LIGO s continuing search for gravitational waves
|
|
|
- Scot Warner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LIGO s continuing search for gravitational waves Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee LIGO Scientific Collaboration
2 LIGO Interferometers LIGO is an interferometric detector» A laser is used to measure the relative lengths of two orthogonal cavities (or arms) causing the interference pattern to change at the photodiode Measure fractional change in arm length h = δl/l As a wave passes, one arm stretches and the other shrinks. 1/13/2004 Caltech 2
3 Three fundamental noise processes frame the frequency window of LIGO detectors these are continuous random processes (almost Gaussian!) LIGO noise budget Shaking of ground transfers through the suspension into movement of the test mirrors Fluctuations in the Challenge of number real LIGO of photons data:» Strong line resonances arriving at the photodiode» Non-gaussian noise bursts» Dynamic calibration due to complicated control systems 1/13/2004 Caltech 3
4 Sources and our analysis strategy Compact binary systems» Neutron star inspiral» LIGO range =20Mpc, N< 1/(4yr)» Black hole inspiral/merger» LIGO range=105mpc, N<1/(2yr) Spinning neutron stars» LMXBs, known & unknown pulsars in our Galaxy» Need months of integration time Neutron star birth» Tumbling bar could be detectable to ~5Mpc (~1/3yr)» Convection within Galaxy (~1/30yr) Stochastic background» Big bang & other early universe» Background of GW bursts LSC Analysis Groups Inspiral analysis group» Brady & Gonzalez Burst analysis group:» Katsavounidis & Whitcomb Pulsar analysis group:» Landry & Papa Stochastic analysis group» Fritschel and Romano Challenge:» Weak and rare sources» Require optimal signal processing 1/13/2004 Caltech 4
5 Computational challenge of optimal signal processing Optimal signal processing:» Use filters which are tuned to the particular type of signal/source Rule of thumb:» As signal complexity increases, number of different filters increases» Attempt to analyze data in equivalent time to acquire it Examples:» Compact binary inspiral depends on masses, spins, eccentricity, orientation: ~100,000 different filters for masses only, giving ~100 GFlop computing problem» Phenomenological waveform from spinning neutron stars depends on sky location (Doppler shifts) and orientation: 1000 s TFlop computing problem Challenge:» Design and implement computationally efficient algorithms for filtering 1/13/2004 Caltech 5
6 Experience gained to date S2 2 nd Science Run end Apr days S1 1 st Science Run end Sept days S3 3 rd Science Run begin Nov days LIGO Target Sensitivity 1/13/2004 Caltech 6
7 Inspiral search pipeline: a case study in LIGO data analysis LIGO is sensitive to:» Gravitational waves from binary systems containing neutron stars & stellar mass black holes» Last several minutes of inspiral driven by GW emission Neutron Star Binaries» Known to exist (Hulse-Taylor)» Waveform accurately modeled» LIGO range =20Mpc, N< 1/(4yr) NS/BH, BH/BH» New science: rates, dynamics of gravitational field, merger waves» LIGO range=105mpc, N<1/(2yr) 1/13/2004 Caltech 71
8 GW Channel + simulated inspiral Optimal signal processing using a matched filter Filter to suppress high/low freq SNR Coalescence Time 1/13/2004 Caltech 8
9 Template filters for inspiral waves Use template based matched filtering algorithm Search for non-spinning binaries» 2.0 post-newtonian waveforms h(t) = (1Mpc/D) x [ sin(a) h I s (t-t0) + cos(a) hi c (t-t0)] D: effective distance a: unknown phase Discrete set of templates labeled by I=(m1, m2) 1/13/2004 Caltech 9
10 Templates for S2 playground data set Search for inspiral signals with matched filtering» Templates: 2 pn stationary phase waveforms 1.0 < (m 1,m 2 ) < 3.0 M sun» Generate bank for each chunk with maximum 3% loss in signal-to-noise» Apply a low frequency cutoff of 100 Hz to data» 15 x 256 sec data segments overlapped by 128 sec» Median power spectral estimate using 15 segments 1/13/2004 Caltech 10
11 Generation of inspiral triggers Resample data to 4096 Hz and high pass at 90 Hz Compute median PSD for 15 segments of length 256 sec Matched filter templates to obtain signal-to-noise If SNR > * compute template based veto, χ 2» Small values of χ 2 indicate that was accumulated in a manner consistent with an inspiral signal: If χ 2 < χ 2 * then record trigger at maximum Triggers are clustered within duration of each template Multiple templates can trigger at same time 1/13/2004 Caltech 11
12 Template based χ 2 test Break inspiral template into p pieces each of which should accumulate 1/p of the total SNR Construct 2 χ 8 i= 1 ( ρ ι ρ / 8) 2 In Gaussian noise, this is distributed Chi squared (2p- 2) degrees of freedom 1/13/2004 Caltech 12
13 Effectiveness of χ 2 veto p=8 Figure: D. Brown 1/13/2004 Caltech 13
14 Nature and origin of inspiral triggers Take a closer look at these triggers Figures: G. Gonzalez 1/13/2004 Caltech 14
15 Origin of striped triggers Non-Gaussian noise burst Coalescence time of trigger does not agree with 1/13/2004 Caltech 15 non-gaussian burst Figure: G. Gonzalez
16 Response of inspiral filters to glitch Figure: D. Brown 1/13/2004 Caltech 16
17 Vetoing non-gaussian noise bursts Construct vetoes to remove spurious inspiral triggers» Some inspiral triggers are due to obvious instrumental glitches» Look for explanation of spurious inspiral triggers in other channels Glitch monitors on auxiliary interferometer channels Physical environment monitoring channels Gravitational Wave Channel Beam Splitter Pick off Tune vetoes on playground then apply to inspiral triggers full data set 1/13/2004 Caltech 17
18 Important lesson from S1 analysis Largest SNR trigger in S1 analysis not a binary neutron star! S/N = 15.9, χ 2 /dof = 2.2 (m1,m2) = (1.3, 1.1) Msun What caused this? Appears to be saturation of a photodiode 1/13/2004 Caltech 18
19 What have we learned about instrumental vetoes so far? SegWizard: P. Shawhan Apply data quality flags up front!» Operators provide first line of defence» Science mode data flagged as it is taken Extra information used in deciding what data to analyze:» Exclude photodiode saturations» Exclude data without calibration lines» Exclude data with invalid timing Other lessons learned» A cattle-guard at Livingston was identified as a problem following an enginering run But.» Still lack good instrumental vetoes» A very difficult problem as expected 1/13/2004 Caltech 19
20 Target Population Simulate gravitational waves from a population of binary neutron stars» Rate of binary inspirals expected to be proportional to star formation rate» Population includes all galaxies out to maximum distance at SNR=5.5 Inject signals from population into data from all three LIGO interferometers» Inject in software» Validated by hardware injections Determine efficiency, ε, for detection of simulated signals at threshold *» Efficiency ε = N det / N inj Image: R. Powell 1/13/2004 Caltech 20
21 Trigger coincidence test Look for coincident triggers» Present in all interferometers» Coincident to within 11 ms between sites, 1 ms at the same site» Each mass parameter in the template must be the same to within 0.03 solar masses.» Compare distances measured at Livingston (D L ) and Hanford (D H ) Livingston and Hanford detectors are not exactly co-aligned So ratio of effective distance varies with sky location and polarization of source D H /D L 1/13/2004 Caltech 21
22 Tuning the amplitude cut Errors in distance estimates expected to decrease with increasing SNR Missed injections in coincidence D L - D H /D L < ε/ρ H + κ ε and κ tunable constants Remove amplitude cut to allow detection of these Milky Way events 1/13/2004 Caltech 22
23 Playground Results: Pipeline Efficiency Detected Andromeda Injections Average L1 Sensitivity Detected Milky Way Injections ε = Average H1 Sensitivity Missed Andromeda Injections (Too far away) 1/13/2004 Caltech 23
24 Automating the analysis chain Search codes run standalone using Condor batch scheduler» Directed Acyclic Graph describes workflow Use LALdataFind to locate data» Interrogation of replica catalog maintained by LDR (S. Koranda) All search code in» LAL and LALApps (many contributors) Inspiral code» Generates triggers from each interferometer Coincidence stage of the search is part of the jobs we run» Can add extra steps quite easily Code ready to run in LSC DataGrid» Plan to do this in /21/03 1
25 Concluding remarks Challenges and status:» Non-Gaussian bursts: still need to get a handle on them» Resonances require care in data processing and interpretation: could improve» Calibration: understanding and implementation are well under way» Algorithm design side of (near) optimal signal processing is in hand» Still lots of implementation work to automate things» Distributed computing is addressing some of computing requirements Implications for science:» Experience from science runs is speeding up analysis» New searches are getting under way» Future is bright for gravitational-wave detection with LIGO» Gravitational-wave astronomy is our ultimate challenge 1/13/2004 Caltech 30
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspirals with LIGO
 Searching for Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspirals with LIGO Duncan Brown University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Inspiral Working Group LIGO-G030671-00-Z S1 Binary
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspirals with LIGO Duncan Brown University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Inspiral Working Group LIGO-G030671-00-Z S1 Binary
Results from LIGO Searches for Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves
 Results from LIGO Searches for Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan (LIGO Laboratory / Caltech) For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration American Physical Society April Meeting May 4, 2004 Denver,
Results from LIGO Searches for Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan (LIGO Laboratory / Caltech) For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration American Physical Society April Meeting May 4, 2004 Denver,
arxiv:gr-qc/ v1 4 Dec 2003
 Testing the LIGO Inspiral Analysis with Hardware Injections arxiv:gr-qc/0312031 v1 4 Dec 2003 Duncan A. Brown 1 for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
Testing the LIGO Inspiral Analysis with Hardware Injections arxiv:gr-qc/0312031 v1 4 Dec 2003 Duncan A. Brown 1 for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
LIGO Observational Results
 LIGO Observational Results Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin Milwaukee on behalf of LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Science Goals Direct verification of two dramatic predictions of Einstein s general
LIGO Observational Results Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin Milwaukee on behalf of LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Science Goals Direct verification of two dramatic predictions of Einstein s general
Search for compact binary systems in LIGO data
 Search for compact binary systems in LIGO data Thomas Cokelaer On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Cardiff University, U.K. LIGO-G060630-00-Z Plan 1) Overview What kind of gravitational waves
Search for compact binary systems in LIGO data Thomas Cokelaer On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Cardiff University, U.K. LIGO-G060630-00-Z Plan 1) Overview What kind of gravitational waves
LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans. Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04
 LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04 Science Goals Physics» Direct verification of the most relativistic prediction of general relativity» Detailed tests of properties of gravitational
LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04 Science Goals Physics» Direct verification of the most relativistic prediction of general relativity» Detailed tests of properties of gravitational
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis
 Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis Peter Shawhan Physics 798G April 12, 2007 Outline Gravitational-wave data General data analysis principles Specific data analysis methods Classification of signals Methods
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis Peter Shawhan Physics 798G April 12, 2007 Outline Gravitational-wave data General data analysis principles Specific data analysis methods Classification of signals Methods
LIGO S2 Inspiral Hardware Injections
 LIGO S2 Inspiral Hardware Injections Steve Fairhurst University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee LSC Inspiral Working Group GWDAW December 19, 2003. LIGO-G030688-00-Z Introduction Hardware injections provide a good
LIGO S2 Inspiral Hardware Injections Steve Fairhurst University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee LSC Inspiral Working Group GWDAW December 19, 2003. LIGO-G030688-00-Z Introduction Hardware injections provide a good
Search for Gravitational Wave Transients. Florent Robinet On behalf of the LSC and Virgo Collaborations
 Search for Gravitational Wave Transients On behalf of the LSC and Virgo Collaborations 1 Gravitational Waves Gravitational waves = "ripples" in space time Weak field approximation : g = h h 1 Wave equation,
Search for Gravitational Wave Transients On behalf of the LSC and Virgo Collaborations 1 Gravitational Waves Gravitational waves = "ripples" in space time Weak field approximation : g = h h 1 Wave equation,
Status and Prospects for LIGO
 Status and Prospects for LIGO Crab Pulsar St Thomas, Virgin Islands Barry C. Barish Caltech 17-March-06 LIGO Livingston, Louisiana 4 km 17-March-06 Confronting Gravity - St Thomas 2 LIGO Hanford Washington
Status and Prospects for LIGO Crab Pulsar St Thomas, Virgin Islands Barry C. Barish Caltech 17-March-06 LIGO Livingston, Louisiana 4 km 17-March-06 Confronting Gravity - St Thomas 2 LIGO Hanford Washington
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 2
 Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 2 Peter S. Shawhan Gravitational Wave Astronomy Summer School May 29, 2012 Outline for Today Matched filtering in the time domain Matched filtering in the frequency
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 2 Peter S. Shawhan Gravitational Wave Astronomy Summer School May 29, 2012 Outline for Today Matched filtering in the time domain Matched filtering in the frequency
S. V. Dhurandhar IUCAA Pune, India
 Extended hierarchical search (EHS) for inspiraling compact binaries S. V. Dhurandhar IUCAA Pune, India * A. Sengupta, A. Lazzarini, P. Shawhan LIGO-G040556-00-R Plan of the Talk The 1-step (flat) search
Extended hierarchical search (EHS) for inspiraling compact binaries S. V. Dhurandhar IUCAA Pune, India * A. Sengupta, A. Lazzarini, P. Shawhan LIGO-G040556-00-R Plan of the Talk The 1-step (flat) search
Status of LIGO. David Shoemaker LISA Symposium 13 July 2004 LIGO-G M
 Status of LIGO David Shoemaker LISA Symposium 13 July 2004 Ground-based interferometric gravitational-wave detectors Search for GWs above lower frequency limit imposed by gravity gradients» Might go as
Status of LIGO David Shoemaker LISA Symposium 13 July 2004 Ground-based interferometric gravitational-wave detectors Search for GWs above lower frequency limit imposed by gravity gradients» Might go as
How to measure a distance of one thousandth of the proton diameter? The detection of gravitational waves
 How to measure a distance of one thousandth of the proton diameter? The detection of gravitational waves M. Tacca Laboratoire AstroParticule et Cosmologie (APC) - Paris Journée GPhys - 2016 July 6th General
How to measure a distance of one thousandth of the proton diameter? The detection of gravitational waves M. Tacca Laboratoire AstroParticule et Cosmologie (APC) - Paris Journée GPhys - 2016 July 6th General
Search for inspiralling neutron stars in LIGO S1 data
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S691 S696 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)68883-6 Search for inspiralling neutron stars in LIGO S1 data Gabriela González
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S691 S696 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)68883-6 Search for inspiralling neutron stars in LIGO S1 data Gabriela González
GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral
 GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral Lazzaro Claudia for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 25 October 2017 GW170817 PhysRevLett.119.161101
GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral Lazzaro Claudia for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 25 October 2017 GW170817 PhysRevLett.119.161101
The LIGO Project: a Status Report
 The LIGO Project: a Status Report LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO Livingston Observatory Laura Cadonati LIGO Laboratory, MIT for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Conference on Gravitational Wave Sources
The LIGO Project: a Status Report LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO Livingston Observatory Laura Cadonati LIGO Laboratory, MIT for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Conference on Gravitational Wave Sources
Searching for gravitational waves. with LIGO detectors
 Werner Berger, ZIB, AEI, CCT Searching for gravitational waves LIGO Hanford with LIGO detectors Gabriela González Louisiana State University On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration KITP Colloquium,
Werner Berger, ZIB, AEI, CCT Searching for gravitational waves LIGO Hanford with LIGO detectors Gabriela González Louisiana State University On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration KITP Colloquium,
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems
 Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems Stephen Fairhurst Cardiff University and LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Outline Motivation Searching for Coalescing Binaries Latest Results
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems Stephen Fairhurst Cardiff University and LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Outline Motivation Searching for Coalescing Binaries Latest Results
GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University. Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne]
![GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University. Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne] GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University. Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne]](/thumbs/79/79556320.jpg) GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne] Summary of talk Review of observational upper limits and current and planned
GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Eanna E. Flanagan Cornell University Presentation to CAA, 30 April 2003 [Some slides provided by Kip Thorne] Summary of talk Review of observational upper limits and current and planned
Gravitational wave detection with Virgo and LIGO experiment - Case of the long bursts
 Gravitational wave detection with Virgo and LIGO experiment - Case of the long bursts Samuel Franco Supervisor: Patrice Hello Laboratoire de l Accélérateur Linéaire (Orsay) 06/12/2013 Samuel Franco (LAL)
Gravitational wave detection with Virgo and LIGO experiment - Case of the long bursts Samuel Franco Supervisor: Patrice Hello Laboratoire de l Accélérateur Linéaire (Orsay) 06/12/2013 Samuel Franco (LAL)
Data Analysis Pipeline and Tuning
 60 Chapter 6 Data Analysis Pipeline and Tuning In this chapter we describe the standard pipeline used to analyze data from GW detectors, such as the LIGO detectors, for GW signals from CBC. In addition,
60 Chapter 6 Data Analysis Pipeline and Tuning In this chapter we describe the standard pipeline used to analyze data from GW detectors, such as the LIGO detectors, for GW signals from CBC. In addition,
Searching for gravitational waves from binary inspirals with LIGO
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S1625 S1633 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)79876-7 Searching for gravitational waves from binary inspirals with LIGO Duncan
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S1625 S1633 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)79876-7 Searching for gravitational waves from binary inspirals with LIGO Duncan
Gravitational wave cosmology Lecture 2. Daniel Holz The University of Chicago
 Gravitational wave cosmology Lecture 2 Daniel Holz The University of Chicago Thunder and lightning Thus far we ve only seen the Universe (and 95% of it is dark: dark matter and dark energy). In the the
Gravitational wave cosmology Lecture 2 Daniel Holz The University of Chicago Thunder and lightning Thus far we ve only seen the Universe (and 95% of it is dark: dark matter and dark energy). In the the
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 3
 Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 3 Peter S. Shawhan Gravitational Wave Astronomy Summer School May 30, 2012 Outline for Today Gaining confidence in a signal candidate Consistency tests Data quality
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 3 Peter S. Shawhan Gravitational Wave Astronomy Summer School May 30, 2012 Outline for Today Gaining confidence in a signal candidate Consistency tests Data quality
Data Analysis Pipeline: The Search for Gravitational Waves in Real life
 Data Analysis Pipeline: The Search for Gravitational Waves in Real life Romain Gouaty LAPP - Université de Savoie - CNRS/IN2P3 On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Data Analysis Pipeline: The Search for Gravitational Waves in Real life Romain Gouaty LAPP - Université de Savoie - CNRS/IN2P3 On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Confronting Theory with Gravitational Wave Observations
 Gravitation: A Decennial Perspective Confronting Theory with Gravitational Wave Observations B F Schutz Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics () Golm/Potsdam Germany The AEI congratulates The
Gravitation: A Decennial Perspective Confronting Theory with Gravitational Wave Observations B F Schutz Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics () Golm/Potsdam Germany The AEI congratulates The
Data quality vetoes and their effect on searches for gravitational waves from compact binary systems
 Data quality vetoes and their effect on searches for gravitational waves from compact binary systems Samantha Usman August 12, 2014 Abstract Data quality flags have been designed to prevent problems caused
Data quality vetoes and their effect on searches for gravitational waves from compact binary systems Samantha Usman August 12, 2014 Abstract Data quality flags have been designed to prevent problems caused
State of LIGO. Barry Barish. S1 sensitivities. LSC Meeting LLO Hanford, WA 10-Nov GEO -- L 2km -- H 4km -- L 4km LIGO-G M
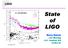 S1 sensitivities -- GEO -- L 2km -- H 4km -- L 4km State of h 0 LIGO Barry Barish LSC Meeting LLO Hanford, WA 10-Nov-03 Goals and Priorities LSC -Aug 02 Interferometer performance» Integrate commissioning
S1 sensitivities -- GEO -- L 2km -- H 4km -- L 4km State of h 0 LIGO Barry Barish LSC Meeting LLO Hanford, WA 10-Nov-03 Goals and Priorities LSC -Aug 02 Interferometer performance» Integrate commissioning
Dynamics of star clusters containing stellar mass black holes: 1. Introduction to Gravitational Waves
 Dynamics of star clusters containing stellar mass black holes: 1. Introduction to Gravitational Waves July 25, 2017 Bonn Seoul National University Outline What are the gravitational waves? Generation of
Dynamics of star clusters containing stellar mass black holes: 1. Introduction to Gravitational Waves July 25, 2017 Bonn Seoul National University Outline What are the gravitational waves? Generation of
First Scientific Results: Analysis of LIGO Data from the S1 Science Run
 First Scientific Results: Analysis of LIGO Data from the S1 Science Run Albert Lazzarini LIGO Laboratory Annual NSF Review of LIGO Laboratory 17-19 November 2003 LIGO Livingston Observatory, LA Outline
First Scientific Results: Analysis of LIGO Data from the S1 Science Run Albert Lazzarini LIGO Laboratory Annual NSF Review of LIGO Laboratory 17-19 November 2003 LIGO Livingston Observatory, LA Outline
The Status of Enhanced LIGO.
 The Status of Enhanced LIGO. Aidan Brooks. December 2008 AIP Congress 2008, Adelaide, Australia 1 Outline Gravitational Waves» Potential sources» Initial LIGO interferometer Enhanced LIGO upgrades» Increased
The Status of Enhanced LIGO. Aidan Brooks. December 2008 AIP Congress 2008, Adelaide, Australia 1 Outline Gravitational Waves» Potential sources» Initial LIGO interferometer Enhanced LIGO upgrades» Increased
Gravitational Wave Detection from the Ground Up
 Gravitational Wave Detection from the Ground Up Peter Shawhan (University of Maryland) for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO-G080393-00-Z From Simple Beginnings Joe Weber circa 1969 AIP Emilio Segre
Gravitational Wave Detection from the Ground Up Peter Shawhan (University of Maryland) for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO-G080393-00-Z From Simple Beginnings Joe Weber circa 1969 AIP Emilio Segre
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves
 Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Barry C. Barish Caltech Argonne National Laboratory 16-Jan-04 LIGO-G030523-00-M
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Barry C. Barish Caltech Argonne National Laboratory 16-Jan-04 LIGO-G030523-00-M
Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars
 Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars Ian Jones D.I.Jones@soton.ac.uk General Relativity Group, Southampton University Ian Jones Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars 1/23
Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars Ian Jones D.I.Jones@soton.ac.uk General Relativity Group, Southampton University Ian Jones Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars 1/23
The direct detection of gravitational waves: The first discovery, and what the future might bring
 The direct detection of gravitational waves: The first discovery, and what the future might bring Chris Van Den Broeck Nikhef - National Institute for Subatomic Physics Amsterdam, The Netherlands Physics
The direct detection of gravitational waves: The first discovery, and what the future might bring Chris Van Den Broeck Nikhef - National Institute for Subatomic Physics Amsterdam, The Netherlands Physics
Gravity -- Studying the Fabric of the Universe
 Gravity -- Studying the Fabric of the Universe Barry C. Barish Caltech "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) AAAS Annual Meeting Denver, Colorado 17-Feb-03
Gravity -- Studying the Fabric of the Universe Barry C. Barish Caltech "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) AAAS Annual Meeting Denver, Colorado 17-Feb-03
Gravitational Wave Astronomy the sound of spacetime. Marc Favata Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics
 Gravitational Wave Astronomy the sound of spacetime Marc Favata Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics What are gravitational waves? Oscillations in the gravitational field ripples in the curvature of
Gravitational Wave Astronomy the sound of spacetime Marc Favata Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics What are gravitational waves? Oscillations in the gravitational field ripples in the curvature of
What can LIGO detect? Abstract
 What can LIGO detect? Adam Getchell Physics Department, University of California, Davis, 95616 Abstract This briey reviews the literature on gravitational wave astronomy, including theoretical basis, experimental
What can LIGO detect? Adam Getchell Physics Department, University of California, Davis, 95616 Abstract This briey reviews the literature on gravitational wave astronomy, including theoretical basis, experimental
Scientific Results from the first LIGO Science Runs
 Scientific Results from the first LIGO Science Runs Introduction to GW s and LIGO The LIGO Science runs Physics, astrophysics, and S1 analysis results:» Binary inspirals» Pulsars and CW Sources» Bursts
Scientific Results from the first LIGO Science Runs Introduction to GW s and LIGO The LIGO Science runs Physics, astrophysics, and S1 analysis results:» Binary inspirals» Pulsars and CW Sources» Bursts
The gravitational wave detector VIRGO
 The gravitational wave detector VIRGO for the VIRGO collaboration Raffaele Flaminio Laboratoire d Annecy-le-Vieux de Physique des Particules (LAPP) IN2P3 - CNRS Summary I. A bit of gravitational wave physics
The gravitational wave detector VIRGO for the VIRGO collaboration Raffaele Flaminio Laboratoire d Annecy-le-Vieux de Physique des Particules (LAPP) IN2P3 - CNRS Summary I. A bit of gravitational wave physics
M.Alessandra Papa. Max Planck Inst. f. Gravitationsphysik and Univ. of Wisconsin- Milwaukee. ICGC Conference 2007, December Pune
 Gravitational Wave Data Analysis M.Alessandra Papa Max Planck Inst. f. Gravitationsphysik and Univ. of Wisconsin- Milwaukee ICGC Conference 2007, December Pune Gravitational wave data analysis * legacy
Gravitational Wave Data Analysis M.Alessandra Papa Max Planck Inst. f. Gravitationsphysik and Univ. of Wisconsin- Milwaukee ICGC Conference 2007, December Pune Gravitational wave data analysis * legacy
Binary Black Holes, Gravitational Waves, & Numerical Relativity Part 1
 1 Binary Black Holes, Gravitational Waves, & Numerical Relativity Part 1 Joan Centrella Chief, Gravitational Astrophysics Laboratory NASA/GSFC Summer School on Nuclear and Particle Astrophysics: Connecting
1 Binary Black Holes, Gravitational Waves, & Numerical Relativity Part 1 Joan Centrella Chief, Gravitational Astrophysics Laboratory NASA/GSFC Summer School on Nuclear and Particle Astrophysics: Connecting
Long-term strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups
 Longterm strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups Barry Barish APPEC Meeting London, UK 29Jan04 International Interferometer Network Simultaneously detect signal (within msec) LIGO
Longterm strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups Barry Barish APPEC Meeting London, UK 29Jan04 International Interferometer Network Simultaneously detect signal (within msec) LIGO
Searches for Gravitational Waves from Binary Neutron Stars: A Review
 LIGO-P070053-A-Z Searches for Gravitational Waves from Binary Neutron Stars: A Review Warren G. Anderson 1 and Jolien D. E. Creighton 2 1 Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee, P.O.
LIGO-P070053-A-Z Searches for Gravitational Waves from Binary Neutron Stars: A Review Warren G. Anderson 1 and Jolien D. E. Creighton 2 1 Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee, P.O.
What have we learned from coalescing Black Hole binary GW150914
 Stas Babak ( for LIGO and VIRGO collaboration). Albert Einstein Institute (Potsdam-Golm) What have we learned from coalescing Black Hole binary GW150914 LIGO_DCC:G1600346 PRL 116, 061102 (2016) Principles
Stas Babak ( for LIGO and VIRGO collaboration). Albert Einstein Institute (Potsdam-Golm) What have we learned from coalescing Black Hole binary GW150914 LIGO_DCC:G1600346 PRL 116, 061102 (2016) Principles
Outline. 1. Basics of gravitational wave transient signal searches. 2. Reconstruction of signal properties
 Gravitational Wave Transients state-of-the-arts: detection confidence and signal reconstruction G.A.Prodi, University of Trento and INFN, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Gravitational Wave Transients state-of-the-arts: detection confidence and signal reconstruction G.A.Prodi, University of Trento and INFN, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
ANALYSIS OF BURST SIGNALS IN LIGO DATA. Irena Zivkovic, Alan Weinstein
 LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY LIGO CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-T010157-00-R 10/15/01 ANALYSIS OF BURST SIGNALS IN LIGO
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY LIGO CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-T010157-00-R 10/15/01 ANALYSIS OF BURST SIGNALS IN LIGO
LIGO and the Quest for Gravitational Waves
 LIGO and the Quest for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) LIGO-G030523-00-M Barry C. Barish Caltech UT Austin 24-Sept-03 1 A Conceptual
LIGO and the Quest for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) LIGO-G030523-00-M Barry C. Barish Caltech UT Austin 24-Sept-03 1 A Conceptual
Strategy for signal classification to improve data quality for Advanced Detectors gravitational-wave searches
 Strategy for signal classification to improve data quality for Advanced Detectors gravitational-wave searches E. Cuoco 1, A.Torres-Forné 2,J.A. Font 2,7, J.Powell 3, R.Lynch 4, D.Trifiró 5 2 Universitat
Strategy for signal classification to improve data quality for Advanced Detectors gravitational-wave searches E. Cuoco 1, A.Torres-Forné 2,J.A. Font 2,7, J.Powell 3, R.Lynch 4, D.Trifiró 5 2 Universitat
Gravitational Waves and LIGO
 Gravitational Waves and LIGO Ray Frey, University of Oregon 1. GW Physics and Astrophysics 2. How to detect GWs The experimental challenge 3. Prospects June 16, 2004 R. Frey QNet 1 General Relativity Some
Gravitational Waves and LIGO Ray Frey, University of Oregon 1. GW Physics and Astrophysics 2. How to detect GWs The experimental challenge 3. Prospects June 16, 2004 R. Frey QNet 1 General Relativity Some
Scientific Results from the first LIGO Science Run
 Scientific Results from the first LIGO Science Run Introduction to GW s,ligo, and the science runs The LIGO S1 run Analysis Organization Physics goals and S1 analysis results:» Burst (Unmodeled transient)
Scientific Results from the first LIGO Science Run Introduction to GW s,ligo, and the science runs The LIGO S1 run Analysis Organization Physics goals and S1 analysis results:» Burst (Unmodeled transient)
LIGO Detection of Gravitational Waves. Dr. Stephen Ng
 LIGO Detection of Gravitational Waves Dr. Stephen Ng Gravitational Waves Predicted by Einstein s general relativity in 1916 Indirect confirmation with binary pulsar PSR B1913+16 (1993 Nobel prize in physics)
LIGO Detection of Gravitational Waves Dr. Stephen Ng Gravitational Waves Predicted by Einstein s general relativity in 1916 Indirect confirmation with binary pulsar PSR B1913+16 (1993 Nobel prize in physics)
Gravity. Newtonian gravity: F = G M1 M2/r 2
 Gravity Einstein s General theory of relativity : Gravity is a manifestation of curvature of 4- dimensional (3 space + 1 time) space-time produced by matter (metric equation? g μν = η μν ) If the curvature
Gravity Einstein s General theory of relativity : Gravity is a manifestation of curvature of 4- dimensional (3 space + 1 time) space-time produced by matter (metric equation? g μν = η μν ) If the curvature
Lecture 3. Alex Nielsen Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics Hanover, Germany. How can we detect gravitational wave signals?
 Lecture 3 Alex Nielsen Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics Hanover, Germany How can we detect gravitational wave signals? 2015 International Summer School on Numerical Relativity and Gravitational
Lecture 3 Alex Nielsen Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics Hanover, Germany How can we detect gravitational wave signals? 2015 International Summer School on Numerical Relativity and Gravitational
Python in Gravitational Waves communities
 Python in Gravitational Waves communities Elena Cuoco (elena.cuoco@ego-gw.it) European Gravitational Observatory on behalf of Virgo Collaboration VIR-0346A-16 Ph.D in Physics, working at EGO Physicist
Python in Gravitational Waves communities Elena Cuoco (elena.cuoco@ego-gw.it) European Gravitational Observatory on behalf of Virgo Collaboration VIR-0346A-16 Ph.D in Physics, working at EGO Physicist
Searching for Stochastic Gravitational Wave Background with LIGO
 Searching for Stochastic Gravitational Wave Background with LIGO Vuk Mandic University of Minnesota 09/21/07 Outline LIGO Experiment:» Overview» Status» Future upgrades Stochastic background of gravitational
Searching for Stochastic Gravitational Wave Background with LIGO Vuk Mandic University of Minnesota 09/21/07 Outline LIGO Experiment:» Overview» Status» Future upgrades Stochastic background of gravitational
Gravitational Wave Astronomy using 0.1Hz space laser interferometer. Takashi Nakamura GWDAW-8 Milwaukee 2003/12/17 1
 Gravitational Wave Astronomy using 0.1Hz space laser interferometer Takashi Nakamura GWDAW-8 Milwaukee 2003/12/17 1 In 2001 we considered what we can do using 0.1 hertz laser interferometer ( Seto, Kawamura
Gravitational Wave Astronomy using 0.1Hz space laser interferometer Takashi Nakamura GWDAW-8 Milwaukee 2003/12/17 1 In 2001 we considered what we can do using 0.1 hertz laser interferometer ( Seto, Kawamura
Astrophysical Source Identification and Signature (ASIS) Group: Implementation for LIGO-I
 Astrophysical Source Identification and Signature (ASIS) Group: Implementation for LIGO-I Bruce Allen Chair, LSC ASIS working group University of Wisconsin - Milwaukee Marcel Grossman 2000.07.02 LIGO Scientific
Astrophysical Source Identification and Signature (ASIS) Group: Implementation for LIGO-I Bruce Allen Chair, LSC ASIS working group University of Wisconsin - Milwaukee Marcel Grossman 2000.07.02 LIGO Scientific
Gravitational Waves: From Einstein to a New Science
 Gravitational Waves: From Einstein to a New Science LIGO-G1602199 Barry C Barish Caltech - LIGO 1.3 Billion Years Ago 2 Black Holes Regions of space created by super dense matter from where nothing can
Gravitational Waves: From Einstein to a New Science LIGO-G1602199 Barry C Barish Caltech - LIGO 1.3 Billion Years Ago 2 Black Holes Regions of space created by super dense matter from where nothing can
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves
 Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves Barry C. Barish Caltech Crab Pulsar Georgia Tech 26-April-06 General Relativity the essential idea G μν = 8πΤ μν Gravity is not a force, but a property of space
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves Barry C. Barish Caltech Crab Pulsar Georgia Tech 26-April-06 General Relativity the essential idea G μν = 8πΤ μν Gravity is not a force, but a property of space
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves
 Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves Barry C. Barish Caltech Crab Pulsar University of Illinois 16-Feb-06 General Relativity the essential idea G μν = 8πΤ μν Gravity is not a force, but a property
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves Barry C. Barish Caltech Crab Pulsar University of Illinois 16-Feb-06 General Relativity the essential idea G μν = 8πΤ μν Gravity is not a force, but a property
Overview Ground-based Interferometers. Barry Barish Caltech Amaldi-6 20-June-05
 Overview Ground-based Interferometers Barry Barish Caltech Amaldi-6 20-June-05 TAMA Japan 300m Interferometer Detectors LIGO Louisiana 4000m Virgo Italy 3000m AIGO Australia future GEO Germany 600m LIGO
Overview Ground-based Interferometers Barry Barish Caltech Amaldi-6 20-June-05 TAMA Japan 300m Interferometer Detectors LIGO Louisiana 4000m Virgo Italy 3000m AIGO Australia future GEO Germany 600m LIGO
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO)! A Brief Overview!
 Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) A Brief Overview Sharon Brunett California Institute of Technology Pacific Research Platform Workshop October 15, 2015 Credit: AEI, CCT, LSU LIGO
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) A Brief Overview Sharon Brunett California Institute of Technology Pacific Research Platform Workshop October 15, 2015 Credit: AEI, CCT, LSU LIGO
Gravitational wave data analysis
 Max Planck Institut für Gravitationsphysik Albert Einstein Institut, Germany Pasadena, June 2011 1 Introduction to gravitational waves 2 3 4 5 6 Gravitational Waves GR can be formulated in terms of a spacetime
Max Planck Institut für Gravitationsphysik Albert Einstein Institut, Germany Pasadena, June 2011 1 Introduction to gravitational waves 2 3 4 5 6 Gravitational Waves GR can be formulated in terms of a spacetime
GW Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger
 GW150914 Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger F. Marion for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration Seminar at CPPM, 2016 March 3 Introduction Sources
GW150914 Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger F. Marion for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration Seminar at CPPM, 2016 March 3 Introduction Sources
Astrophysical Stochastic Gravitational Waves. Jonah Kanner PHYS 798G March 27, 2007
 Astrophysical Stochastic Gravitational Waves Jonah Kanner PHYS 798G March 27, 2007 Introduction Gravitational Waves come from space Require acceleration of dense mass (Think black holes and neutron stars!)
Astrophysical Stochastic Gravitational Waves Jonah Kanner PHYS 798G March 27, 2007 Introduction Gravitational Waves come from space Require acceleration of dense mass (Think black holes and neutron stars!)
Reducing false alarms in searches for gravitational waves from coalescing binary systems
 Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Master's Theses Graduate School 2007 Reducing false alarms in searches for gravitational waves from coalescing binary systems Andres Rodriguez Louisiana
Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Master's Theses Graduate School 2007 Reducing false alarms in searches for gravitational waves from coalescing binary systems Andres Rodriguez Louisiana
Gravitational Waves. Masaru Shibata U. Tokyo
 Gravitational Waves Masaru Shibata U. Tokyo 1. Gravitational wave theory briefly 2. Sources of gravitational waves 2A: High frequency (f > 10 Hz) 2B: Low frequency (f < 10 Hz) (talk 2B only in the case
Gravitational Waves Masaru Shibata U. Tokyo 1. Gravitational wave theory briefly 2. Sources of gravitational waves 2A: High frequency (f > 10 Hz) 2B: Low frequency (f < 10 Hz) (talk 2B only in the case
Searching for Intermediate Mass Black Holes mergers
 Searching for Intermediate Mass Black Holes mergers G. A. Prodi, Università di Trento and INFN for the LIGO Scientific collaboration and the Virgo collaboration special credits to Giulio Mazzolo and Chris
Searching for Intermediate Mass Black Holes mergers G. A. Prodi, Università di Trento and INFN for the LIGO Scientific collaboration and the Virgo collaboration special credits to Giulio Mazzolo and Chris
The LIGO Experiment Present and Future
 The LIGO Experiment Present and Future Keith Riles University of Michigan For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration APS Meeting Denver May 1 4, 2004 LIGO-G040239-00-Z What are Gravitational Waves? Gravitational
The LIGO Experiment Present and Future Keith Riles University of Michigan For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration APS Meeting Denver May 1 4, 2004 LIGO-G040239-00-Z What are Gravitational Waves? Gravitational
LIGO: The Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory
 LIGO: The Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory Credit: Werner Benger/ZIB/AEI/CCT-LSU Michael Landry LIGO Hanford Observatory/Caltech for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration (LSC) http://www.ligo.org
LIGO: The Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory Credit: Werner Benger/ZIB/AEI/CCT-LSU Michael Landry LIGO Hanford Observatory/Caltech for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration (LSC) http://www.ligo.org
GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY
 GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY A. Melatos (Melbourne) 1. GW: physics & astronomy 2. Current- & next-gen detectors & searches 3. Burst sources: CBC, SN GR, cosmology 4. Periodic sources: NS subatomic physics
GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY A. Melatos (Melbourne) 1. GW: physics & astronomy 2. Current- & next-gen detectors & searches 3. Burst sources: CBC, SN GR, cosmology 4. Periodic sources: NS subatomic physics
Gravitational Wave Astronomy
 Gravitational Wave Astronomy Giles Hammond SUPA, University of Glasgow, UK on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 14 th Lomonosov conference on Elementary Particle Physics
Gravitational Wave Astronomy Giles Hammond SUPA, University of Glasgow, UK on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 14 th Lomonosov conference on Elementary Particle Physics
Chirplets pour la détection des ondes gravitationnelles
 Chirplets pour la détection des ondes gravitationnelles Éric Chassande-Mottin AstroParticule et Cosmologie, Paris et collaborateurs : Satya Mohapatra, Miriam Miele, Laura Cadonati, Zacharya Nemtzow Outline
Chirplets pour la détection des ondes gravitationnelles Éric Chassande-Mottin AstroParticule et Cosmologie, Paris et collaborateurs : Satya Mohapatra, Miriam Miele, Laura Cadonati, Zacharya Nemtzow Outline
Overview of Gravitational Wave Physics [PHYS879]
![Overview of Gravitational Wave Physics [PHYS879] Overview of Gravitational Wave Physics [PHYS879]](/thumbs/80/82252021.jpg) Overview of Gravitational Wave Physics [PHYS879] Alessandra Buonanno Maryland Center for Fundamental Physics Joint Space-Science Institute Department of Physics University of Maryland Content: What are
Overview of Gravitational Wave Physics [PHYS879] Alessandra Buonanno Maryland Center for Fundamental Physics Joint Space-Science Institute Department of Physics University of Maryland Content: What are
Interferometric. Gravitational Wav. Detectors. \p World Scientific. Fundamentals of. Peter R. Sawlson. Syracuse University, USA.
 SINGAPORE HONGKONG Fundamentals of Interferometric Gravitational Wav Detectors Second Edition Peter R. Sawlson Martin A. Pomerantz '37 Professor of Physics Syracuse University, USA \p World Scientific
SINGAPORE HONGKONG Fundamentals of Interferometric Gravitational Wav Detectors Second Edition Peter R. Sawlson Martin A. Pomerantz '37 Professor of Physics Syracuse University, USA \p World Scientific
Data Characterization in Gravitational Waves
 Data Characterization in Gravitational Waves Soma Mukherjee Max Planck Institut fuer Gravitationsphysik Golm, Germany. Talk at University of Texas, Brownsville. March 26, 2003 What data do we have? Consists
Data Characterization in Gravitational Waves Soma Mukherjee Max Planck Institut fuer Gravitationsphysik Golm, Germany. Talk at University of Texas, Brownsville. March 26, 2003 What data do we have? Consists
Gravitational Waves & Intermediate Mass Black Holes. Lee Samuel Finn Center for Gravitational Wave Physics
 Gravitational Waves & Intermediate Mass Black Holes Lee Samuel Finn Center for Gravitational Wave Physics Outline What are gravitational waves? How are they produced? How are they detected? Gravitational
Gravitational Waves & Intermediate Mass Black Holes Lee Samuel Finn Center for Gravitational Wave Physics Outline What are gravitational waves? How are they produced? How are they detected? Gravitational
Summer Research Projects for 2018
 Summer Research Projects for 2018 LIGO Livingston (Louisiana) Scattered Light Investigations Light scattered from the main beam path in the Advanced LIGO interferometer can re-enter the beam path after
Summer Research Projects for 2018 LIGO Livingston (Louisiana) Scattered Light Investigations Light scattered from the main beam path in the Advanced LIGO interferometer can re-enter the beam path after
The Quest to Detect Gravitational Waves
 The Quest to Detect Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan California Institute of Technology / LIGO Laboratory What Physicists Do lecture Sonoma State University March 8, 2004 LIGO-G040055-00-E Outline Different
The Quest to Detect Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan California Institute of Technology / LIGO Laboratory What Physicists Do lecture Sonoma State University March 8, 2004 LIGO-G040055-00-E Outline Different
Contents. References... 23
 Contents 1 A Case Study on the Use of Workflow Technologies for Scientific Analysis: Gravitational Wave Data Analysis Duncan A. Brown Patrick R. Brady, Alexander Dietz, Junwei Cao, Ben Johnson, John McNabb.......................................
Contents 1 A Case Study on the Use of Workflow Technologies for Scientific Analysis: Gravitational Wave Data Analysis Duncan A. Brown Patrick R. Brady, Alexander Dietz, Junwei Cao, Ben Johnson, John McNabb.......................................
EINSTEIN TELESCOPE rd. 3 generation GW detector
 EINSTEIN TELESCOPE rd 3 generation GW detector http://www.et-gw.eu/ Dorota Gondek-Rosińska University of Zielona Góra w imieniu polskiego ET konsorcjum (UW, UZG, UwB, PW, CAMK, IMPAN ) Gravitational wave
EINSTEIN TELESCOPE rd 3 generation GW detector http://www.et-gw.eu/ Dorota Gondek-Rosińska University of Zielona Góra w imieniu polskiego ET konsorcjum (UW, UZG, UwB, PW, CAMK, IMPAN ) Gravitational wave
Greedy algorithm for building a reduced basis of gravitational wave templates
 Greedy algorithm for building a reduced basis of gravitational wave templates 1 Chad Galley 2 Frank Herrmann 3 Jan Hesthaven (Advisor) 4 Evan Ochsner 5 Manuel Tiglio 3 1 Brown University, Department of
Greedy algorithm for building a reduced basis of gravitational wave templates 1 Chad Galley 2 Frank Herrmann 3 Jan Hesthaven (Advisor) 4 Evan Ochsner 5 Manuel Tiglio 3 1 Brown University, Department of
Gravitational wave detection. K.A. Strain
 Gravitational wave detection K.A. Strain Contents gravitational waves: introduction sources of waves, amplitudes and rates basics of GW detection current projects future plans and hopes Gravitational Waves:
Gravitational wave detection K.A. Strain Contents gravitational waves: introduction sources of waves, amplitudes and rates basics of GW detection current projects future plans and hopes Gravitational Waves:
Methods for Reducing False Alarms in Searches for Compact Binary Coalescences in LIGO Data
 Syracuse University SURFACE Physics College of Arts and Sciences 4-8-2010 Methods for Reducing False Alarms in Searches for Compact Binary Coalescences in LIGO Data Duncan Brown Department of Physics,
Syracuse University SURFACE Physics College of Arts and Sciences 4-8-2010 Methods for Reducing False Alarms in Searches for Compact Binary Coalescences in LIGO Data Duncan Brown Department of Physics,
LISA: Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves. Tom Prince Caltech/JPL. Laser Interferometer Space Antenna LISA
 : Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves Tom Caltech/JPL Laser Interferometer Space Antenna http://lisa.nasa.gov Gravitational Wave Astronomy is Being Born LIGO, VIRGO, GEO, TAMA 4000m, 3000m, 2000m,
: Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves Tom Caltech/JPL Laser Interferometer Space Antenna http://lisa.nasa.gov Gravitational Wave Astronomy is Being Born LIGO, VIRGO, GEO, TAMA 4000m, 3000m, 2000m,
On the detectability of post-newtonian eects. in gravitational-wave emission of a coalescing. binary 1. Institute of Mathematics
 On the detectability of post-newtonian eects in gravitational-wave emission of a coalescing binary 1 ANDRZEJ KR OLAK a KOSTAS D. KOKKOTAS b GERHARD SCH AFER c PostScript processed by the SLAC/DESY Libraries
On the detectability of post-newtonian eects in gravitational-wave emission of a coalescing binary 1 ANDRZEJ KR OLAK a KOSTAS D. KOKKOTAS b GERHARD SCH AFER c PostScript processed by the SLAC/DESY Libraries
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-P030066-00 December 2, 2003 First upper limits from
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-P030066-00 December 2, 2003 First upper limits from
Detecting the next Galactic supernova
 Detecting the next Galactic supernova Nicolas Arnaud on behalf of the Virgo-LAL group Now fellow at LHCb-CERN Moriond Gravitation 2003 GW supernova amplitudes Burst online filter performances Comparison
Detecting the next Galactic supernova Nicolas Arnaud on behalf of the Virgo-LAL group Now fellow at LHCb-CERN Moriond Gravitation 2003 GW supernova amplitudes Burst online filter performances Comparison
Preparation of the data analysis of the gravitational wave space antenna.
 Preparation of the data analysis of the gravitational wave space antenna. 1) LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna) Why? 2)How? 1 Frequency Limitation Seismic noise cannot be cancelled at low-frequency
Preparation of the data analysis of the gravitational wave space antenna. 1) LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna) Why? 2)How? 1 Frequency Limitation Seismic noise cannot be cancelled at low-frequency
Probing for Gravitational Waves
 Probing for Gravitational Waves LIGO Reach with LIGO AdLIGO Initial LIGO Barry C. Barish Caltech YKIS2005 Kyoto University 1-July-05 Einstein s Theory of Gravitation a necessary consequence of Special
Probing for Gravitational Waves LIGO Reach with LIGO AdLIGO Initial LIGO Barry C. Barish Caltech YKIS2005 Kyoto University 1-July-05 Einstein s Theory of Gravitation a necessary consequence of Special
The Present Gravitational Wave Detection Effort
 The Present Gravitational Wave Detection Effort Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO Scientific Collaboration International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics Rome July 1,
The Present Gravitational Wave Detection Effort Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO Scientific Collaboration International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics Rome July 1,
Searching for gravitational waves
 Searching for gravitational waves Matteo Barsuglia (barsuglia@apc.univ-paris7.fr) CNRS - Laboratoire Astroparticule et Cosmologie 1 The gravitational waves (GW) Perturbations of the space-time metrics
Searching for gravitational waves Matteo Barsuglia (barsuglia@apc.univ-paris7.fr) CNRS - Laboratoire Astroparticule et Cosmologie 1 The gravitational waves (GW) Perturbations of the space-time metrics
First upper limits from LIGO on gravitational wave bursts
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S677 S684 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)68358-4 First upper limits from LIGO on gravitational wave bursts Alan J Weinstein
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S677 S684 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)68358-4 First upper limits from LIGO on gravitational wave bursts Alan J Weinstein
Astrophysical Rates of Gravitational-Wave Compact Binary Sources in O3
 Astrophysical Rates of Gravitational-Wave Compact Binary Sources in O3 Tom Dent (Albert Einstein Institute, Hannover) Chris Pankow (CIERA/Northwestern) for the LIGO and Virgo Collaborations DCC: LIGO-G1800370
Astrophysical Rates of Gravitational-Wave Compact Binary Sources in O3 Tom Dent (Albert Einstein Institute, Hannover) Chris Pankow (CIERA/Northwestern) for the LIGO and Virgo Collaborations DCC: LIGO-G1800370
Gravitational Wave Astronomy s Next Frontier in Computation
 Gravitational Wave Astronomy s Next Frontier in Computation Chad Hanna - Penn State University Penn State Physics Astronomy & Astrophysics Outline 1. Motivation 2. Gravitational waves. 3. Birth of gravitational
Gravitational Wave Astronomy s Next Frontier in Computation Chad Hanna - Penn State University Penn State Physics Astronomy & Astrophysics Outline 1. Motivation 2. Gravitational waves. 3. Birth of gravitational
Compact Binaries as Gravitational-Wave Sources
 Compact Binaries as Gravitational-Wave Sources Chunglee Kim Lund Observatory Extreme Astrophysics for All 10 February, 2009 Outline Introduction Double-neutron-star systems = NS-NS binaries Neutron star
Compact Binaries as Gravitational-Wave Sources Chunglee Kim Lund Observatory Extreme Astrophysics for All 10 February, 2009 Outline Introduction Double-neutron-star systems = NS-NS binaries Neutron star
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory In Operation
 The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory In Operation "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Reported on behalf of LIGO colleagues by Fred
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory In Operation "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Reported on behalf of LIGO colleagues by Fred
The Advanced LIGO detectors at the beginning of the new gravitational wave era
 The Advanced LIGO detectors at the beginning of the new gravitational wave era Lisa Barsotti MIT Kavli Institute LIGO Laboratory on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Document G1600324 LIGO
The Advanced LIGO detectors at the beginning of the new gravitational wave era Lisa Barsotti MIT Kavli Institute LIGO Laboratory on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Document G1600324 LIGO
