Harvesting Lunar Eccentricity?
|
|
|
- Brendan Campbell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Harvesting Lunar Eccentricity? Terry R. McConnell Syracuse University November 7, 2014 Abstract A thought experiment involving elementary physics shows that it is possible, in principle, to extract a large amount of energy from the eccentricity of the moon s orbit. Could it be done in practise? Probably not. 1 Introduction There is an enormous potential source of energy represented by the non-zero value of the eccentricity of the moon s orbit. Currently, that eccentricity is about 0.05, meaning that, roughly speaking, the moon s orbit is 5% out of round. A perfectly circular orbit having the same angular momentum would be a lower energy orbit. The difference in energy amounts to approximately Joules. (See the following section for the calculation of this estimate.) For purposes of comparison, the entire world energy consumption in 2008 has been estimated [7] at approximately J. Imagine that the earth were tethered to the moon with a band made of some very strong elastic material. (It is sufficient to imagine a rubber band.) The end of the rubber band attached to the moon could be fixed in place, since the moon s rotation period is synchronized with its period of revolution around the earth. The end attached to the earth, unfortunately, would have to slip in order to allow for the earth to rotate under it each day. This obviously would considerably complicate the engineering difficulties 1, but need not deter us in a thought experiment. Let us assume the difficulties could be overcome. Since the distance from the moon to the earth varies during each orbit due to the orbital eccentricity, the rubber band would periodically stretch and contract. The elastic forces from the rubber band exert no torque on the earth-moon system, since they are directed through its center of mass, and therefore the addition of the rubber band could not change the angular momentum of the orbit. If the band were perfectly elastic, the energy of the orbit would remain unchanged too, but frictional losses in a real (imperfectly elastic) band would gradually circularize the orbit. The heat produced by these frictional losses could conceivably be harvested for generating electricity. Of course, constructing the quarter million mile band of rubber or any other artificial material needed to reach the moon would be a daunting engineering task, not to mention attaching the band at either end in the appropriate way. On the other hand, there has already been speculation about building tethers from the surface of the earth to satellites in geosynchronous orbits (22,000 miles.) Arthur C. Clarke [1], for example, envisioned such a tether connecting the earth to a permanent space station, built in the 22nd century. Would-be astronauts simply ride an elevator. (A stairway is provided for the fitness-minded.) 2 The Calculation Since we are only interested in a rough estimate, we shall ignore the effect of the sun and other planets and assume the moon orbits the earth in a fixed elliptical orbit with eccentricity e. The total energy, h, of this 1 Engineers on Pluto attempting to tether Charon, the major moon of Pluto, would not face this difficulty: the rotation periods of both Pluto and Charon exactly match their period of revolution. 1
2 orbit is to be compared with the energy h 0 of a circular orbit having the same angular momentum, l. Let a be the earth-moon distance at perigee, and let v be the velocity of the moon (relative to a coordinate system fixed at the center of the earth) at perigee. Since the velocity is perpendicular to the radius vector at that instant, we have l 2 = m 2 v 2 a 2. Here m denotes the mass of the moon, and the square of a vector quantity is to be understood as the squared magnitude. It follows that the kinetic energy of the moon at l perigee is 2 2ma. At the same instant, the potential energy of the moon is mk 2 a, where k = Gm e, m e is the mass of the earth, and G is the universal gravitational constant. Thus, (2.1) h = mk a + l2 2ma 2. Let a 0 be the radius of the circular orbit with the same angular momentum, l. reasoning Then, by the same (2.2) h 0 = mk + l2 a 0 2ma 2. 0 To estimate h h 0, we use a standard formula for eccentricity: (2.3) e = 1 l2 m 2 ka. See, for example, [5], p. 97, formula (Comparison with [5] formula 3.49 for the inverse square force law shows that the k of formula 3.62 needs to be replaced by mk to conform with our notation.) Replacing e with zero in (2.3) shows that l 2 m 2 ka 0 = 1, hence e 2 = l2 m 2 k ( 1 a 0 1 a ). Again from (2.3), l 2 m 2 k = (1 e2 )a, so (2.4) 1 1 a 0 a = e 2 (1 e 2 )a. Subtracting (2.2) from (2.1) and using (2.4), we have ( 1 h h 0 = mk 1 ) ( l2 1 a 0 a 2m a 2 1 ) ( 0 a 2 = mke 2 1 (1 e 2 )a 1 1 ). 2a 0 2a Since the eccentricity of the moon s orbit is small, we may approximate a 0 approximate result h h 0 mke4 a. The following values come from the NASA moon fact sheet [4]: by a, obtaining finally the k = N m 2 /kg m = kg a = m e = Substituting these values yields the estimate of h h 0 announced in the introduction: J. 2
3 3 Appendix After completing this note it occurred to us that a more practical scheme for extracting energy from the lunar orbit would be to have a tether with one end fixed at the Moon and the other end attached to a heavy object that is dragged through the earth s atmosphere. (Due to the non-zero eccentricity of the Moon s orbit, contact with the atmosphere - at least in the beginning - would have to be intermittent in order to avoid unpleasant collisions with the surface of the earth.) While in contact with the atmosphere, the heavy object would be subject to a wind of approximately 1000 miles per hour. If it were, say, a wind turbine, and the tether were made of a conducting material, energy generated by the turbine could be sent up to the Moon, where it might power a lunar civilization. Some of the energy could also be sent back to the earth by various methods. During the extraction process the total angular momentum of the earth-moon system would be constant, but the total energy would decrease as it was used by humans, and ultimately radiated into space as waste heat. The drag on the atmosphere by the turbine would clearly work toward slowing the rotation of the earth, and reciprocally, would have the same effect on the rotation of the moon. Assuming the moon s rotation period remained tidally locked to its period of revolution around the earth, the Moon would necessarily move into higher (more distant) orbits, ones having a longer orbital period. Thus, the human energy grab would hasten the well-known recession of the moon due to its tidal interaction with the earth. Eventually the earth-moon system would reach a state of double tidal lock, similar to the Pluto-Charon system, with the month and day equal in length, and the Moon in a geosynchronous orbit. At that point, energy extraction would grind to a halt, and the heavy object would hang uselessly in the atmosphere. To estimate the total amount of energy that could be extracted by this method, we first need to find the radius a of a circular geosynchronous orbit for which the total angular momentum of the earth-moon system is equal to the present total angular momentum, l. We have l = (I m + I e + ma 2 )ω where I m and I e denote, respectively, the moments of inertia of the Moon and the Earth, m is the mass of the Moon, and ω is the common angular velocity of the Earth and Moon s rotation, and of the Moon s revolution about the Earth. Using Kepler s 3rd Law for the common period of rotation τ, τ = 2π ω = 2π k a 3 2, one finds that a is the solution of the quartic equation l 2 a 3 = k(i m + I e + ma 2 ) 2. According to [6], the Earth s moment of inertia about its polar axis is I e = kg m 2, while, according to [4], I m = mr2 MR I 2 e, where R and M are the radius and mass of the Earth, and r and m are the radius and mass of the Moon. Using the values m M = and r R = , also from [4], we find that I m = kg m 2. To make the size of the numbers more manageable, we use the current value of the semi-major axis of the moon (382,868 kilometers) as distance unit, the current length of a day as the time unit, and the mass of the moon as the mass unit. With this choice of units, we have I e = , I m = , k = , and l = The equation satisfied by final semi-major axis of the moon s orbit is then a 3 = ( )( a 2 ) 2. The solution is a = In other words, the moon s orbit will ultimately grow by about 44%. The length of the day on Earth will then equal the length of the month, measured in current days at days. We can easily compute the difference in energy between the current earth-moon system and it s energy in the doubly tidal locked orbit. Equation (2.2) can be used to find the energy in the orbit itself. One then 3
4 also includes the rotational energy of the earth and moon by including terms 1 2 I eω 2 e I mω 2 m, where ω e and ω m are the present day angular speeds of rotation of the Earth and Moon respectively. The current energy in the lunar orbit turns out to be and the total energy of the earth-moon system to be The total energy at the time of double tidal lock is The energy difference of is equal to approximately Joules. It is curious to note that, at the present time, the total energy of the earth-moon system is positive. This shows that there is enough energy in the spin of the Earth to completely eject the Moon from its orbit around the Earth, assuming all the energy could be directed to that purpose. Once the system reaches double tidal lock, the total energy will have become negative. There is no longer enough energy to eject the Moon. It must be recalled that mankind would be competing for energy with natural dissipation of energy by tidal heating of the earth s crust and other factors such as the effects of decreasing eccentricity of the Earth s orbit. The more quickly energy could be generated by our hypothetical wind turbine, the larger would be mankind s ultimate share of the total. To get a rough estimate of the peak power that could be generated by a turbine, we would need to know its efficiency and cross-sectional area, A. It seems probable that a civilization capable of building a tether from the Earth to the Moon would also be capable of building a very efficient generator, so let us assume an efficiency of 80%. As it passes, the turbine briefly accelerates the air it encounters to nearly its own speed relative to the surface of the earth, in order to spin the blades of the turbine. It leaves behind it a wake of air moving at the same speed, but this wake would quickly interact with the surrounding atmosphere and return to approximately a state of rest with respect to the surface of the Earth by the next time the turbine came around. (This interaction with the rest of the atmosphere is precisely the way the turbine puts the brakes on the Earth s rotation.) In the course of the day, the volume of air encountered is approximately 2πRA. This figure must be multiplied by the mass density of air, by the square of the relative velocity, and by the efficiency in order to obtain an estimate of the energy that might be generated in one day. Air has a density of kg/m 3 at 20 degrees Celsius and 760mm Hg. See [2], F10. According to [3], E88, the radius of the Earth is m, so the mass of air displaced in a day by the turbine is A kg. The Earth rotates at a speed of km/hr, or m/sec. This makes the kinetic energy generated in a day equal to A Joules, or A Joules at 80% efficiency. If the turbine had a radius of one mile, the area A would be approximately 10 8 square meters, resulting in a daily energy production that is similar to current global energy consumption in a year. Clearly our treatment is highly simplified and there are many physical and engineering issues that have not been addressed. For example, what properties would the tether material need to have, and is it even conceivable such materials might exist? Would the tethered turbine tend to swing like a pendulum, and if so, how would this influence the practicality of the scheme? What would be the environmental impacts of dragging an object 2 miles wide through the atmosphere? Students of physics and engineering might enjoy considering these and related questions. References [1] Arthur C. Clarke, The Fountains of Paradise, Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, San Diego, [2] R.C. Weast, CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 65, CRC Press, Boca Raton, [3] The Astronomical Almanac for the Year 2000, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., [4] Moon Fact Sheet, [5] Herbert Goldstein, Classical Mechanics, 2nd Ed., Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, [6] K. Lambeck, The Earth s Variable Rotation, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England,
5 [7] energy consumption 5
Lecture 19: The Moon & Mercury. The Moon & Mercury. The Moon & Mercury
 Lecture 19: The Moon & Mercury The Moon & Mercury The Moon and Mercury are similar in some ways They both have: Heavily cratered Dark colored surfaces No atmosphere No water They also have some interesting
Lecture 19: The Moon & Mercury The Moon & Mercury The Moon and Mercury are similar in some ways They both have: Heavily cratered Dark colored surfaces No atmosphere No water They also have some interesting
The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity. Chapter 4 Lecture
 Chapter 4 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding
Chapter 4 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding
4.1 Describing Motion
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different from weight? How do we describe
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different from weight? How do we describe
How do we describe motion?
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity How do we describe motion? Precise definitions to describe motion: Speed: Rate at which object moves $ speed = distance!#"units
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity How do we describe motion? Precise definitions to describe motion: Speed: Rate at which object moves $ speed = distance!#"units
How do we describe motion?
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different
9/13/ Describing Motion: Examples from Everyday Life. Chapter 4: Making Sense of the Universe Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity
 9/13/17 Lecture Outline 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Everyday Life Chapter 4: Making Sense of the Universe Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion?
9/13/17 Lecture Outline 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Everyday Life Chapter 4: Making Sense of the Universe Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion?
Agenda Announce: 4.1 Describing Motion. Tests. How do we describe motion?
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity Agenda Announce: Stony Brook talk this Friday on Precision Cosmology Project Part I due in one week before class: one paragraph
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity Agenda Announce: Stony Brook talk this Friday on Precision Cosmology Project Part I due in one week before class: one paragraph
4.1 Describing Motion. How do we describe motion? Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different from weight? How do we describe
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different from weight? How do we describe
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Gravitation
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Gravitation 1. Each of five satellites makes a circular orbit about an object that is much more massive than any of the satellites. The mass and orbital radius of each
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Gravitation 1. Each of five satellites makes a circular orbit about an object that is much more massive than any of the satellites. The mass and orbital radius of each
Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017
 A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Daily Life Some of the topics we will explore: How do we describe motion? (Speed,
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Daily Life Some of the topics we will explore: How do we describe motion? (Speed,
EART162: PLANETARY INTERIORS
 EART162: PLANETARY INTERIORS Francis Nimmo Last Week Applications of fluid dynamics to geophysical problems Navier-Stokes equation describes fluid flow: Convection requires solving the coupled equations
EART162: PLANETARY INTERIORS Francis Nimmo Last Week Applications of fluid dynamics to geophysical problems Navier-Stokes equation describes fluid flow: Convection requires solving the coupled equations
III. Work and Energy
 Rotation I. Kinematics - Angular analogs II. III. IV. Dynamics - Torque and Rotational Inertia Work and Energy Angular Momentum - Bodies and particles V. Elliptical Orbits The student will be able to:
Rotation I. Kinematics - Angular analogs II. III. IV. Dynamics - Torque and Rotational Inertia Work and Energy Angular Momentum - Bodies and particles V. Elliptical Orbits The student will be able to:
FIFTH MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS
 Physics 2210 Fall 2005 Paolo Gondolor FIFTH MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A solution set is available on the course web page in pdf format (no solutions for 27-29). 7 1. Assume that the planet Uranus has
Physics 2210 Fall 2005 Paolo Gondolor FIFTH MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A solution set is available on the course web page in pdf format (no solutions for 27-29). 7 1. Assume that the planet Uranus has
Chapter 13. Gravitation. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow
 Chapter 13 Gravitation PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Next one week Today: Ch 13 Wed: Review of Ch 8-11, focusing
Chapter 13 Gravitation PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Next one week Today: Ch 13 Wed: Review of Ch 8-11, focusing
PHYSICS 107 FINAL EXAMINATION
 PRINTED NAME: Problem Score 1 /20 2 /20 3 /20 4 /20 5 /20 6 /20 Total /120 PHYSICS 107 FINAL EXAMINATION January 24, 2001 8:30 11:30 am When you are told to begin, check that this examination booklet contains
PRINTED NAME: Problem Score 1 /20 2 /20 3 /20 4 /20 5 /20 6 /20 Total /120 PHYSICS 107 FINAL EXAMINATION January 24, 2001 8:30 11:30 am When you are told to begin, check that this examination booklet contains
A = 6561 times greater. B. 81 times greater. C. equally strong. D. 1/81 as great. E. (1/81) 2 = 1/6561 as great Pearson Education, Inc.
 Q13.1 The mass of the Moon is 1/81 of the mass of the Earth. Compared to the gravitational force that the Earth exerts on the Moon, the gravitational force that the Moon exerts on the Earth is A. 81 2
Q13.1 The mass of the Moon is 1/81 of the mass of the Earth. Compared to the gravitational force that the Earth exerts on the Moon, the gravitational force that the Moon exerts on the Earth is A. 81 2
Physics 2210 Fall 2011 David Ailion FINAL EXAM. December 14, 2011
 Dd Physics 2210 Fall 2011 David Ailion FINAL EXAM December 14, 2011 PLEASE FILL IN THE INFORMATION BELOW: Name (printed): Name (signed): Student ID Number (unid): u Discussion Instructor: Marc Lindley
Dd Physics 2210 Fall 2011 David Ailion FINAL EXAM December 14, 2011 PLEASE FILL IN THE INFORMATION BELOW: Name (printed): Name (signed): Student ID Number (unid): u Discussion Instructor: Marc Lindley
Understanding Motion, Energy & Gravity
 Speed, Velocity & Acceleration Understanding Motion, Energy & Gravity Chapter 4 speed: distance traveled per unit time (e.g., m/s, mph, km/ hr) velocity: speed & direction acceleration: change in velocity
Speed, Velocity & Acceleration Understanding Motion, Energy & Gravity Chapter 4 speed: distance traveled per unit time (e.g., m/s, mph, km/ hr) velocity: speed & direction acceleration: change in velocity
Part I Multiple Choice (4 points. ea.)
 ach xam usually consists of 10 ultiple choice questions which are conceptual in nature. They are often based upon the assigned thought questions from the homework. There are also 4 problems in each exam,
ach xam usually consists of 10 ultiple choice questions which are conceptual in nature. They are often based upon the assigned thought questions from the homework. There are also 4 problems in each exam,
Understanding Motion, Energy & Gravity
 Speed, Velocity & Acceleration Understanding Motion, Energy & Gravity Chapter 4 speed: distance traveled per unit time (e.g., m/s, mph, km/ hr) velocity: speed & direction acceleration: change in velocity
Speed, Velocity & Acceleration Understanding Motion, Energy & Gravity Chapter 4 speed: distance traveled per unit time (e.g., m/s, mph, km/ hr) velocity: speed & direction acceleration: change in velocity
4.3 Conservation Laws in Astronomy
 4.3 Conservation Laws in Astronomy Our goals for learning: Why do objects move at constant velocity if no force acts on them? What keeps a planet rotating and orbiting the Sun? Where do objects get their
4.3 Conservation Laws in Astronomy Our goals for learning: Why do objects move at constant velocity if no force acts on them? What keeps a planet rotating and orbiting the Sun? Where do objects get their
On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
 Instructor(s): Profs. D. Reitze, H. Chan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2 April 2, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Instructor(s): Profs. D. Reitze, H. Chan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2 April 2, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
PHY2020 Test 2 November 5, Name:
 1 PHY2020 Test 2 November 5, 2014 Name: sin(30) = 1/2 cos(30) = 3/2 tan(30) = 3/3 sin(60) = 3/2 cos(60) = 1/2 tan(60) = 3 sin(45) = cos(45) = 2/2 tan(45) = 1 sin(37) = cos(53) = 0.6 cos(37) = sin(53) =
1 PHY2020 Test 2 November 5, 2014 Name: sin(30) = 1/2 cos(30) = 3/2 tan(30) = 3/3 sin(60) = 3/2 cos(60) = 1/2 tan(60) = 3 sin(45) = cos(45) = 2/2 tan(45) = 1 sin(37) = cos(53) = 0.6 cos(37) = sin(53) =
Lecture 16. Gravitation
 Lecture 16 Gravitation Today s Topics: The Gravitational Force Satellites in Circular Orbits Apparent Weightlessness lliptical Orbits and angular momentum Kepler s Laws of Orbital Motion Gravitational
Lecture 16 Gravitation Today s Topics: The Gravitational Force Satellites in Circular Orbits Apparent Weightlessness lliptical Orbits and angular momentum Kepler s Laws of Orbital Motion Gravitational
How do we describe motion?
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity How do we describe motion? Precise definitions to describe motion: Speed: Rate at which object moves example: speed of
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity How do we describe motion? Precise definitions to describe motion: Speed: Rate at which object moves example: speed of
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 1 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 1 4.1 Describing Motion: Examples from Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we describe motion? How is mass different
Events. Notable. more gravity & orbits Tides. Homework Due Next time; Exam review (Sept. 26) Exam I on Sept. 28 (one week from today)
 Today more gravity & orbits Tides Events Homework Due Next time; Exam review (Sept. 26) Exam I on Sept. 28 (one week from today) Notable Fall equinox (Sept. 22 - tomorrow at 4:02PM) Escape Velocity M r
Today more gravity & orbits Tides Events Homework Due Next time; Exam review (Sept. 26) Exam I on Sept. 28 (one week from today) Notable Fall equinox (Sept. 22 - tomorrow at 4:02PM) Escape Velocity M r
Question 1. GRAVITATION UNIT H.W. ANS KEY
 Question 1. GRAVITATION UNIT H.W. ANS KEY Question 2. Question 3. Question 4. Two stars, each of mass M, form a binary system. The stars orbit about a point a distance R from the center of each star, as
Question 1. GRAVITATION UNIT H.W. ANS KEY Question 2. Question 3. Question 4. Two stars, each of mass M, form a binary system. The stars orbit about a point a distance R from the center of each star, as
AP practice ch 7-8 Multiple Choice
 AP practice ch 7-8 Multiple Choice 1. A spool of thread has an average radius of 1.00 cm. If the spool contains 62.8 m of thread, how many turns of thread are on the spool? "Average radius" allows us to
AP practice ch 7-8 Multiple Choice 1. A spool of thread has an average radius of 1.00 cm. If the spool contains 62.8 m of thread, how many turns of thread are on the spool? "Average radius" allows us to
Basics of Kepler and Newton. Orbits of the planets, moons,
 Basics of Kepler and Newton Orbits of the planets, moons, Kepler s Laws, as derived by Newton. Kepler s Laws Universal Law of Gravity Three Laws of Motion Deriving Kepler s Laws Recall: The Copernican
Basics of Kepler and Newton Orbits of the planets, moons, Kepler s Laws, as derived by Newton. Kepler s Laws Universal Law of Gravity Three Laws of Motion Deriving Kepler s Laws Recall: The Copernican
ΣF=ma SECOND LAW. Make a freebody diagram for EVERY problem!
 PHYSICS HOMEWORK #31 SECOND LAW ΣF=ma NEWTON S LAWS Newton s Second Law of Motion The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied, inversely proportional to the mass of the
PHYSICS HOMEWORK #31 SECOND LAW ΣF=ma NEWTON S LAWS Newton s Second Law of Motion The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied, inversely proportional to the mass of the
Chapter 9-10 Test Review
 Chapter 9-10 Test Review Chapter Summary 9.2. The Second Condition for Equilibrium Explain torque and the factors on which it depends. Describe the role of torque in rotational mechanics. 10.1. Angular
Chapter 9-10 Test Review Chapter Summary 9.2. The Second Condition for Equilibrium Explain torque and the factors on which it depends. Describe the role of torque in rotational mechanics. 10.1. Angular
Ph1a: Solution to the Final Exam Alejandro Jenkins, Fall 2004
 Ph1a: Solution to the Final Exam Alejandro Jenkins, Fall 2004 Problem 1 (10 points) - The Delivery A crate of mass M, which contains an expensive piece of scientific equipment, is being delivered to Caltech.
Ph1a: Solution to the Final Exam Alejandro Jenkins, Fall 2004 Problem 1 (10 points) - The Delivery A crate of mass M, which contains an expensive piece of scientific equipment, is being delivered to Caltech.
Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy?
 Tuesday, June 15, 2010 Page: 1 Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy? A) ML 2 /T 2 B) LT 2 /M C) MLT D) M 2 L 3 T E) ML/T 2 Q2. Two cars are initially 150 kilometers
Tuesday, June 15, 2010 Page: 1 Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy? A) ML 2 /T 2 B) LT 2 /M C) MLT D) M 2 L 3 T E) ML/T 2 Q2. Two cars are initially 150 kilometers
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
AP PHYSICS 1 Learning Objectives Arranged Topically
 AP PHYSICS 1 Learning Objectives Arranged Topically with o Big Ideas o Enduring Understandings o Essential Knowledges o Learning Objectives o Science Practices o Correlation to Knight Textbook Chapters
AP PHYSICS 1 Learning Objectives Arranged Topically with o Big Ideas o Enduring Understandings o Essential Knowledges o Learning Objectives o Science Practices o Correlation to Knight Textbook Chapters
Preview. Circular Motion and Gravitation Section 1. Section 1 Circular Motion. Section 2 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation
 Circular Motion and Gravitation Section 1 Preview Section 1 Circular Motion Section 2 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Section 3 Motion in Space Section 4 Torque and Simple Machines Circular Motion
Circular Motion and Gravitation Section 1 Preview Section 1 Circular Motion Section 2 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Section 3 Motion in Space Section 4 Torque and Simple Machines Circular Motion
Lecture 15: Elasticity (Chapter 11) and Universal Gravity (Chapter 12) 1
 Lecture 15: Elasticity (Chapter 11) and Universal Gravity (Chapter 12) 1 REVIEW: Rotational Equilibrium (Chapter 11) With the use of torques one can solve problems in rotational equilibrium. Rotational
Lecture 15: Elasticity (Chapter 11) and Universal Gravity (Chapter 12) 1 REVIEW: Rotational Equilibrium (Chapter 11) With the use of torques one can solve problems in rotational equilibrium. Rotational
Centripetal acceleration ac = to2r Kinetic energy of rotation KE, = \lto2. Moment of inertia. / = mr2 Newton's second law for rotational motion t = la
 The Language of Physics Angular displacement The angle that a body rotates through while in rotational motion (p. 241). Angular velocity The change in the angular displacement of a rotating body about
The Language of Physics Angular displacement The angle that a body rotates through while in rotational motion (p. 241). Angular velocity The change in the angular displacement of a rotating body about
= o + t = ot + ½ t 2 = o + 2
 Chapters 8-9 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Rotational motion Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the
Chapters 8-9 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Rotational motion Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 15, 2001 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 15, 2001 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
Preview. Circular Motion and Gravitation Section 1. Section 1 Circular Motion. Section 2 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation
 Circular Motion and Gravitation Section 1 Preview Section 1 Circular Motion Section 2 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Section 3 Motion in Space Section 4 Torque and Simple Machines Circular Motion
Circular Motion and Gravitation Section 1 Preview Section 1 Circular Motion Section 2 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Section 3 Motion in Space Section 4 Torque and Simple Machines Circular Motion
11 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation
 Physics 1A, Fall 2003 E. Abers 11 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation 11.1 The Inverse Square Law 11.1.1 The Moon and Kepler s Third Law Things fall down, not in some other direction, because that s
Physics 1A, Fall 2003 E. Abers 11 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation 11.1 The Inverse Square Law 11.1.1 The Moon and Kepler s Third Law Things fall down, not in some other direction, because that s
Universal Gravitation
 Universal Gravitation Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely
Universal Gravitation Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely
31 ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS
 31 ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS 1. Compare and contrast circular motion and rotation? Address the following Which involves an object and which involves a system? Does an object/system in circular motion have
31 ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS 1. Compare and contrast circular motion and rotation? Address the following Which involves an object and which involves a system? Does an object/system in circular motion have
a = v2 R where R is the curvature radius and v is the car s speed. To provide this acceleration, the car needs static friction force f = ma = mv2
 PHY 30 K. Solutions for mid-term test #. Problem 1: The forces acting on the car comprise its weight mg, the normal force N from the road that cancels it, and the static friction force f that provides
PHY 30 K. Solutions for mid-term test #. Problem 1: The forces acting on the car comprise its weight mg, the normal force N from the road that cancels it, and the static friction force f that provides
Afternoon Section. Physics 1210 Exam 2 November 8, ! v = d! r dt. a avg. = v2. ) T 2! w = m g! f s. = v at v 2 1.
 Name Physics 1210 Exam 2 November 8, 2012 Afternoon Section Please write directly on the exam and attach other sheets of work if necessary. Calculators are allowed. No notes or books may be used. Multiple-choice
Name Physics 1210 Exam 2 November 8, 2012 Afternoon Section Please write directly on the exam and attach other sheets of work if necessary. Calculators are allowed. No notes or books may be used. Multiple-choice
Physics I. Unit 1 Methods in Science (Systems of Units) Competencies (Do) Students should be able to demonstrate scientific methods.
 Physics I Unit 1 Methods in Science (Systems of Units) Estimated Time Frame Big Ideas for Units 10 Days Tools are needed for the study of Physics, such as measurement, conversions, significant figures,
Physics I Unit 1 Methods in Science (Systems of Units) Estimated Time Frame Big Ideas for Units 10 Days Tools are needed for the study of Physics, such as measurement, conversions, significant figures,
1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. Meters B. Seconds C. Radians D. Radian per second E. Inches
 AP Physics B Practice Questions: Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. Meters B. Seconds C. Radians D. Radian per second E. Inches
AP Physics B Practice Questions: Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. Meters B. Seconds C. Radians D. Radian per second E. Inches
Name:. Set:. Don: Physics: Pre-U Revision Toytime Rotational and Circular Motion
 Name:. Set:. Don: Physics: Pre-U Revision Toytime 2015-16 Rotational and Circular Motion 1 19 (ii) Place ticks in the table below to identify the effect on waves of light as they refract from diamond into
Name:. Set:. Don: Physics: Pre-U Revision Toytime 2015-16 Rotational and Circular Motion 1 19 (ii) Place ticks in the table below to identify the effect on waves of light as they refract from diamond into
Chapter 12. Recall that when a spring is stretched a distance x, it will pull back with a force given by: F = -kx
 Chapter 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Oscillatory Motion Recall that when a spring is stretched a distance x, it will pull back with a force given by: F = -kx When the mass is released, the spring will pull
Chapter 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Oscillatory Motion Recall that when a spring is stretched a distance x, it will pull back with a force given by: F = -kx When the mass is released, the spring will pull
I pt mass = mr 2 I sphere = (2/5) mr 2 I hoop = mr 2 I disk = (1/2) mr 2 I rod (center) = (1/12) ml 2 I rod (end) = (1/3) ml 2
 Fall 008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 3 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Fall 008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 3 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Circular Motion, Pt 2: Angular Dynamics. Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics
 Circular Motion, Pt 2: Angular Dynamics Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics Formulas: Angular Kinematics (θ must be in radians): s = rθ Arc Length 360 = 2π rads = 1 rev ω = θ t = v t r Angular Velocity α av
Circular Motion, Pt 2: Angular Dynamics Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics Formulas: Angular Kinematics (θ must be in radians): s = rθ Arc Length 360 = 2π rads = 1 rev ω = θ t = v t r Angular Velocity α av
a c = v2 R = ω2 R (1) in a horizontal direction towards the barrel s axis. The horizontal force providing for this acceleration is the normal force
 PHY 302 K. Solutions for mid-term test #3. Problem # 1: A rider in the barrel of fun appears motionless relative to the rotating barrel indeed, the whole point of this ride to stay stuck to the wall when
PHY 302 K. Solutions for mid-term test #3. Problem # 1: A rider in the barrel of fun appears motionless relative to the rotating barrel indeed, the whole point of this ride to stay stuck to the wall when
= W Q H. ɛ = T H T C T H = = 0.20 = T C = T H (1 0.20) = = 320 K = 47 C
 1. Four identical 0.18 kg masses are placed at the corners of a 4.0 x 3.0 m rectangle, and are held there by very light connecting rods which form the sides of the rectangle. What is the moment of inertia
1. Four identical 0.18 kg masses are placed at the corners of a 4.0 x 3.0 m rectangle, and are held there by very light connecting rods which form the sides of the rectangle. What is the moment of inertia
The Main Point. Phases and Motions of the Moon. Lecture #5: Earth, Moon, & Sky II. Lunar Phases and Motions. Tides. Eclipses.
 Lecture #5: Earth, Moon, & Sky II Lunar Phases and Motions. Tides. Eclipses. The Main Point The Moon s size and orbit lead to many interesting phenomena: changing phases, tides, and eclipses. Astro 102/104
Lecture #5: Earth, Moon, & Sky II Lunar Phases and Motions. Tides. Eclipses. The Main Point The Moon s size and orbit lead to many interesting phenomena: changing phases, tides, and eclipses. Astro 102/104
1. A force acts on a particle and displaces it through. The value of x for zero work is 1) 0.5 2) 2 4) 6
 1. A force acts on a particle and displaces it through. The value of x for zero work is 1) 0.5 2) 2 3) +2 4) 6 2. Two bodies with K.E. in the ratio 4 : 1 are moving with same linear momenta. The ratio
1. A force acts on a particle and displaces it through. The value of x for zero work is 1) 0.5 2) 2 3) +2 4) 6 2. Two bodies with K.E. in the ratio 4 : 1 are moving with same linear momenta. The ratio
AP Physics C: Rotation II. (Torque and Rotational Dynamics, Rolling Motion) Problems
 AP Physics C: Rotation II (Torque and Rotational Dynamics, Rolling Motion) Problems 1980M3. A billiard ball has mass M, radius R, and moment of inertia about the center of mass I c = 2 MR²/5 The ball is
AP Physics C: Rotation II (Torque and Rotational Dynamics, Rolling Motion) Problems 1980M3. A billiard ball has mass M, radius R, and moment of inertia about the center of mass I c = 2 MR²/5 The ball is
Downloaded from
 Chapter 8 (Gravitation) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. The earth is an approximate sphere. If the interior contained matter which is not of the same density everywhere, then on
Chapter 8 (Gravitation) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. The earth is an approximate sphere. If the interior contained matter which is not of the same density everywhere, then on
Energy in Planetary Orbits
 Lecture 19: Energy in Orbits, Bohr Atom, Oscillatory Motion 1 Energy in Planetary Orbits Consequences of Kepler s First and Third Laws According to Kepler s First Law of Planetary Motion, all planets move
Lecture 19: Energy in Orbits, Bohr Atom, Oscillatory Motion 1 Energy in Planetary Orbits Consequences of Kepler s First and Third Laws According to Kepler s First Law of Planetary Motion, all planets move
Relating Linear and Angular Kinematics. a rad = v 2 /r = rω 2
 PH2213 : Advanced Examples from Chapter 10 : Rotational Motion NOTE: these are somewhat advanced examples of how we can apply the methods from this chapter, so are beyond what will be on the final exam
PH2213 : Advanced Examples from Chapter 10 : Rotational Motion NOTE: these are somewhat advanced examples of how we can apply the methods from this chapter, so are beyond what will be on the final exam
Page Tides ANIMATION. Tidal forces
 Page 194 7.5 Tides ANIMATION Tidal forces Anyone who has spent even a few hours by the sea knows that the ocean's level rises and falls during the day. A blanket set on the sand 10 feet from the water's
Page 194 7.5 Tides ANIMATION Tidal forces Anyone who has spent even a few hours by the sea knows that the ocean's level rises and falls during the day. A blanket set on the sand 10 feet from the water's
Quantitative Skills in AP Physics 1
 This chapter focuses on some of the quantitative skills that are important in your AP Physics 1 course. These are not all of the skills that you will learn, practice, and apply during the year, but these
This chapter focuses on some of the quantitative skills that are important in your AP Physics 1 course. These are not all of the skills that you will learn, practice, and apply during the year, but these
Basic Physics Content
 Basic Physics Content The purpose of these 38 questions is to let me know what your initial grasp is of the material that lies ahead. This is not graded, so don t stress out. Enjoy thinking about and answering
Basic Physics Content The purpose of these 38 questions is to let me know what your initial grasp is of the material that lies ahead. This is not graded, so don t stress out. Enjoy thinking about and answering
Advanced Higher Physics. Rotational motion
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational motion Problems AH Physics: Rotational Motion 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational motion Problems AH Physics: Rotational Motion 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
r r Sample Final questions for PS 150
 Sample Final questions for PS 150 1) Which of the following is an accurate statement? A) Rotating a vector about an axis passing through the tip of the vector does not change the vector. B) The magnitude
Sample Final questions for PS 150 1) Which of the following is an accurate statement? A) Rotating a vector about an axis passing through the tip of the vector does not change the vector. B) The magnitude
v (m/s) 10 d. displacement from 0-4 s 28 m e. time interval during which the net force is zero 0-2 s f. average velocity from 0-4 s 7 m/s x (m) 20
 Physics Final Exam Mechanics Review Answers 1. Use the velocity-time graph below to find the: a. velocity at 2 s 6 m/s v (m/s) 1 b. acceleration from -2 s 6 c. acceleration from 2-4 s 2 m/s 2 2 4 t (s)
Physics Final Exam Mechanics Review Answers 1. Use the velocity-time graph below to find the: a. velocity at 2 s 6 m/s v (m/s) 1 b. acceleration from -2 s 6 c. acceleration from 2-4 s 2 m/s 2 2 4 t (s)
Radial Acceleration. recall, the direction of the instantaneous velocity vector is tangential to the trajectory
 Radial Acceleration recall, the direction of the instantaneous velocity vector is tangential to the trajectory 1 Radial Acceleration recall, the direction of the instantaneous velocity vector is tangential
Radial Acceleration recall, the direction of the instantaneous velocity vector is tangential to the trajectory 1 Radial Acceleration recall, the direction of the instantaneous velocity vector is tangential
GCE A level 1324/01 PHYSICS PH4 Oscillations and Fields
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE A level 1324/01 PHYSICS PH4 Oscillations and Fields P.M. WEDNESDAY, 11 June 2014 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE A level 1324/01 PHYSICS PH4 Oscillations and Fields P.M. WEDNESDAY, 11 June 2014 1 hour 30 minutes For s use Question Maximum Mark Mark Awarded
Ch 8. Rotational Dynamics
 Ch 8. Rotational Dynamics Rotational W, P, K, & L (a) Translation (b) Combined translation and rotation ROTATIONAL ANALOG OF NEWTON S SECOND LAW FOR A RIGID BODY ROTATING ABOUT A FIXED AXIS = τ Iα Requirement:
Ch 8. Rotational Dynamics Rotational W, P, K, & L (a) Translation (b) Combined translation and rotation ROTATIONAL ANALOG OF NEWTON S SECOND LAW FOR A RIGID BODY ROTATING ABOUT A FIXED AXIS = τ Iα Requirement:
Multiple Choice -- TEST III
 Multiple Choice Test III--Classical Mechanics Multiple Choice -- TEST III 1) n atomic particle whose mass is 210 atomic mass units collides with a stationary atomic particle B whose mass is 12 atomic mass
Multiple Choice Test III--Classical Mechanics Multiple Choice -- TEST III 1) n atomic particle whose mass is 210 atomic mass units collides with a stationary atomic particle B whose mass is 12 atomic mass
Welcome back to Physics 215
 Welcome back to Physics 215 Today s agenda: More rolling without slipping Newtonian gravity Planetary orbits Gravitational Potential Energy Physics 215 Spring 2018 Lecture 13-1 1 Rolling without slipping
Welcome back to Physics 215 Today s agenda: More rolling without slipping Newtonian gravity Planetary orbits Gravitational Potential Energy Physics 215 Spring 2018 Lecture 13-1 1 Rolling without slipping
Use the following to answer question 1:
 Use the following to answer question 1: On an amusement park ride, passengers are seated in a horizontal circle of radius 7.5 m. The seats begin from rest and are uniformly accelerated for 21 seconds to
Use the following to answer question 1: On an amusement park ride, passengers are seated in a horizontal circle of radius 7.5 m. The seats begin from rest and are uniformly accelerated for 21 seconds to
Saint Lucie County Science Scope and Sequence
 Course: Honors Physics 1 Course Code: 2003390 UNIT 4 TOPIC of STUDY: Newton s Laws of Motion and the Law of Gravity STANDARDS: 10: Energy, 12: Motion ~Net force produces motion ~There are four fundamental
Course: Honors Physics 1 Course Code: 2003390 UNIT 4 TOPIC of STUDY: Newton s Laws of Motion and the Law of Gravity STANDARDS: 10: Energy, 12: Motion ~Net force produces motion ~There are four fundamental
PHY218 SPRING 2016 Review for Final Exam: Week 14 Final Review: Chapters 1-11, 13-14
 Final Review: Chapters 1-11, 13-14 These are selected problems that you are to solve independently or in a team of 2-3 in order to better prepare for your Final Exam 1 Problem 1: Chasing a motorist This
Final Review: Chapters 1-11, 13-14 These are selected problems that you are to solve independently or in a team of 2-3 in order to better prepare for your Final Exam 1 Problem 1: Chasing a motorist This
Chapter 13. Universal Gravitation
 Chapter 13 Universal Gravitation Planetary Motion A large amount of data had been collected by 1687. There was no clear understanding of the forces related to these motions. Isaac Newton provided the answer.
Chapter 13 Universal Gravitation Planetary Motion A large amount of data had been collected by 1687. There was no clear understanding of the forces related to these motions. Isaac Newton provided the answer.
AP Physics C Textbook Problems
 AP Physics C Textbook Problems Chapter 13 Pages 412 416 HW-16: 03. A 200-kg object and a 500-kg object are separated by 0.400 m. Find the net gravitational force exerted by these objects on a 50.0-kg object
AP Physics C Textbook Problems Chapter 13 Pages 412 416 HW-16: 03. A 200-kg object and a 500-kg object are separated by 0.400 m. Find the net gravitational force exerted by these objects on a 50.0-kg object
Topic 1: Newtonian Mechanics Energy & Momentum
 Work (W) the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance. Scalar but can be positive or negative ΔE = W = F! d = Fdcosθ Units N m or Joules (J) Work, Energy & Power Power (P) the
Work (W) the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance. Scalar but can be positive or negative ΔE = W = F! d = Fdcosθ Units N m or Joules (J) Work, Energy & Power Power (P) the
1. Which one of the following situations is an example of an object with a non-zero kinetic energy?
 Name: Date: 1. Which one of the following situations is an example of an object with a non-zero kinetic energy? A) a drum of diesel fuel on a parked truck B) a stationary pendulum C) a satellite in geosynchronous
Name: Date: 1. Which one of the following situations is an example of an object with a non-zero kinetic energy? A) a drum of diesel fuel on a parked truck B) a stationary pendulum C) a satellite in geosynchronous
43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms,
 43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms, A) her moment of inertia increases and her rotational kinetic energy remains the same.
43. A person sits on a freely spinning lab stool that has no friction in its axle. When this person extends her arms, A) her moment of inertia increases and her rotational kinetic energy remains the same.
Energy Conservation AP
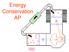 Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Physics. Student Materials Advanced Higher. Tutorial Problems Mechanics HIGHER STILL. Spring 2000
 Spring 2000 HIGHER STILL Physics Student Materials Advanced Higher Tutorial Problems Mechanics TUTORIAL 1 You will find tutorials on each topic. The fully worked out answers are available. The idea is
Spring 2000 HIGHER STILL Physics Student Materials Advanced Higher Tutorial Problems Mechanics TUTORIAL 1 You will find tutorials on each topic. The fully worked out answers are available. The idea is
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
AP Physics QUIZ Gravitation
 AP Physics QUIZ Gravitation Name: 1. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the
AP Physics QUIZ Gravitation Name: 1. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the
Midterm 3 Thursday April 13th
 Welcome back to Physics 215 Today s agenda: rolling friction & review Newtonian gravity Planetary orbits Gravitational Potential Energy Physics 215 Spring 2017 Lecture 13-1 1 Midterm 3 Thursday April 13th
Welcome back to Physics 215 Today s agenda: rolling friction & review Newtonian gravity Planetary orbits Gravitational Potential Energy Physics 215 Spring 2017 Lecture 13-1 1 Midterm 3 Thursday April 13th
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
Name (please print): UW ID# score last first
 Name (please print): UW ID# score last first Question I. (20 pts) Projectile motion A ball of mass 0.3 kg is thrown at an angle of 30 o above the horizontal. Ignore air resistance. It hits the ground 100
Name (please print): UW ID# score last first Question I. (20 pts) Projectile motion A ball of mass 0.3 kg is thrown at an angle of 30 o above the horizontal. Ignore air resistance. It hits the ground 100
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS LSN 8-8: ANGULAR MOMENTUM AND ITS CONSERVATION Questions From Reading Activity? Big Idea(s): The interactions of an object with other objects can be
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS LSN 8-8: ANGULAR MOMENTUM AND ITS CONSERVATION Questions From Reading Activity? Big Idea(s): The interactions of an object with other objects can be
PHYSICS 1. Section I 40 Questions Time 90 minutes. g = 10 m s in all problems.
 Note: To simplify calculations, you may use PHYSICS 1 Section I 40 Questions Time 90 minutes 2 g = 10 m s in all problems. Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by
Note: To simplify calculations, you may use PHYSICS 1 Section I 40 Questions Time 90 minutes 2 g = 10 m s in all problems. Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2011 EXAM #2 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 2, 2011
 PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
Fall 2007 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and 2 Please write your CID Colton
 Fall 007 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 3 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Fall 007 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 3 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
A mass is suspended by a string from a fixed point. The mass moves with constant speed along a circular path in a [1 mark] horizontal plane.
![A mass is suspended by a string from a fixed point. The mass moves with constant speed along a circular path in a [1 mark] horizontal plane. A mass is suspended by a string from a fixed point. The mass moves with constant speed along a circular path in a [1 mark] horizontal plane.](/thumbs/78/77486004.jpg) T6 [200 marks] 1. A mass is suspended by a string from a fixed point. The mass moves with constant speed along a circular path in a horizontal plane. The resultant force acting on the mass is A. zero.
T6 [200 marks] 1. A mass is suspended by a string from a fixed point. The mass moves with constant speed along a circular path in a horizontal plane. The resultant force acting on the mass is A. zero.
5.1. Accelerated Coordinate Systems:
 5.1. Accelerated Coordinate Systems: Recall: Uniformly moving reference frames (e.g. those considered at 'rest' or moving with constant velocity in a straight line) are called inertial reference frames.
5.1. Accelerated Coordinate Systems: Recall: Uniformly moving reference frames (e.g. those considered at 'rest' or moving with constant velocity in a straight line) are called inertial reference frames.
Circular Motion & Gravitation MC Question Database
 (Questions #4,5,6,27,37,38,42 and 58 each have TWO correct answers.) 1) A record player has four coins at different distances from the center of rotation. Coin A is 1 cm away, Coin B is 2 cm away. Coin
(Questions #4,5,6,27,37,38,42 and 58 each have TWO correct answers.) 1) A record player has four coins at different distances from the center of rotation. Coin A is 1 cm away, Coin B is 2 cm away. Coin
Physics 5A Final Review Solutions
 Physics A Final Review Solutions Eric Reichwein Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz November 6, 0. A stone is dropped into the water from a tower 44.m above the ground. Another stone
Physics A Final Review Solutions Eric Reichwein Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz November 6, 0. A stone is dropped into the water from a tower 44.m above the ground. Another stone
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_14 Thursday, November 15, 2007 Page 1
 University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_14 Thursday, November 15, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. An artificial satellite of Earth releases a bomb. Neglecting air resistance, the bomb will: A) strike Earth
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_14 Thursday, November 15, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. An artificial satellite of Earth releases a bomb. Neglecting air resistance, the bomb will: A) strike Earth
Gravitation & Kepler s Laws
 Gravitation & Kepler s Laws What causes YOU to be pulled down to the surface of the earth? THE EARTH.or more specifically the EARTH S MASS. Anything that has MASS has a gravitational pull towards it. F
Gravitation & Kepler s Laws What causes YOU to be pulled down to the surface of the earth? THE EARTH.or more specifically the EARTH S MASS. Anything that has MASS has a gravitational pull towards it. F
Dynamics Examples. Robin Hughes and Anson Cheung. 28 th June, 2010
 Dynamics Examples Robin Hughes and Anson Cheung 28 th June, 2010 1 Newton s Laws Figure 1: 3 connected blocks Figure 2: Masses on a trolley 1. Two blocks of mass m 1 = 1kg and m 2 = 2kg on a frictionless
Dynamics Examples Robin Hughes and Anson Cheung 28 th June, 2010 1 Newton s Laws Figure 1: 3 connected blocks Figure 2: Masses on a trolley 1. Two blocks of mass m 1 = 1kg and m 2 = 2kg on a frictionless
Rotational Motion. Every quantity that we have studied with translational motion has a rotational counterpart
 Rotational Motion & Angular Momentum Rotational Motion Every quantity that we have studied with translational motion has a rotational counterpart TRANSLATIONAL ROTATIONAL Displacement x Angular Displacement
Rotational Motion & Angular Momentum Rotational Motion Every quantity that we have studied with translational motion has a rotational counterpart TRANSLATIONAL ROTATIONAL Displacement x Angular Displacement
