Search for compact binary systems in LIGO data
|
|
|
- Leslie Bradley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Search for compact binary systems in LIGO data Thomas Cokelaer On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Cardiff University, U.K. LIGO-G Z
2 Plan 1) Overview What kind of gravitational waves are we searching for? Data description : S3 and S4 LIGO science runs. 2) The Search : Expected horizon distances, detection methods, effective signal to noise ratio, coincidences between detectors,... 3) The S3 and S4 data results 4) Upper limits 5) Conclusion 2
3 Overview 3
4 GW from compact binary systems Gravitational waves emitted from compact binary systems are known to exist : PSR , first double pulsar J The emission of gravitational waves from compact binaries follows three main phases: Inspiral phase Merging ringdown The last cycles of the inspiral phase (and merger and ringdown) are detectable by ground based interferometers such as LIGO observatories. 4
5 The Inspiral signals (1) The inspiral phase can be modeled, and represented by : The amplitude and duration of hc,s(t) depend on the masses, m1 and m2, of the binary system considered and the lower cut-off frequency FL. Deff contains the physical distance and orientation of the binary system. 5
6 The Inspiral signals (2) Different waveforms led to different search parameters/filtering. 3 BBH 1 BNS PBH 0.35 In this study, we search for : Primordial Black Holes binaries (PBH binaries) : m1, m2 in [0.35, 1.0] Binary neutron stars (BNS): m1, m2 in [1.0, 3.0] Binary Black Holes (BBH) : m1, m2 in [3.0, 80.0] with total mass less than 80. >40 Mo There is a wide range of compact object from sub-solar mass up to tens of solar mass; the duration varies from 25 seconds for m1=m2=1.4 to less than a second for m1=m2= >40 Mo 6
7 The LIGO observatories LIGO consists of 3 detectors, 2 co-located in Hanford (WA) and 1 in Livingston (LA). We use the following abbreviations for each of them: H1 (4km long), H2 (2km long), and L1 (4km long). 7
8 The LIGO data We searched for gravitational waves from coalescence of compact binaries (PBH binaries, BNS, and BBH) in the S3 and S4 LIGO science runs. S3 science run : 31st October 2003 to 9th January S4 science run : 22nd February 2005 to 24th March
9 The search 9
10 What is the horizon distance? A preliminary step is the computation of the horizon distance, (i.e. the distance at which an optimally oriented and located binary system can be seen with a given signal to noise ratio): It is based on the power spectrum density of the real data and the expected waveform parameters Sh(f) are generated every 2048 seconds so as to follow noise fluctuations. 10
11 Horizon distance (2) Example : BBH horizon distance fluctuation (SNR=8) through the entire S4 runs. Similar fluctuations in BNS and PBH binary search: Horizon distance of a 5-5 system (SNR=8) S4 BBH 11
12 Horizon distance (S3 and S4) Horizon distance is useful for sanity check, quick understanding of the detector behaviour, etc. BUT this is not the search itself. 12
13 Search pipeline and Coincidence Coincidence at the input stage: a list of time intervals where at least two detectors operate in science mode. H1H2L1 times H1L1 times H1H2 times H2L1 times S3(hours) S4(hours) Coincidence at the output stage: we keep triggers that are coincident in time and mass parameters. The coincidence reduces the rate of triggers and increases the confidence in detection. 13
14 Difference between PBH binary, BNS and BBH search The BNS and PBH binary searches are very similar: Templates based on second order restricted to post-newtonian waveforms, in the stationary phase approximation. Identical template bank placement. Identical filtering process Similar coincidence windows Hierarchical search Chi square Final triggers associated to an effective SNR which combines the SNR and its Chi square value. The BBH search used the same pipeline but : Target waveform non accurately known. We used templates based on phenomenological waveforms, which uses two phenomenological parameters. Consequences : 1. Different template bank. 2. Different filtering. 3. Non physical mass parameters Coincidence in time, and the 2 phenomenological parameters. No chi square applied. Final triggers associated classical SNR. to the 14
15 Background and simulations The search requires the pipeline to be used in 3 different ways: 1-Injections: we can tune the search parameter such as coincidence windows to be sure not to missed any real GW event. Pr el im in ar y re su l ts 2-Background estimation: we time-shifts the data from the different detectors so as to estimate the accidental rate of triggers. Each search used 100 time-shifts. 3-Results: Finally, we analyse the data (no injections, no time shifts). The resulting triggers constitutes the in-time coincident triggers, or candidate events. S4 BNS 15
16 Effective SNR (BNS and PBH) In PBH and BNS search, we use an effective SNR, that is a statistic which well separates the background triggers from simulated injections. It is defined by Pr el im in ar y re su l ts 16
17 Results 17
18 Comparison between candidates and background From each search (PBH, BNS and BBH), a list of in-time coincident triggers, or candidate events is provided and have to be compared with the background estimate, over 100 realisations. Pr el The comparison is performed by using a combined statistics; we combine the individual SNR in each detector so that it represents a constant false alarm statistic. For instance, in the PBH binary and BNS searches, we use the sum of the SNR squared. im in ar y re su PBH binaries, S4 l ts 18
19 Detection above background? PBH, BNS and BBH, in S3 and S4 shows that distribution of candidate events is consistent with expectation, except S3 BBH (next slide). PBH binaries, S4 BNS, S4 The candidate event with largest combined SNR Pr el im in ar y re su l An event with SNR=8 would be there. ts 19
20 Follow up of candidates Irrespective of the position of the loudest candidate events with respect to the expected background, we follow up the loudest candidates in various ways: What was the status of the instruments? Spectrograms of the data are used to check for obvious instrumental artefacts. In the BBH search, further follow up using physical template families are performed. What are the parameters of the triggers : does the effective distances are consistent? Are the parameters (SNR, masses...) on the edge of coincidence windows... More tests such as Null-stream analysis are used.... First, candidates with largest SNR are investigated. 20
21 Follow up of candidates: example In S3 BBH, one candidate was found above estimated background, in H1H2 coincidence. We know that in the 2 co-located H1 and H2 detectors, the background is under-estimated (right) We used physical template families and shows a large time delay in H1 and H2 (below). Null stream analysis definitely rejected this candidate from our list of plausible candidates. This candidate was rejected after various tests (previous slides) were applied. SNR Time series Dt=38 ms Pr el Time (s) H1 H2 im in ar y re su l ts 21
22 any detection? No detection in S3 or S4, in either of the PBH binary, BNS or BBH search. All triggers in BNS and PBH binary search are consistent with background estimates. One candidate in S3 BBH with large SNR (H1/H2 coincidence but not found in L1), which was rejected by various methods. Loudest candidates in each search were further investigated but none was identified as plausible GW. So, we looked at the upper limits. 22
23 Upper limits 23
24 S4 Upper limit results No detection made, so we derived the upper limits in each search. We used only results from the best sensitive run, namely S4 Expected merger rates (V.Kalogera et al., ApL 614, R. O Shaughnessy et al. ApJ.633, Alcock et al. ApJ,512) BNS : [2 120]10 6 yr 1 L 1 10 BBH : [0.4 ]10 yr L PBH 10 2 yr 1 L = 0.6 Milky Way Equivalent Galaxy. 24
25 S4 Upper limit results The Bayesian upper limit calculation is based on the loudest event statistic (P.Brady et al., CGQ 21) which uses The detection efficiency at the loudest event (how many injections found with combined SNR above the largest candidate event. The background triggers. Galaxy Population Time analysed (about 520 hours in S4) systematics errors such as Monte-Carlo errors, waveform inaccuracy, calibration errors... 25
26 S4 Upper limit results (1) 1- Gaussian distribution PBH binary assuming gaussian distribution around a solar mass system: BNS assuming gaussian distribution around a solar mass system: 4.9 yr 1 L yr 1 L 1 10 BBH : to be released soon (review not fully completed) 26
27 S4 Upper limit results (2) 2- Uniform distribution PBH binaries, S4 BNS, S4 Pr el im in ar y re su l ts 27
28 Conclusion 28
29 No detection of GW signal from coalescing compact binaries nor in S3 neither in S4 New upper limits on merger rates : 4.9 yr L yr L for PBH binaries for BNS to be released soon for BBH Status of the analysis : We have a mature BNS and PBH search pipeline. What we can achieved right now is to clearly identify simulated events at a SNR = 8. Although BBH search is also mature (same pipeline), we will use PN template Families in the future BBH search so as to reduce the background rate. Present and Future : Apply the tools developed on S5 and future science runs. 29
30 Extra : effective distance This figure, based on the S4 BNS search, shows a scatter plot with effective distance corresponding to background coincident triggers AND coincident triggers associated to simulated injections. lim e Pr ts l su e yr r a 30
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems
 Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems Stephen Fairhurst Cardiff University and LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Outline Motivation Searching for Coalescing Binaries Latest Results
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Coalescing Binary Systems Stephen Fairhurst Cardiff University and LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Outline Motivation Searching for Coalescing Binaries Latest Results
Results from LIGO Searches for Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves
 Results from LIGO Searches for Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan (LIGO Laboratory / Caltech) For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration American Physical Society April Meeting May 4, 2004 Denver,
Results from LIGO Searches for Binary Inspiral Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan (LIGO Laboratory / Caltech) For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration American Physical Society April Meeting May 4, 2004 Denver,
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspirals with LIGO
 Searching for Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspirals with LIGO Duncan Brown University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Inspiral Working Group LIGO-G030671-00-Z S1 Binary
Searching for Gravitational Waves from Binary Inspirals with LIGO Duncan Brown University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Inspiral Working Group LIGO-G030671-00-Z S1 Binary
LIGO s continuing search for gravitational waves
 LIGO s continuing search for gravitational waves Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Interferometers LIGO is an interferometric detector» A laser is used
LIGO s continuing search for gravitational waves Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Interferometers LIGO is an interferometric detector» A laser is used
The direct detection of gravitational waves: The first discovery, and what the future might bring
 The direct detection of gravitational waves: The first discovery, and what the future might bring Chris Van Den Broeck Nikhef - National Institute for Subatomic Physics Amsterdam, The Netherlands Physics
The direct detection of gravitational waves: The first discovery, and what the future might bring Chris Van Den Broeck Nikhef - National Institute for Subatomic Physics Amsterdam, The Netherlands Physics
GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral
 GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral Lazzaro Claudia for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 25 October 2017 GW170817 PhysRevLett.119.161101
GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral Lazzaro Claudia for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 25 October 2017 GW170817 PhysRevLett.119.161101
Data Analysis Pipeline: The Search for Gravitational Waves in Real life
 Data Analysis Pipeline: The Search for Gravitational Waves in Real life Romain Gouaty LAPP - Université de Savoie - CNRS/IN2P3 On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Data Analysis Pipeline: The Search for Gravitational Waves in Real life Romain Gouaty LAPP - Université de Savoie - CNRS/IN2P3 On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
LIGO Observational Results
 LIGO Observational Results Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin Milwaukee on behalf of LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Science Goals Direct verification of two dramatic predictions of Einstein s general
LIGO Observational Results Patrick Brady University of Wisconsin Milwaukee on behalf of LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Science Goals Direct verification of two dramatic predictions of Einstein s general
Searching for gravitational waves. with LIGO detectors
 Werner Berger, ZIB, AEI, CCT Searching for gravitational waves LIGO Hanford with LIGO detectors Gabriela González Louisiana State University On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration KITP Colloquium,
Werner Berger, ZIB, AEI, CCT Searching for gravitational waves LIGO Hanford with LIGO detectors Gabriela González Louisiana State University On behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration KITP Colloquium,
Status and Prospects for LIGO
 Status and Prospects for LIGO Crab Pulsar St Thomas, Virgin Islands Barry C. Barish Caltech 17-March-06 LIGO Livingston, Louisiana 4 km 17-March-06 Confronting Gravity - St Thomas 2 LIGO Hanford Washington
Status and Prospects for LIGO Crab Pulsar St Thomas, Virgin Islands Barry C. Barish Caltech 17-March-06 LIGO Livingston, Louisiana 4 km 17-March-06 Confronting Gravity - St Thomas 2 LIGO Hanford Washington
LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans. Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04
 LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04 Science Goals Physics» Direct verification of the most relativistic prediction of general relativity» Detailed tests of properties of gravitational
LIGO Status and Advanced LIGO Plans Barry C Barish OSTP 1-Dec-04 Science Goals Physics» Direct verification of the most relativistic prediction of general relativity» Detailed tests of properties of gravitational
Outline. 1. Basics of gravitational wave transient signal searches. 2. Reconstruction of signal properties
 Gravitational Wave Transients state-of-the-arts: detection confidence and signal reconstruction G.A.Prodi, University of Trento and INFN, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Gravitational Wave Transients state-of-the-arts: detection confidence and signal reconstruction G.A.Prodi, University of Trento and INFN, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Search for Gravitational Wave Transients. Florent Robinet On behalf of the LSC and Virgo Collaborations
 Search for Gravitational Wave Transients On behalf of the LSC and Virgo Collaborations 1 Gravitational Waves Gravitational waves = "ripples" in space time Weak field approximation : g = h h 1 Wave equation,
Search for Gravitational Wave Transients On behalf of the LSC and Virgo Collaborations 1 Gravitational Waves Gravitational waves = "ripples" in space time Weak field approximation : g = h h 1 Wave equation,
Searching for Intermediate Mass Black Holes mergers
 Searching for Intermediate Mass Black Holes mergers G. A. Prodi, Università di Trento and INFN for the LIGO Scientific collaboration and the Virgo collaboration special credits to Giulio Mazzolo and Chris
Searching for Intermediate Mass Black Holes mergers G. A. Prodi, Università di Trento and INFN for the LIGO Scientific collaboration and the Virgo collaboration special credits to Giulio Mazzolo and Chris
LIGO Detection of Gravitational Waves. Dr. Stephen Ng
 LIGO Detection of Gravitational Waves Dr. Stephen Ng Gravitational Waves Predicted by Einstein s general relativity in 1916 Indirect confirmation with binary pulsar PSR B1913+16 (1993 Nobel prize in physics)
LIGO Detection of Gravitational Waves Dr. Stephen Ng Gravitational Waves Predicted by Einstein s general relativity in 1916 Indirect confirmation with binary pulsar PSR B1913+16 (1993 Nobel prize in physics)
M.Alessandra Papa. Max Planck Inst. f. Gravitationsphysik and Univ. of Wisconsin- Milwaukee. ICGC Conference 2007, December Pune
 Gravitational Wave Data Analysis M.Alessandra Papa Max Planck Inst. f. Gravitationsphysik and Univ. of Wisconsin- Milwaukee ICGC Conference 2007, December Pune Gravitational wave data analysis * legacy
Gravitational Wave Data Analysis M.Alessandra Papa Max Planck Inst. f. Gravitationsphysik and Univ. of Wisconsin- Milwaukee ICGC Conference 2007, December Pune Gravitational wave data analysis * legacy
GRB-triggered searches for gravitational waves from compact binary inspirals in LIGO and Virgo data during S5/VSR1
 GRB-triggered searches for gravitational waves from compact binary inspirals in LIGO and Virgo data during S5/VSR1 Nickolas Fotopoulos (UWM) for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
GRB-triggered searches for gravitational waves from compact binary inspirals in LIGO and Virgo data during S5/VSR1 Nickolas Fotopoulos (UWM) for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 2
 Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 2 Peter S. Shawhan Gravitational Wave Astronomy Summer School May 29, 2012 Outline for Today Matched filtering in the time domain Matched filtering in the frequency
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 2 Peter S. Shawhan Gravitational Wave Astronomy Summer School May 29, 2012 Outline for Today Matched filtering in the time domain Matched filtering in the frequency
The Advanced LIGO detectors at the beginning of the new gravitational wave era
 The Advanced LIGO detectors at the beginning of the new gravitational wave era Lisa Barsotti MIT Kavli Institute LIGO Laboratory on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Document G1600324 LIGO
The Advanced LIGO detectors at the beginning of the new gravitational wave era Lisa Barsotti MIT Kavli Institute LIGO Laboratory on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Document G1600324 LIGO
Search for inspiralling neutron stars in LIGO S1 data
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S691 S696 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)68883-6 Search for inspiralling neutron stars in LIGO S1 data Gabriela González
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S691 S696 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)68883-6 Search for inspiralling neutron stars in LIGO S1 data Gabriela González
A template bank to search for gravitational waves from inspiralling compact binaries: II. Phenomenological model
 LIGO-P070089-01-Z A template bank to search for gravitational waves from inspiralling compact binaries: II. Phenomenological model T. Cokelaer 1 1 School of Physics and Astronomy, Cardiff University, Cardiff
LIGO-P070089-01-Z A template bank to search for gravitational waves from inspiralling compact binaries: II. Phenomenological model T. Cokelaer 1 1 School of Physics and Astronomy, Cardiff University, Cardiff
GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY
 GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY A. Melatos (Melbourne) 1. GW: physics & astronomy 2. Current- & next-gen detectors & searches 3. Burst sources: CBC, SN GR, cosmology 4. Periodic sources: NS subatomic physics
GRAVITATIONAL WAVE ASTRONOMY A. Melatos (Melbourne) 1. GW: physics & astronomy 2. Current- & next-gen detectors & searches 3. Burst sources: CBC, SN GR, cosmology 4. Periodic sources: NS subatomic physics
The LIGO Project: a Status Report
 The LIGO Project: a Status Report LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO Livingston Observatory Laura Cadonati LIGO Laboratory, MIT for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Conference on Gravitational Wave Sources
The LIGO Project: a Status Report LIGO Hanford Observatory LIGO Livingston Observatory Laura Cadonati LIGO Laboratory, MIT for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration Conference on Gravitational Wave Sources
The search for continuous gravitational waves: analyses from LIGO s second science run
 The search for continuous gravitational waves: analyses from LIGO s second science run Michael Landry LIGO Hanford Observatory on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration http://www.ligo.org April APS
The search for continuous gravitational waves: analyses from LIGO s second science run Michael Landry LIGO Hanford Observatory on behalf of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration http://www.ligo.org April APS
Compact Binaries as Gravitational-Wave Sources
 Compact Binaries as Gravitational-Wave Sources Chunglee Kim Lund Observatory Extreme Astrophysics for All 10 February, 2009 Outline Introduction Double-neutron-star systems = NS-NS binaries Neutron star
Compact Binaries as Gravitational-Wave Sources Chunglee Kim Lund Observatory Extreme Astrophysics for All 10 February, 2009 Outline Introduction Double-neutron-star systems = NS-NS binaries Neutron star
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis
 Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis Peter Shawhan Physics 798G April 12, 2007 Outline Gravitational-wave data General data analysis principles Specific data analysis methods Classification of signals Methods
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis Peter Shawhan Physics 798G April 12, 2007 Outline Gravitational-wave data General data analysis principles Specific data analysis methods Classification of signals Methods
arxiv:gr-qc/ v1 4 Dec 2003
 Testing the LIGO Inspiral Analysis with Hardware Injections arxiv:gr-qc/0312031 v1 4 Dec 2003 Duncan A. Brown 1 for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
Testing the LIGO Inspiral Analysis with Hardware Injections arxiv:gr-qc/0312031 v1 4 Dec 2003 Duncan A. Brown 1 for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration 1 Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
M.-A. Bizouard, F. Cavalier. GWDAW 8 Milwaukee 19/12/03
 Coincidence and coherent analyses for burst search using interferometers M.-A. Bizouard, F. Cavalier on behalf of the Virgo-Orsay group Network model Results of coincidence analysis: loose and tight coincidence
Coincidence and coherent analyses for burst search using interferometers M.-A. Bizouard, F. Cavalier on behalf of the Virgo-Orsay group Network model Results of coincidence analysis: loose and tight coincidence
Gravitational wave detection with Virgo and LIGO experiment - Case of the long bursts
 Gravitational wave detection with Virgo and LIGO experiment - Case of the long bursts Samuel Franco Supervisor: Patrice Hello Laboratoire de l Accélérateur Linéaire (Orsay) 06/12/2013 Samuel Franco (LAL)
Gravitational wave detection with Virgo and LIGO experiment - Case of the long bursts Samuel Franco Supervisor: Patrice Hello Laboratoire de l Accélérateur Linéaire (Orsay) 06/12/2013 Samuel Franco (LAL)
Overview of Gravitational Wave Observations by LIGO and Virgo
 Overview of Gravitational Wave Observations by LIGO and Virgo Giovanni Andrea Prodi Virgo Group at Padova-Trento, LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration Vulcano Workshop 2016, May 23 Published
Overview of Gravitational Wave Observations by LIGO and Virgo Giovanni Andrea Prodi Virgo Group at Padova-Trento, LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration Vulcano Workshop 2016, May 23 Published
Astrophysical Rates of Gravitational-Wave Compact Binary Sources in O3
 Astrophysical Rates of Gravitational-Wave Compact Binary Sources in O3 Tom Dent (Albert Einstein Institute, Hannover) Chris Pankow (CIERA/Northwestern) for the LIGO and Virgo Collaborations DCC: LIGO-G1800370
Astrophysical Rates of Gravitational-Wave Compact Binary Sources in O3 Tom Dent (Albert Einstein Institute, Hannover) Chris Pankow (CIERA/Northwestern) for the LIGO and Virgo Collaborations DCC: LIGO-G1800370
Chirplets pour la détection des ondes gravitationnelles
 Chirplets pour la détection des ondes gravitationnelles Éric Chassande-Mottin AstroParticule et Cosmologie, Paris et collaborateurs : Satya Mohapatra, Miriam Miele, Laura Cadonati, Zacharya Nemtzow Outline
Chirplets pour la détection des ondes gravitationnelles Éric Chassande-Mottin AstroParticule et Cosmologie, Paris et collaborateurs : Satya Mohapatra, Miriam Miele, Laura Cadonati, Zacharya Nemtzow Outline
Searching for gravitational waves from binary inspirals with LIGO
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S1625 S1633 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)79876-7 Searching for gravitational waves from binary inspirals with LIGO Duncan
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Class. Quantum Grav. 21 (2004) S1625 S1633 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM GRAVITY PII: S0264-9381(04)79876-7 Searching for gravitational waves from binary inspirals with LIGO Duncan
Gravitational Waves & Intermediate Mass Black Holes. Lee Samuel Finn Center for Gravitational Wave Physics
 Gravitational Waves & Intermediate Mass Black Holes Lee Samuel Finn Center for Gravitational Wave Physics Outline What are gravitational waves? How are they produced? How are they detected? Gravitational
Gravitational Waves & Intermediate Mass Black Holes Lee Samuel Finn Center for Gravitational Wave Physics Outline What are gravitational waves? How are they produced? How are they detected? Gravitational
The Dynamical Strong-Field Regime of General Relativity
 The Dynamical Strong-Field Regime of General Relativity Frans Pretorius Princeton University IFT Colloquium Sao Paulo, March 30, 2016 Outline General Relativity @100 the dynamical, strong-field regime
The Dynamical Strong-Field Regime of General Relativity Frans Pretorius Princeton University IFT Colloquium Sao Paulo, March 30, 2016 Outline General Relativity @100 the dynamical, strong-field regime
GW150914: Observation of gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 310 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16310-2 Colloquia: La Thuile 2016 GW150914: Observation of gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger F. Marion on behalf of the LIGO Scientific
IL NUOVO CIMENTO 39 C (2016) 310 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2016-16310-2 Colloquia: La Thuile 2016 GW150914: Observation of gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger F. Marion on behalf of the LIGO Scientific
ANALYSIS OF BURST SIGNALS IN LIGO DATA. Irena Zivkovic, Alan Weinstein
 LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY LIGO CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-T010157-00-R 10/15/01 ANALYSIS OF BURST SIGNALS IN LIGO
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY LIGO CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-T010157-00-R 10/15/01 ANALYSIS OF BURST SIGNALS IN LIGO
Lecture 3. Alex Nielsen Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics Hanover, Germany. How can we detect gravitational wave signals?
 Lecture 3 Alex Nielsen Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics Hanover, Germany How can we detect gravitational wave signals? 2015 International Summer School on Numerical Relativity and Gravitational
Lecture 3 Alex Nielsen Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics Hanover, Germany How can we detect gravitational wave signals? 2015 International Summer School on Numerical Relativity and Gravitational
Detecting the next Galactic supernova
 Detecting the next Galactic supernova Nicolas Arnaud on behalf of the Virgo-LAL group Now fellow at LHCb-CERN Moriond Gravitation 2003 GW supernova amplitudes Burst online filter performances Comparison
Detecting the next Galactic supernova Nicolas Arnaud on behalf of the Virgo-LAL group Now fellow at LHCb-CERN Moriond Gravitation 2003 GW supernova amplitudes Burst online filter performances Comparison
James Clark For The LSC
 A search for gravitational waves associated with the August 2006 timing glitch of the http://arxiv.org/abs/1011.1357 Vela pulsar James Clark For The LSC Introduction This talk: first search for GWs associated
A search for gravitational waves associated with the August 2006 timing glitch of the http://arxiv.org/abs/1011.1357 Vela pulsar James Clark For The LSC Introduction This talk: first search for GWs associated
NEVER IGNORE A COINCIDENCE
 ALEXANDER L. URBAN LEONARD E. PARKER CENTER FOR GRAVITATION, COSMOLOGY & ASTROPHYSICS NEVER IGNORE A COINCIDENCE ENHANCING LIGO SENSITIVITY TO COMPACT BINARY MERGERS WITH GRB COUNTERPARTS 23 RD MIDWEST
ALEXANDER L. URBAN LEONARD E. PARKER CENTER FOR GRAVITATION, COSMOLOGY & ASTROPHYSICS NEVER IGNORE A COINCIDENCE ENHANCING LIGO SENSITIVITY TO COMPACT BINARY MERGERS WITH GRB COUNTERPARTS 23 RD MIDWEST
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves
 Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Barry C. Barish Caltech Argonne National Laboratory 16-Jan-04 LIGO-G030523-00-M
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) Barry C. Barish Caltech Argonne National Laboratory 16-Jan-04 LIGO-G030523-00-M
Reduced Basis in General Relativity: Select-Solve-Represent-Predict
 Reduced Basis in General Relativity: Select-Solve-Represent-Predict Manuel Tiglio University of Maryland In collaboration with Scott Field, Chad Galley, Frank Herrmann, Jan Hesthaven, Evan Ochsner arxiv:1101.3765
Reduced Basis in General Relativity: Select-Solve-Represent-Predict Manuel Tiglio University of Maryland In collaboration with Scott Field, Chad Galley, Frank Herrmann, Jan Hesthaven, Evan Ochsner arxiv:1101.3765
Gravitational waves from the merger of two black holes
 Gravitational waves from the merger of two black holes Opening of the Academic Year by the Department of Physics and Astronomy (DPA) VU, Amsterdam, September 21 2016; Jo van den Brand; jo@nikhef.nl Event
Gravitational waves from the merger of two black holes Opening of the Academic Year by the Department of Physics and Astronomy (DPA) VU, Amsterdam, September 21 2016; Jo van den Brand; jo@nikhef.nl Event
LIGO and the Quest for Gravitational Waves
 LIGO and the Quest for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) LIGO-G030523-00-M Barry C. Barish Caltech UT Austin 24-Sept-03 1 A Conceptual
LIGO and the Quest for Gravitational Waves "Colliding Black Holes" Credit: National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) LIGO-G030523-00-M Barry C. Barish Caltech UT Austin 24-Sept-03 1 A Conceptual
All-sky LIGO Search for Periodic Gravitational Waves in the Fourth Science Run (S4)
 All-sky LIGO Search for Periodic Gravitational Waves in the Fourth Science Run (S4) Keith Riles University of Michigan For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration APS Meeting, Jacksonville, Florida April 14-17,
All-sky LIGO Search for Periodic Gravitational Waves in the Fourth Science Run (S4) Keith Riles University of Michigan For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration APS Meeting, Jacksonville, Florida April 14-17,
Greedy algorithm for building a reduced basis of gravitational wave templates
 Greedy algorithm for building a reduced basis of gravitational wave templates 1 Chad Galley 2 Frank Herrmann 3 Jan Hesthaven (Advisor) 4 Evan Ochsner 5 Manuel Tiglio 3 1 Brown University, Department of
Greedy algorithm for building a reduced basis of gravitational wave templates 1 Chad Galley 2 Frank Herrmann 3 Jan Hesthaven (Advisor) 4 Evan Ochsner 5 Manuel Tiglio 3 1 Brown University, Department of
S. V. Dhurandhar IUCAA Pune, India
 Extended hierarchical search (EHS) for inspiraling compact binaries S. V. Dhurandhar IUCAA Pune, India * A. Sengupta, A. Lazzarini, P. Shawhan LIGO-G040556-00-R Plan of the Talk The 1-step (flat) search
Extended hierarchical search (EHS) for inspiraling compact binaries S. V. Dhurandhar IUCAA Pune, India * A. Sengupta, A. Lazzarini, P. Shawhan LIGO-G040556-00-R Plan of the Talk The 1-step (flat) search
Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars
 Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars Ian Jones D.I.Jones@soton.ac.uk General Relativity Group, Southampton University Ian Jones Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars 1/23
Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars Ian Jones D.I.Jones@soton.ac.uk General Relativity Group, Southampton University Ian Jones Searching for gravitational waves from neutron stars 1/23
in2p , version 1-14 May 2012
 Author manuscript, published in "XLVIth Rencontres de Moriond - Gravitational Waves and Experimental Gravity and GPhyS Colloquium 2011, La Thuile : Italy (2011)" SEARCHES FOR GRAVITATIONAL WAVE TRANSIENTS
Author manuscript, published in "XLVIth Rencontres de Moriond - Gravitational Waves and Experimental Gravity and GPhyS Colloquium 2011, La Thuile : Italy (2011)" SEARCHES FOR GRAVITATIONAL WAVE TRANSIENTS
Data Analysis Pipeline and Tuning
 60 Chapter 6 Data Analysis Pipeline and Tuning In this chapter we describe the standard pipeline used to analyze data from GW detectors, such as the LIGO detectors, for GW signals from CBC. In addition,
60 Chapter 6 Data Analysis Pipeline and Tuning In this chapter we describe the standard pipeline used to analyze data from GW detectors, such as the LIGO detectors, for GW signals from CBC. In addition,
GW Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger
 GW150914 Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger F. Marion for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration Seminar at CPPM, 2016 March 3 Introduction Sources
GW150914 Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger F. Marion for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration Seminar at CPPM, 2016 March 3 Introduction Sources
Current Experimental Limits on Gravitational Waves. Nelson Christensen Artemis, Observatoire de la Côte d Azur, Nice
 Current Experimental Limits on Gravitational Waves Nelson Christensen Artemis, Observatoire de la Côte d Azur, Nice September 28, 2017. DESY Theory Workshop General Relativity 1915: Einstein s Theory of
Current Experimental Limits on Gravitational Waves Nelson Christensen Artemis, Observatoire de la Côte d Azur, Nice September 28, 2017. DESY Theory Workshop General Relativity 1915: Einstein s Theory of
SEARCHING FOR GRAVITATIONAL WAVES FROM BINARY SYSTEMS IN NON-STATIONARY DATA
 SEARCHING FOR GRAVITATIONAL WAVES FROM BINARY SYSTEMS IN NON-STATIONARY DATA A Dissertation Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of the Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College in
SEARCHING FOR GRAVITATIONAL WAVES FROM BINARY SYSTEMS IN NON-STATIONARY DATA A Dissertation Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of the Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College in
The Impact of Gravitational Waves: Detectability and Signatures
 The Impact of Gravitational Waves: Detectability and Signatures Jenna Klemkowsky Wheeling Jesuit University Summer 2013 University of Florida International Research Experience for Undergraduates University
The Impact of Gravitational Waves: Detectability and Signatures Jenna Klemkowsky Wheeling Jesuit University Summer 2013 University of Florida International Research Experience for Undergraduates University
Strong field tests of Gravity using Gravitational Wave observations
 Strong field tests of Gravity using Gravitational Wave observations K. G. Arun Chennai Mathematical Institute Astronomy, Cosmology & Fundamental Physics with GWs, 04 March, 2015 indig K G Arun (CMI) Strong
Strong field tests of Gravity using Gravitational Wave observations K. G. Arun Chennai Mathematical Institute Astronomy, Cosmology & Fundamental Physics with GWs, 04 March, 2015 indig K G Arun (CMI) Strong
Gravitational Wave Detection from the Ground Up
 Gravitational Wave Detection from the Ground Up Peter Shawhan (University of Maryland) for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO-G080393-00-Z From Simple Beginnings Joe Weber circa 1969 AIP Emilio Segre
Gravitational Wave Detection from the Ground Up Peter Shawhan (University of Maryland) for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO-G080393-00-Z From Simple Beginnings Joe Weber circa 1969 AIP Emilio Segre
LIGO S2 Inspiral Hardware Injections
 LIGO S2 Inspiral Hardware Injections Steve Fairhurst University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee LSC Inspiral Working Group GWDAW December 19, 2003. LIGO-G030688-00-Z Introduction Hardware injections provide a good
LIGO S2 Inspiral Hardware Injections Steve Fairhurst University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee LSC Inspiral Working Group GWDAW December 19, 2003. LIGO-G030688-00-Z Introduction Hardware injections provide a good
Gravitational wave cosmology Lecture 2. Daniel Holz The University of Chicago
 Gravitational wave cosmology Lecture 2 Daniel Holz The University of Chicago Thunder and lightning Thus far we ve only seen the Universe (and 95% of it is dark: dark matter and dark energy). In the the
Gravitational wave cosmology Lecture 2 Daniel Holz The University of Chicago Thunder and lightning Thus far we ve only seen the Universe (and 95% of it is dark: dark matter and dark energy). In the the
Strategy for signal classification to improve data quality for Advanced Detectors gravitational-wave searches
 Strategy for signal classification to improve data quality for Advanced Detectors gravitational-wave searches E. Cuoco 1, A.Torres-Forné 2,J.A. Font 2,7, J.Powell 3, R.Lynch 4, D.Trifiró 5 2 Universitat
Strategy for signal classification to improve data quality for Advanced Detectors gravitational-wave searches E. Cuoco 1, A.Torres-Forné 2,J.A. Font 2,7, J.Powell 3, R.Lynch 4, D.Trifiró 5 2 Universitat
Data quality vetoes and their effect on searches for gravitational waves from compact binary systems
 Data quality vetoes and their effect on searches for gravitational waves from compact binary systems Samantha Usman August 12, 2014 Abstract Data quality flags have been designed to prevent problems caused
Data quality vetoes and their effect on searches for gravitational waves from compact binary systems Samantha Usman August 12, 2014 Abstract Data quality flags have been designed to prevent problems caused
Gravitational Wave Astronomy using 0.1Hz space laser interferometer. Takashi Nakamura GWDAW-8 Milwaukee 2003/12/17 1
 Gravitational Wave Astronomy using 0.1Hz space laser interferometer Takashi Nakamura GWDAW-8 Milwaukee 2003/12/17 1 In 2001 we considered what we can do using 0.1 hertz laser interferometer ( Seto, Kawamura
Gravitational Wave Astronomy using 0.1Hz space laser interferometer Takashi Nakamura GWDAW-8 Milwaukee 2003/12/17 1 In 2001 we considered what we can do using 0.1 hertz laser interferometer ( Seto, Kawamura
Newtonian instantaneous action at a distance General Relativity information carried by gravitational radiation at the speed of light
 Modern View of Gravitation Newtonian instantaneous action at a distance G µ = 8 µ # General Relativity information carried by gravitational radiation at the speed of light Gravitational Waves GR predicts
Modern View of Gravitation Newtonian instantaneous action at a distance G µ = 8 µ # General Relativity information carried by gravitational radiation at the speed of light Gravitational Waves GR predicts
Overview of Gravitational Wave Physics [PHYS879]
![Overview of Gravitational Wave Physics [PHYS879] Overview of Gravitational Wave Physics [PHYS879]](/thumbs/80/82252021.jpg) Overview of Gravitational Wave Physics [PHYS879] Alessandra Buonanno Maryland Center for Fundamental Physics Joint Space-Science Institute Department of Physics University of Maryland Content: What are
Overview of Gravitational Wave Physics [PHYS879] Alessandra Buonanno Maryland Center for Fundamental Physics Joint Space-Science Institute Department of Physics University of Maryland Content: What are
Rate (Upper Limit) Calculation
 117 Chapter 9 Rate (Upper Limit) Calculation Whether the search results in a small number of detection candidates or more, we can bound the rate of CBCs in the (nearby) universe. Depending on the significance
117 Chapter 9 Rate (Upper Limit) Calculation Whether the search results in a small number of detection candidates or more, we can bound the rate of CBCs in the (nearby) universe. Depending on the significance
Past and Future in the Quest for Gravitational Wave Transients
 Crab-Chandra NASA/ESA Credit: NASA/COBE Past and Future in the Quest for Gravitational Wave Transients Laura Cadonati - University of Massachusetts, Amherst LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration
Crab-Chandra NASA/ESA Credit: NASA/COBE Past and Future in the Quest for Gravitational Wave Transients Laura Cadonati - University of Massachusetts, Amherst LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration
Gravitational Wave Astronomy s Next Frontier in Computation
 Gravitational Wave Astronomy s Next Frontier in Computation Chad Hanna - Penn State University Penn State Physics Astronomy & Astrophysics Outline 1. Motivation 2. Gravitational waves. 3. Birth of gravitational
Gravitational Wave Astronomy s Next Frontier in Computation Chad Hanna - Penn State University Penn State Physics Astronomy & Astrophysics Outline 1. Motivation 2. Gravitational waves. 3. Birth of gravitational
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO)! A Brief Overview!
 Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) A Brief Overview Sharon Brunett California Institute of Technology Pacific Research Platform Workshop October 15, 2015 Credit: AEI, CCT, LSU LIGO
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) A Brief Overview Sharon Brunett California Institute of Technology Pacific Research Platform Workshop October 15, 2015 Credit: AEI, CCT, LSU LIGO
Kicked Waveforms Observing Black Hole Recoils in Gravitational Wave Signals
 Kicked Waveforms Observing Black Hole Recoils in Gravitational Wave Signals Christopher Moore, DAMTP, Cambridge, UK StronG BaD, Mississippi 1st March 2017 Work done in collaboration with Davide Gerosa
Kicked Waveforms Observing Black Hole Recoils in Gravitational Wave Signals Christopher Moore, DAMTP, Cambridge, UK StronG BaD, Mississippi 1st March 2017 Work done in collaboration with Davide Gerosa
What have we learned from coalescing Black Hole binary GW150914
 Stas Babak ( for LIGO and VIRGO collaboration). Albert Einstein Institute (Potsdam-Golm) What have we learned from coalescing Black Hole binary GW150914 LIGO_DCC:G1600346 PRL 116, 061102 (2016) Principles
Stas Babak ( for LIGO and VIRGO collaboration). Albert Einstein Institute (Potsdam-Golm) What have we learned from coalescing Black Hole binary GW150914 LIGO_DCC:G1600346 PRL 116, 061102 (2016) Principles
Reducing false alarms in searches for gravitational waves from coalescing binary systems
 Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Master's Theses Graduate School 2007 Reducing false alarms in searches for gravitational waves from coalescing binary systems Andres Rodriguez Louisiana
Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Master's Theses Graduate School 2007 Reducing false alarms in searches for gravitational waves from coalescing binary systems Andres Rodriguez Louisiana
Gravitational Waves and LIGO
 Gravitational Waves and LIGO Ray Frey, University of Oregon 1. GW Physics and Astrophysics 2. How to detect GWs The experimental challenge 3. Prospects June 16, 2004 R. Frey QNet 1 General Relativity Some
Gravitational Waves and LIGO Ray Frey, University of Oregon 1. GW Physics and Astrophysics 2. How to detect GWs The experimental challenge 3. Prospects June 16, 2004 R. Frey QNet 1 General Relativity Some
High-energy follow-up studies of gravitational wave transient events
 High-energy follow-up studies of gravitational wave transient events Università di Pisa & INFN - Pisa E-mail: barbara.patricelli@pi.infn.it Massimiliano Razzano Università di Pisa & INFN - Pisa E-mail:
High-energy follow-up studies of gravitational wave transient events Università di Pisa & INFN - Pisa E-mail: barbara.patricelli@pi.infn.it Massimiliano Razzano Università di Pisa & INFN - Pisa E-mail:
Status of LIGO. David Shoemaker LISA Symposium 13 July 2004 LIGO-G M
 Status of LIGO David Shoemaker LISA Symposium 13 July 2004 Ground-based interferometric gravitational-wave detectors Search for GWs above lower frequency limit imposed by gravity gradients» Might go as
Status of LIGO David Shoemaker LISA Symposium 13 July 2004 Ground-based interferometric gravitational-wave detectors Search for GWs above lower frequency limit imposed by gravity gradients» Might go as
Searches for Gravitational waves associated with Gamma-ray bursts
 Searches for Gravitational waves associated with Gamma-ray bursts Raymond Frey University of Oregon for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 1 Current network of groundbased GW
Searches for Gravitational waves associated with Gamma-ray bursts Raymond Frey University of Oregon for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration 1 Current network of groundbased GW
Scientific Results from the first LIGO Science Runs
 Scientific Results from the first LIGO Science Runs Introduction to GW s and LIGO The LIGO Science runs Physics, astrophysics, and S1 analysis results:» Binary inspirals» Pulsars and CW Sources» Bursts
Scientific Results from the first LIGO Science Runs Introduction to GW s and LIGO The LIGO Science runs Physics, astrophysics, and S1 analysis results:» Binary inspirals» Pulsars and CW Sources» Bursts
Testing the strong-field dynamics of general relativity with gravitional waves
 Testing the strong-field dynamics of general relativity with gravitional waves Chris Van Den Broeck National Institute for Subatomic Physics GWADW, Takayama, Japan, May 2014 Statement of the problem General
Testing the strong-field dynamics of general relativity with gravitional waves Chris Van Den Broeck National Institute for Subatomic Physics GWADW, Takayama, Japan, May 2014 Statement of the problem General
LIGO-Virgo Detector Characterization (DetChar)
 LIGO-Virgo Detector Characterization (DetChar) 5th KAGRA Workshop Perugia, 14-15 February 2019 Nicolas Arnaud (narnaud@lal.in2p3.fr) Laboratoire de l Accélérateur Linéaire (CNRS/IN2P3 & Université Paris-Sud)
LIGO-Virgo Detector Characterization (DetChar) 5th KAGRA Workshop Perugia, 14-15 February 2019 Nicolas Arnaud (narnaud@lal.in2p3.fr) Laboratoire de l Accélérateur Linéaire (CNRS/IN2P3 & Université Paris-Sud)
Studying the Effects of Tidal Corrections on Parameter Estimation
 Studying the Effects of Tidal Corrections on Parameter Estimation Leslie Wade Jolien Creighton, Benjamin Lackey, Evan Ochsner Center for Gravitation and Cosmology 1 Outline Background: Physical description
Studying the Effects of Tidal Corrections on Parameter Estimation Leslie Wade Jolien Creighton, Benjamin Lackey, Evan Ochsner Center for Gravitation and Cosmology 1 Outline Background: Physical description
How to listen to the Universe?
 How to listen to the Universe? Optimising future GW observatories for astrophysical sources Stefan Hild NIKHEF, May 2009 Overview Microphones to detect gravitational waves Why haven t we heard GW so far?
How to listen to the Universe? Optimising future GW observatories for astrophysical sources Stefan Hild NIKHEF, May 2009 Overview Microphones to detect gravitational waves Why haven t we heard GW so far?
Gravitational-Wave Astronomy - a Long Time Coming Livia Conti, for the Virgo Collaboration Fred Raab, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration
 Gravitational-Wave Astronomy - a Long Time Coming Livia Conti, for the Virgo Collaboration Fred Raab, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Hanford, WA LIGO Livingston, LA Virgo (Cascina, Italy) What
Gravitational-Wave Astronomy - a Long Time Coming Livia Conti, for the Virgo Collaboration Fred Raab, for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO Hanford, WA LIGO Livingston, LA Virgo (Cascina, Italy) What
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves
 Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves Barry C. Barish Caltech Crab Pulsar Georgia Tech 26-April-06 General Relativity the essential idea G μν = 8πΤ μν Gravity is not a force, but a property of space
Probing the Universe for Gravitational Waves Barry C. Barish Caltech Crab Pulsar Georgia Tech 26-April-06 General Relativity the essential idea G μν = 8πΤ μν Gravity is not a force, but a property of space
State of LIGO. Barry Barish. S1 sensitivities. LSC Meeting LLO Hanford, WA 10-Nov GEO -- L 2km -- H 4km -- L 4km LIGO-G M
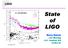 S1 sensitivities -- GEO -- L 2km -- H 4km -- L 4km State of h 0 LIGO Barry Barish LSC Meeting LLO Hanford, WA 10-Nov-03 Goals and Priorities LSC -Aug 02 Interferometer performance» Integrate commissioning
S1 sensitivities -- GEO -- L 2km -- H 4km -- L 4km State of h 0 LIGO Barry Barish LSC Meeting LLO Hanford, WA 10-Nov-03 Goals and Priorities LSC -Aug 02 Interferometer performance» Integrate commissioning
Cosmology with Gravitational Wave Detectors. Maya Fishbach
 Cosmology with Gravitational Wave Detectors Maya Fishbach Part I: Cosmography Compact Binary Coalescenses are Standard Sirens The amplitude* of a GW from a CBC is The timescale is Measuring amplitude,
Cosmology with Gravitational Wave Detectors Maya Fishbach Part I: Cosmography Compact Binary Coalescenses are Standard Sirens The amplitude* of a GW from a CBC is The timescale is Measuring amplitude,
Gravitational waves. Markus Pössel. What they are, how to detect them, and what they re good for. MPIA, March 11, 2016.
 What they are, how to detect them, and what they re good for AstroTechTalk MPIA, March 11, 2016 General relativity Interferometric detectors First direct detection What s next? Einstein s general theory
What they are, how to detect them, and what they re good for AstroTechTalk MPIA, March 11, 2016 General relativity Interferometric detectors First direct detection What s next? Einstein s general theory
Gravitational Radiation of Binaries Coalescence into Intermediate Mass Black Holes
 Commun Theor Phys 57 (22) 56 6 Vol 57 No January 5 22 Gravitational Radiation of Binaries Coalescence into Intermediate Mass Black Holes LI Jin (Ó) HONG Yuan-Hong ( ) 2 and PAN Yu ( ) 3 College of Physics
Commun Theor Phys 57 (22) 56 6 Vol 57 No January 5 22 Gravitational Radiation of Binaries Coalescence into Intermediate Mass Black Holes LI Jin (Ó) HONG Yuan-Hong ( ) 2 and PAN Yu ( ) 3 College of Physics
Methods for Reducing False Alarms in Searches for Compact Binary Coalescences in LIGO Data
 Syracuse University SURFACE Physics College of Arts and Sciences 4-8-2010 Methods for Reducing False Alarms in Searches for Compact Binary Coalescences in LIGO Data Duncan Brown Department of Physics,
Syracuse University SURFACE Physics College of Arts and Sciences 4-8-2010 Methods for Reducing False Alarms in Searches for Compact Binary Coalescences in LIGO Data Duncan Brown Department of Physics,
Gravity. Newtonian gravity: F = G M1 M2/r 2
 Gravity Einstein s General theory of relativity : Gravity is a manifestation of curvature of 4- dimensional (3 space + 1 time) space-time produced by matter (metric equation? g μν = η μν ) If the curvature
Gravity Einstein s General theory of relativity : Gravity is a manifestation of curvature of 4- dimensional (3 space + 1 time) space-time produced by matter (metric equation? g μν = η μν ) If the curvature
Bayesian methods in the search for gravitational waves
 Bayesian methods in the search for gravitational waves Reinhard Prix Albert-Einstein-Institut Hannover Bayes forum Garching, Oct 7 2016 Statistics as applied Probability Theory Probability Theory: extends
Bayesian methods in the search for gravitational waves Reinhard Prix Albert-Einstein-Institut Hannover Bayes forum Garching, Oct 7 2016 Statistics as applied Probability Theory Probability Theory: extends
Gravitational Wave Burst Searches
 Gravitational Wave Burst Searches Peter Shawhan For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration Gravitational Waves 2010 University of Minnesota October 16, 2010 LIGO-G1000998-v3 Worldwide
Gravitational Wave Burst Searches Peter Shawhan For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration Gravitational Waves 2010 University of Minnesota October 16, 2010 LIGO-G1000998-v3 Worldwide
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-P030066-00 December 2, 2003 First upper limits from
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY - LIGO - CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Document Type LIGO-P030066-00 December 2, 2003 First upper limits from
DECAM SEARCHES FOR OPTICAL SIGNATURES OF GW Soares-Santos et al arxiv:
 DECAM SEARCHES FOR OPTICAL SIGNATURES OF GW150914 Soares-Santos et al. 2016 arxiv:1602.04198 Marcelle Soares-Santos The DES Collaboration Fermilab Moriond Cosmology Conference March 20, 2016 INTRODUCTION
DECAM SEARCHES FOR OPTICAL SIGNATURES OF GW150914 Soares-Santos et al. 2016 arxiv:1602.04198 Marcelle Soares-Santos The DES Collaboration Fermilab Moriond Cosmology Conference March 20, 2016 INTRODUCTION
LISA: Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves. Tom Prince Caltech/JPL. Laser Interferometer Space Antenna LISA
 : Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves Tom Caltech/JPL Laser Interferometer Space Antenna http://lisa.nasa.gov Gravitational Wave Astronomy is Being Born LIGO, VIRGO, GEO, TAMA 4000m, 3000m, 2000m,
: Probing the Universe with Gravitational Waves Tom Caltech/JPL Laser Interferometer Space Antenna http://lisa.nasa.gov Gravitational Wave Astronomy is Being Born LIGO, VIRGO, GEO, TAMA 4000m, 3000m, 2000m,
The Present Gravitational Wave Detection Effort
 The Present Gravitational Wave Detection Effort Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO Scientific Collaboration International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics Rome July 1,
The Present Gravitational Wave Detection Effort Keith Riles University of Michigan LIGO Scientific Collaboration International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics Rome July 1,
Search for the gravity wave signature of GRB030329/SN2003dh
 Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Search for the gravity wave signature of GRB030329/SN2003dh ABSTRACT Optimal Integration length Well detectable Sine- Gaussian simulation One
Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) Search for the gravity wave signature of GRB030329/SN2003dh ABSTRACT Optimal Integration length Well detectable Sine- Gaussian simulation One
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 3
 Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 3 Peter S. Shawhan Gravitational Wave Astronomy Summer School May 30, 2012 Outline for Today Gaining confidence in a signal candidate Consistency tests Data quality
Gravitational-Wave Data Analysis: Lecture 3 Peter S. Shawhan Gravitational Wave Astronomy Summer School May 30, 2012 Outline for Today Gaining confidence in a signal candidate Consistency tests Data quality
arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 15 Mar 2010
![arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 15 Mar 2010 arxiv: v1 [gr-qc] 15 Mar 2010](/thumbs/72/66308395.jpg) A tapering window for time-domain templates and simulated signals in the detection of gravitational waves from coalescing compact binaries. LIGO-P0900118-v4. arxiv:1003.2939v1 [gr-qc] 15 Mar 2010 DJA McKechan,
A tapering window for time-domain templates and simulated signals in the detection of gravitational waves from coalescing compact binaries. LIGO-P0900118-v4. arxiv:1003.2939v1 [gr-qc] 15 Mar 2010 DJA McKechan,
Long-term strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups
 Longterm strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups Barry Barish APPEC Meeting London, UK 29Jan04 International Interferometer Network Simultaneously detect signal (within msec) LIGO
Longterm strategy on gravitational wave detection from European groups Barry Barish APPEC Meeting London, UK 29Jan04 International Interferometer Network Simultaneously detect signal (within msec) LIGO
What have we learned from the detection of gravitational waves? Hyung Mok Lee Seoul National University
 What have we learned from the detection of gravitational waves? Hyung Mok Lee Seoul National University Outline Summary of 1st and 2nd Observing Runs Characteristics of detected sources Astrophysical Implications
What have we learned from the detection of gravitational waves? Hyung Mok Lee Seoul National University Outline Summary of 1st and 2nd Observing Runs Characteristics of detected sources Astrophysical Implications
Confronting Theory with Gravitational Wave Observations
 Gravitation: A Decennial Perspective Confronting Theory with Gravitational Wave Observations B F Schutz Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics () Golm/Potsdam Germany The AEI congratulates The
Gravitation: A Decennial Perspective Confronting Theory with Gravitational Wave Observations B F Schutz Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics () Golm/Potsdam Germany The AEI congratulates The
