Spin Acquisition, Violent Disks, Compaction and Quenching
|
|
|
- Blaise Stafford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spin Acquisition, Violent Disks, Compaction and Quenching Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem July 2014 stars 5 kpc
2 Three Provocative Questions concerning high-z massive galaxy formation 1. How do galaxies acquire AM? Gas ~ DM? 2. Do we understand violent disk instability? 3. How do galaxies compactify and quench? Hydro simulations cosmological - 25pc, isolated 1pc resolution - ART (Klypin, Kravtsov, Ceverino) - RAMSES (Teyssier, Bournaud+) Combined with toy modeling
3 1. Angular Momentum: from the cosmic web to disks & spheroids Pichon, Devriendt Pichon, Devriendt Stewart, Bullock+ 2011, 2013 Danovich, Dekel+ 2012, 2014
4 Massive halos at high-sigma nodes are fed by relatively thin dense filaments cold streams Typical halos reside in relatively thick filaments, fed from all directions the millenium cosmological simulation
5 Gas streams along the cosmic web AMR RAMSES Teyssier, AD box 300 kpc res 50 pc z = 5 to 2.5
6 Streams Feeding a Hi-z Galaxy Tweed, Dekel, Teyssier RAMSES Res. 50 pc
7 Co-planar ~3 Streams (in a pancake) influx M yr -1 rad R vir Danovich, Dekel, Teyssier, Hahn 12
8 Narrow dense gas streams at high z versus spherical infall at low z high z low z M=10 12 M ʘ >>M PS M=10 12 M ʘ ~M PS Ocvirk, Pichon, Teyssier 08
9 Cold Streams Penetrate through Hot Halos M v > M 100 kpc Agertz et al 09
10 AM Buildup by Cold Gas in 4 Phases III. inner halo extended tilted ring non-linear torques, dissipation AM loss λ cold 0.04 & alignment Danovich, Dekel, Hahn+ 14 II. outer halo AM transport, j~const. λ cold ~3λ dm ~0.1 DM mix V v I. cosmic web linear tidal torques impact parameter λ cold ~1.7λ dm ~ R v 2R v IV. inner disc (+ bulge) disk instability, outflows λ baryons ~0.03 spin parameter λ ~ J / M 2R V V V
11 TTT outside the halo: λ cold ~1.7λ DM due to quadrupole moment of inertia J tε i ijk T jl I lk R v ~100 kpc cold gas dark matter TTT is applied at max-expansion along the streams, after pre-collapse of gas to the filaments cords
12 AM of Cold Gas R v AM is represented by impact parameters <0.3R v Some counter-rotating In outer halo AM transport by straight streams Most of the AM is in one stream (determines the AM plane at R v ) Deep penetration of the streams
13 How do the streams join the disk? Ceverino, Dekel, Bournaud 2010 ART 35-70pc resolution streams disk 30 kpc interface region A messy interface region: breakup due to shocks, hydro and thermal instabilities, collisions between streams and clumps, heating
14 An Extended Tilted Ring about the Disk gas density 30 kpc stream lines expressway entrance
15 A tilted AM transport rotating ring the in outer the inner halo halo radial inflow AM loss circular orbits AM conserved spiral in alignment with disk color indicates mass in each cell impact parameter ~ const. AM not aligned with disk
16 AM Exchange in the Ring: Torques by Disk torques by an idealized disk Torques in the simulated galaxies
17 Extended Ring: HI Column Density Random lines of sight through ( )R v 30% DLAS HI 60% no HI n > 0.01 H cm -3
18 Detection of an Extended Ring? Bouche z=2.3 Low-Z gas 26 kpc from center V=180 km/s Crighton z=2.4, 54 kpc Steidel+ 2002, Kacprzak+ 2010
19 Outflows do not halt the Inflows DeGraf+ 14 Gas density Temperature Velocity dilute hot z=2.6 M v =7x Dense, cold, metal-poor inflows penetrate into the galaxy - Hot, metal-rich, fast outflows fly through the dilute CGM -300 M yr -1 rad -2 - outflows remove low-angular-momentum gas outflows help quenching SFR +50
20 AM Evolution in Disks Gas-rich -> violent disk instability (VDI) (Noguchi 99; Dekel+ 09) -> torques -> AM outflow and mass inflow (Gammie 01) -> massive spheroids (+BHs) with low AM (Genzel+ 08; Bournaud+11; Dekel+ 13) Stellar and AGN feedback -> outflows remove low-am gas from galaxy centers (Maller & Dekel 02; Governato+ 10; Guedes+ 11) λ gal < λ disk ~ 0.03 λ disk is only slightly smaller than λ DM -> naïve model is ~valid despite the different AM evolution
21 2. Violent Disk Instability Clumpy disk galaxies: Elmegreen+ UDF Genzel, Tacconi, Forster-Schreiber+ SINS Guo, Giavallisco+ 12, 14 CANDELS
22 Clumpy Disk Ceverino, Dekel et al. 10 kpc z=4-2.1
23 Violent Disk Instability (VDI) at High z High gas density disk unstable Q σω G Σ 1 Giant clumps and transient features GΣ R rapid evolution on dynamical time clump 2 Ω 5 kpc Toomre 64 Isolated galaxies: Noguchi 99 Immeli+ 04a,b Bournaud, Elmegreen+ 06, 08 Hopkins+ 12 Bournaud+ 13 In cosmology: Dekel, Sari, Ceverino 09 Agertz et al. 09 Ceverino, AD, Bournaud 10 Ceverino+ 11 Cacciato, AD, Genel 12a,b Genel+ 12 Forbes et al. 12, 13, 14 Self-regulated at Q~1 by torques and inflow high σ/v~1/5 Inflow in disk compact bulge and BH Steady state: disk draining and replenishment, bulge ~ disk
24 Violent Disk Instability (VDI) at High z Ceverino+ ART-AMR cosmological simulations at 25pc resolution highly perturbed, clumpy rotating disk: H/R ~ σ/v ~ f cold ~ 0.2
25 Violent Disk Instability (VDI) at High z Ceverino+ ART-AMR cosmological simulations at 25pc resolution H/R ~ σ/v ~ f cold ~ 0.2
26 z=4 Clumpy Disk in a cosmological steady state VDI is robust at z>1 because of high gas density (cosmological density and intense accretion). In some galaxies from z>7 to z<1. z=3 z=2 z=1.5 z=1 Σ gas [M pc -2 ] Dekel, Sari, Ceverino 09; Ceverino, Dekel, Bournaud 10 Mandelker et al. 14
27 Elmegreen et al Observations vs. Simulations
28 A typical star-forming galaxy at z=2: clumpy, rotating, extended disk & a bulge Hα star-forming regions color-code velocity field Genzel et al 08
29 BzK 6004 (2.4) BzK (2.4) BX 610 (2.2) BX482 (2.2) ZC (2.2) merger merger -160 BX389 (2.2) D3a 6397 (1.51) +50 K20-7 (2.2) BX663 (2.4) MD 41 (2.2) K20-9 (2.0) HDF 242 (2.49) ZC (1.41) BX528 (2.3) (8 kpc) -70 K20-8 (2.2) -170 K20-6 (2.2) K20-5 (2.2) GK2471 (2.43) D3a 4751 (2.27) SA (1.51) 150 HDF 169 (1.2) BX 405 (2.03) GK2252 (2.41) BX 599 (2.33) 100 BzK 4165 (1.7) SMMJ09431 (3.35) H7 H6 HDF 76 (2.20) SA (2.3) BX 502 (2.16) N (2.45) BM 1163 (1.41) GK 167 (2.58) SA (2.2) BX 404 (2.03) (Förster SMMJ Schreiber (3.41) et al. 2006, 2008) SMMJ (1.21) N (2.38) +200 GK 2113 (1.61) (8 kpc) The SINS survey of galaxy kinematics at z~
30 High-z Disks with Giant Clumps Guo et al. 12 CANDELS
31 Simulated hi-z galaxy through Dust SUNRISE low dust RGB colors MW3 z=2.33 Moody+ medium high
32 In-situ (VDI) and Ex-situ (merger) Clumps gas Poster by Nir Mandelker: clump properties, young survival stars under feedback, observable gradients of age/color 10 kpc dark matter stars
33 Clumps in VDI Disks - most hi-z galaxies go through a VDI phase - perturbed by intense inflows including minor mergers - bulge ~ disk in cosmological steady state - giant clumps M~ M R<0.5kpc - in-situ (gaseous, SFR) and ex-situ (stellar, mergers) - half the SFR in clumps - migration to center in ~300 Myr gas+ young stars - clumps >10 8 M survive outflows with mass~constant η~1-2 winds, gas accretion, tidal stripping - less massive clumps disrupt - VDI feed gas & stars to the bulge and BH Expect a weak gradient of clump mass in disks Certain gradient in age/color for in-situ clumps
34 Violent Instability with Q~2-3 Toomre Q Ωσ / Σ 1 Q=1-2 Q=2-5 Q=1-2 Q=5-10 Nonlinear instability - driven by intense inflows with minor mergers, or by the non-linear clumps themselves Compression modes of turbulence r r r σ = σ + σ = r φ + r irrotation solenoid A r
35 Compression Modes of Turbulence: Merger r r r σ = σ + σ = r φ+ r irrotational solenoidal A r Renaud+ 14
36 3. Compaction to Blue Nuggets Quenching to Red Nuggets Cheung+ 12; Fang+13; Barro+ 13,14a,b; Bruce+ 12,14; Williams+ 14; Nelson, van Dokkum+ 14 Dekel & Burkert 2014; Zolotov et al. 2014
37 Inflow in unstable disks Clump migration in ~300 Myr Massive clumps survive feedback Elmegreen, Bournaud+ 07, 08; Genzel+ 06, 08; Dekel, Sari, Ceverino 09; Bournaud+ 14; Dekel+ 14 Inflow in disk, evaluated by torques, dynamical friction, clump encounters, self-regulated instability t 2 inflow f cold t dyn 2 ( V σ) tdyn 10tdyn Gammie 01; Dekel, Sari, Ceverino 09 Wet compaction if 2 tinflow / tsfr εsfr fcold< 1 valid when gas fraction is high (high z) and spin is relatively low Dekel, Burkert 14 Bournaud, Dekel+ 13
38 Red Nuggets and Blue Nuggets Dekel & Burkert 2013; Zolotov et al Compact stellar spheroid dissipative wet inflow to a blue nugget by mergers and/or VDI Inflow is wet if t inflow << t sfr Self-regulated instability Q ~ 1 Wetness parameter M M cold M tot σ δ V tsfr 1 2 w ε sfrδ > 1 ε sfr 0.02 δ 0. 2 t inflow Expect VDI-driven nuggets: - at high z, where f gas is high - for low spin λ, where R gas is low
39 Wet Origin of Bulge: Stellar Birthplace Zolotov, Dekel, Mandelker, Tweed, Ceverino, Primack 2013 Fraction of bulge stars born in different components in bulge 60-30% of the bulge stars form in the bulge wet inflow Driven by wet VDI or wet mergers
40 Compaction and quenching Zolotov ART cosmological simulations, res. 25pc, with radiative fdbk SFR ~outflow ~recycling VDI + merger self-gravitating M stars >M dm wet inflow > SFR
41 Compaction and quenching stars self-gravitating M stars >M dm mergers DM merger gas no mergers VDI outflow inflow wet inflow > SFR SFR ~outflow ~recycling SFR
42 gas + young stars wet compaction max density: blue nugget vdi disk a hole and a ring vela v2 07
43 stars wet compaction max density: blue nugget green nugget red nugget vela v2 07
44 Stellar Component at z=2.3, edge-on Ceverino Overall Sersic n=2-4 Classical bulge n=3-5
45 Blue and Red Nuggets blue nugget Zolotov, AD+ 14 ssfr quenching SFR stars wet compaction z=3.7 central density SFR stars Observed at z~2-3: - compact passive ellipticals - their progenitors: compact star-forming galaxies z=1.2 red nugget
46 Observations: Blue Nuggets > Red Nuggets Barro+ 13 CANDELS z=1-3 Evolution: diffuse compaction quenching
47 Similar Structure for Blue & Red Nuggets Z=2 M * =10 11 M R e =1 kpc σ=300 km s -1 SFR=90 M yr -1 Nelson, vandokkum+ 2014
48 line width evolution in simulated galaxies quenching blue nugget red nugget extended disk compaction Inoue, Zolotov+ Barro+ 14
49 Blue Nuggets by Wet Inflow: Spin and ssfr Simulations confirm model predictions Dekel, Burkert 14; Zolotov+ 14 low-spin disk -> high Σ max 0.7 ssfr 0.5 high-ssfr disk -> high Σ max 0.3 Σ max
50 Two Modes of Evolution: Fast and Slow Barro, Fang, Yesuf, Woo, Faber, Koo, AD quenched ssfr star forming low z Halo quenching Slow: lower Σ gas disk secular inflow halo grows high z Bulge quenching stellar & AGN fdbk morph. quenching Fast: hi Σ gas disk wet VDI or merger inflow starburst diffuse compact Σ
51 critical halo mass ~10 12 M ʘ Virial Shock Heating Dekel & Birnboim t cool < t compress Kravtsov+ in hi-z massive hot halos cold streams penetrate slow cooling -> shock fast cooling > no shock
52 Cold Streams in Big Galaxies at High z M vir [M ʘ ] all hot cold filaments in hot medium M shock ~M * M shock >>M * M shock all cold M * redshift z Dekel & Birnboim 06
53 Two Quenching Mechanisms: Bulge & Halo Compact gaseous bulge -> gas removal by high SFR, outflow, AGN, Q-quenching quenched In halos > M -> long-term shutdown of gas supply by virial shock heating Woo, Dekel, Faber, Koo+ 14 star forming Need both bulge and halo quenching
54 Stream-Fed Galaxies at High z cold streams compact spheroid wet inflow to bulge quenching thick disk hot halo clumpy disk In parallel, mergers outflows clumpy disk VDI SFR spheroid late disk The main mode of galaxy formation hot halo
55 Conclusions High-z massive galaxies at cosmic-web nodes Fed by ~3 co-planar streams penetrating hot CGM Angular-momentum: - effective tidal torques on gas streams, AM transport to inner halo - spiral-in through an extended rotating tilted ring (DLAS?) - disk spin halo spin Typical SFGs have perturbed rotating disks at violent instability (VDI) - Massive clumps (>10 8 M ) survive feedback - off-center in-situ young clumps <300 Myr, showing age/gas gradient - older ex-situ clumps Nonlinear instability driven by inflow+mergers. Compressive turbulence? A characteristic sequence of events: - wet compaction by mergers and VDI into compact SFGs (blue nuggets) - high SFR+AGN, outflows, massive self-gravitating bulge fast quenching to compact ellipticals (red nuggets) +gas rings (?) - long-term quenching by hot massive halo
Three comments on High-z Galaxy Formation. Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
 Three comments on High-z Galaxy Formation Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem August 2014 Outline 1. Angular momentum: buildup in 4 phases 2. Violent disk instability: Nonlinear, Stimulated
Three comments on High-z Galaxy Formation Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem August 2014 Outline 1. Angular momentum: buildup in 4 phases 2. Violent disk instability: Nonlinear, Stimulated
Violent Disk Instability at z=1-4 Outflows; Clump Evolution; Compact Spheroids
 Violent Disk Instability at z=1-4 Outflows; Clump Evolution; Compact Spheroids Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Santa Cruz, August 2013 stars 5 kpc Outline 1. Inflows and Outflows 2. Evolution
Violent Disk Instability at z=1-4 Outflows; Clump Evolution; Compact Spheroids Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Santa Cruz, August 2013 stars 5 kpc Outline 1. Inflows and Outflows 2. Evolution
High-z Galaxy Evolution: VDI and (mostly minor) Mergers
 High-z Galaxy Evolution: VDI and (mostly minor) Mergers Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem UCSC, August 2012 Outline: in-situ (VDI) and ex-situ (mergers) 1. Cold streams: smooth and clumpy
High-z Galaxy Evolution: VDI and (mostly minor) Mergers Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem UCSC, August 2012 Outline: in-situ (VDI) and ex-situ (mergers) 1. Cold streams: smooth and clumpy
Nir Mandelker, H.U.J.I.
 Compressive vs Solenoidal Turbulence and Non-Linear VDI Nir Mandelker, H.U.J.I. IAU Symposium 319, August 11 2015 Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Shigeki Inoue, Daniel Ceverino, Frederic Bournaud, Joel Primack
Compressive vs Solenoidal Turbulence and Non-Linear VDI Nir Mandelker, H.U.J.I. IAU Symposium 319, August 11 2015 Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Shigeki Inoue, Daniel Ceverino, Frederic Bournaud, Joel Primack
The Magic Scale of Galaxy Formation: SNe & Hot CGM --> Compaction & BHs
 The Magic Scale of Galaxy Formation: SNe & Hot CGM --> Compaction & BHs Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Silk 75, December 2017 A Characteristic Mass for Galaxy Formation Efficiency
The Magic Scale of Galaxy Formation: SNe & Hot CGM --> Compaction & BHs Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Silk 75, December 2017 A Characteristic Mass for Galaxy Formation Efficiency
Violent Disk Instability Inflow to Spheroid and Black Hole
 Violent Disk Instability Inflow to Spheroid and Black Hole Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Jerusalem Winter School 101/13 Lecture stars 5 kpc Outline 1. Violent Disk Instability (VDI):
Violent Disk Instability Inflow to Spheroid and Black Hole Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Jerusalem Winter School 101/13 Lecture stars 5 kpc Outline 1. Violent Disk Instability (VDI):
Galaxy Evolution & Black-Hole Growth (review)
 Galaxy Evolution & Black-Hole Growth (review) Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Delivered by Fangzhou Jiang Dali, China, November 2018 See also Claude-Andre s talk and Joel s talk
Galaxy Evolution & Black-Hole Growth (review) Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Delivered by Fangzhou Jiang Dali, China, November 2018 See also Claude-Andre s talk and Joel s talk
Stream-Driven Galaxy Formation at High Redshift
 Stream-Driven Galaxy Formation at High Redshift Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem KooFest, Santa Cruz, August 2011 Outline 1. Streams in pancakes from the cosmic web (Hahn) 2. Is angular
Stream-Driven Galaxy Formation at High Redshift Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem KooFest, Santa Cruz, August 2011 Outline 1. Streams in pancakes from the cosmic web (Hahn) 2. Is angular
Feeding High-z Galaxies from the Cosmic Web
 Feeding High-z Galaxies from the Cosmic Web Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Jerusalem Winter School 2012/13 Lecture 1 z=0 z=2 z=8 Cosmological simulations Toy modeling Oxford Dictionary:
Feeding High-z Galaxies from the Cosmic Web Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Jerusalem Winter School 2012/13 Lecture 1 z=0 z=2 z=8 Cosmological simulations Toy modeling Oxford Dictionary:
Origin of Bi-modality
 Origin of Bi-modality and Downsizing Avishai Dekel HU Jerusalem Galaxies and Structures Through Cosmic Times Venice, March 2006 Summary Q: z
Origin of Bi-modality and Downsizing Avishai Dekel HU Jerusalem Galaxies and Structures Through Cosmic Times Venice, March 2006 Summary Q: z
Unstable Disks: Gas and Stars via an analytic model
 Unstable Disks: Gas and Stars via an analytic model Marcello Cacciato in collaboration with Avishai Dekel Minerva Fellow @ HUJI Theoretical studies and hydrodynamical cosmological simulations have shown
Unstable Disks: Gas and Stars via an analytic model Marcello Cacciato in collaboration with Avishai Dekel Minerva Fellow @ HUJI Theoretical studies and hydrodynamical cosmological simulations have shown
Yicheng Guo (UCO/Lick, UCSC)
 Formation and Evolution of Clumpy Galaxies at z=0.5--3 Yicheng Guo (UCO/Lick, UCSC) Collaborators: Henry Ferguson, Eric Bell, David Koo, Chris Conselice, Mauro Giavalisco, Nir Mandelker, Swara Ravindranatch,
Formation and Evolution of Clumpy Galaxies at z=0.5--3 Yicheng Guo (UCO/Lick, UCSC) Collaborators: Henry Ferguson, Eric Bell, David Koo, Chris Conselice, Mauro Giavalisco, Nir Mandelker, Swara Ravindranatch,
Cosmological simulations of galaxy formation. Romain Teyssier
 Cosmological simulations of galaxy formation 1 Outline Disc formation in LCDM cosmology Star formation efficiency and morphology connection The baryon fraction problem Star formation at high redshift:
Cosmological simulations of galaxy formation 1 Outline Disc formation in LCDM cosmology Star formation efficiency and morphology connection The baryon fraction problem Star formation at high redshift:
Connecting Galaxy Formation to the Cosmic Web
 Connecting Galaxy Formation to the Cosmic Web Andreas Burkert (University of Munich & MPE) Bigiel et al. Properties of the Hubble Sequence Halpha imaging surveys (galaxy assembly in the great wall) (Gavazzi+
Connecting Galaxy Formation to the Cosmic Web Andreas Burkert (University of Munich & MPE) Bigiel et al. Properties of the Hubble Sequence Halpha imaging surveys (galaxy assembly in the great wall) (Gavazzi+
Hydro ART simulations sample
 Hydro ART simulations sample Stellar Merger Trees Dylan Tweed dylan.tweed@googlemail.com Racah Institute of Physics, HUJI, Jerusalem CANDELS Theory Workshop - UCSC - August 8 th 10 th 2012 D. P. Tweed
Hydro ART simulations sample Stellar Merger Trees Dylan Tweed dylan.tweed@googlemail.com Racah Institute of Physics, HUJI, Jerusalem CANDELS Theory Workshop - UCSC - August 8 th 10 th 2012 D. P. Tweed
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Mar 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Mar 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 6 Mar 2015](/thumbs/79/79755642.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 30 (2002) Printed 9 March 2015 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Compaction and quenching of high- galaxies in cosmological simulations: blue and red nuggets arxiv:1412.4783v2
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 30 (2002) Printed 9 March 2015 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Compaction and quenching of high- galaxies in cosmological simulations: blue and red nuggets arxiv:1412.4783v2
Using Hydro-Simulations to Interpret Observed Kinematic Maps of Star-Forming Galaxies
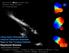 disk from the VELA simulation suite Ceverino, Dekel, Primack, + z = 1.6, young stars Using Hydro-Simulations to Interpret Observed Kinematic Maps of Star-Forming Galaxies Raymond Simons Johns Hopkins University
disk from the VELA simulation suite Ceverino, Dekel, Primack, + z = 1.6, young stars Using Hydro-Simulations to Interpret Observed Kinematic Maps of Star-Forming Galaxies Raymond Simons Johns Hopkins University
Secular Evolution of Galaxies
 Secular Evolution of Galaxies Outline:!Disk size evolution! Bar fraction vs mass & color! AM transfers, radial migrations! Bulges, thick disks Françoise Combes Durham, 19 July 2011 Two modes to assemble
Secular Evolution of Galaxies Outline:!Disk size evolution! Bar fraction vs mass & color! AM transfers, radial migrations! Bulges, thick disks Françoise Combes Durham, 19 July 2011 Two modes to assemble
Characterizing z~2 Galaxies in HYDRO-ART Simulations and Observations
 Characterizing z~2 Galaxies in HYDRO-ART Simulations and Observations Mark Mozena (UCSC) Sandra Faber, Avishai Dekel, Daniel Ceverino, Joel Primack, Kamson Lai, David Koo, David Rosario, Dale Kocevski,
Characterizing z~2 Galaxies in HYDRO-ART Simulations and Observations Mark Mozena (UCSC) Sandra Faber, Avishai Dekel, Daniel Ceverino, Joel Primack, Kamson Lai, David Koo, David Rosario, Dale Kocevski,
Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations and Sunrise Visualizations
 Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations and Sunrise Visualizations Joel Primack, UCSC Daniel Ceverino, HU Madrid Avishai Dekel, HU & UCSC Sandra Faber, UCSC Anatoly Klypin, NMSU Patrik Jonsson, Harvard CfA Chris
Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations and Sunrise Visualizations Joel Primack, UCSC Daniel Ceverino, HU Madrid Avishai Dekel, HU & UCSC Sandra Faber, UCSC Anatoly Klypin, NMSU Patrik Jonsson, Harvard CfA Chris
Origin and Evolution of Disk Galaxy Scaling Relations
 Origin and Evolution of Disk Galaxy Scaling Relations Aaron A. Dutton (CITA National Fellow, University of Victoria) Collaborators: Frank C. van den Bosch (Utah), Avishai Dekel (HU Jerusalem), + DEEP2
Origin and Evolution of Disk Galaxy Scaling Relations Aaron A. Dutton (CITA National Fellow, University of Victoria) Collaborators: Frank C. van den Bosch (Utah), Avishai Dekel (HU Jerusalem), + DEEP2
Rotational support of giant clumps in high-z disc galaxies
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 420, 3490 3520 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.20296.x Rotational support of giant clumps in high-z disc galaxies Daniel Ceverino, 1 Avishai Dekel, 1 Nir Mandelker, 1 Frederic
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 420, 3490 3520 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.20296.x Rotational support of giant clumps in high-z disc galaxies Daniel Ceverino, 1 Avishai Dekel, 1 Nir Mandelker, 1 Frederic
Elad Zinger Hebrew University Jerusalem Spineto, 12 June Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Yuval Birnboim, Daisuke Nagai & Andrey Kravtsov
 Elad Zinger Hebrew University Jerusalem IGM@50, Spineto, 12 June 2015 Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Yuval Birnboim, Daisuke Nagai & Andrey Kravtsov They re still there! Account for most of the accretion.
Elad Zinger Hebrew University Jerusalem IGM@50, Spineto, 12 June 2015 Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Yuval Birnboim, Daisuke Nagai & Andrey Kravtsov They re still there! Account for most of the accretion.
Galaxy Formation: Overview
 Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation
 Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: Example simulations Isolated galaxies, mergers & zooms Benjamin Moster 1 Outline of the lecture course Lecture 1: Motivation & Historical Overview Lecture
Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: Example simulations Isolated galaxies, mergers & zooms Benjamin Moster 1 Outline of the lecture course Lecture 1: Motivation & Historical Overview Lecture
Assembly of Galaxies Across Cosmic Time: Formaton of te Hubble Sequence at High Redshift
 Assembly of Galaxies Across Cosmic Time: Formaton of te Hubble Sequence at High Redshift Yicheng Guo University of Massachusetts Collaborator: Mauro Giavalisco (UMASS), Paolo Cassata (Marseille), Henry
Assembly of Galaxies Across Cosmic Time: Formaton of te Hubble Sequence at High Redshift Yicheng Guo University of Massachusetts Collaborator: Mauro Giavalisco (UMASS), Paolo Cassata (Marseille), Henry
Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem. Presented by: Michael Solway
 Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem Presented by: Michael Solway Papers 1. Vitvitska, M. et al. 2002, The origin of angular momentum in dark matter halos, ApJ 581: 799-809 2. D Onghia, E. 2008,
Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem Presented by: Michael Solway Papers 1. Vitvitska, M. et al. 2002, The origin of angular momentum in dark matter halos, ApJ 581: 799-809 2. D Onghia, E. 2008,
Physical properties of galaxies at high redshifts II
 Physical properties of galaxies at high redshifts II Different galaxies at high z s Luminous Infra Red Galaxies (LIRGs): LFIR > 10 11 L Ultra Luminous Infra Red Galaxies (ULIRGs): LFIR > 10 12 L SubMillimeter-selected
Physical properties of galaxies at high redshifts II Different galaxies at high z s Luminous Infra Red Galaxies (LIRGs): LFIR > 10 11 L Ultra Luminous Infra Red Galaxies (ULIRGs): LFIR > 10 12 L SubMillimeter-selected
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation! Star Formation Efficiency!
 Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 8. Angular Momentum & the Cusp/Core Problem
 Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 8 Angular Momentum & the Cusp/Core Problem Summary to Date We first learned how to construct the Power Spectrum with CDM+baryons. Found CDM agrees with the observed Power Spectrum
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 8 Angular Momentum & the Cusp/Core Problem Summary to Date We first learned how to construct the Power Spectrum with CDM+baryons. Found CDM agrees with the observed Power Spectrum
Two Phase Formation of Massive Galaxies
 Two Phase Formation of Massive Galaxies Focus: High Resolution Cosmological Zoom Simulation of Massive Galaxies ApJ.L.,658,710 (2007) ApJ.,697, 38 (2009) ApJ.L.,699,L178 (2009) ApJ.,725,2312 (2010) ApJ.,744,63(2012)
Two Phase Formation of Massive Galaxies Focus: High Resolution Cosmological Zoom Simulation of Massive Galaxies ApJ.L.,658,710 (2007) ApJ.,697, 38 (2009) ApJ.L.,699,L178 (2009) ApJ.,725,2312 (2010) ApJ.,744,63(2012)
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Dec 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Dec 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Dec 2016](/thumbs/93/117941334.jpg) Gas Accretion and Angular Momentum Kyle R. Stewart arxiv:1612.00513v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Dec 2016 Abstract In this chapter, we review the role of gas accretion to the acquisition of angular momentum, both
Gas Accretion and Angular Momentum Kyle R. Stewart arxiv:1612.00513v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Dec 2016 Abstract In this chapter, we review the role of gas accretion to the acquisition of angular momentum, both
Ken-ichi Tadaki (NAOJ, JSPS research fellow)
 Subaru GLAO Science Workshop June 13-14, 2013 Clumpy galaxies and compact star-forming galaxies giant clumps, compact SFGs ~ 1kpc Ken-ichi Tadaki (NAOJ, JSPS research fellow) Tadayuki Kodama (NAOJ), Ichi
Subaru GLAO Science Workshop June 13-14, 2013 Clumpy galaxies and compact star-forming galaxies giant clumps, compact SFGs ~ 1kpc Ken-ichi Tadaki (NAOJ, JSPS research fellow) Tadayuki Kodama (NAOJ), Ichi
Bright Cluster Galaxy formation and the role of AGN feedback. Romain Teyssier
 Bright Cluster Galaxy formation and the role of AGN feedback Romain Teyssier KITP 2011: Monster Inc. Romain Teyssier 1 Outline - Feedback and galaxy formation - The role of AGN feedback in Milky Way halos
Bright Cluster Galaxy formation and the role of AGN feedback Romain Teyssier KITP 2011: Monster Inc. Romain Teyssier 1 Outline - Feedback and galaxy formation - The role of AGN feedback in Milky Way halos
Gas accretion in Galaxies
 Massive Galaxies Over Cosmic Time 3, Tucson 11/2010 Gas accretion in Galaxies Dušan Kereš TAC, UC Berkeley Hubble Fellow Collaborators: Romeel Davé, Mark Fardal, C.-A. Faucher-Giguere, Lars Hernquist,
Massive Galaxies Over Cosmic Time 3, Tucson 11/2010 Gas accretion in Galaxies Dušan Kereš TAC, UC Berkeley Hubble Fellow Collaborators: Romeel Davé, Mark Fardal, C.-A. Faucher-Giguere, Lars Hernquist,
Cold streams in early massive hot haloes as the main mode of galaxy formation
 Cold streams in early massive hot haloes as the main mode of galaxy formation arxiv:88.553v3 [astro-ph] 16 Jan 29 A. Dekel 1, Y. Birnboim 1, G. Engel 1, J. Freundlich 1,2, T. Goerdt 1, M. Mumcuoglu 1,
Cold streams in early massive hot haloes as the main mode of galaxy formation arxiv:88.553v3 [astro-ph] 16 Jan 29 A. Dekel 1, Y. Birnboim 1, G. Engel 1, J. Freundlich 1,2, T. Goerdt 1, M. Mumcuoglu 1,
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
How do Black Holes Get Their Gas?
 How do Black Holes Get Their Gas? Philip Hopkins Eliot Quataert, Lars Hernquist, T. J. Cox, Kevin Bundy, Jackson DeBuhr, Volker Springel, Dusan Keres, Gordon Richards, Josh Younger, Desika Narayanan, Paul
How do Black Holes Get Their Gas? Philip Hopkins Eliot Quataert, Lars Hernquist, T. J. Cox, Kevin Bundy, Jackson DeBuhr, Volker Springel, Dusan Keres, Gordon Richards, Josh Younger, Desika Narayanan, Paul
Galaxy Evolution Workshop Austin, TX, Nov 2008
 Galaxy Evolution Workshop Austin, TX, Nov 2008 LCDM is a well-specified theory which makes definite predictions about the way structures in the Universe form and evolve. most (all?) of the mass of the
Galaxy Evolution Workshop Austin, TX, Nov 2008 LCDM is a well-specified theory which makes definite predictions about the way structures in the Universe form and evolve. most (all?) of the mass of the
Star cluster formation in dwarf galaxies
 Star cluster formation in dwarf galaxies Florent Renaud University of Surrey Massive clusters in dwarf outskirts Fornax dwarf galaxy, Larsen et al. High specific frequency Beyond optical radius In situ
Star cluster formation in dwarf galaxies Florent Renaud University of Surrey Massive clusters in dwarf outskirts Fornax dwarf galaxy, Larsen et al. High specific frequency Beyond optical radius In situ
Growing and merging massive black holes
 Growing and merging massive black holes Marta Volonteri Institut d Astrophysique de Paris S. Cielo (IAP) R. Bieri (MPA) Y. Dubois (IAP) M. Habouzit (Flatiron Institute) T. Hartwig (IAP) H. Pfister (IAP)
Growing and merging massive black holes Marta Volonteri Institut d Astrophysique de Paris S. Cielo (IAP) R. Bieri (MPA) Y. Dubois (IAP) M. Habouzit (Flatiron Institute) T. Hartwig (IAP) H. Pfister (IAP)
Galaxy interaction and transformation
 Galaxy interaction and transformation Houjun Mo April 13, 2004 A lot of mergers expected in hierarchical models. The main issues: The phenomena of galaxy interaction: tidal tails, mergers, starbursts When
Galaxy interaction and transformation Houjun Mo April 13, 2004 A lot of mergers expected in hierarchical models. The main issues: The phenomena of galaxy interaction: tidal tails, mergers, starbursts When
molecular cloud and a
 A molecular cloud and a Stop me if you ve heard this one before star cluster walk into a bar... Florent Renaud Lund Observatory with E. Emsellem, N. Guillard et al. A complex scale-coupling environment
A molecular cloud and a Stop me if you ve heard this one before star cluster walk into a bar... Florent Renaud Lund Observatory with E. Emsellem, N. Guillard et al. A complex scale-coupling environment
Gravitational heating, clumps, overheating. Yuval Birnboim (Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) Avishai Dekel (Hebrew University)
 Gravitational heating, clumps, overheating Yuval Birnboim (Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) Avishai Dekel (Hebrew University) Basic idea: Cooling flow Clusters need additional energy to reduce
Gravitational heating, clumps, overheating Yuval Birnboim (Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) Avishai Dekel (Hebrew University) Basic idea: Cooling flow Clusters need additional energy to reduce
Cosmological formation of slowly rotating massive elliptical galaxies
 Cosmological formation of slowly rotating massive elliptical galaxies Thorsten Naab with ATLAS 3D MPA L. Oser, M.Hilz, E. Emsellem, M. Cappellari, D. Krajnovic, R. M. McDermid, N. Scott, P. Serra, G. A.
Cosmological formation of slowly rotating massive elliptical galaxies Thorsten Naab with ATLAS 3D MPA L. Oser, M.Hilz, E. Emsellem, M. Cappellari, D. Krajnovic, R. M. McDermid, N. Scott, P. Serra, G. A.
Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing SMBH Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model
 Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing SMBH Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model Motohiro ENOKI (National Astronomical Observatory of Japan) Kaiki Taro INOUE (Kinki University) Masahiro NAGASHIMA
Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing SMBH Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model Motohiro ENOKI (National Astronomical Observatory of Japan) Kaiki Taro INOUE (Kinki University) Masahiro NAGASHIMA
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Three Major Components
 The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
What Doesn t Quench Galaxy Formation?
 What Doesn t Quench Galaxy Formation? Phil Hopkins Dusan Keres, Claude Faucher-Giguere, Jose Onorbe, Freeke van de Voort, Sasha Muratov, Xiangcheng Ma, Lena Murchikova, Norm Murray, Eliot Quataert, James
What Doesn t Quench Galaxy Formation? Phil Hopkins Dusan Keres, Claude Faucher-Giguere, Jose Onorbe, Freeke van de Voort, Sasha Muratov, Xiangcheng Ma, Lena Murchikova, Norm Murray, Eliot Quataert, James
Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers
 Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers Yuexing Li et al Presentation by: William Gray Definitions and Jargon QUASAR stands for QUASI-stellAR radio source Extremely bright and active
Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers Yuexing Li et al Presentation by: William Gray Definitions and Jargon QUASAR stands for QUASI-stellAR radio source Extremely bright and active
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs
 A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
Star formation in interacting and merging galaxies
 Antennae Star formation in interacting and merging galaxies Arp 220 Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris Sapporo, February 2014 M82 N1433 1 Outline 1- How much Star Formation is enhanced in interacting/merging
Antennae Star formation in interacting and merging galaxies Arp 220 Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris Sapporo, February 2014 M82 N1433 1 Outline 1- How much Star Formation is enhanced in interacting/merging
Compact Starbursts: Extreme Star Formation and Feedback at High Density Aleks Diamond-Stanic Grainger Fellow, University of Wisconsin
 Compact Starbursts: Extreme Star Formation and Feedback at High Density Aleks Diamond-Stanic Grainger Fellow, University of Wisconsin Arp 220 (talks by N. Scoville, D. Elbaz) 12 galaxies from our sample
Compact Starbursts: Extreme Star Formation and Feedback at High Density Aleks Diamond-Stanic Grainger Fellow, University of Wisconsin Arp 220 (talks by N. Scoville, D. Elbaz) 12 galaxies from our sample
Disc formation and the origin of clumpy galaxies at high redshift
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 397, L64 L68 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2009.00685.x Disc formation and the origin of clumpy galaxies at high redshift Oscar Agertz, 1 Romain Teyssier 1,2 and Ben Moore 1
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 397, L64 L68 (2009) doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2009.00685.x Disc formation and the origin of clumpy galaxies at high redshift Oscar Agertz, 1 Romain Teyssier 1,2 and Ben Moore 1
The Role of Dissipation in Spheroid Formation
 The Role of Dissipation in Spheroid Formation Philip Hopkins 4/08/08 Lars Hernquist, TJ Cox, John Kormendy, Tod Lauer, Suvendra Dutta, Dusan Keres, Volker Springel Ellipticals & Bulges: Formation in Mergers?
The Role of Dissipation in Spheroid Formation Philip Hopkins 4/08/08 Lars Hernquist, TJ Cox, John Kormendy, Tod Lauer, Suvendra Dutta, Dusan Keres, Volker Springel Ellipticals & Bulges: Formation in Mergers?
Angular Momentum Acquisition in Galaxy Halos
 Angular Momentum Acquisition in Galaxy Halos Kyle Stewart NASA Postdoctoral Fellow Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology Mentor: Leonidas Moustakas The Baryon Cycle, UC Irvine,
Angular Momentum Acquisition in Galaxy Halos Kyle Stewart NASA Postdoctoral Fellow Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology Mentor: Leonidas Moustakas The Baryon Cycle, UC Irvine,
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution. Fabio Fontanot (HITS)
 AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) 21/11/2012 AGN activity in theoretical models of galaxy formation Represents a viable solution for a number of long-standing theoretical problems Properties
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) 21/11/2012 AGN activity in theoretical models of galaxy formation Represents a viable solution for a number of long-standing theoretical problems Properties
Kinematics and Formation Mechanisms of High-Redshift Galaxies
 Kinematics and Formation Mechanisms of High-Redshift Galaxies White Paper Submitted to the Astro 2010 Decadal Survey Science Frontier Panel: Galaxies Across Cosmic Time (GCT) David R. Law (UC Los Angeles;
Kinematics and Formation Mechanisms of High-Redshift Galaxies White Paper Submitted to the Astro 2010 Decadal Survey Science Frontier Panel: Galaxies Across Cosmic Time (GCT) David R. Law (UC Los Angeles;
Two Main Techniques. I: Star-forming Galaxies
 p.1/24 The high redshift universe has been opened up to direct observation in the last few years, but most emphasis has been placed on finding the progenitors of today s massive ellipticals. p.2/24 Two
p.1/24 The high redshift universe has been opened up to direct observation in the last few years, but most emphasis has been placed on finding the progenitors of today s massive ellipticals. p.2/24 Two
The angular momentum of z=1 star forming galaxies from deep MUSE observations
 The angular momentum of z=1 star forming galaxies from deep MUSE observations Nicolas Bouché T. Contini; B. Epinat + MUSE team: R. Bacon (PI); E. Emsellem; J. Brinchman; J. Richard; T. Martinsson; D. Krajnovic;
The angular momentum of z=1 star forming galaxies from deep MUSE observations Nicolas Bouché T. Contini; B. Epinat + MUSE team: R. Bacon (PI); E. Emsellem; J. Brinchman; J. Richard; T. Martinsson; D. Krajnovic;
MASSIVE GALAXIES IN GROUPS vs ISOLATED GALAXIES FROM HYDRODYNAMICAL SIMULATIONS
 MASSIVE GALAXIES IN GROUPS vs ISOLATED GALAXIES FROM HYDRODYNAMICAL SIMULATIONS Rosa Domínguez Tenreiro (1) Paola Alpresa(1) José Oñorbe (1) Fran Martínez-Serrano (2) Arturo Serna (2) (1) Universidad Autónoma
MASSIVE GALAXIES IN GROUPS vs ISOLATED GALAXIES FROM HYDRODYNAMICAL SIMULATIONS Rosa Domínguez Tenreiro (1) Paola Alpresa(1) José Oñorbe (1) Fran Martínez-Serrano (2) Arturo Serna (2) (1) Universidad Autónoma
Morphologies and building blocks of galaxies at high redshift
 Morphologies and building blocks of galaxies at high redshift Mariko Kubo TMT project office, NAOJ The TMT Science Forum 2016 24-26, May Galaxies in the current Universe NASA, ESA, and The Hubble Heritage
Morphologies and building blocks of galaxies at high redshift Mariko Kubo TMT project office, NAOJ The TMT Science Forum 2016 24-26, May Galaxies in the current Universe NASA, ESA, and The Hubble Heritage
Cosmological simulations of galaxy formation
 Cosmological simulations of galaxy formation Modern galaxy formation simulations Mock gri SDSS composite image with dust absorption based on Draine opacity model. NGC4622 as seen from HST Outline - Impact
Cosmological simulations of galaxy formation Modern galaxy formation simulations Mock gri SDSS composite image with dust absorption based on Draine opacity model. NGC4622 as seen from HST Outline - Impact
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009
 Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau
 Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Steady outflows in giant clumps of high-z disc galaxies during migration and growth by accretion
 MNRAS 432, 455 467 (2013) Advance Access publication 2013 April 12 doi:10.1093/mnras/stt480 Steady outflows in giant clumps of high-z disc galaxies during migration and growth by accretion Avishai Dekel
MNRAS 432, 455 467 (2013) Advance Access publication 2013 April 12 doi:10.1093/mnras/stt480 Steady outflows in giant clumps of high-z disc galaxies during migration and growth by accretion Avishai Dekel
quenching and structural & morphological evolution: physics
 quenching and structural & morphological evolution: physics rachel somerville Rutgers University with thanks to: Ryan Brennan, Viraj Pandya, Ena Choi Guillermo Barro, Stijn Wuyts, Dale Kocevski, Arjen
quenching and structural & morphological evolution: physics rachel somerville Rutgers University with thanks to: Ryan Brennan, Viraj Pandya, Ena Choi Guillermo Barro, Stijn Wuyts, Dale Kocevski, Arjen
Survey of Astrophysics A110
 Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Angular Momentum Problems in Disk Formation
 Angular Momentum Problems in Disk Formation MPIA Theory Group Seminar, 07/03/2006 The Standard Picture Disks galaxies are systems in centrifugal equilibrium Structure of disks is governed by angular momentum
Angular Momentum Problems in Disk Formation MPIA Theory Group Seminar, 07/03/2006 The Standard Picture Disks galaxies are systems in centrifugal equilibrium Structure of disks is governed by angular momentum
The theoretical view of high-z Clusters. Nelson Padilla, PUC, Chile Pucón, November 2009
 The theoretical view of high-z Clusters Nelson Padilla, PUC, Chile Pucón, November 2009 The Plan: 1) To see what the observations are telling us using models that agree with the cosmology, and with other
The theoretical view of high-z Clusters Nelson Padilla, PUC, Chile Pucón, November 2009 The Plan: 1) To see what the observations are telling us using models that agree with the cosmology, and with other
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 18: Disk Galaxies
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 18: Disk Galaxies Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 The Structure & Formation of Disk Galaxies In this lecture we discuss the structure and formation
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 18: Disk Galaxies Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 The Structure & Formation of Disk Galaxies In this lecture we discuss the structure and formation
The Iguaçu Lectures. Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures
 April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
AGN in hierarchical galaxy formation models
 AGN in hierarchical galaxy formation models Nikos Fanidakis and C.M. Baugh, R.G. Bower, S. Cole, C. Done, C. S. Frenk Physics of Galactic Nuclei, Ringberg Castle, June 18, 2009 Outline Brief introduction
AGN in hierarchical galaxy formation models Nikos Fanidakis and C.M. Baugh, R.G. Bower, S. Cole, C. Done, C. S. Frenk Physics of Galactic Nuclei, Ringberg Castle, June 18, 2009 Outline Brief introduction
Fundamental Planes and Galaxy Formation
 Fundamental Planes and Galaxy Formation Philip Hopkins, NoviCosmo 2007 Fundamental Planes = Scaling Laws Obeyed by Galaxies vs Origin of scaling laws: Ideally, we d understand every galaxy as an individual:
Fundamental Planes and Galaxy Formation Philip Hopkins, NoviCosmo 2007 Fundamental Planes = Scaling Laws Obeyed by Galaxies vs Origin of scaling laws: Ideally, we d understand every galaxy as an individual:
Summary So Far! M87van der Maerl! NGC4342! van den Bosch! rotation velocity!
 Summary So Far Fundamental plane connects luminosity, scale length, surface brightness, stellar dynamics. age and chemical composition Elliptical galaxies are not randomly distributed within the 3D space
Summary So Far Fundamental plane connects luminosity, scale length, surface brightness, stellar dynamics. age and chemical composition Elliptical galaxies are not randomly distributed within the 3D space
Solving. Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics
 Solving Constraining galaxy formation with gaseous halos Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics X-ray Vision workshop:
Solving Constraining galaxy formation with gaseous halos Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics X-ray Vision workshop:
Mergers and Mass Assembly of Dark Matter Halos & Galaxies
 Mergers and Mass Assembly of Dark Matter Halos & Galaxies Chung-Pei Ma Onsi Fakhouri James McBride (UC Berkeley) Mike Boylan-Kolchin (MPA --> Southern UC) Claude-Andre Faucher-Giguere Dusan Keres (Harvard
Mergers and Mass Assembly of Dark Matter Halos & Galaxies Chung-Pei Ma Onsi Fakhouri James McBride (UC Berkeley) Mike Boylan-Kolchin (MPA --> Southern UC) Claude-Andre Faucher-Giguere Dusan Keres (Harvard
Feedback in Galaxy Clusters
 Feedback in Galaxy Clusters Brian Morsony University of Maryland 1 Not talking about Galaxy-scale feedback Local accretion disk feedback 2 Outline Galaxy cluster properties Cooling flows the need for feedback
Feedback in Galaxy Clusters Brian Morsony University of Maryland 1 Not talking about Galaxy-scale feedback Local accretion disk feedback 2 Outline Galaxy cluster properties Cooling flows the need for feedback
Feedback, AGN and galaxy formation. Debora Sijacki
 Feedback, AGN and galaxy formation Debora Sijacki Formation of black hole seeds: the big picture Planck data, 2013 (new results 2015) Formation of black hole seeds: the big picture CMB black body spectrum
Feedback, AGN and galaxy formation Debora Sijacki Formation of black hole seeds: the big picture Planck data, 2013 (new results 2015) Formation of black hole seeds: the big picture CMB black body spectrum
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes
 Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
modified gravity? Chaire Galaxies et Cosmologie XENON1T Abel & Kaehler
 Dark matter or modified gravity? Chaire Galaxies et Cosmologie Françoise Combes 11 December, 2017 XENON1T Abel & Kaehler Why modified gravity? CDM models beautifully account for LSS, CMB, galaxy formation
Dark matter or modified gravity? Chaire Galaxies et Cosmologie Françoise Combes 11 December, 2017 XENON1T Abel & Kaehler Why modified gravity? CDM models beautifully account for LSS, CMB, galaxy formation
the self-regulated agn feedback loop: chaotic cold accretion
 the self-regulated agn feedback loop: chaotic cold accretion Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics the self-regulated agn feedback loop: raining onto black holes Massimo Gaspari Max Planck
the self-regulated agn feedback loop: chaotic cold accretion Massimo Gaspari Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics the self-regulated agn feedback loop: raining onto black holes Massimo Gaspari Max Planck
Co-Evolution of Central Black Holes and Nuclear Star Clusters
 Co-Evolution of Central Black Holes and Nuclear Star Clusters Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) Globular clusters in the Galaxy median distance from the center is 5 kpc Resolved star cluster highest
Co-Evolution of Central Black Holes and Nuclear Star Clusters Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) Globular clusters in the Galaxy median distance from the center is 5 kpc Resolved star cluster highest
high density low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) Springel (2010)
 GAS MIXES high density Springel (2010) low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) HOT HALO highest resolved density nth= 50x10
GAS MIXES high density Springel (2010) low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) HOT HALO highest resolved density nth= 50x10
8.1 Structure Formation: Introduction and the Growth of Density Perturbations
 8.1 Structure Formation: Introduction and the Growth of Density Perturbations 1 Structure Formation and Evolution From this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10-6 ) to this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10 +2 ) to this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10 +6 ) 2 Origin of Structure
8.1 Structure Formation: Introduction and the Growth of Density Perturbations 1 Structure Formation and Evolution From this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10-6 ) to this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10 +2 ) to this (Δρ/ρ ~ 10 +6 ) 2 Origin of Structure
The Impact of Minor Mergers
 The Impact of Minor Mergers T. J. Cox (CfA) Phil Hopkins (Berkeley) Lars Hernquist (CfA) Rachel Somerville (STScI) Josh Younger (CfA) NGC 7674 Gurtina Besla (CfA), Avishai Dekel (HU), Tiziana Di Matteo
The Impact of Minor Mergers T. J. Cox (CfA) Phil Hopkins (Berkeley) Lars Hernquist (CfA) Rachel Somerville (STScI) Josh Younger (CfA) NGC 7674 Gurtina Besla (CfA), Avishai Dekel (HU), Tiziana Di Matteo
Modelling star formation in galaxy formation simulations
 Modelling star formation in galaxy formation simulations Vadim Semenov (U.Chicago) Andrey Kravtsov University of Chicago Carving through the codes Davos, Switzerland 16 February, 2017 Nick Gnedin (Fermilab)
Modelling star formation in galaxy formation simulations Vadim Semenov (U.Chicago) Andrey Kravtsov University of Chicago Carving through the codes Davos, Switzerland 16 February, 2017 Nick Gnedin (Fermilab)
Major Review: A very dense article" Dawes Review 4: Spiral Structures in Disc Galaxies; C. Dobbs and J Baba arxiv "
 The Components of a Spiral Galaxy-a Bit of a Review- See MBW chap 11! we have discussed this in the context of the Milky Way" Disks:" Rotationally supported, lots of gas, dust, star formation occurs in
The Components of a Spiral Galaxy-a Bit of a Review- See MBW chap 11! we have discussed this in the context of the Milky Way" Disks:" Rotationally supported, lots of gas, dust, star formation occurs in
Galaxy Activity in Semi Analytical Models. Fabio Fontanot (INAF OATs) Ljubljana 05/04/11
 Galaxy Activity in Semi Analytical Models Fabio Fontanot (INAF OATs) Ljubljana 05/04/11 Part I: Theoretical background 1. Baryonic gas falls in the gravitational potential of Dark Matter Halos 2. Baryonic
Galaxy Activity in Semi Analytical Models Fabio Fontanot (INAF OATs) Ljubljana 05/04/11 Part I: Theoretical background 1. Baryonic gas falls in the gravitational potential of Dark Matter Halos 2. Baryonic
Gas in and around z > 2 galaxies
 Gas in and around z > 2 galaxies Michele Fumagalli August 2010 Santa Cruz Xavier Prochaska Daniel Kasen Avishai Dekel In collaboration with: Daniel Ceverino Joel Primack Gas in galaxies from theory Gas
Gas in and around z > 2 galaxies Michele Fumagalli August 2010 Santa Cruz Xavier Prochaska Daniel Kasen Avishai Dekel In collaboration with: Daniel Ceverino Joel Primack Gas in galaxies from theory Gas
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies
 Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Dark matter and galaxy formation
 Dark matter and galaxy formation Galaxy rotation The virial theorem Galaxy masses via K3 Mass-to-light ratios Rotation curves Milky Way Nearby galaxies Dark matter Baryonic or non-baryonic A problem with
Dark matter and galaxy formation Galaxy rotation The virial theorem Galaxy masses via K3 Mass-to-light ratios Rotation curves Milky Way Nearby galaxies Dark matter Baryonic or non-baryonic A problem with
Galaxy Formation and Evolution
 Galaxy Formation and Evolution Houjun Mo Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts 710 North Pleasant Str., Amherst, MA 01003-9305, USA Frank van den Bosch Department of Physics & Astronomy,
Galaxy Formation and Evolution Houjun Mo Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts 710 North Pleasant Str., Amherst, MA 01003-9305, USA Frank van den Bosch Department of Physics & Astronomy,
Barred Galaxies. Morphology Gas in barred galaxies Dynamics: pattern speed Theory: secular evolution, resonances
 Barred Galaxies Morphology Gas in barred galaxies Dynamics: pattern speed Theory: secular evolution, resonances NGC1300: SB(s) fig.6 NGC1512: SB(r) fig.3 NGC2523: SB(r) fig.2 Dust lanes NGC 1300 Star formation
Barred Galaxies Morphology Gas in barred galaxies Dynamics: pattern speed Theory: secular evolution, resonances NGC1300: SB(s) fig.6 NGC1512: SB(r) fig.3 NGC2523: SB(r) fig.2 Dust lanes NGC 1300 Star formation
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges
 Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
Astronomy 330 Lecture Dec 2010
 Astronomy 330 Lecture 26 10 Dec 2010 Outline Clusters Evolution of cluster populations The state of HI sensitivity Large Scale Structure Cluster Evolution Why might we expect it? What does density determine?
Astronomy 330 Lecture 26 10 Dec 2010 Outline Clusters Evolution of cluster populations The state of HI sensitivity Large Scale Structure Cluster Evolution Why might we expect it? What does density determine?
Astro 358/Spring 2008 (49520) Galaxies and the Universe
 Astro 358/Spring 2008 (49520) Galaxies and the Universe Figures + Tables for Lecture 13 on Tu Mar 18 Lectures 9 to 12 1) Evidence for DM ; CDM vs HDM 2) Surface brightness profile and v/σ of Disks, Bulges,
Astro 358/Spring 2008 (49520) Galaxies and the Universe Figures + Tables for Lecture 13 on Tu Mar 18 Lectures 9 to 12 1) Evidence for DM ; CDM vs HDM 2) Surface brightness profile and v/σ of Disks, Bulges,
Galaxy Evolution: Emerging Insights and Future Challenges. University of Texas (UT) Austin Nov 11-14
 Galaxy Evolution: Emerging Insights and Future Challenges University of Texas (UT) Austin Nov 11-14 Thank You! Department of Astronomy & Mc Donald Observatory Board of Visitors Scientific Organizing Committee
Galaxy Evolution: Emerging Insights and Future Challenges University of Texas (UT) Austin Nov 11-14 Thank You! Department of Astronomy & Mc Donald Observatory Board of Visitors Scientific Organizing Committee
PLANET FORMATION BY GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of Arizona. Sagan Summer Workshop, July 2015
 PLANET FORMATION BY GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of Arizona Sagan Summer Workshop, July 2015 PLANET FORMATION BY in GAS! GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of
PLANET FORMATION BY GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of Arizona Sagan Summer Workshop, July 2015 PLANET FORMATION BY in GAS! GRAVITATIONAL INSTABILITY? Kaitlin Kratter University of
