THE EUCLID VIS READ-OUT SHUTTER UNIT: A LOW DISTURBANCE MECHANISM AT CRYOGENIC TEMPERATURE
|
|
|
- Grant Payne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE EUCLID VIS READ-OUT SHUTTER UNIT: A LOW DISTURBANCE MECHANISM AT CRYOGENIC TEMPERATURE C. Larchevêque (2), L. Genolet (1), E. Bozzo (1), S. Paltani (1), D. Manzoni (2), M. Castelli (2), J-P. Heurteau (2), C. Thomas (2), J. Constant (2), R. Michaud (2), A. Marrei (2), N. Martini (2), T. Verhegge (2) (1) Department of Astronomy, University of Geneva, Chemin d Ecogia 16, 1290, Versoix, Switzerland, Enrico.Bozzo@unige.ch (2) APCO Technologies, Chemin de Champex 10, 1860, Aigle, Switzerland, c.larcheveque@apco-technologies.eu ABSTRACT Euclid is the second medium-size mission (M2) of the ESA Cosmic Vision Program, currently scheduled for a launch in The two instruments on-board Euclid, VIS (VISible imager) and NISP (Near Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer), will provide key measurements to investigate the nature of dark energy, advancing our knowledge on cosmology. We present in this contribution the development and manufacturing status of the VIS Read-out Shutter Unit, whose main function is to prevent direct light from falling onto the VIS CCDs during the read-out of the scientific exposures and to allow the dark-current/bias calibrations of the instrument. MISSION Euclid [1] is the second medium-size mission (M2) of the ESA Cosmic Vision Program, currently scheduled for a launch in To accomplish the Euclid mission ESA has selected Thales Alenia Space for the construction of the satellite and its Service Module and Airbus Defence and Space for the Payload Module. Euclid will be equipped with a 1.2 m diameter Silicon Carbide (SiC) mirror telescope manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. The science beam from the telescope will illuminate the VIS and NISP instruments, provided by the Euclid Consortium. The development of the VIS instrument is led by the MSSL (Mullard Space Science Laboratory) and its main goal is to image all galaxies of the Euclid survey with an unprecedentedly high image quality. It will be used to measure the shapes of galaxies and derive the gravitational lensing effects induced on them by large scale structures populating the cosmological Universe. The different subsystems of the VIS instruments are shown on Figure 2. The mission will investigate the distance-redshift relationship and the evolution of cosmic structures out to redshifts ~2, mapping the geometry of the dark Universe over the entire period during which the dark energy played a significant role in the cosmic acceleration. Figure 2: Overview of the VIS subsystems (courtesy EC / VIS team [1]). Figure 1: Artist's impression of the Euclid spacecraft (credits: ESA). We present in this contribution the development and manufacturing status of the VIS Read-out Shutter Unit (RSU), whose main function is to prevent direct light from falling onto the VIS CCDs during the read-out of the scientific exposures and to permit the darkcurrent/bias calibrations of the instrument. Proc. ESMATS 2017, Univ. of Hertfordshire, Hatfield, U.K., September 2017
2 DESIGN REQUIREMENTS Several major challenges have been faced during the development of the RSU due to the harsh conditions of the environment in which the unit will be operated and the strict performance requirements imposed by the needs of the Euclid mission. First of all, the RSU should retain its performances in vacuum over a large range of temperatures, spanning from room 293 K down to 110 K. The low operating temperatures of the RSU are dictated by the proximity of the unit to the VIS focal plane, the latter being equipped with CCDs (charge-coupled device) that reach the highest performances only in cold conditions [2]. This proximity also imposes strict requirements on the cleanliness of the unit and on the stray-light it can induce on the instrument focal plane. The second challenging design aspect is related to the high number of actuations to be performed without any failure, exceeding 1 million when the qualification factor is convolved with the expected number of openings and closures of the RSU during the 6.25 years of Euclid scientific observations. Finally, the RSU is also requested to limit the exported torque and the induced micro-vibrations on the Euclid spacecraft down to an exquisitely low level in order not to degrade the performances of the VIS and NISP instruments. As the motion of the RSU is too short (between 3 and 10 s) to be actively compensated through the usage of the spacecraft attitude and orbit control system (reaction time ~60s), its exported torque and micro-vibrations have to be minimized through a carefully fine-tuned design of the unit. RSU DESCRIPTION The RSU main function to occult the light beam is achieved through the rotation of its relatively large aluminium leaf by 70 deg (see Figure 3). The rotation is driven by a SAFRAN-SAGEM stepper motor with 360 steps per revolution. To counteract the moment created by the rotation of the leaf, a spur gear is introduced to drive the movement of a flywheel (FW) in the opposite direction. The hatch shaft (HS), holding the leaf, and the motor shaft (MS), holding the motor and the FW, are mounted on a titanium alloy base plate through dedicated ball bearings. Two pairs of ball bearings in face-to-face configuration are used for the HS, while a single pair in back-to-back configuration is considered for the MS. Cold and warm redundant end-switches are installed at the tip of the hatch shaft to indicate when the RSU is in the open or closed position. Some more details of the design are discussed in the following sections. VIS CCDs Figure 3: The RSU in both the open and closed positions intersecting the science beam. Flywheel Supporting parts Flywheel Figure 4: An overview of the RSU design. MS ball bearings Figure 5: Details of the RSU mobile parts. KEY FEATURES To fulfil all RSU requirements mentioned before, a number of key features have been implemented in the unit design as detailed below. Depointing Leaf in closed position HS ball bearings Gears Motor rotor Light beam Leaf in open position Leaf Leaf Leaf Counterweight To limit the low frequency (<10Hz) component of the
3 RSU exported loads and minimize the depointing of the Euclid spacecraft, the moment of inertia (MoI) of both the leaf and the flywheel shaft (rotating in opposite directions) are measured through a moment of inertia test stand, developed by Schenck S.A.S. The achievable accuracy in the measurements performed with this machine is as low as 0.1% and adjustment masses have been implemented on the RSU MS side to fine-tune its MoI (see Figure 6). maintained on the rotation axis. This is illustrated in Figure 7 and Eq. 2: d CoGleaf Rotation axis d CoGCW To optimally compensate for the leaf rotation, the MS and HS should be precisely aligned and thus the final machining of the houses of all ball bearings is carried out once all relevant supporting parts are assembled. M Leaf M CW HS balancing masses Levers in aluminium Figure 7: The principle of the thermal stability. M leaf M CW = d CoG CW d CoGleaf = Cst (2) MS balancing masses Counterweights Figure 6: Components introduced to perform the finetuned adjustments of the RSU CoG, MoI, and PoI. The counter-balancing of the torque around the rotation axis is not sufficient, as the product of inertia terms in the equation 1 below contribute to generate exported torques also along the XY directions. The changes in the MoI of one shaft with respect to the other due to the thermal shrinking are also compensated by the RSU design, having been first quantified by analysis and then taken into account to optimize the shape of the FW. The two shafts and all the supporting parts are made of titanium alloy to limit any thermo-elastic distortion. I xx I xy I xz 0 I xz θ z ( I yy I yz ) ( 0 ) = ( I yz θ z ) (1) I zz θ z I xz θ z To limit the impact of the cross inertia matrix terms the design of the leaf has been carefully symmetrized and both shafts have been equipped with adjustable masses to minimize both the static and dynamic unbalances. Thermal stability All the adjustments mentioned before are done at room temperature but shall retain their validity across the entire unit operational temperature range ( K). This is ensured by a careful design of all the RSU mobile parts. As an example, the leaf mass is counter-balanced by a large C-shaped tungsten alloy weight (as shown on Figure 6). This shape allows to have the lever between the rotation axis and the centre of gravity (CoG) of the counterweight (CW) in aluminium alloy. This way, the mass ratio equal the levers ratio independently from the temperature and the global CoG of the assembly is Figure 8: Thermo-elastic displacements. Micro-vibrations The RSU is also expected to limit the "high" frequency (10-500Hz) content of the exported loads to reduce to a negligible level the disturbances to the VIS and NISP instruments. To investigate this aspect, a dedicated model was developed in MATLAB and SIMULINK and we identified the following contributions to the RSU high frequency content of the exported loads: The closed-loop current and the micro-stepping
4 parameters of the motorcontroller; The resistance, inductance, detent torque, back electromotive force constant, torque constant, and hysteresis torque factor of the motor; The gear ratio, backlash, variable mesh stiffness, friction and damping; The friction of the ball bearings; The inertia tensor of the mobile parts (including the corresponding uncertainties as described before); The leaf rigid-body and flexible modes, together with the modal damping; The contacts of the micro-switches; The misalignments in the RSU mounting and between the HS and MS rotation axes. Figure 9: RSU Leaf block diagram The analyses performed with this model permitted to determine all the budgets needed for the balancing, alignment, control precision, and also the influence of the RSU motion profiles. These analyses have also shown that, among all contributors to the high frequency content of the exported loads, the hatch flexible modes are playing a dominant role. This is shown in Figure 11 (see the four green peaks). Figure 11: Exported micro-vibrations induced by the RSU along the Z direction. DESIGN EVOLUTIONS The RSU design has significantly evolved from the early baseline achieved at the end of phase B (see Figure 12) to the current phase C, mainly due to the increased complexity of the available micro-vibration model. Figure 10: The first RSU flexible mode at 120Hz. Figure 12: The RSU design at the end of Phase B. The most relevant changes between the phase B and C design are: an improved configuration of the microswitches, allowing us to increase the motorization margin; the suppression of the mobile Fail-Safe
5 Mechanism (FSM) on the HS, which was shown to degrade the unit reliability; the suppression of the Hold-Down and Release Mechanism (HDRM), as it was shown that the properly balanced MoIs of the two shafts and the stepper motor detent torque were sufficient to keep in place all the mobile parts even when subjected to the largest expected external loads; the introduction of all adjustment capabilities in order to keep the manufacturing feasibility at an acceptable level without degrading the microvibration performances; the introduction of an anti-backlash system in the gears to minimize the micro-vibrations experience during the first dedicated test of the bread-board model (see the next section). the FM design in terms of lengths, wire gauges, and shielding. The mechanical parts have been procured to comply with the established flights standard. The RSU STM is a simplified model designed to be representative of the FM predicted mass and moment of inertia (MoI) and being used for the structural and thermal tests. All the electrical components are replaced by mass dummies, while the rest (materials, coatings, paints, etc) is representative of the flight model. The improved RSU design achieved at the manufacturing review of the flight model is shown in Figure 4. MODEL PHILOSOPHY The entire RSU development program foresees the production of the following different models: An electrical model (EM) to validate all electrical functions and interfaces of the units, verifying its ESD and EMC properties; A structural and thermal model (STM) to validate the test feasibility and to allow vibration and thermal tests at Spacecraft level; A Drive Train Model (DTM) to perform preliminarily micro-vibration tests and develop in house the required RSU control equipment (EGSE); A bread-board model (BM) to carry out the first full micro-vibration and lifetime tests, validating the RSU tribological elements, the driving motor and the micro-switches; A qualification model (QM); A flight model (FM); A flight spare (FS). Figure 14: the RSU Structural and Thermal Model. The RSU BM is used to perform the first measurements of the unit micro-vibration and exported torque performances (evaluated so far only through numerical modelling), together with a first lifetime test. In order to serve these objectives, the RSU BM was designed to include all contributors to the micro-vibrations and exported loads identified by analysis. It also requires that the HS and the MS are fully representative of those of the FM in terms of materials, geometry, lubrication, assembly, adjustment, and balancing procedure. Some geometrical simplification of the support structure is applied for programmatic reasons. The RSU DTM is a simplified version of the BM that can be operated in ambient conditions, making use of wet lubricants and avoiding any paints. Figure 13: The RSU Electrical Model. The RSU EM is representative of all the electronic components of the RSU. The harness is representative of Figure 15: The RSU Drive Train Model.
6 related to the impact of the air flow produced by the moving RSU leaf onto the machine frame. A "bell" has been used to limit this effect, as shown in Figure 18. Figure 16: The RSU Breadboard Model. ASSEMBLY AND INTEGRATION In addition to the usual installations and tools to perform assembly and integration of space mechanisms, 3 specific facilities have been used for the RSU. The first one, mentioned earlier, is the precise Schenck's MoI measurement machine shown in Figure 17 and specifically procured for the RSU project. Figure 18: Machines at Schenck premises used to the perform the balancing of the RSU Hatch Shaft. The last facility that has been critical for the APCO Technologies activities was a vacuum chamber installed in house. The availability of this facility ensures that all actuations and run-in activities of the RSU can take place in a proper environment, preserving at best the dry lubricant applied on all unit tribological elements. Figure 19: The RSU BM inside the vacuum chamber installed at APCO s premises. TEST All the tests foreseen for the full qualification of the RSU have been performed at least once on the DTM, BM, STM, and EM, to de-risk the development of the most critical models (QM, FM, and FS). Figure 17: The Schenck machine, here used to perform the precise measurement of the RSU Hatch Shaft MoI. The second one is a machine available at the Schenck premises that has been used to perform the static and dynamic balancing of the RSU shafts. The major problem that we encountered during these measurements was The ESD and EMC tests have been successfully conducted on the EM, while the compliance of the unit to the foreseen vibration levels has been proven by using the STM and the BM. These tests have also been used to validate the removal of the HDRM. Reduced and complete micro-vibration tests have been carried out on the DTM and the BM, respectively. The lessons learned from these test campaigns are summarized below.
7 Vibration test The BM vibration test demonstrated that the HDRM was not needed. The wear at the mesh location was found to be virtually identical with or without the holding mechanism. An in-depth inspection with the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) was performed to check that the MoS2 layer was still present after the vibration test. Lifetime The BM successfully underwent a lifetime test during which and 21 opening and closing sequences have been performed respectively in vacuum and in air. A new SEM inspection after the test revealed that the coating was in good conditions. In the zone worn by the vibration test, the coating was even more homogeneously distributed than before the lifetime test. Figure 20: Random vibration level passed successfully. Figure 22: The RSU gears SEM inspection before (left) and after (right) the lifetime test. Microvibration The first complete microvibration test was performed at ESA/ESTEC on the Reaction wheel Characterisation Facility (RCF). The measured levels were largely above the expectations, as shown in Figure 23. Figure 21: RSU vibration test performed using a laser vibrometer to avoid accelerometers mounted on the moving parts. Thermal vacuum test The target temperature of 110K is at the limit of the performances of vacuum chambers making use of gas nitrogen GN2 thermal generators. The test has been repeated two times to achieve the targeted temperature of 110 K with the GN2 available at Intespace. This facility allows us to cool down both the cold plate and the shrouds and heat losses were minimizedthrough the inclusion of an additional insulation layer. The experience gained through this test guarantees that a proper QM qualification campaign can be carried out at Intespace. Figure 23: The measured RSU Exported torque at RCF. This test highlighted an issue in the simulation with the implementation of the backlash function and related trade-off concluding that no anti-backlash system was necessary. After the revision of the analysis, an anti-backlash has been designed and tested first on the DTM. The results
8 obtained are promising as shown in Figure 24. The design chosen will allow a late decision to implement or not anti-backlash system on the QM. A second lifetime test on the BM, including the antibacklash system modification, will help in the decision. Figure 24: The RSU DTM induced micro-vibrations measured without (left) and with (right) the anti-backlash system. CONCLUSIONS The RSU design has been continuously improved over the past 6 years to comply with the expected operations in a harsh environment and with all the challenging Euclid and VIS instrument requirements. The RSU EM and STM programs have been completed and the two models successfully passed all foreseen tests. The DTM has proved very helpful in designing the EGSE and performing intermediate tests. The BM model has successfully confirmed the capability of the selected components to sustain the planned longterm operations at cryogenic temperatures in the nominal configuration. In a second lifetime test to be carried out in late 2017, the BM will be used to confirm the compliance of the unit with the long-term operations when the anti-backlash system is included to minimize the micro-vibrations. The design of the RSU is expected to reach full maturity at the end of 2017, when a fully de-risked QM test campaign will be initiated before the manufacturing of the FM and FS (starting in 2018). ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The Euclid team at the University of Geneva and APCO Technologies acknowledges the support from the Swiss State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI) and ESA's PRODEX programme. We also thank all members of the Euclid consortium for the fruitful collaboration and the pleasant working environment. We are grateful to the ESA Prodex team for their extensive support and collaboration on the project. REFERENCES 1. Euclid Consortium's website. Online at (as of 19 th of June 2017) 2. Cropper, M. et al (2016). VIS: the visible imager for Euclid. Proceedings of the SPIE, Volume 9904, id Q 16 pp. 3. Genolet, L. et al (2016). The Read-Out Shutter Unit of the Euclid VIS Instrument. Proceedings of the SPIE, Volume 9904, id U 9 pp.
EUCLID M2 MIRROR MECHANISM
 EUCLID M2 MIRROR MECHANISM Aiala Artiagoitia (1), Carlos Compostizo (1), Laura Rivera (1) (1) SENER, Av. Zugazarte 56, 48930 Las Arenas (Bizkaia) Spain, Email: aiala.artiagoitia@sener.es ABSTRACT Euclid
EUCLID M2 MIRROR MECHANISM Aiala Artiagoitia (1), Carlos Compostizo (1), Laura Rivera (1) (1) SENER, Av. Zugazarte 56, 48930 Las Arenas (Bizkaia) Spain, Email: aiala.artiagoitia@sener.es ABSTRACT Euclid
CALIBRATION MECHANISM FOR INFRARED SPACE TELESCOPE. Patrice Kerhousse
 CALIBRATION MECHANISM FOR INFRARED SPACE TELESCOPE Patrice Kerhousse Alcatel space industries Boulevard du Midi, BP 99-06156 Cannes la Bocca Cedex Telephone : 33-(0)4-92-92-72-38 / Fax : 33-(0)4-92-92--20
CALIBRATION MECHANISM FOR INFRARED SPACE TELESCOPE Patrice Kerhousse Alcatel space industries Boulevard du Midi, BP 99-06156 Cannes la Bocca Cedex Telephone : 33-(0)4-92-92-72-38 / Fax : 33-(0)4-92-92--20
3D metrology with a laser tracker inside a vacuum chamber for NISP test campaign
 In: SPIE astronomical Telescope and Instrumentation, Austin 2018 3D metrology with a laser tracker inside a vacuum chamber for NISP test campaign Anne Costille *,a, Florent Beaumont b, Eric Prieto a, Michael
In: SPIE astronomical Telescope and Instrumentation, Austin 2018 3D metrology with a laser tracker inside a vacuum chamber for NISP test campaign Anne Costille *,a, Florent Beaumont b, Eric Prieto a, Michael
BUILDING LOW-COST NANO-SATELLITES: THE IMPORTANCE OF A PROPER ENVIRONMENTAL TESTS CAMPAIGN. Jose Sergio Almeida INPE (Brazil)
 BUILDING LOW-COST NANO-SATELLITES: THE IMPORTANCE OF A PROPER ENVIRONMENTAL TESTS CAMPAIGN Jose Sergio Almeida INPE (Brazil) 1 st International Academy of Astronautics Latin American Symposium on Small
BUILDING LOW-COST NANO-SATELLITES: THE IMPORTANCE OF A PROPER ENVIRONMENTAL TESTS CAMPAIGN Jose Sergio Almeida INPE (Brazil) 1 st International Academy of Astronautics Latin American Symposium on Small
Mounts for large lens in cooled environment
 Mounts for large lens in cooled environment Thierry VIARD / Christophe DEVILLIERS Thales Alenia Space TAS Cannes La Bocca, France Thierry.viard@thalesaleniaspace.com Vincent COSTES / Didier GANGLOFF Centre
Mounts for large lens in cooled environment Thierry VIARD / Christophe DEVILLIERS Thales Alenia Space TAS Cannes La Bocca, France Thierry.viard@thalesaleniaspace.com Vincent COSTES / Didier GANGLOFF Centre
GAIA M2M POINTING MECHANISM QUALIFICATION
 GAIA M2M POINTING MECHANISM QUALIFICATION Carlos Compostizo (1), Ricardo López (1), Laura Rivera (1) (1) SENER-Structures & Mechanisms Section, Av. Zugazarte 56, 4893 Las Arenas (Vizcaya) Spain Tel: 34944817578
GAIA M2M POINTING MECHANISM QUALIFICATION Carlos Compostizo (1), Ricardo López (1), Laura Rivera (1) (1) SENER-Structures & Mechanisms Section, Av. Zugazarte 56, 4893 Las Arenas (Vizcaya) Spain Tel: 34944817578
Observing the dark Universe with Euclid
 Euclid Imaging Instrument Observing the dark Universe with Euclid 18 november 2009 Jerome Amiaux CEA Saclay EIC System Manager On Behalf of the Euclid Imaging Consortium The presented document is Proprietary
Euclid Imaging Instrument Observing the dark Universe with Euclid 18 november 2009 Jerome Amiaux CEA Saclay EIC System Manager On Behalf of the Euclid Imaging Consortium The presented document is Proprietary
Picometre metrology. The Gaia mission will create an ultra-precise three-dimensional map of about one billion stars
 Picometre metrology in space The Gaia mission will create an ultra-precise three-dimensional map of about one billion stars in our Galaxy. Part of ESA s Cosmic Vision program, the Gaia spacecraft is being
Picometre metrology in space The Gaia mission will create an ultra-precise three-dimensional map of about one billion stars in our Galaxy. Part of ESA s Cosmic Vision program, the Gaia spacecraft is being
ADM-Aeolus Science and Cal/Val Workshop
 ADM-Aeolus Science and Cal/Val Workshop ESA ESRIN, Frascati, ITALY 10 13 February 2015 THE ALADIN INSTRUMENT AND ITS ON-GROUND CHARACTERISATION O. Lecrenier, F. Fabre, J. Lochard Airbus Defense & Space
ADM-Aeolus Science and Cal/Val Workshop ESA ESRIN, Frascati, ITALY 10 13 February 2015 THE ALADIN INSTRUMENT AND ITS ON-GROUND CHARACTERISATION O. Lecrenier, F. Fabre, J. Lochard Airbus Defense & Space
New isostatic mounting concept for a space born Three Mirror Anastigmat (TMA) on the Meteosat Third Generation Infrared Sounder Instrument (MTG-IRS)
 New isostatic mounting concept for a space born Three Mirror Anastigmat (TMA) on the Meteosat Third Generation Infrared Sounder Instrument (MTG-IRS) Maximilian Freudling a, Jesko Klammer a, Gregory Lousberg
New isostatic mounting concept for a space born Three Mirror Anastigmat (TMA) on the Meteosat Third Generation Infrared Sounder Instrument (MTG-IRS) Maximilian Freudling a, Jesko Klammer a, Gregory Lousberg
Space mission environments: sources for loading and structural requirements
 Space structures Space mission environments: sources for loading and structural requirements Prof. P. Gaudenzi Università di Roma La Sapienza, Rome Italy paolo.gaudenzi@uniroma1.it 1 THE STRUCTURAL SYSTEM
Space structures Space mission environments: sources for loading and structural requirements Prof. P. Gaudenzi Università di Roma La Sapienza, Rome Italy paolo.gaudenzi@uniroma1.it 1 THE STRUCTURAL SYSTEM
DESIGN AND QUALIFICATION OF THE CRYOGENIC COVER MECHANISM FOR THE MID-INFRARED INSTRUMENT ON THE JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE
 DESIGN AND QUALIFICATION OF THE CRYOGENIC COVER MECHANISM FOR THE MID-INFRARED INSTRUMENT ON THE JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE U. Langer (1), A. Neukom (1), R. Romano (1), A. Vuilleumier (1) (1) RUAG Aerospace,
DESIGN AND QUALIFICATION OF THE CRYOGENIC COVER MECHANISM FOR THE MID-INFRARED INSTRUMENT ON THE JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE U. Langer (1), A. Neukom (1), R. Romano (1), A. Vuilleumier (1) (1) RUAG Aerospace,
Cold Gas Thruster Qualification for FORMOSAT 5
 Cold Gas Thruster Qualification for FORMOSAT 5 By Hans-Peter HARMANN 1), Tammo ROMBACH 2) and Heiko DARTSCH 1) 1) AST Advanced Space Technologies GmbH, Stuhr, Germany 2) SpaceTech GmbH, Immenstaad, Germany
Cold Gas Thruster Qualification for FORMOSAT 5 By Hans-Peter HARMANN 1), Tammo ROMBACH 2) and Heiko DARTSCH 1) 1) AST Advanced Space Technologies GmbH, Stuhr, Germany 2) SpaceTech GmbH, Immenstaad, Germany
MICRO-VIBRATION PERFORMANCE PREDICTION OF SEPTA24 USING SMESIM (RUAG SPACE MECHANISM SIMULATOR TOOL)
 MICRO-VIBRATION PERFORMANCE PREDICTION OF SEPTA24 USING SMESIM (RUAG SPACE MECHANISM SIMULATOR TOOL) Manolo Omiciuolo, Andreas Lang, Stefan Wismer, Stephan Barth, & Dr. Gerhard Székely RUAG Schweiz AG,
MICRO-VIBRATION PERFORMANCE PREDICTION OF SEPTA24 USING SMESIM (RUAG SPACE MECHANISM SIMULATOR TOOL) Manolo Omiciuolo, Andreas Lang, Stefan Wismer, Stephan Barth, & Dr. Gerhard Székely RUAG Schweiz AG,
Selection Calculations For Linear & Rotary Actuators
 H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
H-8 For Electric Linear Slides and Electric Cylinders First determine your series, then select your product. Select the actuator that you will use based on the following flow charts: Selection Procedure
SAMPLE CANISTER CAPTURE MECHANISM FOR MSR: CONCEPT DESIGN AND TESTING RESULTS INCLUDING 0-G ENVIRONMENT
 SAMPLE CANISTER CAPTURE MECHANISM FOR MSR: CONCEPT DESIGN AND TESTING RESULTS INCLUDING 0-G ENVIRONMENT Authors: Riccardo Carta, Daniele Filippetto, Politecnico di Milano Co-authors: Prof. Michèle Lavagna,
SAMPLE CANISTER CAPTURE MECHANISM FOR MSR: CONCEPT DESIGN AND TESTING RESULTS INCLUDING 0-G ENVIRONMENT Authors: Riccardo Carta, Daniele Filippetto, Politecnico di Milano Co-authors: Prof. Michèle Lavagna,
SPICE SDM: INNOVATIVE APPROACHES FOR LINEAR MOTION AND HEAT MANAGEMENT
 SPICE SDM: INNOVATIVE APPROACHES FOR LINEAR MOTION AND HEAT MANAGEMENT Ken Relecom (1), Cyril Larchevêque (1), Joël Constant (1), Nordahl Autissier (1), Arnaud Pornin (1), Nicolas Martini (1) (1) APCO
SPICE SDM: INNOVATIVE APPROACHES FOR LINEAR MOTION AND HEAT MANAGEMENT Ken Relecom (1), Cyril Larchevêque (1), Joël Constant (1), Nordahl Autissier (1), Arnaud Pornin (1), Nicolas Martini (1) (1) APCO
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)
 James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Engineering the Beginning US Frontiers of Engineering Conference Amy S. Lo JWST System Engineering Space-Based observation has enabled giant leaps in our understanding
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Engineering the Beginning US Frontiers of Engineering Conference Amy S. Lo JWST System Engineering Space-Based observation has enabled giant leaps in our understanding
Influence of electromagnetic stiffness on coupled micro vibrations generated by solar array drive assembly
 Influence of electromagnetic stiffness on coupled micro vibrations generated by solar array drive assembly Mariyam Sattar 1, Cheng Wei 2, Awais Jalali 3 1, 2 Beihang University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,
Influence of electromagnetic stiffness on coupled micro vibrations generated by solar array drive assembly Mariyam Sattar 1, Cheng Wei 2, Awais Jalali 3 1, 2 Beihang University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,
Jitter and Basic Requirements of the Reaction Wheel Assembly in the Attitude Control System
 Jitter and Basic Requirements of the Reaction Wheel Assembly in the Attitude Control System Lulu Liu August, 7 1 Brief Introduction Photometric precision is a major concern in this space mission. A pointing
Jitter and Basic Requirements of the Reaction Wheel Assembly in the Attitude Control System Lulu Liu August, 7 1 Brief Introduction Photometric precision is a major concern in this space mission. A pointing
Dimensional stability testing in thermal vacuum of the CHEOPS optical telescope assembly
 Dimensional stability testing in thermal vacuum of the CHEOPS optical telescope assembly W.A. Klop 1, A.L. Verlaan 2 TNO, Institute of applied physics, Stieltjesweg 1, 2628 CK, The Netherlands, wimar.klop@tno.nl
Dimensional stability testing in thermal vacuum of the CHEOPS optical telescope assembly W.A. Klop 1, A.L. Verlaan 2 TNO, Institute of applied physics, Stieltjesweg 1, 2628 CK, The Netherlands, wimar.klop@tno.nl
TE 75R RESEARCH RUBBER FRICTION TEST MACHINE
 TE 75R RESEARCH RUBBER FRICTION TEST MACHINE Background: The Research Rubber Friction Test Machine offers the ability to investigate fully the frictional behaviour of rubbery materials both in dry and
TE 75R RESEARCH RUBBER FRICTION TEST MACHINE Background: The Research Rubber Friction Test Machine offers the ability to investigate fully the frictional behaviour of rubbery materials both in dry and
DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL ACTIVE ISOLATION CONCEPT 1
 DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL ACTIVE ISOLATION CONCEPT 1 Michiel J. Vervoordeldonk, Theo A.M. Ruijl, Rob M.G. Rijs Philips Centre for Industrial Technology, PO Box 518, 5600 MD Eindhoven, The Netherlands 2 1
DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL ACTIVE ISOLATION CONCEPT 1 Michiel J. Vervoordeldonk, Theo A.M. Ruijl, Rob M.G. Rijs Philips Centre for Industrial Technology, PO Box 518, 5600 MD Eindhoven, The Netherlands 2 1
The Quantum Sensor Challenge Designing a System for a Space Mission. Astrid Heske European Space Agency The Netherlands
 The Quantum Sensor Challenge Designing a System for a Space Mission Astrid Heske European Space Agency The Netherlands Rencontres de Moriond - Gravitation, La Thuile, 2017 Quantum Sensors in Lab Experiments
The Quantum Sensor Challenge Designing a System for a Space Mission Astrid Heske European Space Agency The Netherlands Rencontres de Moriond - Gravitation, La Thuile, 2017 Quantum Sensors in Lab Experiments
Sun Shield. Solar Paddle
 The Institute of Space and Astronautical Science Report SP No.14, December 2000 Current Status of ASTRO-F By Hiroshi Murakami Λ (November 1, 2000) Abstract: The ASTRO-F is the second infrared astronomy
The Institute of Space and Astronautical Science Report SP No.14, December 2000 Current Status of ASTRO-F By Hiroshi Murakami Λ (November 1, 2000) Abstract: The ASTRO-F is the second infrared astronomy
Piezoelectric Actuators and Future Motors for Cryogenic Applications in Space
 Piezoelectric Actuators and Future Motors for Cryogenic Applications in Space Christian Belly*, Francois Barillot* and Fabien Dubois * Abstract The purpose of this paper is to present the current investigation
Piezoelectric Actuators and Future Motors for Cryogenic Applications in Space Christian Belly*, Francois Barillot* and Fabien Dubois * Abstract The purpose of this paper is to present the current investigation
4.3 Planck. Scientific goals. Planck payload
 4.3 Planck In late 1992, the NASA COBE team announced the detection of intrinsic temperature fluctuations in the Cosmic Background Radiation Field (CBRF), observed on the sky at angular scales larger than
4.3 Planck In late 1992, the NASA COBE team announced the detection of intrinsic temperature fluctuations in the Cosmic Background Radiation Field (CBRF), observed on the sky at angular scales larger than
Nanomotion Precision Piezo Ceramic Motors
 Nanomotion Precision Piezo Ceramic Motors The Company Nanomotion was founded in 1992 Developed enabling technology for ultrasonic piezo-ceramic motors Entered the market in 1996, selling products to leading
Nanomotion Precision Piezo Ceramic Motors The Company Nanomotion was founded in 1992 Developed enabling technology for ultrasonic piezo-ceramic motors Entered the market in 1996, selling products to leading
Mechanical and Thermal Design of XMM
 r bulletin 100 december 1999 Mechanical and Thermal Design of XMM K. van Katwijk, T. van der Laan & D. Stramaccioni XMM Project, ESA Directorate for Scientific Programmes, ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands
r bulletin 100 december 1999 Mechanical and Thermal Design of XMM K. van Katwijk, T. van der Laan & D. Stramaccioni XMM Project, ESA Directorate for Scientific Programmes, ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands
THE NEW 1.1 MN m TORQUE STANDARD MACHINE OF THE PTB BRAUNSCHWEIG/GERMANY
 THE NEW 1.1 MN m TORQUE STANDARD MACHINE OF THE PTB BRAUNSCHWEIG/GERMANY D. Peschel 1, D. Mauersberger 1, D. Schwind 2, U. Kolwinski 2 1 Solid mechanics department, PTB, Germany 2 Gassmann Theiss Messtechnik
THE NEW 1.1 MN m TORQUE STANDARD MACHINE OF THE PTB BRAUNSCHWEIG/GERMANY D. Peschel 1, D. Mauersberger 1, D. Schwind 2, U. Kolwinski 2 1 Solid mechanics department, PTB, Germany 2 Gassmann Theiss Messtechnik
E3000 High Power SADM Development
 Stephen G Bamford, BSc Hons EADS Astrium UK Ltd, Gunnels Wood Road, Stevenage, Herts., England, SG1 2AS, +44(0)1438 773339 Stephen.bamford@astrium.eads.net ABSTRACT Maintaining their history of successful
Stephen G Bamford, BSc Hons EADS Astrium UK Ltd, Gunnels Wood Road, Stevenage, Herts., England, SG1 2AS, +44(0)1438 773339 Stephen.bamford@astrium.eads.net ABSTRACT Maintaining their history of successful
Progress in Testing of QM and FM HEMP Thruster Modules
 Progress in Testing of QM and FM HEMP Thruster Modules IEPC-2013-274 Presented at the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference, The George Washington University Washington, D.C. USA A. Lazurenko
Progress in Testing of QM and FM HEMP Thruster Modules IEPC-2013-274 Presented at the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference, The George Washington University Washington, D.C. USA A. Lazurenko
Centre for Electronic Imaging
 Centre for Electronic Imaging Calibration plans for the Soft X-ray Imager s CCDs on SMILE Open University: George Randall, Matthew Soman, David Hall, Andrew Holland, Ross Burgon, Jonathan Keelan, Thomas
Centre for Electronic Imaging Calibration plans for the Soft X-ray Imager s CCDs on SMILE Open University: George Randall, Matthew Soman, David Hall, Andrew Holland, Ross Burgon, Jonathan Keelan, Thomas
EUCLID Mission Baseline Design
 EUCLID Mission Baseline Design Oswald Wallner 1, Klaus Ergenzinger 1, Rainer Wilhelm 1, Ludovic Vaillon 2 Astrium Satellites 1 8839 Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2 31 rue des Cosmonautes, 3142 Toulouse Cedex
EUCLID Mission Baseline Design Oswald Wallner 1, Klaus Ergenzinger 1, Rainer Wilhelm 1, Ludovic Vaillon 2 Astrium Satellites 1 8839 Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2 31 rue des Cosmonautes, 3142 Toulouse Cedex
Product description. Compact Modules. Characteristic features. Further highlights
 4 Compact Modules Product description Characteristic features Five fine-tuned sizes based on a compact precision aluminum profile with two integrated pre-tensioned ball rail systems Identical external
4 Compact Modules Product description Characteristic features Five fine-tuned sizes based on a compact precision aluminum profile with two integrated pre-tensioned ball rail systems Identical external
The James Webb Space Telescope
 The Session: ENGINEERING THE SEARCH FOR EARTH-LIKE EXOPLANETS Author: Amy Lo, Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems Abstract NASA s is the premier space telescope of its time. Set to launch in Oct. 2018,
The Session: ENGINEERING THE SEARCH FOR EARTH-LIKE EXOPLANETS Author: Amy Lo, Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems Abstract NASA s is the premier space telescope of its time. Set to launch in Oct. 2018,
Spacecraft Structures
 Tom Sarafin Instar Engineering and Consulting, Inc. 6901 S. Pierce St., Suite 384, Littleton, CO 80128 303-973-2316 tom.sarafin@instarengineering.com Functions Being Compatible with the Launch Vehicle
Tom Sarafin Instar Engineering and Consulting, Inc. 6901 S. Pierce St., Suite 384, Littleton, CO 80128 303-973-2316 tom.sarafin@instarengineering.com Functions Being Compatible with the Launch Vehicle
THE MICRO ADVANCED STELLAR COMPASS FOR ESA S PROBA 2 MISSION
 THE MICRO ADVANCED STELLAR COMPASS FOR ESA S PROBA 2 MISSION P.S. Jørgensen (1), J.L. Jørgensen (1), T. Denver (1), Pieter van den Braembuche (2) (1) Technical University of Denmark, Ørsted*DTU, Measurement
THE MICRO ADVANCED STELLAR COMPASS FOR ESA S PROBA 2 MISSION P.S. Jørgensen (1), J.L. Jørgensen (1), T. Denver (1), Pieter van den Braembuche (2) (1) Technical University of Denmark, Ørsted*DTU, Measurement
BepiColombo. Project and MPO Status. Comprehensive Explora1on of Planet Mercury
 BepiColombo Project and MPO Status Comprehensive Explora1on of Planet Mercury Joe Zender BepiColombo Deputy PS, ESA/ESTEC BepiColombo Previously: Ø Proba2 Science Coordinator, until 12/2013 Ø ProbaV, Project
BepiColombo Project and MPO Status Comprehensive Explora1on of Planet Mercury Joe Zender BepiColombo Deputy PS, ESA/ESTEC BepiColombo Previously: Ø Proba2 Science Coordinator, until 12/2013 Ø ProbaV, Project
BOWSER Balloon Observatory for Wavelength and Spectral Emission Readings
 COSGC Space Research Symposium 2009 BOWSER Balloon Observatory for Wavelength and Spectral Emission Readings BOWSER 1 Mission Premise 4.3 km above sea level 402.3km above sea level BOWSER 2 Information
COSGC Space Research Symposium 2009 BOWSER Balloon Observatory for Wavelength and Spectral Emission Readings BOWSER 1 Mission Premise 4.3 km above sea level 402.3km above sea level BOWSER 2 Information
Status / Progress of the erosita X ray Observatory:
 Status / Progress of the erosita X ray Observatory: Vadim Burwitz, Max Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik On behalf of the erosita Team IACHEC #9, May 13, 2014, Airlie Center, Warrenton, Virginia,
Status / Progress of the erosita X ray Observatory: Vadim Burwitz, Max Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik On behalf of the erosita Team IACHEC #9, May 13, 2014, Airlie Center, Warrenton, Virginia,
Modelling of a dynamic torque calibration device and determination of model parameters
 ACTA IMEKO June 2014, Volume 3, Number 2, 14 18 www.imeko.org Modelling of a dynamic torque calibration device and determination of model parameters Leonard Klaus, Thomas Bruns, Michael Kobusch Physikalisch-Technische
ACTA IMEKO June 2014, Volume 3, Number 2, 14 18 www.imeko.org Modelling of a dynamic torque calibration device and determination of model parameters Leonard Klaus, Thomas Bruns, Michael Kobusch Physikalisch-Technische
Compact, lightweight, and athermalized mirror and mount for use on JWST's NIRCam instrument
 Compact, lightweight, and athermalized mirror and mount for use on JWST's NIRCam instrument Derek Edinger, Paul Mammini*, Liz Osborne Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center, 3251 Hanover St., Palo
Compact, lightweight, and athermalized mirror and mount for use on JWST's NIRCam instrument Derek Edinger, Paul Mammini*, Liz Osborne Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center, 3251 Hanover St., Palo
Glossary Innovative Measurement Solutions
 Glossary GLOSSARY OF TERMS FOR TRANSDUCERS, LOAD CELLS AND WEIGH MODULES This purpose of this document is to provide a comprehensive, alphabetical list of terms and definitions commonly employed in the
Glossary GLOSSARY OF TERMS FOR TRANSDUCERS, LOAD CELLS AND WEIGH MODULES This purpose of this document is to provide a comprehensive, alphabetical list of terms and definitions commonly employed in the
Appendix G. Solar Orbiter SPICE Thermal Design, Analysis and Testing. Samuel Tustain (RAL Space, United Kingdom)
 137 Appendix G Solar Orbiter SPICE Thermal Design, Analysis and Testing Samuel Tustain (RAL Space, United Kingdom) 138 Solar Orbiter SPICE Thermal Design, Analysis and Testing Abstract 1 The Spectral Imaging
137 Appendix G Solar Orbiter SPICE Thermal Design, Analysis and Testing Samuel Tustain (RAL Space, United Kingdom) 138 Solar Orbiter SPICE Thermal Design, Analysis and Testing Abstract 1 The Spectral Imaging
Design and Development of an Unrestricted Satellite Motion Simulator
 Design and Development of an Unrestricted Satellite Motion Simulator Eryn Culton, Jeffery King, Paige Ward United States Naval Academy Annapolis, MD 21402 POC: jking@usna.edu 31st Annual AIAA/USU Conference
Design and Development of an Unrestricted Satellite Motion Simulator Eryn Culton, Jeffery King, Paige Ward United States Naval Academy Annapolis, MD 21402 POC: jking@usna.edu 31st Annual AIAA/USU Conference
Federico Landini. INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri
 Federico Landini INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri Outline METIS and its occulting system Theoretical estimate of the diffraction pattern on the primary mirror plane Occulter optimization concept
Federico Landini INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri Outline METIS and its occulting system Theoretical estimate of the diffraction pattern on the primary mirror plane Occulter optimization concept
LISA Telescope Assembly Optical Stability Characterization for ESA
 LISA Telescope Assembly Optical Stability Characterization for ESA A.L. Verlaan, H. Hogenhuis, J. Pijnenburg, M. Lemmen TNO, Institute of applied physics Delft, The Netherlands ad.verlaan@tno.nl S. Lucarelli,
LISA Telescope Assembly Optical Stability Characterization for ESA A.L. Verlaan, H. Hogenhuis, J. Pijnenburg, M. Lemmen TNO, Institute of applied physics Delft, The Netherlands ad.verlaan@tno.nl S. Lucarelli,
Open Research Online The Open University s repository of research publications and other research outputs
 Open Research Online The Open University s repository of research publications and other research outputs Developments in efficiency and stability of fluid film bearings using new designs and test techniques
Open Research Online The Open University s repository of research publications and other research outputs Developments in efficiency and stability of fluid film bearings using new designs and test techniques
Thermal Design and Analysis of the BroadBand Radiometer. Oliver Poyntz-Wright (Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, United Kingdom)
 255 Appendix T Thermal Design and Analysis of the BroadBand Radiometer Oliver Poyntz-Wright (Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, United Kingdom) 256 Thermal Design and Analysis of the BroadBand Radiometer
255 Appendix T Thermal Design and Analysis of the BroadBand Radiometer Oliver Poyntz-Wright (Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, United Kingdom) 256 Thermal Design and Analysis of the BroadBand Radiometer
Figure testing of 300 mm Zerodur mirrors at cryogenic temperatures
 Figure testing of 300 mm Zerodur mirrors at cryogenic temperatures J. W. Baer, W. P. Lotz Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. PO Box 1062 Boulder, CO 80306 Keywords: mirrors, figure testing, cryogenic,
Figure testing of 300 mm Zerodur mirrors at cryogenic temperatures J. W. Baer, W. P. Lotz Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. PO Box 1062 Boulder, CO 80306 Keywords: mirrors, figure testing, cryogenic,
An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump
 An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump Young Kuen Cho, Seong Guk Kim, Dae Won Lee, Paul Han and Han Sung Kim Abstract The purpose of this study was to examine the efficiency of the
An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump Young Kuen Cho, Seong Guk Kim, Dae Won Lee, Paul Han and Han Sung Kim Abstract The purpose of this study was to examine the efficiency of the
Control of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna
 Control of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna P. G. Maghami, T. T. Hyde NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Guidance, Navigation and Control Division Greenbelt, MD 20771 J. Kim Swales Aerospace, Inc.
Control of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna P. G. Maghami, T. T. Hyde NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Guidance, Navigation and Control Division Greenbelt, MD 20771 J. Kim Swales Aerospace, Inc.
Spitzer Space Telescope
 Spitzer Space Telescope (A.K.A. The Space Infrared Telescope Facility) The Infrared Imaging Chain 1/38 The infrared imaging chain Generally similar to the optical imaging chain... 1) Source (different
Spitzer Space Telescope (A.K.A. The Space Infrared Telescope Facility) The Infrared Imaging Chain 1/38 The infrared imaging chain Generally similar to the optical imaging chain... 1) Source (different
Euclid Consortium EUCLID NISP INSTRUMENT PRESENTATION. EUCLID CONSORTIUM MEETING BOLOGNA 7&8 September 2011 Authors : NISP TEAM Page : 1
 EUCLID NISP INSTRUMENT PRESENTATION EUCLID CONSORTIUM MEETING BOLOGNA 7&8 September 2011 Authors : NISP TEAM Page : 1 AGENDA NISP TECHNICAL PRESENTATION and STATUS NISP PHOTOMETRY PRESENTATION NISP SPECTROMETRY
EUCLID NISP INSTRUMENT PRESENTATION EUCLID CONSORTIUM MEETING BOLOGNA 7&8 September 2011 Authors : NISP TEAM Page : 1 AGENDA NISP TECHNICAL PRESENTATION and STATUS NISP PHOTOMETRY PRESENTATION NISP SPECTROMETRY
Scientific Capability of the James Webb Space Telescope and the Mid-InfraRed Instrument
 Scientific Capability of the James Webb Space Telescope and the Mid-InfraRed Instrument Oliver Krause (Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg) on behalf of Gillian Wright (Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
Scientific Capability of the James Webb Space Telescope and the Mid-InfraRed Instrument Oliver Krause (Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg) on behalf of Gillian Wright (Royal Observatory Edinburgh)
VIRTUAL TESTING SIMULATION TOOL FOR THE NEW QUAD HEAD EXPANDER ELECTRODYNAMIC SHAKER
 VIRTUAL TESTING SIMULATION TOOL FOR THE NEW QUAD HEAD EXPANDER ELECTRODYNAMIC SHAKER Matteo Appolloni,* AOES BV Alessandro Cozzani, European Space Agency * Matteo.Appolloni@esa.int Outline Introduction
VIRTUAL TESTING SIMULATION TOOL FOR THE NEW QUAD HEAD EXPANDER ELECTRODYNAMIC SHAKER Matteo Appolloni,* AOES BV Alessandro Cozzani, European Space Agency * Matteo.Appolloni@esa.int Outline Introduction
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 8 Balancing Lecture - 1 Introduce To Rigid Rotor Balancing Till
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 8 Balancing Lecture - 1 Introduce To Rigid Rotor Balancing Till
RGS08 Linear Rails: RGS08 Non-Motorized With and Without Guide Screw. RGS08 Non-Motorized Linear Rails
 RGS08 RGS08 Non-Motorized With and Without Guide RGS08 Non-Motorized Linear Rails RG Series linear rails are available: RGS08 Non-Motorized, -driven linear rail RGS08 Non-Motorized linear rail without
RGS08 RGS08 Non-Motorized With and Without Guide RGS08 Non-Motorized Linear Rails RG Series linear rails are available: RGS08 Non-Motorized, -driven linear rail RGS08 Non-Motorized linear rail without
Foundations of Ultraprecision Mechanism Design
 Foundations of Ultraprecision Mechanism Design S.T. Smith University of North Carolina at Charlotte, USA and D.G. Chetwynd University of Warwick, UK GORDON AND BREACH SCIENCE PUBLISHERS Switzerland Australia
Foundations of Ultraprecision Mechanism Design S.T. Smith University of North Carolina at Charlotte, USA and D.G. Chetwynd University of Warwick, UK GORDON AND BREACH SCIENCE PUBLISHERS Switzerland Australia
University of Bath. Publication date: Document Version Early version, also known as pre-print. Link to publication
 Citation for published version: Evans, M, Akehurst, S & Keogh, P 2014, 'Wear mechanisms in polyoxymethylene (POM) spur gears' Paper presented at 5th World Tribology Congress, WTC 2013, Torino, UK United
Citation for published version: Evans, M, Akehurst, S & Keogh, P 2014, 'Wear mechanisms in polyoxymethylene (POM) spur gears' Paper presented at 5th World Tribology Congress, WTC 2013, Torino, UK United
PROBA 1. F. Teston ESA/ESTEC D/TEC-EL
 PROBA 1 F. Teston ESA/ESTEC D/TEC-EL Frederic.Teston@esa.int PROBA 1 launch PROBA 1 has been launched on 21 October 2001 Orbital parameters: Altitude: 681-561 km Near polar (inclination of 97.9 ) Sun-synchronous
PROBA 1 F. Teston ESA/ESTEC D/TEC-EL Frederic.Teston@esa.int PROBA 1 launch PROBA 1 has been launched on 21 October 2001 Orbital parameters: Altitude: 681-561 km Near polar (inclination of 97.9 ) Sun-synchronous
Dynamic Tests on Ring Shear Apparatus
 , July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Dynamic Tests on Ring Shear Apparatus G. Di Massa Member IAENG, S. Pagano, M. Ramondini Abstract Ring shear apparatus are used to determine the ultimate shear strength of
, July 1-3, 2015, London, U.K. Dynamic Tests on Ring Shear Apparatus G. Di Massa Member IAENG, S. Pagano, M. Ramondini Abstract Ring shear apparatus are used to determine the ultimate shear strength of
Introduction To Metrology
 Introduction To Metrology Meaning of Metrology Metrology is the science of measurement. Metrology may be divided depending upon the quantity to be measured like metrology of length, metrology of time.
Introduction To Metrology Meaning of Metrology Metrology is the science of measurement. Metrology may be divided depending upon the quantity to be measured like metrology of length, metrology of time.
Design of Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem
 Design of Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem 1) Control Modes and Requirements Control Modes: Control Modes Explanation 1 ) Spin-Up Mode - Acquisition of Stability through spin-up maneuver -
Design of Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem 1) Control Modes and Requirements Control Modes: Control Modes Explanation 1 ) Spin-Up Mode - Acquisition of Stability through spin-up maneuver -
TROPOMI. Sentinel 5 Precursor instrument for air quality and climate observations. R. Voors Dutch Space. ICSO, 11 October 2012
 TROPOMI Sentinel 5 Precursor instrument for air quality and climate observations R. Voors Dutch Space ICSO, 11 October 2012 Sentinel 5 precursor and the TROPOMI payload Climate and Air quality Precursor
TROPOMI Sentinel 5 Precursor instrument for air quality and climate observations R. Voors Dutch Space ICSO, 11 October 2012 Sentinel 5 precursor and the TROPOMI payload Climate and Air quality Precursor
EQUIPMENT INTERFACE LOAD CHARACTERIZATION IN ACOUSTICS
 1 EQUIPMENT INTERFACE LOAD CHARACTERIZATION IN ACOUSTICS Nicolas Ludovic LARUE (1), Jean Marie LOME (2), Alice PRADINES (3) (1) Mechanical analysis and test engineer, EADS Astrium - 31 avenue des Cosmonautes,
1 EQUIPMENT INTERFACE LOAD CHARACTERIZATION IN ACOUSTICS Nicolas Ludovic LARUE (1), Jean Marie LOME (2), Alice PRADINES (3) (1) Mechanical analysis and test engineer, EADS Astrium - 31 avenue des Cosmonautes,
ADCSS 2017: Sodern presentation
 ADCSS 2017: Sodern presentation 1 Agenda Star trackers road map: a wide range of products End of CCD star trackers: SED26 replaced by Horus as standalone multi mission star tracker Hydra maintained beyond
ADCSS 2017: Sodern presentation 1 Agenda Star trackers road map: a wide range of products End of CCD star trackers: SED26 replaced by Horus as standalone multi mission star tracker Hydra maintained beyond
Pointing and Spectral Assignment Design and Control for MERTIS
 Pointing and Spectral Assignment Design and Control for MERTIS I. Walter; T. Säuberlich; M. Lieder (1); M. Rataj (2) H. Driescher (3); J. Helbert (4); H. Hiesinger (5) (1) German Aerospace Center, Optical
Pointing and Spectral Assignment Design and Control for MERTIS I. Walter; T. Säuberlich; M. Lieder (1); M. Rataj (2) H. Driescher (3); J. Helbert (4); H. Hiesinger (5) (1) German Aerospace Center, Optical
OWL: Further steps in designing the telescope mechanical structure and in assessing its performance
 OWL: Further steps in designing the telescope mechanical structure and in assessing its performance Enzo Brunetto, Franz Koch, Marco Quattri European Southern Observatory ABSTRACT The baseline concept
OWL: Further steps in designing the telescope mechanical structure and in assessing its performance Enzo Brunetto, Franz Koch, Marco Quattri European Southern Observatory ABSTRACT The baseline concept
An auto-balancer device for high spin-drying frequencies (LoWash Project)
 MATEC Web of Conferences 20, 03001 (2015) DOI: 10.1051/matecconf/20152003001 c Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 An auto-balancer device for high spin-drying frequencies (LoWash Project)
MATEC Web of Conferences 20, 03001 (2015) DOI: 10.1051/matecconf/20152003001 c Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 An auto-balancer device for high spin-drying frequencies (LoWash Project)
Mechatronics. MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1
 Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
Plato, Euclid and the New Hard X-Ray mission
 Schiaparelli and his Legacy Meeting on Future planetary, scientific and robotic space missions Biblioteca Nazionale Universitaria, Torino, 21/10/2010 Template reference : 100181670S-EN Plato, Euclid and
Schiaparelli and his Legacy Meeting on Future planetary, scientific and robotic space missions Biblioteca Nazionale Universitaria, Torino, 21/10/2010 Template reference : 100181670S-EN Plato, Euclid and
Spacecraft Bus / Platform
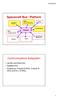 Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Outline. Theoretical estimate of the diffraction pattern on the primary mirror plane
 a b d e c Outline Solar Orbiter and METIS - METIS optical design - METIS Inverted Occulter Theoretical estimate of the diffraction pattern on the primary mirror plane Occulter optimization concept The
a b d e c Outline Solar Orbiter and METIS - METIS optical design - METIS Inverted Occulter Theoretical estimate of the diffraction pattern on the primary mirror plane Occulter optimization concept The
March 4, 2013 Eric P. Smith JWST Program Office
 March 4, 2013 Eric P. Smith JWST Program Office 1 SIMPLIFIED SCHEDULE OTE = Optical Telescope Element OTIS = Optical Telescope + ISIM k months of project funded critical path (mission pacing) schedule
March 4, 2013 Eric P. Smith JWST Program Office 1 SIMPLIFIED SCHEDULE OTE = Optical Telescope Element OTIS = Optical Telescope + ISIM k months of project funded critical path (mission pacing) schedule
Nano-JASMINE: A Small Infrared Astrometry Satellite
 SSC07-VI-4 Nano-JASMINE: A Small Infrared Astrometry Satellite 21 st Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites 14th/August/2007 Intelligent Space Systems Laboratory, University of Tokyo Nobutada Sako,
SSC07-VI-4 Nano-JASMINE: A Small Infrared Astrometry Satellite 21 st Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites 14th/August/2007 Intelligent Space Systems Laboratory, University of Tokyo Nobutada Sako,
Thermal and structural design constraints for radiometers operating in geostationary orbits. G. E. Zurmehly, R. A. Hookman
 Thermal and structural design constraints for radiometers operating in geostationary orbits G. E. Zurmehly, R. A. Hookman ITT Aerospace/Communications Division Fort Wayne, Indiana ABSTRACT For a radiometer
Thermal and structural design constraints for radiometers operating in geostationary orbits G. E. Zurmehly, R. A. Hookman ITT Aerospace/Communications Division Fort Wayne, Indiana ABSTRACT For a radiometer
ALCATEL SPACE PLASMA PROPULSION SUBSYSTEM QUALIFICATION STATUS
 ALCATEL SPACE PLASMA PROPULSION SUBSYSTEM QUALIFICATION STATUS Pascal GARNERO, Olivier DULAU ALCATEL SPACE 100, Bd. du Midi, BP 99 06156 CANNES LA BOCCA Cedex FRANCE Contact : pascal.garnero@space.alcatel.fr,
ALCATEL SPACE PLASMA PROPULSION SUBSYSTEM QUALIFICATION STATUS Pascal GARNERO, Olivier DULAU ALCATEL SPACE 100, Bd. du Midi, BP 99 06156 CANNES LA BOCCA Cedex FRANCE Contact : pascal.garnero@space.alcatel.fr,
THERMAL-VACUUM TESTS OF THE AMAZONIA-1 SATELLITE TM PERFORMED AT INPE WITH SUCCESS
 IAC-16- C2,7,9,x33007 THERMAL-VACUUM TESTS OF THE AMAZONIA-1 SATELLITE TM PERFORMED AT INPE WITH SUCCESS Almeida, J. S.*., Panissi, D. L., Santos, M.B. National Institute for Space Research - INPE Sao
IAC-16- C2,7,9,x33007 THERMAL-VACUUM TESTS OF THE AMAZONIA-1 SATELLITE TM PERFORMED AT INPE WITH SUCCESS Almeida, J. S.*., Panissi, D. L., Santos, M.B. National Institute for Space Research - INPE Sao
Euclid Mission Overview
 Mission Overview René Laureijs G. Racca, L. Stagnaro, J.C. Salvignol, J. Hoar (ESA) Y. Mellier and the EC Synergistic Science with and the SKA Oxford 16 September Outline Setting the scene Science Objectives
Mission Overview René Laureijs G. Racca, L. Stagnaro, J.C. Salvignol, J. Hoar (ESA) Y. Mellier and the EC Synergistic Science with and the SKA Oxford 16 September Outline Setting the scene Science Objectives
Automated Estimation of an Aircraft s Center of Gravity Using Static and Dynamic Measurements
 Proceedings of the IMAC-XXVII February 9-, 009 Orlando, Florida USA 009 Society for Experimental Mechanics Inc. Automated Estimation of an Aircraft s Center of Gravity Using Static and Dynamic Measurements
Proceedings of the IMAC-XXVII February 9-, 009 Orlando, Florida USA 009 Society for Experimental Mechanics Inc. Automated Estimation of an Aircraft s Center of Gravity Using Static and Dynamic Measurements
Concordia University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Fundamentals of Control Systems (ELEC372) S. Hashtrudi Zad
 Concordia University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Fundamentals of Control Systems (ELEC372) S. Hashtrudi Zad Project: Analysis of the Performance of a Satellite Pitch Control System
Concordia University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Fundamentals of Control Systems (ELEC372) S. Hashtrudi Zad Project: Analysis of the Performance of a Satellite Pitch Control System
Mechanical System Laboratory Thermal Analysis & Verification Section (TEC-MTV)
 Mechanical System Laboratory Thermal Analysis & Verification Section (TEC-MTV) Contact: Laboratory Manager MSLmanager@esa.int Core activities: Thermal cycling / thermal balance test in vacuum & at ambient
Mechanical System Laboratory Thermal Analysis & Verification Section (TEC-MTV) Contact: Laboratory Manager MSLmanager@esa.int Core activities: Thermal cycling / thermal balance test in vacuum & at ambient
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
ESA activities towards the Gravitation Waves Space Observatory
 ESA activities towards the Gravitation Waves Space Observatory Frédéric Safa ESA Science Directorate, Future Missions LISA Symposium, Zurich 2016 The Gravitation Wave Observatory in ESA Science Programme
ESA activities towards the Gravitation Waves Space Observatory Frédéric Safa ESA Science Directorate, Future Missions LISA Symposium, Zurich 2016 The Gravitation Wave Observatory in ESA Science Programme
MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTY OF ROTATING TORQUE TRANSDUCERS WHEN USED IN PARTIAL LOAD RANGES
 XVIII IMEKO WORLD CONGRESS Metrology for a Sustainable Development September, 17, 006, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTY OF ROTATING TORQUE TRANSDUCERS WHEN USED IN PARTIAL LOAD RANGES Georg
XVIII IMEKO WORLD CONGRESS Metrology for a Sustainable Development September, 17, 006, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTY OF ROTATING TORQUE TRANSDUCERS WHEN USED IN PARTIAL LOAD RANGES Georg
AE / AER Series. AER Series
 AE / AER Series Characteristic Highlights True helical gear design Precision helical gearing increases tooth to tooth contact ratio by over % vs spur gearing. The helix angle produces smooth and quiet
AE / AER Series Characteristic Highlights True helical gear design Precision helical gearing increases tooth to tooth contact ratio by over % vs spur gearing. The helix angle produces smooth and quiet
MISSION ENGINEERING SPACECRAFT DESIGN
 MISSION ENGINEERING & SPACECRAFT DESIGN Alpbach 2007 - D.J.P. Moura - CNES MISSION ENGINEERING (1) OVERALL MISSION ENGINEERING IS A COMPLEX TASK SINCE AT THE BEGINNING THE PROBLEM IS GENERALLY BADLY EXPRESSED
MISSION ENGINEERING & SPACECRAFT DESIGN Alpbach 2007 - D.J.P. Moura - CNES MISSION ENGINEERING (1) OVERALL MISSION ENGINEERING IS A COMPLEX TASK SINCE AT THE BEGINNING THE PROBLEM IS GENERALLY BADLY EXPRESSED
The next-generation Infrared astronomy mission SPICA Space Infrared Telescope for Cosmology & Astrophysics
 The next-generation Infrared astronomy mission SPICA Space Infrared Telescope for Cosmology & Astrophysics 3.5m cooled telescope mission for mid- and far-infrared astronomy Takao Nakagawa (ISAS/JAXA) for
The next-generation Infrared astronomy mission SPICA Space Infrared Telescope for Cosmology & Astrophysics 3.5m cooled telescope mission for mid- and far-infrared astronomy Takao Nakagawa (ISAS/JAXA) for
ENGINEERING ASPECTS OF THE 200-INCH HALE TELESCOPE. Bruce Rule Mount Wilson and Palomar Observatories
 ENGINEERING ASPECTS OF THE 200-INCH HALE TELESCOPE Bruce Rule Mount Wilson and Palomar Observatories The engineering designs of the 200-inch Hale Telescope were determined largely by the optical accuracy
ENGINEERING ASPECTS OF THE 200-INCH HALE TELESCOPE Bruce Rule Mount Wilson and Palomar Observatories The engineering designs of the 200-inch Hale Telescope were determined largely by the optical accuracy
GG studies at TAS-I: state of the art
 GG studies at TAS-I: state of the art A. Anselmi INRIM, 24-10-2014 83230350-DOC-TAS-EN-002 GG@ThalesAleniaSpace! 1996 Early experiment concept presented to ESA HQ! Industrial support on satellite & drag-free
GG studies at TAS-I: state of the art A. Anselmi INRIM, 24-10-2014 83230350-DOC-TAS-EN-002 GG@ThalesAleniaSpace! 1996 Early experiment concept presented to ESA HQ! Industrial support on satellite & drag-free
Mechatronics Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems Case-Study Exercise
 Mechatronics Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems Case-Study Exercise Goal: This exercise is designed to take a real-world problem and apply the modeling and analysis concepts discussed in class. As
Mechatronics Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems Case-Study Exercise Goal: This exercise is designed to take a real-world problem and apply the modeling and analysis concepts discussed in class. As
Optical Metrology Applications at TAS-I in support of Gravity and Fundamental Physics
 Optical Metrology Applications at TAS-I in support of Gravity and Fundamental Physics Template reference : 100181670S-EN Stefano Cesare, Thales Alenia Space Italia, Torino Workshop GG/GGG: state of the
Optical Metrology Applications at TAS-I in support of Gravity and Fundamental Physics Template reference : 100181670S-EN Stefano Cesare, Thales Alenia Space Italia, Torino Workshop GG/GGG: state of the
DEVELOPMENT OF SEISMIC ISOLATION TABLE COMPOSED OF AN X-Y TABLE AND WIRE ROPE ISOLATORS
 DEVELOPMENT OF SEISMIC ISOLATION TABLE COMPOSED OF AN X-Y TABLE AND WIRE ROPE ISOLATORS 7 Hirokazu SHIMODA, Norio NAGAI, Haruo SHIMOSAKA And Kenichiro OHMATA 4 SUMMARY In this study, a new type of isolation
DEVELOPMENT OF SEISMIC ISOLATION TABLE COMPOSED OF AN X-Y TABLE AND WIRE ROPE ISOLATORS 7 Hirokazu SHIMODA, Norio NAGAI, Haruo SHIMOSAKA And Kenichiro OHMATA 4 SUMMARY In this study, a new type of isolation
Nonlinear effects on the rotor driven by a motor with limited power
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (007) 603-61 Nonlinear effects on the rotor driven by a motor with limited power L. Pst Institute of Thermomechanics, Academy of Sciences of CR, Dolejškova 5,18 00
Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (007) 603-61 Nonlinear effects on the rotor driven by a motor with limited power L. Pst Institute of Thermomechanics, Academy of Sciences of CR, Dolejškova 5,18 00
High-impulse SPT-100D thruster with discharge power of kw
 High-impulse SPT-D thruster with discharge power of 1.0 3.0 kw IEPC-2017-40 Presented at the 35th International Electric Propulsion Conference Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia USA R. Gnizdor
High-impulse SPT-D thruster with discharge power of 1.0 3.0 kw IEPC-2017-40 Presented at the 35th International Electric Propulsion Conference Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia USA R. Gnizdor
EconoPACK TM + A package with enhanced characteristics
 EconoPACK TM + A package with enhanced characteristics Mark Essert, Roman Tschirbs, Indrajit Paul, Wilhelm Rusche, Infineon Technologies AG, Germany Abstract Increasing the efficiency of high power frequency
EconoPACK TM + A package with enhanced characteristics Mark Essert, Roman Tschirbs, Indrajit Paul, Wilhelm Rusche, Infineon Technologies AG, Germany Abstract Increasing the efficiency of high power frequency
The ACES Mission. Fundamental Physics Tests with Cold Atom Clocks in Space. L. Cacciapuoti European Space Agency
 The ACES Mission Fundamental Physics Tests with Cold Atom Clocks in Space L. Cacciapuoti European Space Agency La Thuile, 20-27 March 2011 Gravitational Waves and Experimental Gravity 1 ACES Mission Concept
The ACES Mission Fundamental Physics Tests with Cold Atom Clocks in Space L. Cacciapuoti European Space Agency La Thuile, 20-27 March 2011 Gravitational Waves and Experimental Gravity 1 ACES Mission Concept
Hybrid spacecraft attitude control system
 Int. Jnl. of Multiphysics Volume 1 Number 2 2007 221 Hybrid spacecraft attitude control system Renuganth Varatharajoo *, Ramly Ajir, Tamizi Ahmad Department of Aerospace Engineering, University Putra Malaysia,
Int. Jnl. of Multiphysics Volume 1 Number 2 2007 221 Hybrid spacecraft attitude control system Renuganth Varatharajoo *, Ramly Ajir, Tamizi Ahmad Department of Aerospace Engineering, University Putra Malaysia,
