THE BUGS EXPERIMENT: OVERVIEW AND IN-FLIGHT RESULTS
|
|
|
- Megan Gilbert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE BUGS EXPERIMENT: OVERVIEW AND IN-FLIGHT RESULTS Maria Libera Battagliere (1), Gianpaolo Candini (2), Jacopo Piattoni (2), Emanuele Paolini (1), Fabio Santoni (1), Fabrizio Piergentili (2) (1) Scuola di Ingegneria Aerospaziale, Sapienza University of Roma, Italy (2) DIEM, Univeristy of Bologna Alma Mater Studiorum, Italy ABSTRACT Boom for University Gravity-gradient stabilized Satellite (BUGS) is a student experiment proposed by the Space Robotics Laboratory (SRL) of the II Faculty of Engineering of the University of Bologna Alma Mater Studiorum in cooperation with the School of Aerospace Engineering of the Sapienza, University of Roma. The BUGS experiment was selected to fly on board the sounding rocket REXUS-7 and it has two main goals: the hands-on education and the deployment test, in near microgravity conditions, of a boom for gravity gradient attitude stabilization of small satellites. The educational purpose consists on providing the university students with the opportunity of a practical experience in a real space project during their master and PhD courses. During the whole experiment lifecycle, starting from the experiment selection until the launch campaign and post-flight data analysis, the students are involved in all phases of the project: they analyze the problems, propose solutions and test them. Moreover, they have the opportunity to meet experts coming from different European space agencies and to present the achieved results. The proposed boom is based on an innovative design, exploiting rigidity properties of tape coiled springs. Two boom prototypes, one longer (3 m in deployed configuration) and one shorter (2 m in deployed configuration), were tested on board REXUS-7 with the aim to achieve data related to their dynamic behavior in orbit. These booms were developed by students of the Space Robotics Laboratory of the II Faculty of Engineering of the University of Bologna. Another technological objective of the BUGS experiment was testing the thermal cutter system for boom deployment and the ejection system. The paper gives a general overview of the experiment showing the students participation to the training activities, the experiment design, building and flight. The data analysis and results are also summarized in the paper. 1. INTRODUCTION The BUGS experiment is a student-built experiment developed to fly on board the sounding rocket REXUS-7 (Rocket-borne EXperiments for University Students) with the sponsorship of the ESA s (European Space Agency) Education Office, which supports the participation of European students to the REXUS/BEXUS Programme (Rocket and Balloon Experiments for University Students), on the basis of a call for proposals and experiments selection. The indicative timetable for the experiments is 18 months from the call for proposals. REXUS is conducted by EuroLaunch, a cooperative agreement between the Swedish Space Corporation (SSC) and the German Aerospace Center (DLR), Mobile Rocket Base (MORABA) in the area of suborbital services for sounding rocket launches and stratospheric balloon flights [1]. REXUS is financed by the Swedish National Space Board (SNSB) and the German Aerospace Center (DLR) [1]. A view of REXUS-7 with the integrated experiment modules during the pre-launch phase at the Esrange Space Center, near Kiruna in northern Sweden, is given in Fig.1. In this picture it is possible to see the experiments arrangement and the BUGS position. There is a module for each student experiment: this modularised configuration provides simple interfaces, good flexibility and independence between experiment modules [1]. REXUS-7 was launched on 2th of March 2010 at 8.25 local time carrying three student experiments onboard. The rocket reached an altitude of 83 km and landed north of Esrange Space Center.
2 Figure 2 Tape coil spring employed for boom prototype development. Figure 1 REXUS-7 in the pre-launch configuration The BUGS experiment, born from an idea of the researchers of the Space Robotics Laboratory (SRL) of the II Faculty of Engineering of the University of Bologna Alma Mater Studiorum, was proposed and developed in cooperation with the Sapienza, University of Roma Experiment objectives The main objectives of the BUGS experiments are the boom prototype deployment test in near microgravity conditions and the hands-on education of university students. In order to use the boom on board of a satellite, it is important to calculate how the damping system should work to reduce properly the vibrations caused by the boom deployment. This kind of test can not be performed on the ground, because the absence of the microgravity condition and of the atmosphere do not allow the observation of this effect. Technological objectives can be summarized in following points: - boom deployment test in space-flight conditions (near microgravity conditions); - to try to estimate boom damping time and boom modal frequencies; - to evaluate the reaction of the satellite-body due to the boom deployment in orbit; - to qualify the boom for small and low cost satellite class; - to qualify the thermal cutter and the ejection system. The proposed boom prototype is based on an innovative, low cost concept, which uses the principle of the tape coil spring, Fig. 2; it can be deployed once and it maintains its rigidity since every coil is blocked inside the following one [2]. For the first time this coil spring has been used to develop an experiment named SIRDARIA (Spacecraft Integrated Re-entry Device, Aero-Resistant Increasing Area), hosted on board UNISAT-4 microsatellite [3]. The first manufactured boom prototype was 15 cm long in stowed configuration and 3 m long in the deployed configuration [4]; weight is about 700 g. The second manufactured boom prototype (for the BUGS experiment) is 17 cm long in stowed configuration, 3 m long in the deployed configuration and its diameter is 5 cm. After, a shorter boom prototype was developed. This second boom is a back-up unit; its diameter is 3.5 cm and it is 2 m long in the deployed configuration. Both booms have been assembled and qualified to fly with the BUGS experiment on board REXUS rocket, Fig. 3. Figure 3 Booms prototype mock-up Among the educational activities and objectives there are: - team work and team building; - problem solving; - possibility to work in an international context and to meet experts coming from main European Space Agency; - comparison and cooperation with other student teams; - practice with ESA s procedures and knowledge of ECSS standards; - papers presentation and student participation to symposiums, workshops, conferences.
3 2. EXPERIMENT DESCRIPTION 2.1. Mechanical design and configuration The experiment configuration is based on the boom prototype, the thermal cut system for the boom deployment, the ejection system required to separate the boom before the parachute opening and a camera for the boom behavior monitoring. The system is redundant: there are two booms, two cameras and a double ejection system. A view of the BUGS experiment manufactured and integrated in the REXUS cylindrical experiment module, during the bench tests performed at DLR, is visible in the following Fig. 4. Figure 4 BUGS experiment overview The small boom is placed above the big one; each one of them has its proper thermal cutters, both for deployment and for ejection. An omega in Aluminum helps to fix the larger boom to the structure, while the smallest one is blocked to its base with bands. The cameras are fixed directly on the experiment module and integrated in a mechanical modularized support in order to change easily the camera position and orientation during the tests and the system integration. The first camera uses the REXUS TV downlink channel; the second camera data are recorded in a small data recorder. This minimal configuration has been selected in order to simplify electronics required for the experiment and to improve system reliability. The idea is to use small cameras which do not require a computer for data management and which start working and recording data when the power supply is active. All selected components are commercial: in this way it was possible to reduce the procurement phase time and to manufacture them in a small laboratory reducing also costs and realization times. The electronic board is hosted is hosted in a 3 mm thick Aluminum box, treated with pressurized water and glass powder to increase its rigidity and manufactured with the support of the ESA s mechanical laboratories. The box is placed vertically behind the main structure (Fig. 4) Experiment process flow The experiment process flow is available in Fig. 6. The primary objective of this experiment is the deployment test of boom prototypes in space-flight conditions in order to understand and to evaluate boom dynamic behaviour. Boom must be deployed when REXUS has reached the microgravity conditions and it must be ejected before the parachute opening. Power and signals to switch on BUGS experiment are provided by REXUS service module (RXSM). BUGS electronics is connected to the REXUS power supply via voltage regulators (RXSM Voltage 28 V). The experiment use two signals to control the events sequence [1]. The SODS signal [1] at T0+120s will command the boom deployment: the rocket is about 30 seconds far from the apogee (as estimated by DLR experts), so microgravity condition would have been reached. The thermal cutter lets the boom deploy (SOE+1 sec, Fig. 5, [1, 2]), and the experiment starts. The SOE signal at T0+45s commands the ejection of the first boom. The second boom is deployed at SOE+65s and it is ejected at SOE+110s (Fig. 5). The Time Events based on the predicted flight trajectory is the following for the BUGS experiment is given in Table 1 [5]. Time [s] Event T+0 Lift Off T+0 BUGS camera on T+100 BUGS Hatch Power T+106 BUGS Boom 1 deployment T Apogee T+150 BUGS Boom 1 Ejection (+45s) T+170 BUGS Boom 2 deployment T+215 BUGS Boom 2 ejection T+230 BUGS Hatch SOE T Maximum deceleration (26 km) T+600 Power Off for experiments Table 1 BUGS Time Events The REXUS recovery system is designed to decelerate the velocity to 8 m/s at the impact time (about 358 sec after the ignition [1]). After the landing, the experiment modules are recovered by helicopter within a few hours.
4 Test duration was fixed to 10 minutes to be conservative. Sensor 1 located on the Aluminium support for dynema line reached 86 C, whereas sensor 2 located between the Aluminium plate and the boom in the bottom part reached 79.5 C. The deployment test was performed in the worst conditions after the thermal test, it means when the boom reached the maximum temperature after 10 minutes (86.5 C). Deployment test in this condition was performed successfully. Figure 5 BUGS experiment process flow 3. ENVIRONMENTAL TESTS 3.1. Thermal test Preliminary thermal test of the boom prototype was performed (Fig. 6) in order to verify the nominal boom behaviour in high temperature conditions [2]. The test was performed at DMA Marchiori srl in Aprilia near Rome. Two thermal sensors were employed to measure local temperature on sensible elements as the Aluminium support with the hatch where is located the dynema line and the bottom part of the boom where the interface with the electronic box is arranged. The main goals were to evaluate the boom material (specially springs) behaviour in high temperature conditions and to estimate if there is the possibility to cut accidentally the dynema line when the Aluminium support reaches high temperatures. Tests were performed in a thermal camera operating with the inner environmental temperature in the range 60 C-100 C (pressure 1 atm) Vibration test Vibration test was performed successfully at the Mechanical System Laboratory of ESA-ESTEC with the sponsorship of the ESA s Educational Office, Fig. 7. Requirements were fixed according to REXUS User Manual [1]. According with Eurolaunch vibration tests have been performed only on the Z axis for the experiment acceptance. Random qualification test lasted 60 seconds at 6.0 grms. The shaker vibrations is monitored by accelerometers. The accelerometers provide a feedback signal to the control computer. Figure 7 BUGS experiment vibration test at the ESTEC/ESA From the comparison of the spectra achieved by the test accelerometer before (Fig. 8) and after (Fig. 9) the random vibration, it can be noticed that the resonant frequencies did not change significantly. Thus can be stated that no parts reduced their rigidity during random vibration tests simulating launch phase and the experiment can be considered qualified to be boarded on REXUS launcher. Figure 6 - Thermal camera with two temperature sensors to measure boom local parts
5 Figure 8 Test accelerometer, pre-random sinusoidal sweep Figure 9 Test accelerometer, post-random sinusoidal sweep 4. FLIGHT PERFORMANCES A visual post flight inspection and a preliminary data analysis were performed by the mission team after the recovery of the experiment few hours after the REXUS-7 launch. The mechanical structure of the experiment was recovered in nominal configuration (Fig. 10); it showed the accurate design and sizing of the experiment. A visual inspection of the dynema wires used for thermal cutter and ejection systems demonstrated the right functioning of both these systems for each boom: the wires were cut and not broken (for example due to the vibrations). Fig. 10 shows that both booms were deployed and ejected during the flight. Data recovered from service module housekeeping data confirmed it. In order to obtain information on the vibration due the boom on the rocket, an analysis using Fourier transformation on the angular velocity data (obtained with gyros onboard Rexus7) has been performed. Fig. 11 shows the frequency spectrum of the angular velocity along the axis of the rocket (blue line) and along a perpendicular axis of the rocket (red line) for the shortest boom. For the shortest boom, achieved data show that the value of first frequency along the rocket axis is about zero, while the frequency value with respect to the perpendicular axis is about 0.12Hz. Figure 10 BUGS experiment after the recovery phase at ESRANGE Space Center. Fig. 12 shows the frequency spectrum of the angular velocity of the Boom 1 (the longest one). Achieved data show that the vibration frequency along the rocket longitudinal axis is about 0.04Hz (blu line) while the perpendicular frequency is about 0.4Hz (red line). The frequencies that the booms have induced to the rocket are very low; this suggests that both the booms are suitable to be employed in a gravity gradient stabilization system for small satellites, together with a damping system, for example based on magnetic permeable rods [6]. Figure 11 Boom 2 modal frequency identification Figure 12 Boom 1 modal frequency identification
6 Thanks to the housekeeping data, the profiles of velocities and accelerations of the rocket have been reconstructed. It is clear that the roll velocity decreased when the booms deployments occurred, according to the conservation of angular momentum. Booms performs as yo-yo de-spin system for the rocket. According to the achieved data, it has been evaluated that the part of the rocket in microgravity condition therefore without motor adapter and nosecone had a polar moment of inertia of 1.95 kgm² and a lateral moment of inertia of kgm². The distance between the total centre of mass and BUGS centre of mass has been calculated in 84 mm along the X axis. It was not possible with the available data to evaluate the distance between the two centres of mass along the Y and the Z axis, but an estimation was set thanks to the attitude mathematical model described below. The effect of deployment was calculated imposing the conservation of angular momentum before and after the boom deployment; the force resulted about 76 N. A rocket attitude mathematical model was developed with the main purpose of verifying the accuracy of this result. To evaluate the change in the moments of inertia after the boom deployment, a simple CAD model of the rocket in microgravity configuration was drawn, respecting the actual dimensions, moments of inertia and mass. A model of the boom was then added, obtaining new moments of inertia of the whole body. A comparison between the housekeeping data and a simulation obtained with this mathematical model is given in Fig. 13. The simulation was performed for a 76 N force and a distance between the total centre of mass and BUGS centre of mass of 5.7 cm along Y and 0.5 cm along Z (these are the measurements that minimize the error between model and real data). It is possible to notice in Fig. 13 that the model is quite similar to the real behaviour of the boom, confirming that a force of 76 N is possible, and giving a reasonable evaluation of the distance between the centres of mass Current [da] roll-gyro pitch-gyro yaw-gyro roll-sim pitch-sim yaw-sim Angular speeds [deg/s] 5. CONCLUSIONS REXUS program provided students with the opportunity to participate in a real space project following all phases, from the concept and design until the launch campaign and data analysis. Both booms of the BUGS experiment were deployed and ejected successfully during the REXUS 7 flight and booms modal frequencies were estimated. The thermal cutter and the ejection systems worked nominally. AKNOWLEDGEMENTS Authors wish to thank the ESA for the opportunity given to team members in participation to this project and for support given in vibration test of the BUGS experiment; the DLR, SSC and SNSB for the educational programme REXUS/BEXUS which provide European university students with a very strong and useful experience in space field; ESRANGE Space Center and MORABA s experts for the support during all the phases of the integration and launch campaign. REFERENCES 1. Persson O., Stamminger A., Hellmann H., Fittock M., REXUS User Manual V. 7, Dec Battagliere M. L., Candini G., Piattoni J., Paolini E., Meschini M., BUGS Student Experiment Documentation V.7, Piergentili F., Graziani F., SIRDARIA: A low-cost autonomous deorbiting system for microsatellites, 57th IAC, International Astronautical Congress 2006, Valencia, Spagna, Ottobre 2006, IAC-06-B Piattoni J., Thesis Degree Sistema di stabilizzazione a gradiente di gravità per microsatellite: boom a tip mass attivi (in Italian), University of Bologna Alma Mater Studiorum, y. 2007, Italy. 5. RX REXUS7_Flight_Requirement_Plan 6. Battagliere M. L., Piergentili F., Santoni F., Libration Damping System in the Attitude Stabilization of University Mi-crosatellites, Paper AS , Journal of Automatic Control in Aerospace, Vol 2, July 2008, ISSN Time [s] Figure 13 - Comparison between gyroscopes data and model simulation for the boom deployment.
5th Annual CubeSat Developers' Workshop April 2008 Cal Poly San Luis Obispo, California
 5th Annual CubeSat Developers' Workshop 9-11 April 2008 Cal Poly San Luis Obispo, California From UNISAT to ubesatsat UNICube Chantal CAPPELLETTI, Fabrizio PAOLILLO, Francesco GUARDUCCI, Luigi RIDOLFI
5th Annual CubeSat Developers' Workshop 9-11 April 2008 Cal Poly San Luis Obispo, California From UNISAT to ubesatsat UNICube Chantal CAPPELLETTI, Fabrizio PAOLILLO, Francesco GUARDUCCI, Luigi RIDOLFI
BRINGING YOUR EXPERIMENT INTO SPACE
 BRINGING YOUR EXPERIMENT INTO SPACE Science Service Division SSC - Swedish Space Corporation Space exploration with ESA: opportunities within the ESA programme E3P Stockholm, 13 November 2018 SWEDISH SPACE
BRINGING YOUR EXPERIMENT INTO SPACE Science Service Division SSC - Swedish Space Corporation Space exploration with ESA: opportunities within the ESA programme E3P Stockholm, 13 November 2018 SWEDISH SPACE
The Archimedes Mars balloon project and the MIRIAM test flights Part 1: from Archimedes to MIRIAM
 The Archimedes Mars balloon project and the MIRIAM test flights Part 1: from Archimedes to MIRIAM EMC13-13th European Mars Conference Kai Gehreth Jürgen Herholz Mars Society Deutschland www.marssociety.de
The Archimedes Mars balloon project and the MIRIAM test flights Part 1: from Archimedes to MIRIAM EMC13-13th European Mars Conference Kai Gehreth Jürgen Herholz Mars Society Deutschland www.marssociety.de
Lecture Module 5: Introduction to Attitude Stabilization and Control
 1 Lecture Module 5: Introduction to Attitude Stabilization and Control Lectures 1-3 Stability is referred to as a system s behaviour to external/internal disturbances (small) in/from equilibrium states.
1 Lecture Module 5: Introduction to Attitude Stabilization and Control Lectures 1-3 Stability is referred to as a system s behaviour to external/internal disturbances (small) in/from equilibrium states.
BOWSER Balloon Observatory for Wavelength and Spectral Emission Readings
 COSGC Space Research Symposium 2009 BOWSER Balloon Observatory for Wavelength and Spectral Emission Readings BOWSER 1 Mission Premise 4.3 km above sea level 402.3km above sea level BOWSER 2 Information
COSGC Space Research Symposium 2009 BOWSER Balloon Observatory for Wavelength and Spectral Emission Readings BOWSER 1 Mission Premise 4.3 km above sea level 402.3km above sea level BOWSER 2 Information
AEROTHERMODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF INNOVATIVE HYPERSONIC DEPLOYABLE REENTRY CAPSULES. Raffaele Savino University of Naples Federico II
 AEROTHERMODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF INNOVATIVE HYPERSONIC DEPLOYABLE REENTRY CAPSULES Raffaele Savino University of Naples Federico II Objectives Show the main capabilities of deployable aero-brakes for Earth
AEROTHERMODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF INNOVATIVE HYPERSONIC DEPLOYABLE REENTRY CAPSULES Raffaele Savino University of Naples Federico II Objectives Show the main capabilities of deployable aero-brakes for Earth
Space mission environments: sources for loading and structural requirements
 Space structures Space mission environments: sources for loading and structural requirements Prof. P. Gaudenzi Università di Roma La Sapienza, Rome Italy paolo.gaudenzi@uniroma1.it 1 THE STRUCTURAL SYSTEM
Space structures Space mission environments: sources for loading and structural requirements Prof. P. Gaudenzi Università di Roma La Sapienza, Rome Italy paolo.gaudenzi@uniroma1.it 1 THE STRUCTURAL SYSTEM
IAC-11-A2.5.9 RE-ENTRY ANALYSIS OF RESEARCH ROCKET PAYLOADS
 RE-ENTRY ANALYSIS OF RESEARCH ROCKET PAYLOADS Andreas Stamminger Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR), Mobile Rocket Base, Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany, Tel.: 49-8153-28-1231, Email:
RE-ENTRY ANALYSIS OF RESEARCH ROCKET PAYLOADS Andreas Stamminger Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR), Mobile Rocket Base, Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany, Tel.: 49-8153-28-1231, Email:
FORCE LIMITED VIBRATION TESTING OF CASSINI SPACECRAFT COSMIC DUST ANALYSER
 FORCE LIMITED VIBRATION TESTING OF CASSINI SPACECRAFT COSMIC DUST ANALYSER Heiko Jahn*, Swen Ritzmann*, Kurng Chang**, Terry Scharton** * German Aerospace Research Establishment, Institute for Space Sensor
FORCE LIMITED VIBRATION TESTING OF CASSINI SPACECRAFT COSMIC DUST ANALYSER Heiko Jahn*, Swen Ritzmann*, Kurng Chang**, Terry Scharton** * German Aerospace Research Establishment, Institute for Space Sensor
ACTIVE DEBRIS REMOVAL SYSTEM BASED ON POLYURETHANE FOAM
 ACTIVE DEBRIS REMOVAL SYSTEM BASED ON POLYURETHANE FOAM Rizzitelli Federico (1) f.rizzitelli@gmail.com, Valdatta Marcello (1) marcello.valdatta@gmail.com, Bellini Niccolò (1) niccolo.bellini@gmail.com,
ACTIVE DEBRIS REMOVAL SYSTEM BASED ON POLYURETHANE FOAM Rizzitelli Federico (1) f.rizzitelli@gmail.com, Valdatta Marcello (1) marcello.valdatta@gmail.com, Bellini Niccolò (1) niccolo.bellini@gmail.com,
Six Days at the Edge of Space: 10 Years of HASP Balloon Flight Operations
 Six Days at the Edge of Space: 10 Years of HASP Balloon Flight Operations T. Gregory Guzik, Louisiana Space Grant Consortium Department of Physics & Astronomy Louisiana State University v030316 1 Primary
Six Days at the Edge of Space: 10 Years of HASP Balloon Flight Operations T. Gregory Guzik, Louisiana Space Grant Consortium Department of Physics & Astronomy Louisiana State University v030316 1 Primary
BUILDING LOW-COST NANO-SATELLITES: THE IMPORTANCE OF A PROPER ENVIRONMENTAL TESTS CAMPAIGN. Jose Sergio Almeida INPE (Brazil)
 BUILDING LOW-COST NANO-SATELLITES: THE IMPORTANCE OF A PROPER ENVIRONMENTAL TESTS CAMPAIGN Jose Sergio Almeida INPE (Brazil) 1 st International Academy of Astronautics Latin American Symposium on Small
BUILDING LOW-COST NANO-SATELLITES: THE IMPORTANCE OF A PROPER ENVIRONMENTAL TESTS CAMPAIGN Jose Sergio Almeida INPE (Brazil) 1 st International Academy of Astronautics Latin American Symposium on Small
Structure and algorithms of motion control system's software of the small spacecraft
 Structure and algorithms of motion control system's software of the small spacecraft Filatov A.V., Progress Space Rocket Centre, Samara Tkachenko I.S., Tyugashev A.A., Sopchenko E.V. Samara State Aerospace
Structure and algorithms of motion control system's software of the small spacecraft Filatov A.V., Progress Space Rocket Centre, Samara Tkachenko I.S., Tyugashev A.A., Sopchenko E.V. Samara State Aerospace
Polish Student Activities in Space Research and Education
 Polish Student Activities in Space Research and Education Warsaw University of Technology: Student Astronautical Group Student Space Engineering Scientific Group Radiolocation and Digital Signal Processing
Polish Student Activities in Space Research and Education Warsaw University of Technology: Student Astronautical Group Student Space Engineering Scientific Group Radiolocation and Digital Signal Processing
SAMPLE CANISTER CAPTURE MECHANISM FOR MSR: CONCEPT DESIGN AND TESTING RESULTS INCLUDING 0-G ENVIRONMENT
 SAMPLE CANISTER CAPTURE MECHANISM FOR MSR: CONCEPT DESIGN AND TESTING RESULTS INCLUDING 0-G ENVIRONMENT Authors: Riccardo Carta, Daniele Filippetto, Politecnico di Milano Co-authors: Prof. Michèle Lavagna,
SAMPLE CANISTER CAPTURE MECHANISM FOR MSR: CONCEPT DESIGN AND TESTING RESULTS INCLUDING 0-G ENVIRONMENT Authors: Riccardo Carta, Daniele Filippetto, Politecnico di Milano Co-authors: Prof. Michèle Lavagna,
Autonomous Vision Based Detection of Non-stellar Objects Flying in Formation with Camera Point of View
 Autonomous Vision Based Detection of Non-stellar Objects Flying in Formation with Camera Point of View As.Prof. M. Benn (1), Prof. J. L. Jørgensen () (1) () DTU Space, Elektrovej 37, 4553438, mb@space.dtu.dk,
Autonomous Vision Based Detection of Non-stellar Objects Flying in Formation with Camera Point of View As.Prof. M. Benn (1), Prof. J. L. Jørgensen () (1) () DTU Space, Elektrovej 37, 4553438, mb@space.dtu.dk,
FIRST RESULTS OF THE TRITEL SPACE DOSIMETRY TELESCOPE FROM THE MISSION ON BOARD THE BEXUS-12 STRATOSPHERIC BALLOON
 Hungarian Academy of Sciences Centre for Energy Research FIRST RESULTS OF THE TRITEL SPACE DOSIMETRY TELESCOPE FROM THE MISSION ON BOARD THE BEXUS-12 STRATOSPHERIC BALLOON B. Zábori 1,2, A. Hirn 1, I.
Hungarian Academy of Sciences Centre for Energy Research FIRST RESULTS OF THE TRITEL SPACE DOSIMETRY TELESCOPE FROM THE MISSION ON BOARD THE BEXUS-12 STRATOSPHERIC BALLOON B. Zábori 1,2, A. Hirn 1, I.
Solid Propellant Autonomous DE-Orbit System [SPADES]
![Solid Propellant Autonomous DE-Orbit System [SPADES] Solid Propellant Autonomous DE-Orbit System [SPADES]](/thumbs/72/66345669.jpg) Solid Propellant Autonomous DE-Orbit System [SPADES] Solid Propellant Rocket Motor development Presented: Rogier Schonenborg Study: T. Soares J. Huesing A. Cotuna W. van Meerbeeck I. Carnelli L. Innocenti
Solid Propellant Autonomous DE-Orbit System [SPADES] Solid Propellant Rocket Motor development Presented: Rogier Schonenborg Study: T. Soares J. Huesing A. Cotuna W. van Meerbeeck I. Carnelli L. Innocenti
THE NEWEST HUNGARIAN COSMIC RADIATION MEASUREMENT RESULTS IN THE STRATOSPHERE USING STRATOSPHERIC BALLOONS AND SOUNDING ROCKETS
 THE NEWEST HUNGARIAN COSMIC RADIATION MEASUREMENT RESULTS IN THE STRATOSPHERE USING STRATOSPHERIC BALLOONS AND SOUNDING ROCKETS Balázs Zábori Centre for Energy Research, Hungarian Academy of Sciences zabori.balazs@energia.mta.hu
THE NEWEST HUNGARIAN COSMIC RADIATION MEASUREMENT RESULTS IN THE STRATOSPHERE USING STRATOSPHERIC BALLOONS AND SOUNDING ROCKETS Balázs Zábori Centre for Energy Research, Hungarian Academy of Sciences zabori.balazs@energia.mta.hu
DYNAMIC SIMULATION OF VEGA SRM BENCH FIRING BY USING PROPELLANT COMPLEX CHARACTERIZATION
 DYNAMIC SIMULATION OF VEGA SRM BENCH FIRING BY USING PROPELLANT COMPLEX CHARACTERIZATION MSC Software University Roadshow The information contained in this document is AVIO S.p.A. proprietary and is disclosed
DYNAMIC SIMULATION OF VEGA SRM BENCH FIRING BY USING PROPELLANT COMPLEX CHARACTERIZATION MSC Software University Roadshow The information contained in this document is AVIO S.p.A. proprietary and is disclosed
INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION, A DEPLOYMENT AND MODAL TEST FACILITY
 IAC-02-1.2.06 INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION, A DEPLOYMENT AND MODAL TEST FACILITY Sherry Draisey President, Good Vibrations Engineering Ltd. Toronto, Canada sherry@gve.on.ca ABSTRACT The International Space
IAC-02-1.2.06 INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION, A DEPLOYMENT AND MODAL TEST FACILITY Sherry Draisey President, Good Vibrations Engineering Ltd. Toronto, Canada sherry@gve.on.ca ABSTRACT The International Space
Flight Demonstration of Electrostatic Thruster Under Micro-Gravity
 Flight Demonstration of Electrostatic Thruster Under Micro-Gravity Shin SATORI*, Hiroyuki MAE**, Hiroyuki OKAMOTO**, Ted Mitsuteru SUGIKI**, Yoshinori AOKI # and Atsushi NAGATA # * Hokkaido Institute of
Flight Demonstration of Electrostatic Thruster Under Micro-Gravity Shin SATORI*, Hiroyuki MAE**, Hiroyuki OKAMOTO**, Ted Mitsuteru SUGIKI**, Yoshinori AOKI # and Atsushi NAGATA # * Hokkaido Institute of
VSB-30 sounding rocket: history of flight performance
 doi: 10.5028/jatm.2011. 03032211 Alexandre Garcia * alexandregarciaag@iae.cta.br Sidney Servulo Cunha Yamanaka sidneysscy@iae.cta.br Alexandre Nogueira Barbosa nogueiraanb@iae.cta.br Francisco Carlos Parquet
doi: 10.5028/jatm.2011. 03032211 Alexandre Garcia * alexandregarciaag@iae.cta.br Sidney Servulo Cunha Yamanaka sidneysscy@iae.cta.br Alexandre Nogueira Barbosa nogueiraanb@iae.cta.br Francisco Carlos Parquet
Satellite Components & Systems. Dr. Ugur GUVEN Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) Nuclear Science & Technology Engineer (M.Sc)
 Satellite Components & Systems Dr. Ugur GUVEN Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) Nuclear Science & Technology Engineer (M.Sc) Definitions Attitude: The way the satellite is inclined toward Earth at a certain inclination
Satellite Components & Systems Dr. Ugur GUVEN Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) Nuclear Science & Technology Engineer (M.Sc) Definitions Attitude: The way the satellite is inclined toward Earth at a certain inclination
BEOSAT (BRUNSWICK-EARTH-OBSERVATION-SATELLITE)
 ABSTRACT BEOSAT (BRUNSWICK-EARTH-OBSERVATION-SATELLITE) Rolf Kluge Jörn Pfingstgräff ExperimentalRaumfahrt-InteressenGemeinschaft e.v., Germany r.kluge@tu-braunschweig.de j.pfingstgraeff@tu-braunschweig.de
ABSTRACT BEOSAT (BRUNSWICK-EARTH-OBSERVATION-SATELLITE) Rolf Kluge Jörn Pfingstgräff ExperimentalRaumfahrt-InteressenGemeinschaft e.v., Germany r.kluge@tu-braunschweig.de j.pfingstgraeff@tu-braunschweig.de
Launches and On-Orbit Performance
 Launches and On-Orbit Performance An Update on Nanosatellite Missions at the UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory Daniel D. Kekez,, Robert E. Zee, Freddy M. Pranajaya Space Flight Laboratory University of Toronto
Launches and On-Orbit Performance An Update on Nanosatellite Missions at the UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory Daniel D. Kekez,, Robert E. Zee, Freddy M. Pranajaya Space Flight Laboratory University of Toronto
Balloons - Stable Platforms for Payloads in the Higher Atmosphere
 Balloons - Stable Platforms for Payloads in the Higher Atmosphere The application of balloons for scientific use as a supplement to satellites and ground based instruments has increased in particular during
Balloons - Stable Platforms for Payloads in the Higher Atmosphere The application of balloons for scientific use as a supplement to satellites and ground based instruments has increased in particular during
Leonid Meteor Observer in LEO: A Proposal for a University Microsatellite for the 2001 Leonids
 Leonid Meteor Observer in LEO: A Proposal for a University Microsatellite for the 2001 Leonids Kazuya Yoshida* Hajime Yano** *Tohoku University **Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS) JAPAN
Leonid Meteor Observer in LEO: A Proposal for a University Microsatellite for the 2001 Leonids Kazuya Yoshida* Hajime Yano** *Tohoku University **Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS) JAPAN
Advanced drop tests from stratospheric balloons
 Advanced drop tests from stratospheric balloons Mr Mikael Töyrä SSC, Esrange, P.O. Box 802, SE-981 28 Kiruna, Sweden Stratospheric balloons are used for scientific measurements, drop tests of aerospace
Advanced drop tests from stratospheric balloons Mr Mikael Töyrä SSC, Esrange, P.O. Box 802, SE-981 28 Kiruna, Sweden Stratospheric balloons are used for scientific measurements, drop tests of aerospace
Japanese Sounding Rocket Activities
 Japanese Sounding Rocket Activities Takumi Abe Institute of Space and Astronautical Science Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency April 14-16, 2010 Workshop on Suborbital Platforms and Nanosatellites 1 OUTLINE
Japanese Sounding Rocket Activities Takumi Abe Institute of Space and Astronautical Science Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency April 14-16, 2010 Workshop on Suborbital Platforms and Nanosatellites 1 OUTLINE
Environmental Dosimetry with the Pille TL Space Dosimetry System During the BEXUS-12 Stratospheric Balloon Flight
 Environmental Dosimetry with the Pille TL Space Dosimetry System During the BEXUS-12 Stratospheric Balloon Flight Balázs Zábori 1, Attila Hirn 2, Tamás Pázmándi 2, Péter Szántó 2, Sándor Deme 2, István
Environmental Dosimetry with the Pille TL Space Dosimetry System During the BEXUS-12 Stratospheric Balloon Flight Balázs Zábori 1, Attila Hirn 2, Tamás Pázmándi 2, Péter Szántó 2, Sándor Deme 2, István
Attitude Determination and Control System Design for STU-2A Cubesat and In-Orbit Results
 13 th Annual Summer CubeSat Developer s Workshop August 6-7, 2016, Logan, Utah Attitude Determination and Control System Design for STU-2A Cubesat and In-Orbit Results Presented by Shufan Wu Guowen Sun,
13 th Annual Summer CubeSat Developer s Workshop August 6-7, 2016, Logan, Utah Attitude Determination and Control System Design for STU-2A Cubesat and In-Orbit Results Presented by Shufan Wu Guowen Sun,
PROBA 1. F. Teston ESA/ESTEC D/TEC-EL
 PROBA 1 F. Teston ESA/ESTEC D/TEC-EL Frederic.Teston@esa.int PROBA 1 launch PROBA 1 has been launched on 21 October 2001 Orbital parameters: Altitude: 681-561 km Near polar (inclination of 97.9 ) Sun-synchronous
PROBA 1 F. Teston ESA/ESTEC D/TEC-EL Frederic.Teston@esa.int PROBA 1 launch PROBA 1 has been launched on 21 October 2001 Orbital parameters: Altitude: 681-561 km Near polar (inclination of 97.9 ) Sun-synchronous
REXUS-4: VEHICLE AND SUBSYSTEM DESIGN, FLIGHT PERFORMANCE AND EXPERIMENTS
 REXUS-4: VEHICLE AND SUBSYSTEM DESIGN, FLIGHT PERFORMANCE AND EXPERIMENTS Andreas Stamminger (1), Manuel Czech (2), Hannes Griebel (3), Marcus Hörschgen (4), Olle Persson (5), Markus Pinzer (6), Jens Rießelmann
REXUS-4: VEHICLE AND SUBSYSTEM DESIGN, FLIGHT PERFORMANCE AND EXPERIMENTS Andreas Stamminger (1), Manuel Czech (2), Hannes Griebel (3), Marcus Hörschgen (4), Olle Persson (5), Markus Pinzer (6), Jens Rießelmann
USV TEST FLIGHT BY STRATOSPHERIC BALLOON: PRELIMINARY MISSION ANALYSIS
 USV TEST FLIGHT BY STRATOSPHERIC BALLOON: PRELIMINARY MISSION ANALYSIS A. Cardillo a, I. Musso a, R. Ibba b, O.Cosentino b a Institute of Information Science and Technologies, National Research Council,
USV TEST FLIGHT BY STRATOSPHERIC BALLOON: PRELIMINARY MISSION ANALYSIS A. Cardillo a, I. Musso a, R. Ibba b, O.Cosentino b a Institute of Information Science and Technologies, National Research Council,
Biological Experiments in Space
 Veronica De Micco and Giovanna Aronne Biological Experiments in Space The experience of SAYSOY Space Apparatus to Yield SOYsprouts ARACNE Copyright MMVIII ARACNE editrice S.r.l. www.aracneeditrice.it info@aracneeditrice.it
Veronica De Micco and Giovanna Aronne Biological Experiments in Space The experience of SAYSOY Space Apparatus to Yield SOYsprouts ARACNE Copyright MMVIII ARACNE editrice S.r.l. www.aracneeditrice.it info@aracneeditrice.it
Opportunities for Small Satellites and Space Research Using the K-1 Vehicle
 SSC99-X-5 Opportunities for Small Satellites and Space Research Using the K-1 Vehicle Debra Facktor Lepore, Gary Lai, and Tom Taylor Kistler Aerospace Corporation 3760 Carillon Point, Kirkland, Washington
SSC99-X-5 Opportunities for Small Satellites and Space Research Using the K-1 Vehicle Debra Facktor Lepore, Gary Lai, and Tom Taylor Kistler Aerospace Corporation 3760 Carillon Point, Kirkland, Washington
Pointing Control for Low Altitude Triple Cubesat Space Darts
 Pointing Control for Low Altitude Triple Cubesat Space Darts August 12 th, 2009 U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Washington, D.C. Code 8231-Attitude Control System James Armstrong, Craig Casey, Glenn Creamer,
Pointing Control for Low Altitude Triple Cubesat Space Darts August 12 th, 2009 U.S. Naval Research Laboratory Washington, D.C. Code 8231-Attitude Control System James Armstrong, Craig Casey, Glenn Creamer,
Attitude Control Strategy for HAUSAT-2 with Pitch Bias Momentum System
 SSC06-VII-5 Attitude Control Strategy for HAUSAT-2 with Pitch Bias Momentum System Young-Keun Chang, Seok-Jin Kang, Byung-Hoon Lee, Jung-on Choi, Mi-Yeon Yun and Byoung-Young Moon School of Aerospace and
SSC06-VII-5 Attitude Control Strategy for HAUSAT-2 with Pitch Bias Momentum System Young-Keun Chang, Seok-Jin Kang, Byung-Hoon Lee, Jung-on Choi, Mi-Yeon Yun and Byoung-Young Moon School of Aerospace and
Technical Verification Satellite STARS for Tethered Space Robot
 Technical Verification Satellite STARS for Tethered Space Robot Masahiro Nohmi, Takeshi Yamamoto, and Akira Andatsu Kagawa University nohmi@eng.kagawa-u.ac.jp, s05g528@stmail.eng.kagawa-u.ac.jp, s06g452@stmail.eng.kagawa-u.ac.jp
Technical Verification Satellite STARS for Tethered Space Robot Masahiro Nohmi, Takeshi Yamamoto, and Akira Andatsu Kagawa University nohmi@eng.kagawa-u.ac.jp, s05g528@stmail.eng.kagawa-u.ac.jp, s06g452@stmail.eng.kagawa-u.ac.jp
Solid Propellant Autonomous DE-Orbit System [SPADES] Co-authors: T. Soares J. Huesing A. Cotuna I. Carnelli L. Innocenti
![Solid Propellant Autonomous DE-Orbit System [SPADES] Co-authors: T. Soares J. Huesing A. Cotuna I. Carnelli L. Innocenti Solid Propellant Autonomous DE-Orbit System [SPADES] Co-authors: T. Soares J. Huesing A. Cotuna I. Carnelli L. Innocenti](/thumbs/75/71934053.jpg) Solid Propellant Autonomous DE-Orbit System [SPADES] Co-authors: T. Soares J. Huesing A. Cotuna I. Carnelli L. Innocenti SPADES introduction SPADES is: Cross-cutting system to support the compliance of
Solid Propellant Autonomous DE-Orbit System [SPADES] Co-authors: T. Soares J. Huesing A. Cotuna I. Carnelli L. Innocenti SPADES introduction SPADES is: Cross-cutting system to support the compliance of
The Simplest Tether Control Law in a Small Satellite
 The Simplest Tether Control Law in a Small Satellite Yosuke Nakamura (Kyushu University) Designing of a small satellite based on the Satellite Design Contest is progressing in Kyushu University. This is
The Simplest Tether Control Law in a Small Satellite Yosuke Nakamura (Kyushu University) Designing of a small satellite based on the Satellite Design Contest is progressing in Kyushu University. This is
Development of Deployment System for Small Size Solar Sail Mission
 Trans. JSASS Space Tech. Japan Vol. 7, No. ists6, pp. Pd_87-Pd_9, 9 Development of Deployment System for Small Size Solar Sail Mission By Osamu MORI, ) Hirotaka SAWADA, ) Fuminori HANAOKA, ) Junichiro
Trans. JSASS Space Tech. Japan Vol. 7, No. ists6, pp. Pd_87-Pd_9, 9 Development of Deployment System for Small Size Solar Sail Mission By Osamu MORI, ) Hirotaka SAWADA, ) Fuminori HANAOKA, ) Junichiro
NEW EUMETSAT POLAR SYSTEM ATTITUDE MONITORING SOFTWARE
 NEW EUMETSAT POLAR SYSTEM ATTITUDE MONITORING SOFTWARE Pablo García Sánchez (1), Antonio Pérez Cambriles (2), Jorge Eufrásio (3), Pier Luigi Righetti (4) (1) GMV Aerospace and Defence, S.A.U., Email: pgarcia@gmv.com,
NEW EUMETSAT POLAR SYSTEM ATTITUDE MONITORING SOFTWARE Pablo García Sánchez (1), Antonio Pérez Cambriles (2), Jorge Eufrásio (3), Pier Luigi Righetti (4) (1) GMV Aerospace and Defence, S.A.U., Email: pgarcia@gmv.com,
Individual Adapter Solutions for Multi-Spacecraft Launches on Rockot
 SSC14-IV-9 Individual Adapter Solutions for Multi-Spacecraft Launches on Rockot York Viertel, Peter Freeborn, Markus Poetsch, Anna Zorina Eurockot Launch Services GmbH Flughafenalle 26, 28199 Bremen, Germany
SSC14-IV-9 Individual Adapter Solutions for Multi-Spacecraft Launches on Rockot York Viertel, Peter Freeborn, Markus Poetsch, Anna Zorina Eurockot Launch Services GmbH Flughafenalle 26, 28199 Bremen, Germany
SPACE DEBRIS MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES
 SPACE DEBRIS MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES Rob Hoyt Tethers Unlimited, Inc. The orbital debris population and its potential for continued rapid growth presents a significant threat to DoD, NASA, commercial,
SPACE DEBRIS MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES Rob Hoyt Tethers Unlimited, Inc. The orbital debris population and its potential for continued rapid growth presents a significant threat to DoD, NASA, commercial,
TEXUS AND MAXUS PREPARATIONS FOR THE FUTURE
 TEXUS AND MAXUS PREPARATIONS FOR THE FUTURE Andreas Schütte Astrium GmbH, Airbus-Allee 1, 28199 Bremen, Germany Email: Andreas.Schuette@astrium.eads.net ABSTRACT The sounding rocket program TEXUS & MAXUS
TEXUS AND MAXUS PREPARATIONS FOR THE FUTURE Andreas Schütte Astrium GmbH, Airbus-Allee 1, 28199 Bremen, Germany Email: Andreas.Schuette@astrium.eads.net ABSTRACT The sounding rocket program TEXUS & MAXUS
The European Student Moon Orbiter (ESMO) A Small Mission for Education, Outreach, and Science
 (ESMO) A Small Mission for Education, Outreach, and Science Roger Walker, Matthew Cross Education Projects Unit, ESA Education Office ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands LEAG-ILEWG-SRR Meeting Cape Canaveral,
(ESMO) A Small Mission for Education, Outreach, and Science Roger Walker, Matthew Cross Education Projects Unit, ESA Education Office ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands LEAG-ILEWG-SRR Meeting Cape Canaveral,
Generation X. Attitude Control Systems (ACS) Aprille Ericsson Dave Olney Josephine San. July 27, 2000
 Generation X Attitude Control Systems (ACS) Aprille Ericsson Dave Olney Josephine San July 27, 2000 ACS Overview Requirements Assumptions Disturbance Torque Assessment Component and Control Mode Recommendations
Generation X Attitude Control Systems (ACS) Aprille Ericsson Dave Olney Josephine San July 27, 2000 ACS Overview Requirements Assumptions Disturbance Torque Assessment Component and Control Mode Recommendations
METHODS OF BALLISTIC SUPPORT AND SUPERVISION OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGICAL EXPERIMENTS OF FOTON SC
 METHODS OF BALLISTIC SUPPORT AND SUPERVISION OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGICAL EXPERIMENTS OF FOTON SC Jury. M. Ustalov RSC TsSKB-Progress, Samara, Russia Abstract A wide range of research and technological
METHODS OF BALLISTIC SUPPORT AND SUPERVISION OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGICAL EXPERIMENTS OF FOTON SC Jury. M. Ustalov RSC TsSKB-Progress, Samara, Russia Abstract A wide range of research and technological
Attitude Control Simulator for the Small Satellite and Its Validation by On-orbit Data of QSAT-EOS
 SSC17-P1-17 Attitude Control Simulator for the Small Satellite and Its Validation by On-orbit Data of QSAT-EOS Masayuki Katayama, Yuta Suzaki Mitsubishi Precision Company Limited 345 Kamikmachiya, Kamakura
SSC17-P1-17 Attitude Control Simulator for the Small Satellite and Its Validation by On-orbit Data of QSAT-EOS Masayuki Katayama, Yuta Suzaki Mitsubishi Precision Company Limited 345 Kamikmachiya, Kamakura
Design of Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem
 Design of Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem 1) Control Modes and Requirements Control Modes: Control Modes Explanation 1 ) Spin-Up Mode - Acquisition of Stability through spin-up maneuver -
Design of Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem 1) Control Modes and Requirements Control Modes: Control Modes Explanation 1 ) Spin-Up Mode - Acquisition of Stability through spin-up maneuver -
Toshinori Kuwahara*, Yoshihiro Tomioka, Yuta Tanabe, Masato Fukuyama, Yuji Sakamoto, Kazuya Yoshida, Tohoku University, Japan
 Toshinori Kuwahara*, Yoshihiro Tomioka, Yuta Tanabe, Masato Fukuyama, Yuji Sakamoto, Kazuya Yoshida, Tohoku University, Japan The 3 rd Nano-Satellite Symposium Micro/Nano Satellite & Debris Issues December
Toshinori Kuwahara*, Yoshihiro Tomioka, Yuta Tanabe, Masato Fukuyama, Yuji Sakamoto, Kazuya Yoshida, Tohoku University, Japan The 3 rd Nano-Satellite Symposium Micro/Nano Satellite & Debris Issues December
AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology
 AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology L E C T U R E 22 Part B, Lecture 22 19 April, 2017 C O N T E N T S Attitude stabilization passive and active. Actuators for three axis or active stabilization.
AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology L E C T U R E 22 Part B, Lecture 22 19 April, 2017 C O N T E N T S Attitude stabilization passive and active. Actuators for three axis or active stabilization.
VIRTUAL TESTING SIMULATION TOOL FOR THE NEW QUAD HEAD EXPANDER ELECTRODYNAMIC SHAKER
 VIRTUAL TESTING SIMULATION TOOL FOR THE NEW QUAD HEAD EXPANDER ELECTRODYNAMIC SHAKER Matteo Appolloni,* AOES BV Alessandro Cozzani, European Space Agency * Matteo.Appolloni@esa.int Outline Introduction
VIRTUAL TESTING SIMULATION TOOL FOR THE NEW QUAD HEAD EXPANDER ELECTRODYNAMIC SHAKER Matteo Appolloni,* AOES BV Alessandro Cozzani, European Space Agency * Matteo.Appolloni@esa.int Outline Introduction
Preliminary Development of an Experimental Lightweight Pulsed Plasma Thruster for Solar Sail Attitude Control
 Preliminary Development of an Experimental Lightweight Pulsed Plasma Thruster for Solar Sail Attitude Control Kevin Pryor, Bong Wie, and Pavlos Mikellides Arizona State University 18 th Annual AIAA/USU
Preliminary Development of an Experimental Lightweight Pulsed Plasma Thruster for Solar Sail Attitude Control Kevin Pryor, Bong Wie, and Pavlos Mikellides Arizona State University 18 th Annual AIAA/USU
EQUIPMENT INTERFACE LOAD CHARACTERIZATION IN ACOUSTICS
 1 EQUIPMENT INTERFACE LOAD CHARACTERIZATION IN ACOUSTICS Nicolas Ludovic LARUE (1), Jean Marie LOME (2), Alice PRADINES (3) (1) Mechanical analysis and test engineer, EADS Astrium - 31 avenue des Cosmonautes,
1 EQUIPMENT INTERFACE LOAD CHARACTERIZATION IN ACOUSTICS Nicolas Ludovic LARUE (1), Jean Marie LOME (2), Alice PRADINES (3) (1) Mechanical analysis and test engineer, EADS Astrium - 31 avenue des Cosmonautes,
Challenges in Realizing Large Structures in Space
 Challenges in Realizing Large Structures in Space Gunnar Tibert KTH Space Center Space Rendezvous, 13 Oct 2016 Large Structures in Space My experience on large space structures: Centrifugally deployed
Challenges in Realizing Large Structures in Space Gunnar Tibert KTH Space Center Space Rendezvous, 13 Oct 2016 Large Structures in Space My experience on large space structures: Centrifugally deployed
Spacer Development and Analysis
 Spacer Development and Analysis Mission Overview POPACS MISSION To measure changes in the density of the auroral zone upper atmosphere in response to various solar stimuli DREXEL OBJECTIVE To design and
Spacer Development and Analysis Mission Overview POPACS MISSION To measure changes in the density of the auroral zone upper atmosphere in response to various solar stimuli DREXEL OBJECTIVE To design and
AN OVERVIEW OF THE E.C.S.S. HANDBOOK FOR SPACECRAFT LOADS ANALYSIS
 COMPDYN 2011 III ECCOMAS Thematic Conference on Computational Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering M. Papadrakakis, M. Fragiadakis, V. Plevris (eds.) Corfu, Greece, 25 28 May 2011
COMPDYN 2011 III ECCOMAS Thematic Conference on Computational Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering M. Papadrakakis, M. Fragiadakis, V. Plevris (eds.) Corfu, Greece, 25 28 May 2011
Spacecraft Bus / Platform
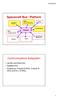 Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Improved Orbit Determination of LEO CubeSats: Project LEDsat
 Improved Orbit Determination of LEO CubeSats: Project LEDsat James Cutler Department of Aerospace Engineering, University of Michigan jwcutler@umich.edu Patrick Seitzer Chris H. Lee Department of Astronomy,
Improved Orbit Determination of LEO CubeSats: Project LEDsat James Cutler Department of Aerospace Engineering, University of Michigan jwcutler@umich.edu Patrick Seitzer Chris H. Lee Department of Astronomy,
CFD Analysis of a Passive Deorbit Device
 CFD Analysis of a Passive Deorbit Device A project present to The Faculty of the Department of Aerospace Engineering San Jose State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
CFD Analysis of a Passive Deorbit Device A project present to The Faculty of the Department of Aerospace Engineering San Jose State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Orbital Debris Mitigation
 Orbital Debris Mitigation R. L. Kelley 1, D. R. Jarkey 2, G. Stansbery 3 1. Jacobs, NASA Johnson Space Center, Houston, TX 77058, USA 2. HX5 - Jacobs JETS Contract, NASA Johnson Space Center, Houston,
Orbital Debris Mitigation R. L. Kelley 1, D. R. Jarkey 2, G. Stansbery 3 1. Jacobs, NASA Johnson Space Center, Houston, TX 77058, USA 2. HX5 - Jacobs JETS Contract, NASA Johnson Space Center, Houston,
Attitude Control on the Pico Satellite Solar Cell Testbed-2
 SSC12-II-1 Attitude Control on the Pico Satellite Solar Cell Testbed-2 Siegfried W. Janson, Brian S. Hardy, Andrew Y. Chin, Daniel L. Rumsey, Daniel A. Ehrlich, and David A. Hinkley The Aerospace Corporation
SSC12-II-1 Attitude Control on the Pico Satellite Solar Cell Testbed-2 Siegfried W. Janson, Brian S. Hardy, Andrew Y. Chin, Daniel L. Rumsey, Daniel A. Ehrlich, and David A. Hinkley The Aerospace Corporation
A FIRST PROTOTYPE OF A SUBORBITAL PLATFORM FOR MULTIPOINT MEASUREMENTS: THE LIGHT AIRBAG PROTECTED LANDER
 A FIRST PROTOTYPE OF A SUBORBITAL PLATFORM FOR MULTIPOINT MEASUREMENTS: THE LIGHT AIRBAG PROTECTED LANDER E. Sund 1, C. Jonsson 1, N. Ivchenko 1, T. Sundberg 1, P. Ahlén 1, M. Gustafsson 1, M. Hedberg
A FIRST PROTOTYPE OF A SUBORBITAL PLATFORM FOR MULTIPOINT MEASUREMENTS: THE LIGHT AIRBAG PROTECTED LANDER E. Sund 1, C. Jonsson 1, N. Ivchenko 1, T. Sundberg 1, P. Ahlén 1, M. Gustafsson 1, M. Hedberg
Fin design mission. Team Members
 Fin design mission Team Members Mission: Your team will determine the best fin design for a model rocket. You will compare highest altitude, flight characteristics, and weathercocking. You will report
Fin design mission Team Members Mission: Your team will determine the best fin design for a model rocket. You will compare highest altitude, flight characteristics, and weathercocking. You will report
Lunar Satellite Attitude Determination System
 Lunar Satellite Attitude Determination System SENIOR DESIGN PROPOSAL PRESENTATION TEAM EPOCH KUPOLUYI, TOLULOPE (LEAD DEVELOPER) SONOIKI, OLUWAYEMISI (LEAD RESEARCHER) WARREN, DANAH (PROJECT MANAGER) NOVEMBER
Lunar Satellite Attitude Determination System SENIOR DESIGN PROPOSAL PRESENTATION TEAM EPOCH KUPOLUYI, TOLULOPE (LEAD DEVELOPER) SONOIKI, OLUWAYEMISI (LEAD RESEARCHER) WARREN, DANAH (PROJECT MANAGER) NOVEMBER
Passive Orbital Debris Removal Using Special Density Materials
 Passive Orbital Debris Removal Using Special Density Materials Hiroshi Hirayama( 平山寛 ) Toshiya Hanada( 花田俊也 ) Yuya Ariyoshi( 有吉雄哉 ) Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan Supported by IHI Corporation, Tokyo,
Passive Orbital Debris Removal Using Special Density Materials Hiroshi Hirayama( 平山寛 ) Toshiya Hanada( 花田俊也 ) Yuya Ariyoshi( 有吉雄哉 ) Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan Supported by IHI Corporation, Tokyo,
Design and performance simulation of a satellite momentum exchange actuator
 Australian Journal of Mechanical Engineering ISSN: 1448-4846 (Print) 2204-2253 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tmec20 Design and performance simulation of a satellite momentum
Australian Journal of Mechanical Engineering ISSN: 1448-4846 (Print) 2204-2253 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tmec20 Design and performance simulation of a satellite momentum
MODULAR AEROPLANE SYSTEM. A CONCEPT AND INITIAL INVESTIGATION
 28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES MODULAR AEROPLANE SYSTEM. A CONCEPT AND INITIAL INVESTIGATION Marcin Figat, Cezary Galiński, Agnieszka Kwiek Warsaw University of Technology mfigat@meil.pw.edu.pl;
28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES MODULAR AEROPLANE SYSTEM. A CONCEPT AND INITIAL INVESTIGATION Marcin Figat, Cezary Galiński, Agnieszka Kwiek Warsaw University of Technology mfigat@meil.pw.edu.pl;
Update on the In-orbit Performances of GIOVE Clocks
 Update on the In-orbit Performances of GIOVE Clocks Pierre Waller, Francisco Gonzalez, Stefano Binda, ESA/ESTEC Ilaria Sesia, Patrizia Tavella, INRiM Irene Hidalgo, Guillermo Tobias, GMV Abstract The Galileo
Update on the In-orbit Performances of GIOVE Clocks Pierre Waller, Francisco Gonzalez, Stefano Binda, ESA/ESTEC Ilaria Sesia, Patrizia Tavella, INRiM Irene Hidalgo, Guillermo Tobias, GMV Abstract The Galileo
The Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX) Mission Design: A Pegasus Class Mission to a High Energy Orbit
 The Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX) Mission Design: A Pegasus Class Mission to a High Energy Orbit Ryan Tyler, D.J. McComas, Howard Runge, John Scherrer, Mark Tapley 1 IBEX Science Requirements IBEX
The Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX) Mission Design: A Pegasus Class Mission to a High Energy Orbit Ryan Tyler, D.J. McComas, Howard Runge, John Scherrer, Mark Tapley 1 IBEX Science Requirements IBEX
THE METEOROLOGICAL ROCKET SYSTEM FOR ATMOSPHERIC RESEARCH
 THE METEOROLOGICAL ROCKET SYSTEM FOR ATMOSPHERIC RESEARCH Komissarenko Alexander I. (1) Kuznetsov Vladimir M. (1) Filippov Valerii V. (1) Ryndina Elena C. (1) (1) State Unitary Enterprise KBP Instrument
THE METEOROLOGICAL ROCKET SYSTEM FOR ATMOSPHERIC RESEARCH Komissarenko Alexander I. (1) Kuznetsov Vladimir M. (1) Filippov Valerii V. (1) Ryndina Elena C. (1) (1) State Unitary Enterprise KBP Instrument
SELENE TRANSLUNAR TRAJECTORY AND LUNAR ORBIT INJECTION
 SELENE TRANSLUNAR TRAJECTORY AND LUNAR ORBIT INJECTION Yasuihiro Kawakatsu (*1) Ken Nakajima (*2), Masahiro Ogasawara (*3), Yutaka Kaneko (*1), Yoshisada Takizawa (*1) (*1) National Space Development Agency
SELENE TRANSLUNAR TRAJECTORY AND LUNAR ORBIT INJECTION Yasuihiro Kawakatsu (*1) Ken Nakajima (*2), Masahiro Ogasawara (*3), Yutaka Kaneko (*1), Yoshisada Takizawa (*1) (*1) National Space Development Agency
Development of Microwave Engine
 Development of Microwave Engine IEPC-01-224 Shin SATORI*, Hiroyuki OKAMOTO**, Ted Mitsuteru SUGIKI**, Yoshinori AOKI #, Atsushi NAGATA #, Yasumasa ITO** and Takayoshi KIZAKI # * Hokkaido Institute of Technology
Development of Microwave Engine IEPC-01-224 Shin SATORI*, Hiroyuki OKAMOTO**, Ted Mitsuteru SUGIKI**, Yoshinori AOKI #, Atsushi NAGATA #, Yasumasa ITO** and Takayoshi KIZAKI # * Hokkaido Institute of Technology
SPACE SHUTTLE ROLL MANEUVER
 SPACE SHUTTLE ROLL MANEUVER Instructional Objectives Students will analyze space shuttle schematics and data to: demonstrate graph and schematic interpretation skills; apply integration techniques to evaluate
SPACE SHUTTLE ROLL MANEUVER Instructional Objectives Students will analyze space shuttle schematics and data to: demonstrate graph and schematic interpretation skills; apply integration techniques to evaluate
MULTI-STAGE SUBORBITAL LAUNCHER MODAL AND DYNAMIC TEST PROGRAM
 Review of the Air Force Academy No 3 (30) 2015 MULTI-STAGE SUBORBITAL LAUNCHER MODAL AND DYNAMIC TEST PROGRAM Mihai MIHAILA-ANDRES*, Flore LICA*, Paul-Virgil ROSU** * Institute for Theoretical & Experimental
Review of the Air Force Academy No 3 (30) 2015 MULTI-STAGE SUBORBITAL LAUNCHER MODAL AND DYNAMIC TEST PROGRAM Mihai MIHAILA-ANDRES*, Flore LICA*, Paul-Virgil ROSU** * Institute for Theoretical & Experimental
CS491/691: Introduction to Aerial Robotics
 CS491/691: Introduction to Aerial Robotics Topic: Midterm Preparation Dr. Kostas Alexis (CSE) Areas of Focus Coordinate system transformations (CST) MAV Dynamics (MAVD) Navigation Sensors (NS) State Estimation
CS491/691: Introduction to Aerial Robotics Topic: Midterm Preparation Dr. Kostas Alexis (CSE) Areas of Focus Coordinate system transformations (CST) MAV Dynamics (MAVD) Navigation Sensors (NS) State Estimation
FIBER OPTIC GYRO-BASED ATTITUDE DETERMINATION FOR HIGH- PERFORMANCE TARGET TRACKING
 FIBER OPTIC GYRO-BASED ATTITUDE DETERMINATION FOR HIGH- PERFORMANCE TARGET TRACKING Elias F. Solorzano University of Toronto (Space Flight Laboratory) Toronto, ON (Canada) August 10 th, 2016 30 th AIAA/USU
FIBER OPTIC GYRO-BASED ATTITUDE DETERMINATION FOR HIGH- PERFORMANCE TARGET TRACKING Elias F. Solorzano University of Toronto (Space Flight Laboratory) Toronto, ON (Canada) August 10 th, 2016 30 th AIAA/USU
21 JSTS Vol. 27, No. 2
 21 JSTS Vol. 27, No. 2 Technical Challenges and Study on Guided Reentry Flight for Capsule Spacecraft Shuichi MATSUMOTO 1), Yoshinori KONDOH 1), Takane IMADA 1) and Naoki SATO 1) 1) Japan Aerospace Exploration
21 JSTS Vol. 27, No. 2 Technical Challenges and Study on Guided Reentry Flight for Capsule Spacecraft Shuichi MATSUMOTO 1), Yoshinori KONDOH 1), Takane IMADA 1) and Naoki SATO 1) 1) Japan Aerospace Exploration
Precision Attitude and Translation Control Design and Optimization
 Precision Attitude and Translation Control Design and Optimization John Mester and Saps Buchman Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, California, U.S.A. Abstract Future
Precision Attitude and Translation Control Design and Optimization John Mester and Saps Buchman Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, California, U.S.A. Abstract Future
Optical Tracking and Attitude Determination of LEO CubeSats with LEDs: A Balloon Demonstration
 AMOS Technologies Conference, 11-14 September 2018, Maui, Hawai`i Optical Tracking and Attitude Determination of LEO CubeSats with LEDs: A Balloon Demonstration Patrick Seitzer University of Michigan,
AMOS Technologies Conference, 11-14 September 2018, Maui, Hawai`i Optical Tracking and Attitude Determination of LEO CubeSats with LEDs: A Balloon Demonstration Patrick Seitzer University of Michigan,
MARS DROP. Matthew A. Eby Mechanical Systems Department. Vehicle Systems Division/ETG The Aerospace Corporation May 25, 2013
 MARS DROP Matthew A. Eby Mechanical Systems Department Vehicle Systems Division/ETG The Aerospace Corporation May 25, 2013 The Aerospace Corporation 2013 The Aerospace Corporation (Aerospace), a California
MARS DROP Matthew A. Eby Mechanical Systems Department Vehicle Systems Division/ETG The Aerospace Corporation May 25, 2013 The Aerospace Corporation 2013 The Aerospace Corporation (Aerospace), a California
Orbit Design Marcelo Suárez. 6th Science Meeting; Seattle, WA, USA July 2010
 Orbit Design Marcelo Suárez Orbit Design Requirements The following Science Requirements provided drivers for Orbit Design: Global Coverage: the entire extent (100%) of the ice-free ocean surface to at
Orbit Design Marcelo Suárez Orbit Design Requirements The following Science Requirements provided drivers for Orbit Design: Global Coverage: the entire extent (100%) of the ice-free ocean surface to at
Net Capture Mechanism for Debris Removal Demonstration Mission
 Net Capture Mechanism for Debris Removal Demonstration Mission Robert Axthelm (1), Barbara Klotz (2), Dr. Ingo Retat (3), Uwe Schlossstein (4), Wolfgang Tritsch (5), Susanne Vahsen (6) Airbus DS, Airbus
Net Capture Mechanism for Debris Removal Demonstration Mission Robert Axthelm (1), Barbara Klotz (2), Dr. Ingo Retat (3), Uwe Schlossstein (4), Wolfgang Tritsch (5), Susanne Vahsen (6) Airbus DS, Airbus
Sub-millimeter size debris monitoring system with IDEA OSG 1
 Sub-millimeter size debris monitoring system with IDEA OSG 1 Masahiko Uetsuhara, Mitsunobu Okada, Yasunori Yamazaki, Astroscale Pte. Ltd. Toshiya Hanada Kyushu University ABSTRACT The 20-kg class microsatellite
Sub-millimeter size debris monitoring system with IDEA OSG 1 Masahiko Uetsuhara, Mitsunobu Okada, Yasunori Yamazaki, Astroscale Pte. Ltd. Toshiya Hanada Kyushu University ABSTRACT The 20-kg class microsatellite
CUBESAT ATMOSPHERIC PROBE FOR EDUCATION (CAPE)
 Presenting author: Christoph Montag Institute of Space Systems, University of Stuttgart montag@irs.uni-stuttgart.de CUBESAT ATMOSPHERIC PROBE FOR EDUCATION (CAPE) Adam S. Pagan (1), Christoph Montag (1),
Presenting author: Christoph Montag Institute of Space Systems, University of Stuttgart montag@irs.uni-stuttgart.de CUBESAT ATMOSPHERIC PROBE FOR EDUCATION (CAPE) Adam S. Pagan (1), Christoph Montag (1),
Design and Development of an Unrestricted Satellite Motion Simulator
 Design and Development of an Unrestricted Satellite Motion Simulator Eryn Culton, Jeffery King, Paige Ward United States Naval Academy Annapolis, MD 21402 POC: jking@usna.edu 31st Annual AIAA/USU Conference
Design and Development of an Unrestricted Satellite Motion Simulator Eryn Culton, Jeffery King, Paige Ward United States Naval Academy Annapolis, MD 21402 POC: jking@usna.edu 31st Annual AIAA/USU Conference
ATTITUDE CONTROL MECHANIZATION TO DE-ORBIT SATELLITES USING SOLAR SAILS
 IAA-AAS-DyCoSS2-14-07-02 ATTITUDE CONTROL MECHANIZATION TO DE-ORBIT SATELLITES USING SOLAR SAILS Ozan Tekinalp, * Omer Atas INTRODUCTION Utilization of solar sails for the de-orbiting of satellites is
IAA-AAS-DyCoSS2-14-07-02 ATTITUDE CONTROL MECHANIZATION TO DE-ORBIT SATELLITES USING SOLAR SAILS Ozan Tekinalp, * Omer Atas INTRODUCTION Utilization of solar sails for the de-orbiting of satellites is
Quadrotor Modeling and Control
 16-311 Introduction to Robotics Guest Lecture on Aerial Robotics Quadrotor Modeling and Control Nathan Michael February 05, 2014 Lecture Outline Modeling: Dynamic model from first principles Propeller
16-311 Introduction to Robotics Guest Lecture on Aerial Robotics Quadrotor Modeling and Control Nathan Michael February 05, 2014 Lecture Outline Modeling: Dynamic model from first principles Propeller
Successful Demonstration for Upper Stage Controlled Re-entry Experiment by H-IIB Launch Vehicle
 11 Successful Demonstration for Upper Stage Controlled Re-entry Experiment by H-IIB Launch Vehicle KAZUO TAKASE *1 MASANORI TSUBOI *2 SHIGERU MORI *3 KIYOSHI KOBAYASHI *3 The space debris created by launch
11 Successful Demonstration for Upper Stage Controlled Re-entry Experiment by H-IIB Launch Vehicle KAZUO TAKASE *1 MASANORI TSUBOI *2 SHIGERU MORI *3 KIYOSHI KOBAYASHI *3 The space debris created by launch
DEOS AUTOMATION AND ROBOTICS PAYLOAD
 w e. c r e a t e. s p a c e. Kayser-Threde GmbH Space Industrial Applications DEOS AUTOMATION AND ROBOTICS PAYLOAD 11th Symposium on Advanced Space Technologies in Robotics and Automation ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk,
w e. c r e a t e. s p a c e. Kayser-Threde GmbH Space Industrial Applications DEOS AUTOMATION AND ROBOTICS PAYLOAD 11th Symposium on Advanced Space Technologies in Robotics and Automation ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk,
INNOVATIVE STRATEGY FOR Z9 REENTRY
 INNOVATIVE STRATEGY FOR Z9 REENTRY Gregor Martens*, Elena Vellutini**, Irene Cruciani* *ELV, Corso Garibaldi, 34 Colleferro (Italy) **Aizoon, Viale Città d Europa 681, 144, Roma (Italy) Abstract Large
INNOVATIVE STRATEGY FOR Z9 REENTRY Gregor Martens*, Elena Vellutini**, Irene Cruciani* *ELV, Corso Garibaldi, 34 Colleferro (Italy) **Aizoon, Viale Città d Europa 681, 144, Roma (Italy) Abstract Large
IXV Thermal Protection System Post-Flight Preliminary analysis
 7 TH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE FOR AERONAUTICS AND SPACE SCIENCES (EUCASS) IXV Thermal Protection System Post-Flight Preliminary analysis François BUFFENOIR*, Thierry PICHON* and Renaud BARRETEAU* *ARIANE Group
7 TH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE FOR AERONAUTICS AND SPACE SCIENCES (EUCASS) IXV Thermal Protection System Post-Flight Preliminary analysis François BUFFENOIR*, Thierry PICHON* and Renaud BARRETEAU* *ARIANE Group
The Torque Rudder: A Novel Semi-Passive Actuator for Small Spacecraft Attitude Control
 The Torque Rudder: A Novel Semi-Passive Actuator for Small Spacecraft Attitude Control Grant Bonin, Vincent Tarantini, Luke Stras, and Robert E. Zee UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory Toronto, On. Canada M3H
The Torque Rudder: A Novel Semi-Passive Actuator for Small Spacecraft Attitude Control Grant Bonin, Vincent Tarantini, Luke Stras, and Robert E. Zee UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory Toronto, On. Canada M3H
Development and qualification of Hall thruster KM-60 and the flow control unit
 Development and qualification of Hall thruster KM-60 and the flow control unit IEPC-2013-055 Presented at the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference, The George Washington University Washington,
Development and qualification of Hall thruster KM-60 and the flow control unit IEPC-2013-055 Presented at the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference, The George Washington University Washington,
MAE 142 Homework #5 Due Friday, March 13, 2009
 MAE 142 Homework #5 Due Friday, March 13, 2009 Please read through the entire homework set before beginning. Also, please label clearly your answers and summarize your findings as concisely as possible.
MAE 142 Homework #5 Due Friday, March 13, 2009 Please read through the entire homework set before beginning. Also, please label clearly your answers and summarize your findings as concisely as possible.
INTRODUCTION. Smooth Passage for an Artificial Satellite - Combustion Test Title - Necessity of Next Term Solid Rocket. Designing the Launch Complex
 R E S E A R C H INTRODUCTION Smooth Passage for an Artificial Satellite - Combustion Test Title - Necessity of Next Term Solid Rocket In September 2006, the "M-V (Mu (µ)-five)," a rocket developed by the
R E S E A R C H INTRODUCTION Smooth Passage for an Artificial Satellite - Combustion Test Title - Necessity of Next Term Solid Rocket In September 2006, the "M-V (Mu (µ)-five)," a rocket developed by the
PRELIMINAJ3.:( 6/8/92 SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION FOR THE DSPSE GUIDANCE, NAVIGATION, AND CONTROL CSCI. Prepared by
 PRELIMINAJ3.:( SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION FOR THE DSPSE GUIDANCE, NAVIGATION, AND CONTROL CSCI Prepared by Space Applications Corporation 6/8/92.. 1 SCOPE 1.1 IDENTIFICATION 1.2 OVERVIEW This
PRELIMINAJ3.:( SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION FOR THE DSPSE GUIDANCE, NAVIGATION, AND CONTROL CSCI Prepared by Space Applications Corporation 6/8/92.. 1 SCOPE 1.1 IDENTIFICATION 1.2 OVERVIEW This
