Influences of environmental moisture on the development and organization of cumulus convection
|
|
|
- Jasmine Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The 6th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso scale Weather Prediction DPRI, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto, Japan, 7 March 2016 Influences of environmental moisture on the development and organization of cumulus convection Tetsuya Takemi Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University
2 Motivation Tropical convection exhibits trimodal characteristics: Cu, Cg, and Cb (Johnson et al. 1999) The large scale variability of moisture in space and time significantly controls the development of cumulus convection; Cumulus activity will play a role in moistening the larger scale atmosphere by transporting moisture. Mixing between cumulus and the environment is a key to understand dynamics and interactions of tropical convection across scales
3 Cloud top height of tropical cumulus With cloud classification algorithm applied to satellite infrared data, cu-type clouds are chosen in 10 deg by 10 deg area over tropical oceanic areas. DRY1 DRY2 Relative humidity profile Cu peak : ~ 285 K Cg peak : ~ 255 K Cb peak : ~ 210 K RAINY (Takemi et al. 2004)
4 Purpose Investigate the interaction between cumulus convection and its environment over the tropical Indian Ocean Conduct high resolution simulations extending two months during Oct Nov 2011 (within the CINDY2011/ DYNAMO field observation period) with WRF/ARW v3.3.1 Domain 1: 4250 x 3000 km@12.5 km 1 way nesting; no feedback from inner domains to outer domains Domain 2: 1500 x 1500 km@2.5 km Domain 3: 300 x 300 km@500 m Domain 4: 100 x 60 km@100 m Domain 1: 51.3 E 91.7 E, 15.7 S 10.9 N Domain 2: E E, S 1.65 N Domain 3: E E, 9.36 S 6.69 N Domain 4: E E, S S; centered at Mirai Obs.
5 Large scale field: Longitude time diagram in Oct/Nov 2011 Observed (JMA Global Analysis) Vertical Velocity (omega) Oct 1 Simulated Precipitable Total Condensate Water Dec 1
6 Comparison with observations: humidity variation Relative humidity Observation: Mirai radiosonde souding Simulation: profile at the Mirai location
7 Tropospheric humidity, stability, and cloud cover in Domain 4 Domain mean relative humidity: at low levels (0 2 km, red), middle levels (2 6 km, green), and upper levels (6 10 km, blue) Domain mean lapse rate in the lower troposphere (0.5 5 km) Time height section of cloud cover
8 Tropospheric temperature lapse rate versus mid level cloud amount Cloud cover versus lapse rate/humidity CC at 4 km vs low level RH CC at 8 km vs low level RH Precipitable water versus mid level cloud amount CC at 8 km vs mid level RH
9 Layer moisture content: Nov Domain 4 versus Domain 4 area within Domain 1 More moistening for higherresolution domain :0 1 km layer (Domain 4) :0 1 km layer (Domain 4 area within Domain 4) :0 4 km layer (Domain 4) :0 4 km layer (Domain 4 area within Domain 4) :Total layer (Precip water) (Domain 4) :Total layer (Precip water) (Domain 1)
10 Convective core : qw > 0.05 g/kg and w > 0.5 m/s Thermodynamic properties of air parcels Analysis for the period of 1 Oct 1 Dec 2011 ~ Height (vapor + liquid + ice) Environment Cloudy Convective core Cloudy Environment Convective core of convective cores does not largely change with total water content. Existence of undiluted, cloud core air parcels Environmental moistening
11 Future work: thermodynamic control for warm season MCSs Locations of the occurrence of quasi stationary convective clusters (QSCCs) in warm season in Japan The importance of low to middlelevel relative humidity for the occurrence of QSCCs (Unuma and Takemi 2016, QJ)
12 Summary This study investigated the relationship between cumulus convection and environmental moisture in the tropical Indian Ocean during CINDY/DYNAMO by conducting convection resolving simulations at the 100 mgrid. The cloud cover exceeding a middle level sharply increases with the increase in precipitable water vapor over 55 mm. The increase in lower layer relative humidity results in the increase in cloud cover above the humid layer. The existence of updraft cores less is demonstrated; contributes to the environmental moistening. The updraft cores play a key role in the interrelationship between cumulus convection and its environment, and are regarded as having a preconditioning influence for the convective initiation of MJO. Takemi, T., 2015: Relationship between cumulus activity and environmental moisture during the CINDY2011/DYNAMO field experiment as revealed from convection resolving simulations. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 93A, 41 58, doi: /jmsj
The 5th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso-scale Weather Prediction, Nagoya University, Higashiyama Campus, Nagoya, 9 March 2015
 The 5th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso-scale Weather Prediction, Nagoya University, Higashiyama Campus, Nagoya, 9 March 2015 The effects of moisture conditions on the organization and intensity
The 5th Research Meeting of Ultrahigh Precision Meso-scale Weather Prediction, Nagoya University, Higashiyama Campus, Nagoya, 9 March 2015 The effects of moisture conditions on the organization and intensity
Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence)
 1 Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence) William M. Gray Professor Emeritus Colorado State University There are many flaws in the global climate models. But
1 Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence) William M. Gray Professor Emeritus Colorado State University There are many flaws in the global climate models. But
WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica
 Introduction Part I WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica Holger Tost Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany Introduction Overview What is a parameterisation and why using it? Fundamentals
Introduction Part I WaVaCS summerschool Autumn 2009 Cargese, Corsica Holger Tost Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, Germany Introduction Overview What is a parameterisation and why using it? Fundamentals
Characterizing Clouds and Convection Associated with the MJO Using the Year of Tropical Convection (YOTC) Collocated A-Train and ECMWF Data Set
 Characterizing Clouds and Convection Associated with the MJO Using the Year of Tropical Convection (YOTC) Collocated A-Train and ECMWF Data Set Wei-Ting Chen Department of Atmospheric Sciences, National
Characterizing Clouds and Convection Associated with the MJO Using the Year of Tropical Convection (YOTC) Collocated A-Train and ECMWF Data Set Wei-Ting Chen Department of Atmospheric Sciences, National
THE ASSOCIATION OF ALBEDO AND OLR RADIATION WITH VARIATIONS OF PRECIPITATION IMPLICATIONS FOR AGW
 1 THE ASSOCIATION OF ALBEDO AND OLR RADIATION WITH VARIATIONS OF PRECIPITATION IMPLICATIONS FOR AGW William M. Gray and Barry Schwartz Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
1 THE ASSOCIATION OF ALBEDO AND OLR RADIATION WITH VARIATIONS OF PRECIPITATION IMPLICATIONS FOR AGW William M. Gray and Barry Schwartz Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model
 Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model S. F. Iacobellis, R. C. J. Somerville, D. E. Lane, and J. Berque Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model S. F. Iacobellis, R. C. J. Somerville, D. E. Lane, and J. Berque Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Challenges in forecasting the MJO
 Challenges in forecasting the MJO Augustin Vintzileos University of Maryland ESSIC/CICS-MD Jon Gottschalck NOAA/NCEP/CPC Outline Forecasting at the interface between weather and climate Multi-scale impacts
Challenges in forecasting the MJO Augustin Vintzileos University of Maryland ESSIC/CICS-MD Jon Gottschalck NOAA/NCEP/CPC Outline Forecasting at the interface between weather and climate Multi-scale impacts
DRY INTRUSION FROM THE INDIAN OCEAN OBSERVED AT SUMATERA ISLAND ON OCTOBER 6-7, 1998
 DRY INTRUSION FROM THE INDIAN OCEAN OBSERVED AT SUMATERA ISLAND ON OCTOBER 6-7, 1998 FUMIE MURATA Research Institute for Humanity and Nature, 335 Takashima-cho, Kamigyo, Kyoto, 602-0878, Japan MANABU D.
DRY INTRUSION FROM THE INDIAN OCEAN OBSERVED AT SUMATERA ISLAND ON OCTOBER 6-7, 1998 FUMIE MURATA Research Institute for Humanity and Nature, 335 Takashima-cho, Kamigyo, Kyoto, 602-0878, Japan MANABU D.
Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~
 2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
Air-Sea Interaction Study in the Tropics by JAMSTEC
 Air-Sea Interaction Study in the Tropics by JAMSTEC History : Major Activities related to Air-Sea Interaction Study 1987 JENEX-87 (Japanese El Niño Experiment - 87) * This was the first trial for El Niño
Air-Sea Interaction Study in the Tropics by JAMSTEC History : Major Activities related to Air-Sea Interaction Study 1987 JENEX-87 (Japanese El Niño Experiment - 87) * This was the first trial for El Niño
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #1 Page 1 of 7
 1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
1) What is generally true about the stratosphere: a) Has turbulent updrafts and downdrafts. b) Has either a stable or increasing temperature profile with altitude. c) Where the auroras occur. d) Both a)
Why do GCMs have trouble with the MJO?
 Why do GCMs have trouble with the MJO? The Madden-Julian Oscillation West East 200 [hpa] 500 Cool & dry Cool & dry p 700 850 SST Lag Day +20 +15 +10 +5 0-5 -10-15 -20 ~20 days ~10 days ~10-15 days
Why do GCMs have trouble with the MJO? The Madden-Julian Oscillation West East 200 [hpa] 500 Cool & dry Cool & dry p 700 850 SST Lag Day +20 +15 +10 +5 0-5 -10-15 -20 ~20 days ~10 days ~10-15 days
Chapter 14 Thunderstorm Fundamentals
 Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
Application of Radio Occultation Data in Analyses and Forecasts of Tropical Cyclones Using an Ensemble Assimilation System
 Application of Radio Occultation Data in Analyses and Forecasts of Tropical Cyclones Using an Assimilation System Hui Liu, Jeff Anderson, and Bill Kuo NCAR Acknowledgment: C. Snyder, Y. Chen, T. Hoar,
Application of Radio Occultation Data in Analyses and Forecasts of Tropical Cyclones Using an Assimilation System Hui Liu, Jeff Anderson, and Bill Kuo NCAR Acknowledgment: C. Snyder, Y. Chen, T. Hoar,
Moisture modes, cloud-radiative feedbacks and the MJO
 Moisture modes, cloud-radiative feedbacks and the MJO Adam Sobel Eric Maloney, Shuguang Wang, Daehyun Kim, also bits from Jim Benedict; thanks also Gilles Bellon, Dargan Frierson FDEPS, Kyoto Source: Matt
Moisture modes, cloud-radiative feedbacks and the MJO Adam Sobel Eric Maloney, Shuguang Wang, Daehyun Kim, also bits from Jim Benedict; thanks also Gilles Bellon, Dargan Frierson FDEPS, Kyoto Source: Matt
Forecasting at the interface between weather and climate: beyond the RMM-index
 Forecasting at the interface between weather and climate: beyond the RMM-index Augustin Vintzileos University of Maryland ESSIC/CICS-MD Jon Gottschalck NOAA/NCEP/CPC Outline The Global Tropics Hazards
Forecasting at the interface between weather and climate: beyond the RMM-index Augustin Vintzileos University of Maryland ESSIC/CICS-MD Jon Gottschalck NOAA/NCEP/CPC Outline The Global Tropics Hazards
1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents
 CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
CHAPTER 6 HUMIDITY, SATURATION, AND STABILITY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1., annual precipitation is greater than annual evapotranspiration. a. On the ocean *b. On the continents 2., annual precipitation
Chapter Introduction. Weather. Patterns. Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Weather Weather Patterns Weather Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up How do scientists describe and predict weather? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Weather Weather Patterns Weather Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up How do scientists describe and predict weather? What do you think? Before you begin,
Mr. P s Science Test!
 WEATHER- 2017 Mr. P s Science Test! # Name Date 1. Draw and label a weather station model. (10 pts) 2. The is the layer of the atmosphere with our weather. 3. Meteorologists classify clouds in about different
WEATHER- 2017 Mr. P s Science Test! # Name Date 1. Draw and label a weather station model. (10 pts) 2. The is the layer of the atmosphere with our weather. 3. Meteorologists classify clouds in about different
Moisture modes, cloud-radiative feedbacks and the MJO
 Moisture modes, cloud-radiative feedbacks and the MJO Adam Sobel Eric Maloney with bits from Shuguang Wang, Jim Benedict; thanks also Gilles Bellon, Dargan Frierson, Daehyun Kim EUCLIPSE summer school
Moisture modes, cloud-radiative feedbacks and the MJO Adam Sobel Eric Maloney with bits from Shuguang Wang, Jim Benedict; thanks also Gilles Bellon, Dargan Frierson, Daehyun Kim EUCLIPSE summer school
Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology
 S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics
 12.818 Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics Lodovica Illari 1 Background The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun whose intensity peaks in the visible. In order to maintain energy balance
12.818 Project 3 Convection and Atmospheric Thermodynamics Lodovica Illari 1 Background The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun whose intensity peaks in the visible. In order to maintain energy balance
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas INTRODUCTION TO ATMOSPHERIC MOISTURE Atmospheric Moisture The Nature of Water The Hydrologic Cycle Evaporation Measures of Humidity Condensation The Buoyancy of Air Precipitation
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas INTRODUCTION TO ATMOSPHERIC MOISTURE Atmospheric Moisture The Nature of Water The Hydrologic Cycle Evaporation Measures of Humidity Condensation The Buoyancy of Air Precipitation
DYNAMO Review. Chidong Zhang RSMAS, University of Miami. US Clivar Summit July 9-11, 2014 Denver, CO
 DYNAMO Review Chidong Zhang RSMAS, University of Miami US Clivar Summit July 9-11, 2014 Denver, CO DYNAMO: Dynamics of the Madden-Julian Oscillation CINDY2011: Cooperative Indian Ocean Investigation on
DYNAMO Review Chidong Zhang RSMAS, University of Miami US Clivar Summit July 9-11, 2014 Denver, CO DYNAMO: Dynamics of the Madden-Julian Oscillation CINDY2011: Cooperative Indian Ocean Investigation on
Unseasonable weather conditions in Japan in August 2014
 Unseasonable weather conditions in Japan in August 2014 Summary of analysis by the TCC Advisory Panel on Extreme Climatic Events In an extraordinary session held at the Japan Meteorological Agency on 3
Unseasonable weather conditions in Japan in August 2014 Summary of analysis by the TCC Advisory Panel on Extreme Climatic Events In an extraordinary session held at the Japan Meteorological Agency on 3
Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers
 Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 4 8/13/2012 Why inner core dynamics is important? Current TC intensity and structure forecasts contain
Inner core dynamics: Eyewall Replacement and hot towers FIU Undergraduate Hurricane Internship Lecture 4 8/13/2012 Why inner core dynamics is important? Current TC intensity and structure forecasts contain
Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation
 Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation Adam Sobel Columbia University NCAR IMAGe Workshop, Nov. 3 2005 In the tropics, our picture of the dynamics should
Parameterizing large-scale dynamics using the weak temperature gradient approximation Adam Sobel Columbia University NCAR IMAGe Workshop, Nov. 3 2005 In the tropics, our picture of the dynamics should
777 GROUNDSCHOOL Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms
 777 GROUNDSCHOOL 2018 Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms The Atmosphere Heating Transfer of heat occurs thru Radiation Advection Convection Matter changes states due to the amount of heat
777 GROUNDSCHOOL 2018 Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms The Atmosphere Heating Transfer of heat occurs thru Radiation Advection Convection Matter changes states due to the amount of heat
Guided Notes: Atmosphere Layers of the Atmosphere
 Guided Notes: Atmosphere Layers of the Atmosphere Atmosphere: Absorbs solar radiation, Burns up meteors, transports and recycles water, and other chemicals, and moderates climate Main Components: o Meteorology
Guided Notes: Atmosphere Layers of the Atmosphere Atmosphere: Absorbs solar radiation, Burns up meteors, transports and recycles water, and other chemicals, and moderates climate Main Components: o Meteorology
Aircraft Observations for ONR DRI and DYNAMO. Coupled Air-sea processes: Q. Wang, D. Khelif, L. Mahrt, S. Chen
 Aircraft Observations for ONR DRI and DYNAMO (NOAA/ONR/NSF) Coupled Air-sea processes: Q. Wang, D. Khelif, L. Mahrt, S. Chen Deep convection/mjo initiation: Dave Jorgensen, S. Chen, R. Houze Aerosol/Cloud
Aircraft Observations for ONR DRI and DYNAMO (NOAA/ONR/NSF) Coupled Air-sea processes: Q. Wang, D. Khelif, L. Mahrt, S. Chen Deep convection/mjo initiation: Dave Jorgensen, S. Chen, R. Houze Aerosol/Cloud
Radiative-Convective Models. The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation. Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1
 Climate Modeling Lecture 8 Radiative-Convective Models Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1 The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation Prepare for Mid-Term (Friday 9 am) Review Course Notes
Climate Modeling Lecture 8 Radiative-Convective Models Manabe and Strickler (1964) Course Notes chapter 5.1 The Hydrological Cycle Hadley Circulation Prepare for Mid-Term (Friday 9 am) Review Course Notes
Chapter 5. Atmospheric Moisture
 Chapter 5 Atmospheric Moisture hydrologic cycle--movement of water in all forms between earth & atmosphere Humidity: amount of water vapor in air vapor pressure saturation vapor pressure absolute humidity
Chapter 5 Atmospheric Moisture hydrologic cycle--movement of water in all forms between earth & atmosphere Humidity: amount of water vapor in air vapor pressure saturation vapor pressure absolute humidity
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans
![Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans](/thumbs/96/128963638.jpg) Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Boundary layer equilibrium [2005] over tropical oceans Alan K. Betts [akbetts@aol.com] Based on: Betts, A.K., 1997: Trade Cumulus: Observations and Modeling. Chapter 4 (pp 99-126) in The Physics and Parameterization
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63%
 Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
Temp 54 Dew Point 41 Relative Humidity 63% Water in the Atmosphere Evaporation Water molecules change from the liquid to gas phase Molecules in liquids move slowly Heat energy makes them move faster When
The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study
 The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study Amanda M. Sheffield and Susan C. van den Heever Colorado State University Dynamics and Predictability of Middle Latitude
The Role of Post Cold Frontal Cumulus Clouds in an Extratropical Cyclone Case Study Amanda M. Sheffield and Susan C. van den Heever Colorado State University Dynamics and Predictability of Middle Latitude
MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016
 MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016 We have reviewed the reasons why NWP models need to
MEA 716 Exercise, BMJ CP Scheme With acknowledgements to B. Rozumalski, M. Baldwin, and J. Kain Optional Review Assignment, distributed Th 2/18/2016 We have reviewed the reasons why NWP models need to
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises 78% of the Earth atmosphere by volume.
 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises 78% of the Earth atmosphere by volume. A. Oxygen B. Water Vapor C. Carbon Dioxide D. Nitrogen An isobar is a line of constant. A.
The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises 78% of the Earth atmosphere by volume. A. Oxygen B. Water Vapor C. Carbon Dioxide D. Nitrogen An isobar is a line of constant. A.
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation: Clouds and Precipitation. Dr. Michael J Passow
 Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation: Clouds and Precipitation Dr. Michael J Passow What Processes Lift Air? Clouds require three things: water vapor, a condensation nucleus, and cooling Cooling usually
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation: Clouds and Precipitation Dr. Michael J Passow What Processes Lift Air? Clouds require three things: water vapor, a condensation nucleus, and cooling Cooling usually
Weather Notes. Chapter 16, 17, & 18
 Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Day Microphysics RGB Nephanalysis in daytime. Meteorological Satellite Center, JMA
 Day Microphysics RGB Nephanalysis in daytime Meteorological Satellite Center, JMA What s Day Microphysics RGB? R : B04 (N1 0.86) Range : 0~100 [%] Gamma : 1.0 G : B07(I4 3.9) (Solar component) Range :
Day Microphysics RGB Nephanalysis in daytime Meteorological Satellite Center, JMA What s Day Microphysics RGB? R : B04 (N1 0.86) Range : 0~100 [%] Gamma : 1.0 G : B07(I4 3.9) (Solar component) Range :
Introduction. Effect of aerosols on precipitation: - challenging problem - no agreement between the results (quantitative and qualitative)
 Introduction Atmospheric aerosols affect the cloud mycrophysical structure & formation (observations, numerical studies) An increase of the aerosol particles: - increases CCN concentrations - decreases
Introduction Atmospheric aerosols affect the cloud mycrophysical structure & formation (observations, numerical studies) An increase of the aerosol particles: - increases CCN concentrations - decreases
Shear-Parallel Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Moist Low- Inhibition Mei-Yu Front Environment. Liu and Moncrieff (2017 JAS)
 Shear-Parallel Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Moist Low- Inhibition Mei-Yu Front Environment Liu and Moncrieff (2017 JAS) Introduction Balance of lower-tropospheric wind shear and strength of evaporation-generated
Shear-Parallel Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Moist Low- Inhibition Mei-Yu Front Environment Liu and Moncrieff (2017 JAS) Introduction Balance of lower-tropospheric wind shear and strength of evaporation-generated
Fluid Circulation Review. Vocabulary. - Dark colored surfaces absorb more energy.
 Fluid Circulation Review Vocabulary Absorption - taking in energy as in radiation. For example, the ground will absorb the sun s radiation faster than the ocean water. Air pressure Albedo - Dark colored
Fluid Circulation Review Vocabulary Absorption - taking in energy as in radiation. For example, the ground will absorb the sun s radiation faster than the ocean water. Air pressure Albedo - Dark colored
Pd: Date: Page # Weather Patterns -- Lesson 2 Study Guide
 Name: Pd: Date: Page # Weather Patterns -- Lesson 2 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 What are two types of pressure systems? 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 What drives weather patterns? 1
Name: Pd: Date: Page # Weather Patterns -- Lesson 2 Study Guide Rating Before Learning Goals Rating After 1 2 3 4 What are two types of pressure systems? 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 What drives weather patterns? 1
Air-Sea Interaction and the MJO
 Air-Sea Interaction and the MJO Julia Slingo with thanks to Dan Bernie, Eric Guilyardi, Pete Inness, Hilary Spencer and Steve Woolnough NCAS Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling University of Reading
Air-Sea Interaction and the MJO Julia Slingo with thanks to Dan Bernie, Eric Guilyardi, Pete Inness, Hilary Spencer and Steve Woolnough NCAS Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling University of Reading
Chapter 6 Clouds. Cloud Development
 Chapter 6 Clouds Chapter overview Processes causing saturation o Cooling, moisturizing, mixing Cloud identification and classification Cloud Observations Fog Why do we care about clouds in the atmosphere?
Chapter 6 Clouds Chapter overview Processes causing saturation o Cooling, moisturizing, mixing Cloud identification and classification Cloud Observations Fog Why do we care about clouds in the atmosphere?
a. Air is more dense b. Associated with cold air (more dense than warm air) c. Associated with sinking air
 Meteorology 1. Air pressure the weight of air pressing down on Earth 2. Temperature and altitude determine air pressure 3. The more air particles are present, the more air density or pressure exists 4.
Meteorology 1. Air pressure the weight of air pressing down on Earth 2. Temperature and altitude determine air pressure 3. The more air particles are present, the more air density or pressure exists 4.
Answers to Clicker Questions
 Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
Answers to Clicker Questions Chapter 1 What component of the atmosphere is most important to weather? A. Nitrogen B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Ozone E. Water What location would have the lowest surface
Clouds on Mars Cloud Classification
 Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time. It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the
 Weather Notes Weather Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the The sun is the force that weather The sun s energy
Weather Notes Weather Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the The sun is the force that weather The sun s energy
Clouds and turbulent moist convection
 Clouds and turbulent moist convection Lecture 2: Cloud formation and Physics Caroline Muller Les Houches summer school Lectures Outline : Cloud fundamentals - global distribution, types, visualization
Clouds and turbulent moist convection Lecture 2: Cloud formation and Physics Caroline Muller Les Houches summer school Lectures Outline : Cloud fundamentals - global distribution, types, visualization
9D.3 THE INFLUENCE OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON DEEP CONVECTION IN THE TROPICS
 9D.3 THE INFLUENCE OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON DEEP CONVECTION IN THE TROPICS Ulrike Wissmeier, Robert Goler University of Munich, Germany 1 Introduction One does not associate severe storms with the tropics
9D.3 THE INFLUENCE OF VERTICAL WIND SHEAR ON DEEP CONVECTION IN THE TROPICS Ulrike Wissmeier, Robert Goler University of Munich, Germany 1 Introduction One does not associate severe storms with the tropics
Masahiro Kazumori, Takashi Kadowaki Numerical Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency
 Development of an all-sky assimilation of microwave imager and sounder radiances for the Japan Meteorological Agency global numerical weather prediction system Masahiro Kazumori, Takashi Kadowaki Numerical
Development of an all-sky assimilation of microwave imager and sounder radiances for the Japan Meteorological Agency global numerical weather prediction system Masahiro Kazumori, Takashi Kadowaki Numerical
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models
 Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
Large-scale changes in the atmospheric water cycle in models and observations
 Large-scale changes in the atmospheric water cycle in models and observations Richard Allan University of Reading Strength of Feedback (Wm-2/oC) Uncertainty in strength of cloud feedback Total range Range
Large-scale changes in the atmospheric water cycle in models and observations Richard Allan University of Reading Strength of Feedback (Wm-2/oC) Uncertainty in strength of cloud feedback Total range Range
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE During a rainstorm, the air feels moist On a clear, cloudless day, the air may feel dry As the sun heats the land and oceans, the amount of water in the atmosphere changes Water
Chapter 12 Section 12.1 The causes of weather
 Chapter 12 Section 12.1 The causes of weather Main Idea: Air masses have different temperatures and amounts of moisture because of the uneven heating of earth's surface. What is Meteorology The study of
Chapter 12 Section 12.1 The causes of weather Main Idea: Air masses have different temperatures and amounts of moisture because of the uneven heating of earth's surface. What is Meteorology The study of
Assimilating cloud information from satellite cloud products with an Ensemble Kalman Filter at the convective scale
 Assimilating cloud information from satellite cloud products with an Ensemble Kalman Filter at the convective scale Annika Schomburg, Christoph Schraff This work was funded by the EUMETSAT fellowship programme.
Assimilating cloud information from satellite cloud products with an Ensemble Kalman Filter at the convective scale Annika Schomburg, Christoph Schraff This work was funded by the EUMETSAT fellowship programme.
Seasonal Climate Watch November 2017 to March 2018
 Seasonal Climate Watch November 2017 to March 2018 Date issued: Oct 26, 2017 1. Overview The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) continues to develop towards a La Niña state, and is expected to be in at
Seasonal Climate Watch November 2017 to March 2018 Date issued: Oct 26, 2017 1. Overview The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) continues to develop towards a La Niña state, and is expected to be in at
Moisture transport to Syowa Station and Dome Fuji Station, Antarctica
 Session 5: Science Using Ground-Based and Satellite Measurements Moisture transport to Syowa Station and Dome Fuji Station, Antarctica Kazue Suzuki, Takashi Yamanouchi, Naohiko Hirasawa and Hideaki Motoyama
Session 5: Science Using Ground-Based and Satellite Measurements Moisture transport to Syowa Station and Dome Fuji Station, Antarctica Kazue Suzuki, Takashi Yamanouchi, Naohiko Hirasawa and Hideaki Motoyama
Chapter 4 Water Vapor
 Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Introduction Outline Big picture Cloud types according to WMO Appendix. Atmospheric Physics. An Introduction to Clouds: From the Microscale to Climate
 Atmospheric Physics An Introduction to Clouds: From the Microscale to Climate Ulrike Lohmann and Alexander Beck ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science 19. 9. 2018 Ulrike Lohmann (IACETH)
Atmospheric Physics An Introduction to Clouds: From the Microscale to Climate Ulrike Lohmann and Alexander Beck ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science 19. 9. 2018 Ulrike Lohmann (IACETH)
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Atmosphere SECTION 11.1 Atmospheric Basics In your textbook, read about the composition of the atmosphere. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Most of Earth s atmosphere
Atmosphere SECTION 11.1 Atmospheric Basics In your textbook, read about the composition of the atmosphere. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement. 1. Most of Earth s atmosphere
Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans
 Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans Judith A. Curry and Peter J. Webster PROGRAM IN ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO USA
Thermodynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans Judith A. Curry and Peter J. Webster PROGRAM IN ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO BOULDER, COLORADO USA
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 3 Content: Weather Instruments Notes
 Introduction In order for meteorologists to accurately predict the weather, they take thousands of different weather measurements each day. Meteorologists need to use many tools in order to draw an accurate
Introduction In order for meteorologists to accurately predict the weather, they take thousands of different weather measurements each day. Meteorologists need to use many tools in order to draw an accurate
A "New" Mechanism for the Diurnal Variation of Convection over the Tropical Western Pacific Ocean
 A "New" Mechanism for the Diurnal Variation of Convection over the Tropical Western Pacific Ocean D. B. Parsons Atmospheric Technology Division National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Boulder,
A "New" Mechanism for the Diurnal Variation of Convection over the Tropical Western Pacific Ocean D. B. Parsons Atmospheric Technology Division National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Boulder,
Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation. Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation Water vapor's role in the Earth's weather is major. Its the product of evaporation. It is lifted up, condenses and forms clouds. It is also a greenhouse
Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation Water vapor's role in the Earth's weather is major. Its the product of evaporation. It is lifted up, condenses and forms clouds. It is also a greenhouse
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE I. Humidity A. Defined as water vapor or moisture in the air (from evaporation and condensation). B. The atmosphere gains moisture from the evaporation of water from oceans, lakes,
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE I. Humidity A. Defined as water vapor or moisture in the air (from evaporation and condensation). B. The atmosphere gains moisture from the evaporation of water from oceans, lakes,
Modulation of the diurnal cycle of tropical deep convective clouds
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L20704, doi:10.1029/2006gl027752, 2006 Modulation of the diurnal cycle of tropical deep convective clouds by the MJO Baijun Tian, 1 Duane
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L20704, doi:10.1029/2006gl027752, 2006 Modulation of the diurnal cycle of tropical deep convective clouds by the MJO Baijun Tian, 1 Duane
Chapter The transition from water vapor to liquid water is called. a. condensation b. evaporation c. sublimation d.
 Chapter-6 Multiple Choice Questions 1. The transition from water vapor to liquid water is called. a. condensation b. evaporation c. sublimation d. deposition 2. The movement of water among the great global
Chapter-6 Multiple Choice Questions 1. The transition from water vapor to liquid water is called. a. condensation b. evaporation c. sublimation d. deposition 2. The movement of water among the great global
CLIMATE. UNIT TWO March 2019
 CLIMATE UNIT TWO March 2019 OUTCOME 9.2.1Demonstrate an understanding of the basic features of Canada s landscape and climate. identify and locate major climatic regions of Canada explain the characteristics
CLIMATE UNIT TWO March 2019 OUTCOME 9.2.1Demonstrate an understanding of the basic features of Canada s landscape and climate. identify and locate major climatic regions of Canada explain the characteristics
PALM - Cloud Physics. Contents. PALM group. last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015
 PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
The TRMM Precipitation Radar s View of Shallow, Isolated Rain
 OCTOBER 2003 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE 1519 The TRMM Precipitation Radar s View of Shallow, Isolated Rain COURTNEY SCHUMACHER AND ROBERT A. HOUZE JR. Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington,
OCTOBER 2003 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE 1519 The TRMM Precipitation Radar s View of Shallow, Isolated Rain COURTNEY SCHUMACHER AND ROBERT A. HOUZE JR. Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington,
Quantifying the Role of Tropospheric Relative Humidity on the Development of Tropical Cyclones
 Quantifying the Role of Tropospheric Relative Humidity on the Development of Tropical Cyclones 1 R., 2 B. Ríos-Berríos Tang and S. S. 1University of Puerto Rico at Mayagüez 1Significant Opportunities in
Quantifying the Role of Tropospheric Relative Humidity on the Development of Tropical Cyclones 1 R., 2 B. Ríos-Berríos Tang and S. S. 1University of Puerto Rico at Mayagüez 1Significant Opportunities in
A Preliminary Assessment of the Simulation of Cloudiness at SHEBA by the ECMWF Model. Tony Beesley and Chris Bretherton. Univ.
 A Preliminary Assessment of the Simulation of Cloudiness at SHEBA by the ECMWF Model Tony Beesley and Chris Bretherton Univ. of Washington 16 June 1998 Introduction This report describes a preliminary
A Preliminary Assessment of the Simulation of Cloudiness at SHEBA by the ECMWF Model Tony Beesley and Chris Bretherton Univ. of Washington 16 June 1998 Introduction This report describes a preliminary
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
The Maritime Continent as a Prediction Barrier
 The Maritime Continent as a Prediction Barrier for the MJO Augustin Vintzileos EMC/NCEP SAIC Points to take back home. Forecast of the MJO is at, average, skillful for lead times of up to circa 2 weeks.
The Maritime Continent as a Prediction Barrier for the MJO Augustin Vintzileos EMC/NCEP SAIC Points to take back home. Forecast of the MJO is at, average, skillful for lead times of up to circa 2 weeks.
Global and Regional OSEs at JMA
 Global and Regional OSEs at JMA Yoshiaki SATO and colleagues Japan Meteorological Agency / Numerical Prediction Division 1 JMA NWP SYSTEM Global OSEs Contents AMSU A over coast, MHS over land, (related
Global and Regional OSEs at JMA Yoshiaki SATO and colleagues Japan Meteorological Agency / Numerical Prediction Division 1 JMA NWP SYSTEM Global OSEs Contents AMSU A over coast, MHS over land, (related
Temperature (T) degrees Celsius ( o C) arbitrary scale from 0 o C at melting point of ice to 100 o C at boiling point of water Also (Kelvin, K) = o C
 1 2 3 4 Temperature (T) degrees Celsius ( o C) arbitrary scale from 0 o C at melting point of ice to 100 o C at boiling point of water Also (Kelvin, K) = o C plus 273.15 0 K is absolute zero, the minimum
1 2 3 4 Temperature (T) degrees Celsius ( o C) arbitrary scale from 0 o C at melting point of ice to 100 o C at boiling point of water Also (Kelvin, K) = o C plus 273.15 0 K is absolute zero, the minimum
Transient/Eddy Flux. Transient and Eddy. Flux Components. Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Why transients/eddies matter to zonal and time means?
 Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
JMA s Ensemble Prediction System for One-month and Seasonal Predictions
 JMA s Ensemble Prediction System for One-month and Seasonal Predictions Akihiko Shimpo Japan Meteorological Agency Seasonal Prediction Modeling Team: H. Kamahori, R. Kumabe, I. Ishikawa, T. Tokuhiro, S.
JMA s Ensemble Prediction System for One-month and Seasonal Predictions Akihiko Shimpo Japan Meteorological Agency Seasonal Prediction Modeling Team: H. Kamahori, R. Kumabe, I. Ishikawa, T. Tokuhiro, S.
Parameterizing large-scale circulations based on the weak temperature gradient approximation
 Parameterizing large-scale circulations based on the weak temperature gradient approximation Bob Plant, Chimene Daleu, Steve Woolnough and thanks to GASS WTG project participants Department of Meteorology,
Parameterizing large-scale circulations based on the weak temperature gradient approximation Bob Plant, Chimene Daleu, Steve Woolnough and thanks to GASS WTG project participants Department of Meteorology,
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate
 Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Chapter 5 - Atmospheric Moisture
 Chapter 5 - Atmospheric Moisture Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt Water Water Vapor - water in a gaseous form, not droplets. Water can also achieve solid and liquid phases on Earth Temperature
Chapter 5 - Atmospheric Moisture Understanding Weather and Climate Aguado and Burt Water Water Vapor - water in a gaseous form, not droplets. Water can also achieve solid and liquid phases on Earth Temperature
Precipitation. GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 12 Ahrens: Chapter 7
 Precipitation GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 12 Ahrens: Chapter 7 Last lecture! Atmospheric stability! Condensation! Cloud condensation nuclei (CCN)! Types of clouds Precipitation! Why clouds don t fall! Terminal
Precipitation GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 12 Ahrens: Chapter 7 Last lecture! Atmospheric stability! Condensation! Cloud condensation nuclei (CCN)! Types of clouds Precipitation! Why clouds don t fall! Terminal
THUNDERSTORMS Brett Ewing October, 2003
 THUNDERSTORMS Brett Ewing October, 2003 A natural hazard that occurs often on a daily basis in the lower and mid-latitudes is thunderstorms. Thunderstorms is a weather system that can produce lightning,tornadoes,
THUNDERSTORMS Brett Ewing October, 2003 A natural hazard that occurs often on a daily basis in the lower and mid-latitudes is thunderstorms. Thunderstorms is a weather system that can produce lightning,tornadoes,
Introduction. Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere. How Much Heat Is Brought Upward By Water Vapor?
 Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere Introduction Over 70% of the planet is covered by water Water is unique in that it can simultaneously exist in all three states (solid, liquid, gas) at the same temperature
Lecture 6: Water in Atmosphere Introduction Over 70% of the planet is covered by water Water is unique in that it can simultaneously exist in all three states (solid, liquid, gas) at the same temperature
Monday 7 October 2013, Class #15
 Monday 7 October 2013, Class #15 Concepts for Today (Basics for Thermodynamics) Weather versus climate Lapse Rate (Adiabatic Lapse Rate) Ideal Gas Law Adiabatic Processes Potential Temperature Hydrostatic
Monday 7 October 2013, Class #15 Concepts for Today (Basics for Thermodynamics) Weather versus climate Lapse Rate (Adiabatic Lapse Rate) Ideal Gas Law Adiabatic Processes Potential Temperature Hydrostatic
Chapter 6. Cloud Development and Forms
 Cloud Formation Chapter 6 Cloud Development and Forms Condensation (i.e. clouds,fog) results from: Diabatic cooling (important for fog) Adiabatic cooling (important for clouds) Clouds form due to adiabatic
Cloud Formation Chapter 6 Cloud Development and Forms Condensation (i.e. clouds,fog) results from: Diabatic cooling (important for fog) Adiabatic cooling (important for clouds) Clouds form due to adiabatic
Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms
 Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms Basic radiative feedbacks (Plank, Water Vapor, Lapse-Rate Feedbacks) Ice albedo & Vegetation-Climate feedback Cloud feedback Biogeochemical feedbacks
Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms Basic radiative feedbacks (Plank, Water Vapor, Lapse-Rate Feedbacks) Ice albedo & Vegetation-Climate feedback Cloud feedback Biogeochemical feedbacks
Meteorology. I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth.
 Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
Meteorology I. The Atmosphere - the thin envelope of gas that surrounds the earth. A. Atmospheric Structure - the atmosphere is divided into five distinct layers that are based on their unique characteristics.
How to display RGB imagery by SATAID
 How to display RGB imagery by SATAID Akihiro SHIMIZU Meteorological Satellite Center (MSC), Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) Ver. 2015110500 RGB imagery on SATAID SATAID software has a function of overlapping
How to display RGB imagery by SATAID Akihiro SHIMIZU Meteorological Satellite Center (MSC), Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) Ver. 2015110500 RGB imagery on SATAID SATAID software has a function of overlapping
1. CLIMATOLOGY: 2. ATMOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY:
 What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
True or false: The atmosphere is always in hydrostatic balance. A. True B. False
 Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
How our atmosphere is heated.
 How our atmosphere is heated. How is heat transferred around our atmosphere? 1) Radiation from the sun to the Earth. 2) Conduction passes heat from the Earth to the atmosphere. 3) Convection moves heat
How our atmosphere is heated. How is heat transferred around our atmosphere? 1) Radiation from the sun to the Earth. 2) Conduction passes heat from the Earth to the atmosphere. 3) Convection moves heat
Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback
 Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Human Activities Climate Sensitivity Climate Feedback 1 Climate Sensitivity and Feedback (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) 2 Definition and Mathematic
Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Human Activities Climate Sensitivity Climate Feedback 1 Climate Sensitivity and Feedback (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) 2 Definition and Mathematic
SPI Analyze data to identify events associated with heat convection in the atmosphere. SPI Recognize the connection between the
 SPI 0607.8.1 - Analyze data to identify events associated with heat convection in the atmosphere. SPI 0607.8.2 - Recognize the connection between the sun s energy and the wind. o Energy from the Sun creates
SPI 0607.8.1 - Analyze data to identify events associated with heat convection in the atmosphere. SPI 0607.8.2 - Recognize the connection between the sun s energy and the wind. o Energy from the Sun creates
P R O L O G U E CORRELATION COEF. dsst/dt during wintertime (i.e., end of Feb. minus beginning of Dec, using 11-day averaged climatology)
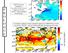 P R O L O G U E dsst/dt during wintertime (i.e., end of Feb. minus beginning of Dec, using 11-day averaged climatology) Correlation between total precipitable water (from NVAP-M) and total cloud (from
P R O L O G U E dsst/dt during wintertime (i.e., end of Feb. minus beginning of Dec, using 11-day averaged climatology) Correlation between total precipitable water (from NVAP-M) and total cloud (from
Remote Sensing of Precipitation
 Lecture Notes Prepared by Prof. J. Francis Spring 2003 Remote Sensing of Precipitation Primary reference: Chapter 9 of KVH I. Motivation -- why do we need to measure precipitation with remote sensing instruments?
Lecture Notes Prepared by Prof. J. Francis Spring 2003 Remote Sensing of Precipitation Primary reference: Chapter 9 of KVH I. Motivation -- why do we need to measure precipitation with remote sensing instruments?
