Forecasting Earthquakes and Space Weather
|
|
|
- Beverly Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 On the Ground at the AGU Conference Forecasting Earthquakes and Space Weather By Peter Martinson SAN FRANCISCO, Dec. 7, 2011 The most revolutionary and important advances in human knowledge always bear on improving the ability of human civilization, not just to survive in our Universe, but to harness more power over it through knowledge. Two such revolutionary investigations were presented on Tuesday, at the second day of the American Geophysical Union conference in San Francisco: first, the ability to forecast and warn of oncoming devastating earthquakes, up to several days in advance; and second, the ability to forecast and warn of oncoming coronal mass ejections, whose impact could wipe out entire national power grids for weeks to months. Forecasting earthquakes requires the integration of multiple parameters, measurements of a number of precursory indications emitted by impending earthquake rupture zones, several hours to days before eruption. This was emphasized by the chairman of the session on monitoring mega-earthquake precursors, NASA-Goddard scientist Dimitar Ouzounov, who listed off the usual precursory signals, such as ionospheric variations, infrared radiation anomalies, and ultra-low frequency (ULF) changes in the local geomagnetic field. He also added to the list new parameters, such as anomalous motions of the static vertical pendulum, electrical signals propagating through the ground, measurements of gravitational change with superconducting gravimeters, and others. Based on test predictions made on 26 major earthquakes between 2003 to 2009, Ouzounov presented findings showing that reproducible combinations of the multiple precursors could have been used to forecast every quake. Even the recent August 2011 earthquake in Mineral, Va., produced reliable signals across the spectrum, several days in advance. Ouzounov declared that in order for forecasting to move from research to operational, real funding would need to be provided to a relatively small group of graduate students and scientists, to assemble an historical baseline of data with which to compare an array of precursory evidence. In other words, forecasting is almost an immediate proposition, were there financial support.
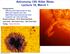
2 Dr. Ouzounov's graphic showing the dramatic increase of infrared emissions from above the epicenter of the devastating March 11 earthquake in Japan. Ouzounov was followed by one after the other presentation of the analysis of individual precursory signals emitted before large earthquakes. Katsumi Hattori of Chiba University, Japan, demonstrated the anomalous changes in ionospheric total electron content (TEC) associated with all the greater-than-magnitude-6 quakes in Japan from , and also with the devastating March 11 Tohoku earthquake. Then, on behalf of Russian scientist Sergey Pulinets who could not attend the meeting, Ouzounov presented a series of different measurements taken days before the April 2009 L'Aquilla magnitude-6.3 earthquake. The geochemical, atmospheric, very low frequency (VLF) radio, and ionospheric TEC measurements all showed anomalous changes several days before the earthquake. This may indicate a demonstration of the theory of Pulinets, of a coupling between the lithosphere, atmosphere, and ionosphere during the lead-up to an earthquake. The image that emerged was that, earthquakes are not only able to be forecasted, but they are also potentially predictable. One presenter, Vladimir Kossabokov, compared the location of the 12 deadliest earthquakes in the past decade with the Global Seismic Hazard Assessment Program maps, to show a total disagreement. Indeed, all the magnitude 7.5 or greater quakes that happened in the past decade would have been declared a "surprise" by these maps. Xuhui Shen presented a China that is moving immediately on earthquake forecasting. It is planning to launch a spacecraft in 2014, named after the Chinese scientist who invented the first seismometer, which is designed specifically to monitor changes in the ionosphere for earthquake precursors. China is also in the process of building a network of ground ionospheric sounders by 2015.
3 The resounding conclusion of this series of presentations is that, yes, indeed, earthquakes are susceptible to forecast, and the loss of hundreds of thousands of lives in the past decade alone does not need to be repeated. What is needed in addition to funding and a group of dedicated scientists working together closely in real-time is a change in fundamental beliefs about the planet we live on. Besides demonstrating that earthquakes can, in principle, be forecast, these presentations showed that our current understanding of earthquakes is limited by an overreliance on pure seismic methods. Our planet is biogeochemical, not simply geological, and these researches are the forefront in discovering what deep processes are driving surface phenomena. Space Weather Forecasting The ability to forecast significant space weather events, on the other hand, demonstrates both the need for, and the promise of, direct government involvement with the types of forecasting that requires multiple precursory measurements. A NASA press conference was given by five scientists involved with forecasting space weather, to describe the state of the art, and the implications of forecasting. By "Space Weather," is meant the impact upon our planet's magnetic field by various transient emissions from the Sun, and the effects upon our satellites, electricity transmission systems, and other systems that depend upon electricity to function. The most important types of this solar radiation are in the form of radiation storms (bursts of energetic particles from active regions of the Sun), coronal mass ejections (large emissions of magnetically charged matter from the corona), and high speed streams of the solar wind. The press conference panelists drew an image of what it is like living within the outer atmosphere of a star, one that has been going through a mood shift recently. The recent solar minimum was one of the longest on record, but as each of the panelists noted in turn, devastating events can come from a relatively quiet Sun. The 1859 Carrington Event, which would wipe out entire national grids if it happened today, occurred during a weaker solar cycle than the last one. Until about 10 years ago, the results of transient solar events on our electrical systems had become well understood, although the ability to forecast them was about equal to shooting in the dark. All of these radiations had been either difficult or impossible to see before they hit the Earth. Now, with a growing array of solar observatories, we can begin to model, and perhaps track, the progress of impending radiations that could endanger our planet. The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) was launched in 1995, and has given us the first clear space view of the initial stages of a CME eruption. The GOES spacecraft are equipped to register emissions of high energy X-ray flares as soon as 8 minutes after eruption. The two STEREO spacecraft provide the first three-dimensional view of the Sun, and can show us active regions before they rotate towards the Earth, while at the same time providing the first three dimensional imagery of coronal mass ejections as they occur.
4 Artist's depiction of a GOES satellite. These satellites provide continuous monitoring, orbiting in a geosynchronous orbit that matches the Earth's rotation. These spacecraft, among a growing array of others, provide the initial weathervane data to be entered into serious modeling software at Goddard Space Flight Center to project the prospective tracks of the slower radiations from the Sun, such as high-speed solar wind streams and coronal mass ejections. The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), launched in 2010, provides high-resolution imagery in several bands of radiation, to help us see the mechanisms leading up to solar eruptions in fine detail. Discoveries made from looking at these data have helped improve the models used for tracking storms before they hit the Earth. For CMEs, our models have improved significantly, such that they are now being issued through NOAA's National Weather Service. Indeed, these scientists claim that the ability to forecast the impact of coronal mass ejections is at about the same place as scientific weather forecasting was in the early days, and will only improve with the production of improved satellite and computer technology. At this point, only a few minutes of warning are possible for other types of solar events than CMEs, such as radiation storms, which hit only a few minutes after energetic particles are ejected from the Sun. Warning for these storms comes from measurements taken by our Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE), located at the L1 libration point about 1.5 million miles away from the Earth towards the Sun. ACE can register the dramatically increased flux of energetic electrons and protons only a few minutes before they impact our planetary system, where they potentially could blow out satellites. With the recent spacecraft additions, improvements in "solar storm tracks" are coming steadily. Rodney Viereck, the director of NOAA's Space Weather Prediction test bed, pointed out that, as the current solar cycle began to crank up, the number of subscribers to NOAA space weather forecasts has begun to increase exponentially, now over 19,000 customers. The immediate next steps, according to Michael Hesse, chief of the Goddard Space Weather Laboratory, include getting spacecraft up that can monitor
5 all sides of the Sun continuously, instead of only intermittently, like the STEREO spacecraft. In reality, both modes of forecasting earthquakes and the impact of solar emissions require the same mode of thinking. Both emit a variety of very faint signals minutes to days before impact, many of which signals we recognize, and undoubtedly other signals of which we are as yet unaware. The signals are very faint, and require very sensitive instrumentation to measure. The signals are also produced by other, usually benign, sources. Therefore, in order to eliminate the benign signals from the ones that indicate danger, it is necessary to combine several of the sensed signals in a triangulation. In other words, just because someone may smell like an ape, doesn't mean he is an ape. We are getting closer to the reality of not just understanding, but controlling our near space environment, to the effect of being able not just to increase our population, but to protect the existing population from currently uncontrollable, devastating events. Expect more from this conference!
Sun Earth Connection Missions
 Sun Earth Connection Missions ACE Advanced Composition Explorer The Earth is constantly bombarded with a stream of accelerated particles arriving not only from the Sun, but also from interstellar and galactic
Sun Earth Connection Missions ACE Advanced Composition Explorer The Earth is constantly bombarded with a stream of accelerated particles arriving not only from the Sun, but also from interstellar and galactic
Space Weather and Satellite System Interaction
 Space Engineering International Course, Kyutech, 4 th Quarter Semester 2017 Space Weather and Satellite System Interaction Lecture 2: Space Weather Concept, Reporting and Forecasting Assoc. Prof. Ir. Dr.
Space Engineering International Course, Kyutech, 4 th Quarter Semester 2017 Space Weather and Satellite System Interaction Lecture 2: Space Weather Concept, Reporting and Forecasting Assoc. Prof. Ir. Dr.
Geomagnetic storms. Measurement and forecasting
 Geomagnetic storms. Measurement and forecasting Anna Gustavsson 17 October 2006 Project of the Space Physics Course 2006 Umeå University 1 Introduction Effects of magnetic storms on technology Geomagnetic
Geomagnetic storms. Measurement and forecasting Anna Gustavsson 17 October 2006 Project of the Space Physics Course 2006 Umeå University 1 Introduction Effects of magnetic storms on technology Geomagnetic
Tracking Solar Eruptions to Their Impact on Earth Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA September 2016 Bonus
 Tracking Solar Eruptions to Their Impact on Earth Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA September 2016 Bonus In June 2015, the Sun emitted several M-Class flares over a 2-day period. These flares were concurrent with
Tracking Solar Eruptions to Their Impact on Earth Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA September 2016 Bonus In June 2015, the Sun emitted several M-Class flares over a 2-day period. These flares were concurrent with
Geomagnetic Disturbances (GMDs) History and Prediction
 Geomagnetic Disturbances (GMDs) History and Prediction J. Patrick Donohoe, Ph.D., P.E. Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Mississippi State University Box 9571 Miss. State, MS 39762 donohoe@ece.msstate.edu
Geomagnetic Disturbances (GMDs) History and Prediction J. Patrick Donohoe, Ph.D., P.E. Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Mississippi State University Box 9571 Miss. State, MS 39762 donohoe@ece.msstate.edu
The Magnetic Sun. CESAR s Booklet
 The Magnetic Sun CESAR s Booklet 1 Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium Most of the planets in our Solar system are enclosed by huge magnetic structures, named magnetospheres
The Magnetic Sun CESAR s Booklet 1 Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium Most of the planets in our Solar system are enclosed by huge magnetic structures, named magnetospheres
THE SOLAR WIND & SOLAR VARIABILITY
 The Sun-Earth System: CONTENTS AN OVERVIEW The Stars Around Us 1 Our Dependence on the Sun 3 The Sun s Inconstancy 3 Intruders from Afar 5 What Gets By 5 Voyages of Discovery in an Age of Exploration 6
The Sun-Earth System: CONTENTS AN OVERVIEW The Stars Around Us 1 Our Dependence on the Sun 3 The Sun s Inconstancy 3 Intruders from Afar 5 What Gets By 5 Voyages of Discovery in an Age of Exploration 6
Acceleration of the Solar Wind
 From Sun to Mud: Solar and Space Physics for the UG Classroom Acceleration of the Andrew Jordan All images from SOHO spacecraft This presentation helps introductory physics students apply their skills
From Sun to Mud: Solar and Space Physics for the UG Classroom Acceleration of the Andrew Jordan All images from SOHO spacecraft This presentation helps introductory physics students apply their skills
Solar Observation Class Project
 Name: School: Grade or Level: Lesson Plan #: Date: Object Solar Observation Class Project The object of this classroom exercise to involve as individuals or as teams, students in the actual astronomical
Name: School: Grade or Level: Lesson Plan #: Date: Object Solar Observation Class Project The object of this classroom exercise to involve as individuals or as teams, students in the actual astronomical
Geomagnetic Disturbance Report Reeve Observatory
 Event type: Various geomagnetic disturbances including coronal hole high-speed stream, coronal mass ejection, sudden impulse and reverse shock effects Background: This background section defines the various
Event type: Various geomagnetic disturbances including coronal hole high-speed stream, coronal mass ejection, sudden impulse and reverse shock effects Background: This background section defines the various
Extended Missions. Dr. Art Poland Heliophysics Senior Review Chair George Mason University
 Extended Missions Dr. Art Poland Heliophysics Senior Review Chair George Mason University My Experience Experiment scientist on Skylab 1973- Experiment scientist on SMM 1980- US project Scientist for the
Extended Missions Dr. Art Poland Heliophysics Senior Review Chair George Mason University My Experience Experiment scientist on Skylab 1973- Experiment scientist on SMM 1980- US project Scientist for the
Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge. Chi Wang. National Space Science Center, CAS
 Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge Chi Wang National Space Science Center, CAS Feb.25, 2014 Contents Significant advances from the past decade Key scientific challenges Future missions
Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge Chi Wang National Space Science Center, CAS Feb.25, 2014 Contents Significant advances from the past decade Key scientific challenges Future missions
High energy particles from the Sun. Arto Sandroos Sun-Earth connections
 High energy particles from the Sun Arto Sandroos Sun-Earth connections 25.1.2006 Background In addition to the solar wind, there are also particles with higher energies emerging from the Sun. First observations
High energy particles from the Sun Arto Sandroos Sun-Earth connections 25.1.2006 Background In addition to the solar wind, there are also particles with higher energies emerging from the Sun. First observations
Solar Energetic Particles measured by AMS-02
 Solar Energetic Particles measured by AMS-02 Physics and Astronomy Department, University of Hawaii at Manoa, 96822, HI, US E-mail: bindi@hawaii.edu AMS-02 collaboration The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer
Solar Energetic Particles measured by AMS-02 Physics and Astronomy Department, University of Hawaii at Manoa, 96822, HI, US E-mail: bindi@hawaii.edu AMS-02 collaboration The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer
Geomagnetic Disturbance Report Reeve Observatory
 Event type: Geomagnetic disturbances due to recurrent coronal hole high-speed stream Background: This background section defines the events covered. A coronal hole is a large dark region of less dense
Event type: Geomagnetic disturbances due to recurrent coronal hole high-speed stream Background: This background section defines the events covered. A coronal hole is a large dark region of less dense
INTERPLANETARY ASPECTS OF SPACE WEATHER
 INTERPLANETARY ASPECTS OF SPACE WEATHER Richard G. Marsden Research & Scientific Support Dept. of ESA, ESTEC, P.O. Box 299, 2200 AG Noordwijk, NL, Email: Richard.Marsden@esa.int ABSTRACT/RESUME Interplanetary
INTERPLANETARY ASPECTS OF SPACE WEATHER Richard G. Marsden Research & Scientific Support Dept. of ESA, ESTEC, P.O. Box 299, 2200 AG Noordwijk, NL, Email: Richard.Marsden@esa.int ABSTRACT/RESUME Interplanetary
1.3j describe how astronomers observe the Sun at different wavelengths
 1.3j describe how astronomers observe the Sun at different wavelengths 1.3k demonstrate an understanding of the appearance of the Sun at different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including
1.3j describe how astronomers observe the Sun at different wavelengths 1.3k demonstrate an understanding of the appearance of the Sun at different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including
The Solar Wind Space physics 7,5hp
 The Solar Wind Space physics 7,5hp Teknisk fysik '07 1 Contents History... 3 Introduction... 3 Two types of solar winds... 4 Effects of the solar wind... 5 Magnetospheres... 5 Atmospheres... 6 Solar storms...
The Solar Wind Space physics 7,5hp Teknisk fysik '07 1 Contents History... 3 Introduction... 3 Two types of solar winds... 4 Effects of the solar wind... 5 Magnetospheres... 5 Atmospheres... 6 Solar storms...
About the Van Allen Probes Mission
 Van Allen Probes Exploring th About the Van Allen Probes Mission To help us understand how Earth responds to changes in the sun s energy and how that response affects life and society, NASA launched the
Van Allen Probes Exploring th About the Van Allen Probes Mission To help us understand how Earth responds to changes in the sun s energy and how that response affects life and society, NASA launched the
Solar-terrestrial relation and space weather. Mateja Dumbović Hvar Observatory, University of Zagreb Croatia
 Solar-terrestrial relation and space weather Mateja Dumbović Hvar Observatory, University of Zagreb Croatia Planets Comets Solar wind Interplanetary magnetic field Cosmic rays Satellites Astronauts HELIOSPHERE
Solar-terrestrial relation and space weather Mateja Dumbović Hvar Observatory, University of Zagreb Croatia Planets Comets Solar wind Interplanetary magnetic field Cosmic rays Satellites Astronauts HELIOSPHERE
Solar eruptive phenomena
 Solar eruptive phenomena Andrei Zhukov Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence SIDC, Royal Observatory of Belgium 26/01/2018 1 Eruptive solar activity Solar activity exerts continous influence on the solar
Solar eruptive phenomena Andrei Zhukov Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence SIDC, Royal Observatory of Belgium 26/01/2018 1 Eruptive solar activity Solar activity exerts continous influence on the solar
STCE Newsletter. 7 Dec Dec 2015
 Published by the STCE - this issue : 18 Dec 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
Published by the STCE - this issue : 18 Dec 2015. Available online at http://www.stce.be/newsletter/. The Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence (STCE) is a collaborative network of the Belgian Institute
8.2 The Sun pg Stars emit electromagnetic radiation, which travels at the speed of light.
 8.2 The Sun pg. 309 Key Concepts: 1. Careful observation of the night sky can offer clues about the motion of celestial objects. 2. Celestial objects in the Solar System have unique properties. 3. Some
8.2 The Sun pg. 309 Key Concepts: 1. Careful observation of the night sky can offer clues about the motion of celestial objects. 2. Celestial objects in the Solar System have unique properties. 3. Some
Radio Observations and Space Weather Research
 Radio Observations and Space Weather Research Jasmina Magdalenić Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence SIDC, Royal Observatory of Belgium What is space weather and why is it important? Eruptive processes:
Radio Observations and Space Weather Research Jasmina Magdalenić Solar-Terrestrial Centre of Excellence SIDC, Royal Observatory of Belgium What is space weather and why is it important? Eruptive processes:
Lecture 17 The Sun October 31, 2018
 Lecture 17 The Sun October 31, 2018 1 2 Exam 2 Information Bring a #2 pencil! Bring a calculator. No cell phones or tablets allowed! Contents: Free response problems (2 questions, 10 points) True/False
Lecture 17 The Sun October 31, 2018 1 2 Exam 2 Information Bring a #2 pencil! Bring a calculator. No cell phones or tablets allowed! Contents: Free response problems (2 questions, 10 points) True/False
The Structure of the Sun. CESAR s Booklet
 How stars work In order to have a stable star, the energy it emits must be the same as it can produce. There must be an equilibrium. The main source of energy of a star it is nuclear fusion, especially
How stars work In order to have a stable star, the energy it emits must be the same as it can produce. There must be an equilibrium. The main source of energy of a star it is nuclear fusion, especially
An Introduction to Space Weather. J. Burkepile High Altitude Observatory / NCAR
 An Introduction to Space Weather J. Burkepile High Altitude Observatory / NCAR What is Space Weather? Space Weather refers to conditions in interplanetary space, produced by the Sun, that can disrupt
An Introduction to Space Weather J. Burkepile High Altitude Observatory / NCAR What is Space Weather? Space Weather refers to conditions in interplanetary space, produced by the Sun, that can disrupt
1 A= one Angstrom = 1 10 cm
 Our Star : The Sun )Chapter 10) The sun is hot fireball of gas. We observe its outer surface called the photosphere: We determine the temperature of the photosphere by measuring its spectrum: The peak
Our Star : The Sun )Chapter 10) The sun is hot fireball of gas. We observe its outer surface called the photosphere: We determine the temperature of the photosphere by measuring its spectrum: The peak
The Project. National Schools Observatory
 Sunspots The Project This project is devised to give students a good understanding of the structure and magnetic field of the Sun and how this effects solar activity. Students will work with sunspot data
Sunspots The Project This project is devised to give students a good understanding of the structure and magnetic field of the Sun and how this effects solar activity. Students will work with sunspot data
Activities of the Japanese Space Weather Forecast Center at Communications Research Laboratory
 J. RADIAT. RES., 43: SUPPL., S53 S57 (2002) Activities of the Japanese Space Weather Forecast Center at Communications Research Laboratory SHINICHI WATARI 1 * and FUMIHIKO TOMITA 1 Space weather / ISES/SEP
J. RADIAT. RES., 43: SUPPL., S53 S57 (2002) Activities of the Japanese Space Weather Forecast Center at Communications Research Laboratory SHINICHI WATARI 1 * and FUMIHIKO TOMITA 1 Space weather / ISES/SEP
Solar Activity during the Rising Phase of Solar Cycle 24
 International Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 213, 3, 212-216 http://dx.doi.org/1.4236/ijaa.213.3325 Published Online September 213 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijaa) Solar Activity during the
International Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 213, 3, 212-216 http://dx.doi.org/1.4236/ijaa.213.3325 Published Online September 213 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijaa) Solar Activity during the
SOLAR WIND PROTON DENSITY INCREASE AND GEOMAGNETIC BACKGROUND ANOMALIES BEFORE STRONG M6+ EARTHQUAKES. V. Straser*, G. Cataldi
 SOLAR WIND PROTON DENSITY INCREASE AND GEOMAGNETIC BACKGROUND ANOMALIES BEFORE STRONG M6+ EARTHQUAKES V. Straser*, G. Cataldi *International Earthquake and Volcano Prediction Center E-mail: valentino.straser@alice.it
SOLAR WIND PROTON DENSITY INCREASE AND GEOMAGNETIC BACKGROUND ANOMALIES BEFORE STRONG M6+ EARTHQUAKES V. Straser*, G. Cataldi *International Earthquake and Volcano Prediction Center E-mail: valentino.straser@alice.it
Sun s Properties. Overview: The Sun. Composition of the Sun. Sun s Properties. The outer layers. Photosphere: Surface. Nearest.
 Overview: The Sun Properties of the Sun Sun s outer layers Photosphere Chromosphere Corona Solar Activity Sunspots & the sunspot cycle Flares, prominences, CMEs, aurora Sun s Interior The Sun as an energy
Overview: The Sun Properties of the Sun Sun s outer layers Photosphere Chromosphere Corona Solar Activity Sunspots & the sunspot cycle Flares, prominences, CMEs, aurora Sun s Interior The Sun as an energy
Multi-parameter observations of atmospheric pre-earthquake signals and their validation: Potential for Future
 Multi-parameter observations of atmospheric pre-earthquake signals and their validation: Potential for Future Dimitar Ouzounov and Menas Kafatos Chapman University, Orange, CA CSEP Workshop, May 5-7, 2013
Multi-parameter observations of atmospheric pre-earthquake signals and their validation: Potential for Future Dimitar Ouzounov and Menas Kafatos Chapman University, Orange, CA CSEP Workshop, May 5-7, 2013
Space environment (natural and artificial) Realtime solar activity and space environment information for spacecraft operation
 ISO 2008 All rights reserved ISO TC 20/SC 14 N873 Date: 2012-07-31 ISO/CDV 16709 ISO TC 20/SC 14/WG 4 Secretariat: Space environment (natural and artificial) Realtime solar activity and space environment
ISO 2008 All rights reserved ISO TC 20/SC 14 N873 Date: 2012-07-31 ISO/CDV 16709 ISO TC 20/SC 14/WG 4 Secretariat: Space environment (natural and artificial) Realtime solar activity and space environment
Toward Interplanetary Space Weather: Strategies for Manned Missions to Mars
 centre for fusion, space and astrophysics Toward Interplanetary Space Weather: Strategies for Manned Missions to Mars Presented by: On behalf of: Jennifer Harris Claire Foullon, E. Verwichte, V. Nakariakov
centre for fusion, space and astrophysics Toward Interplanetary Space Weather: Strategies for Manned Missions to Mars Presented by: On behalf of: Jennifer Harris Claire Foullon, E. Verwichte, V. Nakariakov
 1 2 3 US Air Force 557 th Weather Wing maintains a website with many operational products both on terrestrial as on space weather. The operational holy grail for the military are stoplight charts, indicating
1 2 3 US Air Force 557 th Weather Wing maintains a website with many operational products both on terrestrial as on space weather. The operational holy grail for the military are stoplight charts, indicating
Solar Activity The Solar Wind
 Solar Activity The Solar Wind The solar wind is a flow of particles away from the Sun. They pass Earth at speeds from 400 to 500 km/s. This wind sometimes gusts up to 1000 km/s. Leaves Sun at highest speeds
Solar Activity The Solar Wind The solar wind is a flow of particles away from the Sun. They pass Earth at speeds from 400 to 500 km/s. This wind sometimes gusts up to 1000 km/s. Leaves Sun at highest speeds
The Sun sends the Earth:
 The Sun sends the Earth: Solar Radiation - peak wavelength.visible light - Travels at the speed of light..takes 8 minutes to reach Earth Solar Wind, Solar flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections of Plasma (ionized
The Sun sends the Earth: Solar Radiation - peak wavelength.visible light - Travels at the speed of light..takes 8 minutes to reach Earth Solar Wind, Solar flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections of Plasma (ionized
Solar Dynamics Affecting Skywave Communications
 Solar Dynamics Affecting Skywave Communications Ken Larson KJ6RZ October 2010 1 Page Subject 3 1.0 Introduction 3 2.0 Structure of the Sun 3 2.1 Core 3 2.2 Radiation Zone 4 2.3 Convection Zone 4 2.4 Photosphere
Solar Dynamics Affecting Skywave Communications Ken Larson KJ6RZ October 2010 1 Page Subject 3 1.0 Introduction 3 2.0 Structure of the Sun 3 2.1 Core 3 2.2 Radiation Zone 4 2.3 Convection Zone 4 2.4 Photosphere
Astronomy 150: Killer Skies. Lecture 18, March 1
 Assignments: Astronomy 150: Killer Skies HW6 due next Friday at start of class HW5 and Computer Lab 1 due Night Observing continues next week Lecture 18, March 1 Computer Lab 1 due next Friday Guest Lecturer:
Assignments: Astronomy 150: Killer Skies HW6 due next Friday at start of class HW5 and Computer Lab 1 due Night Observing continues next week Lecture 18, March 1 Computer Lab 1 due next Friday Guest Lecturer:
Space Weather. S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT
![Space Weather. S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT Space Weather. S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT](/thumbs/89/99030303.jpg) Space Weather S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT Outline Overview of Space Weather I. Space disasters II. Space weather III. Sun IV. Solar wind (interplanetary space) V. Magnetosphere VI. Recent Space
Space Weather S. Abe and A. Ikeda [1] ICSWSE [2] KNCT Outline Overview of Space Weather I. Space disasters II. Space weather III. Sun IV. Solar wind (interplanetary space) V. Magnetosphere VI. Recent Space
Astronomy Chapter 12 Review
 Astronomy Chapter 12 Review Approximately how massive is the Sun as compared to the Earth? A. 100 times B. 300 times C. 3000 times D. 300,000 times E. One million times Approximately how massive is the
Astronomy Chapter 12 Review Approximately how massive is the Sun as compared to the Earth? A. 100 times B. 300 times C. 3000 times D. 300,000 times E. One million times Approximately how massive is the
Sun-Earth Connection Missions
 ACE (1997 ) Cosmic and Heliospheric Study of the physics and chemistry Advanced Composition Explorer Learning Center of the solar corona, the solar wind, http://helios.gsfc.nasa.gov/ace/ http://helios.gsfc.nasa.gov
ACE (1997 ) Cosmic and Heliospheric Study of the physics and chemistry Advanced Composition Explorer Learning Center of the solar corona, the solar wind, http://helios.gsfc.nasa.gov/ace/ http://helios.gsfc.nasa.gov
MAGNETISM QUIZ MAGNETISM
 MAGNETISM QUIZ MAGNETISM 1. What force steers particles in a supercollider? A. Centrifugal B. Electric C. Magnetic D. Gravity 2. What can we learn from the paths of charged particles after a supercollider
MAGNETISM QUIZ MAGNETISM 1. What force steers particles in a supercollider? A. Centrifugal B. Electric C. Magnetic D. Gravity 2. What can we learn from the paths of charged particles after a supercollider
michele piana dipartimento di matematica, universita di genova cnr spin, genova
 michele piana dipartimento di matematica, universita di genova cnr spin, genova first question why so many space instruments since we may have telescopes on earth? atmospheric blurring if you want to
michele piana dipartimento di matematica, universita di genova cnr spin, genova first question why so many space instruments since we may have telescopes on earth? atmospheric blurring if you want to
Operational Impacts of Space Weather
 Operational Impacts of Space Weather R. Lambour, A. J. Coster, R. Clouser, L. E. Thornton, J. Sharma, and A. Cott 2001 Space Control Conference 3 April 2001 2001 Space Control Conf. -1 Outline Introduction
Operational Impacts of Space Weather R. Lambour, A. J. Coster, R. Clouser, L. E. Thornton, J. Sharma, and A. Cott 2001 Space Control Conference 3 April 2001 2001 Space Control Conf. -1 Outline Introduction
Hydrogen Lines. What can we learn from light? Spectral Classification. Visible Hydrogen Spectrum Lines: Series. Actual Spectrum from SDSS
 What can we learn from light? Hydrogen Lines Temperature Energy Chemical Composition Speed towards or away from us All from the! Lower E, Lower f, λ Visible! Higher E, Higher f, λ Visible Hydrogen Spectrum
What can we learn from light? Hydrogen Lines Temperature Energy Chemical Composition Speed towards or away from us All from the! Lower E, Lower f, λ Visible! Higher E, Higher f, λ Visible Hydrogen Spectrum
Solar Flares and CMEs. Solar Physics 1
 Solar Flares and CMEs Solar Physics 1 What is a solar flare? What is a CME? A solar flare is a sudden eruption of energetic charged particles from the Sun s corona. A coronal mass ejection (CME) is, by
Solar Flares and CMEs Solar Physics 1 What is a solar flare? What is a CME? A solar flare is a sudden eruption of energetic charged particles from the Sun s corona. A coronal mass ejection (CME) is, by
A Closer Look at the Sun
 Our Star A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning Why was the Sun s energy source a major mystery? Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun s structure? Why was the Sun s energy source a major mystery?
Our Star A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning Why was the Sun s energy source a major mystery? Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun s structure? Why was the Sun s energy source a major mystery?
Solar Wind Ion Composition Measurements: Direct Measurements of Properties of the Corona
 Solar Wind Ion Composition Measurements: Direct Measurements of Properties of the Corona White Paper Submitted to the Decadal Survey Panel on Solar and Heliospheric Physics November 12, 2010 Stefano A.
Solar Wind Ion Composition Measurements: Direct Measurements of Properties of the Corona White Paper Submitted to the Decadal Survey Panel on Solar and Heliospheric Physics November 12, 2010 Stefano A.
An x-ray image of teeth. Can you see the filling?
 X-Rays APA National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Science Mission Directorate. (2010). X-Rays. Retrieved December 12, 2012, from Mission:Science website: http://missionscience.nasa.gov /ems/11_xrays.html
X-Rays APA National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Science Mission Directorate. (2010). X-Rays. Retrieved December 12, 2012, from Mission:Science website: http://missionscience.nasa.gov /ems/11_xrays.html
Convection causes granules. Photosphere isn t actually smooth! Granules Up-Close: like boiling water. Corona or of the Sun. Chromosphere: sphere of
 Overview Properties of the Sun Sun s outer layers Photosphere Chromosphere Corona Solar Activity Sunspots & the sunspot cycle Flares, prominences, CMEs, aurora Sun s Interior The Sun as an energy source
Overview Properties of the Sun Sun s outer layers Photosphere Chromosphere Corona Solar Activity Sunspots & the sunspot cycle Flares, prominences, CMEs, aurora Sun s Interior The Sun as an energy source
First European Space Weather Week. Space weather - atmospheres, drag, global change future needs. 29 November-3 December 2004
 First European Space Weather Week Space weather - atmospheres, drag, global change future needs 29 November-3 December 2004 Timescales of important phenomena Weather Climate No single statement of requirement
First European Space Weather Week Space weather - atmospheres, drag, global change future needs 29 November-3 December 2004 Timescales of important phenomena Weather Climate No single statement of requirement
Directed Reading. Section: Viewing the Universe THE VALUE OF ASTRONOMY. Skills Worksheet. 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Chapter 10 Our Star. X-ray. visible
 Chapter 10 Our Star X-ray visible Radius: 6.9 10 8 m (109 times Earth) Mass: 2 10 30 kg (300,000 Earths) Luminosity: 3.8 10 26 watts (more than our entire world uses in 1 year!) Why does the Sun shine?
Chapter 10 Our Star X-ray visible Radius: 6.9 10 8 m (109 times Earth) Mass: 2 10 30 kg (300,000 Earths) Luminosity: 3.8 10 26 watts (more than our entire world uses in 1 year!) Why does the Sun shine?
Chapter 8 Geospace 1
 Chapter 8 Geospace 1 Previously Sources of the Earth's magnetic field. 2 Content Basic concepts The Sun and solar wind Near-Earth space About other planets 3 Basic concepts 4 Plasma The molecules of an
Chapter 8 Geospace 1 Previously Sources of the Earth's magnetic field. 2 Content Basic concepts The Sun and solar wind Near-Earth space About other planets 3 Basic concepts 4 Plasma The molecules of an
The Sun. Never look directly at the Sun, especially NOT through an unfiltered telescope!!
 The Sun Introduction We will meet in class for a brief discussion and review of background material. We will then go outside for approximately 1 hour of telescope observing. The telescopes will already
The Sun Introduction We will meet in class for a brief discussion and review of background material. We will then go outside for approximately 1 hour of telescope observing. The telescopes will already
Space Weather Awareness in the Arctic. Torsten Neubert Head of Section for Solar System Physics
 Space Weather Awareness in the Arctic Torsten Neubert Head of Section for Solar System Physics Technology in the Arctic There is significant potential Resources Tourism helped by receding ocean ice There
Space Weather Awareness in the Arctic Torsten Neubert Head of Section for Solar System Physics Technology in the Arctic There is significant potential Resources Tourism helped by receding ocean ice There
Living in a Star. Sarah Gibson (NCAR/HAO)
 Living in a Star Sarah Gibson (NCAR/HAO) 3D real-time astronomy Solar eruption (CME) Earth s magnetosphere We are observing a stellar system from within What we see may impact us in near-real time Unescapably
Living in a Star Sarah Gibson (NCAR/HAO) 3D real-time astronomy Solar eruption (CME) Earth s magnetosphere We are observing a stellar system from within What we see may impact us in near-real time Unescapably
As Sun Storms Ramp Up, Electric Grid Braces for Impact
 National Geographic Daily News As Sun Storms Ramp Up, Electric Grid Braces for Impact Electric transformer failures, like this dramatic one, are a risk if solar storms create extra electrical currents
National Geographic Daily News As Sun Storms Ramp Up, Electric Grid Braces for Impact Electric transformer failures, like this dramatic one, are a risk if solar storms create extra electrical currents
Rationale for a European Space Weather Programme
 Rationale for a European Space Weather Programme Hannu Koskinen Finnish Meteorological Institute ESWS Final Presentation ESTEC, 6 December, 2001 Scope WP 300 of ESWS: Establishment of detailed rationale
Rationale for a European Space Weather Programme Hannu Koskinen Finnish Meteorological Institute ESWS Final Presentation ESTEC, 6 December, 2001 Scope WP 300 of ESWS: Establishment of detailed rationale
Forecasting Solar Energetic Particle Events Using Changes in Electron Flux
 Forecasting Solar Energetic Particle Events Using Changes in Electron Flux Sierra Ashley, University of Denver Mentor: Dr. Lisa Winter, Atmospheric and Environmental Research SOHO (NASA /ESA) Background
Forecasting Solar Energetic Particle Events Using Changes in Electron Flux Sierra Ashley, University of Denver Mentor: Dr. Lisa Winter, Atmospheric and Environmental Research SOHO (NASA /ESA) Background
The Sun ASTR /17/2014
 The Sun ASTR 101 11/17/2014 1 Radius: 700,000 km (110 R ) Mass: 2.0 10 30 kg (330,000 M ) Density: 1400 kg/m 3 Rotation: Differential, about 25 days at equator, 30 days at poles. Surface temperature: 5800
The Sun ASTR 101 11/17/2014 1 Radius: 700,000 km (110 R ) Mass: 2.0 10 30 kg (330,000 M ) Density: 1400 kg/m 3 Rotation: Differential, about 25 days at equator, 30 days at poles. Surface temperature: 5800
1-4-1A. Sun Structure
 Sun Structure A cross section of the Sun reveals its various layers. The Core is the hottest part of the internal sun and is the location of nuclear fusion. The heat and energy produced in the core is
Sun Structure A cross section of the Sun reveals its various layers. The Core is the hottest part of the internal sun and is the location of nuclear fusion. The heat and energy produced in the core is
If the Sun is so quiet, why is the Earth still ringing?
 If the Sun is so quiet, why is the Earth still ringing? Sarah Gibson Talk outline Overview of differences between current and past solar minima (with extreme bias towards comparison to space age cycles!)
If the Sun is so quiet, why is the Earth still ringing? Sarah Gibson Talk outline Overview of differences between current and past solar minima (with extreme bias towards comparison to space age cycles!)
COSMIC RAYS DAY INTRODUCTION TO COSMIC RAYS WINDWARD COMMUNITY COLLEGE - SEPTEMBER 26, 2015 VERONICA BINDI - UNIVERSITY OH HAWAII
 COSMIC RAYS DAY WINDWARD COMMUNITY COLLEGE - SEPTEMBER 26, 2015 VERONICA BINDI - UNIVERSITY OH HAWAII INTRODUCTION TO COSMIC RAYS MAJOR QUESTIONS: Are there forms of matter in the Universe that do not
COSMIC RAYS DAY WINDWARD COMMUNITY COLLEGE - SEPTEMBER 26, 2015 VERONICA BINDI - UNIVERSITY OH HAWAII INTRODUCTION TO COSMIC RAYS MAJOR QUESTIONS: Are there forms of matter in the Universe that do not
AUTOMATIC PREDICTION OF SOLAR FLARES USING A NEURAL NETWORK. James Negus University of Chicago Mentor: Andrew Jones LASP
 AUTOMATIC PREDICTION OF SOLAR FLARES USING A NEURAL NETWORK James Negus University of Chicago Mentor: Andrew Jones LASP SOLAR FLARE A flare is defined as a sudden, rapid, and intense variation in brightness.
AUTOMATIC PREDICTION OF SOLAR FLARES USING A NEURAL NETWORK James Negus University of Chicago Mentor: Andrew Jones LASP SOLAR FLARE A flare is defined as a sudden, rapid, and intense variation in brightness.
Interdisciplinary Framework to Reveal Earthquake Precursory Phenomena in Seismically Active Areas
 Interdisciplinary Framework to Reveal Earthquake Precursory Phenomena in Seismically Active Areas D.Ouzounov 1,2, S.Pulinets 3, M.Kafatos 1, P.Taylor 2 1 Chapman University, Orange, CA 92866, USA 2 NASA
Interdisciplinary Framework to Reveal Earthquake Precursory Phenomena in Seismically Active Areas D.Ouzounov 1,2, S.Pulinets 3, M.Kafatos 1, P.Taylor 2 1 Chapman University, Orange, CA 92866, USA 2 NASA
NASA s STEREO Mission
 NASA s STEREO Mission J.B. Gurman STEREO Project Scientist W.T. Thompson STEREO Chief Observer Solar Physics Laboratory, Helophysics Division NASA Goddard Space Flight Center 1 The STEREO Mission Science
NASA s STEREO Mission J.B. Gurman STEREO Project Scientist W.T. Thompson STEREO Chief Observer Solar Physics Laboratory, Helophysics Division NASA Goddard Space Flight Center 1 The STEREO Mission Science
Is There Really Weather in Space?
 SOHO, NASA/ESA Is There Really Weather in Space? Looking at the sky with the naked eye, the Sun seems static, placid, constant. From the ground, the only noticeable variations in the Sun are its location
SOHO, NASA/ESA Is There Really Weather in Space? Looking at the sky with the naked eye, the Sun seems static, placid, constant. From the ground, the only noticeable variations in the Sun are its location
A Correlative Study of Climate Changes and Solar Activity
 10 A Correlative Study of Climate Changes and Solar Activity S. R. Lahauriya and A. P. Mishra Department of Physics, Govt. P. G. Autonomous College, Datia (M.P.) Abstract:- The Sun is ultimate source of
10 A Correlative Study of Climate Changes and Solar Activity S. R. Lahauriya and A. P. Mishra Department of Physics, Govt. P. G. Autonomous College, Datia (M.P.) Abstract:- The Sun is ultimate source of
AIA DATA ANALYSIS OVERVIEW OF THE AIA INSTRUMENT
 AIA DATA ANALYSIS OVERVIEW OF THE AIA INSTRUMENT SDO SUMMER SCHOOL ~ August 2010 ~ Yunnan, China Marc DeRosa (LMSAL) ~ derosa@lmsal.com WHAT IS SDO? The goal of Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is to understand:
AIA DATA ANALYSIS OVERVIEW OF THE AIA INSTRUMENT SDO SUMMER SCHOOL ~ August 2010 ~ Yunnan, China Marc DeRosa (LMSAL) ~ derosa@lmsal.com WHAT IS SDO? The goal of Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is to understand:
Space Weather and Amateur Radio: Science, Forecasting and Effects. The Aerospace Corporation Dayton Hamvention Antenna Forum 19 May 2017
 Space Weather and Amateur Radio: Science, Forecasting and Effects The Aerospace Corporation Dayton Hamvention Antenna Forum 19 May 2017 What is Space Weather? Essentially Space Weather is: A planet s interaction
Space Weather and Amateur Radio: Science, Forecasting and Effects The Aerospace Corporation Dayton Hamvention Antenna Forum 19 May 2017 What is Space Weather? Essentially Space Weather is: A planet s interaction
Space Weather. Dr Thomas J Bogdan Director, Space Weather Prediction Center Boulder, CO
 Space Weather Dr Thomas J Bogdan Director, Space Weather Prediction Center Boulder, CO 2011 DIB CIP Meeting 25 August 2011 Space Weather Prediction Center Our Mission: To provide space weather products
Space Weather Dr Thomas J Bogdan Director, Space Weather Prediction Center Boulder, CO 2011 DIB CIP Meeting 25 August 2011 Space Weather Prediction Center Our Mission: To provide space weather products
The importance of ground-based observations of the solar corona
 The importance of ground-based observations of the solar corona J. Burkepile 1, S. Tomczyk 1, P. Nelson 1, A.G. dewijn 1, S. Sewell 1, D. Elmore 2, L. Sutherland 1, R. Summers 1, D. Kolinski 1, L. Sitongia
The importance of ground-based observations of the solar corona J. Burkepile 1, S. Tomczyk 1, P. Nelson 1, A.G. dewijn 1, S. Sewell 1, D. Elmore 2, L. Sutherland 1, R. Summers 1, D. Kolinski 1, L. Sitongia
Mitsubishi Electric Power Products Inc. and Duquesne Light Co.
 Mitsubishi Electric Power Products Inc. and Duquesne Light Co. Overview on Geomagnetically Induced Current Revision #00 March 2017 Presented by: Elizabeth Cook (DLC) and Wesley Terek (MEPPI) Overview on
Mitsubishi Electric Power Products Inc. and Duquesne Light Co. Overview on Geomagnetically Induced Current Revision #00 March 2017 Presented by: Elizabeth Cook (DLC) and Wesley Terek (MEPPI) Overview on
Outline. Astronomy: The Big Picture. Earth Sun comparison. Nighttime observing is over, but a makeup observing session may be scheduled. Stay tuned.
 Nighttime observing is over, but a makeup observing session may be scheduled. Stay tuned. Next homework due Oct 24 th. I will not be here on Wednesday, but Paul Ricker will present the lecture! My Tuesday
Nighttime observing is over, but a makeup observing session may be scheduled. Stay tuned. Next homework due Oct 24 th. I will not be here on Wednesday, but Paul Ricker will present the lecture! My Tuesday
EFFECT OF SOLAR AND INTERPLANETARY DISTURBANCES ON SPACE WEATHER
 Indian J.Sci.Res.3(2) : 121-125, 2012 EFFECT OF SOLAR AND INTERPLANETARY DISTURBANCES ON SPACE WEATHER a1 b c SHAM SINGH, DIVYA SHRIVASTAVA AND A.P. MISHRA Department of Physics, A.P.S.University, Rewa,M.P.,
Indian J.Sci.Res.3(2) : 121-125, 2012 EFFECT OF SOLAR AND INTERPLANETARY DISTURBANCES ON SPACE WEATHER a1 b c SHAM SINGH, DIVYA SHRIVASTAVA AND A.P. MISHRA Department of Physics, A.P.S.University, Rewa,M.P.,
MONITORING OF COSMIC RAYS IN REAL TIME AND INFORMATION SYSTEM OF THE MOSCOW COSMIC RAY STATION
 MONITORING OF COSMIC RAYS IN REAL TIME AND INFORMATION SYSTEM OF THE MOSCOW COSMIC RAY STATION A.V. Belov, M.A. Belov, R.T. Gushchina, E.A. Eroshenko, V.G. Kartyshev, A.B. Struminsky, V.G. Yanke Institute
MONITORING OF COSMIC RAYS IN REAL TIME AND INFORMATION SYSTEM OF THE MOSCOW COSMIC RAY STATION A.V. Belov, M.A. Belov, R.T. Gushchina, E.A. Eroshenko, V.G. Kartyshev, A.B. Struminsky, V.G. Yanke Institute
Living With A Star. Gauging the space weather. Madhulika Guhathakurta SUN-EARTH CONNECTIONS DIVISION NASA, OFFICE OF SPACE SCIENCE
 Living With A Star Gauging the space weather Madhulika Guhathakurta SUN-EARTH CONNECTIONS DIVISION NASA, OFFICE OF SPACE SCIENCE The LWS Philosophy - At the center of our solar system lives a highly variable
Living With A Star Gauging the space weather Madhulika Guhathakurta SUN-EARTH CONNECTIONS DIVISION NASA, OFFICE OF SPACE SCIENCE The LWS Philosophy - At the center of our solar system lives a highly variable
Chapter 14 Lecture. Chapter 14: Our Star Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Lecture Chapter 14: Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is it on FIRE? Is it on FIRE?
Chapter 14 Lecture Chapter 14: Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is it on FIRE? Is it on FIRE?
This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie-Sklodowska-Curie grant
 This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie-Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement number 721624. Space weather and the variable
This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie-Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement number 721624. Space weather and the variable
The Dancing Lights Program
 The Sun Teacher Background: The Dancing Lights Program Margaux Krahe Many people think the Sun is just a fiery yellow ball. The Sun is not actually burning because fire requires oxygen. Really, the Sun
The Sun Teacher Background: The Dancing Lights Program Margaux Krahe Many people think the Sun is just a fiery yellow ball. The Sun is not actually burning because fire requires oxygen. Really, the Sun
GAMMA RAYS. 1 P a g e
 GAMMA RAYS 1 P a g e 2 P a g e 3 P a g e Death Stars Do the most powerful blasts of energy in the universe threaten Earth? You don't want to be anywhere near a giant star when it dies. In just a few seconds,
GAMMA RAYS 1 P a g e 2 P a g e 3 P a g e Death Stars Do the most powerful blasts of energy in the universe threaten Earth? You don't want to be anywhere near a giant star when it dies. In just a few seconds,
New NASA Views of Storms in Space
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP New NASA Views of Storms in Space Presented by Dr. Eric Christian January 19, 2011 1 New NASA Views of Storms In Space The Sun as a Star Magnetism and the Sun Solar
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP New NASA Views of Storms in Space Presented by Dr. Eric Christian January 19, 2011 1 New NASA Views of Storms In Space The Sun as a Star Magnetism and the Sun Solar
MONITORING VARIATIONS TO THE NEAR-EARTH SPACE ENVIRONMENT DURING HIGH SOLAR ACTIVITY USING ORBITING ROCKET BODIES
 MONITORING VARIATIONS TO THE NEAR-EARTH SPACE ENVIRONMENT DURING HIGH SOLAR ACTIVITY USING ORBITING ROCKET BODIES Van Romero, William H. Ryan, and Eileen V. Ryan Magdalena Ridge Observatory, New Mexico
MONITORING VARIATIONS TO THE NEAR-EARTH SPACE ENVIRONMENT DURING HIGH SOLAR ACTIVITY USING ORBITING ROCKET BODIES Van Romero, William H. Ryan, and Eileen V. Ryan Magdalena Ridge Observatory, New Mexico
H. Koshiishi, H. Matsumoto, A. Chishiki, T. Goka, and T. Omodaka. Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
 9 th Workshop on Radiation Monitoring for the International Space Station Evaluation of Neutron Radiation Environment inside the International Space Station based on the Bonner Ball Neutron Detector Experiment
9 th Workshop on Radiation Monitoring for the International Space Station Evaluation of Neutron Radiation Environment inside the International Space Station based on the Bonner Ball Neutron Detector Experiment
Astronomy Ch 16 The Sun. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch 16 The Sun MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The light we see from the Sun comes from which layer?
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch 16 The Sun MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The light we see from the Sun comes from which layer?
Chapter 14 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Our Star Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is
Chapter 14 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is
Introduction to Space Weather and Propagation
 Introduction to Space Weather and Propagation Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA ARRL Vice Director, Central Division k9la@arrl.net https://k9la.us K9LA 1 What Is Space Weather? Space weather is the quiet Sun Electromagnetic
Introduction to Space Weather and Propagation Carl Luetzelschwab K9LA ARRL Vice Director, Central Division k9la@arrl.net https://k9la.us K9LA 1 What Is Space Weather? Space weather is the quiet Sun Electromagnetic
A Concept for Real-Time Solar Wind Monitor at Multiple Locations
 A Concept for Real-Time Solar Wind Monitor at Multiple Locations L5 in Tandem with L1: Future Space-Weather Missions Workshop March 8 th, 2017 George C. Ho Sector Science and Space Instrumentation Branch
A Concept for Real-Time Solar Wind Monitor at Multiple Locations L5 in Tandem with L1: Future Space-Weather Missions Workshop March 8 th, 2017 George C. Ho Sector Science and Space Instrumentation Branch
Solar Activity Space Debris
 The Hazards To Space Systems Solar Activity Space Debris The Threat From The Sun Major solar events, (Solar Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections) have the potential to generate significant effects on satellites,
The Hazards To Space Systems Solar Activity Space Debris The Threat From The Sun Major solar events, (Solar Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections) have the potential to generate significant effects on satellites,
Activity 7: Be an Aurora Forecaster
 ACTIVITY 7 NASA/STEREO Be an Aurora Forecaster Iñupiaq value: Respect for Nature We can predict when the northern lights are likely to occur by monitoring solar activity. When a solar storm such as a coronal
ACTIVITY 7 NASA/STEREO Be an Aurora Forecaster Iñupiaq value: Respect for Nature We can predict when the northern lights are likely to occur by monitoring solar activity. When a solar storm such as a coronal
NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center Data and Services. Terry Onsager and Howard Singer NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center
 NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center Data and Services Terry Onsager and Howard Singer NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center Terry.Onsager@noaa.gov Customer Subscriptions to Space Weather Services Frequent
NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center Data and Services Terry Onsager and Howard Singer NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center Terry.Onsager@noaa.gov Customer Subscriptions to Space Weather Services Frequent
An L5 Mission Concept for Compelling New Space Weather Science
 An L5 Mission Concept for Compelling New Space Weather Science RESCO (China) REal-time Sun-earth Connections Observatory INSTANT (Europe) INvestigation of Solar-Terrestrial Associated Natural Threats Ying
An L5 Mission Concept for Compelling New Space Weather Science RESCO (China) REal-time Sun-earth Connections Observatory INSTANT (Europe) INvestigation of Solar-Terrestrial Associated Natural Threats Ying
Long term data for Heliospheric science Nat Gopalswamy NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA
 Long term data for Heliospheric science Nat Gopalswamy NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA IAU340 1-day School, Saturday 24th February 2018 Jaipur India CMEs & their Consequences
Long term data for Heliospheric science Nat Gopalswamy NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA IAU340 1-day School, Saturday 24th February 2018 Jaipur India CMEs & their Consequences
SPACE WEATHER: STORMS FROM THE SUN
 GIFT 2013 - Natural Hazards Vienna, Austria, 10 April 2013 SPACE WEATHER: STORMS FROM THE SUN Norma B. Crosby Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy Ringlaan-3-Avenue Circulaire, B-1180 Brussels, Belgium
GIFT 2013 - Natural Hazards Vienna, Austria, 10 April 2013 SPACE WEATHER: STORMS FROM THE SUN Norma B. Crosby Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy Ringlaan-3-Avenue Circulaire, B-1180 Brussels, Belgium
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 7, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 7, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 1.e Students know the Sun is typical star and is powered by nuclear reactions, primarily the fusion
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 4, Week 7, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: Earth Sciences 1.e Students know the Sun is typical star and is powered by nuclear reactions, primarily the fusion
Saving NASA's STEREO-B the 189-millionmile road to recovery 14 December 2015, by Sarah Frazier
 Saving NASA's STEREO-B the 189-millionmile road to recovery 14 December 2015, by Sarah Frazier On Oct. 1, 2014, NASA mission operations lost communication with one of the two spacecraft of the Solar and
Saving NASA's STEREO-B the 189-millionmile road to recovery 14 December 2015, by Sarah Frazier On Oct. 1, 2014, NASA mission operations lost communication with one of the two spacecraft of the Solar and
