GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
|
|
|
- Mervin Price
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Question Paper & Answer Keys
2 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis. Question Paper & Answer keys : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:
3 ANALYSIS OF GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Manufacturing Engineering, 18 Industrial Engineering, 1 Engineering Mathematics, 14 Engineering Mechanics, 5 Mechanics of Materials, 6 Thermodynamics, 1 Theory of Machines, 10 Heat Transfer, 9 Fluid Mechanics, 8 Machine Design, 6 : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 3
4 - SUBJECT Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics Heat Transfer Thermodynamics Manufacturing Engineering Industrial Engineering NO OF QUESTION 1M:4 M:5 1M:1 M: 1M: M: 1M: M:4 1M:0 M:3 1M:0 M:4 1M:1 M:4 1M:4 M:4 1M:4 M:7 1M: M:5 Topics Asked in Paper Linear Algebra, Calculus Laplace transform Probability and Distribution Differential Equations Friction, Complex Variables Work & Energy Methods Complex Stress & Strain Torsion Deflection of Beams Mechanisms Vibrations Gear Trains Design for Dynamic Loading Design of Spur Gears Hydraulic Machines Fluid Kinematics Flow Through Pipes Laminar and Turbulent Flow Convection, Heat Exchanger Conduction, Radiation, Radiation Entropy Work and Heat Refrigeration First Law of Thermodynamics Air Standard Cycles and IC Engine Second Law of Thermodynamics Power Plant Engineering Materials Metal Cutting Casting Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) Non-Traditional Machining Process Metrology and Inspection PERT and CPM Forecasting Inventory Control Operation Research Scheduling and Loading Total Marks Total : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 4
5 GATE 009 Examination CHANICAL ENGINEERING Q.1 to Q. 0 Carries One Mark Each. 1. For a matrix[ ] [ x ], the transpose of the matrix is equal to the inverse of the matrix [ ] [ ]. The value of x is given by (A) ( ) (B) ( ). The divergence of the vector field xz xy yz at a point (1,1,1) is equal to (A) 7 (B) 4 (C) (D) (C) 3 (D) 0 3. The inverse Laplace transform of s 1 s (A) e (C) 1 e (B) e (D) e 4. If three coins are tossed simultaneously, the probability of getting at least one head is (A) 1/8 (C) 1/ (B) 3/8 (D) 7/8 is 5. If a closed system is undergoing an irreversible process, the entropy of the system (A) Must increase (C) Must decrease (B) Always remains constant (D) Can increase, decrease or remain constant 6. A coolant fluid at C flows over a heated flat plate maintained at a constant temperature of C. The boundary layer temperature distribution at a given location on the plate may be approximated as T = exp ( y) where y (in m) is the distance normal to the plate and T is in C. If thermal conductivity of the fluid is 1.0W/mK, the local convective heat transfer coefficient (in W/ K) at that location will be (A) 0. (B) 1 (C) 5 (D) 10 : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 5
6 7. A frictionless piston-cylinder device contains a gas initially at 0.8MPa and m 3. It expands quasi-statically at constant temperature to a final volume of m 3. The work output (in kj) during this process will be (A) 8.3 (B) 1.00 (C) (D) In an ideal vapour compression refrigeration cycle, the specific enthalpy of refrigerant (in kj/kg) at the following states is given as: Inlet of condenser: 83 Exit of condenser: 116 Exit of evaporator: 3 The COP of this cycle is (A).7 (B).75 (C) 3.7 (D) A compressor undergoes a reversible, steady flow process. The gas at inlet and outlet of the compressor is designated as state 1 and state respectively. Potential and kinetic energy changes are to be ignored. The following notation are used: v = specific volume and P = pressure of the gas. The specific work required to be supplied to the compressor for this gas compression process is (A) dv (C) v ( ) (D) (v v ) (B) vdp 10. A block weighing 981 N is resting on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the block and the horizontal surface is = 0.. A vertical cable attached to the block provides partial support as shown. A man can pull horizontally with a force of 100N. What will be the tension, T (in N) in the cable if the man is just able to move the block to the right? T G (A) 176. (B) (C) (D) : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 6
7 11. If the principal stresses in a plane stress problem, are the magnitude of the maximum shear stress (in MPa) will be (A) 60 (B) 50 (C) 30 (D) 0 1. A simple quick return mechanism is shown in the figure. The forward to return ratio of the quick return mechanism is :1. If the radius of the crank O 1 is then the dist nce d (in ) between the crank centre to lever pivot centre point should be Q P d (A) (B) 16.5 (C) 40.0 (D) The rotor shaft of a large electric motor supported between short bearings at both the end shows a deflection of 1.8mm in the middle of the rotor. Assuming the rotor to be perfectly balanced and supported at knife edges at both the ends, the likely critical speed (in rpm) of the shaft is (A) 350 (C) 810 (B) 705 (D) A solid circular shaft of diameter d is subjected to a combined bending moment M and torque, T. The material property to be used for designing the shaft using the relation d is (A) ultimate tensile strength (S u ) (B) tensile yield strength (S y ) (C) torsional yield strength (S sy ) (D) endurance strength (S e ) 15. The effective number of lattice points in the unit cell of simple cubic, body centered cubic, and face centered cubic space lattices, respectively, are (A) 1,, (C),3,4 (B) 1,,4 (D),4,4 16. Friction at the tool-chip interface can be reduced by (A) decreasing the rake angle (B) increasing the depth of cut (C) decreasing the cutting speed. (D) increasing the cutting speed. : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 7
8 17. Two streams of liquid metal, which are not hot enough to fuse properly result into a casting defect known as (A) cold shut (C) sand wash (B) swell (D) scab 18. The expected time (t ) of a PERT activity in terms of optimistic time (t ), pessimistic time (t ) and most likely time (t )is given by t t t t t t ( ) t ( ) t ( ) t t t t ( ) t t t t 19. Which of the following is the correct data structure for solid models? (A) solid part faces edges vertices (C) vertices edges faces solid parts (B) solid part edges faces vertices (D) vertices faces edges solid parts 0. Which of the following forecasting methods takes a fraction of forecast error into account for the next period forecast? (A) simple average method (C) weighted moving average method (B) moving average method (D) exponential smoothening method Q.1 to Q. 60 Carries Two Marks Each. 1. An analytic function of a complex variable z = x + iy is expressed as f(z) = u(x, y) +iv(x, y) where i = 1. If u = xy, the expression of v should be x y y (A) k (C) x y x (B) k (D) x y k k. The solution of x y x with the condition y( ) is (A) y (B) y (C) y (D) y : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 8
9 3. A path AB in the form of one quarter of a circle of unit radius is shown in the figure. Integration of x y Y B on path AB traversed in a counter-clockwise sense is (A) A X (C) (B) (D) 1 4. The distance between the origin and the point nearest to it on the surface (A) 1 (B) 5. The area enclosed between the curves (A) (B) 8 y 4x and x 4y is (C) (D) 16 (C) (D) z 1 xy is 6. The standard deviation of the critical path is (A) 0.33 (B) 0.55 [Ans. *] (C) 0.77 (D) Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe where the diameter is reduced from 0cm to 10cm. The pressure in the 0cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150 kpa. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50kPa and a specific weight of 5 kn/m 3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m 3 /s) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation is (A) 0.05 (C) 0.7 (B) 0.16 (D) In a parallel flow heat exchanger operating under steady state, the heat capacity rates (product of specific heat at constant pressure and mass flow rate) of the hot and cold fluid are equal. The hot fluid, flowing at 1 kg/s with Cp= 4kJ/kgK, enters the heat exchanger at 10 C, while the cold fluid has an inlet temperature of 15 C. The overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger is estimated to be and the corresponding heat transfer surface area is 5. Neglect heat transfer between the heat exchanger and the ambient. The heat exchanger is characterized by the following relation: exp( ). The exit temperature (in C) for the cold fluid is (A) 45 (B) 55 (C) 65 (D) 75 : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 9
10 9. In an air-standard Otto cycle, the compression ratio is 10. The condition at the beginning of the compression process is 100kPa and C. Heat added at constant volume is 1500 kj/kg, while 700 kj/kg of heat is rejected during the other constant volume process in the cycle. Specific gas constant for air = 0.87kJ/kgK. The mean effective pressure (in kpa) of the cycle is (A) 103 (C) 515 (B) 310 (D) An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50kW. The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at C and. The rate (in kw) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is (A) 50 (C) 300 (B) 50 (D) You are asked to evaluate assorted fluid flows for their suitability in a given laboratory application. The following three flow choices, expressed in terms of the two-dimensional velocity fields in the x-y plane, are made available. P. u = y, v = -3x; Q. u = 3xy, v = 0; R. u = x, v = y Which flows(s) should be recommended when the application requires the flow to be incompressible and irrotational? (A) P and R (B) Q (C) Q and R (D) R 3. Water at C is flowing through a 1.0 km long G.I pipe of 00mm diameter at the rate of 0.07 /s. If value of Darcy friction factor for this pipe is 0.0 and density of water is 1000 kg/, the pumping power (in kw) required to maintain the flow is (A) 1.8 (B) 17.4 (C) 0.5 (D) Consider steady-state heat conduction across the thickness in a plane composite wall (as shown in the figure) exposed to convection conditions on both sides. h 1 h Given: h h : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 10
11 and Assuming negligible contact resistance between the wall surfaces, the interface temperature, T (in C), of the two walls will be (A) 0.50 (C) 3.75 (B).75 (D) The velocity profile of a fully developed laminar flow in a straight circular pipe, as shown in the figure, is given by the expression u (r) = ( ) ( ) where is a constant. The average velocity of fluid in the pipe is r x u(r) R ( ) ( dp dx ) ( ) ( dp dx ) ( ) ( dp dx ) ( ) ( dp dx ) 35. A solid shaft of diameter, d and length L is fixed at both the ends. A torque, T 0 is applied at a distance, L/4 from the left end as shown in the figure given below. T0 L/4 3L/4 The maximum shear stress in the shaft is ( ) d ( ) d ( ) ( ) d d 36. An epicyclic gear train is shown schematically in the adjacent figure. The sun gear on the input shaft is a 0 teeth external gear. The planet gear 3 is a 40 teeth external gear. The ring gear 5 is a 100 teeth internal gear. The ring gear 5 is fixed and the gear is rotating at 60 rpm ccw (ccw = counter-clockwise and cw = clockwise). The arm 4 attached to the output shaft will rotate at : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 11
12 5 3 4 (A) 10 rpm ccw (B) 10 rpm cw (C) 1 rpm cw (D) 1 rpm ccw 37. A forged steel link with uniform diameter of 30mm at the centre is subjected to an axial force that varies from 40kN in compression to 160kN in tension. The tensile ( ), yield ( ) and corrected endurance ( ) strengths of the steel material are 600MPa, 40MPa and 40MPa respectively. The factor of safety against fatigue endur nce s per oderberg s criterion is (A) 1.6 (C) 1.45 (B) 1.37 (D) An automotive engine weighing 40kg is supported on four springs with linear characteristics. Each of the front two springs have a stiffness of 16MN/m while the stiffness of each rear spring is 3MN/m. The engine speed (in rpm), at which resonance is likely to occur, is (A) 6040 (C) 144 (B) 300 (D) A vehicle suspension system consists of a spring and a damper. The stiffness of the spring is 3.6kN/m and the damping constant of the damper is 400Ns/m. If the mass is 50kg, then the damping factor (d) and damped natural frequency (f ), respectively, are (A) and 1.19Hz (C) and 1.35Hz (B) and 7.48Hz (D) and 8.50Hz 40. A frame of two arms of equal length L is shown in the below figure. The flexural rigidity of each arm of the frame is EI. The vertical deflection at the point of application of load P is L P L ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 1
13 41. A uniform rigid rod of mass M and length L is hinged at one end as shown in the adjacent figure. A force P is applied at a distance of L/3 from the hinge so that the rod swings to the right. The reaction at the hinge is P L/3 L (A) P (B) 0 (C) P/3 (D) P/3 4. Match the approaches given below to perform stated kinematics / dynamics analysis of machine Analysis Approach P. Continuous relative rotation 1. le bert s principle Q. Velocity and acceleration. Grubler s criterion R. Mobility 3. Gr shoff s l w S. Dynamic-static analysis 4. ennedy s theore (A) (B) (C) (D) 43. A company uses 555 units of an item annually. Delivery lead time is 8 days. The recorder point (in number of units) to achieve optimum inventory is (A) 7 (C) 56 (B) 8 (D) Consider the following Linear Programming Problem (LPP): Maximum z x x Subject to x x ; x x ; x x (A) The LPP has a unique optimal solution (B) The LPP is infeasible 45. Six jobs arrived in a sequence as given below: Jobs Processing Time (days) I 4 II 9 III 5 IV 10 V 6 VI 8 (C) The LPP is unbounded (D) The LPP has multiple optimal solutions : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 13
14 Average flow time (in days) for the above jobs using Shortest Processing Time rule is (A) 0.83 (C) (B) 3.16 (D) Minimum shear strain in orthogonal turning with a cutting tool of zero rake angle is (A) 0.0 (B) 0.5 (C) 1.0 (D) Electrochemical machining is performed to remove material from an iron surface of 0mm 0mm under the following conditions: Inter electrode gap= 0.mm Supply voltage (DC)= 1V Specific resistance of electrolyte Ωc Atomic weight of Iron= Valency of Iron = F r d y s const nt 9 oulo bs The material removal rate (in g/s) is (A) (B) (C) (D) Match the following: NC Code Definition P. M05 1. Absolute coordinate system Q. G01. Dwell R. G04 3. Spindle stop S. G90 4. Linear interpolation (A) (B) (C) (D) 49. What are the upper and lower limits of the shaft represented by 60 f? Use the following data: Diameter 60 lies in the diameter step of 50-80mm. Fundamental tolerance unit, i = in m = 0.45, where D is the representative size in mm; oler nce v lue for i Fund ent l devi tion for f shaft = 5.5 (A) Lower limit = 59.94mm, Upper Limit = mm (B) Lower limit = mm, Upper Limit = mm (C) Lower limit = mm, Upper Limit = mm (D) Lower limit = 60.00mm, Upper Limit = mm : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 14
15 50. Match the items in Column I and Column II. Column I Column II P. Metallic Chills 1. Support for the core Q. Metallic Chaplets. Reservoir of the molten metal R. Riser 3. Control cooling of critical sections S. Exothermic Padding 4. Progressive solidification (A) (B) (C) (D) Common Data Questions Common Data for Questions 51 and 5 The inlet and the outlet conditions of steam for an adiabatic steam turbine are as indicated in the notations are as usually followed h = 300kJ/kg = 160m/s = 10m = 3MPa 51. If mass flow rate of steam through the turbine is 0kg/s, the power output of the turbine (in MW ) is (A) (C) (B) (D) Assume the above turbine to be part of a simple Rankine cycle. The density of water at the inlet to the pump is 1000kg/m 3. Ignoring kinetic and potential energy effects, the specific work (in kj/kg) supplied to the pump is (A) 0.93 (B) h = 600kJ/kg = 100m/s = 6m = 70kPa (C).930 (D) Common Data for Questions 53 and 54 Radiative heat transfer is intended between the inner surfaces of two very large isothermal parallel metal plates. While the upper plate (designated as plate 1) is a black surface and the warmer one being maintained at, the lower plate ( plate ) is a diffuse and gray surface with an emissivity of 0.7 and is kept at. Assume that the surfaces are sufficiently large to form a two-surface enclosure and steady state conditions to exist. Stefan Boltzmann constant is given as The irradiation (in kw/ ) for the upper plate (plate 1) is (A).5 (B) 3.6 (C) 17.0 (D) 19.5 : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 15
16 54. If plate 1 is also a diffuse and gray surface with an emissivity value of 0.8, the net radiation heat exchange (in kw/ ) between plate 1 and plate is (A) 17.0 (C) 3.0 (B) 19.5 (D) 31.7 Common Data for Questions 55 and 56 Consider the following PERT network: The optimistic time, most likely time and pessimistic time of all the activities are given in the table below. Activity Optimistic time (days) Most likely time (days) Pessimistic time (days) The critical path duration of the network (in days) is (A) 11 (B) 14 (C) 17 (D) The standard deviation of the critical path is (A) 0.33 (B) 0.55 [Ans. *] (C) 0.77 (D) 1.66 Linked Answer Questions Statement for Linked Answer Questions 57 and 58 In a machining experiment, tool life was found to vary with the cutting speed in the following manner: Cutting speed (m/ min) Tool life (minutes) The exponent (n) and constant (k) of the ylor s tool life equ tion re (A) n = 0.5 and k = 540 (C) n = 1 and k = 0.74 (B) n = 1 and k = 4860 (D) n = 0.5 and k = : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 16
17 58. What is the percentage increase in tool life when the cutting speed is halved? (A) 50% (C) 300% (B) 00% (D) 400% Statement for Linked Answer Questions 59 and 60 A full depth involute spur pinion of 4 mm module and 1 teeth is to transmit 15 kw at 960 rpm. Its face width is 5 mm 59. The tangential force transmitted (in N ) is (A) 355 (B) 611 (C) 1776 (D) Given that the tooth geometry factor is 0.3 and the combined effect of dynamic load and allied factors intensifying the stress is 1.5; the minimum allowable stress (in MPa) for the gear material is (A) 4.0 (C) 11.0 (B) (D) 74.0 : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 17
GATE 2009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper
 GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper. For a matrix [M]= x [M]. The value of x is given by GATE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 009 (ME) GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper Q. No. 0 Carry One
GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper. For a matrix [M]= x [M]. The value of x is given by GATE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 009 (ME) GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper Q. No. 0 Carry One
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
Set 1. a. 100 kj/kg b. 110 kj/kg c. 140 kj/kg d. 150 kj/kg
 Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
Topic wise Tests. Complex Variables, Numerical Methods and Probability and Statistics.
 ME-01 ME-02 ME-03 ME-04 GEM-1 GEM-2 GMC 1 Mechanics) GHT 1 Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
ME-01 ME-02 ME-03 ME-04 GEM-1 GEM-2 GMC 1 Mechanics) GHT 1 Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1
 Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix 2 6 0 the matrix 4 12 8 is 2 0 4 1 3 0 2 6 4 1 0 2 is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) 96 2. x sin x Lt 1 cosx
Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix 2 6 0 the matrix 4 12 8 is 2 0 4 1 3 0 2 6 4 1 0 2 is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) 96 2. x sin x Lt 1 cosx
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
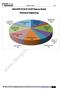 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper II. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
Answers to questions in each section should be tied together and handed in separately.
 EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2007
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2007
Civil Services Examination-1989
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Chapter Four fluid flow mass, energy, Bernoulli and momentum
 4-1Conservation of Mass Principle Consider a control volume of arbitrary shape, as shown in Fig (4-1). Figure (4-1): the differential control volume and differential control volume (Total mass entering
4-1Conservation of Mass Principle Consider a control volume of arbitrary shape, as shown in Fig (4-1). Figure (4-1): the differential control volume and differential control volume (Total mass entering
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
General Aptitude (GA) Set-1. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are.
 GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-1 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Going by the that many hands make light work, the school involved all the students in the task. The words that best fill the blanks
GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-1 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Going by the that many hands make light work, the school involved all the students in the task. The words that best fill the blanks
Objectives. Conservation of mass principle: Mass Equation The Bernoulli equation Conservation of energy principle: Energy equation
 Objectives Conservation of mass principle: Mass Equation The Bernoulli equation Conservation of energy principle: Energy equation Conservation of Mass Conservation of Mass Mass, like energy, is a conserved
Objectives Conservation of mass principle: Mass Equation The Bernoulli equation Conservation of energy principle: Energy equation Conservation of Mass Conservation of Mass Mass, like energy, is a conserved
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW SVCET
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 7. KFUPM Housam Binous CHE 303
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 7 1 Thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy and entropy balances Fluid mechanics encompasses the above balances and conservation of momentum
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 7 1 Thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy and entropy balances Fluid mechanics encompasses the above balances and conservation of momentum
Where F1 is the force and dl1 is the infinitesimal displacement, but F1 = p1a1
 In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
1. Choose answer and indicate by writing only the corresponding capital letter (A, B, C, D) as the case may be).
 1. Choose answer and indicate by writing only the corresponding capital letter (A, B, C, D) as the case may be). 1.1 The manufacturing area of a plat is divided into four quadrants. Four machines have
1. Choose answer and indicate by writing only the corresponding capital letter (A, B, C, D) as the case may be). 1.1 The manufacturing area of a plat is divided into four quadrants. Four machines have
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
CLASS Fourth Units (Second part)
 CLASS Fourth Units (Second part) Energy analysis of closed systems Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. MOVING BOUNDARY WORK Moving boundary work (P
CLASS Fourth Units (Second part) Energy analysis of closed systems Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. MOVING BOUNDARY WORK Moving boundary work (P
Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS IN SECTION B Graph paper will be provided.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2017-2018 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES AND LAWS ENG-4002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2017-2018 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES AND LAWS ENG-4002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS
Set 2 (d) 150 C (a) 0.45 (d) can be positive, negative or zero (C) 8.5 J/K (a) 0.1
 Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
If there is convective heat transfer from outer surface to fluid maintained at T W.
 Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
SILVER OAK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ADITYA SILVER OAK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (2131905) (ME) DATE: 11-08-2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Answer following questions in short/brief: 1. Energy of an isolated system is always
SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (2131905) (ME) DATE: 11-08-2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Answer following questions in short/brief: 1. Energy of an isolated system is always
FE Fluids Review March 23, 2012 Steve Burian (Civil & Environmental Engineering)
 Topic: Fluid Properties 1. If 6 m 3 of oil weighs 47 kn, calculate its specific weight, density, and specific gravity. 2. 10.0 L of an incompressible liquid exert a force of 20 N at the earth s surface.
Topic: Fluid Properties 1. If 6 m 3 of oil weighs 47 kn, calculate its specific weight, density, and specific gravity. 2. 10.0 L of an incompressible liquid exert a force of 20 N at the earth s surface.
10 minutes reading time is allowed for this paper.
 EGT1 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IB Tuesday 31 May 2016 2 to 4 Paper 4 THERMOFLUID MECHANICS Answer not more than four questions. Answer not more than two questions from each section. All questions carry the
EGT1 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IB Tuesday 31 May 2016 2 to 4 Paper 4 THERMOFLUID MECHANICS Answer not more than four questions. Answer not more than two questions from each section. All questions carry the
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems
 First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
PES Institute of Technology
 PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT
 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
In the next lecture...
 16 1 In the next lecture... Solve problems from Entropy Carnot cycle Exergy Second law efficiency 2 Problem 1 A heat engine receives reversibly 420 kj/cycle of heat from a source at 327 o C and rejects
16 1 In the next lecture... Solve problems from Entropy Carnot cycle Exergy Second law efficiency 2 Problem 1 A heat engine receives reversibly 420 kj/cycle of heat from a source at 327 o C and rejects
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
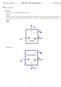 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 DYNAMICALLY EQUIVALENT SYSTEM. Structure. Objectives. 4.1 Introduction
 UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. Candidates should attempt
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. Candidates should attempt
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
GATE: 2006 ME: Mechanical Engineering
 GATE: 2006 ME: Mechanical Engineering Q. 1 Q. 20 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Match the items in columns I and II. Column I (P) Gauss-Seidel method (Q) Forward Newton-Gauss method (R) Runge-Kutta method (S)
GATE: 2006 ME: Mechanical Engineering Q. 1 Q. 20 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Match the items in columns I and II. Column I (P) Gauss-Seidel method (Q) Forward Newton-Gauss method (R) Runge-Kutta method (S)
GATE : Mechanical
 GATE -2015 : Mechanical Following Topics are very important for GATE Examination Grade-A Subjects.more than 10 revisions required Mathematics Manufacturing Science/Production SOM TOM Industrial Engineering
GATE -2015 : Mechanical Following Topics are very important for GATE Examination Grade-A Subjects.more than 10 revisions required Mathematics Manufacturing Science/Production SOM TOM Industrial Engineering
12/21/2014 7:39 PM. Chapter 2. Energy and the 1st Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 2 Energy and the 1st Law of Thermodynamics 1 2 Homework Assignment # 2 Problems: 1, 7, 14, 20, 30, 36, 42, 49, 56 Design and open end problem: 2.1D Due Monday 22/12/2014 3 Work and Kinetic Energy
Chapter 2 Energy and the 1st Law of Thermodynamics 1 2 Homework Assignment # 2 Problems: 1, 7, 14, 20, 30, 36, 42, 49, 56 Design and open end problem: 2.1D Due Monday 22/12/2014 3 Work and Kinetic Energy
A B C November 29 Exam 3 Physics 105. σ = W m 2 K 4 L v = J/kg R = J/(K mol) c w = 4186 J/(kg K) N A = 6.
 L 2012 November 29 Exam 3 Physics 105 Physical Constants Properties of H 2 O σ = 5.6704 10 8 W m 2 K 4 L v = 2.26 10 6 J/kg R = 8.3145 J/(K mol) c w = 4186 J/(kg K) N A = 6.0221 10 23 L f = 3.33 10 5 J/kg
L 2012 November 29 Exam 3 Physics 105 Physical Constants Properties of H 2 O σ = 5.6704 10 8 W m 2 K 4 L v = 2.26 10 6 J/kg R = 8.3145 J/(K mol) c w = 4186 J/(kg K) N A = 6.0221 10 23 L f = 3.33 10 5 J/kg
ME 200 Final Exam December 12, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems. Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 18 Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics Equilibrium & temperature scales Thermal expansion Exchange of heat First law of thermodynamics Heat conduction
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 18 Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics Equilibrium & temperature scales Thermal expansion Exchange of heat First law of thermodynamics Heat conduction
Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002
 16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 For the given fluctuating fatigue load, the values of stress amplitude and stress ratio are respectively MPa 250 200 150 100 50 0 Time (A) 100 MPa and 5 (B) 250 MPa
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 For the given fluctuating fatigue load, the values of stress amplitude and stress ratio are respectively MPa 250 200 150 100 50 0 Time (A) 100 MPa and 5 (B) 250 MPa
Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS IN SECTION B Linear graph paper will be provided.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES AND LAWS ENG-4002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES AND LAWS ENG-4002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS
MC 405 MODEL TEST PAPER - 1 THERMAL SCIENCE & ENGINEERING. Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100
 THERMAL SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question (a, b, etc. ) should
THERMAL SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question (a, b, etc. ) should
Fluid Mechanics Answer Key of Objective & Conventional Questions
 019 MPROVEMENT Mechanical Engineering Fluid Mechanics Answer Key of Objective & Conventional Questions 1 Fluid Properties 1. (c). (b) 3. (c) 4. (576) 5. (3.61)(3.50 to 3.75) 6. (0.058)(0.05 to 0.06) 7.
019 MPROVEMENT Mechanical Engineering Fluid Mechanics Answer Key of Objective & Conventional Questions 1 Fluid Properties 1. (c). (b) 3. (c) 4. (576) 5. (3.61)(3.50 to 3.75) 6. (0.058)(0.05 to 0.06) 7.
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA
 Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
GATE 2018 Online Test Series - Mechanincal Engineering. Numerical Methods,Vector Calculus,Complex Engineering Mathematics-III Analysis
 Test Difficulty No of Max Test Type of test Test Live from Test details Test Syllabus No level questions Marks duration 1 Engineering Mathematics-I Linear Algebra,Statistics 2 Engineering Mathematics-II
Test Difficulty No of Max Test Type of test Test Live from Test details Test Syllabus No level questions Marks duration 1 Engineering Mathematics-I Linear Algebra,Statistics 2 Engineering Mathematics-II
Tuesday, February 11, Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK : AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING.
 Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : Mechanics of Fluids : A00 : II-I- B. Tech Year : 0 0 Course Coordinator
Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : Mechanics of Fluids : A00 : II-I- B. Tech Year : 0 0 Course Coordinator
20 m neon m propane. g 20. Problems with solutions:
 Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -11. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before. attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling.
 SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling. Find: Determine the value of the critical speed of rotation for the shaft. Schematic and
SOLUTION (17.3) Known: A simply supported steel shaft is connected to an electric motor with a flexible coupling. Find: Determine the value of the critical speed of rotation for the shaft. Schematic and
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPIC WISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2017) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPIC WISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2017) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 U N IT - 1 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS 1. 1 kg of gas at 1.1 bar, 27 o C is compressed
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 U N IT - 1 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS 1. 1 kg of gas at 1.1 bar, 27 o C is compressed
Shafts Introduction. Shafts 509
 Shafts 509 C H A P T E R 14 Shafts 1. Introduction.. Material Used for Shafts.. Manufacturing of Shafts. 4. Types of Shafts. 5. Standard Sizes of Transmission Shafts. 6. Stresses in Shafts. 7. Maximum
Shafts 509 C H A P T E R 14 Shafts 1. Introduction.. Material Used for Shafts.. Manufacturing of Shafts. 4. Types of Shafts. 5. Standard Sizes of Transmission Shafts. 6. Stresses in Shafts. 7. Maximum
GATE SOLUTIONS E N G I N E E R I N G
 GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS IN SECTION B Linear graph paper will be provided.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2016-2017 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES AND LAWS ENG-4002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2016-2017 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES AND LAWS ENG-4002Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A and ANY TWO QUESTIONS
Department of Mechanical Engineering
 UNDERGRADUATE COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 15102 Statics 3 Cr. Basic concepts. Forces, moments, and couples. Equilibrium of particles and rigid bodies. First and second moments. Structures (trusses, frames, machines).
UNDERGRADUATE COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 15102 Statics 3 Cr. Basic concepts. Forces, moments, and couples. Equilibrium of particles and rigid bodies. First and second moments. Structures (trusses, frames, machines).
Lesson 6 Review of fundamentals: Fluid flow
 Lesson 6 Review of fundamentals: Fluid flow The specific objective of this lesson is to conduct a brief review of the fundamentals of fluid flow and present: A general equation for conservation of mass
Lesson 6 Review of fundamentals: Fluid flow The specific objective of this lesson is to conduct a brief review of the fundamentals of fluid flow and present: A general equation for conservation of mass
MEMS Project 2 Assignment. Design of a Shaft to Transmit Torque Between Two Pulleys
 MEMS 029 Project 2 Assignment Design of a Shaft to Transmit Torque Between Two Pulleys Date: February 5, 206 Instructor: Dr. Stephen Ludwick Product Definition Shafts are incredibly important in order
MEMS 029 Project 2 Assignment Design of a Shaft to Transmit Torque Between Two Pulleys Date: February 5, 206 Instructor: Dr. Stephen Ludwick Product Definition Shafts are incredibly important in order
The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that brings the system into equilibrium with aheat reservoir. (4.
 Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
Torsion Stresses in Tubes and Rods
 Torsion Stresses in Tubes and Rods This initial analysis is valid only for a restricted range of problem for which the assumptions are: Rod is initially straight. Rod twists without bending. Material is
Torsion Stresses in Tubes and Rods This initial analysis is valid only for a restricted range of problem for which the assumptions are: Rod is initially straight. Rod twists without bending. Material is
Unit Workbook 2 - Level 5 ENG U64 Thermofluids 2018 UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Public Service Commission, West Bengal
 Public Service Commission, West Bengal Syllabus for the Written Test for recruitment to the posts of ASSISTANT ENGINEER (Agri - Mechanical) in West Bengal Service of Agricultural Engineers Mechanical Engineering
Public Service Commission, West Bengal Syllabus for the Written Test for recruitment to the posts of ASSISTANT ENGINEER (Agri - Mechanical) in West Bengal Service of Agricultural Engineers Mechanical Engineering
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
UNIVERSITY POLYTECHNIC B.I.T., MESRA, RANCHI
 COURSE STRUCTURE Diploma in Technology (W.E.F. 2011 Batch Students) SEMESTER IV (Total Unit 7.5) Mechanical Course Theory Unit Course Sessional Unit Code Code DAE 4001 Thermal Engineering 1.0 DAE 4002
COURSE STRUCTURE Diploma in Technology (W.E.F. 2011 Batch Students) SEMESTER IV (Total Unit 7.5) Mechanical Course Theory Unit Course Sessional Unit Code Code DAE 4001 Thermal Engineering 1.0 DAE 4002
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION. 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance in thermodynamics.
 QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
 CE 6303 MECHANICS OF FLUIDS L T P C QUESTION BANK 3 0 0 3 UNIT I FLUID PROPERTIES AND FLUID STATICS PART - A 1. Define fluid and fluid mechanics. 2. Define real and ideal fluids. 3. Define mass density
CE 6303 MECHANICS OF FLUIDS L T P C QUESTION BANK 3 0 0 3 UNIT I FLUID PROPERTIES AND FLUID STATICS PART - A 1. Define fluid and fluid mechanics. 2. Define real and ideal fluids. 3. Define mass density
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 General ptitude G Set-8 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The chairman requested the aggrieved shareholders to him. () bare with () bore with (C) bear with (D) bare Q.2 Identify the correct spelling out
General ptitude G Set-8 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The chairman requested the aggrieved shareholders to him. () bare with () bore with (C) bear with (D) bare Q.2 Identify the correct spelling out
General Aptitude (GA) Set-2. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance.
 GATE 018 General Aptitude (GA) Set- Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are
GATE 018 General Aptitude (GA) Set- Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are
ES201 - Examination III Richards, North, Berry Fall November 2000 NAME BOX NUMBER
 ES201 - Examination III Richards, North, Berry Fall 2000-2001 2 November 2000 NAME BOX NUMBER Problem 1 Problem 2 ( 30 ) ( 30 ) Problem 3 ( 40 ) Total ( 100 ) INSTRUCTIONS Closed book/notes exam. (Unit
ES201 - Examination III Richards, North, Berry Fall 2000-2001 2 November 2000 NAME BOX NUMBER Problem 1 Problem 2 ( 30 ) ( 30 ) Problem 3 ( 40 ) Total ( 100 ) INSTRUCTIONS Closed book/notes exam. (Unit
General Aptitude - GA Set-3. Q.1 Based on the given statements, select the appropriate option with respect to grammar and usage.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Based on the given statements, select the appropriate option with respect to grammar and usage. Statements (i) (ii) The height of
GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Based on the given statements, select the appropriate option with respect to grammar and usage. Statements (i) (ii) The height of
10.52 Mechanics of Fluids Spring 2006 Problem Set 3
 10.52 Mechanics of Fluids Spring 2006 Problem Set 3 Problem 1 Mass transfer studies involving the transport of a solute from a gas to a liquid often involve the use of a laminar jet of liquid. The situation
10.52 Mechanics of Fluids Spring 2006 Problem Set 3 Problem 1 Mass transfer studies involving the transport of a solute from a gas to a liquid often involve the use of a laminar jet of liquid. The situation
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13
 Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13 (1.1). Thermodynamic system An isolated system is a system that exchanges neither mass nor energy with its environment. An insulated rigid tank
Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13 (1.1). Thermodynamic system An isolated system is a system that exchanges neither mass nor energy with its environment. An insulated rigid tank
Therefore, the control volume in this case can be treated as a solid body, with a net force or thrust of. bm # V
 When the mass m of the control volume remains nearly constant, the first term of the Eq. 6 8 simply becomes mass times acceleration since 39 CHAPTER 6 d(mv ) CV m dv CV CV (ma ) CV Therefore, the control
When the mass m of the control volume remains nearly constant, the first term of the Eq. 6 8 simply becomes mass times acceleration since 39 CHAPTER 6 d(mv ) CV m dv CV CV (ma ) CV Therefore, the control
GATE Question Papers Mechanical Engineering 2006 (ME)
 Q. Q. Carry One Mark Each.. Match the items in columns I and II. Column I (p) Gauss-Seidel method (Q) Forward Newton-Gauss method (R) Runge-kutta method (S) Trapezoidal Rule P Q 4 R S P Q 4 R S P Q R S
Q. Q. Carry One Mark Each.. Match the items in columns I and II. Column I (p) Gauss-Seidel method (Q) Forward Newton-Gauss method (R) Runge-kutta method (S) Trapezoidal Rule P Q 4 R S P Q 4 R S P Q R S
