Validation of a mesoscale meteorological simulation over Po Valley
|
|
|
- Felix Hunter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int. J. Environment and Pollution, 1 Validation of a mesoscale meteorological simulation over Po Valley E. Pisoni 1 *, E. Batchvarova 2, G. Candiani 1, C. Carnevale 1, G. Finzi 1 1 Department of Information Engineering, University of Brescia, Italy 2National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Bulgaria *Corresponding author Abstract: Very high ground level concentrations of PM in winter and of ozone in summer often occur in Northern Italy, due to the high anthropogenic emissions and frequent stagnant meteorological conditions that characterize the area. These problems are not only related to urban, but also to suburban areas through the entire Po Valley. In such a situation it is important to use deterministic Chemical Transport Models, that allow the evaluation of the effect of different air quality control policies on secondary pollution concentrations. Chemical Transport Models generally are part of more complex deterministic modelling systems, encompassing also emission models, meteorological models, and initial and boundary condition processors. Meteorological models are an important module of deterministic modelling systems and, due to their complexity, require high computational costs to perform simulations. Within the HPC-EUROPA (Pan-European Research Infrastructure on High Performance Computing) cooperation project, that allows the use of clusters of CPUs all around Europe, the meteorological fields over Northern Italy have been simulated using RAMS, creating a database for future air quality assessments. Keywords: meteorological model, model validation, air quality models. Copyright 1997 Inderscience Enterprises Ltd.
2 2 Book reviews Biographical notes: Enrico Pisoni is an assistant professor at the University of Brescia. His research interests include modelling and simulation of non linear systems, system identification and optimization techniques. Ekaterina. Batchvarova is senior scientist at the National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology in Sofia, Bulgaria. She holds a DSc degree in physics for research in the field of boundary layer meteorology. G. Candiani is a PhD student at the University of Brescia. His main research activity includes the use of data assimilation techniques for air quality modelling. C. Carnevale, is an assistant professor at the University of Brescia. His research fields include modelling and control of environmental systems, system identification, nonlinear programming. G. Finzi is full professor of Automatic Control at the University of Brescia. She works on environmental control and management in the frame of national and international scientific projects. 1 Introduction Chemical Transport Models (CTMs) (Carnevale et al., 2008a) are useful tools to plan air quality control policies. These CTMs are part of more complex modelling systems (Volta and Finzi, 2006), also encompassing emission models and meteorological models. Meteorological models, focus of the application presented in this work, are generally constructed around the full set of nonhydrostatic, compressible
3 Book reviews 3 equations that describe atmospheric dynamics and thermodynamics, plus conservation equations for scalar quantities such as water vapour and liquid and ice hydrometeor mixing ratios. These equations are supplemented with a large selection of parameterizations for turbulent diffusion, solar and terrestrial radiation, moist processes including the formation and interaction of clouds and precipitating liquid and ice hydrometeors, kinematic effects of terrain, cumulus convection, and sensible and latent heat exchange between the atmosphere and the surface (which consists of multiple soil layers, vegetation, snow cover, canopy air, and surface water). Due to their complexity, meteorological models are very time consuming; a solution to this computational time demand is through the use of supercomputers, or cluster of computers. This aspect is even more important when the final target is to perform long-term simulations with air quality models, and so also the meteorological model has to be run for long periods (as in example for 1-year long simulation, as presented here). Focus of the study presented in this paper is to develop and validate a long-term meteorological simulation (1-year) for air quality applications. The meteorological model applied in this work has been run in the frame of the HPC- EUROPA project (Pan-European Research Infrastructure on High Performance Computing). The presented application is devoted to the evaluation of the performances of a mesoscale meteorological model (RAMS, Cotton et al., 2001) over the area of Northern Italy for the year 2004; the created meteorological dataset will be used for a future air quality application. In this paper a comparison of modelled and measured meteorological fields is performed for two
4 4 Book reviews stations located one in the Eastern and one in the Western part of the Italian domain. The selected domain is often affected by severe secondary pollution episodes (Pisoni et al., 2009a), and for this reason is of extreme importance to develop for this area sound meteorological and air quality modeling applications (Pisoni et al., 2009b). 2 Domain features and modelling setup RAMS, the Regional Atmospheric Modelling System (Pielke et al., 1992; Cotton et al., 2001) is a well-known numerical code for simulating and forecasting meteorological phenomena, and it has been applied in this study. The model (version 4.4) has been applied over Northern Italy, an area with very high secondary pollution concentrations, and where it is particularly difficult to implement effective air quality control policies. This domain is extremely interesting because it contains the Lombardia region, an area counting 10 million inhabitants, and one of the most industrialized in Italy, characterized by high urban and industrial emissions. Furthermore in this area stagnant meteorological conditions, low wind speed and temperature inversion are frequent both in winter and summer. For these reasons, the European PM10 legislation is often not respected. In this domain PM measurement campaigns (Vecchi et al., 2004, Giugliano et al., 2005, Lonati et al., 2005) and multiphase modelling applications (Volta and Finzi, 2006, Cuvelier et al., 2007, Carnevale et al., 2008b) have been performed in the domain suggesting that the secondary fraction of PM10 on the considered area is relevant. From these issues it is clear how the reconstruction of
5 Book reviews 5 correct meteorological fields over this domain is of vital importance to correctly feed Chemical Transport Models. To be able to consider in the simulation both synoptic and local meteorological patterns, three nested grids have been created for RAMS simulation (Figure 1). With the first grid the modelling simulation covers an area that encompasses the entire Europe, with latitude roughly between 23 and 59 degrees, and longitude between -13 and 31; the second grid, focused on Mediterranean sea, has latitude from 32 to 55, and longitude from -4 to 24; the third one, limited to Po Valley area, has latitude from 42 to 49 and longitude from 4 to 14. The resolution of the three grids are respectively 128 km, 32 km and 8 km. The number of cells for the three grids is respectively 40x40, 86x86 and 102x102, with 33 vertical levels covering the atmospheric layers from surface to roughly 20 km height. The entire year 2004 has been simulated through 72 simulations of 126 hours each, considering a spin-up time of 6 hours and using 16 CPUs for each simulation, with a total computational time of hours. Standard dataset of RAMS have been used, i.e. USGS (United States Geological Survey) topography and land use at 30s spatial resolution, and global monthly climatological sea surface temperature data at 1 degree resolution. NCAR reanalysys (Kalnay et al., 1996) data with 2.5 degrees of resolution have been used to provide initial and boundary conditions to RAMS simulations. No measurements have been ingested in the model simulation. Chen scheme (Cotton et al., 2001) have been used for both short wave and long wave radiation parameterizations.
6 6 Book reviews 3 Model evaluation and analysis To validate the model, measurements have been derived by the DS464.0 NCEP (National Centre for Environmental Prediction) ADP (Automated Data Processing) Global Surface Observations dataset. These data, that can be freely downloaded by are available from February 1975, and include SYNOP and METAR measurement networks. Time series of temperature, wind speed and wind direction measurements have been extracted by the DS464.0 NCEP ADP dataset for the entire The validation stations are shown in Figure 2. In this work results are shown for only two validation stations: LIMU (in the South-West corner of the domain) and LIPQ (in the North-East part of it). Measurement station data have been compared with modelled time series derived by the 8 km simulation, considering (for the comparison) the cells of the model in which the different measurement stations fall. 3.1 Temperature validation In Figure 3 and 4 the modelled (blue continuous line) and observed (red crosses) daily mean Temperature are shown, for the entire 2004 and for the two selected stations. LIMU station is close to the sea, and so influenced by sea breeze; LIPQ station is instead more in the hinterland and more representative of Po Valley meteorology. For both stations it is possible to appreciate how the model is overestimating temperature during winter, and underestimating during summer.
7 Book reviews 7 The same information is shown in Figure 7 for monthly mean temperature. While at LIMU station the model is performing better than LIPQ one, it is clear the overestimation/underestimation trend stressed in Figure 3 and 4. This trend is common to roughly all the considered validation stations (not shown here). 3.2 Wind validation In Figure 5 and 6 the modelled (blue continuous line) and observed (red crosses) daily mean wind speed is shown. In both stations it is possible to stress how the model is overestimating wind speed values, even if in LIMU stations performances are slightly better. The overestimation problem is a common one in Po Valley (Bedogni et al., 2005); this case study application confirms that it is necessary a) to simulate with higher spatial resolution and b) to assimilate meteorological measurements in the modelling simulation, to grasp the Northern Italy wind speed features. In Figure 8 modelled and observed monthly mean wind speed are shown. Performances are better when measured wind speed values are higher (LIMU station) while worse where measured mean wind speed are lower (LIPQ station). This feature has been verified also in the other validation stations (not shown here). In terms of wind rose, in Figure 9 results are shown for LIMU (left) and LIPQ (right), for measurements (top) and models (bottom). As stressed in Figure 5 and Figure 6, LIMU station wind reconstruction (left) is better than LIPQ one (right). More precisely, in the case of LIMU station there
8 8 Book reviews are two main wind directions, NE and S, and the model is able to represent mainly only the NE direction. In the case of LIPQ station (right) the model wind rose reconstruction is not able to represent the measured wind speed and direction. 4 Conclusions During the HPC-EUROPA cooperation project between University of Brescia and the Bulgarian National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, a long-term meteorological model run has been simulated. The entire 2004 has been simulated over Northern Italy, and a meteorological dataset for a future air quality application has been prepared. The validation of the long-term meteorological simulation shows that temperature is generally overestimated in winter and underestimated in summer, while wind speed is always overestimated. These modeling limitations can affect air quality simulation results. To improve meteorological model results it is possible to a) improve model spatial resolution; b) assimilate ground measurements in the meteorological simulation; c) investigate in details the role of the surface exchange schemes and parameters used in the model comparing measurements and used initial values. Acknowledgments This work was carried out under the HPC-EUROPA project 911, with the support of the European Community - Research Infrastructure Action under the
9 Book reviews 9 FP6 Structuring the European Research Area Programme. The cooperation is also in line with COST728 activities at both institutions. References Bedogni M., Carnevale C., Minguzzi E. and Pirovano G., Sentitivity of CTM simulations to meteorological input, International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 24, Carnevale C., Decanini E. and Volta M., 2008a. Design and validation of a multiphase 3D model to simulate tropospheric pollution. Science of The Total Environment, 390, Carnevale C., Finzi G., Pisoni E. and Volta M., 2008b. Modelling assessment of PM10 exposure control policies in Northern Italy, Ecological Modelling, 217, Cotton W. R., Pielke Sr. R. A., Walko R. L., Liston G. E., Tremback C. J., Jiang H., McAnelly R. L., Harrington J. Y., Nicholls M. E., Carrio G. G. and McFadden J. P., RAMS 2001: Current status and future directions, Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 82, Cuvelier et al., CityDelta: A model intercomparison study to explore the impact of emission reductions in European cities in Atmospheric Environment, 41, Giugliano, M., Lonati, G., Butelli, P., Romele, L., Tardivo and R., Grosso, M., 005. Fine particulate (PM2.5-PM1) at urban sites with different traffic xposure. Atmospheric Environment, 39, Kalnay et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project, Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, , Lonati, G., Giugliano, M., Butelli, P., Romele, L. and Tardivo, R., Major chemical components of PM2.5 in Milan (Italy). Atmospheric Environment 39, Pielke, R.A., W.R. Cotton, R.L. Walko, C.J. Tremback, W.A. Lyons, L.D. Grasso, M.E. Nicholls, M.D. Moran, D.A. Wesley, T.J. Lee, and J.H. Copeland, 1992: A comprehensive meteorological modeling system -- RAMS. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 49, Pisoni E. and Volta M., 2009a. Modeling Pareto Efficient PM10 control policies in Northern Italy to reduce health effects, Atmospheric Environment, 43, Pisoni E., Carnevale C. and Volta M., 2009b. Multi-criteria analysis for PM10 planning, Atmospheric Environment, 43, Vecchi, R., Marcazzan, G., Valli, G., Ceriani, M. and Antoniazzi, C., The role of atmospheric dispersion in the seasonal variation of PM1 and PM2.5. Atmospheric Environment, 38, Volta, M. and Finzi, G., GAMES, a comprehensive Gas Aerosol Modelling Evaluation System. Environ. Model. Software 21,
10 10 Book reviews Figures Figure 1: The three nested domain considered in this study Figure 2: Location of all the validation measurement stations considered in this study, with stressed in orange the LIMU and LIPQ stations.
11 Book reviews 11 Figure 3: Daily mean temperature (2m level) comparison, between modelled (MOD) and observed (OBS) values at LIMU station (x-axis: days; y-axis: temperature in Celsius degrees). Figure 4: Daily mean temperature (2m level) comparison, between modelled (MOD) and observed (OBS) values at LIPQ station (x-axis: days; y-axis: temperature in Celsius degrees).
12 12 Book reviews Figure 5: Daily wind speed (10m level) comparison, between modelled (MOD) and observed (OBS) values at LIMU station (x-axis: days; y-axis: wind speed in m/s). Figure 6: Daily wind speed (10m level) comparison, between modelled (MOD) and observed (OBS) values at LIPQ station (x-axis: days; y-axis: wind speed in m/s).
13 Book reviews 13 Figure 7: Monthly mean temperature (2m level) comparison, between modelled (MOD) and observed (OBS) values at LIMU (left panel) and LIPQ (right panel) (x-axis: months; y-axis: temperature in Celsius degrees). Figure 8: Monthly wind speed (10m level) comparison, between modelled (MOD) and observed (OBS) values at LIMU (left panel) and LIPQ (right panel) (x-axis: months; y-axis: wind speed in m/s).
14 14 Book reviews Figure 9: Wind rose for LIMU station (left) and LIPQ (right), for measurement (top) and model (bottom) data.
MODELING AND MEASUREMENTS OF THE ABL IN SOFIA, BULGARIA
 MODELING AND MEASUREMENTS OF THE ABL IN SOFIA, BULGARIA P58 Ekaterina Batchvarova*, **, Enrico Pisoni***, Giovanna Finzi***, Sven-Erik Gryning** *National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Sofia,
MODELING AND MEASUREMENTS OF THE ABL IN SOFIA, BULGARIA P58 Ekaterina Batchvarova*, **, Enrico Pisoni***, Giovanna Finzi***, Sven-Erik Gryning** *National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Sofia,
MODELLING THE METEOROLOGY AND TRAFFIC POLLUTANT DISPERSION IN HIGHLY COMPLEX TERRAIN: THE ALPNAP ALPINE SPACE PROJECT.
 MODELLING THE METEOROLOGY AND TRAFFIC POLLUTANT DISPERSION IN HIGHLY COMPLEX TERRAIN: THE ALPNAP ALPINE SPACE PROJECT. S. Trini Castelli 1, G. Belfiore 1, D. Anfossi 1 and E. Elampe 2 1 Institute of Atmospheric
MODELLING THE METEOROLOGY AND TRAFFIC POLLUTANT DISPERSION IN HIGHLY COMPLEX TERRAIN: THE ALPNAP ALPINE SPACE PROJECT. S. Trini Castelli 1, G. Belfiore 1, D. Anfossi 1 and E. Elampe 2 1 Institute of Atmospheric
1.21 SENSITIVITY OF LONG-TERM CTM SIMULATIONS TO METEOROLOGICAL INPUT
 1.21 SENSITIVITY OF LONG-TERM CTM SIMULATIONS TO METEOROLOGICAL INPUT Enrico Minguzzi 1 Marco Bedogni 2, Claudio Carnevale 3, and Guido Pirovano 4 1 Hydrometeorological Service of Emilia Romagna (SIM),
1.21 SENSITIVITY OF LONG-TERM CTM SIMULATIONS TO METEOROLOGICAL INPUT Enrico Minguzzi 1 Marco Bedogni 2, Claudio Carnevale 3, and Guido Pirovano 4 1 Hydrometeorological Service of Emilia Romagna (SIM),
1.07 A FOUR MODEL INTERCOMPARISON CONCERNING CHEMICAL MECHANISMS AND NUMERICAL INTEGRATION METHODS
 1.7 A FOUR MODEL INTERCOMPARISON CONCERNING CHEMICAL MECHANISMS AND NUMERICAL INTEGRATION METHODS Bedogni M. 1, Carnevale C. 2, Pertot C. 3, Volta M. 2 1 Mobility and Environmental Ag. of Milan, Milan,
1.7 A FOUR MODEL INTERCOMPARISON CONCERNING CHEMICAL MECHANISMS AND NUMERICAL INTEGRATION METHODS Bedogni M. 1, Carnevale C. 2, Pertot C. 3, Volta M. 2 1 Mobility and Environmental Ag. of Milan, Milan,
PROCEEDINGS 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE October 2017 ON HARMONISATION WITHIN ATMOSPHERIC DISPERSION MODELLING FOR REGULATORY PURPOSES
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION WITHIN ATMOSPHERIC DISPERSION MODELLING FOR REGULATORY PURPOSES PROCEEDINGS 9-12 October 2017 CNR Research Area Bologna Italy 18th International Conference
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION WITHIN ATMOSPHERIC DISPERSION MODELLING FOR REGULATORY PURPOSES PROCEEDINGS 9-12 October 2017 CNR Research Area Bologna Italy 18th International Conference
PM10 LONG-TERM ASSESSMENT OF EMISSION REDUCTION SCENARIOS OVER NORTHERN ITALY
 PM1 LONG-TERM ASSESSMENT OF EMISSION REDUCTION SCENARIOS OVER NORTHERN ITALY Elisabetta Angelino 1, Marco Bedogni 2, Claudio Carnevale 3, Enrico Minguzzi 4, Edoardo Peroni 1, Cesare Pertot 5 and Guido
PM1 LONG-TERM ASSESSMENT OF EMISSION REDUCTION SCENARIOS OVER NORTHERN ITALY Elisabetta Angelino 1, Marco Bedogni 2, Claudio Carnevale 3, Enrico Minguzzi 4, Edoardo Peroni 1, Cesare Pertot 5 and Guido
7.6 AEROSOL IMPACTS ON TROPICAL CYCLONES
 7.6 AEROSOL IMPACTS ON TROPICAL CYCLONES William R. Cotton, Gustavo G. Carrio, and S Herbener Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION Previous
7.6 AEROSOL IMPACTS ON TROPICAL CYCLONES William R. Cotton, Gustavo G. Carrio, and S Herbener Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION Previous
6 th INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON SAND/DUSTSTORMS AND ASSOCIATED DUSTFALL 7-9 September 2011, Athens, Greece
 6 th INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON SAND/DUSTSTORMS AND ASSOCIATED DUSTFALL Motivations Importance of Numerical Prediction Models to mineral dust cycle evaluation of dust effects over Italian region Identify
6 th INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON SAND/DUSTSTORMS AND ASSOCIATED DUSTFALL Motivations Importance of Numerical Prediction Models to mineral dust cycle evaluation of dust effects over Italian region Identify
SAN JUAN, PUERTO RICO
 2.2 A VALIDATION STUDY OF THE URBAN HEAT ISLAND IN THE TROPICAL COASTAL CITY OF SAN JUAN, PUERTO RICO Daniel E. Comarazamy 1, Jorge E. González* 2, Jeff Luvall 3, Douglas Rickman 3, Ana Picón 1 1 University
2.2 A VALIDATION STUDY OF THE URBAN HEAT ISLAND IN THE TROPICAL COASTAL CITY OF SAN JUAN, PUERTO RICO Daniel E. Comarazamy 1, Jorge E. González* 2, Jeff Luvall 3, Douglas Rickman 3, Ana Picón 1 1 University
Creating Meteorology for CMAQ
 Creating Meteorology for CMAQ Tanya L. Otte* Atmospheric Sciences Modeling Division NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Research Triangle Park, NC * On assignment to the National Exposure Research Laboratory,
Creating Meteorology for CMAQ Tanya L. Otte* Atmospheric Sciences Modeling Division NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Research Triangle Park, NC * On assignment to the National Exposure Research Laboratory,
Application of a Three-Dimensional Prognostic Model During the ETEX Real-Time Modeling Exercise: Evaluatin of Results (u)
 WSRC-MS-96-0766 COdF- 9 7 0 9 1 9 m - 9 Application of a Three-Dimensional Prognostic Model During the ETEX Real-Time Modeling Exercise: Evaluatin of Results (u) by D. P. Griggs Westinghouse Savannah River
WSRC-MS-96-0766 COdF- 9 7 0 9 1 9 m - 9 Application of a Three-Dimensional Prognostic Model During the ETEX Real-Time Modeling Exercise: Evaluatin of Results (u) by D. P. Griggs Westinghouse Savannah River
Mesoscale meteorological models. Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen
 Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Simulation of Air Quality Using RegCM Model
 Simulation of Air Quality Using RegCM Model The Regional Climate Model (RegCM) The Regional Climate Model (RegCM) is one of the RCMs that was originally developed at the National Center for Atmospheric
Simulation of Air Quality Using RegCM Model The Regional Climate Model (RegCM) The Regional Climate Model (RegCM) is one of the RCMs that was originally developed at the National Center for Atmospheric
A Subgrid Surface Scheme for the Analysis of the Urban Heat Island of Rome
 A Subgrid Surface Scheme for the Analysis of the Urban Heat Island of Rome Antonio Cantelli, Paolo Monti, Giovanni Leuzzi Dipartimento di Idraulica, Trasporti e Strade Summary Analysis of the atmospheric
A Subgrid Surface Scheme for the Analysis of the Urban Heat Island of Rome Antonio Cantelli, Paolo Monti, Giovanni Leuzzi Dipartimento di Idraulica, Trasporti e Strade Summary Analysis of the atmospheric
Evaluation of BRAMS Turbulence Schemes during a Squall Line Occurrence in São Paulo, Brazil
 American Journal of Environmental Engineering 2013, 3(1): 1-7 DOI: 10.5923/j.ajee.20130301.01 Evaluation of BRAMS Turbulence Schemes during a Squall Line Occurrence in São Paulo, Brazil Andréia Bender
American Journal of Environmental Engineering 2013, 3(1): 1-7 DOI: 10.5923/j.ajee.20130301.01 Evaluation of BRAMS Turbulence Schemes during a Squall Line Occurrence in São Paulo, Brazil Andréia Bender
Effects of Soil Moisture of the Asian Continent upon the Baiu Front
 Present and Future of Modeling Global Environmental Change: Toward Integrated Modeling, Eds., T. Matsuno and H. Kida, pp. 101 109. by TERRAPUB, 2001. Effects of Soil Moisture of the Asian Continent upon
Present and Future of Modeling Global Environmental Change: Toward Integrated Modeling, Eds., T. Matsuno and H. Kida, pp. 101 109. by TERRAPUB, 2001. Effects of Soil Moisture of the Asian Continent upon
Numerical simulation of relationship between climatic factors and ground ozone concentration over Kanto area using the MM5/CMAQ Model
 251 Numerical simulation of relationship between climatic factors and ground ozone concentration over Kanto area using the MM5/CMAQ Model Mai Van KHIEM, Ryozo OOKA, Hong HUANG and Hiroshi HAYAMI In recent
251 Numerical simulation of relationship between climatic factors and ground ozone concentration over Kanto area using the MM5/CMAQ Model Mai Van KHIEM, Ryozo OOKA, Hong HUANG and Hiroshi HAYAMI In recent
Water Balance in the Murray-Darling Basin and the recent drought as modelled with WRF
 18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 2009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Water Balance in the Murray-Darling Basin and the recent drought as modelled with WRF Evans, J.P. Climate
18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 2009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Water Balance in the Murray-Darling Basin and the recent drought as modelled with WRF Evans, J.P. Climate
Applicability of RAMS for A Simulation of Wind and Temperature Fields in Bang Pakong Area, Thailand
 Proceedings of the 7th WSEAS International Conference on Simulation, Modelling and Optimization, Beijing, China, September 5-7, 7 34 Applicability of RAMS for A Simulation of Wind and Temperature Fields
Proceedings of the 7th WSEAS International Conference on Simulation, Modelling and Optimization, Beijing, China, September 5-7, 7 34 Applicability of RAMS for A Simulation of Wind and Temperature Fields
J5.12 INFLUENCE OF VARIATIONS IN LOW-LEVEL MOISTURE AND SOIL MOISTURE ON THE ORGANIZATION OF SUMMER CONVECTIVE SYSTEMS IN THE U. S.
 J5.12 INFLUENCE OF VARIATIONS IN LOW-LEVEL MOISTURE AND SOIL MOISTURE ON THE ORGANIZATION OF SUMMER CONVECTIVE SYSTEMS IN THE U. S. MIDWEST Jimmy O. Adegoke* 1, Sajith Vezhapparambu 1, Christopher L. Castro
J5.12 INFLUENCE OF VARIATIONS IN LOW-LEVEL MOISTURE AND SOIL MOISTURE ON THE ORGANIZATION OF SUMMER CONVECTIVE SYSTEMS IN THE U. S. MIDWEST Jimmy O. Adegoke* 1, Sajith Vezhapparambu 1, Christopher L. Castro
Influence of variations in low-level moisture and soil moisture on the organization of summer convective systems in the US Midwest
 Influence of variations in low-level moisture and soil moisture on the organization of summer convective systems in the US Midwest Jimmy O. Adegoke 1, Sajith Vezhapparambu 1, Christopher L. Castro 2, Roger
Influence of variations in low-level moisture and soil moisture on the organization of summer convective systems in the US Midwest Jimmy O. Adegoke 1, Sajith Vezhapparambu 1, Christopher L. Castro 2, Roger
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Surface Level Wind Forecast Simulation over the Land-Sea area and Mountain- Valley area in Thailand
 Surface Level Wind Forecast Simulation over the Land-Sea area and Mountain- Valley area in Thailand Rudklao Pan-Aram, Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand (EGAT), Thailand Phurichr Viryasiri, Electricity
Surface Level Wind Forecast Simulation over the Land-Sea area and Mountain- Valley area in Thailand Rudklao Pan-Aram, Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand (EGAT), Thailand Phurichr Viryasiri, Electricity
RAMS. Regional Atmospheric Modeling System. Version 6+ User's Guide - Introduction. By: Craig J.Tremback & Robert L. Walko.
 RAMS Regional Atmospheric Modeling System Version 6+ User's Guide - Introduction By: Craig J.Tremback & Robert L. Walko Updated by: Stephen Saleeby Department of Atmospheric Science Colorado State University
RAMS Regional Atmospheric Modeling System Version 6+ User's Guide - Introduction By: Craig J.Tremback & Robert L. Walko Updated by: Stephen Saleeby Department of Atmospheric Science Colorado State University
Mesoscale predictability under various synoptic regimes
 Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics (2001) 8: 429 438 Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics c European Geophysical Society 2001 Mesoscale predictability under various synoptic regimes W. A. Nuss and D. K. Miller
Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics (2001) 8: 429 438 Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics c European Geophysical Society 2001 Mesoscale predictability under various synoptic regimes W. A. Nuss and D. K. Miller
DISPERSION MODELLING OF PM 10 FOR CHRISTCHURCH, NEW ZEALAND: AN INTERCOMPARISON BETWEEN MM5 AND TAPM
 DISPERSION MODELLING OF PM 10 FOR CHRISTCHURCH, NEW ZEALAND: AN INTERCOMPARISON BETWEEN MM5 AND TAPM Peyman Zawar-Reza, Mikhail Titov and Andrew Sturman Centre for Atmospheric Research, Department of Geography,
DISPERSION MODELLING OF PM 10 FOR CHRISTCHURCH, NEW ZEALAND: AN INTERCOMPARISON BETWEEN MM5 AND TAPM Peyman Zawar-Reza, Mikhail Titov and Andrew Sturman Centre for Atmospheric Research, Department of Geography,
14.4 MOUNTAIN- SLOPE AFFORESTATION FOR VALLEY URBAN AIR-QUALITY IMPROVEMENT
 1 14.4 MOUNTAIN- SLOPE AFFORESTATION FOR VALLEY URBAN AIR-QUALITY IMPROVEMENT Peter C Chu Naval Ocean- Atmospheric Prediction Laboratory, Oceanography Department Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, California,
1 14.4 MOUNTAIN- SLOPE AFFORESTATION FOR VALLEY URBAN AIR-QUALITY IMPROVEMENT Peter C Chu Naval Ocean- Atmospheric Prediction Laboratory, Oceanography Department Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, California,
Modeling Atmospheric Deposition from a Cesium Release in Spain Using a Stochastic Transport Model
 WSRC-MS-99-00660 Modeling Atmospheric Deposition from a Cesium Release in Spain Using a Stochastic Transport Model Robert L. Buckley Westinghouse Savannah River Company Savannah River Site Aiken, SC 29808
WSRC-MS-99-00660 Modeling Atmospheric Deposition from a Cesium Release in Spain Using a Stochastic Transport Model Robert L. Buckley Westinghouse Savannah River Company Savannah River Site Aiken, SC 29808
1 INTRODUCTION 2 DESCRIPTION OF THE MODELS. In 1989, two models were able to make smog forecasts; the MPA-model and
 The national smog warning system in The Netherlands; a combination of measuring and modelling H. Noordijk Laboratory of Air Research, National Institute of Public Health and Environmental Protection (WFM;,
The national smog warning system in The Netherlands; a combination of measuring and modelling H. Noordijk Laboratory of Air Research, National Institute of Public Health and Environmental Protection (WFM;,
Graduate Courses Meteorology / Atmospheric Science UNC Charlotte
 Graduate Courses Meteorology / Atmospheric Science UNC Charlotte In order to inform prospective M.S. Earth Science students as to what graduate-level courses are offered across the broad disciplines of
Graduate Courses Meteorology / Atmospheric Science UNC Charlotte In order to inform prospective M.S. Earth Science students as to what graduate-level courses are offered across the broad disciplines of
Regional Climate Simulations with WRF Model
 WDS'3 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 8 84, 23. ISBN 978-8-737852-8 MATFYZPRESS Regional Climate Simulations with WRF Model J. Karlický Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Mathematics
WDS'3 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 8 84, 23. ISBN 978-8-737852-8 MATFYZPRESS Regional Climate Simulations with WRF Model J. Karlický Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Mathematics
Supplement to the. Final Report on the Project TRACHT-MODEL. Transport, Chemistry and Distribution of Trace Gases in the Tropopause Region: Model
 Anhang 2 Supplement to the Final Report on the Project TRACHT-MODEL Transport, Chemistry and Distribution of Trace Gases in the Tropopause Region: Model H. Feldmann, A. Ebel, Rheinisches Institut für Umweltforschung
Anhang 2 Supplement to the Final Report on the Project TRACHT-MODEL Transport, Chemistry and Distribution of Trace Gases in the Tropopause Region: Model H. Feldmann, A. Ebel, Rheinisches Institut für Umweltforschung
AFFORESTATION FOR IMPROVING VALLEY URBAN AIR-QUALITY
 AFFORESTATION FOR IMPROVING VALLEY URBAN AIR-QUALITY Peter C Chu, Yuchun Chen*, and Shihua Lu* Naval Ocean- Atmospheric Prediction Laboratory, Oceanography Department Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey,
AFFORESTATION FOR IMPROVING VALLEY URBAN AIR-QUALITY Peter C Chu, Yuchun Chen*, and Shihua Lu* Naval Ocean- Atmospheric Prediction Laboratory, Oceanography Department Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey,
Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio
 JP2.14 ON ADAPTING A NEXT-GENERATION MESOSCALE MODEL FOR THE POLAR REGIONS* Keith M. Hines 1 and David H. Bromwich 1,2 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University,
JP2.14 ON ADAPTING A NEXT-GENERATION MESOSCALE MODEL FOR THE POLAR REGIONS* Keith M. Hines 1 and David H. Bromwich 1,2 1 Polar Meteorology Group, Byrd Polar Research Center, The Ohio State University,
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Application of a non-hydrostatic mesoscale meteorological model to the Aveiro Region, Portugal M. Coutinho," T. Flassak,* C. Borrego" ^Department of Environmental and Planning, University of Aveiro, 3800
Application of a non-hydrostatic mesoscale meteorological model to the Aveiro Region, Portugal M. Coutinho," T. Flassak,* C. Borrego" ^Department of Environmental and Planning, University of Aveiro, 3800
A Quick Report on a Dynamical Downscaling Simulation over China Using the Nested Model
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 6, 325 329 A Quick Report on a Dynamical Downscaling Simulation over China Using the Nested Model YU En-Tao 1,2,3, WANG Hui-Jun 1,2, and SUN Jian-Qi
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 6, 325 329 A Quick Report on a Dynamical Downscaling Simulation over China Using the Nested Model YU En-Tao 1,2,3, WANG Hui-Jun 1,2, and SUN Jian-Qi
MARINE BOUNDARY-LAYER HEIGHT ESTIMATED FROM NWP MODEL OUTPUT BULGARIA
 MARINE BOUNDARY-LAYER HEIGHT ESTIMATED FROM NWP MODEL OUTPUT Sven-Erik Gryning 1 and Ekaterina Batchvarova 1, 1 Wind Energy Department, Risø National Laboratory, DK-4 Roskilde, DENMARK National Institute
MARINE BOUNDARY-LAYER HEIGHT ESTIMATED FROM NWP MODEL OUTPUT Sven-Erik Gryning 1 and Ekaterina Batchvarova 1, 1 Wind Energy Department, Risø National Laboratory, DK-4 Roskilde, DENMARK National Institute
Methodology for the creation of meteorological datasets for Local Air Quality modelling at airports
 Methodology for the creation of meteorological datasets for Local Air Quality modelling at airports Nicolas DUCHENE, James SMITH (ENVISA) Ian FULLER (EUROCONTROL Experimental Centre) About ENVISA Noise
Methodology for the creation of meteorological datasets for Local Air Quality modelling at airports Nicolas DUCHENE, James SMITH (ENVISA) Ian FULLER (EUROCONTROL Experimental Centre) About ENVISA Noise
6.13 SYSTEMATIC ANALYSIS OF METEOROLOGICAL CONDITIONS CAUSING SEVERE URBAN AIR POLLUTION EPISODES IN THE CENTRAL PO VALLEY
 6.13 SYSTEMATIC ANALYSIS OF METEOROLOGICAL CONDITIONS CAUSING SEVERE URBAN AIR POLLUTION EPISODES IN THE CENTRAL PO VALLEY Sandro Finardi 1, and Umberto Pellegrini 2 1 ARIANET, via Gilino 9, 2128 Milano,
6.13 SYSTEMATIC ANALYSIS OF METEOROLOGICAL CONDITIONS CAUSING SEVERE URBAN AIR POLLUTION EPISODES IN THE CENTRAL PO VALLEY Sandro Finardi 1, and Umberto Pellegrini 2 1 ARIANET, via Gilino 9, 2128 Milano,
URBAN HEAT ISLAND IN SEOUL
 URBAN HEAT ISLAND IN SEOUL Jong-Jin Baik *, Yeon-Hee Kim ** *Seoul National University; ** Meteorological Research Institute/KMA, Korea Abstract The spatial and temporal structure of the urban heat island
URBAN HEAT ISLAND IN SEOUL Jong-Jin Baik *, Yeon-Hee Kim ** *Seoul National University; ** Meteorological Research Institute/KMA, Korea Abstract The spatial and temporal structure of the urban heat island
Climate Modeling: From the global to the regional scale
 Climate Modeling: From the global to the regional scale Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste, Italy ESA summer school on Earth System Monitoring and Modeling Frascati, Italy, 31 July 11 August 2006
Climate Modeling: From the global to the regional scale Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste, Italy ESA summer school on Earth System Monitoring and Modeling Frascati, Italy, 31 July 11 August 2006
MEAN CLIMATE AND ANNUAL CYCLE IN A REGIONAL CLIMATE CHANGE EXPERIMENT OVER SOUTHERN SOUTH AMERICA. II: CLIMATE CHANGE SCENARIOS ( ).
 MEAN CLIMATE AND ANNUAL CYCLE IN A REGIONAL CLIMATE CHANGE EXPERIMENT OVER SOUTHERN SOUTH AMERICA. II: CLIMATE CHANGE SCENARIOS (2081-2090). Mario N. Nuñez*, Silvina Solman and María Fernanda Cabré Centro
MEAN CLIMATE AND ANNUAL CYCLE IN A REGIONAL CLIMATE CHANGE EXPERIMENT OVER SOUTHERN SOUTH AMERICA. II: CLIMATE CHANGE SCENARIOS (2081-2090). Mario N. Nuñez*, Silvina Solman and María Fernanda Cabré Centro
European Developments in Mesoscale Modelling for Air Pollution Applications Activities of the COST 728 Action
 European Developments in Mesoscale Modelling for Air Pollution Applications Activities of the COST 728 Action R S Sokhi*, A Baklanov, H Schlünzen, M Sofiev, M Athanassiadou, Peter Builtjes and COST 728
European Developments in Mesoscale Modelling for Air Pollution Applications Activities of the COST 728 Action R S Sokhi*, A Baklanov, H Schlünzen, M Sofiev, M Athanassiadou, Peter Builtjes and COST 728
Large eddy simulation of microburst winds flowing around a building
 Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 46 & 47 (1993) 229-237 229 Elsevier Large eddy simulation of microburst winds flowing around a building M. NICHOLLS Research Associate, Department
Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 46 & 47 (1993) 229-237 229 Elsevier Large eddy simulation of microburst winds flowing around a building M. NICHOLLS Research Associate, Department
P10.1 TORNADOGENESIS IN A SIMULATED HP SUPERCELL
 Preprints, 21 st Conference on Severe Local Storms 12-16 August 2002, San Antonio, Texas P10.1 TORNADOGENESIS IN A SIMULATED HP SUPERCELL 1. INTRODUCTION Catherine A. Finley * Department of Earth Sciences
Preprints, 21 st Conference on Severe Local Storms 12-16 August 2002, San Antonio, Texas P10.1 TORNADOGENESIS IN A SIMULATED HP SUPERCELL 1. INTRODUCTION Catherine A. Finley * Department of Earth Sciences
THE INFLUENCE OF HIGHLY RESOLVED SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURES ON METEOROLOGICAL SIMULATIONS OFF THE SOUTHEAST US COAST
 THE INFLUENCE OF HIGHLY RESOLVED SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURES ON METEOROLOGICAL SIMULATIONS OFF THE SOUTHEAST US COAST Peter Childs, Sethu Raman, and Ryan Boyles State Climate Office of North Carolina and
THE INFLUENCE OF HIGHLY RESOLVED SEA SURFACE TEMPERATURES ON METEOROLOGICAL SIMULATIONS OFF THE SOUTHEAST US COAST Peter Childs, Sethu Raman, and Ryan Boyles State Climate Office of North Carolina and
INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS, NW GREECE), ON PRECIPITATION, DURING THE WARM PERIOD OF THE YEAR
 Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference of Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS,
Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference of Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS,
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Model physical parameterizations: The study uses the single-layer urban canopy model (SLUCM: Kusaka et al. 2001; Kusaka and Kimura 2004; Liu et al. 2006; Chen and Dudhia 2001; Chen
Supplementary Material Model physical parameterizations: The study uses the single-layer urban canopy model (SLUCM: Kusaka et al. 2001; Kusaka and Kimura 2004; Liu et al. 2006; Chen and Dudhia 2001; Chen
Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002
 Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002 Soon-Ung Park, Jae-In Jeong* Center for Atmospheric and Environmental Modeling *School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Seoul National
Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002 Soon-Ung Park, Jae-In Jeong* Center for Atmospheric and Environmental Modeling *School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Seoul National
Aiguo Dai * and Kevin E. Trenberth National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) $, Boulder, CO. Abstract
 9.2 AMS 14 th Symposium on Global Change and Climate Variations, 9-13 Feb. 2003, Long Beach, CA. Diurnal Variations in the Community Climate System Model Aiguo Dai * and Kevin E. Trenberth National Center
9.2 AMS 14 th Symposium on Global Change and Climate Variations, 9-13 Feb. 2003, Long Beach, CA. Diurnal Variations in the Community Climate System Model Aiguo Dai * and Kevin E. Trenberth National Center
Thermally forced mesoscale atmospheric flow over complex terrain in Southern Italy
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO VOL. 21 C, N. 4 Luglio-Agosto 1998 Thermally forced mesoscale atmospheric flow over complex terrain in Southern Italy Istituto di Fisica dell Atmosfera (CNR) - Roma, Italy (ricevuto il
IL NUOVO CIMENTO VOL. 21 C, N. 4 Luglio-Agosto 1998 Thermally forced mesoscale atmospheric flow over complex terrain in Southern Italy Istituto di Fisica dell Atmosfera (CNR) - Roma, Italy (ricevuto il
RSMC WASHINGTON USER'S INTERPRETATION GUIDELINES ATMOSPHERIC TRANSPORT MODEL OUTPUTS
 RSMC WASHINGTON USER'S INTERPRETATION GUIDELINES ATMOSPHERIC TRANSPORT MODEL OUTPUTS -Version 2.0- (January 2007) 1. Introduction In the context of current agreements between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric
RSMC WASHINGTON USER'S INTERPRETATION GUIDELINES ATMOSPHERIC TRANSPORT MODEL OUTPUTS -Version 2.0- (January 2007) 1. Introduction In the context of current agreements between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Improvement of Meteorological Inputs for Air Quality Study
 July 21, 2008 NCAR GEO Turbulance Improvement of Meteorological Inputs for Air Quality Study Fong (Fantine) Ngan Daewon W. Byun DaeGyun Lee, Soontae Kim, XiangShang Li and Peter Percell Institute for Multidimensional
July 21, 2008 NCAR GEO Turbulance Improvement of Meteorological Inputs for Air Quality Study Fong (Fantine) Ngan Daewon W. Byun DaeGyun Lee, Soontae Kim, XiangShang Li and Peter Percell Institute for Multidimensional
Influence of 3D Model Grid Resolution on Tropospheric Ozone Levels
 Influence of 3D Model Grid Resolution on Tropospheric Ozone Levels Pedro Jiménez nez, Oriol Jorba and José M. Baldasano Laboratory of Environmental Modeling Technical University of Catalonia-UPC (Barcelona,
Influence of 3D Model Grid Resolution on Tropospheric Ozone Levels Pedro Jiménez nez, Oriol Jorba and José M. Baldasano Laboratory of Environmental Modeling Technical University of Catalonia-UPC (Barcelona,
Guo-Yuan Lien*, Eugenia Kalnay, and Takemasa Miyoshi University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 2. METHODOLOGY
 9.2 EFFECTIVE ASSIMILATION OF GLOBAL PRECIPITATION: SIMULATION EXPERIMENTS Guo-Yuan Lien*, Eugenia Kalnay, and Takemasa Miyoshi University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 1. INTRODUCTION * Precipitation
9.2 EFFECTIVE ASSIMILATION OF GLOBAL PRECIPITATION: SIMULATION EXPERIMENTS Guo-Yuan Lien*, Eugenia Kalnay, and Takemasa Miyoshi University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 1. INTRODUCTION * Precipitation
ON THE VALIDATION OF THE SIMULATION OF EARLY SEASON PRECIPITATION IN THE ISLAND OF PUERTO RICO USING A MESOSCALE ATMOSPHERIC MODEL
 JP1.7 ON THE VALIDATION OF THE SIMULATION OF EARLY SEASON PRECIPITATION IN THE ISLAND OF PUERTO RICO USING A MESOSCALE ATMOSPHERIC MODEL Daniel E. Comarazamy, J. E. González* Santa Clara University, Santa
JP1.7 ON THE VALIDATION OF THE SIMULATION OF EARLY SEASON PRECIPITATION IN THE ISLAND OF PUERTO RICO USING A MESOSCALE ATMOSPHERIC MODEL Daniel E. Comarazamy, J. E. González* Santa Clara University, Santa
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2013
 Application and verification of EMWF products 2013 Hellenic National Meteorological Service (HNMS) Flora Gofa and Theodora Tzeferi 1. Summary of major highlights In order to determine the quality of the
Application and verification of EMWF products 2013 Hellenic National Meteorological Service (HNMS) Flora Gofa and Theodora Tzeferi 1. Summary of major highlights In order to determine the quality of the
Implementation of Modeling the Land-Surface/Atmosphere Interactions to Mesoscale Model COAMPS
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Implementation of Modeling the Land-Surface/Atmosphere Interactions to Mesoscale Model COAMPS Dr. Bogumil Jakubiak Interdisciplinary
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Implementation of Modeling the Land-Surface/Atmosphere Interactions to Mesoscale Model COAMPS Dr. Bogumil Jakubiak Interdisciplinary
Weather and Wind Modeling in Egypt Meso-scale Meteorological (Weather Forecast) Modeling
 Weather and Wind Modeling in Egypt Meso-scale Meteorological (Weather Forecast) Modeling Presented By; Atef O. Sherif Aerospace Department Faculty of Engineering Cairo University Collaborators Hamada Sultan
Weather and Wind Modeling in Egypt Meso-scale Meteorological (Weather Forecast) Modeling Presented By; Atef O. Sherif Aerospace Department Faculty of Engineering Cairo University Collaborators Hamada Sultan
Unanswered Questions
 Unanswered Questions Roger A. Pielke Sr. Colorado State University and Duke University Presented at the Workshop on Vertical Temperature Trends Asheville, North Carolina October 27-29, 2003 Is the Surface
Unanswered Questions Roger A. Pielke Sr. Colorado State University and Duke University Presented at the Workshop on Vertical Temperature Trends Asheville, North Carolina October 27-29, 2003 Is the Surface
Investigation of feedback mechanisms between soil moisture, land use and precipitation in West Africa
 Water Resources Systems Water Availability and Global Change (Proceedings of symposium HS02a held during IUGG2003 at Sapporo, July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 280, 2003. 1 Investigation of feedback mechanisms
Water Resources Systems Water Availability and Global Change (Proceedings of symposium HS02a held during IUGG2003 at Sapporo, July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 280, 2003. 1 Investigation of feedback mechanisms
The Challenge of. Guy Brasseur
 The Challenge of Monitoring and Predicting Chemical Weather Guy Brasseur Introduction: What is Chemical Weather? What is Chemical Weather? Local, regional, and global distributions of important trace gases
The Challenge of Monitoring and Predicting Chemical Weather Guy Brasseur Introduction: What is Chemical Weather? What is Chemical Weather? Local, regional, and global distributions of important trace gases
Logistics. Goof up P? R? Can you log in? Requests for: Teragrid yes? NCSA no? Anders Colberg Syrowski Curtis Rastogi Yang Chiu
 Logistics Goof up P? R? Can you log in? Teragrid yes? NCSA no? Requests for: Anders Colberg Syrowski Curtis Rastogi Yang Chiu Introduction to Numerical Weather Prediction Thanks: Tom Warner, NCAR A bit
Logistics Goof up P? R? Can you log in? Teragrid yes? NCSA no? Requests for: Anders Colberg Syrowski Curtis Rastogi Yang Chiu Introduction to Numerical Weather Prediction Thanks: Tom Warner, NCAR A bit
Figure ES1 demonstrates that along the sledging
 UPPLEMENT AN EXCEPTIONAL SUMMER DURING THE SOUTH POLE RACE OF 1911/12 Ryan L. Fogt, Megan E. Jones, Susan Solomon, Julie M. Jones, and Chad A. Goergens This document is a supplement to An Exceptional Summer
UPPLEMENT AN EXCEPTIONAL SUMMER DURING THE SOUTH POLE RACE OF 1911/12 Ryan L. Fogt, Megan E. Jones, Susan Solomon, Julie M. Jones, and Chad A. Goergens This document is a supplement to An Exceptional Summer
14.4 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF AIR POLLUTION OVER KANTO AREA IN JAPAN USING THE MM5/CMAQ MODEL
 . NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF AIR POLLUTION OVER KANTO AREA IN JAPAN USING THE MM/CMAQ MODEL - COMPARISON OF AIR POLLUTION CONCENTRATION BETWEEN TWO DIFFERENT CLIMATIC DAYS - Hong HUANG*,a, Ryozo OOKA a, Mai
. NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF AIR POLLUTION OVER KANTO AREA IN JAPAN USING THE MM/CMAQ MODEL - COMPARISON OF AIR POLLUTION CONCENTRATION BETWEEN TWO DIFFERENT CLIMATIC DAYS - Hong HUANG*,a, Ryozo OOKA a, Mai
Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation
 Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation Renhe Zhang 1,2 Ruonan Zhang 2 Zhiyan Zuo 2 1 Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, Fudan University 2 Chinese Academy of Meteorological
Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation Renhe Zhang 1,2 Ruonan Zhang 2 Zhiyan Zuo 2 1 Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, Fudan University 2 Chinese Academy of Meteorological
Urban heat island in the metropolitan area of São Paulo and the influence of warm and dry air masses during summer
 Urban heat island in the metropolitan area of São Paulo and the influence of warm and dry air masses during summer Flavia N. D. Ribeiro1, Arissa S. umezaki1, Jhonathan F. T. de Souza1, Jacyra Soares2,
Urban heat island in the metropolitan area of São Paulo and the influence of warm and dry air masses during summer Flavia N. D. Ribeiro1, Arissa S. umezaki1, Jhonathan F. T. de Souza1, Jacyra Soares2,
PERFORMANCE OF THE WRF-ARW IN THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF SALT LAKE CITY
 P2.17 PERFORMANCE OF THE WRF-ARW IN THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF SALT LAKE CITY Jeffrey E. Passner U.S. Army Research Laboratory White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico 1. INTRODUCTION The Army Research Laboratory
P2.17 PERFORMANCE OF THE WRF-ARW IN THE COMPLEX TERRAIN OF SALT LAKE CITY Jeffrey E. Passner U.S. Army Research Laboratory White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico 1. INTRODUCTION The Army Research Laboratory
MESOSCALE MODELLING OVER AREAS CONTAINING HEAT ISLANDS. Marke Hongisto Finnish Meteorological Institute, P.O.Box 503, Helsinki
 MESOSCALE MODELLING OVER AREAS CONTAINING HEAT ISLANDS Marke Hongisto Finnish Meteorological Institute, P.O.Box 503, 00101 Helsinki INTRODUCTION Urban heat islands have been suspected as being partially
MESOSCALE MODELLING OVER AREAS CONTAINING HEAT ISLANDS Marke Hongisto Finnish Meteorological Institute, P.O.Box 503, 00101 Helsinki INTRODUCTION Urban heat islands have been suspected as being partially
Study of particulate matters pollution related with meteorological factors for a city from South-Central of Romania
 European Journal of Sustainable Development (214), 3, 4, 17-28 ISSN: 2239-938 Doi: 1.1427/ejsd.214.v3n4p17 Study of particulate matters pollution related with meteorological factors for a city from South-Central
European Journal of Sustainable Development (214), 3, 4, 17-28 ISSN: 2239-938 Doi: 1.1427/ejsd.214.v3n4p17 Study of particulate matters pollution related with meteorological factors for a city from South-Central
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Nested dispersion simulation over the Lisbon region R. Kunz,* M. Coutinho,^ C. Borrego^ N. Moussiopoulos' "Institute for Technical Thermodynamics, University of Karlsruhe, 76128 Karlsruhe, Germany ^Department
Nested dispersion simulation over the Lisbon region R. Kunz,* M. Coutinho,^ C. Borrego^ N. Moussiopoulos' "Institute for Technical Thermodynamics, University of Karlsruhe, 76128 Karlsruhe, Germany ^Department
Battlefield Meteorology Including Urban Areas - Research Needs And Current Capabilities
 Battlefield Meteorology Including Urban Areas - Research Needs And Current Capabilities R.A. Pielke Sr. and Major T.E. Nobis August 4 th, 2005 VTC Seminar with ARL Cooperative Institute for Research in
Battlefield Meteorology Including Urban Areas - Research Needs And Current Capabilities R.A. Pielke Sr. and Major T.E. Nobis August 4 th, 2005 VTC Seminar with ARL Cooperative Institute for Research in
P1.34 MULTISEASONALVALIDATION OF GOES-BASED INSOLATION ESTIMATES. Jason A. Otkin*, Martha C. Anderson*, and John R. Mecikalski #
 P1.34 MULTISEASONALVALIDATION OF GOES-BASED INSOLATION ESTIMATES Jason A. Otkin*, Martha C. Anderson*, and John R. Mecikalski # *Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, University of
P1.34 MULTISEASONALVALIDATION OF GOES-BASED INSOLATION ESTIMATES Jason A. Otkin*, Martha C. Anderson*, and John R. Mecikalski # *Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, University of
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016 RHMS of Serbia 1 Summary of major highlights ECMWF forecast products became the backbone in operational work during last several years. Starting from
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016 RHMS of Serbia 1 Summary of major highlights ECMWF forecast products became the backbone in operational work during last several years. Starting from
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies
 Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
!"#$%&'()#*+,-./0123 = = = = = ====1970!"#$%& '()* 1980!"#$%&'()*+,-./01"2 !"#$% ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH
 www.climatechange.cn = = = = = 7 = 6!"#$% 211 11 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH Vol. 7 No. 6 November 211!"1673-1719 (211) 6-385-8!"#$%&'()#*+,-./123 N O N=!"# $%&=NMMMUNO=!"#$!%&'()*+=NMMNMN = 1979
www.climatechange.cn = = = = = 7 = 6!"#$% 211 11 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH Vol. 7 No. 6 November 211!"1673-1719 (211) 6-385-8!"#$%&'()#*+,-./123 N O N=!"# $%&=NMMMUNO=!"#$!%&'()*+=NMMNMN = 1979
Observational validation of an extended mosaic technique for capturing subgrid scale heterogeneity in a GCM
 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved C 2007 The Authors Journal compilation C 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard TELLUS Observational validation of an extended mosaic technique for capturing subgrid scale
Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved C 2007 The Authors Journal compilation C 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard TELLUS Observational validation of an extended mosaic technique for capturing subgrid scale
Sensitivity of precipitation forecasts to convective parameterization in the October 2007 Flash Flood in the Valencia Region (Eastern Spain)
 Adv. Geosci., 26, 7 11, 2010 doi:10.5194/adgeo-26-7-2010 Author(s) 2010. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Geosciences Sensitivity of precipitation forecasts to convective parameterization in the
Adv. Geosci., 26, 7 11, 2010 doi:10.5194/adgeo-26-7-2010 Author(s) 2010. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Geosciences Sensitivity of precipitation forecasts to convective parameterization in the
DESCRIPTION OF THE CANADIAN REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL. 1. Introduction
 DESCRIPTION OF THE CANADIAN REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL D. CAYA ~, R. LAPRISE ~, M. GIGUI~RE ', G. BERGERON ~, J. P. BLANCHET ~, B. J. STOCKS z, G. J. BOER 3 and N. A. McFARLANE 3 1Cooperative Centre for Research
DESCRIPTION OF THE CANADIAN REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL D. CAYA ~, R. LAPRISE ~, M. GIGUI~RE ', G. BERGERON ~, J. P. BLANCHET ~, B. J. STOCKS z, G. J. BOER 3 and N. A. McFARLANE 3 1Cooperative Centre for Research
The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 219 224 The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times LU Ri-Yu 1, LI Chao-Fan 1,
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 219 224 The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times LU Ri-Yu 1, LI Chao-Fan 1,
Climatic study of the surface wind field and extreme winds over the Greek seas
 C O M E C A P 2 0 1 4 e - b o o k o f p r o c e e d i n g s v o l. 3 P a g e 283 Climatic study of the surface wind field and extreme winds over the Greek seas Vagenas C., Anagnostopoulou C., Tolika K.
C O M E C A P 2 0 1 4 e - b o o k o f p r o c e e d i n g s v o l. 3 P a g e 283 Climatic study of the surface wind field and extreme winds over the Greek seas Vagenas C., Anagnostopoulou C., Tolika K.
Atmospheric Processes
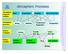 Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007
 Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007 National Meteorological Administration Romania 1. Summary of major highlights The medium range forecast activity within the National Meteorological
Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007 National Meteorological Administration Romania 1. Summary of major highlights The medium range forecast activity within the National Meteorological
Role of Meteorology on Urban Air Pollution Dispersion: A 20yr Analysis for Delhi, India
 Simple Interactive Models for Better Air Quality Role of Meteorology on Urban Air Pollution Dispersion: A 20yr Analysis for Delhi, India Dr. Sarath Guttikunda January, 2010 Delhi, India SIM-air Working
Simple Interactive Models for Better Air Quality Role of Meteorology on Urban Air Pollution Dispersion: A 20yr Analysis for Delhi, India Dr. Sarath Guttikunda January, 2010 Delhi, India SIM-air Working
Egyptian Meteorological Authority Cairo Numerical Weather prediction centre
 JOINT WMO TECHNICAL PROGRESS REPORT ON THE GLOBAL DATA PROCESSING AND FORECASTING SYSTEM AND NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION RESEARCH ACTIVITIES FOR 2016 Egyptian Meteorological Authority Cairo Numerical
JOINT WMO TECHNICAL PROGRESS REPORT ON THE GLOBAL DATA PROCESSING AND FORECASTING SYSTEM AND NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION RESEARCH ACTIVITIES FOR 2016 Egyptian Meteorological Authority Cairo Numerical
Report of the Scientific Project Manager
 Report of the Scientific Project Manager G. Doms, DWD, 4th COSMO General Meeting, Warsaw, Poland Status of the LM LM Version 2.13 (18 January 2002) - Option for use of Wind profiler/rass reports - Adjustments
Report of the Scientific Project Manager G. Doms, DWD, 4th COSMO General Meeting, Warsaw, Poland Status of the LM LM Version 2.13 (18 January 2002) - Option for use of Wind profiler/rass reports - Adjustments
P1M.4 COUPLED ATMOSPHERE, LAND-SURFACE, HYDROLOGY, OCEAN-WAVE, AND OCEAN-CURRENT MODELS FOR MESOSCALE WATER AND ENERGY CIRCULATIONS
 P1M.4 COUPLED ATMOSPHERE, LAND-SURFACE, HYDROLOGY, OCEAN-WAVE, AND OCEAN-CURRENT MODELS FOR MESOSCALE WATER AND ENERGY CIRCULATIONS Haruyasu NAGAI *, Takuya KOBAYASHI, Katsunori TSUDUKI, and Kyeongok KIM
P1M.4 COUPLED ATMOSPHERE, LAND-SURFACE, HYDROLOGY, OCEAN-WAVE, AND OCEAN-CURRENT MODELS FOR MESOSCALE WATER AND ENERGY CIRCULATIONS Haruyasu NAGAI *, Takuya KOBAYASHI, Katsunori TSUDUKI, and Kyeongok KIM
A 3DVAR Land Data Assimilation Scheme: Part 2, Test with ECMWF ERA-40
 A 3DVAR Land Data Assimilation Scheme: Part 2, Test with ECMWF ERA-40 Lanjun Zou 1 * a,b,c Wei Gao a,d Tongwen Wu b Xiaofeng Xu b Bingyu Du a,and James Slusser d a Sino-US Cooperative Center for Remote
A 3DVAR Land Data Assimilation Scheme: Part 2, Test with ECMWF ERA-40 Lanjun Zou 1 * a,b,c Wei Gao a,d Tongwen Wu b Xiaofeng Xu b Bingyu Du a,and James Slusser d a Sino-US Cooperative Center for Remote
Modeling rainfall diurnal variation of the North American monsoon core using different spatial resolutions
 Modeling rainfall diurnal variation of the North American monsoon core using different spatial resolutions Jialun Li, X. Gao, K.-L. Hsu, B. Imam, and S. Sorooshian Department of Civil and Environmental
Modeling rainfall diurnal variation of the North American monsoon core using different spatial resolutions Jialun Li, X. Gao, K.-L. Hsu, B. Imam, and S. Sorooshian Department of Civil and Environmental
Regional climate modelling in the future. Ralf Döscher, SMHI, Sweden
 Regional climate modelling in the future Ralf Döscher, SMHI, Sweden The chain Global H E H E C ( m 3/s ) Regional downscaling 120 adam 3 C HAM 4 adam 3 C HAM 4 trl A2 A2 B2 B2 80 40 0 J F M A M J J A S
Regional climate modelling in the future Ralf Döscher, SMHI, Sweden The chain Global H E H E C ( m 3/s ) Regional downscaling 120 adam 3 C HAM 4 adam 3 C HAM 4 trl A2 A2 B2 B2 80 40 0 J F M A M J J A S
A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS
 A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS Wei Yu, Yubao Liu, Tom Warner, Randy Bullock, Barbara Brown and
A COMPARISON OF VERY SHORT-TERM QPF S FOR SUMMER CONVECTION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN AREAS, WITH THE NCAR/ATEC WRF AND MM5-BASED RTFDDA SYSTEMS Wei Yu, Yubao Liu, Tom Warner, Randy Bullock, Barbara Brown and
Global reanalysis: Some lessons learned and future plans
 Global reanalysis: Some lessons learned and future plans Adrian Simmons and Sakari Uppala European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts With thanks to Per Kållberg and many other colleagues from ECMWF
Global reanalysis: Some lessons learned and future plans Adrian Simmons and Sakari Uppala European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts With thanks to Per Kållberg and many other colleagues from ECMWF
Abstract. Key words: LCLU Change, Climate Change, Regional Modeling 1. INTRODUCTION
 TOTAL CLIMATE CHANGES IN TROPICAL COASTAL AREAS: LCLU + GREEN HOUSE GASES Jorge E. González* *, Daniel E. Comarazamy** *The City College of New York, New York, NY USA; **Santa Clara University, Santa Clara,
TOTAL CLIMATE CHANGES IN TROPICAL COASTAL AREAS: LCLU + GREEN HOUSE GASES Jorge E. González* *, Daniel E. Comarazamy** *The City College of New York, New York, NY USA; **Santa Clara University, Santa Clara,
4.5 Comparison of weather data from the Remote Automated Weather Station network and the North American Regional Reanalysis
 4.5 Comparison of weather data from the Remote Automated Weather Station network and the North American Regional Reanalysis Beth L. Hall and Timothy. J. Brown DRI, Reno, NV ABSTRACT. The North American
4.5 Comparison of weather data from the Remote Automated Weather Station network and the North American Regional Reanalysis Beth L. Hall and Timothy. J. Brown DRI, Reno, NV ABSTRACT. The North American
REGIONAL VARIABILITY OF CAPE AND DEEP SHEAR FROM THE NCEP/NCAR REANALYSIS ABSTRACT
 REGIONAL VARIABILITY OF CAPE AND DEEP SHEAR FROM THE NCEP/NCAR REANALYSIS VITTORIO A. GENSINI National Weather Center REU Program, Norman, Oklahoma Northern Illinois University, DeKalb, Illinois ABSTRACT
REGIONAL VARIABILITY OF CAPE AND DEEP SHEAR FROM THE NCEP/NCAR REANALYSIS VITTORIO A. GENSINI National Weather Center REU Program, Norman, Oklahoma Northern Illinois University, DeKalb, Illinois ABSTRACT
J1.7 SOIL MOISTURE ATMOSPHERE INTERACTIONS DURING THE 2003 EUROPEAN SUMMER HEATWAVE
 J1.7 SOIL MOISTURE ATMOSPHERE INTERACTIONS DURING THE 2003 EUROPEAN SUMMER HEATWAVE E Fischer* (1), SI Seneviratne (1), D Lüthi (1), PL Vidale (2), and C Schär (1) 1 Institute for Atmospheric and Climate
J1.7 SOIL MOISTURE ATMOSPHERE INTERACTIONS DURING THE 2003 EUROPEAN SUMMER HEATWAVE E Fischer* (1), SI Seneviratne (1), D Lüthi (1), PL Vidale (2), and C Schär (1) 1 Institute for Atmospheric and Climate
Meteorological and Dispersion Modelling Using TAPM for Wagerup
 Meteorological and Dispersion Modelling Using TAPM for Wagerup Phase 1: Meteorology Appendix A: Additional modelling details Prepared for: Alcoa World Alumina Australia, P. O. Box 252, Applecross, Western
Meteorological and Dispersion Modelling Using TAPM for Wagerup Phase 1: Meteorology Appendix A: Additional modelling details Prepared for: Alcoa World Alumina Australia, P. O. Box 252, Applecross, Western
Sensitivity of precipitation forecasts to cumulus parameterizations in Catalonia (NE Spain)
 Sensitivity of precipitation forecasts to cumulus parameterizations in Catalonia (NE Spain) Jordi Mercader (1), Bernat Codina (1), Abdelmalik Sairouni (2), Jordi Cunillera (2) (1) Dept. of Astronomy and
Sensitivity of precipitation forecasts to cumulus parameterizations in Catalonia (NE Spain) Jordi Mercader (1), Bernat Codina (1), Abdelmalik Sairouni (2), Jordi Cunillera (2) (1) Dept. of Astronomy and
Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical
 1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
