalysts for Highly
Spontaneous lateral composition modulation in InAlAs and InGaAs short-period superlattices
 Physica E 2 (1998) 325 329 Spontaneous lateral composition modulation in InAlAs and InGaAs short-period superlattices D.M. Follstaedt *, R.D. Twesten, J. Mirecki Millunchick, S.R. Lee, E.D. Jones, S.P.
Physica E 2 (1998) 325 329 Spontaneous lateral composition modulation in InAlAs and InGaAs short-period superlattices D.M. Follstaedt *, R.D. Twesten, J. Mirecki Millunchick, S.R. Lee, E.D. Jones, S.P.
In situ optical characterization of LaAlO 3 epitaxy on SrTiO 3 (001)
 February 2015 EPL, 109 (2015) 37006 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/109/37006 www.epljournal.org In situ optical characterization of LaAlO 3 epitaxy on SrTiO 3 (001) X. D. Zhu 1(a), Sebastian Wicklein 2, Felix
February 2015 EPL, 109 (2015) 37006 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/109/37006 www.epljournal.org In situ optical characterization of LaAlO 3 epitaxy on SrTiO 3 (001) X. D. Zhu 1(a), Sebastian Wicklein 2, Felix
Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
I. Vrejoiu, E. Pippel, E. Nikulina, and D. Hesse Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics, D Halle, Germany. (Dated: October 18, 2018)
 Magnetic Properties of Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 Superlattices M. Ziese Division of Superconductivity and Magnetism, University of Leipzig, D-04103 Leipzig, Germany arxiv:1103.2299v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Magnetic Properties of Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 Superlattices M. Ziese Division of Superconductivity and Magnetism, University of Leipzig, D-04103 Leipzig, Germany arxiv:1103.2299v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Unclassified Unclassified Unclassified UL Standard Form 2981Rev. 2-89) (EG)
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE 1 Form Approved R R OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE 1 Form Approved R R OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing
Correlation-Driven Charge Order at a Mott Insulator - Band Insulator Digital Interface
 Correlation-Driven Charge Order at a Mott Insulator - Band Insulator Digital Interface Rossitza Pentcheva 1 and Warren E. Pickett 2 1 Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Munich,
Correlation-Driven Charge Order at a Mott Insulator - Band Insulator Digital Interface Rossitza Pentcheva 1 and Warren E. Pickett 2 1 Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Munich,
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered
 Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Internal friction and Jahn-Teller effect in the charge-ordered La 1-x Ca x MnO 3 (0.5 x 0.87) R. K. Zheng, R. X. Huang, A. N. Tang, G. Li, X. G. Li a) Structure Research Laboratory, Department of Materials
Effects of substrate on the dielectric and tunable properties of epitaxial SrTiO 3 thin films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 100, 114107 2006 Effects of substrate on the dielectric and tunable properties of epitaxial SrTiO 3 thin films J. H. Hao a Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 100, 114107 2006 Effects of substrate on the dielectric and tunable properties of epitaxial SrTiO 3 thin films J. H. Hao a Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
Two dimensional electron gas at oxide interfaces
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Theses, Dissertations, and Student Research: Department of Physics and Astronomy Physics and Astronomy, Department of Fall
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Theses, Dissertations, and Student Research: Department of Physics and Astronomy Physics and Astronomy, Department of Fall
Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x. O 3 perovskite material
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Mg coating induced superconductivity in the FeSe ultrathin film
 Mg coating induced superconductivity in the FeSe ultrathin film Wenbin Qiu 2, Zongqing Ma 1, 2, Yongchang Liu 1, Xiaolin Wang 2, Shi Xue Dou 2 1 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Composite and Functional Materials,
Mg coating induced superconductivity in the FeSe ultrathin film Wenbin Qiu 2, Zongqing Ma 1, 2, Yongchang Liu 1, Xiaolin Wang 2, Shi Xue Dou 2 1 Tianjin Key Laboratory of Composite and Functional Materials,
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Electrostatic Tuning of Superconductivity. Allen M. Goldman School of Physics and Astronomy University of Minnesota
 Electrostatic Tuning of Superconductivity Allen M. Goldman School of Physics and Astronomy University of Minnesota Paarticipating Graduate Students Yen-Hsiang Lin Kevin Parendo (US Patent Office) Sarwa
Electrostatic Tuning of Superconductivity Allen M. Goldman School of Physics and Astronomy University of Minnesota Paarticipating Graduate Students Yen-Hsiang Lin Kevin Parendo (US Patent Office) Sarwa
Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface
 Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface SLAC-PUB-15439 J.-S. Lee 1,*, Y. W. Xie 2, H. K. Sato 3, C. Bell 3, Y. Hikita 3, H. Y. Hwang 2,3, C.-C. Kao 1 1 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation
Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface SLAC-PUB-15439 J.-S. Lee 1,*, Y. W. Xie 2, H. K. Sato 3, C. Bell 3, Y. Hikita 3, H. Y. Hwang 2,3, C.-C. Kao 1 1 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation
Origin of the 2DEG at the LAO/STO Interface
 Origin of the 2DEG at the LAO/STO Interface Umberto Scotti di Uccio S. Amoruso, C. Aruta, R. Bruzzese, E. Di Gennaro, A. Sambri, X. Wang and F. Miletto Granozio University FEDERICO II & CNRSPIN, Napoli
Origin of the 2DEG at the LAO/STO Interface Umberto Scotti di Uccio S. Amoruso, C. Aruta, R. Bruzzese, E. Di Gennaro, A. Sambri, X. Wang and F. Miletto Granozio University FEDERICO II & CNRSPIN, Napoli
Curvature-enhanced Spin-orbit Coupling and Spinterface Effect in Fullerene-based Spin Valves
 Supplementary Information Curvature-enhanced Spin-orbit Coupling and Spinterface Effect in Fullerene-based Spin Valves Shiheng Liang 1, Rugang Geng 1, Baishun Yang 2, Wenbo Zhao 3, Ram Chandra Subedi 1,
Supplementary Information Curvature-enhanced Spin-orbit Coupling and Spinterface Effect in Fullerene-based Spin Valves Shiheng Liang 1, Rugang Geng 1, Baishun Yang 2, Wenbo Zhao 3, Ram Chandra Subedi 1,
Controlling Kondo like Scattering at the SrTiO 3 based Interfaces
 Controlling Kondo like Scattering at the SrTiO 3 based Interfaces K. Han, 1,2 N. Palina, 1,3 S. W. Zeng, 1,2 Z. Huang,*,1 C. J. Li, 1 W. X. Zhou, 1,2 D Y. Wan, 1,2 L. C. Zhang, 1,2 X. Chi, 3 R. Guo, 1,4
Controlling Kondo like Scattering at the SrTiO 3 based Interfaces K. Han, 1,2 N. Palina, 1,3 S. W. Zeng, 1,2 Z. Huang,*,1 C. J. Li, 1 W. X. Zhou, 1,2 D Y. Wan, 1,2 L. C. Zhang, 1,2 X. Chi, 3 R. Guo, 1,4
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Lateral heterojunctions within monolayer MoSe 2 -WSe 2 semiconductors Chunming Huang 1,#,*, Sanfeng Wu 1,#,*, Ana M. Sanchez 2,#,*, Jonathan J. P. Peters 2, Richard Beanland 2, Jason S. Ross 3, Pasqual
Lateral heterojunctions within monolayer MoSe 2 -WSe 2 semiconductors Chunming Huang 1,#,*, Sanfeng Wu 1,#,*, Ana M. Sanchez 2,#,*, Jonathan J. P. Peters 2, Richard Beanland 2, Jason S. Ross 3, Pasqual
A constant potential of 0.4 V was maintained between electrodes 5 and 6 (the electrode
 (a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of changing po 2 on the field-enhanced conductance A constant potential of 0.4 V was maintained between electrodes 5 and 6 (the electrode configuration is shown
(a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of changing po 2 on the field-enhanced conductance A constant potential of 0.4 V was maintained between electrodes 5 and 6 (the electrode configuration is shown
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 9 Aug 2006
 Correlation-Driven Charge Order at a Mott Insulator - Band Insulator Digital Interface Rossitza Pentcheva 1 and Warren E. Pickett 2 1 Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Munich,
Correlation-Driven Charge Order at a Mott Insulator - Band Insulator Digital Interface Rossitza Pentcheva 1 and Warren E. Pickett 2 1 Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Munich,
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR:
 High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Electrochemical synthesis of metal and semimetal nanotube-nanowire heterojunctions and their electronic transport properties Dachi Yang, ab Guowen Meng,* a Shuyuan Zhang, c Yufeng
Supplementary information Electrochemical synthesis of metal and semimetal nanotube-nanowire heterojunctions and their electronic transport properties Dachi Yang, ab Guowen Meng,* a Shuyuan Zhang, c Yufeng
TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE
 International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental setup for crystal growth. Schematic drawing of the experimental setup for C 8 -BTBT crystal growth.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental setup for crystal growth. Schematic drawing of the experimental setup for C 8 -BTBT crystal growth. Supplementary Figure 2 AFM study of the C 8 -BTBT crystal growth
Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental setup for crystal growth. Schematic drawing of the experimental setup for C 8 -BTBT crystal growth. Supplementary Figure 2 AFM study of the C 8 -BTBT crystal growth
When transition metals are incorporated into a certain site of the BiT, some of BiT-LaTMO 3
 Band gap tuning in ferroelectric Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 by alloying LaTMO 3 (TM = Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, and Al) Woo Seok Choi and Ho Nyung Lee Materials Science and Technology Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Band gap tuning in ferroelectric Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 by alloying LaTMO 3 (TM = Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, and Al) Woo Seok Choi and Ho Nyung Lee Materials Science and Technology Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Thermoelectric Oxide Materials For Electric Power Generation
 Thermoelectric Oxide Materials For Electric Power Generation Kunihito Koumoto Nagoya University, Graduate School of Engineering CREST, Japan Science and Technology Agency 1. Thermoelectric Energy Conversion
Thermoelectric Oxide Materials For Electric Power Generation Kunihito Koumoto Nagoya University, Graduate School of Engineering CREST, Japan Science and Technology Agency 1. Thermoelectric Energy Conversion
Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light. Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film
 Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film Fengang Zheng, a,b, * Peng Zhang, a Xiaofeng Wang, a Wen Huang,
Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film Fengang Zheng, a,b, * Peng Zhang, a Xiaofeng Wang, a Wen Huang,
From 180º stripe domains to more exotic patterns of polarization in ferroelectric nanostructures. A first principles view
 From 180º stripe domains to more exotic patterns of polarization in ferroelectric nanostructures. A first principles view Pablo Aguado-Puente Javier Junquera Ferroelectricity: Basic definitions Existence
From 180º stripe domains to more exotic patterns of polarization in ferroelectric nanostructures. A first principles view Pablo Aguado-Puente Javier Junquera Ferroelectricity: Basic definitions Existence
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Notes, Supplementary Tables, Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Notes, Supplementary Tables, Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1 Illustration of the reaction chamber
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Notes, Supplementary Tables, Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1 Illustration of the reaction chamber
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting information Colossal permittivity with ultralow dielectric loss
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting information Colossal permittivity with ultralow dielectric loss
Material Science II. d Electron systems
 Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Hall effect and dielectric properties of Mn-doped barium titanate
 Microelectronic Engineering 66 (200) 855 859 www.elsevier.com/ locate/ mee Hall effect and dielectric properties of Mn-doped barium titanate a a a a b, * Xiang Wang, Min Gu, Bin Yang, Shining Zhu, Wenwu
Microelectronic Engineering 66 (200) 855 859 www.elsevier.com/ locate/ mee Hall effect and dielectric properties of Mn-doped barium titanate a a a a b, * Xiang Wang, Min Gu, Bin Yang, Shining Zhu, Wenwu
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 1 Jun 2007
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 1 Jun 2007 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 1 Jun 2007](/thumbs/73/69210846.jpg) Electronic reconstruction at SrMnO 3 LaMnO 3 superlattice interfaces Şerban Smadici, 1 Peter Abbamonte, 1 Anand Bhattacharya, Xiaofang Zhai, 1 Andrivo Rusydi, 3 James N. Eckstein, 1 Samuel D. Bader, and
Electronic reconstruction at SrMnO 3 LaMnO 3 superlattice interfaces Şerban Smadici, 1 Peter Abbamonte, 1 Anand Bhattacharya, Xiaofang Zhai, 1 Andrivo Rusydi, 3 James N. Eckstein, 1 Samuel D. Bader, and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI:.38/NMAT4855 A magnetic heterostructure of topological insulators as a candidate for axion insulator M. Mogi, M. Kawamura, R. Yoshimi, A. Tsukazaki,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI:.38/NMAT4855 A magnetic heterostructure of topological insulators as a candidate for axion insulator M. Mogi, M. Kawamura, R. Yoshimi, A. Tsukazaki,
Localized vs. delocalized character of charge carriers in LaAlO 3 / SrTiO 3. superlattices
 Localized vs. delocalized character of charge carriers in LaAlO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices Kejin Zhou 1, Milan Radovic 2,1, Justine Schlappa 1, Vladimir Strocov 1, Ruggero Frison 3, Joel Mesot 1,2, Luc
Localized vs. delocalized character of charge carriers in LaAlO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices Kejin Zhou 1, Milan Radovic 2,1, Justine Schlappa 1, Vladimir Strocov 1, Ruggero Frison 3, Joel Mesot 1,2, Luc
Si, X. X. Xi, and Q. X. JIA
 LA-UR-01-1929 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 THIN FILMS WITH VARIOUS STRAIN STATES Author(s): B. H. PARK, E. J. PETERSON, J. LEE,
LA-UR-01-1929 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 THIN FILMS WITH VARIOUS STRAIN STATES Author(s): B. H. PARK, E. J. PETERSON, J. LEE,
Transport and Magnetic Properties of La 0.85 Ca Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Interfacial Coherency and Ferroelectricity of BaTiO 3 /SrTiO 3 Superlattice Films
 Boise State University ScholarWorks Physics Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Physics 12-18-2007 Interfacial Coherency and Ferroelectricity of BaTiO 3 /SrTiO 3 Superlattice Films Y.
Boise State University ScholarWorks Physics Faculty Publications and Presentations Department of Physics 12-18-2007 Interfacial Coherency and Ferroelectricity of BaTiO 3 /SrTiO 3 Superlattice Films Y.
Superconducting (Li, Fe)OHFeSe film of high quality and high critical parameters
 Superconducting (Li, Fe)OHFeSe film of high quality and high critical parameters Yulong Huang 1,2,+, Zhongpei Feng 1,2,+, Shunli Ni 1,2,+, Jun Li 4, Wei Hu 1,2, Shaobo Liu 1,2, Yiyuan Mao 1,2, Huaxue Zhou
Superconducting (Li, Fe)OHFeSe film of high quality and high critical parameters Yulong Huang 1,2,+, Zhongpei Feng 1,2,+, Shunli Ni 1,2,+, Jun Li 4, Wei Hu 1,2, Shaobo Liu 1,2, Yiyuan Mao 1,2, Huaxue Zhou
Spectroscopy of correlated electrons in nickelates and titanates
 Spectroscopy of correlated electrons in nickelates and titanates Metal-insulator transitions and novel 2DEGs Dept. of Physics University of CA, Santa Barbara Strong Electron Correlations Materials which
Spectroscopy of correlated electrons in nickelates and titanates Metal-insulator transitions and novel 2DEGs Dept. of Physics University of CA, Santa Barbara Strong Electron Correlations Materials which
Evolution of microstructure, strain and physical properties in oxide nanocomposite films
 Intensity(a.u.) LSMO(002) ZnO(110) LAO(002) Supporting Information for Evolution of microstructure, strain and physical properties in oxide nanocomposite films Aiping Chen 1, *, Marcus Weigand 1, Zhenxing
Intensity(a.u.) LSMO(002) ZnO(110) LAO(002) Supporting Information for Evolution of microstructure, strain and physical properties in oxide nanocomposite films Aiping Chen 1, *, Marcus Weigand 1, Zhenxing
PCCP PAPER. 1 Introduction TH Vladislav Borisov,* ab Sergey Ostanin b and Ingrid Mertig ab. View Article Online View Journal View Issue
 PAPER View Article Online View Journal View Issue Cite this: Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17, 12812 Two-dimensional electron gas and its electric control at the interface between ferroelectric and antiferromagnetic
PAPER View Article Online View Journal View Issue Cite this: Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17, 12812 Two-dimensional electron gas and its electric control at the interface between ferroelectric and antiferromagnetic
Magnetism in correlated-electron materials
 Magnetism in correlated-electron materials B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research focus on delocalized electrons in metals and superconductors localized electrons: Hinkov talk outline
Magnetism in correlated-electron materials B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research focus on delocalized electrons in metals and superconductors localized electrons: Hinkov talk outline
3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI. Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea
 3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea Content 3D Dirac metals Search for 3D generalization of graphene Bi 1-x
3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea Content 3D Dirac metals Search for 3D generalization of graphene Bi 1-x
Giant exchange bias in a single-phase magnet with two magnetic
 Giant exchange bias in a single-phase magnet with two magnetic sublattices Y. Sun, 1,a) J.-Z. Cong, 1 Y.-S. Chai, 1 L.-Q. Yan, 1 Y.-L. Zhao, 1 S.-G. Wang, 1 W. Ning, 2 and Y.-H Zhang 2 1 Beijing National
Giant exchange bias in a single-phase magnet with two magnetic sublattices Y. Sun, 1,a) J.-Z. Cong, 1 Y.-S. Chai, 1 L.-Q. Yan, 1 Y.-L. Zhao, 1 S.-G. Wang, 1 W. Ning, 2 and Y.-H Zhang 2 1 Beijing National
Rashba spin-orbit coupling in the oxide 2D structures: The KTaO 3 (001) Surface
 Rashba spin-orbit coupling in the oxide 2D structures: The KTaO 3 (001) Surface Sashi Satpathy Department of Physics University of Missouri, Columbia, USA E Ref: K. V. Shanavas and S. Satpathy, Phys. Rev.
Rashba spin-orbit coupling in the oxide 2D structures: The KTaO 3 (001) Surface Sashi Satpathy Department of Physics University of Missouri, Columbia, USA E Ref: K. V. Shanavas and S. Satpathy, Phys. Rev.
Molecular Beam Epitaxy Growth of Tetragonal FeS Film on
 Molecular Beam Epitaxy Growth of Tetragonal FeS Film on SrTiO3(001) Substrate Kun Zhao( 赵琨 ) 1, Haicheng Lin( 林海城 ) 1, Wantong Huang( 黄万通 ) 1, Xiaopeng Hu( 胡小鹏 ) 1,2, Xi Chen( 陈曦 ) 1,2, Qi-Kun Xue( 薛其坤
Molecular Beam Epitaxy Growth of Tetragonal FeS Film on SrTiO3(001) Substrate Kun Zhao( 赵琨 ) 1, Haicheng Lin( 林海城 ) 1, Wantong Huang( 黄万通 ) 1, Xiaopeng Hu( 胡小鹏 ) 1,2, Xi Chen( 陈曦 ) 1,2, Qi-Kun Xue( 薛其坤
performance electrocatalytic or electrochemical devices. Nanocrystals grown on graphene could have
 Nanocrystal Growth on Graphene with Various Degrees of Oxidation Hailiang Wang, Joshua Tucker Robinson, Georgi Diankov, and Hongjie Dai * Department of Chemistry and Laboratory for Advanced Materials,
Nanocrystal Growth on Graphene with Various Degrees of Oxidation Hailiang Wang, Joshua Tucker Robinson, Georgi Diankov, and Hongjie Dai * Department of Chemistry and Laboratory for Advanced Materials,
