The Mystery in the Design of A. R. Guilmet
|
|
|
- Daisy Wilcox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Mystery in the Design of A. R. Guilmet Everybody loves a good mystery. Today, fortunes are made de- Based on my measurements, the I ll bet Guilmet did the same thing. vising television shows, movies, suspension point would need to be and books with mysterious plots. moved back by only 1/1,000th of In the late 1880s the Society des an inch away from the direction of Horologers helped satisfy the desire for mystery through ingenious replace the loss. swing at the end of every swing to devices, including A. R. Guilmet s Let us look at it another way. mystery clock. Take a pendulum and suspend it Guilmet was a creative engineer who designed practical me- will hang stationary under the sus- from a point. The pendulum bob chanical devices and held several pension point. Now move the suspension one inch to the right. The patents, or brevets, for clocks and electric motors, but he wanted to bob will start to swing to the right design a clock that would mystify of center under the suspension. observers. If the works didn t seem However, a body in motion will connected to the pendulum, people would wonder how the clock dulum will continue to the right, tend to stay in motion ; the pen- kept time. Because everyone knew passing left under the suspension that a pendulum must have an impulse to keep it going, he needed to any losses, to the right of the sus- point to a point one inch, minus devise a very accurate clock with a pension point. Now at this point pendulum that oscillated continually with no apparent power or at- back to the left, where it started. move the suspension one inch tachment to the hands. Guilmet At this moment the bob would figured it out and left it to others to be approximately two inches to decipher the mystery. the right of the suspension point. How did he do it? He must have If you kept this up, the pendulum would swing to its maximum thought of the principle that a free pendulum, held a distance away swing. If you try this with a ball on from the vertical (say point A) a string, you will find that timing possesses a certain amount of potential energy and wants to swing to keeping the ball in motion. You your hand movement is essential back to the vertical. This energy An A. R. Guilmet mystery clock, ca. late 1880s. will also find that the amount of is proportional to the distance the hand movement is not very much pendulum is away from the vertical line under the point to keep the oscillation going. of suspension. A free-swinging pendulum will lose a bit To replace the loss in amplitude of each swing, it would of the swing distance with each swing due to external only be necessary to move the suspension point back and losses. If he could devise a way to make up for the loss forth by 1/1,000th of an inch. If the suspension point of each swing, the pendulum would continue to swing. is moved more than one 1/1,000th inch, the angle and Guilmet s solution was to move the suspension point the energy are increased and the swing of the pendulum away from the end of the swing by the amount of the increases. The increase in path also causes an increase in loss of each swing. losses. If the movement of the suspension is within the To satisfy my curiosity, I took a mystery clock I was limits of the pendulum swing, the swing distance equalizes to be constant at some point. repairing and mounted the statue with the pendulum so that the tip of the pendulum could be seen free swinging I have seen this difference in swing among the several in front of a ruler. It was not very scientific, but I only Guilmet statue clocks I have repaired. The movement of wanted a rough estimation of the decrease in the swing the suspension point can be adjusted from 1,000th to for 500 oscillations, or 1,000 swings, of the pendulum. I 2,000th of an inch. The amplitude of the pendulum is counted 500 complete oscillations, and the decrease was increased with greater movement of the arm, but the motion of the arm holding the suspension of the pendulum less than an inch. Therefore, the amount of swing loss with each swing was a little less than 1/1,000th of an is imperceptible to the eye. inch. The loss of each swing was imperceptible to the eye National Association of Watch and Clock Collectors, Inc. Reproduction prohibited without written permission. by Robert Boyd (NH) NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin September/October
2 September/October 2013 NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin
3 After working out the above reasoning, Guilmet had to design a mechanism that could sense the position and direction of swing of the pendulum. It was not an easy task. The suspension arm s movement must be the opposite of the direction of the pendulum swing and occur near the end of the swing. He achieved this action by a clever sensing mechanism that detects the pull on the statue arm by the pendulum. The swinging pendulum not only pulls down on the suspension point, but, when swinging, pulls horizontally. He mounted the statue on a base that could rotate on its vertical axis. The statue s arm, with the suspension point of the pendulum, is like a wrench on a pipe you are going to turn. Any sidewise pull on the arm will result in a twisting force on the statue. A like axis arm (see 1 in Figure 1A) inside the bottom of the base, points out from the swivel axis and protrudes inside the works. The end of this arm is fitted with a small ball (2) that penetrates the clockworks. This four-inch-long arm mimics the arm on the statue, transmitting any sidewise pull of the pendulum to the small ball at its end. The ball protrudes into a slot in the bottom of a long crutch (3) running up the front plate of the works, and the crutch is pivoted at the bottom of the works (4) a short distance from the point of contact of the ball. The lever ratio from the ball is about 1:24 to the slot at the top end of this crutch (5). This long lever gives a sensitivity advantage to any lateral movement of the ball. There is a pin attached at the top point of the stirrup (6) that extends through a slot in the trapeze (7) and extends into a slot in the top of the crutch (5). The slot in the trapeze has clearance on each side for the pin to pass through. This clearance is very important to the sensing because it allows the upper end of the crutch and stirrup pin to move slightly sideways without having to move the trapeze. The pin on the stirrup is less than half the distance from the stirrup pivot point to the bottom of the stirrup, allowing the bottom of the stirrup to move twice the distance the pin moves. This series of levers makes the lower part of the stirrup very sensitive to any lateral motion of the ball. The overall ratio from the statue s hand to the lower part of the stirrup is more than 1:100. This lever ratio allows the works to sense the sideways and directional pull of the pendulum as it passes through the center of its swing. In actuality, you can move the pendulum less than ±10 degrees off center, and the stirrup pallets will move to the right or left enough to clear the pin and release the crank. The lateral movement of the stirrup is limited by the clearance of the pin through the slot in the trapeze. The stirrup can t move the trapeze because the long leg of the trapeze is coupled to the crank on the end of the last pinion of the works, defining the limits. From Figure 1A, if the pendulum moves to the left of center, the lower part of the stirrup will also move to the left. From Figure 4A (see page 520), if the pendulum moves to the right, the lower stirrup will move right. Because of the 100:1 ratio of the levers, the statue s hand would have to move only.0002" to move the stirrup.020". The statue is a very sensitive lady! This sensitive series of levers was the key to Guilmet s mystery of the pendulum, which seemed to be completely detached from the works. Without any apparent connection, the works could detect when the pendulum was starting its swing from center in either direction and trigger the direction and movement of the suspension. This very clever lever and trapeze mechanism synchronized the pendulum with the clockworks and timed the movement of the suspension point. It should be noted that if the works are not well cared for or out of adjustment, the clock may run and the crank turn erratically but not be synchronized with the pendulum; this could cause it to either stop or run erratically. With synchronizing done, the movement must now impart the movement of the suspension point. The bottom tips of the stirrup have on either side a flat pallet that stop and hold a pin on a crank (8). Two crank pins (8 and 9), one at each end of the crank bar, are slightly offset from each other. Each pin is aligned with the position of one of the stirrup pallets (see Figure 1A). The pull of the pendulum swing to the left side of center is sensed through the levers and causes the slight movement of the stirrup to the left. Remember that the wide slot in the trapeze allows the stirrup to be moved without any Front of movement showing pendulum sensing mechanism. NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin September/October
4 10 9 movement of the trapeze. The pin on the crank will fall off the pallet and the crank will start to rotate clockwise one-half turn, powered by the works (Figure 2A). Now it is the movement s turn to move the statue. As the crank rotates clockwise, it moves the lower end of the long arm of the trapeze to the left. As the trapeze swings to the left, it will contact the pin on the stirrup (10 in Figure 2A) and move the top of the crutch to the left, causing the lower part of the crutch to move the ball slightly to the right. Here the movement of the stirrup-to-statue ratio is reversed, and the statue s hand movement is about 1/100 the movement of the top of the crutch. The hand rotates only about 2/1,000ths of an inch to the right, opposite to the direction of the swing. The movement is not perceptible to the eye. Those who want to analyze a complete cycle may look at Figures 3A and 4A to see the sensing of the pendulum moving back to the right as it repeats the process of sensing and movement of the statue arm back to the left. My Guilmet pendulum beats around 7,200 b/hr. Other Guilmet Clocks Guilmet s clocks won top prizes at the Societe des Horologers in He made many improvements to his clocks, mainly in the trapeze. The later trapeze arrangement is shown below in Figures 1B and 2B. It basically works the same way. Guilmet also made several versions of a torsion pendulum clock. The rotation of the 520 September/October 2013 NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin
5 pendulum is sensed by the same trapeze arrangement, but the works are very similar, although smaller in size, and he eliminated the last gear and pinion in the train and mounted the crank on the next to last. The rotation of the crank is counterclockwise and moves faster but less often, because the period of the torsion pendulum is much longer. I measured 1,860 b/hr on a large statue holding the clock above her head. The clock has a bracket at the bottom holding the top of the suspension spring, which gives the spring an imperceptible twist in the opposite direction of the pendulum rotation. Guilmet s clocks were not only mystifying but also very accurate. When set up properly, they maintain accuracy of better than a minute a week. Most methods of giving impulse to pendulums also impede their free swinging. Guilmet s method of moving the suspension to make up for free-swinging losses is ingenious because it does not interfere with the free motion of the pendulum, yet gives a very precise impulse that is not affected by the power of the works. Other than turbulence and external vibrations, Guilmet s method is very close to a free-swinging pendulum. These clocks are usually very heavy, which helps reduce the variability of vibration. A sturdy shelf also helps. This Clock In Action Readers interested in seeing the movement mechanism decribed in this article in action should access the addenda to this article at: watch-a-clock-bulletin/w-a-c-bulletin-addenda. About the Author Bob Boyd grew up in Indianapolis, spent about 40 years in New Jersey, and has enjoyed the last 20 in New Hampshire. A graduate of Purdue with an MBA from the University of Michigan, he s a retired professional engineer who specialized in electro-mechanical design. He s been a member of the NAWCC for about 45 years, and started collecting clocks a few years before becoming a member. Bob enjoys repairing complicated movements using CAD to design the lost parts and then make them using a gearcutter and other tools he has made. He figures out what the maker intended by using the spacing of old pivot holes, and sometimes shadows on the plates, along with a bit of math. He especially welcomes the challenge of designing and reconstructing missing or broken parts. He welcomes all to his extensive workshop and will provide plenty of talk and information about clocks. Indeed, sharing his love of clocks and how they work has led to many wonderful and far-flung friendships. He d love to hear your comments about this article, or any other clock topic at bobboyd@rlbpab.com. NAWCC Watch & Clock Bulletin September/October
Casting Physics Simplified Part Two. Frames of Reference
 Casting Physics Simplified Part Two Part one of this paper discussed physics that applies to linear motion, i.e., motion in a straight line. This section of the paper will expand these concepts to angular
Casting Physics Simplified Part Two Part one of this paper discussed physics that applies to linear motion, i.e., motion in a straight line. This section of the paper will expand these concepts to angular
2013 Antiquarian Horological Society. Reproduction prohibited without permission.
 2013 Antiquarian Horological Society. Reproduction prohibited without permission. ANTIQUARIAN HOROLOGY Picture Gallery 30-hour iron wall clock dated 1748 The painted dial with the minute hand shorter than
2013 Antiquarian Horological Society. Reproduction prohibited without permission. ANTIQUARIAN HOROLOGY Picture Gallery 30-hour iron wall clock dated 1748 The painted dial with the minute hand shorter than
Experiment 9: Compound Pendulum
 COMSATS nstitute of nformation Technology, slamabad Campus PHYS - 108 Experiment 9: Compound Pendulum A compound pendulum (also known as a physical pendulum) consists of a rigid body oscillating about
COMSATS nstitute of nformation Technology, slamabad Campus PHYS - 108 Experiment 9: Compound Pendulum A compound pendulum (also known as a physical pendulum) consists of a rigid body oscillating about
VECTORS & EQUILIBRIUM Experiment 4
 Physical Science 14 VECTORS & EQUILIBRIUM Experiment 4 INTRODUCTION: Pictures are often more descriptive than words. In physics it is useful to represent some quantities by an arrow, called vector, where
Physical Science 14 VECTORS & EQUILIBRIUM Experiment 4 INTRODUCTION: Pictures are often more descriptive than words. In physics it is useful to represent some quantities by an arrow, called vector, where
Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere
 Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 32 Introduction To Comparators, Mechanical Comparators (Refer Slide Time: 00:15) I welcome you
Metrology Prof. Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 32 Introduction To Comparators, Mechanical Comparators (Refer Slide Time: 00:15) I welcome you
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion Chapter 8 Rotational Motion In this chapter you will: Learn how to describe and measure rotational motion. Learn how torque changes rotational velocity. Explore factors that
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion Chapter 8 Rotational Motion In this chapter you will: Learn how to describe and measure rotational motion. Learn how torque changes rotational velocity. Explore factors that
Lecture T2 The Pendulum-Based Start Gate (US 8,016,639 B2)
 1 Lecture T2 The Pendulum-Based Start Gate (US 8,016,639 B2) INTRODUCTION Literally millions of Pinewood Derby races have been run since the inception of the race in 1953, mostly by Cub Scouts and their
1 Lecture T2 The Pendulum-Based Start Gate (US 8,016,639 B2) INTRODUCTION Literally millions of Pinewood Derby races have been run since the inception of the race in 1953, mostly by Cub Scouts and their
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum
 Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the
Lectures Chapter 10 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition)
 PH 201-4A spring 2007 Simple Harmonic Motion Lectures 24-25 Chapter 10 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 The Ideal Spring Springs are objects that exhibit elastic behavior. It will return back
PH 201-4A spring 2007 Simple Harmonic Motion Lectures 24-25 Chapter 10 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 The Ideal Spring Springs are objects that exhibit elastic behavior. It will return back
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
Practice Test SHM with Answers
 Practice Test SHM with Answers MPC 1) If we double the frequency of a system undergoing simple harmonic motion, which of the following statements about that system are true? (There could be more than one
Practice Test SHM with Answers MPC 1) If we double the frequency of a system undergoing simple harmonic motion, which of the following statements about that system are true? (There could be more than one
Figure Two. Then the two vector equations of equilibrium are equivalent to three scalar equations:
 2004- v 10/16 2. The resultant external torque (the vector sum of all external torques) acting on the body must be zero about any origin. These conditions can be written as equations: F = 0 = 0 where the
2004- v 10/16 2. The resultant external torque (the vector sum of all external torques) acting on the body must be zero about any origin. These conditions can be written as equations: F = 0 = 0 where the
Question 13.1a Harmonic Motion I
 Question 13.1a Harmonic Motion I A mass on a spring in SHM has a) 0 amplitude A and period T. What b) A/2 is the total distance traveled by c) A the mass after a time interval T? d) 2A e) 4A Question 13.1a
Question 13.1a Harmonic Motion I A mass on a spring in SHM has a) 0 amplitude A and period T. What b) A/2 is the total distance traveled by c) A the mass after a time interval T? d) 2A e) 4A Question 13.1a
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
Chapter 14: Periodic motion
 Chapter 14: Periodic motion Describing oscillations Simple harmonic motion Energy of simple harmonic motion Applications of simple harmonic motion Simple pendulum & physical pendulum Damped oscillations
Chapter 14: Periodic motion Describing oscillations Simple harmonic motion Energy of simple harmonic motion Applications of simple harmonic motion Simple pendulum & physical pendulum Damped oscillations
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 4.8-kg block attached to a spring executes simple harmonic motion on a frictionless
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 4.8-kg block attached to a spring executes simple harmonic motion on a frictionless
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
Service Information Letter SIL # 017
 Service Information Letter SIL # 017 Trunnion Adjustment - Double Barrels Only Equipment: Double Barrels With Sloped Trunnions Date Issued: 9-24-03 Additional Reference: SIL # 016 Revised: Revision #:
Service Information Letter SIL # 017 Trunnion Adjustment - Double Barrels Only Equipment: Double Barrels With Sloped Trunnions Date Issued: 9-24-03 Additional Reference: SIL # 016 Revised: Revision #:
Educational Objectives Determine which variable affects the frequency of a simple pendulum.
 Physics Workshop Main Topic Subtopic Learning Level Technology Level Activity Type Motion Periodic Motion Middle Low Student Teacher s Notes Description: Test the length, mass, and amplitude of a pendulum
Physics Workshop Main Topic Subtopic Learning Level Technology Level Activity Type Motion Periodic Motion Middle Low Student Teacher s Notes Description: Test the length, mass, and amplitude of a pendulum
Ballistic Pendulum. Caution
 Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the ball,
Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the ball,
Specimen Paper. Physics. AQA Level 1/2 Certificate in Physics Specimen Paper. Paper 2 TOTAL. Time allowed 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number Specimen Paper For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark AQA Level 1/2 Certificate in Physics Specimen Paper 1 2 Physics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number Specimen Paper For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark AQA Level 1/2 Certificate in Physics Specimen Paper 1 2 Physics
PARTS LIST / TECHNICAL GUIDE
 PARTS LIST / TECHNICAL GUIDE Automatic [SPECIFICATIONS] Item Cal. No. 6R20/6R21 6R20 6R21 3 hands (hour, minute and second hands) Date/Day indication Power reserve indicator Driving system Time indication
PARTS LIST / TECHNICAL GUIDE Automatic [SPECIFICATIONS] Item Cal. No. 6R20/6R21 6R20 6R21 3 hands (hour, minute and second hands) Date/Day indication Power reserve indicator Driving system Time indication
It is obviously illogical. What
 Illogical: What Else Would You Call It? by Dr. Clayton Boyer (CA) Author s Note: The beautiful mechanisms shown in this article were all imaginatively crafted through the artistry of Forrest Burnett. The
Illogical: What Else Would You Call It? by Dr. Clayton Boyer (CA) Author s Note: The beautiful mechanisms shown in this article were all imaginatively crafted through the artistry of Forrest Burnett. The
Measuring the Universal Gravitational Constant, G
 Measuring the Universal Gravitational Constant, G Introduction: The universal law of gravitation states that everything in the universe is attracted to everything else. It seems reasonable that everything
Measuring the Universal Gravitational Constant, G Introduction: The universal law of gravitation states that everything in the universe is attracted to everything else. It seems reasonable that everything
Lab 12: Periodic Motion
 Lab 12: Periodic Motion Objectives: To devise an experiment to test variables that might affect the period of a pendulum To carry out an experiment testing variables that might affect the period of a pendulum,
Lab 12: Periodic Motion Objectives: To devise an experiment to test variables that might affect the period of a pendulum To carry out an experiment testing variables that might affect the period of a pendulum,
Equilibrium in Two Dimensions
 C h a p t e r 6 Equilibrium in Two Dimensions In this chapter, you will learn the following to World Class standards: 1. The Ladder Against the Wall 2. The Street Light 3. The Floor Beam 6-1 The Ladder
C h a p t e r 6 Equilibrium in Two Dimensions In this chapter, you will learn the following to World Class standards: 1. The Ladder Against the Wall 2. The Street Light 3. The Floor Beam 6-1 The Ladder
Chapter 12 Vibrations and Waves Simple Harmonic Motion page
 Chapter 2 Vibrations and Waves 2- Simple Harmonic Motion page 438-45 Hooke s Law Periodic motion the object has a repeated motion that follows the same path, the object swings to and fro. Examples: a pendulum
Chapter 2 Vibrations and Waves 2- Simple Harmonic Motion page 438-45 Hooke s Law Periodic motion the object has a repeated motion that follows the same path, the object swings to and fro. Examples: a pendulum
Winmeen Tnpsc Group 1 & 2 Study Materials
 5. Measurement and Measuring Instrument 1. What was the writing of Claudius Ptolemy? He wrote that the moon, the sun and all the planets around the Earth in an almost circular path. 2. Who was the first
5. Measurement and Measuring Instrument 1. What was the writing of Claudius Ptolemy? He wrote that the moon, the sun and all the planets around the Earth in an almost circular path. 2. Who was the first
Harmonic Motion: The Pendulum Lab Advanced Version
 Harmonic Motion: The Pendulum Lab Advanced Version In this lab you will set up a pendulum using rulers, string, and small weights and measure how different variables affect the period of the pendulum.
Harmonic Motion: The Pendulum Lab Advanced Version In this lab you will set up a pendulum using rulers, string, and small weights and measure how different variables affect the period of the pendulum.
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium. 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium Name 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction 1. The distance between a turning axis and the
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium Name 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction 1. The distance between a turning axis and the
COMPOUND PENDULUM. AIM: 01. To determine the radius of gyration k of given compo pendulum. 02. To verify the relation
 COMPOUND PENDULUM AIM: 01. To determine the radius of gyration k of given compo pendulum. 02. To verify the relation T= 2 π 2 2 K + (OG) g (OG) Where, T = Periodic time sec. K = Radius of gyration about
COMPOUND PENDULUM AIM: 01. To determine the radius of gyration k of given compo pendulum. 02. To verify the relation T= 2 π 2 2 K + (OG) g (OG) Where, T = Periodic time sec. K = Radius of gyration about
Experimenting with Forces
 A mother hears a loud crash in the living room. She walks into the room to see her seven-year-old son looking at a broken vase on the floor. How did that happen? she asks. I don t know. The vase just fell
A mother hears a loud crash in the living room. She walks into the room to see her seven-year-old son looking at a broken vase on the floor. How did that happen? she asks. I don t know. The vase just fell
LAW WOODEN CLOCK 5 SHT 1 OF 9 SHTS. General Assembly 1 NTS FEB Designed by: BRLAW
 2 43 31 42 4 32 39 14 29 21 2 21 22 40 23 22 20 18 1 17 1 4 8 7 9 15 20 29 40 ITEM NO. QTY. PART NO. 1 1 back 2 1 front 4 1 Pendulum hanger 4 Dial spacer 7 1 Pendulum head 8 1 Pendulum pivot 9 1 Pendulum
2 43 31 42 4 32 39 14 29 21 2 21 22 40 23 22 20 18 1 17 1 4 8 7 9 15 20 29 40 ITEM NO. QTY. PART NO. 1 1 back 2 1 front 4 1 Pendulum hanger 4 Dial spacer 7 1 Pendulum head 8 1 Pendulum pivot 9 1 Pendulum
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Dial removed for clarity
 8 7 4 1 18 19 15 1 9 24 21 24 29 17 14 20 21 29 23 22 3 40 22 25 2 44 41 39 2 32 12 33 13 12 31 43 42 ITEM QTY PART NO. DESCRIPTION 1 1 Back 2 1 Front 3 3 Spacer top 4 1 Pendulum hanger 5 1 Clock dial
8 7 4 1 18 19 15 1 9 24 21 24 29 17 14 20 21 29 23 22 3 40 22 25 2 44 41 39 2 32 12 33 13 12 31 43 42 ITEM QTY PART NO. DESCRIPTION 1 1 Back 2 1 Front 3 3 Spacer top 4 1 Pendulum hanger 5 1 Clock dial
How do the physical aspects of the oscillators affect the Period?
 LAST NAME FIRST NAME DATE 10.4 The Pendulum & Spring Mass Oscillator Conceptual Questions 10, 11, 12, 13 page 314 Problems 40 page 317 How do the physical aspects of the oscillators affect the Period?
LAST NAME FIRST NAME DATE 10.4 The Pendulum & Spring Mass Oscillator Conceptual Questions 10, 11, 12, 13 page 314 Problems 40 page 317 How do the physical aspects of the oscillators affect the Period?
1 Oscillations MEI Conference 2009
 1 Oscillations MEI Conference 2009 Some Background Information There is a film clip you can get from Youtube of the Tacoma Narrows Bridge called Galloping Gertie. This shows vibrations in the bridge increasing
1 Oscillations MEI Conference 2009 Some Background Information There is a film clip you can get from Youtube of the Tacoma Narrows Bridge called Galloping Gertie. This shows vibrations in the bridge increasing
Simple Harmonic Motion *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m54154 1 Simple Harmonic Motion * OpenStax HS Physics This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 : By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m54154 1 Simple Harmonic Motion * OpenStax HS Physics This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 : By the end of this section,
ConcepTest 11.1a Harmonic Motion I
 ConcepTest 11.1a Harmonic Motion I A mass on a spring in SHM has amplitude A and period T. What is the total distance traveled by the mass after a time interval T? 1) 0 2) A/2 3) A 4) 2A 5) 4A ConcepTest
ConcepTest 11.1a Harmonic Motion I A mass on a spring in SHM has amplitude A and period T. What is the total distance traveled by the mass after a time interval T? 1) 0 2) A/2 3) A 4) 2A 5) 4A ConcepTest
Lab 2: Equilibrium. Note: the Vector Review from the beginning of this book should be read and understood prior to coming to class!
 Lab 2: Equilibrium Note: This lab will be conducted over 2 weeks, with half the class working with forces while the other half works with torques the first week, and then switching the second week. Description
Lab 2: Equilibrium Note: This lab will be conducted over 2 weeks, with half the class working with forces while the other half works with torques the first week, and then switching the second week. Description
Ballistic Pendulum. Equipment- ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale PRECAUTION
 Ballistic Pendulum Equipment- ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale PRECAUTION In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally
Ballistic Pendulum Equipment- ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale PRECAUTION In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally
LAB 10: HARMONIC MOTION AND THE PENDULUM
 163 Name Date Partners LAB 10: HARMONIC MOION AND HE PENDULUM Galileo reportedly began his study of the pendulum in 1581 while watching this chandelier swing in Pisa, Italy OVERVIEW A body is said to be
163 Name Date Partners LAB 10: HARMONIC MOION AND HE PENDULUM Galileo reportedly began his study of the pendulum in 1581 while watching this chandelier swing in Pisa, Italy OVERVIEW A body is said to be
Gravitational Constant Brett Waite and Daniel Klinge
 Gravitational Constant Brett Waite and Daniel Klinge The universal gravitational constant was discovered by Henry Cavendish during the years of 1797-1798 His goal was to determine the density of the earth
Gravitational Constant Brett Waite and Daniel Klinge The universal gravitational constant was discovered by Henry Cavendish during the years of 1797-1798 His goal was to determine the density of the earth
Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Introduction to vibration
 Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Introduction to vibration Module 15 Lecture 38 Vibration of Rigid Bodies Part-1 Today,
Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Introduction to vibration Module 15 Lecture 38 Vibration of Rigid Bodies Part-1 Today,
KNIFE EDGE FLAT ROLLER
 EXPERIMENT N0. 1 To Determine jumping speed of cam Equipment: Cam Analysis Machine Aim: To determine jumping speed of Cam Formulae used: Upward inertial force = Wvω 2 /g Downward force = W + Ks For good
EXPERIMENT N0. 1 To Determine jumping speed of cam Equipment: Cam Analysis Machine Aim: To determine jumping speed of Cam Formulae used: Upward inertial force = Wvω 2 /g Downward force = W + Ks For good
LAB #8: SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 OBJECTIVES: LAB #8: SIPLE HARONIC OTION To study the motion of two systems that closely resembles simple harmonic motion. EQUIPENT: Equipment Needed Qty Equipment Needed Qty Balance 1 Table Clamp w/rod
OBJECTIVES: LAB #8: SIPLE HARONIC OTION To study the motion of two systems that closely resembles simple harmonic motion. EQUIPENT: Equipment Needed Qty Equipment Needed Qty Balance 1 Table Clamp w/rod
Introduction. Physics E-1a Expt 5: The Sweet Spot Fall 2006
 Physics E-1a Expt 5: The Sweet Spot all 2006 The center of percussion () is the place on a bat where it may be struck without causing a reaction at the point of support. When a ball is hit at the the contact
Physics E-1a Expt 5: The Sweet Spot all 2006 The center of percussion () is the place on a bat where it may be struck without causing a reaction at the point of support. When a ball is hit at the the contact
TG MANUAL. OPEN SOURCE TIMING SOFTWARE. Oscillo-Escape. The first devices of this sort appeared around Let's say they were electronic devices.
 TG MANUAL. OPEN SOURCE TIMING SOFTWARE. Oscillo-Escape The origin of the watch timing machine. We call a "timing machine" a device that allows, in its most basic function, to determine the performance
TG MANUAL. OPEN SOURCE TIMING SOFTWARE. Oscillo-Escape The origin of the watch timing machine. We call a "timing machine" a device that allows, in its most basic function, to determine the performance
Exercise Torque Magnitude Ranking Task. Part A
 Exercise 10.2 Calculate the net torque about point O for the two forces applied as in the figure. The rod and both forces are in the plane of the page. Take positive torques to be counterclockwise. τ 28.0
Exercise 10.2 Calculate the net torque about point O for the two forces applied as in the figure. The rod and both forces are in the plane of the page. Take positive torques to be counterclockwise. τ 28.0
MITOCW ocw-18_02-f07-lec02_220k
 MITOCW ocw-18_02-f07-lec02_220k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW ocw-18_02-f07-lec02_220k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
CBRD30CP3 & BOWRD30CP INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 CBRD30CP3 & BOWRD30CP INSTRUCTION MANUAL PROLOGUE Your BSA Illuminated sight is for use on both compound and standard bows. Each version of the BSA illuminated sight has a specific reticle to help maintain
CBRD30CP3 & BOWRD30CP INSTRUCTION MANUAL PROLOGUE Your BSA Illuminated sight is for use on both compound and standard bows. Each version of the BSA illuminated sight has a specific reticle to help maintain
Restoration of an English Eight-day longcase clock by Charles Robotham, Leicester. Circa 1790
 Restoration of an English Eight-day longcase clock by Charles Robotham, Leicester Circa 1790 Background This Report has been produced in order to summarise the work undertaken on the restoration of an
Restoration of an English Eight-day longcase clock by Charles Robotham, Leicester Circa 1790 Background This Report has been produced in order to summarise the work undertaken on the restoration of an
Lab 10: Harmonic Motion and the Pendulum
 Lab 10 Harmonic Motion and the Pendulum 119 Name Date Partners Lab 10: Harmonic Motion and the Pendulum OVERVIEW A body is said to be in a position of stable equilibrium if, after displacement in any direction,
Lab 10 Harmonic Motion and the Pendulum 119 Name Date Partners Lab 10: Harmonic Motion and the Pendulum OVERVIEW A body is said to be in a position of stable equilibrium if, after displacement in any direction,
Pendulum Activity! Frequency, Length, and Gravity. Materials
 Pendulum Activity! Frequency, Length, and Gravity A Pendulum is a weight (bob) that swings back and forth. Frequency is how many times something happens in a certain amount of time like how many times
Pendulum Activity! Frequency, Length, and Gravity A Pendulum is a weight (bob) that swings back and forth. Frequency is how many times something happens in a certain amount of time like how many times
8. What is the period of a pendulum consisting of a 6-kg object oscillating on a 4-m string?
 1. In the produce section of a supermarket, five pears are placed on a spring scale. The placement of the pears stretches the spring and causes the dial to move from zero to a reading of 2.0 kg. If the
1. In the produce section of a supermarket, five pears are placed on a spring scale. The placement of the pears stretches the spring and causes the dial to move from zero to a reading of 2.0 kg. If the
CHAPTER 6 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES 6.1 VIBRATIONS
 (b) To test hypothesis (i), try at least three different lengths of chains with the controls being the same amplitude, same child, and same effort put into the push. To test hypothesis (ii), try at least
(b) To test hypothesis (i), try at least three different lengths of chains with the controls being the same amplitude, same child, and same effort put into the push. To test hypothesis (ii), try at least
Force Table: Force Vector Components
 Physics Bridging Course 0885-398-01 Adding Vectors By Components Topic: Adding Vectors By Components Preparation: GR&R: Read Chapter 2 WebAssign: To followup this workshop, do Week 2: Force and Equilibrium
Physics Bridging Course 0885-398-01 Adding Vectors By Components Topic: Adding Vectors By Components Preparation: GR&R: Read Chapter 2 WebAssign: To followup this workshop, do Week 2: Force and Equilibrium
Coupled Oscillators. 1 Introduction. 2 Theory. PHY 300 Lab 2 Fall 2012
 Coupled Oscillators 1 Introduction In this experiment you are going to observe the normal modes of oscillation of several different mechanical systems, first on the air tracks and then using some coupled
Coupled Oscillators 1 Introduction In this experiment you are going to observe the normal modes of oscillation of several different mechanical systems, first on the air tracks and then using some coupled
Design and Development of Hand Water Pump with a Pendulum
 Volume-5, Issue-6, December-2015 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 357-361 Design and Development of Hand Water Pump with a Pendulum D. Apparao¹, Y. Sagar² 1,2 Department
Volume-5, Issue-6, December-2015 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 357-361 Design and Development of Hand Water Pump with a Pendulum D. Apparao¹, Y. Sagar² 1,2 Department
Harmonic Motion: Exercises
 Harmonic Motion: Exercises 1. The following is a list of forces, each of which is the net external force acting on an object with mass number m that is free to move in onedimension only. Assume that s
Harmonic Motion: Exercises 1. The following is a list of forces, each of which is the net external force acting on an object with mass number m that is free to move in onedimension only. Assume that s
1 The diagram shows an object of weight W and an object of weight Z balanced on a uniform metre rule. object of weight W. object of weight Z
 1 The diagram shows an object of weight W and an object of weight Z balanced on a uniform metre rule. object of weight W a b 50 cm mark object of weight Z metre rule Which equation relating to W, Z, a
1 The diagram shows an object of weight W and an object of weight Z balanced on a uniform metre rule. object of weight W a b 50 cm mark object of weight Z metre rule Which equation relating to W, Z, a
When: Before the Planetarium visits your school. Type of activity: Observation, visualization, discovery
 CLASSROOM ACTIVITY Sundials General information Grade level: Elementary cycle three Students per group: Individual activity When: Before the Planetarium visits your school Duration: One to two 50-minute
CLASSROOM ACTIVITY Sundials General information Grade level: Elementary cycle three Students per group: Individual activity When: Before the Planetarium visits your school Duration: One to two 50-minute
ConcepTest 14.6a Period of a Spring I
 ConcepTest 14.6a Period of a Spring I A glider with a spring attached to each end oscillates with a certain period. If the mass of the glider is doubled, what will happen to the period? 1) period will
ConcepTest 14.6a Period of a Spring I A glider with a spring attached to each end oscillates with a certain period. If the mass of the glider is doubled, what will happen to the period? 1) period will
PhET Pendulum Lab. l g. f 1. Part I: Pendulum Basics
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS PhET Pendulum Lab Introduction: Old grandfather clocks have large pendulums that swing back and forth to keep time. A Foucault pendulum
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS PhET Pendulum Lab Introduction: Old grandfather clocks have large pendulums that swing back and forth to keep time. A Foucault pendulum
Test, Lesson 7 Waves - Answer Key Page 1
 Test, Lesson 7 Waves - Answer Key Page 1 1. Match the proper units with the following: W. wavelength 1. nm F. frequency 2. /sec V. velocity 3. m 4. ms -1 5. Hz 6. m/sec (A) W: 1, 3 F: 2, 4, 5 V: 6 (B)
Test, Lesson 7 Waves - Answer Key Page 1 1. Match the proper units with the following: W. wavelength 1. nm F. frequency 2. /sec V. velocity 3. m 4. ms -1 5. Hz 6. m/sec (A) W: 1, 3 F: 2, 4, 5 V: 6 (B)
Lab: Simple Harmonic Motion: Pendulum Mr. Fineman
 Lab Partners: Lab: Simple Harmonic Motion: Pendulum Mr. Fineman Objective: Students will determine the factors that affect the period of a pendulum, and explain how their experimental results differ to
Lab Partners: Lab: Simple Harmonic Motion: Pendulum Mr. Fineman Objective: Students will determine the factors that affect the period of a pendulum, and explain how their experimental results differ to
1. [30] Y&F a) Assuming a small angle displacement θ max < 0.1 rad, the period is very nearly
![1. [30] Y&F a) Assuming a small angle displacement θ max < 0.1 rad, the period is very nearly 1. [30] Y&F a) Assuming a small angle displacement θ max < 0.1 rad, the period is very nearly](/thumbs/84/89548463.jpg) PH1140 D09 Homework 3 Solution 1. [30] Y&F 13.48. a) Assuming a small angle displacement θ max < 0.1 rad, the period is very nearly T = π L =.84 s. g b) For the displacement θ max = 30 = 0.54 rad we use
PH1140 D09 Homework 3 Solution 1. [30] Y&F 13.48. a) Assuming a small angle displacement θ max < 0.1 rad, the period is very nearly T = π L =.84 s. g b) For the displacement θ max = 30 = 0.54 rad we use
Larry Triplett has sent excellent photos and some descriptive details of a
 by Snowden Taylor, research committee Contributors to the Research Committee may send information directly to Snowden Taylor via USPS: Snowden Taylor, 318 Western Highway Tappan, NY 10983, or e-mail to
by Snowden Taylor, research committee Contributors to the Research Committee may send information directly to Snowden Taylor via USPS: Snowden Taylor, 318 Western Highway Tappan, NY 10983, or e-mail to
LEP Coupled pendula
 1.3.5 Related topics Spiral spring, gravity pendulum, spring constant, torsional vibration, torque, beat, angular velocity, angular acceleration, characteristic frequency. Principle and task Two equal
1.3.5 Related topics Spiral spring, gravity pendulum, spring constant, torsional vibration, torque, beat, angular velocity, angular acceleration, characteristic frequency. Principle and task Two equal
Name: AP Homework 9.1. Simple Harmonic Motion. Date: Class Period:
 AP Homework 9.1 Simple Harmonic Motion (1) If an object on a horizontal, frictionless surface is attached to a spring, displaced, and then released, it will oscillate. If it is displaced 0.120 m from its
AP Homework 9.1 Simple Harmonic Motion (1) If an object on a horizontal, frictionless surface is attached to a spring, displaced, and then released, it will oscillate. If it is displaced 0.120 m from its
Lab 1: Damped, Driven Harmonic Oscillator
 1 Introduction Lab 1: Damped, Driven Harmonic Oscillator The purpose of this experiment is to study the resonant properties of a driven, damped harmonic oscillator. This type of motion is characteristic
1 Introduction Lab 1: Damped, Driven Harmonic Oscillator The purpose of this experiment is to study the resonant properties of a driven, damped harmonic oscillator. This type of motion is characteristic
The student will be able to: 1 Determine the torque of an applied force and solve related problems.
 Honors Physics Assignment Rotational Mechanics Reading Chapters 10 and 11 Objectives/HW The student will be able to: HW: 1 Determine the torque of an applied force and solve related problems. (t = rx r
Honors Physics Assignment Rotational Mechanics Reading Chapters 10 and 11 Objectives/HW The student will be able to: HW: 1 Determine the torque of an applied force and solve related problems. (t = rx r
Chapter 15 Periodic Motion
 Chapter 15 Periodic Motion Slide 1-1 Chapter 15 Periodic Motion Concepts Slide 1-2 Section 15.1: Periodic motion and energy Section Goals You will learn to Define the concepts of periodic motion, vibration,
Chapter 15 Periodic Motion Slide 1-1 Chapter 15 Periodic Motion Concepts Slide 1-2 Section 15.1: Periodic motion and energy Section Goals You will learn to Define the concepts of periodic motion, vibration,
Brown University Physics 0030 Physics Department Lab 5
 Oscillatory Motion Experiment 1: Oscillations of a spring As described in the text, a system of a simple spring exhibits simple harmonic motion and is a good introduction to a study of oscillations, which
Oscillatory Motion Experiment 1: Oscillations of a spring As described in the text, a system of a simple spring exhibits simple harmonic motion and is a good introduction to a study of oscillations, which
Tic, Toc: Pendulum Motion
 Tic, Toc: Pendulum Motion Activity 25 Pendulum motion has long fascinated people. Galileo studied pendulum motion by watching a swinging chandelier and timing it with his pulse. In 1851 Jean Foucault demonstrated
Tic, Toc: Pendulum Motion Activity 25 Pendulum motion has long fascinated people. Galileo studied pendulum motion by watching a swinging chandelier and timing it with his pulse. In 1851 Jean Foucault demonstrated
Chapter 9: Circular Motion
 Text: Chapter 9 Think and Explain: 1-5, 7-9, 11 Think and Solve: --- Chapter 9: Circular Motion NAME: Vocabulary: rotation, revolution, axis, centripetal, centrifugal, tangential speed, Hertz, rpm, rotational
Text: Chapter 9 Think and Explain: 1-5, 7-9, 11 Think and Solve: --- Chapter 9: Circular Motion NAME: Vocabulary: rotation, revolution, axis, centripetal, centrifugal, tangential speed, Hertz, rpm, rotational
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. When a spring is compressed 10 cm, compared to its
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. When a spring is compressed 10 cm, compared to its
2008 FXA THREE FORCES IN EQUILIBRIUM 1. Candidates should be able to : TRIANGLE OF FORCES RULE
 THREE ORCES IN EQUILIBRIUM 1 Candidates should be able to : TRIANGLE O ORCES RULE Draw and use a triangle of forces to represent the equilibrium of three forces acting at a point in an object. State that
THREE ORCES IN EQUILIBRIUM 1 Candidates should be able to : TRIANGLE O ORCES RULE Draw and use a triangle of forces to represent the equilibrium of three forces acting at a point in an object. State that
Lab 1: damped, driven harmonic oscillator
 Lab 1: damped, driven harmonic oscillator 1 Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to study the resonant properties of a driven, damped harmonic oscillator. This type of motion is characteristic
Lab 1: damped, driven harmonic oscillator 1 Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to study the resonant properties of a driven, damped harmonic oscillator. This type of motion is characteristic
Conservation of Energy Lab Packet
 Conservation of Energy Lab Packet Unit # 3 Main Topic: Pendulum Duration: 10 days NAME: Contents/Page Number Day 2 (2/1/16): The Pendulum Lab Day 1 (2/2/16): The Physics of Pendulum Day 3 (2/3/16): The
Conservation of Energy Lab Packet Unit # 3 Main Topic: Pendulum Duration: 10 days NAME: Contents/Page Number Day 2 (2/1/16): The Pendulum Lab Day 1 (2/2/16): The Physics of Pendulum Day 3 (2/3/16): The
Cabrillo College Physics 10L. LAB 8 Magnetism. Read Hewitt Chapter 24
 Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 8 Magnetism Read Hewitt Chapter 24 What to learn and explore Magnetic forces are very closely related to electric forces--for example, they share the property that
Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 8 Magnetism Read Hewitt Chapter 24 What to learn and explore Magnetic forces are very closely related to electric forces--for example, they share the property that
Lever Lab: First Class Lever
 Lever Lab 2 Name: Lever Lab: First Class Lever Objective: To investigate the use of a lever as a simple machine. Materials: Workshop Stand, Lever, Bolt, Hooked Masses Background: A lever is one of the
Lever Lab 2 Name: Lever Lab: First Class Lever Objective: To investigate the use of a lever as a simple machine. Materials: Workshop Stand, Lever, Bolt, Hooked Masses Background: A lever is one of the
STATIC EQUILIBRIUM. Purpose
 Purpose Theory STATIC EQUILIBRIUM a. To understand torque by experimentally measuring and manipulating them. b. To determine static equilibrium conditions by different torques that operate on a system.
Purpose Theory STATIC EQUILIBRIUM a. To understand torque by experimentally measuring and manipulating them. b. To determine static equilibrium conditions by different torques that operate on a system.
Forces. Name and Surname: Class: L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S. What is a force? How are forces measured? What do forces do?
 F O R C E S P A G E 1 L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S Forces What is a force? Y E A R 9, C H A P T E R 2 G J Z A H R A B. E D ( H O N S ) How are forces measured? What do forces do? Why do we need to think
F O R C E S P A G E 1 L E A R N I N G O U T C O M E S Forces What is a force? Y E A R 9, C H A P T E R 2 G J Z A H R A B. E D ( H O N S ) How are forces measured? What do forces do? Why do we need to think
Part A Pendulum Worksheet (Period and Energy):
 Pendulum Lab Name: 4 th Grade PSI Part A Pendulum Worksheet (Period and Energy): The weight at the end of the rod is called the pendulum bob. Pull one of the bobs back and hold it. What type of energy
Pendulum Lab Name: 4 th Grade PSI Part A Pendulum Worksheet (Period and Energy): The weight at the end of the rod is called the pendulum bob. Pull one of the bobs back and hold it. What type of energy
SIMPLE PENDULUM AND PROPERTIES OF SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 SIMPE PENDUUM AND PROPERTIES OF SIMPE HARMONIC MOTION Purpose a. To investigate the dependence of time period of a simple pendulum on the length of the pendulum and the acceleration of gravity. b. To study
SIMPE PENDUUM AND PROPERTIES OF SIMPE HARMONIC MOTION Purpose a. To investigate the dependence of time period of a simple pendulum on the length of the pendulum and the acceleration of gravity. b. To study
HB Coupled Pendulums Lab Coupled Pendulums
 HB 04-19-00 Coupled Pendulums Lab 1 1 Coupled Pendulums Equipment Rotary Motion sensors mounted on a horizontal rod, vertical rods to hold horizontal rod, bench clamps to hold the vertical rods, rod clamps
HB 04-19-00 Coupled Pendulums Lab 1 1 Coupled Pendulums Equipment Rotary Motion sensors mounted on a horizontal rod, vertical rods to hold horizontal rod, bench clamps to hold the vertical rods, rod clamps
Finding a Relationship
 - Regression Modelling - A Historic Note Next to the famous leaning tower of Pisa is the beautiful Santa Maria Assunta Duomo or cathedral. The famous tower is the bell tower of the Duomo. It is said that
- Regression Modelling - A Historic Note Next to the famous leaning tower of Pisa is the beautiful Santa Maria Assunta Duomo or cathedral. The famous tower is the bell tower of the Duomo. It is said that
Winding the mainspring, adjusting the hand, day/date is done by the below procedure. day adjustment hand adjustment date adjustment
 method Winding the mainspring, adjusting the hand, day/date is done by the below procedure. day adjustment hand adjustment date adjustment (1) Winding the mainspring Automatic winding watch can also be
method Winding the mainspring, adjusting the hand, day/date is done by the below procedure. day adjustment hand adjustment date adjustment (1) Winding the mainspring Automatic winding watch can also be
LAW WOODEN CLOCK 1 GENERAL ASSEMBLY SHT 1 OF 10 SHTS. Designed by: BRLAW
 Woodenclocks Clock1 The drawings on the following pages contain plans to build the wooden clock shown above. For further information and more detailed rendered images visit SHT 1 OF 10 SHTS GENERAL ASSEMBLY
Woodenclocks Clock1 The drawings on the following pages contain plans to build the wooden clock shown above. For further information and more detailed rendered images visit SHT 1 OF 10 SHTS GENERAL ASSEMBLY
A-level Physics (7407/7408)
 A-level Physics (7407/7408) Further Mechanics Test Name: Class: Date: September 2016 Time: 55 Marks: 47 Page 1 Q1.The diagram shows a strobe photograph of a mark on a trolley X, moving from right to left,
A-level Physics (7407/7408) Further Mechanics Test Name: Class: Date: September 2016 Time: 55 Marks: 47 Page 1 Q1.The diagram shows a strobe photograph of a mark on a trolley X, moving from right to left,
Mechanics. Determining the gravitational constant with the gravitation torsion balance after Cavendish. LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets P
 Mechanics Measuring methods Determining the gravitational constant LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets P1.1.3.1 Determining the gravitational constant with the gravitation torsion balance after Cavendish Measuring
Mechanics Measuring methods Determining the gravitational constant LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets P1.1.3.1 Determining the gravitational constant with the gravitation torsion balance after Cavendish Measuring
Use the following equation to calculate the moment of child B about the pivot of the see-saw. moment of a force = force distance
 Q1.Two children, A and B, are sitting on a see-saw, as shown in the figure below. The see-saw is balanced. (a) Use the following equation to calculate the moment of child B about the pivot of the see-saw.
Q1.Two children, A and B, are sitting on a see-saw, as shown in the figure below. The see-saw is balanced. (a) Use the following equation to calculate the moment of child B about the pivot of the see-saw.
product manual H-3220A Benkelman Beam
 05.12 product manual H-3220A Benkelman Beam General The H-3220A Benkelman Beam Apparatus is a convenient and accurate device used for measuring the deflection of flexible pavements under moving wheel
05.12 product manual H-3220A Benkelman Beam General The H-3220A Benkelman Beam Apparatus is a convenient and accurate device used for measuring the deflection of flexible pavements under moving wheel
Episode 304: Simple pendulum
 Episode 304: Simple pendulum This episode reinforces many of the fundamental ideas about SHM. Note a complication: a simple pendulum shows SHM only for small amplitude oscillations. Summary Student experiment:
Episode 304: Simple pendulum This episode reinforces many of the fundamental ideas about SHM. Note a complication: a simple pendulum shows SHM only for small amplitude oscillations. Summary Student experiment:
NowGeen. Ridley Shetler, Sarah Martin and Chad Dorais. Engineering 151 s final project is to create a functioning Rube-Goldberg device that will
 EF 151 Project 1 NowGeen Ridley Shetler, Sarah Martin and Chad Dorais Engineering 151 s final project is to create a functioning Rube-Goldberg device that will stamp anywhere on an eight by five sheet
EF 151 Project 1 NowGeen Ridley Shetler, Sarah Martin and Chad Dorais Engineering 151 s final project is to create a functioning Rube-Goldberg device that will stamp anywhere on an eight by five sheet
AP/Honors Lab 18.1 Coulomb s Law
 Name School Date AP/Honors Lab 18.1 Coulomb s Law Purpose To observe the effect of the electrostatic force on light-weight charged objects. To experimentally determine the charge on a sphere small sphere
Name School Date AP/Honors Lab 18.1 Coulomb s Law Purpose To observe the effect of the electrostatic force on light-weight charged objects. To experimentally determine the charge on a sphere small sphere
Figure 5.16 Compound pendulum: (a) At rest in equilibrium, (b) General position with coordinate θ, Freebody
 Lecture 27. THE COMPOUND PENDULUM Figure 5.16 Compound pendulum: (a) At rest in equilibrium, (b) General position with coordinate θ, Freebody diagram The term compound is used to distinguish the present
Lecture 27. THE COMPOUND PENDULUM Figure 5.16 Compound pendulum: (a) At rest in equilibrium, (b) General position with coordinate θ, Freebody diagram The term compound is used to distinguish the present
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
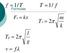 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
