Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations and Sunrise Visualizations
|
|
|
- Harvey Dawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations and Sunrise Visualizations Joel Primack, UCSC Daniel Ceverino, HU Madrid Avishai Dekel, HU & UCSC Sandra Faber, UCSC Anatoly Klypin, NMSU Patrik Jonsson, Harvard CfA Chris Moody, UCSC Mark Mozena, UCSC Sebastian Trujillo-Gomez, NMSU Dylan Tweed, HU
2 Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations Galaxy formation is so complicated that observations and theory cannot give us a clear picture of how galaxies form without working hand-in-hand. Fortunately, new observations at z > 1.5 are clarifying the processes by which most of the stars in the universe formed, and at z < 1.5 how present-day galaxies assembled. And observations are finally closing in on the ΛCDM cosmological parameters, so that we have a definite cosmological framework within which to model galaxies. We have run ~20 high-resolution cosmological hydrodynamic simulations of galaxy formation and evolution, and we are now gearing up to run hundreds more so that we can have a statistical sample of such simulations. We use our Sunrise code to model stellar evolution and radiative transfer through dusty galaxies, in order to produce realistic images in all accessible wavebands.
3 Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations We are using the Hydro Adaptive Refinement Tree (hydroart) code, currently the most efficient of the three Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) codes used for high-resolution galaxy simulations. The other AMR codes are ENZO and RAMSES. We will also be doing a high-resolution galaxy simulation comparison project using all three of these codes with the same initial conditions, and perhaps also the Gasoline, Gadget, and AREPO Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) codes. The resolution of our hydroart galaxy cosmological sims is pc, with higher resolution studies of subregions as shown below. Gas column density in a galactic chimney, which reaches T~10 8 K with outflow velocities >10 3 km/s. The volume is a 4 kpc cube, with 8-16 pc resolution. (From Ceverino & Klypin 2009.)
4 Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations Physical phenomena included in ART simulations analyzed thus far: Dark matter and baryons, metal and molecular hydrogen cooling to ~100K, UV background with self-shielding, star formation, energy input from stellar winds and supernovae, advection of metals. See Ceverino & Klypin 2009; Dekel, Sari, & Ceverino 2009; Ceverino, Dekel, & Bournaud 2010; Goerdt, Dekel, Sternberg, Ceverino, Teyssier, & Primack 2010; Fumagalli, Prochaska, Kasen, Dekel, Ceverino, & Primack 2011; Ceverino, Dekel, Mandelker, Bournaud, Burkert, Genzel, & Primack 2011; Kasen et al and other papers in preparation. Additional phenomena included in ART simulations currently running: Radiative feedback from luminous stars and from AGN.
5 Stars
6 Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations Gas surface density and projected velocity field within the halo of simulated galaxy A at z = 2.3. Long streams of cold gas and merging galaxies feed a central rotating disc through a messy interphase region. Arrows represent the velocity field (white arrow is 200 km/s). (From Ceverino et al. 2011, to be submitted this week.)
7 Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations Face-on view Edge-on view Galaxy A at z = 2.3, which has a disk of young stars (about half forming in the clumps) and a bulge of older stars formed largely by merging clumps. Ceverino, Dekel, & Bournaud 2010
8 Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations Face-on views Simulated galaxy A at z = 2.3 (Mvir = 4x10 11 Msun) Edge-on views viewed face-on and edge-on compared with similar appearing real galaxies Ceverino, Dekel, & Bournaud 2010
9 Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations Gas surface density of galaxy E disk at z = 3 to 2. Mvir = 1.5x10 12 Msun at z = 2.3. Identified clumps are numbered; #1, 2, and 4 were small galaxies that merged. (From Ceverino et al. 2011, to be submitted this week.)
10 Galaxy Hydrodynamic Simulations Hydrogen column density in galaxy A at z = 2.3 using the STAR model, which includes ionizing radiation from local sources as well as the UV background. Most of the gas in the streams is ionized by electron collisions and the UVB, while photons from newly born stars affect the high column density inside the central and satellite galaxies and their surroundings. Column density distribution function from observations at z 3.7 (colors: Prochaska et al. 2010) and simulations for the STAR (solid line) and the UVB (dashed line) models at z = 3.5 within the virial radius. Fumagalli, Prochaska, Kasen, Dekel, Ceverino, & Primack 2011
11 Sunrise Visualizations Dust in galaxies is important Absorbs about 40% of the local bolometric luminosity Makes brightness of spirals inclination-dependent Completely hides the most spectacular bursts of star formation Makes high-redshift star formation very uncertain Dust in galaxies is complicated The mixed geometry of stars and dust makes dust effects geometry-dependent and nontrivial to deduce Needs full radiative transfer model to calculate realistically Previous efforts have used 2 strategies Assume a simple, schematic geometry like exponential disks, or Simulate star-forming regions in some detail, assuming the galaxy is made up of such independent regions Have not used information from hydrodynamic simulations The Sunrise code starts from hydro simulations
12 Sunrise Visualizations In order to calculate the effects of stellar age, metallicity and dust, we use the open-source Monte-Carlo radiative-transfer code Sunrise (Jonsson 2006, Jonsson, Cox, Primack, & Somerville 2006). The stellar SEDs are calculated using Starburst (or Bruzual & Charlot, etc.). The spectral energy distribution of all stars in a given timestep is propagated through the dusty interstellar medium of the simulated galaxies. Sunrise uses a polychromatic algorithm, where every Monte-Carlo ray samples every wavelength. This algorithm makes it possible to calculate spectra efficiently with unprecedented spectral resolution. Sunrise uses subgrid models of star-forming regions from the photoionization/dust code MAPPINGS-III (Jonsson, Groves, & Cox 2009). Emission from diffuse dust is calculated selfconsistently from the local radiation field, allowing calculation of spectral energy distributions out to the far-ir for comparison with Spitzer and Herschel data. This is the most computationally intensive part of the calculation, but it can be sped up by a factor of ~50 using an Nvidia Tesla graphic processor unit (Jonsson & Primack 2010).
13 Sunrise Visualizations For every simulation snapshot: SED calculation Adaptive grid construction Monte Carlo radiative transfer Polychromatic rays save CPU time Photons are emitted and scattered/ absorbed stochastically
14 Galaxy Merger Simulation Visualized with Sunrise This image and the following video shows a merger between two Sbc galaxies, each simulated with 1.7 million particles using Gadget. The images are realistic color composites of u, r, and z-band images. Dust absorbs up to 90% of the light, and reradiates the energy in the far infrared. We calculate this radiative transfer using ~10 6 light rays per image. The simulation was run by Greg Novak and Joel Primack, and the visualization is by Patrik Jonsson.
15
16 Sunrise Visualizations 1 μm 10 μm 100 μm
17 Sunrise Visualizations 1 μm 10 μm 100 μm
18 Sunrise Visualizations The simulated galaxies (solid lines) with the best-fitting SINGS galaxy (symbols) overplotted. The inclination that best matched a SINGS galaxy was chosen. All SEDs are normalized to observations in the K band. (Jonsson, Groves, & Cox 2010.)
19 Simulation edge-on Simulation face-on w/ Dust w/o Dust w/ Dust w/o Dust Simulation shown is MW3 at z=2.33 imaged to match the CANDELS observations in ACS-Vband and WFC3-Hband Pixel scale - convolved with simulated psfs - noise and background derived from ERS observations (same field as examples shown) MW3 was imaged at face-on and edge-on viewing angles both with and without including dust models Mark Mozena
20 Sunrise Visualizations UCSC grad student Chris Moody (working with Primack, Matt Turk, and Patrik Jonsson) has created a pipeline to process ART simulation outputs efficiently to create multiwavelength Sunrise images. UCSC grad student Mark Mozena (working with Faber, Dekel, Koo, Lotz, and Primack) has perfected methods to convolve with appropriate PSFs and add noise to these Sunrise images, so that they can be compared directly with observations. We know that Sunrise with standard dust assumptions matches SEDs of nearby galaxies. We plan to run a number of dust models on hydro simulations of z ~2 to 3 galaxies to see what dust models will best agree with observed SEDs for similar galaxies. We plan to generate simulated images in ~5 wavebands of ~10 orientations of ~10 timesteps of the ~20 simulated galaxies that we have now (leading to about 10 4 images). We plan to expand this by an order of magnitude over the next year or so (producing ~10 5 images). We are also looking into machine classification of real and simulated galaxy images.
Visualizing High-Resolution Simulations of Galaxy Formation and Comparing to the Latest Observations from Hubble and Other Telescopes
 Third Annual SRL / ISSDM Research Symposium - UCSC Systems Oktoberfest October 18-19, 2011 Visualizing High-Resolution Simulations of Galaxy Formation and Comparing to the Latest Observations from Hubble
Third Annual SRL / ISSDM Research Symposium - UCSC Systems Oktoberfest October 18-19, 2011 Visualizing High-Resolution Simulations of Galaxy Formation and Comparing to the Latest Observations from Hubble
Characterizing z~2 Galaxies in HYDRO-ART Simulations and Observations
 Characterizing z~2 Galaxies in HYDRO-ART Simulations and Observations Mark Mozena (UCSC) Sandra Faber, Avishai Dekel, Daniel Ceverino, Joel Primack, Kamson Lai, David Koo, David Rosario, Dale Kocevski,
Characterizing z~2 Galaxies in HYDRO-ART Simulations and Observations Mark Mozena (UCSC) Sandra Faber, Avishai Dekel, Daniel Ceverino, Joel Primack, Kamson Lai, David Koo, David Rosario, Dale Kocevski,
Violent Disk Instability at z=1-4 Outflows; Clump Evolution; Compact Spheroids
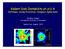 Violent Disk Instability at z=1-4 Outflows; Clump Evolution; Compact Spheroids Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Santa Cruz, August 2013 stars 5 kpc Outline 1. Inflows and Outflows 2. Evolution
Violent Disk Instability at z=1-4 Outflows; Clump Evolution; Compact Spheroids Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Santa Cruz, August 2013 stars 5 kpc Outline 1. Inflows and Outflows 2. Evolution
Gas in and around z > 2 galaxies
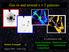 Gas in and around z > 2 galaxies Michele Fumagalli August 2010 Santa Cruz Xavier Prochaska Daniel Kasen Avishai Dekel In collaboration with: Daniel Ceverino Joel Primack Gas in galaxies from theory Gas
Gas in and around z > 2 galaxies Michele Fumagalli August 2010 Santa Cruz Xavier Prochaska Daniel Kasen Avishai Dekel In collaboration with: Daniel Ceverino Joel Primack Gas in galaxies from theory Gas
High-z Galaxy Evolution: VDI and (mostly minor) Mergers
 High-z Galaxy Evolution: VDI and (mostly minor) Mergers Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem UCSC, August 2012 Outline: in-situ (VDI) and ex-situ (mergers) 1. Cold streams: smooth and clumpy
High-z Galaxy Evolution: VDI and (mostly minor) Mergers Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem UCSC, August 2012 Outline: in-situ (VDI) and ex-situ (mergers) 1. Cold streams: smooth and clumpy
Understanding isolated and satellite galaxies through simulations
 Understanding isolated and satellite galaxies through simulations Kenza Arraki! Blue Waters Graduate Fellow! New Mexico State University! Anatoly Klypin! Daniel Ceverino! Sebastian Trujillo-Gomez! Joel
Understanding isolated and satellite galaxies through simulations Kenza Arraki! Blue Waters Graduate Fellow! New Mexico State University! Anatoly Klypin! Daniel Ceverino! Sebastian Trujillo-Gomez! Joel
Hydro ART simulations sample
 Hydro ART simulations sample Stellar Merger Trees Dylan Tweed dylan.tweed@googlemail.com Racah Institute of Physics, HUJI, Jerusalem CANDELS Theory Workshop - UCSC - August 8 th 10 th 2012 D. P. Tweed
Hydro ART simulations sample Stellar Merger Trees Dylan Tweed dylan.tweed@googlemail.com Racah Institute of Physics, HUJI, Jerusalem CANDELS Theory Workshop - UCSC - August 8 th 10 th 2012 D. P. Tweed
Yicheng Guo (UCO/Lick, UCSC)
 Formation and Evolution of Clumpy Galaxies at z=0.5--3 Yicheng Guo (UCO/Lick, UCSC) Collaborators: Henry Ferguson, Eric Bell, David Koo, Chris Conselice, Mauro Giavalisco, Nir Mandelker, Swara Ravindranatch,
Formation and Evolution of Clumpy Galaxies at z=0.5--3 Yicheng Guo (UCO/Lick, UCSC) Collaborators: Henry Ferguson, Eric Bell, David Koo, Chris Conselice, Mauro Giavalisco, Nir Mandelker, Swara Ravindranatch,
The Magic Scale of Galaxy Formation: SNe & Hot CGM --> Compaction & BHs
 The Magic Scale of Galaxy Formation: SNe & Hot CGM --> Compaction & BHs Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Silk 75, December 2017 A Characteristic Mass for Galaxy Formation Efficiency
The Magic Scale of Galaxy Formation: SNe & Hot CGM --> Compaction & BHs Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Silk 75, December 2017 A Characteristic Mass for Galaxy Formation Efficiency
Using Hydro-Simulations to Interpret Observed Kinematic Maps of Star-Forming Galaxies
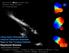 disk from the VELA simulation suite Ceverino, Dekel, Primack, + z = 1.6, young stars Using Hydro-Simulations to Interpret Observed Kinematic Maps of Star-Forming Galaxies Raymond Simons Johns Hopkins University
disk from the VELA simulation suite Ceverino, Dekel, Primack, + z = 1.6, young stars Using Hydro-Simulations to Interpret Observed Kinematic Maps of Star-Forming Galaxies Raymond Simons Johns Hopkins University
Feeding High-z Galaxies from the Cosmic Web
 Feeding High-z Galaxies from the Cosmic Web Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Jerusalem Winter School 2012/13 Lecture 1 z=0 z=2 z=8 Cosmological simulations Toy modeling Oxford Dictionary:
Feeding High-z Galaxies from the Cosmic Web Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Jerusalem Winter School 2012/13 Lecture 1 z=0 z=2 z=8 Cosmological simulations Toy modeling Oxford Dictionary:
Sunrise: Patrik Jonsson. Panchromatic SED Models of Simulated Galaxies. Lecture 2: Working with Sunrise. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
 Sunrise: Panchromatic SED Models of Simulated Galaxies Lecture 2: Working with Sunrise Patrik Jonsson Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Lecture outline Lecture 1: Why Sunrise? What does it do?
Sunrise: Panchromatic SED Models of Simulated Galaxies Lecture 2: Working with Sunrise Patrik Jonsson Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Lecture outline Lecture 1: Why Sunrise? What does it do?
Origin of Bi-modality
 Origin of Bi-modality and Downsizing Avishai Dekel HU Jerusalem Galaxies and Structures Through Cosmic Times Venice, March 2006 Summary Q: z
Origin of Bi-modality and Downsizing Avishai Dekel HU Jerusalem Galaxies and Structures Through Cosmic Times Venice, March 2006 Summary Q: z
DEEP2 Galaxy Mergers and X-ray Selected AGN to z=1.4
 Sackler Black Hole Conference - Harvard 5-17-06 ACS Picture of The Mice by Ford et al. DEEP2 Galaxy Mergers and X-ray Selected AGN to z=1.4 Joel R. Primack (UCSC) Matt Covington (UCSC) T. J. Cox (UCSC
Sackler Black Hole Conference - Harvard 5-17-06 ACS Picture of The Mice by Ford et al. DEEP2 Galaxy Mergers and X-ray Selected AGN to z=1.4 Joel R. Primack (UCSC) Matt Covington (UCSC) T. J. Cox (UCSC
Spin Acquisition, Violent Disks, Compaction and Quenching
 Spin Acquisition, Violent Disks, Compaction and Quenching Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem July 2014 stars 5 kpc Three Provocative Questions concerning high-z massive galaxy formation 1.
Spin Acquisition, Violent Disks, Compaction and Quenching Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem July 2014 stars 5 kpc Three Provocative Questions concerning high-z massive galaxy formation 1.
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS
 GALAXY FORMATION - Durham -18 July 2011 THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS JOEL PRIMACK, UCSC ΛCDM Cosmological Parameters for Bolshoi and BigBolshoi Halo Mass Function is 10x
GALAXY FORMATION - Durham -18 July 2011 THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS JOEL PRIMACK, UCSC ΛCDM Cosmological Parameters for Bolshoi and BigBolshoi Halo Mass Function is 10x
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline A galaxy is a collection of 100 billion stars! Our Milky Way Galaxy (1)Components - HII regions, Dust Nebulae, Atomic Gas (2) Shape & Size (3) Rotation of
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline A galaxy is a collection of 100 billion stars! Our Milky Way Galaxy (1)Components - HII regions, Dust Nebulae, Atomic Gas (2) Shape & Size (3) Rotation of
Stream-Driven Galaxy Formation at High Redshift
 Stream-Driven Galaxy Formation at High Redshift Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem KooFest, Santa Cruz, August 2011 Outline 1. Streams in pancakes from the cosmic web (Hahn) 2. Is angular
Stream-Driven Galaxy Formation at High Redshift Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem KooFest, Santa Cruz, August 2011 Outline 1. Streams in pancakes from the cosmic web (Hahn) 2. Is angular
The Impact of Minor Mergers
 The Impact of Minor Mergers T. J. Cox (CfA) Phil Hopkins (Berkeley) Lars Hernquist (CfA) Rachel Somerville (STScI) Josh Younger (CfA) NGC 7674 Gurtina Besla (CfA), Avishai Dekel (HU), Tiziana Di Matteo
The Impact of Minor Mergers T. J. Cox (CfA) Phil Hopkins (Berkeley) Lars Hernquist (CfA) Rachel Somerville (STScI) Josh Younger (CfA) NGC 7674 Gurtina Besla (CfA), Avishai Dekel (HU), Tiziana Di Matteo
Three comments on High-z Galaxy Formation. Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
 Three comments on High-z Galaxy Formation Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem August 2014 Outline 1. Angular momentum: buildup in 4 phases 2. Violent disk instability: Nonlinear, Stimulated
Three comments on High-z Galaxy Formation Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem August 2014 Outline 1. Angular momentum: buildup in 4 phases 2. Violent disk instability: Nonlinear, Stimulated
GALAXY EVOLUTION STUDIES AND HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTING
 GALAXY EVOLUTION STUDIES AND HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTING Andreas Efstathiou European University Cyprus Astrophysics and HPC group ACTIVE AREAS OF ASTRONOMY OPPORTUNITIES FOR THEORETICAL, OBSERVATIONAL AND
GALAXY EVOLUTION STUDIES AND HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTING Andreas Efstathiou European University Cyprus Astrophysics and HPC group ACTIVE AREAS OF ASTRONOMY OPPORTUNITIES FOR THEORETICAL, OBSERVATIONAL AND
Nir Mandelker, H.U.J.I.
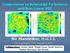 Compressive vs Solenoidal Turbulence and Non-Linear VDI Nir Mandelker, H.U.J.I. IAU Symposium 319, August 11 2015 Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Shigeki Inoue, Daniel Ceverino, Frederic Bournaud, Joel Primack
Compressive vs Solenoidal Turbulence and Non-Linear VDI Nir Mandelker, H.U.J.I. IAU Symposium 319, August 11 2015 Collaborators: Avishai Dekel, Shigeki Inoue, Daniel Ceverino, Frederic Bournaud, Joel Primack
Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content
 Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content arxiv:1005.1289 arxiv:1002.3660 S. Trujillo-Gomez (NMSU) in collaboration with: A. Klypin (NMSU), J. Primack (UCSC)
Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content arxiv:1005.1289 arxiv:1002.3660 S. Trujillo-Gomez (NMSU) in collaboration with: A. Klypin (NMSU), J. Primack (UCSC)
GALAXY MERGERS: Simulations, Observations, and Active Galactic Nuclei. University of Pennsylvania
 University of Pennsylvania April 16, 2007 GALAXY MERGERS: Joel R. Primack (UCSC) Thomas J. Cox (UCSC CfA) Patrik Jonsson (UCSC) Jennifer Lotz (UCSC Arizona) Simulations, Observations, and Active Galactic
University of Pennsylvania April 16, 2007 GALAXY MERGERS: Joel R. Primack (UCSC) Thomas J. Cox (UCSC CfA) Patrik Jonsson (UCSC) Jennifer Lotz (UCSC Arizona) Simulations, Observations, and Active Galactic
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33
 Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments. S. Oey
 The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments S. Oey It has been known for decades that superbubbles generated by massive star winds and supernovae are smaller than expected based on
The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments S. Oey It has been known for decades that superbubbles generated by massive star winds and supernovae are smaller than expected based on
Cosmological Background Radiation and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Opacity
 Cosmological Background Radiation and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Opacity Rudy Gilmore SISSA TeV Particle Astrophysics July 21, 2010 Collaborators: Joel Primack - UCSC Rachel Somerville - STScI (Baltimore)
Cosmological Background Radiation and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Opacity Rudy Gilmore SISSA TeV Particle Astrophysics July 21, 2010 Collaborators: Joel Primack - UCSC Rachel Somerville - STScI (Baltimore)
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation! Star Formation Efficiency!
 Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION
 Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Lecture Presentation 14.0 the Milky Way galaxy How do we know the Milky Way exists? We can see it even though
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Lecture Presentation 14.0 the Milky Way galaxy How do we know the Milky Way exists? We can see it even though
Cosmological simulations of galaxy formation. Romain Teyssier
 Cosmological simulations of galaxy formation 1 Outline Disc formation in LCDM cosmology Star formation efficiency and morphology connection The baryon fraction problem Star formation at high redshift:
Cosmological simulations of galaxy formation 1 Outline Disc formation in LCDM cosmology Star formation efficiency and morphology connection The baryon fraction problem Star formation at high redshift:
LECTURE 1: Introduction to Galaxies. The Milky Way on a clear night
 LECTURE 1: Introduction to Galaxies The Milky Way on a clear night VISIBLE COMPONENTS OF THE MILKY WAY Our Sun is located 28,000 light years (8.58 kiloparsecs from the center of our Galaxy) in the Orion
LECTURE 1: Introduction to Galaxies The Milky Way on a clear night VISIBLE COMPONENTS OF THE MILKY WAY Our Sun is located 28,000 light years (8.58 kiloparsecs from the center of our Galaxy) in the Orion
Violent Disk Instability Inflow to Spheroid and Black Hole
 Violent Disk Instability Inflow to Spheroid and Black Hole Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Jerusalem Winter School 101/13 Lecture stars 5 kpc Outline 1. Violent Disk Instability (VDI):
Violent Disk Instability Inflow to Spheroid and Black Hole Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Jerusalem Winter School 101/13 Lecture stars 5 kpc Outline 1. Violent Disk Instability (VDI):
Our goals for learning: 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. We see our galaxy edge-on. Primary features: disk, bulge, halo, globular clusters All-Sky View
 Our Galaxy Chapter 19 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed What does our galaxy look like? What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? Seventh Edition Our Galaxy
Our Galaxy Chapter 19 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed What does our galaxy look like? What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? Seventh Edition Our Galaxy
2008 ASPEN WINTER WORKSHOP The first 2 billion years of Galaxy Formation. Gustavo Yepes Universidad Autónoma de Madrid
 2008 ASPEN WINTER WORKSHOP The first 2 billion years of Galaxy Formation Gustavo Yepes Universidad Autónoma de Madrid MNCP The MareNostrum Numerical Cosmology Project International collaboration to perform
2008 ASPEN WINTER WORKSHOP The first 2 billion years of Galaxy Formation Gustavo Yepes Universidad Autónoma de Madrid MNCP The MareNostrum Numerical Cosmology Project International collaboration to perform
The Galaxy. (The Milky Way Galaxy)
 The Galaxy (The Milky Way Galaxy) Which is a picture of the Milky Way? A A is what we see from Earth inside the Milky Way while B is what the Milky Way might look like if we were far away looking back
The Galaxy (The Milky Way Galaxy) Which is a picture of the Milky Way? A A is what we see from Earth inside the Milky Way while B is what the Milky Way might look like if we were far away looking back
Galaxies. The majority of known galaxies fall into one of three major classes: spirals (78 %), ellipticals (18 %) and irregulars (4 %).
 Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Gas accretion in Galaxies
 Massive Galaxies Over Cosmic Time 3, Tucson 11/2010 Gas accretion in Galaxies Dušan Kereš TAC, UC Berkeley Hubble Fellow Collaborators: Romeel Davé, Mark Fardal, C.-A. Faucher-Giguere, Lars Hernquist,
Massive Galaxies Over Cosmic Time 3, Tucson 11/2010 Gas accretion in Galaxies Dušan Kereš TAC, UC Berkeley Hubble Fellow Collaborators: Romeel Davé, Mark Fardal, C.-A. Faucher-Giguere, Lars Hernquist,
THE ROLE OF RADIATION PRESSURE IN HIGH-Z DWARF GALAXIES
 THE ROLE OF RADIATION PRESSURE IN HIGH-Z DWARF GALAXIES John Wise (Georgia Tech) Tom Abel (Stanford), Michael Norman (UC San Diego), Britton Smith (Michigan State), Matthew Turk (Columbia) 14 Dec 2012
THE ROLE OF RADIATION PRESSURE IN HIGH-Z DWARF GALAXIES John Wise (Georgia Tech) Tom Abel (Stanford), Michael Norman (UC San Diego), Britton Smith (Michigan State), Matthew Turk (Columbia) 14 Dec 2012
Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei
 Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei A black hole is a region of spacetime from which gravity prevents anything, including light, from escaping. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently
Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei A black hole is a region of spacetime from which gravity prevents anything, including light, from escaping. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently
Joop Schaye (Leiden) (Yope Shea)
 Overview of sub-grid models in cosmological simulations Joop Schaye (Leiden) (Yope Shea) Length Scales (cm) Subgrid models Cosmological simulations 8 0 2 11 18 20 22 24 28 interparticle distance in stars
Overview of sub-grid models in cosmological simulations Joop Schaye (Leiden) (Yope Shea) Length Scales (cm) Subgrid models Cosmological simulations 8 0 2 11 18 20 22 24 28 interparticle distance in stars
A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation. Carlton Baugh Institute for Computational Cosmology
 A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation Carlton Baugh Institute for Computational Cosmology M81 Angel Lopez Sanchez A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation Lacey et al. 2015 arxiv:1509.08473
A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation Carlton Baugh Institute for Computational Cosmology M81 Angel Lopez Sanchez A unified multi-wavelength model of galaxy formation Lacey et al. 2015 arxiv:1509.08473
Two Phase Formation of Massive Galaxies
 Two Phase Formation of Massive Galaxies Focus: High Resolution Cosmological Zoom Simulation of Massive Galaxies ApJ.L.,658,710 (2007) ApJ.,697, 38 (2009) ApJ.L.,699,L178 (2009) ApJ.,725,2312 (2010) ApJ.,744,63(2012)
Two Phase Formation of Massive Galaxies Focus: High Resolution Cosmological Zoom Simulation of Massive Galaxies ApJ.L.,658,710 (2007) ApJ.,697, 38 (2009) ApJ.L.,699,L178 (2009) ApJ.,725,2312 (2010) ApJ.,744,63(2012)
Solving. Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics
 Solving Constraining galaxy formation with gaseous halos Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics X-ray Vision workshop:
Solving Constraining galaxy formation with gaseous halos Andrey Kravtsov The University of Chicago Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics X-ray Vision workshop:
University of California High-Performance AstroComputing Center JOEL PRIMACK UCSC
 University of California High-Performance AstroComputing Center JOEL PRIMACK UCSC http://hipacc.ucsc.edu/ As computing and observational power continue to increase rapidly, the most difficult problems
University of California High-Performance AstroComputing Center JOEL PRIMACK UCSC http://hipacc.ucsc.edu/ As computing and observational power continue to increase rapidly, the most difficult problems
A100 Exploring the Universe: The Milky Way as a Galaxy. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100 Exploring the Universe: The Milky Way as a Galaxy Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100-mdw@courses.umass.edu November 12, 2014 Read: Chap 19 11/12/14 slide 1 Exam #2 Returned and posted tomorrow
A100 Exploring the Universe: The Milky Way as a Galaxy Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100-mdw@courses.umass.edu November 12, 2014 Read: Chap 19 11/12/14 slide 1 Exam #2 Returned and posted tomorrow
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Chapter 21 Galaxy Evolution. How do we observe the life histories of galaxies?
 Chapter 21 Galaxy Evolution How do we observe the life histories of galaxies? Deep observations show us very distant galaxies as they were much earlier in time (old light from young galaxies). 1 Observing
Chapter 21 Galaxy Evolution How do we observe the life histories of galaxies? Deep observations show us very distant galaxies as they were much earlier in time (old light from young galaxies). 1 Observing
Lecture 25 The Milky Way Galaxy November 29, 2017
 Lecture 25 The Milky Way Galaxy November 29, 2017 1 2 Size of the Universe The Milky Way galaxy is very much larger than the solar system Powers of Ten interactive applet 3 Galaxies Large collections of
Lecture 25 The Milky Way Galaxy November 29, 2017 1 2 Size of the Universe The Milky Way galaxy is very much larger than the solar system Powers of Ten interactive applet 3 Galaxies Large collections of
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau
 Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Dust radiative transfer modelling. Maarten Baes
 Dust radiative transfer modelling Maarten Baes Outline 1. Dust radiative transfer: what and why? 2. 3D radiative transfer: how? 3. Simple mock galaxies 4. More realistic mock galaxies 5. Inverse radiative
Dust radiative transfer modelling Maarten Baes Outline 1. Dust radiative transfer: what and why? 2. 3D radiative transfer: how? 3. Simple mock galaxies 4. More realistic mock galaxies 5. Inverse radiative
University of California AstroComputing Institute, Supercomputer Simulations,
 University of California AstroComputing Institute, Supercomputer Simulations, Using GPUs for Visualization Joel Primack University of California, Santa Cruz Topics New University of California AstroComputing
University of California AstroComputing Institute, Supercomputer Simulations, Using GPUs for Visualization Joel Primack University of California, Santa Cruz Topics New University of California AstroComputing
Multi-scale and multi-physics numerical models of galaxy formation
 Multi-scale and multi-physics numerical models of galaxy formation M. Rieder and RT, 2016, MNRAS, 457, 1722 J. Rosdahl, J. Schaye, RT and O. Agertz, 2015, MNRAS, 451, 34 RAMSES: parallel Adaptive Mesh
Multi-scale and multi-physics numerical models of galaxy formation M. Rieder and RT, 2016, MNRAS, 457, 1722 J. Rosdahl, J. Schaye, RT and O. Agertz, 2015, MNRAS, 451, 34 RAMSES: parallel Adaptive Mesh
Gas 1: Molecular clouds
 Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
View of the Galaxy from within. Lecture 12: Galaxies. Comparison to an external disk galaxy. Where do we lie in our Galaxy?
 Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
The Milky Way. Overview: Number of Stars Mass Shape Size Age Sun s location. First ideas about MW structure. Wide-angle photo of the Milky Way
 Figure 70.01 The Milky Way Wide-angle photo of the Milky Way Overview: Number of Stars Mass Shape Size Age Sun s location First ideas about MW structure Figure 70.03 Shapely (~1900): The system of globular
Figure 70.01 The Milky Way Wide-angle photo of the Milky Way Overview: Number of Stars Mass Shape Size Age Sun s location First ideas about MW structure Figure 70.03 Shapely (~1900): The system of globular
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Central dark matter distribution in dwarf galaxies
 Central dark matter distribution in dwarf galaxies Se-Heon Oh (ICRAR/UWA) Content cusp/core controversy in ΛCDM simulations Dark matter distribution of THINGS dwarf galaxies High-resolution N-body+SPH
Central dark matter distribution in dwarf galaxies Se-Heon Oh (ICRAR/UWA) Content cusp/core controversy in ΛCDM simulations Dark matter distribution of THINGS dwarf galaxies High-resolution N-body+SPH
Dust. The four letter word in astrophysics. Interstellar Emission
 Dust The four letter word in astrophysics Interstellar Emission Why Dust Dust attenuates and scatters UV/optical/NIR Amount of attenuation and spectral shape depends on dust properties (grain size/type)
Dust The four letter word in astrophysics Interstellar Emission Why Dust Dust attenuates and scatters UV/optical/NIR Amount of attenuation and spectral shape depends on dust properties (grain size/type)
The Milky Way Galaxy
 1/5/011 The Milky Way Galaxy Distribution of Globular Clusters around a Point in Sagittarius About 00 globular clusters are distributed in random directions around the center of our galaxy. 1 1/5/011 Structure
1/5/011 The Milky Way Galaxy Distribution of Globular Clusters around a Point in Sagittarius About 00 globular clusters are distributed in random directions around the center of our galaxy. 1 1/5/011 Structure
Astronomy 114. Lecture 27: The Galaxy. Martin D. Weinberg. UMass/Astronomy Department
 Astronomy 114 Lecture 27: The Galaxy Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 27 18 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 25,26 Astronomy 114 1/23 Announcements Quiz #2: we re
Astronomy 114 Lecture 27: The Galaxy Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 27 18 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 25,26 Astronomy 114 1/23 Announcements Quiz #2: we re
Chapter 19: Our Galaxy
 Chapter 19 Lecture Chapter 19: Our Galaxy Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like?
Chapter 19 Lecture Chapter 19: Our Galaxy Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like?
Components of Galaxies Gas The Importance of Gas
 Components of Galaxies Gas The Importance of Gas Fuel for star formation (H 2 ) Tracer of galaxy kinematics/mass (HI) Tracer of dynamical history of interaction between galaxies (HI) The Two-Level Atom
Components of Galaxies Gas The Importance of Gas Fuel for star formation (H 2 ) Tracer of galaxy kinematics/mass (HI) Tracer of dynamical history of interaction between galaxies (HI) The Two-Level Atom
Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is our own galaxy viewed from the inside. It is a vast collection of more than 200 billion stars, planets, nebulae, clusters, dust and gas. Our own sun and
Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is our own galaxy viewed from the inside. It is a vast collection of more than 200 billion stars, planets, nebulae, clusters, dust and gas. Our own sun and
Advanced Cosmological Simulations
 Advanced Cosmological Simulations John Wise (Georgia Tech) Enzo Workshop 19 Oct 2013 1 Outline We will consider additional physics in Thursday s AMR (no nested grids) cosmology simulation. Refresher on
Advanced Cosmological Simulations John Wise (Georgia Tech) Enzo Workshop 19 Oct 2013 1 Outline We will consider additional physics in Thursday s AMR (no nested grids) cosmology simulation. Refresher on
Geometrically Thick Dust Layer in Edge-on Galaxies
 Geometrically Thick Dust Layer in Edge-on Galaxies A Case Study of NGC 891! Kwang-Il Seon 1, Adolf N. Witt 2, Jong-Ho Shinn 1, & Il-Joong Kim 1!! 1 Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute! 2 University
Geometrically Thick Dust Layer in Edge-on Galaxies A Case Study of NGC 891! Kwang-Il Seon 1, Adolf N. Witt 2, Jong-Ho Shinn 1, & Il-Joong Kim 1!! 1 Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute! 2 University
Dark Matter. ASTR 333/433 Spring Today Stars & Gas. essentials about stuff we can see. First Homework on-line Due Feb. 4
 Dark Matter ASTR 333/433 Spring 2016 Today Stars & Gas essentials about stuff we can see First Homework on-line Due Feb. 4 Galaxies are made of stars - D. Silva (1990) private communication Stars Majority
Dark Matter ASTR 333/433 Spring 2016 Today Stars & Gas essentials about stuff we can see First Homework on-line Due Feb. 4 Galaxies are made of stars - D. Silva (1990) private communication Stars Majority
Our Galaxy. We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky.
 Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 8. Angular Momentum & the Cusp/Core Problem
 Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 8 Angular Momentum & the Cusp/Core Problem Summary to Date We first learned how to construct the Power Spectrum with CDM+baryons. Found CDM agrees with the observed Power Spectrum
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 8 Angular Momentum & the Cusp/Core Problem Summary to Date We first learned how to construct the Power Spectrum with CDM+baryons. Found CDM agrees with the observed Power Spectrum
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 23. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 23 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Units of Chapter 23 23.1 Our Parent Galaxy 23.2 Measuring the Milky Way Discovery 23-1 Early Computers
Lecture Outlines Chapter 23 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Units of Chapter 23 23.1 Our Parent Galaxy 23.2 Measuring the Milky Way Discovery 23-1 Early Computers
Superbubble Feedback in Galaxy Formation
 Superbubble Feedback in Galaxy Formation Ben Keller (McMaster University) James Wadsley, Samantha Benincasa, Hugh Couchman Paper: astro-ph/1405.2625 (Accepted MNRAS) Keller, Wadsley, Benincasa & Couchman
Superbubble Feedback in Galaxy Formation Ben Keller (McMaster University) James Wadsley, Samantha Benincasa, Hugh Couchman Paper: astro-ph/1405.2625 (Accepted MNRAS) Keller, Wadsley, Benincasa & Couchman
ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 We observe star-gas-star cycle operating in Milky Way s disk using many different wavelengths of light! ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Infrared light reveals stars whose visible light
We observe star-gas-star cycle operating in Milky Way s disk using many different wavelengths of light! ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Infrared light reveals stars whose visible light
Structure of Dark Matter Halos
 Structure of Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos profiles: DM only: NFW vs. Einasto Halo concentration: evolution with time Dark matter halos profiles: Effects of baryons Adiabatic contraction Cusps and
Structure of Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos profiles: DM only: NFW vs. Einasto Halo concentration: evolution with time Dark matter halos profiles: Effects of baryons Adiabatic contraction Cusps and
Stellar Life Cycle in Giant Galactic Nebula NGC 3603
 Stellar Life Cycle in Giant Galactic Nebula NGC 3603 edited by David L. Alles Western Washington University e-mail: alles@biol.wwu.edu Last Updated 2009-11-20 Note: In PDF format most of the images in
Stellar Life Cycle in Giant Galactic Nebula NGC 3603 edited by David L. Alles Western Washington University e-mail: alles@biol.wwu.edu Last Updated 2009-11-20 Note: In PDF format most of the images in
Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation
 Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation The interstellar medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation The interstellar medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
PART 3 Galaxies. Gas, Stars and stellar motion in the Milky Way
 PART 3 Galaxies Gas, Stars and stellar motion in the Milky Way The Interstellar Medium The Sombrero Galaxy Space is far from empty! Clouds of cold gas Clouds of dust In a galaxy, gravity pulls the dust
PART 3 Galaxies Gas, Stars and stellar motion in the Milky Way The Interstellar Medium The Sombrero Galaxy Space is far from empty! Clouds of cold gas Clouds of dust In a galaxy, gravity pulls the dust
Chapter 19 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Our Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 19 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: Where are we located within our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like?
Chapter 19 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: Where are we located within our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like?
BROCK UNIVERSITY. Test 2, March 2015 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02 Number of Students: 420 Date of Examination: March 5, 2015
 BROCK UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 9 Test 2, March 2015 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02 Number of Students: 420 Date of Examination: March 5, 2015 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 18:00 18:50
BROCK UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 9 Test 2, March 2015 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02 Number of Students: 420 Date of Examination: March 5, 2015 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 18:00 18:50
What do we need to know about galaxy formation?
 What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
Galaxy Formation: Overview
 Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
The Birth Of Stars. How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation
 Goals: The Birth Of Stars How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation Interstellar Medium Gas and dust between stars is the interstellar
Goals: The Birth Of Stars How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation Interstellar Medium Gas and dust between stars is the interstellar
ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies We observe star-gas-star cycle operating in Milky Way s disk using many different wavelengths of light Infrared light reveals stars whose visible light
ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies We observe star-gas-star cycle operating in Milky Way s disk using many different wavelengths of light Infrared light reveals stars whose visible light
A Unified Model for AGN. Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006
 A Unified Model for AGN Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006 Overview Introduction to AGN Evidence for unified model Structure Radiative transfer models for dusty torus Active Galactic Nuclei Emission-line
A Unified Model for AGN Ryan Yamada Astro 671 March 27, 2006 Overview Introduction to AGN Evidence for unified model Structure Radiative transfer models for dusty torus Active Galactic Nuclei Emission-line
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines!
 Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem. Presented by: Michael Solway
 Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem Presented by: Michael Solway Papers 1. Vitvitska, M. et al. 2002, The origin of angular momentum in dark matter halos, ApJ 581: 799-809 2. D Onghia, E. 2008,
Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem Presented by: Michael Solway Papers 1. Vitvitska, M. et al. 2002, The origin of angular momentum in dark matter halos, ApJ 581: 799-809 2. D Onghia, E. 2008,
Growing and merging massive black holes
 Growing and merging massive black holes Marta Volonteri Institut d Astrophysique de Paris S. Cielo (IAP) R. Bieri (MPA) Y. Dubois (IAP) M. Habouzit (Flatiron Institute) T. Hartwig (IAP) H. Pfister (IAP)
Growing and merging massive black holes Marta Volonteri Institut d Astrophysique de Paris S. Cielo (IAP) R. Bieri (MPA) Y. Dubois (IAP) M. Habouzit (Flatiron Institute) T. Hartwig (IAP) H. Pfister (IAP)
Galaxy Evolution & Black-Hole Growth (review)
 Galaxy Evolution & Black-Hole Growth (review) Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Delivered by Fangzhou Jiang Dali, China, November 2018 See also Claude-Andre s talk and Joel s talk
Galaxy Evolution & Black-Hole Growth (review) Avishai Dekel The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & UCSC Delivered by Fangzhou Jiang Dali, China, November 2018 See also Claude-Andre s talk and Joel s talk
The Milky Way Galaxy and Interstellar Medium
 The Milky Way Galaxy and Interstellar Medium Shape of the Milky Way Uniform distribution of stars in a band across the sky lead Thomas Wright, Immanuel Kant, and William Herschel in the 18th century to
The Milky Way Galaxy and Interstellar Medium Shape of the Milky Way Uniform distribution of stars in a band across the sky lead Thomas Wright, Immanuel Kant, and William Herschel in the 18th century to
Gas Accretion & Outflows from Redshift z~1 Galaxies
 Gas Accretion & Outflows from Redshift z~1 Galaxies David C. Koo Kate Rubin, Ben Weiner, Drew Phillips, Jason Prochaska, DEEP2, TKRS, & AEGIS Teams UCO/Lick Observatory, University of California, Santa
Gas Accretion & Outflows from Redshift z~1 Galaxies David C. Koo Kate Rubin, Ben Weiner, Drew Phillips, Jason Prochaska, DEEP2, TKRS, & AEGIS Teams UCO/Lick Observatory, University of California, Santa
The Dark Matter - Galaxy Connection: HOD Estimation from Large Volume Hydrodynamical Simulations
 The Dark Matter - Galaxy Connection: HOD Estimation from Large Volume Hydrodynamical Simulations J. CASADO GÓMEZ (UAM) R. DOMÍNGUEZ-TENREIRO J. OÑORBE (UCA/Irvine) F. MARTINEZ - SERRANO (UMH) A. KNEBE
The Dark Matter - Galaxy Connection: HOD Estimation from Large Volume Hydrodynamical Simulations J. CASADO GÓMEZ (UAM) R. DOMÍNGUEZ-TENREIRO J. OÑORBE (UCA/Irvine) F. MARTINEZ - SERRANO (UMH) A. KNEBE
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics
 Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
Radiation-hydrodynamics from Mpc to sub-pc scales with RAMSES-RT
 Radiation-hydrodynamics from Mpc to sub-pc scales with RAMSES-RT Joki Rosdahl Centre de Recherche Astrophysique de Lyon With Aubert, Blaizot, Bieri, Biernacki, Commercon, Costa, Dubois, Geen, Katz, Kimm,
Radiation-hydrodynamics from Mpc to sub-pc scales with RAMSES-RT Joki Rosdahl Centre de Recherche Astrophysique de Lyon With Aubert, Blaizot, Bieri, Biernacki, Commercon, Costa, Dubois, Geen, Katz, Kimm,
Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing SMBH Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model
 Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing SMBH Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model Motohiro ENOKI (National Astronomical Observatory of Japan) Kaiki Taro INOUE (Kinki University) Masahiro NAGASHIMA
Gravitational Radiation from Coalescing SMBH Binaries in a Hierarchical Galaxy Formation Model Motohiro ENOKI (National Astronomical Observatory of Japan) Kaiki Taro INOUE (Kinki University) Masahiro NAGASHIMA
9. Evolution with redshift - z > 1.5. Selection in the rest-frame UV
 11-5-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c09-1 11-5-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c09-2 9. Evolution with redshift - z > 1.5 Selection in
11-5-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c09-1 11-5-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c09-2 9. Evolution with redshift - z > 1.5 Selection in
 ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI I. AN INTRODUCTION Sebastian F. Hoenig Lecturer & Marie Curie Fellow Outline and learning goals I. Phenomenology What are AGN? How are they identified? II. Energy output Where is
ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI I. AN INTRODUCTION Sebastian F. Hoenig Lecturer & Marie Curie Fellow Outline and learning goals I. Phenomenology What are AGN? How are they identified? II. Energy output Where is
Number of Stars: 100 billion (10 11 ) Mass : 5 x Solar masses. Size of Disk: 100,000 Light Years (30 kpc)
 THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
Survey of Astrophysics A110
 Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Galaxies with Active Nuclei. Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes
 Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Galaxies with Active Nuclei Active Galactic Nuclei Seyfert Galaxies Radio Galaxies Quasars Supermassive Black Holes Active Galactic Nuclei About 20 25% of galaxies do not fit well into Hubble categories
Chapter 19 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective. Seventh Edition. Our Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 19 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: Where are we located within our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like? How do stars
Chapter 19 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: Where are we located within our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like? How do stars
A Monster at any other Epoch:
 A Monster at any other Epoch: Are Intermediate Redshift ULIRGs the Progenitors of QSO Host Galaxies? Barry Rothberg Large Binocular Telescope Observatory/George Mason University Co-Is: J. Fischer (NRL),
A Monster at any other Epoch: Are Intermediate Redshift ULIRGs the Progenitors of QSO Host Galaxies? Barry Rothberg Large Binocular Telescope Observatory/George Mason University Co-Is: J. Fischer (NRL),
