High Energy Large Area Surveys,
|
|
|
- Victoria Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 High Energy Large Area Surveys, the history of accretion in the Universe and galaxy evolution Fabrizio Fiore and the HELLAS2XMM collaboration: (A. Baldi, M. Brusa, N. Carangelo, P. Ciliegi, F. Cocchia, A. Comastri, V. D Elia, C. Feruglio, F. La Franca, R. Maiolino, G. Matt, M. Mignoli, S. Molendi, G.C. Perola, S. Puccetti, C. Vignali) + M. Elvis, P. Severgnini, N. Sacchi, N. Menci, A. Cavaliere, G. Pareschi, O. Citterio...
2 Hard X-ray Surveys Most direct probe of the super-massive black hole (SMBH) accretion activity, recorded in the CXB spectral energy density SMBH census Strong constraints to models for the formation and evolution of structure in the Universe AGN number and luminosity evolution AGN clustering and its evolution
3 The Cosmic X-ray Background
4 Hard X-ray Surveys Most direct probe of the super-massive black hole (SMBH) accretion activity, recorded in the CXB spectral energy density SMBH census Strong constraints to models for the formation and evolution of structure in the Universe AGN number and luminosity evolution AGN clustering and its evolution
5
6 Optical (and soft X-ray) surveys gives values 2-3 times lower than those obtained from the CXB (and of the F.&M. and G. et al. estimates)
7 Hard X-ray Surveys Most direct probe of the super-massive black hole (SMBH) accretion activity, recorded in the CXB spectral energy density SMBH census Strong constraints to models for the formation and evolution of structure in the Universe AGN number and luminosity evolution AGN clustering and its evolution
8 XMM/Chandra Surveys Wide and medium-deep 2 several deg sources/xmm field, Fx % of the CXB LX-Z diagram coverage Rare and peculiar sources, avoid cosmic variance Relatively easy multiwavelength follow-up (ESOVLT,3.6m, ATCA, VLA, TNG & Chandra) HELLAS2XMM CDFN CDFS Lockman Hole
9 Some 2-10 kev surveys CDFN-CDFS 0.03deg2-16 XMM LH 0.12deg 2 50% z spec. XMM/ELAIS 0.5deg 2 Cont. XMM/COSMOS 2deg 2 Cont. Log Flux CHAMP - SEXSI % z spec.? Kim/Green/Wilkes Harrison/Helfand 1-10 deg2 HELLAS2XMM 1-4deg2 80% z spec. -13 XMM BSS-HS 25deg 2-12 nearly 100% z spec. Caccianiga/Della Ceca 2004
10 The HELLAS2XMM survey deg2 of sky covered, keV sources down to F 2-10keV= cgs - nearly complete photometry down to R~25 - nearly complete spectroscopy down to R~24: 160 z broad line AGN; 41 narrow line AGN and gal. 16 have loglx>44 QSO2! - 11 XBONGs; 1 star; 3 groups of galaxies - 40 sources with X/O>8, 19 z - 6 broad line AGN; 13 narrow line AGN (12 QSO2!) Fiore et al A&A, Cocchia et al. in preparation
11 X-ray to optical flux ratio 15-20% of the sources have X/O>10 over a large flux range 30-40% have X/O>3. Optical identification of sources with X/O>3-10 is possible in the shallower surveys! HELLAS2XMM CDFN SSA13 Large area surveys at Fx can be used to gain info on the fainter sources, making the remaining half of the CXB!!! Lockman Hole
12 High X/O = QSO2! Mignoli, Cocchia et al. 2004
13 X-ray obscured AGN Perola, Puccetti et al A&A PKS0312_22 PKS0537_111 QSO1 z=2.14 X/O=3.1 R=25 X/O=50 lognh=22.8 lognh 23 PKS0537_153 R>25 X/O>21 lognh 23 PKS0537_11a QSO2 z=0.981 LX=44.2 X/O=30 lognh=22.2
14 XBONGs O = type 1 AGN =type 2 AGN = Early type Gals.
15 The HELLAS2XMM survey in a context HELLAS2XMM 1.5 deg2-232 sources F2-10keV cgs Fiore et al Lockman Hole deg2-55 sources F2-10keV cgs (Mainieri et al 2002) CDFN deg2-88 sources F2-10keV cgs CDFN deg2-44 sources F2-10keV cgs (Barger et al. 2002) CDFS deg2-80 sources F2-10keV cgs CDFS deg2-43 sources F2-10keV cgs SSA deg2-20 sources F2-10keV cgs Barger et al HEAO1 (Grossan) - 26,000 deg2-63 sources F2-10keV cgs
16 452 sources (Hellas2XMM + LH + CDFN + CDFS +SSA13) -15<logFx<-13.3, 304 z-spec + (29 z-phot) Broad line AGN Non Broad line AGN Fiore et al A&A
17 X/O of optically obscured AGN
18 X/O of optically obscured AGN (including EROs photo-z limits from Mignoli et al. 2004)
19 X/O-LX X-photometric z! z/(1+z)= opticaly obscured AGN with logl(2-10)>42 from H2, CDFS, CDFN, LH and SSA13 with robust z-spec.
20 High z optically obscured AGN
21 High z optically obscured AGN: the X-ray K correction 2 3 Z=4
22 High X/O = high NH QSO2! EROs Unobscured Obscured Perola et al. 2004
23 Luminosity Function and Redshift distribution Combined sample (Opt + stat. ids) all fluxes 10-15<F(2-10keV)<10-14 cgs
24 The evolution of number and luminosity densities Non parametric determination Fiore et al A&A
25 Black hole mass density A ~ 5x1039 erg s-1mpc-3 A (1- ) LBol. BH ~ c2 =0.1 LX LBol/LX=40. BH ~ 3x10-5 M? Yr-1 Mpc-3 BH ~ 4x105 M? Mpc-3
26 2-10 kev AGN luminosity function models Solid = observed dashed = best fit LDDE with constant NH distribution La Franca et al. 2005
27 2-10 kev AGN luminosity function models LDDE with variable absorbed AGN fraction La Franca et al. 2005
28 Fraction of obscured AGN La Franca et al. 2005
29
30 Type 2 QSOs number density
31 Lx-z plane: source number density
32 Comparison with CDM HC models Menci,Fiore,Perola & Cavaliere 2004 Processes of galaxy formation and evolution described by a semianalytic model. Galaxy interactions: main triggers of accretion (Cavaliere & Vittorini 2000) L(2-10keV)=0.01 L(bol.) no other parameter tuning
33
34
35
36
37 Comparison with CDM HC models Menci,Fiore,Perola & Cavaliere 2004
38 CXB Resolved fraction LogL< <LogL<44.5 LogL>44.5 Menci et al 2004
39 Summary most of the CXB <6-8keV is resolved in sources Black Hole mass density ~2 times higher than that estimated from optical and soft X-rays: better agreement with CXB estimates and with local space density Differential evolution of number and luminosity densities. Nice agreement between the evolution of luminous QSO and CDM HC models. Problems with low luminosity AGN? Revision of Unified Schemes
40 Revision of Unified Schemes Mild.
41 Revision of Unified Schemes Strong: Low L Seyfers and powerful QSO: different populations. A working scenario: Seyferts associated to galaxies with merging histories characterized by small mass progenitors. Feedback is effective in self-regulating accretion and SF, cold gas is left available for subsequent nuclear activation produced by loose galaxy encounters (fly-by). QSOs associated to galaxies with large mass progenitors. Feedback is less effective, most gas is quickly converted in stars and accreted during a few major mergers at high Eddington rates. The obscuration properties of the two populations can be different in term of geometry, gas density, covering factor, ionization state, metallicity, dust content etc..
42 What s next? 1) Paucity of high z loglx<44.5 sources? Real or are we missing highly obscured AGNs? 2) Compare the obscuration properties of Seyfert 2 galaxies and QSO2 3) Deconvolve accr. rate and BH mass: 4) Seyfert-QSO/galaxy clustering and its evolution
43 1) Paucity of Seyfert like z>1 is real? Or, is it, at least partly, a selection effect? Are we missing in Chandra and XMM surveys highly obscured (NH 1024 cm-2) AGN? Which are common in the local Universe
44 Imaging surveys up to 8-10 kev (ASCA,BSAX, Chandra, XMM): most of the CXB <6-7 kev is resolved in sources. But only 40-50% in the 5-10 kev band. Few % E>10keV. The light-up and evolution of obscured accreting SMBH is still largely unknown Worsley et a. 2004
45 What s needed? Sensitive observations at the peak of the CXB (~20-40 kev) to probe highly X-ray obscured AGN But.. How deep should we go? and how hard should we go?
46 Residual CXB after subtracting the resolved fraction below 10 kev Comastri 2004 We need to resolve: 80% of (similar to Chandra and XMM deep fields below 10 kev) 50% of 20-40keV
47 CXB fraction >50% res.cxb >80% res.cxb F(20-40keV)< cgs or 0.75 µcrab cgs or 0.1 µcrab F(10-30keV)< cgs or 0.65 µcrab cgs or 0.13 µcrab
48 What s next (3) Franceschini et al Marconi et al 2004 Deconvolve accr. rate and BH mass: Optically unobscured AGN: MBH from broad line FWHM Optically obscured AGN: MBH from bulge light
49 Unobscured sources A detailed spectral analysis allows to make use of the correlations between FWHM of the broad emission lines and BH masses Spectroscopy FWHM emission lines MBH Mclure & Jarvis 2002 Vestergaard 2002
50 Obscured sources The nucleus is obscured so we can study the host galaxy Imaging Morphology Bulge MBH Mc Lure et al Log(MBH/Mo) = -0.5 MR 2.96
51 Hellas2XMM BPM16274 #69 B/T = 1 Pks0312 #31 B/T = 0.8
52 The GOODS sample We extended our analisys to a sample of optically obscured sources in the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS) fields taking advantage of the superior quality of the HST images Z band Ks band
53 B/T =0.39 B/T =0.5
54 MBH, L/LEDD of obscured and unobscured AGN * = broad line AGN
55 What s next (4) AGN clustering D Elia et al. 2004
56 AGN clustering D Elia et al =10
57 ELAIS S1 XMM-SWIRE X-ray sources clustering and evolution XMM PN+MOS 50ks net expo. 0.5 deg2 479 X-ray sources R=16.8 R=17.1
58 FX= cgs
59 ELAIS S1 XMM-SWIRE 6 extended sources in the 0.5 deg2 field R=19.5 FX= R=20.3
60 XMM survey of ELAIS S1: detections Palermo waveleth detection algorithm: kev 479 sources 396 with optical counterpart (85 %) 2-10 kev 204 sources with optical counterpart (92.5%) 30 have X/O>10 (15%) 5 sources not detected in the kev band kev 371 sources 28 sources not detected in the kev band 5-10 kev 31 sources
61 ELAIS-S1 number counts Unobscured Obscured
62 Clustering in the ELAIS-S1 field 2-10 kev: 0=11+/-6 arcsec 0.5-2keV 0=4+/-2.5 arcsec
63 What s next How galaxy activity traces the cosmic WEB (direct comparison with models for the evolution of the structure in the universe) COSMOS! ACS-XMM-VIMOS-Chandra
64 COSMOS multiwavelength project COSMOS is an HST/ACS Treasury project (..) Goal: Interplay between Large Scake Structure, evolution and formation of galaxies, dark matter and AGNs Need to go to larger scales 2 sq. deg.
65 COSMOS project: overview MULTIWAVELENGTH DATA Scheduled/observed: HST/ACS (600 orbits), XMM-Newton (0.8 Ms), SUBARU (b,v,r,i,z), VLA, GALEX, CFHT, Mambo proposed: Chandra (1.4 Ms), XMM (additional 0.8 Ms) + Spitzer (200 orbits), VLT/VIMOS (70 nights)
66 800 ksec XMM-Newton Cosmos field PI: G. Hasinger; 25 pointings 32 ksec each XMM pn true color image (courtesy I. Lehmann)
67
68 Direct Imaging at E=10-80 kev 1µCrab = 250 sources deg2 = 12 sources X 15 diam. FOV 0.5 µcrab = 550 deg2 = 27 sources X 15 diam. FOV 0.1µCrab = 2350 deg2 = 120 sources X 15 diam. FOV
69 Designing a mission concept: Goals?µCrab sensitivity, FOV; 1 µcrab=0.2 cts/msec/cm kev; S/N=3, Csource=Cbkg cts/msec Aeff 30 kev. 20 T. Area - grazing angle - t. diameter/focal length mirror coating tradeoffs: Aeff FL inc R F = focal lenght R = reflectivity L = mirror height θ= inclination angle
70 Possible solutions based on Wolter-1 design: Telescope 60cm diameter, <0.1deg, long focal lenght, e.g m, small A/F.L. e.g Vs (XMM e Chandra): SIMBOL-X baseline Focal plane of 5-8 FWHM Telescope 30cm diameter deg, 8-12m F.L., + multilayer coatings + multiple units: HEXIT-SAT Focal plane of FWHM Telescope 90cm diameter, deg, 20-30m F.L., + multilayer coatings: Simbol-X development study Focal plane of FWHM
71 Image quality: which PSF do we need? 50 HPD; eq. 2 Crab HPD Eq.2 Crab 1 15 HPD Eq.0.2 Crab
72 Image quality: which PSF do we need?
73 HEXIT-SAT 4 mirror modules (XMM technology) 8m focal length 33cm diameter 200 bilayers W/Si kev
74 HEXIT-SAT flux limit 1Msec: /3 µcrab 10-30keV 1/10 µcrab
75 Flux limits
76 Flux limits S/N=3 1Msec Markarian 3: a highly obscured (NH=5 1023cm-2), high luminosity (logl20-100kev=43.8) Seyfert at 60Mpc BeppoSAX MECS-PDS data Mark3 X 10 a QSO2
77 Flux limits S/N=3 1Msec Circinus galaxy: a nearby (4Mpc), highly obscured (NH=2 1024cm-2), low luminosity (logl20-100kev=41.7) AGN BeppoSAX MECS-PDS data Circinus X 100 a bright Seyfert
78 Flux limits S/N=3 1Msec NGC1068: a Compton thick (NH= 1025cm-2) AGN at 20 Mpc observed luminosity logl20-100kev=42, unobscured luminosity logl20-100kev? 44, A nearby QSO2??!! BeppoSAX MECS,PDS NGC1068 X 10 a QSO2
79 Possible solutions based on Wolter-1 design: Assume telescope diameter <60cm <0.1deg, long focal lenght, e.g m, small A/F.L. e.g Vs (XMM e Chandra) Focal plane of 5-8 FWHM deg, 8-12m F.L., + multilayer coatings + multiple units Focal plane of FWHM
80 Wide band Multilayer (supermirrors) if the d-spacing is varied in a continuous way (supermirror) and the absorption is negligible (E > 10 kev) it is possible to reflection bands 34 times wider than those for total reflection in mirrors with a single layer of e.g. Au, Pt, Ir. The d-spacing follows a power law distribution: d(i) = a / (b+i)c i = bi-layer index a /(2 sin c) c 0.25 b> -1
81 Main characteristics Number of modules 4 Number of nested mirror shells 50 Reflecting coating Geometrical profile 200 bilayers W/Si Wolter I (lin. approx) Focal Length 8000 mm Total Shell Height 800 mm Plate scale Total Shell Height Material of the mirror walls Min-MaxTop Diameter 26 arcsec/mm 800 mm electroformed Ni mm Min - Max angle of incidence deg Min-Max wallweight thickness Total Mirror ( mm module) Field-of-View (diameter 65 FWHM) Single module effective area 15 arcmin 75 cm kev
82 XEUS-I Multilayer optimization From Pareschi & Cotroneo: 50m focal lenght 200 W/Si bi-layers on shells from 1.3m to 2.8m diameter. 30 W/Si bi-layers on shells From 2.8m to 4m kev
83 Background LEO Active shields instrument Sky+particle ind. Dark Earth BeppoSAX PDS: CXB Phoswich NaI(Tl) 3mm detector CsI(Na) 50mm active shield
84 Internal Background LEO Low inclination (4 degrees) orbit: low and regular background Total average BKG = cts/s/cm2/kev/mm PL average BKG = cts/s/cm2/kev/mm 13-60keV
85 Internal Background HEO Active shield instrument EXOSAT 200,000 km apogee 500 km perigee ME Argon 1-15 kev ME Xenon 5-50 kev 1.5cm thick ME Xenon total internal BKG kev = cts/s/detector cts/s/kev/cm2 = cts/s/kev/cm2/mm 10 times less than XMM MOS
86 Internal Background HEO Simulations From Armstrong et al Montecarlo for an L2 orbit Assuming 90% efficiency anticoincidences, total BKG= 10-4 cts/s/cm2/kev/mm Within a factor of 2 of that seen by EXOSAT ME 20 times less than XMM MOS 2-3 times higher than LEO low inclination orbit BKG
87 CXB from outside the FOV Reference PIB=10-4 counts/s/cm2/kev CXB(20-40keV)= erg/s/cm2/deg2 = ph/s/cm2/deg2 Det. Spot= (HPR/plate scale)2 #mod. Spot(HX)= (7.5 /260 /cm)2 4 = 0.01 cm2 Spot(Xeus)=(5 /41.3 /cm)2 = cm2 Spot(SXB)=(15 /69 /cm)2 = 0.15 cm2 Spot(SXM)=(7.5 /69 /cm)2 = cm2 CXB(HX) = counts/s/deg2 PIB(HX) = counts/s CXB(Xeus) = counts/s/deg2 PIB(Xeus) = counts/s CXB(SXB) = counts/s/deg2 PIB(SXB) = counts/s CXB(SXM) = counts/s/deg2 PIB(SXM) = counts/s
88
89
90
91 Conclusions To improve the present knowledge on the sources making the CXB, to have a more complete census of SMBH up to z=1-2, i.e. the golden age of AGN and galaxy activity, we should go down to fluxes where: 80% of the 10-30keV CXB is resolved in sources (0.1 Crab); 50% of the 20-40keV CXB is resolved in sources (0.75 Crab) This can be done with lightweight (<400kg), multilayer optics with Aeff 500 kev and 15 HPD
Scientific cases for Simbol-X of interest of the Italian community
 Scientific cases for Simbol-X of interest of the Italian community Based on the High Energy Astrophysics study: Fields of interest and perspective for the national community ASI 2003-2004 Fabrizio Fiore
Scientific cases for Simbol-X of interest of the Italian community Based on the High Energy Astrophysics study: Fields of interest and perspective for the national community ASI 2003-2004 Fabrizio Fiore
X ray Survey Results on AGN Physics and Evolution Niel Brandt
 X ray Survey Results on AGN Physics and Evolution Niel Brandt Chandra XMM Newton Photon statistics Hard response ACIS Best positions Highest sens. < 6 kev 50 250 times sens. of previous missions Good positions
X ray Survey Results on AGN Physics and Evolution Niel Brandt Chandra XMM Newton Photon statistics Hard response ACIS Best positions Highest sens. < 6 kev 50 250 times sens. of previous missions Good positions
The Bright Side of the X-ray Sky The XMM-Newton Bright Survey. R. Della Ceca. INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera,Milan
 The Bright Side of the X-ray Sky The XMM-Newton Bright Survey T. Maccacaro A. Caccianiga P. Severgnini V. Braito R. Della Ceca INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera,Milan On behalf of the XMM-Newton Survey
The Bright Side of the X-ray Sky The XMM-Newton Bright Survey T. Maccacaro A. Caccianiga P. Severgnini V. Braito R. Della Ceca INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera,Milan On behalf of the XMM-Newton Survey
Feeding the Beast. Chris Impey (University of Arizona)
 Feeding the Beast Chris Impey (University of Arizona) Note: the box is growing due to cosmic expansion but this is factored out. Heirarchical Structure Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Nuclear activity in
Feeding the Beast Chris Impey (University of Arizona) Note: the box is growing due to cosmic expansion but this is factored out. Heirarchical Structure Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Nuclear activity in
The quest for early Black Holes
 The quest for early Black Holes Andrea Comastri (INAF-Bologna) Roberto Gilli (INAF-Bologna) Cristian Vignali (Bologna University) Marcella Brusa (MPE) and many others Outline High redshift (z > 3) AGN
The quest for early Black Holes Andrea Comastri (INAF-Bologna) Roberto Gilli (INAF-Bologna) Cristian Vignali (Bologna University) Marcella Brusa (MPE) and many others Outline High redshift (z > 3) AGN
Results from the Chandra Deep Field North
 Results from the Chandra Deep Field North Brandt, Alexander, Bauer, Garmire, Hornschemeier, Immler, Lehmer, Schneider, Vignali, Wu, Barger, Cowie, Bautz, Nousek, Sargent, Townsley Chandra Deep Field North
Results from the Chandra Deep Field North Brandt, Alexander, Bauer, Garmire, Hornschemeier, Immler, Lehmer, Schneider, Vignali, Wu, Barger, Cowie, Bautz, Nousek, Sargent, Townsley Chandra Deep Field North
The Chandra COSMOS X-ray Survey
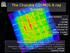 The Chandra COSMOS X-ray Survey Vital Statistics: 1.8 Ms 1/2sq.deg @160 ksec 1761 sources Dec 06-June 07 Catalog in press ApJS Martin Elvis, Francesca Civano, Aldcroft T., Fruscione A., Harvard Smithsonian
The Chandra COSMOS X-ray Survey Vital Statistics: 1.8 Ms 1/2sq.deg @160 ksec 1761 sources Dec 06-June 07 Catalog in press ApJS Martin Elvis, Francesca Civano, Aldcroft T., Fruscione A., Harvard Smithsonian
The quest for Type 2 quasars: What are the X-ray observations of optically selected QSOs2 telling us?
 The quest for Type 2 quasars: What are the X-ray observations of optically selected QSOs2 telling us? Cristian Vignali Dipartimento di Astronomia, Universita`degli Studi di Bologna In collaboration with
The quest for Type 2 quasars: What are the X-ray observations of optically selected QSOs2 telling us? Cristian Vignali Dipartimento di Astronomia, Universita`degli Studi di Bologna In collaboration with
X RAY EMITTING EROS AS TRACERS OF BLACK HOLES-GALAXIES COEVOLUTION
 1 X RAY EMITTING EROS AS TRACERS OF BLACK HOLES-GALAXIES COEVOLUTION M. Brusa 1, A. Comastri 2, E. Daddi 3, M. Mignoli 2, C. Vignali 4, G. Zamorani 2, F. Fiore 5, and L. Pozzetti 2 1 Max Planck Institut
1 X RAY EMITTING EROS AS TRACERS OF BLACK HOLES-GALAXIES COEVOLUTION M. Brusa 1, A. Comastri 2, E. Daddi 3, M. Mignoli 2, C. Vignali 4, G. Zamorani 2, F. Fiore 5, and L. Pozzetti 2 1 Max Planck Institut
Radiation Backgrounds Observations across the Electromagnetic Spectrum. Günther Hasinger, MPE Garching & TUM
 Radiation Backgrounds Observations across the Electromagnetic Spectrum Günther Hasinger, MPE Garching & TUM The History of Nuclear Black Holes in Galaxies Harvard University, May 18, 2006 WMAP mm Sky Backgrounds
Radiation Backgrounds Observations across the Electromagnetic Spectrum Günther Hasinger, MPE Garching & TUM The History of Nuclear Black Holes in Galaxies Harvard University, May 18, 2006 WMAP mm Sky Backgrounds
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 30 Jul 2004
 HEXIT-SAT: a mission concept for X-ray grazing incidence telescopes from 0.5 to 70 kev arxiv:astro-ph/0407647v1 30 Jul 2004 Fabrizio Fiore a, Giuseppe C. Perola b, Giovanni Pareschi c Oberto Citterio c,
HEXIT-SAT: a mission concept for X-ray grazing incidence telescopes from 0.5 to 70 kev arxiv:astro-ph/0407647v1 30 Jul 2004 Fabrizio Fiore a, Giuseppe C. Perola b, Giovanni Pareschi c Oberto Citterio c,
The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen,W-H Wang and Y. Yang
 The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen,W-H Wang and Y. Yang Active Galaxies (AKA quasars, Seyfert galaxies etc) are radiating massive black holes with L~10 8-10 14
The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen,W-H Wang and Y. Yang Active Galaxies (AKA quasars, Seyfert galaxies etc) are radiating massive black holes with L~10 8-10 14
A galaxy without its SMBH: implications for feedback
 A galaxy without its SMBH: implications for feedback Francesca Civano (SAO) M. Elvis, G. Lanzuisi,, L. Blecha, A. Loeb, T. Aldcroft, M. Trichas A. Bongiorno, M. Brusa, A. Comastri, M. Salvato, A. Fruscione,
A galaxy without its SMBH: implications for feedback Francesca Civano (SAO) M. Elvis, G. Lanzuisi,, L. Blecha, A. Loeb, T. Aldcroft, M. Trichas A. Bongiorno, M. Brusa, A. Comastri, M. Salvato, A. Fruscione,
Surveys for high-redshift (z>6) AGN with AXIS (cf. Athena) James Aird. University of Cambridge (-> University of Leicester)
 Surveys for high-redshift (z>6) AGN with AXIS (cf. Athena) James Aird University of Cambridge (-> University of Leicester) SMBH seed formation mechanisms Pop III star remnants MBH ~ 100 M z~20-30 Direct
Surveys for high-redshift (z>6) AGN with AXIS (cf. Athena) James Aird University of Cambridge (-> University of Leicester) SMBH seed formation mechanisms Pop III star remnants MBH ~ 100 M z~20-30 Direct
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 6 Dec 1999
 RESULTS FROM X-RAY SURVEYS WITH ASCA arxiv:astro-ph/9912084v1 6 Dec 1999 Yoshihiro Ueda Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Kanagawa 229-8510, Japan ABSTRACT We present main results from X-ray
RESULTS FROM X-RAY SURVEYS WITH ASCA arxiv:astro-ph/9912084v1 6 Dec 1999 Yoshihiro Ueda Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Kanagawa 229-8510, Japan ABSTRACT We present main results from X-ray
The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen, and Y. Yang
 The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen, and Y. Yang Active Galaxies (AKA quasars, Seyfert galaxies etc) are radiating massive black holes with L~10 8-10 14 L sun The
The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen, and Y. Yang Active Galaxies (AKA quasars, Seyfert galaxies etc) are radiating massive black holes with L~10 8-10 14 L sun The
Revealing powerful outflows in z~1.5 obscured QSOs
 Revealing powerful outflows in z~1.5 obscured QSOs Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna 2) Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik / Garching, Germany
Revealing powerful outflows in z~1.5 obscured QSOs Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna 2) Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik / Garching, Germany
Extragalactic X-ray Surveys: Source Populations and their Evolution. Paul Green SAO
 Extragalactic X-ray Surveys: Source Populations and their Evolution Paul Green SAO X-ray School 2011 I ll speak only about serendipitous, extragalactic X-ray surveys from focusing telescopes, and almost
Extragalactic X-ray Surveys: Source Populations and their Evolution Paul Green SAO X-ray School 2011 I ll speak only about serendipitous, extragalactic X-ray surveys from focusing telescopes, and almost
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability. Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida
 Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
X-raying High-Redshift AGNs and the First Black Holes: From Chandra to Lynx
 X-raying High-Redshift AGNs and the First Black Holes: From Chandra to Lynx Niel Brandt, Fabio Vito, the Chandra Deep Fields Team, and the Lynx First Accretion Light Working Group Some Relevant Results
X-raying High-Redshift AGNs and the First Black Holes: From Chandra to Lynx Niel Brandt, Fabio Vito, the Chandra Deep Fields Team, and the Lynx First Accretion Light Working Group Some Relevant Results
Extended Chandra Multi-Wavelength Project (ChaMPx): Source Catalog and Applications
 Extended Chandra Multi-Wavelength Project (ChaMPx): Source Catalog and Applications Dong-Woo Kim, P. Green, T. L. Aldcroft, W. Barkhouse, D. Haggard, V. Kashyap, A. Mossman, M. A. Agueros, A. Constantin,
Extended Chandra Multi-Wavelength Project (ChaMPx): Source Catalog and Applications Dong-Woo Kim, P. Green, T. L. Aldcroft, W. Barkhouse, D. Haggard, V. Kashyap, A. Mossman, M. A. Agueros, A. Constantin,
High Redshift Universe
 High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
The Connection between Major Galaxy Mergers, Black Hole Growth and Galaxy Evolution from Multiwavelength Observations Ezequiel Treister
 The Connection between Major Galaxy Mergers, Black Hole Growth and Galaxy Evolution from Multiwavelength Observations Ezequiel Treister P. Universidad Católica Collaborators: Franz Bauer (PUC), George
The Connection between Major Galaxy Mergers, Black Hole Growth and Galaxy Evolution from Multiwavelength Observations Ezequiel Treister P. Universidad Católica Collaborators: Franz Bauer (PUC), George
Active Galactic Alexander David M Nuclei
 d.m.alexander@durham.ac.uk Durham University David M Alexander Active Galactic Nuclei The Power Source QuickTime and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. Black hole is one billionth
d.m.alexander@durham.ac.uk Durham University David M Alexander Active Galactic Nuclei The Power Source QuickTime and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. Black hole is one billionth
The PRIsm MUlti-object Survey (PRIMUS)
 The PRIsm MUlti-object Survey (PRIMUS) Alison Coil University of Arizona Steward Observatory March 2008 Overview: Galaxy evolution to z ~ 1 is still cosmic variance limited: DEEP2, VVDS, COMBO-17, COSMOS
The PRIsm MUlti-object Survey (PRIMUS) Alison Coil University of Arizona Steward Observatory March 2008 Overview: Galaxy evolution to z ~ 1 is still cosmic variance limited: DEEP2, VVDS, COMBO-17, COSMOS
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 1 Nov 2000
 The New Era of Wide Field Astronomy ASP Conference Series, Vol. 000, 2001 R.G. Clowes, A.J. Adamson, G.E. Bromage The evolution of AGN in the Hard X-rays from HELLAS arxiv:astro-ph/0011008v1 1 Nov 2000
The New Era of Wide Field Astronomy ASP Conference Series, Vol. 000, 2001 R.G. Clowes, A.J. Adamson, G.E. Bromage The evolution of AGN in the Hard X-rays from HELLAS arxiv:astro-ph/0011008v1 1 Nov 2000
The BAT AGN Survey - Progress Report J. Tueller, C. Markwardt, L. Winter and R. Mushotzky Goddard Space Flight Center
 The BAT AGN Survey - Progress Report J. Tueller, C. Markwardt, L. Winter and R. Mushotzky Goddard Space Flight Center The Swift BAT (Burst and Transient Telescope) has been observing the whole sky in the
The BAT AGN Survey - Progress Report J. Tueller, C. Markwardt, L. Winter and R. Mushotzky Goddard Space Flight Center The Swift BAT (Burst and Transient Telescope) has been observing the whole sky in the
Hard X-ray selected sample of AGN: population studies
 Hard X-ray selected sample of AGN: population studies Angela Malizia INCREASE OF AGN POPULATION IN THE INTEGRAL SURVEYS most of the unidentified objects have been subsequently classified as AGN Many more
Hard X-ray selected sample of AGN: population studies Angela Malizia INCREASE OF AGN POPULATION IN THE INTEGRAL SURVEYS most of the unidentified objects have been subsequently classified as AGN Many more
Active Galactic Nuclei SEDs as a function of type and luminosity
 Active Galactic Nuclei SEDs as a function of type and luminosity Mari Polletta (IASF-INAF Milan) Collaborators: L. Chiappetti (IASF-INAF), L. Maraschi, M. Giorgetti, G. Trinchieri (Brera-INAF), B. Wilkes
Active Galactic Nuclei SEDs as a function of type and luminosity Mari Polletta (IASF-INAF Milan) Collaborators: L. Chiappetti (IASF-INAF), L. Maraschi, M. Giorgetti, G. Trinchieri (Brera-INAF), B. Wilkes
THE X-RAY BACKGROUND AND THE DEEP X-RAY SURVEYS
 THE X-RAY BACKGROUND AND THE DEEP X-RAY SURVEYS R. Gilli 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0303115 v1 5 Mar 2003 1 Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica (INAF), Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Largo E. Fermi 5, 50125
THE X-RAY BACKGROUND AND THE DEEP X-RAY SURVEYS R. Gilli 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0303115 v1 5 Mar 2003 1 Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica (INAF), Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Largo E. Fermi 5, 50125
New Suzaku Results on Active Galaxies. or Reflections on AGN. James Reeves (Keele) and Suzaku team (given by Lance Miller)
 New Suzaku Results on Active Galaxies or Reflections on AGN James Reeves (Keele) and Suzaku team (given by Lance Miller) Overview Overview of Suzaku and instrument performance. Why Suzaku is important
New Suzaku Results on Active Galaxies or Reflections on AGN James Reeves (Keele) and Suzaku team (given by Lance Miller) Overview Overview of Suzaku and instrument performance. Why Suzaku is important
The The largest assembly ESO high-redshift. Lidia Tasca & VUDS collaboration
 The The largest assembly ESO high-redshift of massive Large galaxies Programme at 2
The The largest assembly ESO high-redshift of massive Large galaxies Programme at 2
Future X-rayX Spectroscopy Missions. Jan-Willem den Herder
 Future X-rayX Spectroscopy Missions Jan-Willem den Herder contents Plasma diagnostics in the 0.1 to 10 kev band with resolution > 100 X-ray spectrometers: instrumental promises Future missions (a dream)
Future X-rayX Spectroscopy Missions Jan-Willem den Herder contents Plasma diagnostics in the 0.1 to 10 kev band with resolution > 100 X-ray spectrometers: instrumental promises Future missions (a dream)
Active Galactic Nuclei in the infrared: identification, energetic and properties of the obscuring material
 Active Galactic Nuclei in the infrared: identification, energetic and properties of the obscuring material Mari Polletta (Institut d Astrophysique de Paris) Collaborators: D. Weedman (Cornell U.), S. Hoenig
Active Galactic Nuclei in the infrared: identification, energetic and properties of the obscuring material Mari Polletta (Institut d Astrophysique de Paris) Collaborators: D. Weedman (Cornell U.), S. Hoenig
The search for. COSMOS and CDFS. Marcella Brusa
 The search for obscured AGN in COSMOS and CDFS Marcella Brusa MPE - High Energy Group XMM view of the COSMOS field Results obtained in the framework of the COSMOS & CDFS/MUSIC teams: Bongiorno, Brunner,
The search for obscured AGN in COSMOS and CDFS Marcella Brusa MPE - High Energy Group XMM view of the COSMOS field Results obtained in the framework of the COSMOS & CDFS/MUSIC teams: Bongiorno, Brunner,
Starburst-AGN connection: a mutual relation?
 Starburst-AGN connection: a mutual relation? Marcella Brusa Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik Garching, Germany XMM view of the COSMOS field The Starburst-AGN connection under the multiwavelength
Starburst-AGN connection: a mutual relation? Marcella Brusa Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik Garching, Germany XMM view of the COSMOS field The Starburst-AGN connection under the multiwavelength
LeMMINGs the emerlin radio legacy survey of nearby galaxies Ranieri D. Baldi
 LeMMINGs the emerlin radio legacy survey of nearby galaxies Ranieri D. Baldi in collaboration with I. McHardy, D. Williams, R. Beswick and many others The radio-loud / radio-quiet dichotomy Among the many
LeMMINGs the emerlin radio legacy survey of nearby galaxies Ranieri D. Baldi in collaboration with I. McHardy, D. Williams, R. Beswick and many others The radio-loud / radio-quiet dichotomy Among the many
Quasars ASTR 2120 Sarazin. Quintuple Gravitational Lens Quasar
 Quasars ASTR 2120 Sarazin Quintuple Gravitational Lens Quasar Quasars Quasar = Quasi-stellar (radio) source Optical: faint, blue, star-like objects Radio: point radio sources, faint blue star-like optical
Quasars ASTR 2120 Sarazin Quintuple Gravitational Lens Quasar Quasars Quasar = Quasi-stellar (radio) source Optical: faint, blue, star-like objects Radio: point radio sources, faint blue star-like optical
Compton-thick AGN. SWIFT/BAT 70 month survey (+ CDFS 7Ms + models) I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens
 Compton-thick AGN SWIFT/BAT 70 month survey (+ CDFS 7Ms + models) I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens A. Akylas, P. Ranalli, A. Corral, G. Lanzuisi Talk Outline Rationale: Why heavily obscured
Compton-thick AGN SWIFT/BAT 70 month survey (+ CDFS 7Ms + models) I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens A. Akylas, P. Ranalli, A. Corral, G. Lanzuisi Talk Outline Rationale: Why heavily obscured
SIMBOL-X X optics: design and implementation
 SIMBOL-X X optics: design and implementation Giovanni Pareschi, Oberto Citterio INAF Brera Astronomical Observatory 23807 Merate (Lc) ITALY E-mail: pareschi@merate.mi.astro.it 30 m Outline the SIMBOL-X
SIMBOL-X X optics: design and implementation Giovanni Pareschi, Oberto Citterio INAF Brera Astronomical Observatory 23807 Merate (Lc) ITALY E-mail: pareschi@merate.mi.astro.it 30 m Outline the SIMBOL-X
THE HELLAS2XMM SURVEY. VII. THE HARD X-RAY LUMINOSITY FUNCTION OF AGNs UP TO z =4: MORE ABSORBED AGNs AT LOW LUMINOSITIES AND HIGH REDSHIFTS
 The Astrophysical Journal, 635:864 879, 2005 December 20 # 2005. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. THE HELLAS2XMM SURVEY. VII. THE HARD X-RAY LUMINOSITY FUNCTION
The Astrophysical Journal, 635:864 879, 2005 December 20 # 2005. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. THE HELLAS2XMM SURVEY. VII. THE HARD X-RAY LUMINOSITY FUNCTION
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics
 Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
MASSIVE BLACK HOLES AMY REINES IN NEARBY DWARF GALAXIES HUBBLE FELLOW NATIONAL OPTICAL ASTRONOMY OBSERVATROY
 MASSIVE BLACK HOLES IN NEARBY DWARF GALAXIES AMY REINES HUBBLE FELLOW NATIONAL OPTICAL ASTRONOMY OBSERVATROY Motivation: The origin of massive black holes (BHs) Massive BHs are fundamental components of
MASSIVE BLACK HOLES IN NEARBY DWARF GALAXIES AMY REINES HUBBLE FELLOW NATIONAL OPTICAL ASTRONOMY OBSERVATROY Motivation: The origin of massive black holes (BHs) Massive BHs are fundamental components of
Radio Properties Of X-Ray Selected AGN
 Radio Properties Of X-Ray Selected AGN Manuela Molina In collaboration with: M. Polletta, L. Chiappetti, L. Paioro (INAF/IASF-Mi), G.Trinchieri (OA Brera), F. Owen (NRAO) and Chandra/SWIRE Team. Astrosiesta,
Radio Properties Of X-Ray Selected AGN Manuela Molina In collaboration with: M. Polletta, L. Chiappetti, L. Paioro (INAF/IASF-Mi), G.Trinchieri (OA Brera), F. Owen (NRAO) and Chandra/SWIRE Team. Astrosiesta,
Obscured AGN. I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens
 Obscured AGN I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens Talk Outline Rationale: Why obscured AGN are important (especially the Compton-thick AGN) Obscured AGN from X-ray surveys (Chandra, XMM, Swift/BAT,
Obscured AGN I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens Talk Outline Rationale: Why obscured AGN are important (especially the Compton-thick AGN) Obscured AGN from X-ray surveys (Chandra, XMM, Swift/BAT,
MULTI-WAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF X-RAY SELECTED AGN: WHAT WE NEED AND WHY
 1 MULTI-WAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF X-RAY SELECTED AGN: WHAT WE NEED AND WHY M. Polletta 1,2 and D. M. Alexander 3 1 INAF - IASF Milan, via E. Bassini 15, 20133 Milan, Italy 2 Institut d Astrophysique de
1 MULTI-WAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF X-RAY SELECTED AGN: WHAT WE NEED AND WHY M. Polletta 1,2 and D. M. Alexander 3 1 INAF - IASF Milan, via E. Bassini 15, 20133 Milan, Italy 2 Institut d Astrophysique de
The Correlation Between the Hard-X-ray Photon Index and the Accretion Rate in AGN: Probing Black-Hole Growth Across Cosmic Time
 The Correlation Between the Hard-X-ray Photon Index and the Accretion Rate in AGN: Probing Black-Hole Growth Across Cosmic Time Ohad Shemmer Pennsylvania State University Collaborators: Niel Brandt (Penn
The Correlation Between the Hard-X-ray Photon Index and the Accretion Rate in AGN: Probing Black-Hole Growth Across Cosmic Time Ohad Shemmer Pennsylvania State University Collaborators: Niel Brandt (Penn
Hunting for feeding and feedback signatures in a sample of hard X-ray selected NLS1
 Hunting for feeding and feedback signatures in a sample of hard X-ray selected NLS1 Manuela Molina (INAF/IASF Bologna), A. Malizia, (INAF/IASF Bologna), C. Feruglio (INAF/OA Trieste), F. Fiore (INAF/OA
Hunting for feeding and feedback signatures in a sample of hard X-ray selected NLS1 Manuela Molina (INAF/IASF Bologna), A. Malizia, (INAF/IASF Bologna), C. Feruglio (INAF/OA Trieste), F. Fiore (INAF/OA
The parsec scale of. ac-ve galac-c nuclei. Mar Mezcua. International Max Planck Research School for Astronomy and Astrophysics
 The parsec scale of ESO ac-ve galac-c nuclei International Max Planck Research School for Astronomy and Astrophysics COST Ac(on MP0905 - Black Holes in a Violent Universe In collaboration with A. Prieto,
The parsec scale of ESO ac-ve galac-c nuclei International Max Planck Research School for Astronomy and Astrophysics COST Ac(on MP0905 - Black Holes in a Violent Universe In collaboration with A. Prieto,
Hard X-ray AGN and the Cosmic X-ray Background
 Hard X-ray AGN and the Cosmic X-ray Background Sergey Sazonov Space Research Institute, Moscow, Russia 1 Rome, Oct. 17, 2013 Plan Cosmic X-ray background: measurements, modeling and implications for heavily
Hard X-ray AGN and the Cosmic X-ray Background Sergey Sazonov Space Research Institute, Moscow, Russia 1 Rome, Oct. 17, 2013 Plan Cosmic X-ray background: measurements, modeling and implications for heavily
PROBING THE AGN/GALAXY CO-EVOLUTION AT ITS EXTREME
 THE MOST LUMINOUS QUASARS: PROBING THE AGN/GALAXY CO-EVOLUTION AT ITS EXTREME Enrico Piconcelli Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma - INAF! A. Bongiorno, F. Fiore, M. Bischetti, L. Zappacosta OA-Roma! C.
THE MOST LUMINOUS QUASARS: PROBING THE AGN/GALAXY CO-EVOLUTION AT ITS EXTREME Enrico Piconcelli Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma - INAF! A. Bongiorno, F. Fiore, M. Bischetti, L. Zappacosta OA-Roma! C.
Obscured QSOs in the golden epoch of AGN-galaxy evolution placing objects in the mergers sequence (with NIR and mm observations)
 Obscured QSOs in the golden epoch of AGN-galaxy evolution placing objects in the mergers sequence (with NIR and mm observations) Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna
Obscured QSOs in the golden epoch of AGN-galaxy evolution placing objects in the mergers sequence (with NIR and mm observations) Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna
Deep Surveys or How We Learn About the Early Universe When We Can t Measure All that Would Be Nice!
 Deep Surveys or How We Learn About the Early Universe When We Can t Measure All that Would Be Nice! Presented at the AAS Seminar on Infrared Astronomy, AAS Meeting, Jan 7, 2003, Seattle Marcia Rieke mrieke@as.
Deep Surveys or How We Learn About the Early Universe When We Can t Measure All that Would Be Nice! Presented at the AAS Seminar on Infrared Astronomy, AAS Meeting, Jan 7, 2003, Seattle Marcia Rieke mrieke@as.
Optical studies of an ultraluminous X-ray source: NGC1313 X-2
 Optical studies of an ultraluminous X-ray source: NGC1313 X-2 Jifeng Liu Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in collaboration with Joel Bregman, Jon Miller, Philip Kaaret outline background: ultraluminous
Optical studies of an ultraluminous X-ray source: NGC1313 X-2 Jifeng Liu Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in collaboration with Joel Bregman, Jon Miller, Philip Kaaret outline background: ultraluminous
GALAXIES. Edmund Hodges-Kluck Andrew Ptak
 GALAXIES Edmund Hodges-Kluck Andrew Ptak Galaxy Science with AXIS How does gas get into and out of galaxies? How important is hot accretion for L* or larger galaxies? How does star formation/black hole
GALAXIES Edmund Hodges-Kluck Andrew Ptak Galaxy Science with AXIS How does gas get into and out of galaxies? How important is hot accretion for L* or larger galaxies? How does star formation/black hole
Science with Simbol-X
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 79, 38 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Science with Simbol-X F. Fiore 1, M. Arnaud 2, U. Briel 3, M. Cappi 4, A. Comastri 5, A. Decourchelle 2, R. Della Ceca 6, P. Ferrando 7, C. Feruglio 1,
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 79, 38 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Science with Simbol-X F. Fiore 1, M. Arnaud 2, U. Briel 3, M. Cappi 4, A. Comastri 5, A. Decourchelle 2, R. Della Ceca 6, P. Ferrando 7, C. Feruglio 1,
Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies
 Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI) Dan Batcheldor (RIT) Marc Postman (STScI) Rachel Somerville (STScI)
Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI) Dan Batcheldor (RIT) Marc Postman (STScI) Rachel Somerville (STScI)
Background Picture: Millennium Simulation (MPA); Spectrum-Roentgen-Gamma satellite (P. Predehl 2011)
 By Collaborators Alex Kolodzig (MPA) Marat Gilfanov (MPA,IKI), Gert Hütsi (MPA), Rashid Sunyaev (MPA,IKI) Publications Kolodzig et al. 2013b, A&A, 558, 90 (ArXiv : 1305.0819) Hüsti et al. 2014, submitted
By Collaborators Alex Kolodzig (MPA) Marat Gilfanov (MPA,IKI), Gert Hütsi (MPA), Rashid Sunyaev (MPA,IKI) Publications Kolodzig et al. 2013b, A&A, 558, 90 (ArXiv : 1305.0819) Hüsti et al. 2014, submitted
The Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES) The Evolution of the FIR/SMM Luminosity Function and of the Cosmic SFRD
 The Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES) The Evolution of the FIR/SMM Luminosity Function and of the Cosmic SFRD Lucia Marchetti University of Padova - Open University Mattia Vaccari - University
The Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES) The Evolution of the FIR/SMM Luminosity Function and of the Cosmic SFRD Lucia Marchetti University of Padova - Open University Mattia Vaccari - University
The Hard X-Ray Luminosity Function of High-Redshift (z > 3) AGN
 The Hard X-Ray Luminosity Function of High-Redshift (z > 3) AGN Fabio Vito Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia - Università di Bologna INAF-OABo F Vito, RGilli, C Vignali, A Comastri, M Brusa, N Cappelluti,
The Hard X-Ray Luminosity Function of High-Redshift (z > 3) AGN Fabio Vito Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia - Università di Bologna INAF-OABo F Vito, RGilli, C Vignali, A Comastri, M Brusa, N Cappelluti,
Physics of the hot evolving Universe
 Physics of the hot evolving Universe Science themes for a New-Generation X-ray Telescope Günther Hasinger Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik Garching ESA Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 Workshop,
Physics of the hot evolving Universe Science themes for a New-Generation X-ray Telescope Günther Hasinger Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik Garching ESA Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 Workshop,
Astronomy. Astrophysics. An XMM Newton study of the hard X ray sky. E. Piconcelli 1,2,3, M. Cappi 1, L. Bassani 1,G.DiCocco 1, and M.
 A&A 412, 689 705 (2003) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20031490 c ESO 2003 Astronomy & Astrophysics An XMM Newton study of the hard X ray sky E. Piconcelli 1,2,3, M. Cappi 1, L. Bassani 1,G.DiCocco 1, and M. Dadina
A&A 412, 689 705 (2003) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20031490 c ESO 2003 Astronomy & Astrophysics An XMM Newton study of the hard X ray sky E. Piconcelli 1,2,3, M. Cappi 1, L. Bassani 1,G.DiCocco 1, and M. Dadina
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 29 Mar 2000
 WHAT S WRONG WITH AGN MODELS FOR THE X-RAY BACKGROUND? arxiv:astro-ph/0003437v1 29 Mar 2000 Andrea Comastri Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, via Ranzani 1, I 40127 Bologna, Italy ABSTRACT The origin
WHAT S WRONG WITH AGN MODELS FOR THE X-RAY BACKGROUND? arxiv:astro-ph/0003437v1 29 Mar 2000 Andrea Comastri Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, via Ranzani 1, I 40127 Bologna, Italy ABSTRACT The origin
Lecture 11: SDSS Sources at Other Wavelengths: From X rays to radio. Astr 598: Astronomy with SDSS
 Astr 598: Astronomy with SDSS Spring Quarter 4, University of Washington, Željko Ivezić Lecture : SDSS Sources at Other Wavelengths: From X rays to radio Large Surveys at Many Wavelengths SDSS: UV-IR five-band
Astr 598: Astronomy with SDSS Spring Quarter 4, University of Washington, Željko Ivezić Lecture : SDSS Sources at Other Wavelengths: From X rays to radio Large Surveys at Many Wavelengths SDSS: UV-IR five-band
What s the fuss about AGN?
 What s the fuss about AGN? Mari Polletta (IASF-INAF Milan, Italy) 1 Outline What is an Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN)? AGN role and importance AGN evolutionary models and feedback Star-formation and AGN
What s the fuss about AGN? Mari Polletta (IASF-INAF Milan, Italy) 1 Outline What is an Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN)? AGN role and importance AGN evolutionary models and feedback Star-formation and AGN
The bolometric output of AGN in the XMM-COSMOS survey
 The bolometric output of AGN in the XMM-COSMOS survey Elisabeta Lusso Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna-INAF/OABO A. Comastri, C. Vignali, G. Zamorani, M. Brusa, E. Treister, R. Gilli, M.
The bolometric output of AGN in the XMM-COSMOS survey Elisabeta Lusso Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna-INAF/OABO A. Comastri, C. Vignali, G. Zamorani, M. Brusa, E. Treister, R. Gilli, M.
Quasars (and AGN) with the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) Fiona Harrison Caltech
 Quasars (and AGN) with the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) Fiona Harrison Caltech INTEGRAL, Swi? BAT NuSTAR Focal spot Grazing incidence op6cs 3 Sensi6vity Satellite (instrument) INTEGRAL
Quasars (and AGN) with the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) Fiona Harrison Caltech INTEGRAL, Swi? BAT NuSTAR Focal spot Grazing incidence op6cs 3 Sensi6vity Satellite (instrument) INTEGRAL
Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically faint ellipticals. Part 3. After Chandra?
 Hot gas and AGN Feedback in Nearby Groups and Galaxies Part 1. Cool cores and outbursts from supermassive black holes in clusters, groups and normal galaxies Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically
Hot gas and AGN Feedback in Nearby Groups and Galaxies Part 1. Cool cores and outbursts from supermassive black holes in clusters, groups and normal galaxies Part 2. Hot gas halos and SMBHs in optically
ROSAT Roentgen Satellite. Chandra X-ray Observatory
 ROSAT Roentgen Satellite Joint facility: US, Germany, UK Operated 1990 1999 All-sky survey + pointed observations Chandra X-ray Observatory US Mission Operating 1999 present Pointed observations How do
ROSAT Roentgen Satellite Joint facility: US, Germany, UK Operated 1990 1999 All-sky survey + pointed observations Chandra X-ray Observatory US Mission Operating 1999 present Pointed observations How do
ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: optical spectroscopy. From AGN classification to Black Hole mass estimation
 ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: optical spectroscopy From AGN classification to Black Hole mass estimation Second Lecture Reverberation Mapping experiments & virial BH masses estimations Estimating AGN black hole
ACTIVE GALACTIC NUCLEI: optical spectroscopy From AGN classification to Black Hole mass estimation Second Lecture Reverberation Mapping experiments & virial BH masses estimations Estimating AGN black hole
The cosmic X ray background: abundance and evolu8on of hidden black holes. R. Gilli (INAF OaBologna) with the XMM CDFS, 4Ms CDFS, COSMOS, WFXT teams
 The cosmic X ray background: abundance and evolu8on of hidden black holes R. Gilli (INAF OaBologna) with the XMM CDFS, 4Ms CDFS, COSMOS, WFXT teams Cosmic X ray background spectrum = radiamve imprint of
The cosmic X ray background: abundance and evolu8on of hidden black holes R. Gilli (INAF OaBologna) with the XMM CDFS, 4Ms CDFS, COSMOS, WFXT teams Cosmic X ray background spectrum = radiamve imprint of
The Rela(on Between Bars and AGN locally and at high redshi8
 The Rela(on Between Bars and AGN locally and at high redshi8 Mauricio Cisternas Ins(tuto de Astrofisica de Canarias The Triggering Mechanisms for AGN, Leiden, July 24, 2013 What is triggering most AGN?
The Rela(on Between Bars and AGN locally and at high redshi8 Mauricio Cisternas Ins(tuto de Astrofisica de Canarias The Triggering Mechanisms for AGN, Leiden, July 24, 2013 What is triggering most AGN?
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 31 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 31 Mar 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 31 Mar 2014](/thumbs/74/69931176.jpg) Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2014) 00, 1?? arxiv:1403.7974v1 [astro-ph.ga] 31 Mar 2014 Probing obscured, high redshift galaxies using deep P-band continuum imaging with GMRT Yogesh Wadadekar 1, Sandeep Sirothia
Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2014) 00, 1?? arxiv:1403.7974v1 [astro-ph.ga] 31 Mar 2014 Probing obscured, high redshift galaxies using deep P-band continuum imaging with GMRT Yogesh Wadadekar 1, Sandeep Sirothia
The X-Ray Universe. The X-Ray Universe
 The X-Ray Universe The X-Ray Universe Potsdam University Dr. Lidia Oskinova Sommersemester 2017 lida@astro.physik.uni-potsdam.de astro.physik.uni-potsdam.de ~lida/vorlesungxrayso17.html Chandra X-ray,
The X-Ray Universe The X-Ray Universe Potsdam University Dr. Lidia Oskinova Sommersemester 2017 lida@astro.physik.uni-potsdam.de astro.physik.uni-potsdam.de ~lida/vorlesungxrayso17.html Chandra X-ray,
X- & γ-ray Instrumentation
 X- & γ-ray Instrumentation Used nuclear physics detectors Proportional Counters Scintillators The Dark Ages Simple collimators HEAO A1 & A2: 2 x 8 degree field of view Confusion limit is about 200 sources
X- & γ-ray Instrumentation Used nuclear physics detectors Proportional Counters Scintillators The Dark Ages Simple collimators HEAO A1 & A2: 2 x 8 degree field of view Confusion limit is about 200 sources
The growth and evolution of super massive black holes
 The growth and evolution of super massive black holes A white paper submitted to the Decadal Survey Committee Authors: S. Murray 1, R. Gilli 2, P. Tozzi 3, M. Paolillo 4, N. Brandt 8, G. Tagliaferri 9,
The growth and evolution of super massive black holes A white paper submitted to the Decadal Survey Committee Authors: S. Murray 1, R. Gilli 2, P. Tozzi 3, M. Paolillo 4, N. Brandt 8, G. Tagliaferri 9,
Stellar populations of quasar host galaxies
 Knud Jahnke AIP Galaxies division Hauskolloquium 10.01.2003 Introduction/motivation Multicolour imaging On-nucleus spectroscopy What does this teach us? Outlook Overview Introduction Introduction HE 1043
Knud Jahnke AIP Galaxies division Hauskolloquium 10.01.2003 Introduction/motivation Multicolour imaging On-nucleus spectroscopy What does this teach us? Outlook Overview Introduction Introduction HE 1043
X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies. Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts
 X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts Chandra survey of diffuse X-ray emission from 53 edge-on galaxies i > 60 o, D < 30 Mpc (Li, J.-T. & Wang, Q.D.
X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts Chandra survey of diffuse X-ray emission from 53 edge-on galaxies i > 60 o, D < 30 Mpc (Li, J.-T. & Wang, Q.D.
Probing the Origin of Supermassive Black Hole Seeds with Nearby Dwarf Galaxies. Amy Reines Einstein Fellow NRAO Charlottesville
 Probing the Origin of Supermassive Black Hole Seeds with Nearby Dwarf Galaxies Amy Reines Einstein Fellow NRAO Charlottesville Motivation: The origin of supermassive BH seeds Motivation: The origin of
Probing the Origin of Supermassive Black Hole Seeds with Nearby Dwarf Galaxies Amy Reines Einstein Fellow NRAO Charlottesville Motivation: The origin of supermassive BH seeds Motivation: The origin of
Chandra was launched aboard Space Shuttle Columbia on July 23, 1999!!!
 Chandra was launched aboard Space Shuttle Columbia on July 23, 1999!!! Crew Lost During Re-Entry Modern X-ray Telescopes and Detectors X-ray Telescopes X-ray Instruments Some early highlights Observations
Chandra was launched aboard Space Shuttle Columbia on July 23, 1999!!! Crew Lost During Re-Entry Modern X-ray Telescopes and Detectors X-ray Telescopes X-ray Instruments Some early highlights Observations
Extragalactic Surveys: Prospects from Herschel-PACS
 Extragalactic Surveys: Prospects from Herschel-PACS Bruno Altieri Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Garching PACS Team, PACS GT extragalactic survey (PEP) Team PI: Dieter Lutz PEP in a
Extragalactic Surveys: Prospects from Herschel-PACS Bruno Altieri Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Garching PACS Team, PACS GT extragalactic survey (PEP) Team PI: Dieter Lutz PEP in a
Connection between AGN and Star Formation activities, or not?
 Connection between AGN and Star Formation activities, or not? Y.Sophia Dai ( 戴昱 ) National Astronomical Observatories of China (NAOC) daysophia@gmail.com Close Correlations between SMBH and hosts M SMBH
Connection between AGN and Star Formation activities, or not? Y.Sophia Dai ( 戴昱 ) National Astronomical Observatories of China (NAOC) daysophia@gmail.com Close Correlations between SMBH and hosts M SMBH
A Supermassive Black Hole in the Dwarf Starburst Galaxy Henize Amy Reines Einstein Fellow National Radio Astronomy Observatory
 A Supermassive Black Hole in the Dwarf Starburst Galaxy Henize 2-10 Amy Reines Einstein Fellow National Radio Astronomy Observatory Supermassive black holes and galaxy evolution Supermassive black holes
A Supermassive Black Hole in the Dwarf Starburst Galaxy Henize 2-10 Amy Reines Einstein Fellow National Radio Astronomy Observatory Supermassive black holes and galaxy evolution Supermassive black holes
The Peculiar Case of Was 49b: An Over-Massive AGN in a Minor Merger?
 The Peculiar Case of Was 49b: An Over-Massive AGN in a Minor Merger? Nathan Secrest NRC Postdoctoral Fellow, U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Henrique Schmitt (NRL), Laura Blecha (UMD), Barry Rothberg (LBT),
The Peculiar Case of Was 49b: An Over-Massive AGN in a Minor Merger? Nathan Secrest NRC Postdoctoral Fellow, U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Henrique Schmitt (NRL), Laura Blecha (UMD), Barry Rothberg (LBT),
X-Ray observability of WHIM and our new mission concept DIOS Intergalactic. Oxygen. Surveyor ) Noriko Yamasaki ISAS/JAXA
 X-Ray observability of WHIM and our new mission concept DIOS (Diffuse Intergalactic Oxygen Surveyor ) Noriko Yamasaki ISAS/JAXA 1 Cosmic Baryon Budget requires missing baryon The observed baryons are only
X-Ray observability of WHIM and our new mission concept DIOS (Diffuse Intergalactic Oxygen Surveyor ) Noriko Yamasaki ISAS/JAXA 1 Cosmic Baryon Budget requires missing baryon The observed baryons are only
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11096 Spectroscopic redshifts of CDF-N X-ray sources We have taken a recent compilation 13 as our main source of spectroscopic redshifts. These redshifts are given to two decimal places,
doi:10.1038/nature11096 Spectroscopic redshifts of CDF-N X-ray sources We have taken a recent compilation 13 as our main source of spectroscopic redshifts. These redshifts are given to two decimal places,
Galaxies. Galaxy Diversity. Galaxies, AGN and Quasars. Physics 113 Goderya
 Galaxies, AGN and Quasars Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 16 and 17 Learning Outcomes: Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars. Large variety of shapes
Galaxies, AGN and Quasars Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 16 and 17 Learning Outcomes: Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars. Large variety of shapes
Transient iron fluorescence: new clues on the AGN disk/corona?
 Transient iron fluorescence: new clues on the AGN disk/corona? Emanuele Nardini Horizon 2020 INAF/Arcetri AstroFIt2/MSCA in collaboration with: D. Porquet (CNRS/Strasbourg), J. Reeves (Keele+UMBC), V.
Transient iron fluorescence: new clues on the AGN disk/corona? Emanuele Nardini Horizon 2020 INAF/Arcetri AstroFIt2/MSCA in collaboration with: D. Porquet (CNRS/Strasbourg), J. Reeves (Keele+UMBC), V.
Cosmology The Road Map
 Cosmology The Road Map Peter Schneider Institut für Astrophysik, Bonn University on behalf of the Astronomy Working Group Cosmology s Themes Fundamental Cosmology Probing inflation Investigating Dark Energy
Cosmology The Road Map Peter Schneider Institut für Astrophysik, Bonn University on behalf of the Astronomy Working Group Cosmology s Themes Fundamental Cosmology Probing inflation Investigating Dark Energy
Geant4-based simulations of the background for the erosita space observatory (with connections to IXO and Suzaku)
 Geant4-based simulations of the background for the erosita space observatory (with connections to IXO and Suzaku) Emanuele Perinati 1,2 1 IAAT - Institut fϋr Astronomie und Astrophysik, Universität Tϋbingen,
Geant4-based simulations of the background for the erosita space observatory (with connections to IXO and Suzaku) Emanuele Perinati 1,2 1 IAAT - Institut fϋr Astronomie und Astrophysik, Universität Tϋbingen,
The Contribution of Active Galactic Nuclei to the Excess Cosmic Radio Background at 1.4 GHz
 The Contribution of Active Galactic Nuclei to the Excess Cosmic Radio Background at 1.4 GHz David R. Ballantyne Center for Relativistic Astrophysics, School of Physics, Georgia Tech The Cosmic Backgrounds
The Contribution of Active Galactic Nuclei to the Excess Cosmic Radio Background at 1.4 GHz David R. Ballantyne Center for Relativistic Astrophysics, School of Physics, Georgia Tech The Cosmic Backgrounds
Broadband X-ray emission from radio-quiet Active Galactic Nuclei
 29 th ASI Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 3, pp 19 23 Edited by Pushpa Khare & C. H. Ishwara-Chandra Broadband X-ray emission from radio-quiet Active Galactic Nuclei G. C. Dewangan Inter-University
29 th ASI Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 3, pp 19 23 Edited by Pushpa Khare & C. H. Ishwara-Chandra Broadband X-ray emission from radio-quiet Active Galactic Nuclei G. C. Dewangan Inter-University
PoS(SWIFT 10)153. SWIFT/BAT AGN2 reveal broad emission lines in the NIR: the first virial measure of their black hole masses
 SWIFT/BAT AGN2 reveal broad emission lines in the NIR: the first virial measure of their black hole masses a Fabio La Franca a, Federica Ricci a, Marcella Brusa b, Eleonora Sani c, Roberto Maiolino d,
SWIFT/BAT AGN2 reveal broad emission lines in the NIR: the first virial measure of their black hole masses a Fabio La Franca a, Federica Ricci a, Marcella Brusa b, Eleonora Sani c, Roberto Maiolino d,
Identifying distant* hidden monsters with NuSTAR
 Identifying distant* hidden monsters with NuSTAR * z ~ 0.05 1 log (L X / erg s -1 ) ~ 43 45 George Lansbury Durham University with David Alexander, James Aird, Daniel Stern, Poshak Gandhi, the NuSTAR science
Identifying distant* hidden monsters with NuSTAR * z ~ 0.05 1 log (L X / erg s -1 ) ~ 43 45 George Lansbury Durham University with David Alexander, James Aird, Daniel Stern, Poshak Gandhi, the NuSTAR science
X-ray Astronomy F R O M V - R O CKETS TO AT HENA MISSION. Thanassis Akylas
 X-ray Astronomy F R O M V - R O CKETS TO AT HENA MISSION Thanassis Akylas Telescopes & Light Gallileo turned his telescope into the sky 400 years ago He enhanced his natural vision or the so called natural
X-ray Astronomy F R O M V - R O CKETS TO AT HENA MISSION Thanassis Akylas Telescopes & Light Gallileo turned his telescope into the sky 400 years ago He enhanced his natural vision or the so called natural
Presentation by Indian Delegation. to 49 th STSC UNCOPUOS. February 2012 Vienna
 Presentation by Indian Delegation to 49 th STSC UNCOPUOS February 2012 Vienna ASTROSAT Astrosat is India s first dedicated multiwavelength astronomy satellite with a capability to observe target sources
Presentation by Indian Delegation to 49 th STSC UNCOPUOS February 2012 Vienna ASTROSAT Astrosat is India s first dedicated multiwavelength astronomy satellite with a capability to observe target sources
Neutron Stars at X-ray Wavelengths: NASA's Constellation-X Mission. Divas Sanwal (JHU/GSFC) Constellation-X NASA GSFC
 Constellation-X NASA GSFC Neutron Stars at X-ray Wavelengths: NASA's Constellation-X Mission Divas Sanwal (JHU/GSFC) Project Scientist: Nick White (GSFC) FST Chair: Harvey Tananbaum (SAO) Project Manager:
Constellation-X NASA GSFC Neutron Stars at X-ray Wavelengths: NASA's Constellation-X Mission Divas Sanwal (JHU/GSFC) Project Scientist: Nick White (GSFC) FST Chair: Harvey Tananbaum (SAO) Project Manager:
Radio Quiet AGN: Black Hole & Host Galaxy Proper;es
 Radio Quiet AGN: Black Hole & Host Galaxy Proper;es (ESO) Collaborators: V. Mainieri, P. Padovani, P. Rosa6, N. Miller, K. I. Kellermann, P. Tozzi, S. Va>akunnel, A. Bongiorno, + PEP Collaboration Credit:
Radio Quiet AGN: Black Hole & Host Galaxy Proper;es (ESO) Collaborators: V. Mainieri, P. Padovani, P. Rosa6, N. Miller, K. I. Kellermann, P. Tozzi, S. Va>akunnel, A. Bongiorno, + PEP Collaboration Credit:
Observational Evidence of AGN Feedback
 10 de maio de 2012 Sumário Introduction AGN winds Galaxy outflows From the peak to the late evolution of AGN and quasars Mergers or secular evolution? The AGN feedback The interaction process between the
10 de maio de 2012 Sumário Introduction AGN winds Galaxy outflows From the peak to the late evolution of AGN and quasars Mergers or secular evolution? The AGN feedback The interaction process between the
Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, 27 Ottobre 2011
 Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, 27 Ottobre 2011 BASIC PARADIGM: Copious energy output from AGN (10 9-10 13 L Θ ) from accretion of material onto a Supermassive Black Hole SMBH ( 10 6-10 9 M Θ ). AGN
Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, 27 Ottobre 2011 BASIC PARADIGM: Copious energy output from AGN (10 9-10 13 L Θ ) from accretion of material onto a Supermassive Black Hole SMBH ( 10 6-10 9 M Θ ). AGN
