Surface magnetic fields across the HR Diagram
|
|
|
- Lynne Glenn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surface magnetic fields across the HR Diagram John Landstreet University of Western Ontario London, Upper Canada & Armagh Observatory Armagh, Northern Ireland
2 Objective of this talk... This meeting combines specialists in different felds (the Sun, various kinds of stars), with people new to polarimetry Stellar polarimetry reveals scattering material around stars, and their magnetic felds The point of this talk is to give people a kind of simple road map to help to navigate the talks about magnetic felds in stars
3 Why do we need polarimetry to study stellar magnetic fields?? To detect magnetic felds, we use the Zeeman effect. In many hot stars, this is the only detectable symptom of a feld. Zeeman effect splits a single line into multiple components, separated in wavelength and polarised Components are separated by roughly Δλ(A) ~ B(G) 2 λ (A) ~ A/kG
4 Zeeman effect in the intensity spectrum
5 Zeeman splitting in 6kG field of magnetic Ap star HD 94660
6 Weaker fields (HD 96446) show polarisation, but no splitting
7 Recent advances in instruments Recent advances in instrument construction make most of HRD accesible to useful measure Much higher throughput Largely achromatic over wide spectrum Huge spectral range, e.g. all of optical window Several top-end instruments available as facility instruments
8 Improved analysis too! Notice that (circular) V/I polarisation signals are very similar from line to line. Averaging is possible to increase signal-to-noise ratio. Sensitivity to small felds then depends on effcient spectropolarimetry over broad wavelength band high density of fairly deep spectral lines small v sin i (narrow spectral lines) can reach polarimetric sensitivity of
9
10 Mapping We fnd that many stars have felds with static or slowly changing structure. Series of polarimetric spectra in all Stokes components, taken as a star rotates, make mapping possible (Piskunov, Kochukhov, Donati, P. Petit). Such maps reveal magnetic feld structure at low to moderate spatial resolution, and often associated temperature or local abundance variations
11 Map of B2V magnetic star HD (Kochukhov et al 11)
12 The overall picture today Improvement in instrumentation has led to many major surveys and at least some feld detections all over HR diagramme!! PMS stars: T Tau and a few Herbig AeBe stars Main sequence (MS): rapidly rotating low mass stars, small fraction of O, B, A (Ap/Bp) stars Giants & AGB stars: a few Ap descendant(?) felds, some weak dynamo felds in both RG, AGB stars Fraction of white dwarfs, many neutron stars
13 Field structures Studying the magnetic felds found, we recognise two main types: dynamo (solar-type) fields, complex topology, changing structure on many short timescales, feld strength larger for shorter rotation periods, in cool stars. Field is currently being generated by a dynamo. fossil fields, roughly dipolar topology, structure virtually constant over tens of years, feld strength independent of rotation rate, in hot stars. Remmnant (fossil) of earlier phase.
14 Fields in pre-main sequence stars Both low and intermediate mass PMS stars pass through "T Tau" (deep convection) phase: rapid rotation, strong dynamo felds, up to ~3 kg (Johns-Krull et al, Donati et al) Intermediate and high mass stars then pass into Herbig AeBe (mostly radiative) phase: a few % show weak fossil felds, 10s or 100s of G at surface (Catala et al, Wade et al, Alecian et al)
15 Classical T Tau star BP Tau: surface & magnetosphere (Donati 2008)
16 Main sequence and evolved stars Low mass main sequence stars have dynamos that depend strongly on rotation rate, <~ 3 kg (Donati et al, P. Petit et al, Morin et al) Small fraction of intermediate and high mass MS stars have fossil felds, Bz ~ kg (Babcock, Preston, Landstreet et al, Mathys, Wade et al (especially MiMeS)) Massive stars can trap stellar wind in closed felds lines - produce emission lines, eclipses...
17 Trapped magnetosphere in σ Ori E
18 Red giants have dynamo felds of a few G or less, depending on rotation, but magnetic Ap star descendants have felds of ~ G even when rotation is very slow (Auriere et al, Konstantinova-Antova et al) Many massive AGB stars have dynamo felds of ~ 1G (Grunhut et al). N.B.: detected felds might be ~1% of actual felds... Fields are detected in most giants that show indirect indicators of magnetism - Ca II H & K line emission, strong X-rays, "rapid" rotation
19 Magnetic fields in red giants
20 Dynamo effect in red giants Normal M giant felds show usual dynamo dependance on rotation velocity (Konstantinova -Antova et al 2013)
21 Collapsed stars White dwarfs reveal felds via usual Zeeman effect and/or continuum polarisation Fields are found in a few % of all white 4 9 dwarfs. Fields range 10 to 10 G. Field structure roughly dipolar, and the felds are fossils Most or all neutron stars have fossil felds for a while (as pulsars), ranging from 109 to 1015 G
22 White dwarf magnetism Intensity and polarisation spectrum of white dwarf GD229 which has a feld of several hundred MG (cf Schmidt et al 1996)
23 Global evolution of fields Now have observational evidence that (some) felds occurs in most major evolution stages In low mass stars, dynamos seem to occur at most stages until fnal collapse to white dwarf In more massive stars, situation is very interesting! T Tau (dynamo) -> Herbig (fossil) -> MS (fossil) -> RG, AGB (dynamo) -> white dwarf or neutron star (fossil). This complex evolution is FAR FROM UNDERSTOOD.
24 Theoretical framework Surface felds are a consequence of internal electric currents and motions In cool stars observed felds may be mainly determined by present convection zone and distribution of angular momentum But we see from strong feld red giants, thought to be descendants of magnetic Ap stars, that earlier feld is also important What happens when giant -> hot white dwarf?
25 Theoretical framework In massive stars, high Teff phases clearly lack contemporary dynamo - insuffcient convection Today's surface feld is the fossil that results from the feld left in star by earlier evolution phases, modifed by Ohmic decay, feld relaxation, instabilities, stellar structure changes and internal shear fows (Braithwaite, Mathis) Fossil felds may be due to evolution in close binary
26 Can we observe field evolution within a single phase? With sample of stars of given mass with welldetermined relative ages (e.g. fraction of main sequence completed, or evolution position on giant branch) we can observe feld evolution statistically This has been carried out for main sequence evolution of stars of 2-5 M0, using a sample of magnetic stars in open clusters of known age
27 Using a cluster Ap star sample, Landstreet et al (2008) showed that RMS magnetic feld declines with stellar age during MS. top: 4-5 Mo; middle 3-4Mo, bottom 2-3Mo.
28 Lots of work left to do. Thanks to my many collaborators, especially Stefano Bagnulo Evelyne Alecian Luca Fossati Oleg Kochukhov Coralie Neiner Gregg Wade Jeffrey Bailey Jessie Silaj Jean-Francois Donati and others! And to you for your attention
29
30
Magnetic Fields in Early-Type Stars
 Magnetic Fields in Early-Type Stars Jason Grunhut (ESO Garching Fellow) Coralie Neiner (LESIA) Magnetism in intermediate-mass AB stars >400 magnetic A/B stars (Bychkov+ 2009) Small fraction of all intermediate-mass
Magnetic Fields in Early-Type Stars Jason Grunhut (ESO Garching Fellow) Coralie Neiner (LESIA) Magnetism in intermediate-mass AB stars >400 magnetic A/B stars (Bychkov+ 2009) Small fraction of all intermediate-mass
The BRITE spectropolarimetric survey
 The BRITE spectropolarimetric survey Coralie Neiner LESIA, Paris Observatory, France with inputs from A. Blazère, A. Lèbre, J. Morin, G. Wade 1 Spectropolarimetric survey: targets ~600 stars with V
The BRITE spectropolarimetric survey Coralie Neiner LESIA, Paris Observatory, France with inputs from A. Blazère, A. Lèbre, J. Morin, G. Wade 1 Spectropolarimetric survey: targets ~600 stars with V
Magnetohydrodynamics and the magnetic fields of white dwarfs
 Magnetohydrodynamics and the magnetic fields of white dwarfs JDL Decay of large scale magnetic fields We have seen that some upper main sequence stars host magnetic fields of global scale and dipolar topology
Magnetohydrodynamics and the magnetic fields of white dwarfs JDL Decay of large scale magnetic fields We have seen that some upper main sequence stars host magnetic fields of global scale and dipolar topology
Magnetic fields in Intermediate Mass T-Tauri Stars
 Magnetic fields in Intermediate Mass T-Tauri Stars Alexis Lavail Uppsala Universitet alexis.lavail@physics.uu.se Supervisors: Oleg Kochukhov & Nikolai Piskunov Alexis Lavail SU/UU PhD days @Uppsala - 2014.04.10
Magnetic fields in Intermediate Mass T-Tauri Stars Alexis Lavail Uppsala Universitet alexis.lavail@physics.uu.se Supervisors: Oleg Kochukhov & Nikolai Piskunov Alexis Lavail SU/UU PhD days @Uppsala - 2014.04.10
Magnetic fields of (young) massive stars
 Magnetic fields of (young) massive stars Gregg Wade!! Royal Military College of Canada! Queen s University! Véronique Petit!! Florida Institute of Technology! From Stars to Massive Stars, April 2016 Acknowledgments!
Magnetic fields of (young) massive stars Gregg Wade!! Royal Military College of Canada! Queen s University! Véronique Petit!! Florida Institute of Technology! From Stars to Massive Stars, April 2016 Acknowledgments!
The magnetic properties of Main Sequence Stars, White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars
 The magnetic properties of Main Sequence Stars, White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars Lilia Ferrario Mathematical Sciences Institute Australian National University Properties of MWDs High Field MWDs ~ 10 6-10
The magnetic properties of Main Sequence Stars, White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars Lilia Ferrario Mathematical Sciences Institute Australian National University Properties of MWDs High Field MWDs ~ 10 6-10
The evolution of magnetic fields from the main-sequence to very late stages
 Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, 162 169, (218) The evolution of magnetic fields from the main-sequence to very late stages A.J.Martin LESIA, Observatoire de Paris, PSL Research University, CNRS,
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, 162 169, (218) The evolution of magnetic fields from the main-sequence to very late stages A.J.Martin LESIA, Observatoire de Paris, PSL Research University, CNRS,
Pulsations and Magnetic Fields in Massive Stars. Matteo Cantiello KITP Fellow Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics, UCSB
 Pulsations and Magnetic Fields in Massive Stars Matteo Cantiello KITP Fellow Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics, UCSB Massive stars Energy / Momentum in ISM Stellar Winds, SNe Nucleosynthesis Remnants:
Pulsations and Magnetic Fields in Massive Stars Matteo Cantiello KITP Fellow Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics, UCSB Massive stars Energy / Momentum in ISM Stellar Winds, SNe Nucleosynthesis Remnants:
Rotation and activity in low-mass stars
 Rotation and activity in low-mass stars ät öttingen Outline I. Introduction: Magnetic activity and why we care about it II. III. Spin-up and spin-down: Rotational evolution of sun-like stars Magnetic field
Rotation and activity in low-mass stars ät öttingen Outline I. Introduction: Magnetic activity and why we care about it II. III. Spin-up and spin-down: Rotational evolution of sun-like stars Magnetic field
Stellar magnetic fields of young sun-like stars. Aline Vidotto Swiss National Science Foundation Ambizione Fellow University of Geneva
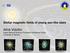 Swiss National Science Foundation Ambizione Fellow University of Geneva Age-rotation-activity relation Skumanich 72 rotation velocity (km/s) chromospheric activity Young stars = fast rotation & high activity
Swiss National Science Foundation Ambizione Fellow University of Geneva Age-rotation-activity relation Skumanich 72 rotation velocity (km/s) chromospheric activity Young stars = fast rotation & high activity
Doppler Imaging & Doppler Tomography. Ilian Iliev Institute of Astronomy & Rozhen NAO
 Doppler Imaging & Doppler Tomography Ilian Iliev Institute of Astronomy & Rozhen NAO Indirect imaging of stellar surfaces and flattened structures means restoring spatial distribution of some physical
Doppler Imaging & Doppler Tomography Ilian Iliev Institute of Astronomy & Rozhen NAO Indirect imaging of stellar surfaces and flattened structures means restoring spatial distribution of some physical
Zeeman Doppler Imaging of a Cool Star Using Line Profiles in All Four Stokes Parameters for the First Time
 Zeeman Doppler Imaging of a Cool Star Using Line Profiles in All Four Stokes Parameters for the First Time L. Rosén 1, O. Kochukhov 1, G. A. Wade 2 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Uppsala University,
Zeeman Doppler Imaging of a Cool Star Using Line Profiles in All Four Stokes Parameters for the First Time L. Rosén 1, O. Kochukhov 1, G. A. Wade 2 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Uppsala University,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 5 Dec 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 5 Dec 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 5 Dec 2007](/thumbs/74/70065005.jpg) Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 1, 1 6, (2007) Magnetic, Chemical and Rotational Properties of the Herbig Ae/Be Binary System HD 72106 arxiv:0712.0771v1 [astro-ph] 5 Dec 2007 C.P. Folsom 1,2,3, G.A.Wade
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 1, 1 6, (2007) Magnetic, Chemical and Rotational Properties of the Herbig Ae/Be Binary System HD 72106 arxiv:0712.0771v1 [astro-ph] 5 Dec 2007 C.P. Folsom 1,2,3, G.A.Wade
Magnetic mapping of solar-type stars
 Magnetic mapping of solar-type stars Pascal Petit figure: M. Jardine Magnetic mapping of solar-type stars introduction: scientific context tomographic tools magnetic maps of active stars stellar differential
Magnetic mapping of solar-type stars Pascal Petit figure: M. Jardine Magnetic mapping of solar-type stars introduction: scientific context tomographic tools magnetic maps of active stars stellar differential
Magnetometry of M dwarfs: methodology & results
 Magnetometry of M dwarfs: methodology & results Julien Morin Laboratoire Univers et Particules de Montpellier First MaTYSSE meeting - Toulouse 2nd November 2015 Outline 1 Magnetic fields: a crucial ingredient
Magnetometry of M dwarfs: methodology & results Julien Morin Laboratoire Univers et Particules de Montpellier First MaTYSSE meeting - Toulouse 2nd November 2015 Outline 1 Magnetic fields: a crucial ingredient
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 18 Sep 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 18 Sep 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 18 Sep 2010](/thumbs/81/82869065.jpg) Active OB stars Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 272, 2010 A.C. Editor, B.D. Editor & C.E. Editor, eds. c 2010 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X The MiMeS Project: Overview and
Active OB stars Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 272, 2010 A.C. Editor, B.D. Editor & C.E. Editor, eds. c 2010 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X The MiMeS Project: Overview and
Surface Magnetism of Cool and evolved stars 10-year Harvest with the Spectropolarimeters
 Surface Magnetism of Cool and evolved stars 10-year Harvest with the Spectropolarimeters ESPaDOnS@CFHT Narval@TBL HARPSpol@ESO Agnès Lèbre, University of Montpellier, France Agnes.Lebre@umontpellier.fr
Surface Magnetism of Cool and evolved stars 10-year Harvest with the Spectropolarimeters ESPaDOnS@CFHT Narval@TBL HARPSpol@ESO Agnès Lèbre, University of Montpellier, France Agnes.Lebre@umontpellier.fr
NIGHT TIME POLARIMETRY. Stefano Bagnulo (Armagh Observatory)
 NIGHT TIME POLARIMETRY Stefano Bagnulo (Armagh Observatory) (Position) Intensity Intensity vs. time Intensity vs. wavelength Intensity vs. time AND vs. wavelength HOW MUCH? POLARIZATION BY ABSORPTION
NIGHT TIME POLARIMETRY Stefano Bagnulo (Armagh Observatory) (Position) Intensity Intensity vs. time Intensity vs. wavelength Intensity vs. time AND vs. wavelength HOW MUCH? POLARIZATION BY ABSORPTION
Astronomy. Chapter 15 Stellar Remnants: White Dwarfs, Neutron Stars, and Black Holes
 Astronomy Chapter 15 Stellar Remnants: White Dwarfs, Neutron Stars, and Black Holes are hot, compact stars whose mass is comparable to the Sun's and size to the Earth's. A. White dwarfs B. Neutron stars
Astronomy Chapter 15 Stellar Remnants: White Dwarfs, Neutron Stars, and Black Holes are hot, compact stars whose mass is comparable to the Sun's and size to the Earth's. A. White dwarfs B. Neutron stars
Observing and modelling stellar magnetic fields. 2. Models
 Observing and modelling stellar magnetic fields. 2. Models John D Landstreet Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Western Ontario London, Canada West In the previous episode... We explored the
Observing and modelling stellar magnetic fields. 2. Models John D Landstreet Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Western Ontario London, Canada West In the previous episode... We explored the
29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Second Hour Exam November 10, 2010 Form A
 29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Second Hour Exam November 10, 2010 Form A There are 20 questions (Note: There will be 32 on the real thing). Read each question and all of the choices before choosing.
29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Second Hour Exam November 10, 2010 Form A There are 20 questions (Note: There will be 32 on the real thing). Read each question and all of the choices before choosing.
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4
 Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 15 1. Emission nebulas emit light because a) they absorb high energy radiation (mostly UV) from nearby bright hot stars and re-emit it in visible wavelengths.
Stellar Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 4 Chapter 15 1. Emission nebulas emit light because a) they absorb high energy radiation (mostly UV) from nearby bright hot stars and re-emit it in visible wavelengths.
Rotation, Emission, & Evolution of the Magnetic Early B-type Stars
 Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, 175 179, (2018) Rotation, Emission, & Evolution of the Magnetic Early B-type Stars M.Shultz 1, G.A.Wade 2, Th.Rivinius 3, C.Neiner 4, O.Kochukhov 1 and E.Alecian
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, 175 179, (2018) Rotation, Emission, & Evolution of the Magnetic Early B-type Stars M.Shultz 1, G.A.Wade 2, Th.Rivinius 3, C.Neiner 4, O.Kochukhov 1 and E.Alecian
Formation and evolution of the intermediate mass Herbig Ae/Be pre-main sequence stars
 School of Physics and Astronomy FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES Formation and evolution of the intermediate mass Herbig Ae/Be pre-main sequence stars René Oudmaijer (Leeds, UK) John Fairlamb,
School of Physics and Astronomy FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND PHYSICAL SCIENCES Formation and evolution of the intermediate mass Herbig Ae/Be pre-main sequence stars René Oudmaijer (Leeds, UK) John Fairlamb,
Chapter 16 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Birth Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Evolution of High Mass stars
 Evolution of High Mass stars Neutron Stars A supernova explosion of a M > 8 M Sun star blows away its outer layers. The central core will collapse into a compact object of ~ a few M Sun. Pressure becomes
Evolution of High Mass stars Neutron Stars A supernova explosion of a M > 8 M Sun star blows away its outer layers. The central core will collapse into a compact object of ~ a few M Sun. Pressure becomes
Neutron Stars. Properties of Neutron Stars. Formation of Neutron Stars. Chapter 14. Neutron Stars and Black Holes. Topics for Today s Class
 Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Phys1403 Introductory Astronomy Instructor: Dr. Goderya Chapter 14 Neutron Stars and Black Holes Cengage Learning 2016 Topics for Today s Class Neutron Stars What is
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Phys1403 Introductory Astronomy Instructor: Dr. Goderya Chapter 14 Neutron Stars and Black Holes Cengage Learning 2016 Topics for Today s Class Neutron Stars What is
Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars
 Doppler Shift At each point the emitter is at the center of a circular wavefront extending out from its present location. Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html
Doppler Shift At each point the emitter is at the center of a circular wavefront extending out from its present location. Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html
THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES
 THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES DAVID F. GRAY University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the first edition Preface to the
THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES DAVID F. GRAY University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the first edition Preface to the
21. Neutron Stars. The Crab Pulsar: On & Off. Intensity Variations of a Pulsar
 21. Neutron Stars Neutron stars were proposed in the 1930 s Pulsars were discovered in the 1960 s Pulsars are rapidly rotating neutron stars Pulsars slow down as they age Neutron stars are superfluid &
21. Neutron Stars Neutron stars were proposed in the 1930 s Pulsars were discovered in the 1960 s Pulsars are rapidly rotating neutron stars Pulsars slow down as they age Neutron stars are superfluid &
FORMATION AND EVOLUTION OF COMPACT BINARY SYSTEMS
 FORMATION AND EVOLUTION OF COMPACT BINARY SYSTEMS Main Categories of Compact Systems Formation of Compact Objects Mass and Angular Momentum Loss Evolutionary Links to Classes of Binary Systems Future Work
FORMATION AND EVOLUTION OF COMPACT BINARY SYSTEMS Main Categories of Compact Systems Formation of Compact Objects Mass and Angular Momentum Loss Evolutionary Links to Classes of Binary Systems Future Work
The stellar magnetic dynamo during the evolution across the main sequence
 Solar and Stellar Variability: Impact on Earth and Planets Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 264, 2009 A. G. Kosovichev, A. H. Andrei & J.-P. Rozelot, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921309992596
Solar and Stellar Variability: Impact on Earth and Planets Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 264, 2009 A. G. Kosovichev, A. H. Andrei & J.-P. Rozelot, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921309992596
The BCool project: Studying the magnetic activity of cool stars
 The BCool project: Studying the magnetic activity of cool stars Stephen Marsden (University of Southern Queensland)! with Pascal Petit, Sandra Jeffers, Julien Morin and Aline Vidotto What is BCool? International
The BCool project: Studying the magnetic activity of cool stars Stephen Marsden (University of Southern Queensland)! with Pascal Petit, Sandra Jeffers, Julien Morin and Aline Vidotto What is BCool? International
Evolution of Intermediate-Mass Stars
 Evolution of Intermediate-Mass Stars General properties: mass range: 2.5 < M/M < 8 early evolution differs from M/M < 1.3 stars; for 1.3 < M/M < 2.5 properties of both mass ranges MS: convective core and
Evolution of Intermediate-Mass Stars General properties: mass range: 2.5 < M/M < 8 early evolution differs from M/M < 1.3 stars; for 1.3 < M/M < 2.5 properties of both mass ranges MS: convective core and
Week 8: Stellar winds So far, we have been discussing stars as though they have constant masses throughout their lifetimes. On the other hand, toward
 Week 8: Stellar winds So far, we have been discussing stars as though they have constant masses throughout their lifetimes. On the other hand, toward the end of the discussion of what happens for post-main
Week 8: Stellar winds So far, we have been discussing stars as though they have constant masses throughout their lifetimes. On the other hand, toward the end of the discussion of what happens for post-main
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 22. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 22 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 22 Neutron Stars and Black Holes Units of Chapter 22 22.1 Neutron Stars 22.2 Pulsars 22.3 Neutron-Star Binaries 22.4 Gamma-Ray
Lecture Outlines Chapter 22 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 22 Neutron Stars and Black Holes Units of Chapter 22 22.1 Neutron Stars 22.2 Pulsars 22.3 Neutron-Star Binaries 22.4 Gamma-Ray
V. Stars.
 V. Stars http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html 0. The local HR diagram We saw that locally we can make an HR diagram of absolute luminosity against temperature. We find a main sequence, giants and
V. Stars http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html 0. The local HR diagram We saw that locally we can make an HR diagram of absolute luminosity against temperature. We find a main sequence, giants and
An evolution of the magnetic fields of massive stars. A.F. Kholtygin. Saint-Petersburg University, Russia. Tartu Observatory December 15, 2015
 An evolution of the magnetic fields of massive stars A.F. Kholtygin Saint-Petersburg University, Russia Tartu Observatory December 15, 2015 LPV and Magnetic field Line profiles in spectra of massive stars
An evolution of the magnetic fields of massive stars A.F. Kholtygin Saint-Petersburg University, Russia Tartu Observatory December 15, 2015 LPV and Magnetic field Line profiles in spectra of massive stars
Astronomy Notes Chapter 13.notebook. April 11, 2014
 All stars begin life in a similar way the only difference is in the rate at which they move through the various stages (depends on the star's mass). A star's fate also depends on its mass: 1) Low Mass
All stars begin life in a similar way the only difference is in the rate at which they move through the various stages (depends on the star's mass). A star's fate also depends on its mass: 1) Low Mass
First evidence of a magnetic field on Vega
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Lignieres c ESO 2018 June 4, 2018 First evidence of a magnetic field on Vega Towards a new class of magnetic A-type stars F. Lignières 1,2, P. Petit 1,2, T. Böhm
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Lignieres c ESO 2018 June 4, 2018 First evidence of a magnetic field on Vega Towards a new class of magnetic A-type stars F. Lignières 1,2, P. Petit 1,2, T. Böhm
Astronomy 100 Spring 2006 Lecture Questions Twelve Weeks Review
 Astronomy 100 Spring 2006 Lecture Questions Twelve Weeks Review 16-1 Fusion in the Sun The solar corona has temperatures roughly the same as temperatures in the Sun's core, where nuclear fusion takes place.
Astronomy 100 Spring 2006 Lecture Questions Twelve Weeks Review 16-1 Fusion in the Sun The solar corona has temperatures roughly the same as temperatures in the Sun's core, where nuclear fusion takes place.
Physics Homework Set 2 Sp 2015
 1) A large gas cloud in the interstellar medium that contains several type O and B stars would appear to us as 1) A) a reflection nebula. B) a dark patch against a bright background. C) a dark nebula.
1) A large gas cloud in the interstellar medium that contains several type O and B stars would appear to us as 1) A) a reflection nebula. B) a dark patch against a bright background. C) a dark nebula.
Stellar Evolution: Outline
 Stellar Evolution: Outline Interstellar Medium (dust) Hydrogen and Helium Small amounts of Carbon Dioxide (makes it easier to detect) Massive amounts of material between 100,000 and 10,000,000 solar masses
Stellar Evolution: Outline Interstellar Medium (dust) Hydrogen and Helium Small amounts of Carbon Dioxide (makes it easier to detect) Massive amounts of material between 100,000 and 10,000,000 solar masses
Things to do 2/28/17. Topics for Today. C-N-O Fusion Cycle. Main sequence (MS) stars. ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies
 Topics for Today ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Winds from Massive Star Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 13 Tues 28 Feb 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Briefly look at life
Topics for Today ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Winds from Massive Star Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 13 Tues 28 Feb 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Briefly look at life
Daily agenda & scientific program
 Daily agenda & scientific program Sunday June 22, 2014 Welcome reception 16h00-19h00 welcome and registration reception at the Science history museum Villa Bartholoni 128, route de Lausanne 1201 Genève
Daily agenda & scientific program Sunday June 22, 2014 Welcome reception 16h00-19h00 welcome and registration reception at the Science history museum Villa Bartholoni 128, route de Lausanne 1201 Genève
The Later Evolution of Low Mass Stars (< 8 solar masses)
 The Later Evolution of Low Mass Stars (< 8 solar masses) http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html The sun - past and future central density also rises though average density decreases During 10 billion
The Later Evolution of Low Mass Stars (< 8 solar masses) http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html The sun - past and future central density also rises though average density decreases During 10 billion
For instance, due to the solar wind, the Sun will lose about 0.1% of its mass over its main sequence existence.
 7/7 For instance, due to the solar wind, the Sun will lose about 0.1% of its mass over its main sequence existence. Once a star evolves off the main sequence, its mass changes more drastically. Some stars
7/7 For instance, due to the solar wind, the Sun will lose about 0.1% of its mass over its main sequence existence. Once a star evolves off the main sequence, its mass changes more drastically. Some stars
! p. 1. Observations. 1.1 Parameters
 1 Observations 11 Parameters - Distance d : measured by triangulation (parallax method), or the amount that the star has dimmed (if it s the same type of star as the Sun ) - Brightness or flux f : energy
1 Observations 11 Parameters - Distance d : measured by triangulation (parallax method), or the amount that the star has dimmed (if it s the same type of star as the Sun ) - Brightness or flux f : energy
Analyzing X-Ray Pulses from Stellar Cores Pencil & Paper Version
 Analyzing X-Ray Pulses from Stellar Cores Pencil & Paper Version Purpose: To determine if two end products of stellar evolution GK Per and Cen X-3 could be white dwarfs or neutron stars by calculating
Analyzing X-Ray Pulses from Stellar Cores Pencil & Paper Version Purpose: To determine if two end products of stellar evolution GK Per and Cen X-3 could be white dwarfs or neutron stars by calculating
Remember from Stefan-Boltzmann that 4 2 4
 Lecture 17 Review Most stars lie on the Main sequence of an H&R diagram including the Sun, Sirius, Procyon, Spica, and Proxima Centauri. This figure is a plot of logl versus logt. The main sequence is
Lecture 17 Review Most stars lie on the Main sequence of an H&R diagram including the Sun, Sirius, Procyon, Spica, and Proxima Centauri. This figure is a plot of logl versus logt. The main sequence is
The structure and evolution of stars
 The structure and evolution of stars Lecture 9: Computation of stellar evolutionary models 1 Learning Outcomes The student will learn How to interpret the models of modern calculations - (in this case
The structure and evolution of stars Lecture 9: Computation of stellar evolutionary models 1 Learning Outcomes The student will learn How to interpret the models of modern calculations - (in this case
Preparing for observations
 Preparing for observations Signal to noise ratio should be calculated in the continuum. Use parts where no lines are present S/N Linear fit or, if normalization is good enough, Imean = 1 Calculate standard
Preparing for observations Signal to noise ratio should be calculated in the continuum. Use parts where no lines are present S/N Linear fit or, if normalization is good enough, Imean = 1 Calculate standard
The Deaths of Stars. The Southern Crab Nebula (He2-104), a planetary nebula (left), and the Crab Nebula (M1; right), a supernova remnant.
 The Deaths of Stars The Southern Crab Nebula (He2-104), a planetary nebula (left), and the Crab Nebula (M1; right), a supernova remnant. Once the giant phase of a mediummass star ends, it exhales its outer
The Deaths of Stars The Southern Crab Nebula (He2-104), a planetary nebula (left), and the Crab Nebula (M1; right), a supernova remnant. Once the giant phase of a mediummass star ends, it exhales its outer
Tests of stellar physics with high-precision data from eclipsing binary stars
 Tests of stellar physics with high-precision data from eclipsing binary stars Ignasi Ribas Institut de Ciències de l Espai (CSIC-IEEC, Barcelona) Barcelona, April 2013 Eclipsing binary systems Eclipsing
Tests of stellar physics with high-precision data from eclipsing binary stars Ignasi Ribas Institut de Ciències de l Espai (CSIC-IEEC, Barcelona) Barcelona, April 2013 Eclipsing binary systems Eclipsing
Chapter 14. Outline. Neutron Stars and Black Holes. Note that the following lectures include. animations and PowerPoint effects such as
 Note that the following lectures include animations and PowerPoint effects such as fly ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). Chapter 14 Neutron
Note that the following lectures include animations and PowerPoint effects such as fly ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). Chapter 14 Neutron
Lecture 24: Testing Stellar Evolution Readings: 20-6, 21-3, 21-4
 Lecture 24: Testing Stellar Evolution Readings: 20-6, 21-3, 21-4 Key Ideas HR Diagrams of Star Clusters Ages from the Main Sequence Turn-off Open Clusters Young clusters of ~1000 stars Blue Main-Sequence
Lecture 24: Testing Stellar Evolution Readings: 20-6, 21-3, 21-4 Key Ideas HR Diagrams of Star Clusters Ages from the Main Sequence Turn-off Open Clusters Young clusters of ~1000 stars Blue Main-Sequence
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jul 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jul 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jul 2009](/thumbs/77/74886407.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 14 (2009) Printed 12 May 2017 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Magnetism and binarity of the Herbig Ae star V380 Ori arxiv:0907.5113v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jul 2009 E. Alecian 12,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 14 (2009) Printed 12 May 2017 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Magnetism and binarity of the Herbig Ae star V380 Ori arxiv:0907.5113v1 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jul 2009 E. Alecian 12,
Spectro-Polarimetry of Magnetic Hot Stars
 Solar Polarization 4 ASP Conference Series, Vol. 358, 2006 R. Casini and B. W. Lites Spectro-Polarimetry of Magnetic Hot Stars O. Kochukhov Department of Astronomy and Space Physics, Uppsala University,
Solar Polarization 4 ASP Conference Series, Vol. 358, 2006 R. Casini and B. W. Lites Spectro-Polarimetry of Magnetic Hot Stars O. Kochukhov Department of Astronomy and Space Physics, Uppsala University,
Chapter 11 Review. 1) Light from distant stars that must pass through dust arrives bluer than when it left its star. 1)
 Chapter 11 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Light from distant stars that must pass through dust arrives bluer than when it left its star. 1)
Chapter 11 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Light from distant stars that must pass through dust arrives bluer than when it left its star. 1)
Principles of Astrophysics and Cosmology
 Principles of Astrophysics and Cosmology Welcome Back to PHYS 3368 Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel July 22, 1784 March 17, 1846 Announcements - Reading Assignments: Chapter 4.1-4.3. - Problem Set 6 is due Wednesday,
Principles of Astrophysics and Cosmology Welcome Back to PHYS 3368 Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel July 22, 1784 March 17, 1846 Announcements - Reading Assignments: Chapter 4.1-4.3. - Problem Set 6 is due Wednesday,
Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12)
 Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12) To classify stars we determine the following properties for stars: 1. Distance : Needed to determine how much energy stars produce and radiate away by using
Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12) To classify stars we determine the following properties for stars: 1. Distance : Needed to determine how much energy stars produce and radiate away by using
1. Convective throughout deliver heat from core to surface purely by convection.
 6/30 Post Main Sequence Evolution: Low-Mass Stars 1. Convective throughout deliver heat from core to surface purely by convection. 2. Convection mixes the material of the star is the material carries the
6/30 Post Main Sequence Evolution: Low-Mass Stars 1. Convective throughout deliver heat from core to surface purely by convection. 2. Convection mixes the material of the star is the material carries the
Chapter 16: Star Birth
 Chapter 16 Lecture Chapter 16: Star Birth Star Birth 16.1 Stellar Nurseries Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Where do stars form? Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds
Chapter 16 Lecture Chapter 16: Star Birth Star Birth 16.1 Stellar Nurseries Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Where do stars form? Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds
This class: Life cycle of high mass stars Supernovae Neutron stars, pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars Quark-nova stars Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)
 This class: Life cycle of high mass stars Supernovae Neutron stars, pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars Quark-nova stars Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)!1 Cas$A$ All$Image$&$video$credits:$Chandra$X7ray$ Observatory$
This class: Life cycle of high mass stars Supernovae Neutron stars, pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars Quark-nova stars Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)!1 Cas$A$ All$Image$&$video$credits:$Chandra$X7ray$ Observatory$
Chapter 16 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Birth Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth Star Birth 16.1 Stellar Nurseries Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Where do stars form? Star-Forming
Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth Star Birth 16.1 Stellar Nurseries Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Where do stars form? Star-Forming
Magnetic fields in T Tauri stars
 Magnetic fields in T Tauri stars Gaitee A.J. Hussain ghussain@eso.org MaPP: Magnetic Protostars and Planets J.-F. Donati, J. Bouvier, S. Gregory, T. Montmerle, A. Maggio, C. Argiroffi, E. Flaccomio, F.
Magnetic fields in T Tauri stars Gaitee A.J. Hussain ghussain@eso.org MaPP: Magnetic Protostars and Planets J.-F. Donati, J. Bouvier, S. Gregory, T. Montmerle, A. Maggio, C. Argiroffi, E. Flaccomio, F.
Astro 1050 Wed. Apr. 5, 2017
 Astro 1050 Wed. Apr. 5, 2017 Today: Ch. 17, Star Stuff Reading in Horizons: For Mon.: Finish Ch. 17 Star Stuff Reminders: Rooftop Nighttime Observing Mon, Tues, Wed. 1 Ch.9: Interstellar Medium Since stars
Astro 1050 Wed. Apr. 5, 2017 Today: Ch. 17, Star Stuff Reading in Horizons: For Mon.: Finish Ch. 17 Star Stuff Reminders: Rooftop Nighttime Observing Mon, Tues, Wed. 1 Ch.9: Interstellar Medium Since stars
The physics of stars. A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure.
 Lecture 4 Stars The physics of stars A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure. X-ray ultraviolet infrared radio To understand
Lecture 4 Stars The physics of stars A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure. X-ray ultraviolet infrared radio To understand
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Sep 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Sep 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Sep 2007](/thumbs/74/71075445.jpg) Exploring the origin of neutron star magnetic field: magnetic properties of the progenitor OB stars Véronique Petit,, Gregg A. Wade, Laurent Drissen, and Thierry Montmerle arxiv:0709.4526v1 [astro-ph]
Exploring the origin of neutron star magnetic field: magnetic properties of the progenitor OB stars Véronique Petit,, Gregg A. Wade, Laurent Drissen, and Thierry Montmerle arxiv:0709.4526v1 [astro-ph]
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 12 Sep 2005
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. discovery February 5, 2008 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Discovery of the pre-main sequence progenitors of the magnetic Ap/Bp stars? G.A. Wade, D. Drouin,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. discovery February 5, 2008 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Discovery of the pre-main sequence progenitors of the magnetic Ap/Bp stars? G.A. Wade, D. Drouin,
Stellar Structure and Evolution
 Stellar Structure and Evolution Achim Weiss Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik 01/2014 Stellar Structure p.1 Stellar evolution overview 01/2014 Stellar Structure p.2 Mass ranges Evolution of stars with
Stellar Structure and Evolution Achim Weiss Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik 01/2014 Stellar Structure p.1 Stellar evolution overview 01/2014 Stellar Structure p.2 Mass ranges Evolution of stars with
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Observing Highlights. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Lab Observing Trip Next week: Tues (9/28) & Thurs (9/30) let me know ASAP if you have an official conflict (class, work) - website: http://astro.physics.uiowa.edu/~clang/sgu_fall10/observing_trip.html
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Lab Observing Trip Next week: Tues (9/28) & Thurs (9/30) let me know ASAP if you have an official conflict (class, work) - website: http://astro.physics.uiowa.edu/~clang/sgu_fall10/observing_trip.html
Star-Forming Clouds. Stars form in dark clouds of dusty gas in interstellar space. The gas between the stars is called the interstellar medium.
 Star Birth Chapter 16 Lecture 16.1 Stellar Nurseries The Cosmic Perspective Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Seventh Edition Star Birth Where do stars form? Star-Forming
Star Birth Chapter 16 Lecture 16.1 Stellar Nurseries The Cosmic Perspective Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Seventh Edition Star Birth Where do stars form? Star-Forming
Chapter 18 Reading Quiz Clickers. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Pearson Education, Inc.
 Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What supports
Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What supports
The atmospheric chemistry of magnetic Bp stars
 Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository August 2013 The atmospheric chemistry of magnetic Bp stars Jeffrey D. Bailey The University of Western Ontario Supervisor
Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository August 2013 The atmospheric chemistry of magnetic Bp stars Jeffrey D. Bailey The University of Western Ontario Supervisor
@ CFHT. Isabelle Boisse (LAM) and the SPIRou team France, Canada, CFHT, Brazil, Hawaii, Taiwan, Switzerland & Portugal
 @ CFHT Isabelle Boisse (LAM) and the SPIRou team France, Canada, CFHT, Brazil, Hawaii, Taiwan, Switzerland & Portugal Consortium PIs Jean-François Donati (IRAP, France) - René Doyon (Canada) Project scientists
@ CFHT Isabelle Boisse (LAM) and the SPIRou team France, Canada, CFHT, Brazil, Hawaii, Taiwan, Switzerland & Portugal Consortium PIs Jean-François Donati (IRAP, France) - René Doyon (Canada) Project scientists
Star Formation and Protostars
 Stellar Objects: Star Formation and Protostars 1 Star Formation and Protostars 1 Preliminaries Objects on the way to become stars, but extract energy primarily from gravitational contraction are called
Stellar Objects: Star Formation and Protostars 1 Star Formation and Protostars 1 Preliminaries Objects on the way to become stars, but extract energy primarily from gravitational contraction are called
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015
 Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015 Today: Continue Ch. 13: Star Stuff Reading in Bennett: For Monday: Finish Chapter 13 Star Stuff Reminders: Ch. 12 HW now on Mastering Astronomy, due Monday. Ch. 13 will be
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015 Today: Continue Ch. 13: Star Stuff Reading in Bennett: For Monday: Finish Chapter 13 Star Stuff Reminders: Ch. 12 HW now on Mastering Astronomy, due Monday. Ch. 13 will be
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 21 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 21 Sep 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 21 Sep 2013](/thumbs/94/119876361.jpg) 1 arxiv:1309.5497v1 [astro-ph.sr] 21 Sep 2013 Magnetic fields in β Cep, SPB, and Be stars Schöller M. 1, Hubrig S. 2, Briquet M. 3, Ilyin I. 2 1 European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2,
1 arxiv:1309.5497v1 [astro-ph.sr] 21 Sep 2013 Magnetic fields in β Cep, SPB, and Be stars Schöller M. 1, Hubrig S. 2, Briquet M. 3, Ilyin I. 2 1 European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2,
Magnetic Fields in the Atmospheres of the Sun and Stars
 Saas Fee 39 Magnetic Fields in the Atmospheres of the Sun and Stars Sami K. Solanki Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research Before starting... Concentrate on observations: only few equations Will
Saas Fee 39 Magnetic Fields in the Atmospheres of the Sun and Stars Sami K. Solanki Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research Before starting... Concentrate on observations: only few equations Will
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Oct 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Oct 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Oct 2018](/thumbs/89/100122483.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. article_final c ESO 2018 October 31, 2018 The magnetic fields of intermediate-mass T Tauri stars : I. Magnetic detections and fundamental stellar parameters F. Villebrun
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. article_final c ESO 2018 October 31, 2018 The magnetic fields of intermediate-mass T Tauri stars : I. Magnetic detections and fundamental stellar parameters F. Villebrun
Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars
 Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars Guidepost The last chapter introduced you to the gas and dust between the stars that are raw material for new stars. Here you will begin putting together
Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars Guidepost The last chapter introduced you to the gas and dust between the stars that are raw material for new stars. Here you will begin putting together
Neutron Stars. But what happens to the super-dense core? It faces two possible fates:
 Neutron Stars When a massive star runs out of fuel, its core collapses from the size of the Earth to a compact ball of neutrons just ten miles or so across. Material just outside the core falls onto this
Neutron Stars When a massive star runs out of fuel, its core collapses from the size of the Earth to a compact ball of neutrons just ten miles or so across. Material just outside the core falls onto this
The exceptional Herbig Ae star HD : The first detection of resolved magnetically split lines and the presence of chemical spots in a Herbig star
 Astron. Nachr. / AN 331, No. 4, 361 367 (2010) / DOI 10.1002/asna.201011346 The exceptional Herbig Ae star HD 101412: The first detection of resolved magnetically split lines and the presence of chemical
Astron. Nachr. / AN 331, No. 4, 361 367 (2010) / DOI 10.1002/asna.201011346 The exceptional Herbig Ae star HD 101412: The first detection of resolved magnetically split lines and the presence of chemical
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Apr 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Apr 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Apr 2013](/thumbs/73/68434749.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 21467 c ESO 2013 April 26, 2013 Are there tangled magnetic fields on HgMn stars? O. Kochukhov 1, V. Makaganiuk 1, N. Piskunov 1, S. V. Jeffers 2, C. M. Johns-Krull
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 21467 c ESO 2013 April 26, 2013 Are there tangled magnetic fields on HgMn stars? O. Kochukhov 1, V. Makaganiuk 1, N. Piskunov 1, S. V. Jeffers 2, C. M. Johns-Krull
The Interior Structure of the Sun
 The Interior Structure of the Sun Data for one of many model calculations of the Sun center Temperature 1.57 10 7 K Pressure 2.34 10 16 N m -2 Density 1.53 10 5 kg m -3 Hydrogen 0.3397 Helium 0.6405 The
The Interior Structure of the Sun Data for one of many model calculations of the Sun center Temperature 1.57 10 7 K Pressure 2.34 10 16 N m -2 Density 1.53 10 5 kg m -3 Hydrogen 0.3397 Helium 0.6405 The
Lecture 21. Stellar Size
 Lecture 21 Stellar Mass; The Main Sequence Visual and Spectroscopic Binaries Mass and the Main Sequence Explaining the Main Sequence Mar 8, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 21 1 Stellar Size Taking ratios to the
Lecture 21 Stellar Mass; The Main Sequence Visual and Spectroscopic Binaries Mass and the Main Sequence Explaining the Main Sequence Mar 8, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 21 1 Stellar Size Taking ratios to the
Stellar Explosions (ch. 21)
 Stellar Explosions (ch. 21) First, a review of low-mass stellar evolution by means of an illustration I showed in class. You should be able to talk your way through this diagram and it should take at least
Stellar Explosions (ch. 21) First, a review of low-mass stellar evolution by means of an illustration I showed in class. You should be able to talk your way through this diagram and it should take at least
10/25/2010. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline. Reading Quiz #9 Wednesday (10/27)
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Reading Quiz #9 Wednesday (10/27) HW#8 in ICON due Friday (10/29) by 5 pm - available Wednesday 1 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline 1. Black Holes
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Reading Quiz #9 Wednesday (10/27) HW#8 in ICON due Friday (10/29) by 5 pm - available Wednesday 1 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline 1. Black Holes
Atoms and Star Formation
 Atoms and Star Formation What are the characteristics of an atom? Atoms have a nucleus of protons and neutrons about which electrons orbit. neutrons protons electrons 0 charge +1 charge 1 charge 1.67 x
Atoms and Star Formation What are the characteristics of an atom? Atoms have a nucleus of protons and neutrons about which electrons orbit. neutrons protons electrons 0 charge +1 charge 1 charge 1.67 x
Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei
 Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei A black hole is a region of spacetime from which gravity prevents anything, including light, from escaping. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently
Black Holes and Active Galactic Nuclei A black hole is a region of spacetime from which gravity prevents anything, including light, from escaping. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently
Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation
 Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation The interstellar medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation The interstellar medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
ASTRONOMY 1 EXAM 3 a Name
 ASTRONOMY 1 EXAM 3 a Name Identify Terms - Matching (20 @ 1 point each = 20 pts.) Multiple Choice (25 @ 2 points each = 50 pts.) Essays (choose 3 of 4 @ 10 points each = 30 pt 1.Luminosity D 8.White dwarf
ASTRONOMY 1 EXAM 3 a Name Identify Terms - Matching (20 @ 1 point each = 20 pts.) Multiple Choice (25 @ 2 points each = 50 pts.) Essays (choose 3 of 4 @ 10 points each = 30 pt 1.Luminosity D 8.White dwarf
Today. When does a star leave the main sequence?
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nick Featherstone Lecture 13 Tues 27 Feb 07 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Crab Nebula -- Supernova Remnant Today Recall that C-N-O
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nick Featherstone Lecture 13 Tues 27 Feb 07 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Crab Nebula -- Supernova Remnant Today Recall that C-N-O
Magnetic fields and chemical maps of Ap stars from four Stokes parameter observations
 Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Science and Technology 1349 Magnetic fields and chemical maps of Ap stars from four Stokes parameter observations NAUM RUSOMAROV
Digital Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Science and Technology 1349 Magnetic fields and chemical maps of Ap stars from four Stokes parameter observations NAUM RUSOMAROV
Mass loss from stars
 Mass loss from stars Can significantly affect a star s evolution, since the mass is such a critical parameter (e.g., L ~ M 4 ) Material ejected into interstellar medium (ISM) may be nuclear-processed:
Mass loss from stars Can significantly affect a star s evolution, since the mass is such a critical parameter (e.g., L ~ M 4 ) Material ejected into interstellar medium (ISM) may be nuclear-processed:
Late Stages of Stellar Evolution. Late Stages of Stellar Evolution
 Late Stages of Stellar Evolution The star enters the Asymptotic Giant Branch with an active helium shell burning and an almost dormant hydrogen shell Again the stars size and luminosity increase, leading
Late Stages of Stellar Evolution The star enters the Asymptotic Giant Branch with an active helium shell burning and an almost dormant hydrogen shell Again the stars size and luminosity increase, leading
Pulsars ASTR2110 Sarazin. Crab Pulsar in X-rays
 Pulsars ASTR2110 Sarazin Crab Pulsar in X-rays Test #2 Monday, November 13, 11-11:50 am Ruffner G006 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other
Pulsars ASTR2110 Sarazin Crab Pulsar in X-rays Test #2 Monday, November 13, 11-11:50 am Ruffner G006 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other
Topics for Today s Class
 Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 11 Formation of Stars and Structure of Stars Topics for Today s Class 1. Making Stars from the Interstellar Medium 2. Evidence of Star Formation: The Orion Nebula
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 11 Formation of Stars and Structure of Stars Topics for Today s Class 1. Making Stars from the Interstellar Medium 2. Evidence of Star Formation: The Orion Nebula
In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes
 In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes Stellar velocity fields MW Distant galaxies Gas motions gas disks around nearby black holes
In a dense region all roads lead to a black Hole (Rees 1984 ARAA) Deriving the Mass of SuperMassive Black Holes Stellar velocity fields MW Distant galaxies Gas motions gas disks around nearby black holes
