CHAPTER 6 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES 6.1 VIBRATIONS
|
|
|
- Clyde Mitchell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (b) To test hypothesis (i), try at least three different lengths of chains with the controls being the same amplitude, same child, and same effort put into the push. To test hypothesis (ii), try at least three different amplitudes with the same length of swing, same child, and same effort put into the push. To test hypothesis (iii), try pushing at least three different children of different masses with the controls being the same length, same amplitude and the same push. For testing (iv), try different pushes (gentle, medium, and hard) with the controls being the same length, the same amplitude, and the same child. 9. Graph A is the correct graph because as the temperature increases, the speed of sound increases. Making Connections 0. Answers will vary. An example could be a guitar with an amplifier to improve the sound.. Acoustics are the qualities of an auditorium that determine how well sound is heard. An auditorium with good acoustics will cause the sound to reflect off surfaces to ensure that everyone in the auditorium will hear the sound. An important acoustics property of an auditorium is its reverberation time (the time required for the sound intensity to drop to its original value).. Look for answers that involve feeling or seeing the vibrations that produce sound waves. CHAPTER 6 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES Try This Activity: Wave Action (Page 95) This experiment is a good way to demonstrate some examples of waves. Students will note how the particles in a wave move. 6. VIBRATIONS PRACTICE (Page 98) Understanding Concepts. (a) The tree undergoes transverse vibrations. (b) The needle undergoes longitudinal vibrations.. (a) T 5 s 5 cycles T 0. (b) T 5 cycles T 4.0 s (c) T cycles T.4 0 s 3 Unit 3 Waves and Sound Copyright 00 Nelson Thomson Learning
2 3. f T 80 s f 80 Hz 4. f 0 cycles 5 s f 0.80 Hz 5. f cycles f Hz 6. (a) f 88 cycles 0.0 s f Hz 3600 cycles (b) f f 60 Hz 5 s T or T f 0 cycles T. s 0.80 Hz T. s T 400 Hz T s (c) f cycles f 75 Hz 7. T 63.8 d 6 cycles T 7.30 d 8. As you walk, the movement of your right leg is in phase with your left arm and out of phase with your right arm. Investigation 6.. The Pendulum (Pages 99 0) Purpose The purpose of this investigation is to determine the factor(s) that influence the frequency of a swing of a pendulum. Question What are the relationships between the frequency of a simple pendulum and its mass, amplitude, and length? Hypothesis/Prediction (a) It is expected that the frequency of a pendulum is determined solely by its length. Watching people on playground swings, it would appear that a person s mass does not influence the rate at which the apparatus swings back and forth. The amplitude also does not seem to play a role. As a person allows the swing to come to rest with the amplitude gradually decreasing, the frequency does not appear to change. Design A simple pendulum was constructed and allowed to swing, measuring the frequency in each trial. While two of the factors (mass, amplitude, and length) are controlled, the third was varied to determine its influence, if any, on the frequency. Once the factor was identified, a quantitative analysis of its influence was sought. Copyright 00 Nelson Thomson Learning Chapter 6 Vibrations and Waves 33
3 Materials utility stand clamp test-tube clamp split rubber stopper string stopwatch metre stick metal masses (50 g, 00 g, 00 g) Procedure. A pendulum was constructed using a string with a mass suspended from its end. The other end of the string was secured in a split rubber stopper held in place on a retort stand with a test-tube clamp.. The pendulum was adjusted in each trial so that its length was the distance from the point where the string passes through the rubber stopper to the middle of the suspended metal mass. 3. In the first set of trials the pendulum s length was set at cm using a 00.0-g mass. The mass was pulled to the side, keeping the string tight, to an amplitude of cm and then released. The time for the pendulum to complete 0 full cycles was measured. This was repeated two more times and the average value of the three attempts was recorded in Table. 4. Step 3 was repeated using an amplitude of 0.0 cm and again with an amplitude of 30.0 cm. 5. In a second set of trials, the pendulum s length remained at cm and the amplitude at cm. The mass was varied, suspending masses of 50.0 g, g, and 00.0 g in turn, each time measuring and recording the average the time taken for 0 full cycles. The results were recorded in Table. 6. In a third set of trials, the pendulum s mass remained constant at g and the amplitude at cm. The length varied using values of cm, 80.0 cm, 60.0 cm, cm, and 0.0 cm. The average time in each case was recorded in Table. Observations In each trial the pendulum was seen to swing back and forth at a constant rate. The time to complete 0 full cycles was measured three times for every set of values of mass, amplitude, and length. The average of these times was recorded in Table. When these times are divided by 0, the period of the pendulum s swing was found. Its frequency (also recorded) was calculated using the expression f. Using the first measurements in Table as an example: T average time for 0 full cycles: 39.5 s period of swing: T 3.95 s.98 s 0 frequency of swing: f T Hz.98 s It was noted that in the first two sets of trials the pendulum s frequency did not appear to vary with either changing amplitude or changing mass. In the third set of trials where the mass and amplitude were fixed and the pendulum s length was allowed to vary, there was a noticeable difference in its frequency at various lengths. The pendulum appeared to swing with a smaller period (greater frequency), as it became increasingly shorter. Table Factors Affecting the Frequency of a Pendulum Length (cm) Mass (g) Amplitude (cm) Average Time for 0 Full Cycles (s) Frequency (Hz) Analysis (b) Graphs of Frequency Amplitude, (Figure ); Frequency Mass, (Figure ); and Frequency Length, (Figure 3) are plotted on the next page. 34 Unit 3 Waves and Sound Copyright 00 Nelson Thomson Learning
4 (i) Figure Frequency and Amplitude (ii) Figure Frequency and Mass (iii) Figure 3 Frequency and Length (c) The results indicate that the factor that determines the frequency of a pendulum is its length. The mass and amplitude did not play a role. The frequency decreased as the length increased. (d) The periods of the pendula in the third set of trials were determined and recorded in Table. The period was calculated in each case using T. For example, in the first set of results for the trials where length was the variable: f f Hz T f Hz T.00 s Table Period and Length of Pendula, Constant Mass and Amplitude Length (cm) Period (s) Copyright 00 Nelson Thomson Learning Chapter 6 Vibrations and Waves 35
5 The results of Table are plotted in Figure 4. Figure 4 Period and Length The nature of the relationship between period and length is illustrated by the shape of Figure 4. As the length of the pendulum increases, the period of its swing increases. Table 3 is a summary of period and the square root of the pendulum s length. Table 3 Period and Square Root of Length Period (s) Square root of length ( cm ) The data in Table 3 are plotted in Figure 5. Figure 5 Period and Square Root of Length It is apparent from this graph that the period of a pendulum s swing is directly proportional to the square root of its length. Evaluation (e) The predictions made in the hypothesis were correct. The only factor determining the frequency of a pendulum is its length. From the mathematical analysis, it can be concluded that the frequency of a pendulum is inversely proportional to the square root of its length. (f) There were a number of experimental errors associated with this investigation. The largest source of error involved obtaining accurate values for the time. The observer had to use best judgement when deciding when the pendulum had reached the end of its swing. Hand-eye coordination also played a role when starting the stopwatch at the beginning of the swing. The retort stand was seen to sway slightly from side to side as the pendulum swung back and forth. This may have had an effect on the results, perhaps resulting in times that were slightly greater than theoretical values. The pendulum did not always make uniform swings over the 0 full cycles. In some cases the plane of the pendulum s swing slowly rotated about the top of the pendulum. It is expected that this would have a negligible effect on the pendulum s frequency. 36 Unit 3 Waves and Sound Copyright 00 Nelson Thomson Learning
6 To improve the experimental design, a more rigid support stand could be used. Improvements to timing could be made by starting the pendulum swinging and then begin timing when the pendulum reaches its highest point on some subsequent swing rather than beginning when the pendulum is first released. Synthesis (g) A pendulum that is cm long has a mass of g suspended from its end. It is pulled to the side, giving it an amplitude of 50.0 cm. As the pendulum is displaced sideways, it becomes raised vertically giving it some gravitational potential energy. Upon its release, the gravitational potential energy it had gained is converted into kinetic energy as it swings downward. Its speed at the bottom of the swing can be calculated as follows. Using Pythagorus: x (( cm) (50.0 cm) ) x 86.6 cm h cm 86.6 cm h 3.4 cm (0.34 m) Gain in gravitational potential energy when pendulum is raised: m g (0.000 kg) E g mgh g 9.8 N/kg kg(9.8 N/kg)(0.34 m) h 0.34 m E g 0.3 J Gain in kinetic energy when pendulum swings through the lowest point: E K 0.3 J m kg E ke 0.3 J v E k m 0.3 J kg v.6 m/s The speed of the pendulum at its lowest point is.6 m/s. Section 6. Questions (Pages 0 0) Understanding Concepts. (a) transverse vibration (b) transverse vibration (c) longitudinal vibration. (a) The pendulum undergoes transverse vibrations. (b) The amplitude of vibration is 8.5 cm. (c) In one cycle, the mass moves 7 cm 34 cm. In five cycles, the mass moves a total distance of 5 34 cm 70 cm (assuming the amplitude remains constant). 3. (a) f T 800 pictures f 30 Hz 800 pictures T s Copyright 00 Nelson Thomson Learning Chapter 6 Vibrations and Waves 37
7 800 beats 0.0 s (b) f T 0.0 s 800 beats f 90 Hz T. 0 s 460 cycles (c) f T 460 cycles f 7.7 Hz T 0.3 s 640 cycles f T 640 cycles f 0.7 Hz or Hz T s 60 cycles (d) f T 60 cycles f Hz T s (e) f 60 cycles 3600 s T 3600 s 60 cycles f.7 0 Hz T 4. (a) This is a longitudinal vibration. (b) The amplitude of vibration is 3.5 cm. (c) In one cycle, the mass moves cm 4 cm. In 3.5 cycles, the mass moves cm 49 cm (assuming the amplitude remains constant). 5. (a) The period and frequency are reciprocals of each other. They are inversely related f. T (b) As the length increases, the period of the pendulum increases. The period of a pendulum is directly proportional to the square root of its length. (c) The mass and frequency of a pendulum are independent of each other; there is no relationship between mass and frequency. 6. Moving the mass closer to the pivot point to shorten the length of the pendulum can increase the frequency. This could be demonstrated using a metronome. 7. If the force of gravity is lower, the period will be higher and the frequency will be lower Tα and g ( fα g); the clock will run slower. To increase the frequency of the pendulum to compensate, the weight would have to be moved up, which decreases the effective length of the pendulum and increases the frequency. 8. The balance wheel of a mechanical clock is a tensional pendulum (See Figure (c), section 6., page 96). The pendulum rotates back and froth with energy supplied by a spring mechanism. 9. (a) On the Moon, the gravitational force is lower than on Earth, so the period is higher Tα g. (b) On Jupiter, the gravitational force is higher than on Earth, so the period is lower. l 0. T π g 4π l g T 4 π (.00 m) (.00 s) g 9.86 m/s. butterfly stroke: in-phase arm motion backstroke: out-of-phase arm motion breaststroke: in-phase arm motion freestyle: out-of-phase arm motion 38 Unit 3 Waves and Sound Copyright 00 Nelson Thomson Learning
8 Applying Inquiry Skills. One method for determining the length of a swing without measuring it would be to measure the time for one cycle (T). Use the pendulum equation to solve for length (l). T π T l 4π l g g 6. WAVE MOTION Investigation 6.. Wave Transmission: Pulses on a Coiled Spring (Pages 03 05) Purpose The purpose of this investigation was to study pulses travelling along springs/ropes and their characteristics and then apply these characteristics to waves in order to understand their behaviours. Question (i) How do pulses move along a coiled spring? (ii) How are pulses reflected from a fixed-end and a free-end? Hypothesis/Prediction (i) Pulses travel along a coiled spring through the motion of the individual coils which move back and forth as the pulse travels past a certain point. (ii) Since the pulses are travelling along a material object, it is expected that some energy should be lost along the path due to friction. As such, the amplitude of the reflected pulse will likely be smaller than the amplitude of the original pulse, but the amplitude itself will not likely affect the speed of the pulse. (iii) In step 8, as the tension of the spring is increased (i.e. the spring is stretched further), the speed of the pulses will increase since the spring is tighter. Design In this investigation, a coiled spring was stretched across the floor and subjected to various conditions (length of stretch, pulse amplitude, pulse phase, condition of end) as pulses were generated by the motion of a student s hand. The motion of the coils and behaviour of the pulses sent (speed, amplitude, phase) was observed. The following variables and controls applied in the various cases (note that part (d) was completed only if various spring types were available): Case Independent Variable Dependent Variable Controls (a) type of end (fixed or free) reflected pulse phase incident pulse phase, amplitude, spring tension (b) incident pulse amplitude speed of pulse spring tension, pulse phase, type of end (c) spring tension speed of pulse pulse amplitude, pulse phase, type of end (d) spring type speed of pulse spring tension, amplitude, pulse phase, end type Materials coiled spring (Slinky toy) piece of paper various spring types (if available) masking tape stopwatch metre stick 4.0-m string Copyright 00 Nelson Thomson Learning Chapter 6 Vibrations and Waves 39
Student Worksheet for Activity The Pendulum. Question. Materials
 Student Worksheet for Activity 6.1.1 The Pendulum Questioning Hypothesizing Predicting Planning Conducting INQUIRY SKILLS Recording Analyzing Evaluating Communicating A pendulum swings with a regular period,
Student Worksheet for Activity 6.1.1 The Pendulum Questioning Hypothesizing Predicting Planning Conducting INQUIRY SKILLS Recording Analyzing Evaluating Communicating A pendulum swings with a regular period,
Vibrations 8.1. Amplitude, Period, Frequency, and Phase of Vibrations. 338 MHR Unit 4 Waves
 8.1 Vibrations SECTION Describe and explain amplitude, frequency, and phase of vibration. nalyze and experiment with the components of, and conditions required for, resonance to occur in a vibrating object.
8.1 Vibrations SECTION Describe and explain amplitude, frequency, and phase of vibration. nalyze and experiment with the components of, and conditions required for, resonance to occur in a vibrating object.
Practice Test SHM with Answers
 Practice Test SHM with Answers MPC 1) If we double the frequency of a system undergoing simple harmonic motion, which of the following statements about that system are true? (There could be more than one
Practice Test SHM with Answers MPC 1) If we double the frequency of a system undergoing simple harmonic motion, which of the following statements about that system are true? (There could be more than one
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
Chapter 13, Vibrations and Waves. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to compress it only m. What is the spring constant of the spring?
 CHAPTER 13 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to compress it only 0.010 m. What is the spring constant of the spring? a. 125 000 N/m b. 15 000 N/m c. 15 N/m d. 1.5 N/m 2. A 0.20-kg object is attached
CHAPTER 13 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to compress it only 0.010 m. What is the spring constant of the spring? a. 125 000 N/m b. 15 000 N/m c. 15 N/m d. 1.5 N/m 2. A 0.20-kg object is attached
1. a) A flag waving in the breeze flaps once each s. What is the period and frequency of the flapping flag?
 PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
Virbations and Waves
 Virbations and Waves 1.1 Observe and find a pattern Try the following simple experiments and describe common patterns concerning the behavior of the block. (a) Fill in the table that follows. Experiment
Virbations and Waves 1.1 Observe and find a pattern Try the following simple experiments and describe common patterns concerning the behavior of the block. (a) Fill in the table that follows. Experiment
PhET Pendulum Lab. l g. f 1. Part I: Pendulum Basics
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS PhET Pendulum Lab Introduction: Old grandfather clocks have large pendulums that swing back and forth to keep time. A Foucault pendulum
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS PhET Pendulum Lab Introduction: Old grandfather clocks have large pendulums that swing back and forth to keep time. A Foucault pendulum
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
9.1 Harmonic Motion. Motion in cycles. linear motion - motion that goes from one place to another without repeating.
 9.1 Harmonic Motion A bicyclist pedaling past you on the street moves in linear motion. Linear motion gets us from one place to another (Figure 9.1A). This chapter is about another kind of motion called
9.1 Harmonic Motion A bicyclist pedaling past you on the street moves in linear motion. Linear motion gets us from one place to another (Figure 9.1A). This chapter is about another kind of motion called
PHYSICS 1 Simple Harmonic Motion
 Advanced Placement PHYSICS 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Student 014-015 What I Absolutely Have to Know to Survive the AP* Exam Whenever the acceleration of an object is proportional to its displacement and
Advanced Placement PHYSICS 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Student 014-015 What I Absolutely Have to Know to Survive the AP* Exam Whenever the acceleration of an object is proportional to its displacement and
ConcepTest 14.6a Period of a Spring I
 ConcepTest 14.6a Period of a Spring I A glider with a spring attached to each end oscillates with a certain period. If the mass of the glider is doubled, what will happen to the period? 1) period will
ConcepTest 14.6a Period of a Spring I A glider with a spring attached to each end oscillates with a certain period. If the mass of the glider is doubled, what will happen to the period? 1) period will
Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes
 Physics 1 Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes Date 1. Define work. 2. Define energy. 3. Determine the work done by a constant force. Period 4. Determine the work done by a
Physics 1 Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes Date 1. Define work. 2. Define energy. 3. Determine the work done by a constant force. Period 4. Determine the work done by a
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
 CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz. FINAL EXAM December 10, :00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS
 Seat # Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz FINAL EXAM December 10, 2001 8:00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS 1. Sit in SEAT # given above. 2. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. 3. Print your name (last
Seat # Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz FINAL EXAM December 10, 2001 8:00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS 1. Sit in SEAT # given above. 2. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. 3. Print your name (last
AP Physics 1 Multiple Choice Questions - Chapter 9
 1 If an object of mass m attached to a light spring is replaced by one of mass 9m, the frequency of the vibrating system changes by what multiplicative factor? a 1/9 b 1/3 c 3 d 9 e 6 2 A mass of 0.40
1 If an object of mass m attached to a light spring is replaced by one of mass 9m, the frequency of the vibrating system changes by what multiplicative factor? a 1/9 b 1/3 c 3 d 9 e 6 2 A mass of 0.40
EXAM 1. WAVES, OPTICS AND MODERN PHYSICS 15% of the final mark
 EXAM 1 WAVES, OPTICS AND MODERN PHYSICS 15% of the final mark Autumn 2018 Name: Each multiple-choice question is worth 3 marks. 1. A light beam is deflected by two mirrors, as shown. The incident beam
EXAM 1 WAVES, OPTICS AND MODERN PHYSICS 15% of the final mark Autumn 2018 Name: Each multiple-choice question is worth 3 marks. 1. A light beam is deflected by two mirrors, as shown. The incident beam
AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound 1. 1977-5 (Mechanical Waves/Sound) Two loudspeakers, S 1 and S 2 a distance d apart as shown in the diagram below left, vibrate in
AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound 1. 1977-5 (Mechanical Waves/Sound) Two loudspeakers, S 1 and S 2 a distance d apart as shown in the diagram below left, vibrate in
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984
 Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Chapter 13. Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition. Next Week!
 Chapter 13 Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition Next Week! Review Physics 2A: Springs, Pendula & Circular Motion Elastic Systems F = kx Small Vibrations
Chapter 13 Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition Next Week! Review Physics 2A: Springs, Pendula & Circular Motion Elastic Systems F = kx Small Vibrations
CHAPTER 11 TEST REVIEW
 AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
CHAPTER 7: OSCILLATORY MOTION REQUIRES A SET OF CONDITIONS
 CHAPTER 7: OSCILLATORY MOTION REQUIRES A SET OF CONDITIONS 7.1 Period and Frequency Anything that vibrates or repeats its motion regularly is said to have oscillatory motion (sometimes called harmonic
CHAPTER 7: OSCILLATORY MOTION REQUIRES A SET OF CONDITIONS 7.1 Period and Frequency Anything that vibrates or repeats its motion regularly is said to have oscillatory motion (sometimes called harmonic
m k F = "kx T = 2# L T = 2# Notes on Ch. 11 Equations: F = "kx The force (F, measured in Newtons) produced by a spring is equal to the L g T = 2#
 Name: Physics Chapter 11 Study Guide ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Useful Information: F = "kx T = 2# L T = 2# m v = f$ PE g k e
Name: Physics Chapter 11 Study Guide ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Useful Information: F = "kx T = 2# L T = 2# m v = f$ PE g k e
LECTURE 3 ENERGY AND PENDULUM MOTION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 3 ENERGY AND PENDULUM MOTION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 3 2 14.4: Energy in simple harmonic motion Finding the frequency for simple harmonic motion 14.5: Pendulum motion Physical pendulum
LECTURE 3 ENERGY AND PENDULUM MOTION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 3 2 14.4: Energy in simple harmonic motion Finding the frequency for simple harmonic motion 14.5: Pendulum motion Physical pendulum
Question 13.1a Harmonic Motion I
 Question 13.1a Harmonic Motion I A mass on a spring in SHM has a) 0 amplitude A and period T. What b) A/2 is the total distance traveled by c) A the mass after a time interval T? d) 2A e) 4A Question 13.1a
Question 13.1a Harmonic Motion I A mass on a spring in SHM has a) 0 amplitude A and period T. What b) A/2 is the total distance traveled by c) A the mass after a time interval T? d) 2A e) 4A Question 13.1a
RELEASED. Go to next page. 2. The graph shows the acceleration of a car over time.
 1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
Investigation 3.1.1: Analyzing Uniform Circular Motion
 Student Worksheet Investigation 3.1.1: Analyzing Uniform Circular Motion LSM 3.1-1 Questioning Hypothesizing Predicting Planning Conducting I N Q U I R Y S K I L L S Recording Analyzing Evaluating Communicating
Student Worksheet Investigation 3.1.1: Analyzing Uniform Circular Motion LSM 3.1-1 Questioning Hypothesizing Predicting Planning Conducting I N Q U I R Y S K I L L S Recording Analyzing Evaluating Communicating
14.4 Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion 14.5 Pendulum Motion.notebook January 25, 2018
 The interplay between kinetic and potential energy is very important for understanding simple harmonic motion. Section 14.4 Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion For a mass on a spring, when the object is at
The interplay between kinetic and potential energy is very important for understanding simple harmonic motion. Section 14.4 Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion For a mass on a spring, when the object is at
AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to
Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to
Chapter 14: Periodic motion
 Chapter 14: Periodic motion Describing oscillations Simple harmonic motion Energy of simple harmonic motion Applications of simple harmonic motion Simple pendulum & physical pendulum Damped oscillations
Chapter 14: Periodic motion Describing oscillations Simple harmonic motion Energy of simple harmonic motion Applications of simple harmonic motion Simple pendulum & physical pendulum Damped oscillations
Oscillations. PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER. Simple harmonic motion Mass-spring system Energy in SHM Pendulums
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 15 Oscillations Simple harmonic motion Mass-spring system Energy in SHM Pendulums 1. The displacement of a particle oscillating along the x axis is given as a function
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 15 Oscillations Simple harmonic motion Mass-spring system Energy in SHM Pendulums 1. The displacement of a particle oscillating along the x axis is given as a function
Lab 12: Periodic Motion
 Lab 12: Periodic Motion Objectives: To devise an experiment to test variables that might affect the period of a pendulum To carry out an experiment testing variables that might affect the period of a pendulum,
Lab 12: Periodic Motion Objectives: To devise an experiment to test variables that might affect the period of a pendulum To carry out an experiment testing variables that might affect the period of a pendulum,
AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations 1975B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is drawn aside through
AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations 1975B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is drawn aside through
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form D
 Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form D Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form D Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form B
 Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form B Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form B Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form A
 Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form A Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form A Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form C
 Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form C Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Midterm Test Form C Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron. Keep questions/cheat
GCSE PHYSICS. Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a scientific calculator the Physics Equations Sheet (enclosed).
 Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE PHYSICS Foundation Tier Paper 2F F Specimen 2018 (set 2) Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE PHYSICS Foundation Tier Paper 2F F Specimen 2018 (set 2) Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
Harmonic Motion: The Pendulum Lab Advanced Version
 Harmonic Motion: The Pendulum Lab Advanced Version In this lab you will set up a pendulum using rulers, string, and small weights and measure how different variables affect the period of the pendulum.
Harmonic Motion: The Pendulum Lab Advanced Version In this lab you will set up a pendulum using rulers, string, and small weights and measure how different variables affect the period of the pendulum.
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves. The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position.
 Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
2016 AP Physics Unit 6 Oscillations and Waves.notebook December 09, 2016
 AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems
 Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
4 A mass-spring oscillating system undergoes SHM with a period T. What is the period of the system if the amplitude is doubled?
 Slide 1 / 52 1 A block with a mass M is attached to a spring with a spring constant k. The block undergoes SHM. Where is the block located when its velocity is a maximum in magnitude? A 0 B + or - A C
Slide 1 / 52 1 A block with a mass M is attached to a spring with a spring constant k. The block undergoes SHM. Where is the block located when its velocity is a maximum in magnitude? A 0 B + or - A C
A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion
 1. Simple harmonic motion and the greenhouse effect (a) A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion. 1. 2. (b) In a simple model
1. Simple harmonic motion and the greenhouse effect (a) A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion. 1. 2. (b) In a simple model
Chapter 9: Circular Motion
 Text: Chapter 9 Think and Explain: 1-5, 7-9, 11 Think and Solve: --- Chapter 9: Circular Motion NAME: Vocabulary: rotation, revolution, axis, centripetal, centrifugal, tangential speed, Hertz, rpm, rotational
Text: Chapter 9 Think and Explain: 1-5, 7-9, 11 Think and Solve: --- Chapter 9: Circular Motion NAME: Vocabulary: rotation, revolution, axis, centripetal, centrifugal, tangential speed, Hertz, rpm, rotational
5. A car moves with a constant speed in a clockwise direction around a circular path of radius r, as represented in the diagram above.
 1. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is 20. Newtons. If the mass of each object were doubled, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the objects would be A) 5.0 N B)
1. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is 20. Newtons. If the mass of each object were doubled, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the objects would be A) 5.0 N B)
The children have already done several experiments with gravity from Functional
 1. Purpose of Experiments with Gravity The children have already done several experiments with gravity from Functional Geography and learned about its importance in the formation of the universe. This
1. Purpose of Experiments with Gravity The children have already done several experiments with gravity from Functional Geography and learned about its importance in the formation of the universe. This
Contents. Lehman College Department of Physics and Astronomy. Lab manual for PHY 141 Sound, speech and music 1 PENDULUM EXPERIMENT 3
 Lehman College Department of Physics and Astronomy Lab manual for PHY 141 Sound, speech and music Contents 1 PENDULUM EXPERIMENT 3 2 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION 9 3 STANDING WAVES ON STRINGS 15 4 STANDING WAVES
Lehman College Department of Physics and Astronomy Lab manual for PHY 141 Sound, speech and music Contents 1 PENDULUM EXPERIMENT 3 2 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION 9 3 STANDING WAVES ON STRINGS 15 4 STANDING WAVES
Chapter 14 Preview Looking Ahead
 Chapter 14 Preview Looking Ahead Text: p. 438 Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Preview Looking Back: Springs and Restoring Forces In Chapter 8, you learned that a stretched spring exerts a restoring force proportional
Chapter 14 Preview Looking Ahead Text: p. 438 Slide 14-1 Chapter 14 Preview Looking Back: Springs and Restoring Forces In Chapter 8, you learned that a stretched spring exerts a restoring force proportional
How do the physical aspects of the oscillators affect the Period?
 LAST NAME FIRST NAME DATE 10.4 The Pendulum & Spring Mass Oscillator Conceptual Questions 10, 11, 12, 13 page 314 Problems 40 page 317 How do the physical aspects of the oscillators affect the Period?
LAST NAME FIRST NAME DATE 10.4 The Pendulum & Spring Mass Oscillator Conceptual Questions 10, 11, 12, 13 page 314 Problems 40 page 317 How do the physical aspects of the oscillators affect the Period?
Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1
 Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1 Name Multiple Choice Questions 1. A block with a mass M is attached to a spring with a spring constant k. The block undergoes SHM. Where is the
Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1 Name Multiple Choice Questions 1. A block with a mass M is attached to a spring with a spring constant k. The block undergoes SHM. Where is the
Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that.
 Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that. NAME: 4. Units of power include which of the following?
Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that. NAME: 4. Units of power include which of the following?
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test
 AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
Episode 304: Simple pendulum
 Episode 304: Simple pendulum This episode reinforces many of the fundamental ideas about SHM. Note a complication: a simple pendulum shows SHM only for small amplitude oscillations. Summary Student experiment:
Episode 304: Simple pendulum This episode reinforces many of the fundamental ideas about SHM. Note a complication: a simple pendulum shows SHM only for small amplitude oscillations. Summary Student experiment:
Second Semester Review
 Second Semester Review Name Section 4.2 1. Define energy What is energy? Explain if it is scalar or vector in nature. 2. Explain what factors affect the speed of a rollercoaster. Whether a rollercoaster
Second Semester Review Name Section 4.2 1. Define energy What is energy? Explain if it is scalar or vector in nature. 2. Explain what factors affect the speed of a rollercoaster. Whether a rollercoaster
Unit 7: Oscillations
 Text: Chapter 15 Unit 7: Oscillations NAME: Problems (p. 405-412) #1: 1, 7, 13, 17, 24, 26, 28, 32, 35 (simple harmonic motion, springs) #2: 45, 46, 49, 51, 75 (pendulums) Vocabulary: simple harmonic motion,
Text: Chapter 15 Unit 7: Oscillations NAME: Problems (p. 405-412) #1: 1, 7, 13, 17, 24, 26, 28, 32, 35 (simple harmonic motion, springs) #2: 45, 46, 49, 51, 75 (pendulums) Vocabulary: simple harmonic motion,
SPRING 2004 Final Exam, Part A
 Physics 151 SPRING 2004 Final Exam, Part A Roster No.: Score: 23 pts. possible Exam time limit: 120 minutes. You may use calculators and both sides of 2 pages of notes, handwritten only. Closed book; no
Physics 151 SPRING 2004 Final Exam, Part A Roster No.: Score: 23 pts. possible Exam time limit: 120 minutes. You may use calculators and both sides of 2 pages of notes, handwritten only. Closed book; no
ConcepTest 11.1a Harmonic Motion I
 ConcepTest 11.1a Harmonic Motion I A mass on a spring in SHM has amplitude A and period T. What is the total distance traveled by the mass after a time interval T? 1) 0 2) A/2 3) A 4) 2A 5) 4A ConcepTest
ConcepTest 11.1a Harmonic Motion I A mass on a spring in SHM has amplitude A and period T. What is the total distance traveled by the mass after a time interval T? 1) 0 2) A/2 3) A 4) 2A 5) 4A ConcepTest
Chapter 12 Vibrations and Waves Simple Harmonic Motion page
 Chapter 2 Vibrations and Waves 2- Simple Harmonic Motion page 438-45 Hooke s Law Periodic motion the object has a repeated motion that follows the same path, the object swings to and fro. Examples: a pendulum
Chapter 2 Vibrations and Waves 2- Simple Harmonic Motion page 438-45 Hooke s Law Periodic motion the object has a repeated motion that follows the same path, the object swings to and fro. Examples: a pendulum
Experimenting with Forces
 A mother hears a loud crash in the living room. She walks into the room to see her seven-year-old son looking at a broken vase on the floor. How did that happen? she asks. I don t know. The vase just fell
A mother hears a loud crash in the living room. She walks into the room to see her seven-year-old son looking at a broken vase on the floor. How did that happen? she asks. I don t know. The vase just fell
Waves Final Review. Name: Date: 1. On which one of the following graphs is the wavelength λ and the amplitude a of a wave correctly represented?
 Name: Date: Waves Final Review 1. On which one of the following graphs is the wavelength λ and the amplitude a of a wave correctly represented? A. Displacement λ a Distance along wave B. Displacement λ
Name: Date: Waves Final Review 1. On which one of the following graphs is the wavelength λ and the amplitude a of a wave correctly represented? A. Displacement λ a Distance along wave B. Displacement λ
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. When a spring is compressed 10 cm, compared to its
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. When a spring is compressed 10 cm, compared to its
The maximum kinetic energy is directly proportional to the frequency. The time for one oscillation is directly proportional to the frequency.
 Q1.For a body performing simple harmonic motion, which one of the following statements is correct? The maximum kinetic energy is directly proportional to the frequency. The time for one oscillation is
Q1.For a body performing simple harmonic motion, which one of the following statements is correct? The maximum kinetic energy is directly proportional to the frequency. The time for one oscillation is
Name. VCE Physics Unit 3 Preparation Work
 Name. VCE Physics Unit 3 Preparation Work Transition into 2019 VCE Physics Unit 3+4 Units 3 and 4 include four core areas of study plus one detailed study. Unit 3: How do fields explain motion and electricity?
Name. VCE Physics Unit 3 Preparation Work Transition into 2019 VCE Physics Unit 3+4 Units 3 and 4 include four core areas of study plus one detailed study. Unit 3: How do fields explain motion and electricity?
G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam
 G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Exam Instructions The final exam will be weighted as follows: Modules 1 6 15 20% Modules
G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Exam Instructions The final exam will be weighted as follows: Modules 1 6 15 20% Modules
Measuring Simple Harmonic Motion
 SECTION 2 Plan and Prepare Preview Vocabulary Scientific Meanings Explain that everyday words have more specialized meanings in science. Ask students the meaning of frequency. They are likely to use the
SECTION 2 Plan and Prepare Preview Vocabulary Scientific Meanings Explain that everyday words have more specialized meanings in science. Ask students the meaning of frequency. They are likely to use the
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Healy/DiMurro. Vibrations 2016
 Name Vibrations 2016 Healy/DiMurro 1. In the diagram below, an ideal pendulum released from point A swings freely through point B. 4. As the pendulum swings freely from A to B as shown in the diagram to
Name Vibrations 2016 Healy/DiMurro 1. In the diagram below, an ideal pendulum released from point A swings freely through point B. 4. As the pendulum swings freely from A to B as shown in the diagram to
LAB 6 - GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES
 83 Name Date Partners LAB 6 - GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW And thus Nature will be very conformable to herself and very simple, performing all the great Motions of the heavenly
83 Name Date Partners LAB 6 - GRAVITATIONAL AND PASSIVE FORCES OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW And thus Nature will be very conformable to herself and very simple, performing all the great Motions of the heavenly
Conservation of Mechanical Energy
 Core Skill Lab Conservation of Mechanical Energy A mass on a spring will oscillate vertically when it is lifted to the length of the relaxed spring and released. The gravitational potential energy increases
Core Skill Lab Conservation of Mechanical Energy A mass on a spring will oscillate vertically when it is lifted to the length of the relaxed spring and released. The gravitational potential energy increases
Part I Multiple Choice (4 points. ea.)
 ach xam usually consists of 10 ultiple choice questions which are conceptual in nature. They are often based upon the assigned thought questions from the homework. There are also 4 problems in each exam,
ach xam usually consists of 10 ultiple choice questions which are conceptual in nature. They are often based upon the assigned thought questions from the homework. There are also 4 problems in each exam,
Standing waves [49 marks]
![Standing waves [49 marks] Standing waves [49 marks]](/thumbs/92/110837906.jpg) Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
SOUND. Representative Sample Physics: Sound. 1. Periodic Motion of Particles PLANCESS CONCEPTS
 Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
THE CONSERVATION OF ENERGY - PENDULUM -
 THE CONSERVATION OF ENERGY - PENDULUM - Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to measure the potential energy and the kinetic energy of a mechanical system and to quantitatively compare the two
THE CONSERVATION OF ENERGY - PENDULUM - Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to measure the potential energy and the kinetic energy of a mechanical system and to quantitatively compare the two
Test Booklet. Subject: SC, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics. Student name:
 Test ooklet Subject: S, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics Student name: uthor: North arolina istrict: North arolina Released Tests Printed: Monday July 09, 2012 1 n object is launched across a room.
Test ooklet Subject: S, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics Student name: uthor: North arolina istrict: North arolina Released Tests Printed: Monday July 09, 2012 1 n object is launched across a room.
Simple Harmonic Motion: A Special Periodic Motion
 Simple Harmonic Motion: A Special Periodic Motion Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The oscillations of a system in which the net force can be described by Hooke s law are of special importance, because they are very
Simple Harmonic Motion: A Special Periodic Motion Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The oscillations of a system in which the net force can be described by Hooke s law are of special importance, because they are very
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Conservation of Energy Lab Packet
 Conservation of Energy Lab Packet Unit # 3 Main Topic: Pendulum Duration: 10 days NAME: Contents/Page Number Day 2 (2/1/16): The Pendulum Lab Day 1 (2/2/16): The Physics of Pendulum Day 3 (2/3/16): The
Conservation of Energy Lab Packet Unit # 3 Main Topic: Pendulum Duration: 10 days NAME: Contents/Page Number Day 2 (2/1/16): The Pendulum Lab Day 1 (2/2/16): The Physics of Pendulum Day 3 (2/3/16): The
https://njctl.org/courses/science/ap-physics-c-mechanics/attachments/summerassignment-3/
 AP Physics C Summer Assignment 2017 1. Complete the problem set that is online, entitled, AP C Physics C Summer Assignment 2017. I also gave you a copy of the problem set. You may work in groups as a matter
AP Physics C Summer Assignment 2017 1. Complete the problem set that is online, entitled, AP C Physics C Summer Assignment 2017. I also gave you a copy of the problem set. You may work in groups as a matter
s_3x03 Page 1 Physics Samples
 Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
Physics 1C. Lecture 12C
 Physics 1C Lecture 12C Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of simple harmonic motion. Making a quick force diagram of the situation, we find:! The tension in the string cancels out with
Physics 1C Lecture 12C Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of simple harmonic motion. Making a quick force diagram of the situation, we find:! The tension in the string cancels out with
LABORATORY IV OSCILLATIONS
 LABORATORY IV OSCILLATIONS You are familiar with many objects that oscillate -- a tuning fork, a pendulum, the strings of a guitar, or the beating of a heart. At the microscopic level, you have probably
LABORATORY IV OSCILLATIONS You are familiar with many objects that oscillate -- a tuning fork, a pendulum, the strings of a guitar, or the beating of a heart. At the microscopic level, you have probably
AP PHYSICS 1. Energy 2016 EDITION
 AP PHYSICS 1 Energy 2016 EDITION Copyright 2016 National Math + Initiative, Dallas, Texas. All rights reserved. Visit us online at www.nms.org. 1 Pre-Assessment Questions Consider a system which could
AP PHYSICS 1 Energy 2016 EDITION Copyright 2016 National Math + Initiative, Dallas, Texas. All rights reserved. Visit us online at www.nms.org. 1 Pre-Assessment Questions Consider a system which could
Ballistic Pendulum. Caution
 Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the ball,
Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the ball,
Simple Harmonic Motion *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m54154 1 Simple Harmonic Motion * OpenStax HS Physics This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 : By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m54154 1 Simple Harmonic Motion * OpenStax HS Physics This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 : By the end of this section,
Oscillations. The Force. The Motion
 Team Oscillations Oscillatory motion is motion that repeats itself. Oscillations are everywhere: guitar string, pendulum, piston, neutron star (pulsar), drumhead, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), alternating
Team Oscillations Oscillatory motion is motion that repeats itself. Oscillations are everywhere: guitar string, pendulum, piston, neutron star (pulsar), drumhead, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), alternating
FIGURE P13.5 FIGURE P13.6. Chapter 13 Problems
 Chapter 13 Problems 1, 2, 3 = straightforward, intermediate, challenging Section 13.1 Hooke s Law 5. The springs 1 and 2 in Figure P13.5 have spring constants of 40.0 N/cm and 25.0 N/cm, respectively.
Chapter 13 Problems 1, 2, 3 = straightforward, intermediate, challenging Section 13.1 Hooke s Law 5. The springs 1 and 2 in Figure P13.5 have spring constants of 40.0 N/cm and 25.0 N/cm, respectively.
Thursday March 30 Topics for this Lecture: Simple Harmonic Motion Kinetic & Potential Energy Pendulum systems Resonances & Damping.
 Thursday March 30 Topics for this Lecture: Simple Harmonic Motion Kinetic & Potential Energy Pendulum systems Resonances & Damping Assignment 11 due Friday Pre-class due 15min before class Help Room: Here,
Thursday March 30 Topics for this Lecture: Simple Harmonic Motion Kinetic & Potential Energy Pendulum systems Resonances & Damping Assignment 11 due Friday Pre-class due 15min before class Help Room: Here,
PHYSICS 1. Section I 40 Questions Time 90 minutes. g = 10 m s in all problems.
 Note: To simplify calculations, you may use PHYSICS 1 Section I 40 Questions Time 90 minutes 2 g = 10 m s in all problems. Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by
Note: To simplify calculations, you may use PHYSICS 1 Section I 40 Questions Time 90 minutes 2 g = 10 m s in all problems. Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
Lab 10: Harmonic Motion and the Pendulum
 Lab 10 Harmonic Motion and the Pendulum 119 Name Date Partners Lab 10: Harmonic Motion and the Pendulum OVERVIEW A body is said to be in a position of stable equilibrium if, after displacement in any direction,
Lab 10 Harmonic Motion and the Pendulum 119 Name Date Partners Lab 10: Harmonic Motion and the Pendulum OVERVIEW A body is said to be in a position of stable equilibrium if, after displacement in any direction,
PHYSICS I1 EXAM 3 FALL 2005
 PHYSCS 1 EXAM 3 FALL 2005 37. A 0.02 kg mass is attached to a massless spring as shown to the right and vibrates with simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 5.0 cm. The spring constant is 300 Nlm.
PHYSCS 1 EXAM 3 FALL 2005 37. A 0.02 kg mass is attached to a massless spring as shown to the right and vibrates with simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 5.0 cm. The spring constant is 300 Nlm.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 4.8-kg block attached to a spring executes simple harmonic motion on a frictionless
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 4.8-kg block attached to a spring executes simple harmonic motion on a frictionless
Simple Harmonic Motion Test Tuesday 11/7
 Simple Harmonic Motion Test Tuesday 11/7 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 1 If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is
Simple Harmonic Motion Test Tuesday 11/7 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 1 If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is
Test, Lesson 7 Waves - Answer Key Page 1
 Test, Lesson 7 Waves - Answer Key Page 1 1. Match the proper units with the following: W. wavelength 1. nm F. frequency 2. /sec V. velocity 3. m 4. ms -1 5. Hz 6. m/sec (A) W: 1, 3 F: 2, 4, 5 V: 6 (B)
Test, Lesson 7 Waves - Answer Key Page 1 1. Match the proper units with the following: W. wavelength 1. nm F. frequency 2. /sec V. velocity 3. m 4. ms -1 5. Hz 6. m/sec (A) W: 1, 3 F: 2, 4, 5 V: 6 (B)
8. What is the period of a pendulum consisting of a 6-kg object oscillating on a 4-m string?
 1. In the produce section of a supermarket, five pears are placed on a spring scale. The placement of the pears stretches the spring and causes the dial to move from zero to a reading of 2.0 kg. If the
1. In the produce section of a supermarket, five pears are placed on a spring scale. The placement of the pears stretches the spring and causes the dial to move from zero to a reading of 2.0 kg. If the
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
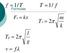 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
