All-sky LIGO Search for Periodic Gravitational Waves in the Fourth Science Run (S4)
|
|
|
- Angela Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 All-sky LIGO Search for Periodic Gravitational Waves in the Fourth Science Run (S4) Keith Riles University of Michigan For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration APS Meeting, Jacksonville, Florida April 14-17, 2007 LIGO DCC: G Z
2 LIGO Interferometers & S4 Run Sensitivities Hanford Livingston H1 (4 km) H2 (2 km) L1 (4 km)
3 Searching for Spinning Neutron Stars ( Pulsars ) with LIGO Courtesy: NASA Signals expected to be weak need long integration times Coherent all-sky searches over entire data period are computationally intractable because of parameter space explosion: Doppler modulation corrections require ever-finer sky gridding as the observation time increases Alternative method: Semi-coherent summing of spectra from many shorter time intervals: Advantage: computationally tractable Disadvantage: unable to exploit full intrinsic sensitivity of detector
4 Will summarize and present results from three different methods explored within LIGO to carry out a semi-coherent search: Stack-Slide Hough PowerFlux All methods correct for Doppler modulations: (daily and annual) Frequency Frequency bin Time Time Number of sky grid points scales like (frequency) 2
5 Comparing the Methods What exactly is summed? StackSlide Normalized power (power divided by estimated noise) Averaging gives expectation of 1.0 in absence of signal Hough Weighted binary counts (0/1 = normalized power below/above SNR), with weighting based on antenna pattern and detector noise PowerFlux Average strain power with weighting based on antenna pattern and detector noise Signal estimator is direct excess strain power (circular polarization and 4 linear polarization projections)
6 Sample 0.25-Hz bands Hough (2 of 92 sky patches shown) Determines limit (highest-snr patch) Hough count (North Pole) (Equator) Counts PowerFlux Limit StackSlide Determines limit Strain limit StackSlide power
7 Comparing the Methods (cont.) What kind of limits are set? StackSlide & Hough PowerFlux Population-based frequentist limits on h 0 Averaged over sky location and pulsar orientation Strict frequentist limits on circular and linear polarization amplitudes h 0 CIRC and h 0 LIN Results interpreted as limits on best-case and worst-case pulsar amplitudes h 0 Limits placed separately on tiny sky patches Worst limit over fiducial sky is quoted
8 Sample PowerFlux circular-polarization strain H1 upper limits in Hz band Simulated Pulsar (A + = A - = 8.4 x nearly circ. polarized) R.A. PRELIMINARY Dec.
9 StackSlide & Hough Line Removal: Known lines replaced by random noise (Effects included in Monte Carlo simulation) PowerFlux Line Avoidance: Regions of Doppler stationarity excluded from quoted limits (frequency & spindown dependent)
10 Results What frequency & spindown ranges are covered? [ Hz for all] StackSlide & PowerFlux: 1.0 x 10-8 Hz/s < df/dt < 0 Hough: 2.2 x 10-9 Hz/s < df/dt < 0 What interferometer data is analyzed? StackSlide & PowerFlux H1 and L1 individually (coincidence checks for high-snr candidates) Hough H1, H2, and L1 combined powers (coincidence check for high-snr candidates; also: sample single-ifo limits produced for comparison)
11 H1 (Hanford 4-km) and Multi-IFO Results PRELIMINARY
12 L1 (Livingston 4-km) and Multi-IFO Results PRELIMINARY
13 Results & Prospects Carried out follow-up coincidence (frequency, spindown, sky location) studies on outliers from individual interferometers No plausible candidates found Now carrying out analysis of data from ongoing S5 data run with PowerFlux as first look algorithm (see talk by V. Dergachev) StackSlide & Hough incorporated into distributed-computing project called using longer coherence times and a hierarchical search algorithm (see talk by B. Owen) You can help! Go to Upper limits improving and now probing interesting astrophysical territory (h < ) Stay tuned
14 END OF SLIDES
15 Comparing the Methods How are instrumental lines handled? StackSlide & Hough PowerFlux Direct removal of known lines from spectrum (replaced with random noise) Allows entire sky to be searched (population-based limits) Spectral lines flagged on the fly and bins marked for avoidance Source occupancy tracked no limits placed if source would be lost Leads to exclusion of Doppler-stationary skybands (dependent on frequency and spindown)
Searches for Continuous Gravitational Waves
 Searches for Continuous Gravitational Waves Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration Guenakh Fest University of Florida March 30, 2018 LIGO-G1800421
Searches for Continuous Gravitational Waves Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration Guenakh Fest University of Florida March 30, 2018 LIGO-G1800421
The search for continuous gravitational waves: analyses from LIGO s second science run
 The search for continuous gravitational waves: analyses from LIGO s second science run Michael Landry LIGO Hanford Observatory on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration http://www.ligo.org April APS
The search for continuous gravitational waves: analyses from LIGO s second science run Michael Landry LIGO Hanford Observatory on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration http://www.ligo.org April APS
Work of the LSC Pulsar Upper Limits Group (PULG) Graham Woan, University of Glasgow on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration
 Work of the LSC Pulsar Upper Limits Group (PULG) Graham Woan, University of Glasgow on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration GWDAW 2003 1 Pulsar Upper Limits Group (PULG) Community of LSC members
Work of the LSC Pulsar Upper Limits Group (PULG) Graham Woan, University of Glasgow on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration GWDAW 2003 1 Pulsar Upper Limits Group (PULG) Community of LSC members
Prospects of continuous gravitational waves searches from Fermi-LAT sources
 S. Mastrogiovanni for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration Prospects of continuous gravitational waves searches from Fermi-LAT sources Outline Aim of the talk: I would like to
S. Mastrogiovanni for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration Prospects of continuous gravitational waves searches from Fermi-LAT sources Outline Aim of the talk: I would like to
Recent Searches for Periodic Continuous Gravitational Waves with the LIGO & Virgo Detectors!
 Recent Searches for Periodic Continuous Gravitational Waves with the LIGO & Virgo Detectors! Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration Texas Symposium!
Recent Searches for Periodic Continuous Gravitational Waves with the LIGO & Virgo Detectors! Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration Texas Symposium!
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis
 Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis Peter Shawhan Physics 798G April 12, 2007 Outline Gravitational-wave data General data analysis principles Specific data analysis methods Classification of signals Methods
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis Peter Shawhan Physics 798G April 12, 2007 Outline Gravitational-wave data General data analysis principles Specific data analysis methods Classification of signals Methods
LIGO Observational Results
 LIGO Observational Results Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin Milwaukee on behalf of LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Science Goals Direct verification of two dramatic predictions of Einstein s general
LIGO Observational Results Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin Milwaukee on behalf of LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Science Goals Direct verification of two dramatic predictions of Einstein s general
Continuous Gravitational Waves from Neutron Stars!
 Continuous Gravitational Waves from Neutron Stars Greg Mendell LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration Binary Neutron Star Coalescence as a Fundamental Physics
Continuous Gravitational Waves from Neutron Stars Greg Mendell LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration Binary Neutron Star Coalescence as a Fundamental Physics
LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans. Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04
 LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04 Science Goals Physics» Direct verification of the most relativistic prediction of general relativity» Detailed tests of properties of gravitational
LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04 Science Goals Physics» Direct verification of the most relativistic prediction of general relativity» Detailed tests of properties of gravitational
Searches for signals from unknown or poorly known sources
 Searches for signals from unknown or poorly known sources Alicia M Sintes Dept. Física & IAC3 - Universitat de les Illes Balears & Institut d'estudis Espacials de Catalunya (IEEC). For the LIGO Scientific
Searches for signals from unknown or poorly known sources Alicia M Sintes Dept. Física & IAC3 - Universitat de les Illes Balears & Institut d'estudis Espacials de Catalunya (IEEC). For the LIGO Scientific
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspirals with LIGO
 Searching for Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspirals with LIGO Duncan Brown University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Inspiral Working Group LIGO-G030671-00-Z S1 Binary
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspirals with LIGO Duncan Brown University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Inspiral Working Group LIGO-G030671-00-Z S1 Binary
Status and Prospects for LIGO
 Status and Prospects for LIGO Crab Pulsar St Thomas, Virgin Islands Barry C. Barish Caltech 17-March-06 LIGO Livingston, Louisiana 4 km 17-March-06 Confronting Gravity - St Thomas 2 LIGO Hanford Washington
Status and Prospects for LIGO Crab Pulsar St Thomas, Virgin Islands Barry C. Barish Caltech 17-March-06 LIGO Livingston, Louisiana 4 km 17-March-06 Confronting Gravity - St Thomas 2 LIGO Hanford Washington
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 2
 Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 2 Peter S. Shawhan Gravitational Wave Astronomy Summer School May 29, 2012 Outline for Today Matched filtering in the time domain Matched filtering in the frequency
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 2 Peter S. Shawhan Gravitational Wave Astronomy Summer School May 29, 2012 Outline for Today Matched filtering in the time domain Matched filtering in the frequency
Search for compact binary systems in LIGO data
 Search for compact binary systems in LIGO data Thomas Cokelaer On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Cardiff University, U.K. LIGO-G060630-00-Z Plan 1) Overview What kind of gravitational waves
Search for compact binary systems in LIGO data Thomas Cokelaer On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Cardiff University, U.K. LIGO-G060630-00-Z Plan 1) Overview What kind of gravitational waves
Overview Ground-based Interferometers. Barry Barish Caltech Amaldi-6 20-June-05
 Overview Ground-based Interferometers Barry Barish Caltech Amaldi-6 20-June-05 TAMA Japan 300m Interferometer Detectors LIGO Louisiana 4000m Virgo Italy 3000m AIGO Australia future GEO Germany 600m LIGO
Overview Ground-based Interferometers Barry Barish Caltech Amaldi-6 20-June-05 TAMA Japan 300m Interferometer Detectors LIGO Louisiana 4000m Virgo Italy 3000m AIGO Australia future GEO Germany 600m LIGO
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems
 Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems Stephen Fairhurst Cardiff University and LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Outline Motivation Searching for Coalescing Binaries Latest Results
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems Stephen Fairhurst Cardiff University and LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Outline Motivation Searching for Coalescing Binaries Latest Results
Broad-band CW searches in LIGO and GEO S2 and S3 data. B. Allen, Y. Itoh, M.A. Papa, X. Siemens. AEI and UWM
 Broad-band CW searches in LIGO and GEO S2 and S3 data B. Allen, Y. Itoh, M.A. Papa, X. Siemens AEI and UWM GWDAW-8 December 18, 2003 LIGO Scientific Collaboration, UW - Milwaukee 1LIGO-G030651-00-Z What
Broad-band CW searches in LIGO and GEO S2 and S3 data B. Allen, Y. Itoh, M.A. Papa, X. Siemens AEI and UWM GWDAW-8 December 18, 2003 LIGO Scientific Collaboration, UW - Milwaukee 1LIGO-G030651-00-Z What
The LIGO Project: a Status Report
 The LIGO Project: a Status Report LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO Livingston Observatory Laura Cadonati LIGO Laboratory, MIT for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Conference on Gravitational Wave Sources
The LIGO Project: a Status Report LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO Livingston Observatory Laura Cadonati LIGO Laboratory, MIT for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Conference on Gravitational Wave Sources
Searching for gravitational waves. with LIGO detectors
 Werner Berger, ZIB, AEI, CCT Searching for gravitational waves LIGO Hanford with LIGO detectors Gabriela González Louisiana State University On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration KITP Colloquium,
Werner Berger, ZIB, AEI, CCT Searching for gravitational waves LIGO Hanford with LIGO detectors Gabriela González Louisiana State University On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration KITP Colloquium,
Long-term strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups
 Longterm strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups Barry Barish APPEC Meeting London, UK 29Jan04 International Interferometer Network Simultaneously detect signal (within msec) LIGO
Longterm strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups Barry Barish APPEC Meeting London, UK 29Jan04 International Interferometer Network Simultaneously detect signal (within msec) LIGO
arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 25 Jul 2008
![arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 25 Jul 2008 arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 25 Jul 2008](/thumbs/90/103451395.jpg) Source Tracking for Sco X-1 arxiv:87.4171v1 [gr-qc] 25 Jul 28 1. Introduction K Hayama 1, S D Mohanty 1, S Desai 2, M Rakhmanov 1, T Summerscales 3, S Yoshida 4 1 The University of Texas at Brownsville,
Source Tracking for Sco X-1 arxiv:87.4171v1 [gr-qc] 25 Jul 28 1. Introduction K Hayama 1, S D Mohanty 1, S Desai 2, M Rakhmanov 1, T Summerscales 3, S Yoshida 4 1 The University of Texas at Brownsville,
Searches for con,nuous gravita,onal waves in LIGO/Virgo data and the post-merger remnant following the binary neutron star merger GW170817
 Searches for con,nuous gravita,onal waves in LIGO/Virgo data and the post-merger remnant following the binary neutron star merger GW170817 Evan Goetz for the LIGO Scien,fic Collabora,on and Virgo Collabora,on
Searches for con,nuous gravita,onal waves in LIGO/Virgo data and the post-merger remnant following the binary neutron star merger GW170817 Evan Goetz for the LIGO Scien,fic Collabora,on and Virgo Collabora,on
The LIGO Experiment Present and Future
 The LIGO Experiment Present and Future Keith Riles University of Michigan For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration APS Meeting Denver May 1 4, 2004 LIGO-G040239-00-Z What are Gravitational Waves? Gravitational
The LIGO Experiment Present and Future Keith Riles University of Michigan For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration APS Meeting Denver May 1 4, 2004 LIGO-G040239-00-Z What are Gravitational Waves? Gravitational
The Advanced LIGO detectors at the beginning of the new gravitational wave era
 The Advanced LIGO detectors at the beginning of the new gravitational wave era Lisa Barsotti MIT Kavli Institute LIGO Laboratory on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Document G1600324 LIGO
The Advanced LIGO detectors at the beginning of the new gravitational wave era Lisa Barsotti MIT Kavli Institute LIGO Laboratory on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Document G1600324 LIGO
arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 14 Feb 2015
![arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 14 Feb 2015 arxiv: v2 [gr-qc] 14 Feb 2015](/thumbs/94/121294688.jpg) Postprocessing methods used in the search for continuous gravitational-wave signals from the Galactic Center arxiv:141.5997v2 [gr-qc] 14 Feb 215 Berit Behnke, 1, a Maria Alessandra Papa, 1, 2, b and Reinhard
Postprocessing methods used in the search for continuous gravitational-wave signals from the Galactic Center arxiv:141.5997v2 [gr-qc] 14 Feb 215 Berit Behnke, 1, a Maria Alessandra Papa, 1, 2, b and Reinhard
The Present Gravitational Wave Detection Effort
 The Present Gravitational Wave Detection Effort Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO Scientific Collaboration International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics Rome July 1,
The Present Gravitational Wave Detection Effort Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO Scientific Collaboration International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics Rome July 1,
Search for inspiralling neutron stars in LIGO S1 data
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S691 S696 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)68883-6 Search for inspiralling neutron stars in LIGO S1 data Gabriela González
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S691 S696 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)68883-6 Search for inspiralling neutron stars in LIGO S1 data Gabriela González
Plans for the LIGO TAMA joint search for gravitational wave bursts
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S1801 S1807 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)79467-8 Plans for the LIGO TAMA joint search for gravitational wave bursts Patrick
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S1801 S1807 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)79467-8 Plans for the LIGO TAMA joint search for gravitational wave bursts Patrick
The direct detection of gravitational waves: The first discovery, and what the future might bring
 The direct detection of gravitational waves: The first discovery, and what the future might bring Chris Van Den Broeck Nikhef - National Institute for Subatomic Physics Amsterdam, The Netherlands Physics
The direct detection of gravitational waves: The first discovery, and what the future might bring Chris Van Den Broeck Nikhef - National Institute for Subatomic Physics Amsterdam, The Netherlands Physics
M.Alessandra Papa. Max Planck Inst. f. Gravitationsphysik and Univ. of Wisconsin- Milwaukee. ICGC Conference 2007, December Pune
 Gravitational Wave Data Analysis M.Alessandra Papa Max Planck Inst. f. Gravitationsphysik and Univ. of Wisconsin- Milwaukee ICGC Conference 2007, December Pune Gravitational wave data analysis * legacy
Gravitational Wave Data Analysis M.Alessandra Papa Max Planck Inst. f. Gravitationsphysik and Univ. of Wisconsin- Milwaukee ICGC Conference 2007, December Pune Gravitational wave data analysis * legacy
What can LIGO detect? Abstract
 What can LIGO detect? Adam Getchell Physics Department, University of California, Davis, 95616 Abstract This briey reviews the literature on gravitational wave astronomy, including theoretical basis, experimental
What can LIGO detect? Adam Getchell Physics Department, University of California, Davis, 95616 Abstract This briey reviews the literature on gravitational wave astronomy, including theoretical basis, experimental
Not-Quite-Continuous Gravitational Waves
 Not-Quite-Continuous Gravitational Waves Challenges and Opportunities Reinhard Prix Albert-Einstein-Institute Hannover INT Workshop on Astro-solids and GWs 18 April 2018 LIGO-G1800726-v3 1 Outline 1 Why
Not-Quite-Continuous Gravitational Waves Challenges and Opportunities Reinhard Prix Albert-Einstein-Institute Hannover INT Workshop on Astro-solids and GWs 18 April 2018 LIGO-G1800726-v3 1 Outline 1 Why
Results of O1 narrow-band searches with the 5-vectors method
 Simone Mastrogiovanni on behalf of Rome CW group Results of O1 narrow-band searches with the 5-vectors method DCC: G1601736 1 Outline: Physical motivation Reminder of 5-Vectors narrow-band pipeline Target
Simone Mastrogiovanni on behalf of Rome CW group Results of O1 narrow-band searches with the 5-vectors method DCC: G1601736 1 Outline: Physical motivation Reminder of 5-Vectors narrow-band pipeline Target
Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars
 Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars Ian Jones D.I.Jones@soton.ac.uk General Relativity Group, Southampton University Ian Jones Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars 1/23
Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars Ian Jones D.I.Jones@soton.ac.uk General Relativity Group, Southampton University Ian Jones Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars 1/23
Results from LIGO Searches for Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves
 Results from LIGO Searches for Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan (LIGO Laboratory / Caltech) For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration American Physical Society April Meeting May 4, 2004 Denver,
Results from LIGO Searches for Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan (LIGO Laboratory / Caltech) For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration American Physical Society April Meeting May 4, 2004 Denver,
Astrophysical Source Identification and Signature (ASIS) Group: Implementation for LIGO-I
 Astrophysical Source Identification and Signature (ASIS) Group: Implementation for LIGO-I Bruce Allen Chair, LSC ASIS working group University of Wisconsin - Milwaukee Marcel Grossman 2000.07.02 LIGO Scientific
Astrophysical Source Identification and Signature (ASIS) Group: Implementation for LIGO-I Bruce Allen Chair, LSC ASIS working group University of Wisconsin - Milwaukee Marcel Grossman 2000.07.02 LIGO Scientific
GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY
 GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY A. Melatos (Melbourne) 1. GW: physics & astronomy 2. Current- & next-gen detectors & searches 3. Burst sources: CBC, SN GR, cosmology 4. Periodic sources: NS subatomic physics
GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY A. Melatos (Melbourne) 1. GW: physics & astronomy 2. Current- & next-gen detectors & searches 3. Burst sources: CBC, SN GR, cosmology 4. Periodic sources: NS subatomic physics
LIGO s continuing search for gravitational waves
 LIGO s continuing search for gravitational waves Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Interferometers LIGO is an interferometric detector» A laser is used
LIGO s continuing search for gravitational waves Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Interferometers LIGO is an interferometric detector» A laser is used
Gravitational Waves & Intermediate Mass Black Holes. Lee Samuel Finn Center for Gravitational Wave Physics
 Gravitational Waves & Intermediate Mass Black Holes Lee Samuel Finn Center for Gravitational Wave Physics Outline What are gravitational waves? How are they produced? How are they detected? Gravitational
Gravitational Waves & Intermediate Mass Black Holes Lee Samuel Finn Center for Gravitational Wave Physics Outline What are gravitational waves? How are they produced? How are they detected? Gravitational
Scientific Results from the first LIGO Science Runs
 Scientific Results from the first LIGO Science Runs Introduction to GW s and LIGO The LIGO Science runs Physics, astrophysics, and S1 analysis results:» Binary inspirals» Pulsars and CW Sources» Bursts
Scientific Results from the first LIGO Science Runs Introduction to GW s and LIGO The LIGO Science runs Physics, astrophysics, and S1 analysis results:» Binary inspirals» Pulsars and CW Sources» Bursts
Enhancing Long Transient Power Spectra with Filters
 Enhancing Long Transient Power Spectra with Filters Avi Vajpeyi The College of Wooster Pia Astone and Andrew Miller The Sapienza University of Rome (Dated: August 5, 2017) A challenge with gravitational
Enhancing Long Transient Power Spectra with Filters Avi Vajpeyi The College of Wooster Pia Astone and Andrew Miller The Sapienza University of Rome (Dated: August 5, 2017) A challenge with gravitational
Prospects for joint transient searches with LOFAR and the LSC/Virgo gravitational wave interferometers
 Prospects for joint transient searches with LOFAR and the LSC/Virgo gravitational wave interferometers Ed Daw - University of Sheffield On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo collaboration
Prospects for joint transient searches with LOFAR and the LSC/Virgo gravitational wave interferometers Ed Daw - University of Sheffield On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo collaboration
Gravitational wave data analysis
 Max Planck Institut für Gravitationsphysik Albert Einstein Institut, Germany Pasadena, June 2011 1 Introduction to gravitational waves 2 3 4 5 6 Gravitational Waves GR can be formulated in terms of a spacetime
Max Planck Institut für Gravitationsphysik Albert Einstein Institut, Germany Pasadena, June 2011 1 Introduction to gravitational waves 2 3 4 5 6 Gravitational Waves GR can be formulated in terms of a spacetime
Searching for gravitational waves
 Searching for gravitational waves Matteo Barsuglia (barsuglia@apc.univ-paris7.fr) CNRS - Laboratoire Astroparticule et Cosmologie 1 The gravitational waves (GW) Perturbations of the space-time metrics
Searching for gravitational waves Matteo Barsuglia (barsuglia@apc.univ-paris7.fr) CNRS - Laboratoire Astroparticule et Cosmologie 1 The gravitational waves (GW) Perturbations of the space-time metrics
arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 21 Mar 2019
![arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 21 Mar 2019 arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 21 Mar 2019](/thumbs/95/122844181.jpg) Results from an Einstein@Home search for continuous gravitational waves from Cassiopeia A, Vela Jr. and G347.3 arxiv:193.9119v1 [gr-qc] 21 Mar 219 J. Ming, 1, 2, a M.A. Papa, 1, 3, 2, b A. Singh, 1, 2,
Results from an Einstein@Home search for continuous gravitational waves from Cassiopeia A, Vela Jr. and G347.3 arxiv:193.9119v1 [gr-qc] 21 Mar 219 J. Ming, 1, 2, a M.A. Papa, 1, 3, 2, b A. Singh, 1, 2,
Gravitational Wave Astronomy s Next Frontier in Computation
 Gravitational Wave Astronomy s Next Frontier in Computation Chad Hanna - Penn State University Penn State Physics Astronomy & Astrophysics Outline 1. Motivation 2. Gravitational waves. 3. Birth of gravitational
Gravitational Wave Astronomy s Next Frontier in Computation Chad Hanna - Penn State University Penn State Physics Astronomy & Astrophysics Outline 1. Motivation 2. Gravitational waves. 3. Birth of gravitational
Testing GR with GW polarizations
 Testing GR with GW polarizations using LIGO and Virgo Maximiliano Isi July 12, 2017 @ Amaldi12 LIGO Laboratory, California Institute of Technology Testing GR with GWs we have already learned a lot from
Testing GR with GW polarizations using LIGO and Virgo Maximiliano Isi July 12, 2017 @ Amaldi12 LIGO Laboratory, California Institute of Technology Testing GR with GWs we have already learned a lot from
Astrophysics to z~10 with Gravitational Waves
 Astrophysics to z~10 with Gravitational Waves Robin Stebbins U.S. LISA Project Scientist University of Maryland Physics Seminar College Park, MD 1 May 2007 My Problem Gravitational wave detection is capability-driven,
Astrophysics to z~10 with Gravitational Waves Robin Stebbins U.S. LISA Project Scientist University of Maryland Physics Seminar College Park, MD 1 May 2007 My Problem Gravitational wave detection is capability-driven,
Search for Gravitational Wave Transients. Florent Robinet On behalf of the LSC and Virgo Collaborations
 Search for Gravitational Wave Transients On behalf of the LSC and Virgo Collaborations 1 Gravitational Waves Gravitational waves = "ripples" in space time Weak field approximation : g = h h 1 Wave equation,
Search for Gravitational Wave Transients On behalf of the LSC and Virgo Collaborations 1 Gravitational Waves Gravitational waves = "ripples" in space time Weak field approximation : g = h h 1 Wave equation,
Status of LIGO. David Shoemaker LISA Symposium 13 July 2004 LIGO-G M
 Status of LIGO David Shoemaker LISA Symposium 13 July 2004 Ground-based interferometric gravitational-wave detectors Search for GWs above lower frequency limit imposed by gravity gradients» Might go as
Status of LIGO David Shoemaker LISA Symposium 13 July 2004 Ground-based interferometric gravitational-wave detectors Search for GWs above lower frequency limit imposed by gravity gradients» Might go as
Gravitational Wave Astronomy
 Gravitational Wave Astronomy Giles Hammond SUPA, University of Glasgow, UK on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 14 th Lomonosov conference on Elementary Particle Physics
Gravitational Wave Astronomy Giles Hammond SUPA, University of Glasgow, UK on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 14 th Lomonosov conference on Elementary Particle Physics
arxiv:gr-qc/ v1 10 Dec 2003
 Searching for gravitational waves from the Crab pulsar - the problem of timing noise arxiv:gr-qc/0312057v1 10 Dec 2003 Matthew Pitkin and Graham Woan Department of Physics and Astronomy, Kelvin Building,
Searching for gravitational waves from the Crab pulsar - the problem of timing noise arxiv:gr-qc/0312057v1 10 Dec 2003 Matthew Pitkin and Graham Woan Department of Physics and Astronomy, Kelvin Building,
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves
 Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves Barry C. Barish Caltech Crab Pulsar University of Illinois 16-Feb-06 General Relativity the essential idea G μν = 8πΤ μν Gravity is not a force, but a property
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves Barry C. Barish Caltech Crab Pulsar University of Illinois 16-Feb-06 General Relativity the essential idea G μν = 8πΤ μν Gravity is not a force, but a property
Mapping Inspiral Sensitivity of Gravitational Wave Detectors
 Mapping Inspiral Sensitivity of Gravitational Wave Detectors Anthony D. Castiglia Mentor: John T. Whelan Rochester Institute of Technology 12 August, 2011 Acknowledgments Mentor: John T. Whelan NSF Grant
Mapping Inspiral Sensitivity of Gravitational Wave Detectors Anthony D. Castiglia Mentor: John T. Whelan Rochester Institute of Technology 12 August, 2011 Acknowledgments Mentor: John T. Whelan NSF Grant
Gravitational wave cosmology Lecture 2. Daniel Holz The University of Chicago
 Gravitational wave cosmology Lecture 2 Daniel Holz The University of Chicago Thunder and lightning Thus far we ve only seen the Universe (and 95% of it is dark: dark matter and dark energy). In the the
Gravitational wave cosmology Lecture 2 Daniel Holz The University of Chicago Thunder and lightning Thus far we ve only seen the Universe (and 95% of it is dark: dark matter and dark energy). In the the
Binary Black Holes, Gravitational Waves, & Numerical Relativity Part 1
 1 Binary Black Holes, Gravitational Waves, & Numerical Relativity Part 1 Joan Centrella Chief, Gravitational Astrophysics Laboratory NASA/GSFC Summer School on Nuclear and Particle Astrophysics: Connecting
1 Binary Black Holes, Gravitational Waves, & Numerical Relativity Part 1 Joan Centrella Chief, Gravitational Astrophysics Laboratory NASA/GSFC Summer School on Nuclear and Particle Astrophysics: Connecting
Gravitational wave detection with Virgo and LIGO experiment - Case of the long bursts
 Gravitational wave detection with Virgo and LIGO experiment - Case of the long bursts Samuel Franco Supervisor: Patrice Hello Laboratoire de l Accélérateur Linéaire (Orsay) 06/12/2013 Samuel Franco (LAL)
Gravitational wave detection with Virgo and LIGO experiment - Case of the long bursts Samuel Franco Supervisor: Patrice Hello Laboratoire de l Accélérateur Linéaire (Orsay) 06/12/2013 Samuel Franco (LAL)
Results from an search for continuous gravitational waves from Cassiopeia A, Vela Jr. and G347.3
 Results from an Einstein@Home search for continuous gravitational waves from Cassiopeia A, Vela Jr. and G347.3 J. Ming, 1, 2, a M.A. Papa, 1, 3, 2, b A. Singh, 1, 2, 4 H.-B. Eggenstein, 1, 2 S. J. Zhu,
Results from an Einstein@Home search for continuous gravitational waves from Cassiopeia A, Vela Jr. and G347.3 J. Ming, 1, 2, a M.A. Papa, 1, 3, 2, b A. Singh, 1, 2, 4 H.-B. Eggenstein, 1, 2 S. J. Zhu,
Data Analysis Pipeline: The Search for Gravitational Waves in Real life
 Data Analysis Pipeline: The Search for Gravitational Waves in Real life Romain Gouaty LAPP - Université de Savoie - CNRS/IN2P3 On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Data Analysis Pipeline: The Search for Gravitational Waves in Real life Romain Gouaty LAPP - Université de Savoie - CNRS/IN2P3 On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves
 Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Barry C. Barish Caltech Argonne National Laboratory 16-Jan-04 LIGO-G030523-00-M
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Barry C. Barish Caltech Argonne National Laboratory 16-Jan-04 LIGO-G030523-00-M
Searching for Big Bang relicts with LIGO. Stefan W. Ballmer For the LSC/VIRGO collaboration GW2010, University of Minnesota October 16, 2010
 Searching for Big Bang relicts with LIGO Stefan W. Ballmer For the LSC/VIRGO collaboration GW2010, University of Minnesota October 16, 2010 Outline The search for a stochastic GW background» Motivation»
Searching for Big Bang relicts with LIGO Stefan W. Ballmer For the LSC/VIRGO collaboration GW2010, University of Minnesota October 16, 2010 Outline The search for a stochastic GW background» Motivation»
arxiv:gr-qc/ v1 4 Dec 2003
 Testing the LIGO Inspiral Analysis with Hardware Injections arxiv:gr-qc/0312031 v1 4 Dec 2003 Duncan A. Brown 1 for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
Testing the LIGO Inspiral Analysis with Hardware Injections arxiv:gr-qc/0312031 v1 4 Dec 2003 Duncan A. Brown 1 for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
State of LIGO. Barry Barish. S1 sensitivities. LSC Meeting LLO Hanford, WA 10-Nov GEO -- L 2km -- H 4km -- L 4km LIGO-G M
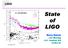 S1 sensitivities -- GEO -- L 2km -- H 4km -- L 4km State of h 0 LIGO Barry Barish LSC Meeting LLO Hanford, WA 10-Nov-03 Goals and Priorities LSC -Aug 02 Interferometer performance» Integrate commissioning
S1 sensitivities -- GEO -- L 2km -- H 4km -- L 4km State of h 0 LIGO Barry Barish LSC Meeting LLO Hanford, WA 10-Nov-03 Goals and Priorities LSC -Aug 02 Interferometer performance» Integrate commissioning
Binary Pulsar Discovery using Global Volunteer Compu9ng. How has already jumped from physics to astronomy
 Binary Pulsar Discovery using Global Volunteer Compu9ng How Einstein@Home has already jumped from physics to astronomy Eric Myers June 2012 Summary: LIGO is a physics experiment which is attempting to
Binary Pulsar Discovery using Global Volunteer Compu9ng How Einstein@Home has already jumped from physics to astronomy Eric Myers June 2012 Summary: LIGO is a physics experiment which is attempting to
LIGO Status and Plans. Barry Barish / Gary Sanders 13-May-02
 LIGO Status and Plans Barry Barish / Gary Sanders 13-May-02 LIGO overall strategy! Strategy presented to NSB by Thorne / Barish in 1994! Search with a first generation interferometer where detection of
LIGO Status and Plans Barry Barish / Gary Sanders 13-May-02 LIGO overall strategy! Strategy presented to NSB by Thorne / Barish in 1994! Search with a first generation interferometer where detection of
Gravity. Newtonian gravity: F = G M1 M2/r 2
 Gravity Einstein s General theory of relativity : Gravity is a manifestation of curvature of 4- dimensional (3 space + 1 time) space-time produced by matter (metric equation? g μν = η μν ) If the curvature
Gravity Einstein s General theory of relativity : Gravity is a manifestation of curvature of 4- dimensional (3 space + 1 time) space-time produced by matter (metric equation? g μν = η μν ) If the curvature
GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY
 GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY A. Melatos (Melbourne) 1. GW: physics & astronomy 2. Current- & next-gen detectors & searches 3. Burst sources: CBC, SN GR, cosmology 4. Periodic sources: NS subatomic physics
GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY A. Melatos (Melbourne) 1. GW: physics & astronomy 2. Current- & next-gen detectors & searches 3. Burst sources: CBC, SN GR, cosmology 4. Periodic sources: NS subatomic physics
LIGO Detection of Gravitational Waves. Dr. Stephen Ng
 LIGO Detection of Gravitational Waves Dr. Stephen Ng Gravitational Waves Predicted by Einstein s general relativity in 1916 Indirect confirmation with binary pulsar PSR B1913+16 (1993 Nobel prize in physics)
LIGO Detection of Gravitational Waves Dr. Stephen Ng Gravitational Waves Predicted by Einstein s general relativity in 1916 Indirect confirmation with binary pulsar PSR B1913+16 (1993 Nobel prize in physics)
GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University. Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne]
![GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University. Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne] GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University. Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne]](/thumbs/79/79556320.jpg) GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne] Summary of talk Review of observational upper limits and current and planned
GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne] Summary of talk Review of observational upper limits and current and planned
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO)! A Brief Overview!
 Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) A Brief Overview Sharon Brunett California Institute of Technology Pacific Research Platform Workshop October 15, 2015 Credit: AEI, CCT, LSU LIGO
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) A Brief Overview Sharon Brunett California Institute of Technology Pacific Research Platform Workshop October 15, 2015 Credit: AEI, CCT, LSU LIGO
LIGO & VIRGO Continuous Wave Searches
 LIGO & VIRGO Continuous Wave Searches Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO-Virgo Collaboration Workshop on Probing Neutron Stars with Gravitational Waves Pennsylvania State University June 18, 2009
LIGO & VIRGO Continuous Wave Searches Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO-Virgo Collaboration Workshop on Probing Neutron Stars with Gravitational Waves Pennsylvania State University June 18, 2009
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves
 Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves Barry C. Barish Caltech Crab Pulsar Georgia Tech 26-April-06 General Relativity the essential idea G μν = 8πΤ μν Gravity is not a force, but a property of space
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves Barry C. Barish Caltech Crab Pulsar Georgia Tech 26-April-06 General Relativity the essential idea G μν = 8πΤ μν Gravity is not a force, but a property of space
Gravitational waves from neutron stars: theoretical challenges. Ian Jones University of Southampton IGWM, 17 th May 2017
 Gravitational waves from neutron stars: theoretical challenges Ian Jones University of Southampton IGWM, 17 th May 2017 Three gravitational wave emission mechanisms Mountains non-axisymmetric deformation
Gravitational waves from neutron stars: theoretical challenges Ian Jones University of Southampton IGWM, 17 th May 2017 Three gravitational wave emission mechanisms Mountains non-axisymmetric deformation
First upper limits from LIGO on gravitational wave bursts
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S677 S684 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)68358-4 First upper limits from LIGO on gravitational wave bursts Alan J Weinstein
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S677 S684 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)68358-4 First upper limits from LIGO on gravitational wave bursts Alan J Weinstein
Searching for Ripples in Space-Time with Your Home Computer"
 Einstein@Home: Searching for Ripples in Space-Time with Your Home Computer Eric Myers LIGO Hanford Observatory! Hanford, Washington! Amateur Astronomers Association of New York 11 April 2008 Overview q
Einstein@Home: Searching for Ripples in Space-Time with Your Home Computer Eric Myers LIGO Hanford Observatory! Hanford, Washington! Amateur Astronomers Association of New York 11 April 2008 Overview q
Probing for Gravitational Waves
 Probing for Gravitational Waves LIGO Reach with LIGO AdLIGO Initial LIGO Barry C. Barish Caltech YKIS2005 Kyoto University 1-July-05 Einstein s Theory of Gravitation a necessary consequence of Special
Probing for Gravitational Waves LIGO Reach with LIGO AdLIGO Initial LIGO Barry C. Barish Caltech YKIS2005 Kyoto University 1-July-05 Einstein s Theory of Gravitation a necessary consequence of Special
GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral
 GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral Lazzaro Claudia for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 25 October 2017 GW170817 PhysRevLett.119.161101
GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral Lazzaro Claudia for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 25 October 2017 GW170817 PhysRevLett.119.161101
Outline. 1. Basics of gravitational wave transient signal searches. 2. Reconstruction of signal properties
 Gravitational Wave Transients state-of-the-arts: detection confidence and signal reconstruction G.A.Prodi, University of Trento and INFN, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Gravitational Wave Transients state-of-the-arts: detection confidence and signal reconstruction G.A.Prodi, University of Trento and INFN, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Chirplets pour la détection des ondes gravitationnelles
 Chirplets pour la détection des ondes gravitationnelles Éric Chassande-Mottin AstroParticule et Cosmologie, Paris et collaborateurs : Satya Mohapatra, Miriam Miele, Laura Cadonati, Zacharya Nemtzow Outline
Chirplets pour la détection des ondes gravitationnelles Éric Chassande-Mottin AstroParticule et Cosmologie, Paris et collaborateurs : Satya Mohapatra, Miriam Miele, Laura Cadonati, Zacharya Nemtzow Outline
Gravitational Wave Detection from the Ground Up
 Gravitational Wave Detection from the Ground Up Peter Shawhan (University of Maryland) for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO-G080393-00-Z From Simple Beginnings Joe Weber circa 1969 AIP Emilio Segre
Gravitational Wave Detection from the Ground Up Peter Shawhan (University of Maryland) for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO-G080393-00-Z From Simple Beginnings Joe Weber circa 1969 AIP Emilio Segre
Spacecraft clocks and General Relativity
 Raymond Angélil Prasenjit Saha May 22, 2013 Clocks in space - nothing new universe s expansion history stellar composition binary neutron star orbit determination galaxy rotation curves exoplanet discovery
Raymond Angélil Prasenjit Saha May 22, 2013 Clocks in space - nothing new universe s expansion history stellar composition binary neutron star orbit determination galaxy rotation curves exoplanet discovery
Past and Future in the Quest for Gravitational Wave Transients
 Crab-Chandra NASA/ESA Credit: NASA/COBE Past and Future in the Quest for Gravitational Wave Transients Laura Cadonati - University of Massachusetts, Amherst LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration
Crab-Chandra NASA/ESA Credit: NASA/COBE Past and Future in the Quest for Gravitational Wave Transients Laura Cadonati - University of Massachusetts, Amherst LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration
Optimal search for CW directed targets
 Optimal search for CW directed targets Jing Ming Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics Albert Einstein Institute Golm and Hannover, Germany jing.ming@aei.mpg.de 20-06-205 GWPAW Osaka AEI (Hannover)
Optimal search for CW directed targets Jing Ming Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics Albert Einstein Institute Golm and Hannover, Germany jing.ming@aei.mpg.de 20-06-205 GWPAW Osaka AEI (Hannover)
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-P030066-00 December 2, 2003 First upper limits from
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-P030066-00 December 2, 2003 First upper limits from
LIGO Present and Future. Barry Barish Directory of the LIGO Laboratory
 LIGO Present and Future Barry Barish Directory of the LIGO Laboratory LIGO I Schedule and Plan LIGO I has been built by LIGO Lab (Caltech & MIT) 1996 Construction Underway (mostly civil) 1997 Facility
LIGO Present and Future Barry Barish Directory of the LIGO Laboratory LIGO I Schedule and Plan LIGO I has been built by LIGO Lab (Caltech & MIT) 1996 Construction Underway (mostly civil) 1997 Facility
ANALYSIS OF BURST SIGNALS IN LIGO DATA. Irena Zivkovic, Alan Weinstein
 LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY LIGO CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-T010157-00-R 10/15/01 ANALYSIS OF BURST SIGNALS IN LIGO
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY LIGO CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-T010157-00-R 10/15/01 ANALYSIS OF BURST SIGNALS IN LIGO
Detecting the next Galactic supernova
 Detecting the next Galactic supernova Nicolas Arnaud on behalf of the Virgo-LAL group Now fellow at LHCb-CERN Moriond Gravitation 2003 GW supernova amplitudes Burst online filter performances Comparison
Detecting the next Galactic supernova Nicolas Arnaud on behalf of the Virgo-LAL group Now fellow at LHCb-CERN Moriond Gravitation 2003 GW supernova amplitudes Burst online filter performances Comparison
What have we learned from the detection of gravitational waves? Hyung Mok Lee Seoul National University
 What have we learned from the detection of gravitational waves? Hyung Mok Lee Seoul National University Outline Summary of 1st and 2nd Observing Runs Characteristics of detected sources Astrophysical Implications
What have we learned from the detection of gravitational waves? Hyung Mok Lee Seoul National University Outline Summary of 1st and 2nd Observing Runs Characteristics of detected sources Astrophysical Implications
Astrophysical Rates of Gravitational-Wave Compact Binary Sources in O3
 Astrophysical Rates of Gravitational-Wave Compact Binary Sources in O3 Tom Dent (Albert Einstein Institute, Hannover) Chris Pankow (CIERA/Northwestern) for the LIGO and Virgo Collaborations DCC: LIGO-G1800370
Astrophysical Rates of Gravitational-Wave Compact Binary Sources in O3 Tom Dent (Albert Einstein Institute, Hannover) Chris Pankow (CIERA/Northwestern) for the LIGO and Virgo Collaborations DCC: LIGO-G1800370
Confronting Theory with Gravitational Wave Observations
 Gravitation: A Decennial Perspective Confronting Theory with Gravitational Wave Observations B F Schutz Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics () Golm/Potsdam Germany The AEI congratulates The
Gravitation: A Decennial Perspective Confronting Theory with Gravitational Wave Observations B F Schutz Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics () Golm/Potsdam Germany The AEI congratulates The
M.-A. Bizouard, F. Cavalier. GWDAW 8 Milwaukee 19/12/03
 Coincidence and coherent analyses for burst search using interferometers M.-A. Bizouard, F. Cavalier on behalf of the Virgo-Orsay group Network model Results of coincidence analysis: loose and tight coincidence
Coincidence and coherent analyses for burst search using interferometers M.-A. Bizouard, F. Cavalier on behalf of the Virgo-Orsay group Network model Results of coincidence analysis: loose and tight coincidence
Metropolis-Hastings algorithm for extracting periodic gravitational wave signals from laser interferometric detector data
 Metropolis-Hastings algorithm for extracting periodic gravitational wave signals from laser interferometric detector data Nelson Christensen, 1, * Réjean J. Dupuis, 2, Graham Woan, 2, and Renate Meyer
Metropolis-Hastings algorithm for extracting periodic gravitational wave signals from laser interferometric detector data Nelson Christensen, 1, * Réjean J. Dupuis, 2, Graham Woan, 2, and Renate Meyer
Gravitational-Wave Astronomy - a Long Time Coming Livia Conti, for the Virgo Collaboration Fred Raab, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration
 Gravitational-Wave Astronomy - a Long Time Coming Livia Conti, for the Virgo Collaboration Fred Raab, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Hanford, WA LIGO Livingston, LA Virgo (Cascina, Italy) What
Gravitational-Wave Astronomy - a Long Time Coming Livia Conti, for the Virgo Collaboration Fred Raab, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Hanford, WA LIGO Livingston, LA Virgo (Cascina, Italy) What
Gravitational Waves Listening to the Universe. Teviet Creighton LIGO Laboratory California Institute of Technology
 Gravitational Waves Listening to the Universe Teviet Creighton LIGO Laboratory California Institute of Technology Summary So far, nearly all our knowledge of the Universe comes from electromagnetic radiation.
Gravitational Waves Listening to the Universe Teviet Creighton LIGO Laboratory California Institute of Technology Summary So far, nearly all our knowledge of the Universe comes from electromagnetic radiation.
Gravitational waves. Markus Pössel. What they are, how to detect them, and what they re good for. MPIA, March 11, 2016.
 What they are, how to detect them, and what they re good for AstroTechTalk MPIA, March 11, 2016 General relativity Interferometric detectors First direct detection What s next? Einstein s general theory
What they are, how to detect them, and what they re good for AstroTechTalk MPIA, March 11, 2016 General relativity Interferometric detectors First direct detection What s next? Einstein s general theory
continuous waves from rotating neutron stars
 continuous waves from rotating neutron stars Matthew Pitkin - University of Glasgow DAWN Workshop 7 May 2015 LIGO G1500603 0 continuous wave sources Rotating neutron stars with a non-axisymmetric deformation
continuous waves from rotating neutron stars Matthew Pitkin - University of Glasgow DAWN Workshop 7 May 2015 LIGO G1500603 0 continuous wave sources Rotating neutron stars with a non-axisymmetric deformation
Astrophysical Stochastic Gravitational Waves. Jonah Kanner PHYS 798G March 27, 2007
 Astrophysical Stochastic Gravitational Waves Jonah Kanner PHYS 798G March 27, 2007 Introduction Gravitational Waves come from space Require acceleration of dense mass (Think black holes and neutron stars!)
Astrophysical Stochastic Gravitational Waves Jonah Kanner PHYS 798G March 27, 2007 Introduction Gravitational Waves come from space Require acceleration of dense mass (Think black holes and neutron stars!)
First Scientific Results: Analysis of LIGO Data from the S1 Science Run
 First Scientific Results: Analysis of LIGO Data from the S1 Science Run Albert Lazzarini LIGO Laboratory Annual NSF Review of LIGO Laboratory 17-19 November 2003 LIGO Livingston Observatory, LA Outline
First Scientific Results: Analysis of LIGO Data from the S1 Science Run Albert Lazzarini LIGO Laboratory Annual NSF Review of LIGO Laboratory 17-19 November 2003 LIGO Livingston Observatory, LA Outline
The Status of Enhanced LIGO.
 The Status of Enhanced LIGO. Aidan Brooks. December 2008 AIP Congress 2008, Adelaide, Australia 1 Outline Gravitational Waves» Potential sources» Initial LIGO interferometer Enhanced LIGO upgrades» Increased
The Status of Enhanced LIGO. Aidan Brooks. December 2008 AIP Congress 2008, Adelaide, Australia 1 Outline Gravitational Waves» Potential sources» Initial LIGO interferometer Enhanced LIGO upgrades» Increased
Parameter estimation
 Parameter estimation Alberto Vecchio University of Birmingham UK 5 th LISA Symposium ESTEC, 12 th 15 th July 2004 Outline Computing the expected minimum mean squared error: Variance-covariance matrix Assumptions
Parameter estimation Alberto Vecchio University of Birmingham UK 5 th LISA Symposium ESTEC, 12 th 15 th July 2004 Outline Computing the expected minimum mean squared error: Variance-covariance matrix Assumptions
