No. 371,306. Patented 00t, ll, l887.
|
|
|
- Samson Derrick Henry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (No Model.) 4. Sheets-Sheet 1. H. CON ANT. ASTRONOMICAL CL00K. No. 371,306. Patented 00t, ll, l887. INVENTOR: ATTORNEYS, PETERs, Photo-Lithographer. Washinxton, C. *
2 (No Model.) 4. Sheets-Sheet 2. H. CONANT ASTRONOMICAL CLOCK, No. 371,306. Patented 00t, ll, WITNESSES : m INVENTOR: 644-v. { BY -(lwv- S. ATTORNEYS.
3 (No Model.) 4. Sheets-Sheet 3, H. CONANT ASTRONOMICAL CLOCK. No , Patented 00t, ll, WITNESSES: INVENTOR; 484 toe- BY Muwu. fe ATTORNEYS, N. Peters, Photo-Lithographer, Washington, D.C.
4 (No Model.) O 24/ H. CONANT, ASTRONOMICAL CLOCK, 4. Sheets-Sheet NË 4, zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzºzzzzzzzzºzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz?zzzzzzzz?zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz 27?tilltiIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII I ZZZZZZZYZZ 2 NWENTOR: 74. BY Muvvu C ATTORNEYS, Patented 00t, ll, Photo-Lithographer. Washington, D.C.
5 UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE. HEZEKIAH CONANT, OF PAWTUCKET, RHODE ISLAND. ASTRONOMICAL CLOCK. SPECIFICATION forming part of Letters Patent No. 371,306, dated October 11, Application filed March 9, Serial No. 230,241. (No model.) To al/ tuflon, it may concern, D is set to sidereal time, and actuates, by the Be it known that I, HEZEKIAH CONANT, of usual connections, the hour and minute hands Pawtucket, in the county of Providence and I and I", indicating sidereal time on the dial 55 State of Rhode Island, have invented a new I, divided into twenty-four hours and subdi 5 and Improved Astronomical Clock, of which visions. The escape - wheel shaft J of the the following is a full, clear, and exact de pendulum F carries the second-hand J", indi Scription. cating on the seconds-dial J, formed on the The object of my invention is to provide a face of the dial I. The hands on the dials G" new and improved astronomical time-keeping and I thus indicate mean solar time and side IO instrument indicating the correct solar and real time, respectively, in hours, minutes, and sidereal time, and also at the same time the seconds. Each of the escape-wheel shafts H right ascension of the mean sun. and J may be provided (instead of pendulum The invention consists of two independent escapements) with an escapement of any ap regulators or clocks, of which one is regulated proved construction. I5 to mark mean solar time and the other side On each of the escape-wheel shafts Hand J real time, the difference of the two movements of the regulators or clocks C and D is secured being indicated by a third movement on a dial, a bevel gear - wheel, K or K", respectively, indicating right ascension of the mean sun. meshing into the pinions Land L, respectively, The invention also consists of various parts secured to the lower ends of the shafts N and and details and combinations of the same, as N', respectively, carrying on their upper ends will be fully described hereinafter, and then the bevel gear-wheels O and O', respectively, pointed out in the claims. meshing into the bevel gear-wheels P and P', Reference is to be had to the accompanying both loosely mounted on the shaft Q, which car drawings, forming a part of this specification, ries on its outer end the hand Q, indicating Sec 25 in which similar letters of reference indicate onds on the seconds-dial Q, formed on the main corresponding parts in all the figures. dial R. On the shaft Qis also secured the cross Figure l is a perspective view of my im piece S, carrying on one outer end the bevel provement. Fig. 2 is an enlarged view of the planetary gear-wheel S, which meshes on One dials. Fig. 3 is a front elevation of the clock side into the bevelgear-wheelp, formed on the 3O mechanism, the dials being removed; and Fig. inside of the bevel gear-wheel P, and the said 4 is a vertical cross-section of the same on the bevel planetary gear-wheel S also meshes on line acac of Fig. 3. its other side into the bevel gear-wheel P', My invention, presently to be described, is formed on the inside of the bevel gear-wheel based on the principle that the difference be. P. The corresponding gear-wheels of the two 35 tween mean Solar time and sidereal time is mechanisms above described, connecting the the mean right ascension of the sun. two regulators with the planetary wheel S, My improved clock is mounted in the casing are alike in number of their teeth. A, in which is secured the clock-frame B, in The gear-wheels K and K make a revolu- 9o the lower part of which are mounted the regu tion once in every minute, and the train of lators or clocks C and D, of any approved con gear-wheels connected with the said wheels K. struction. Preferably, each of the regulators K is such as to impart a rotary motion to the or clocks C and D has a one-second pendulum, gear-wheels P and Pat double the speed of EF, respectively, of which the pendulum E the said gear-wheels K and K. This is nec-95 is regulated to mean solar time, and actuates essary to indicate on the shaft Q, by means of 45 by the usual connections the hour and minute the planetary gear-wheel S, any existing dif hands G and G', indicating mean time on the ference between the gear-wheels K and K, and dial G", which is divided into twelve hours to indicate this difference on the dial Q" by the and subdivisions. The escape-wheel shaft H. hand Q, so that when the second-hand J on Ioo of the pendulum E carries the second-hand H', the shaft J, carrying the said gear-wheel K", 5C indicating on the seconds-dial H, formed on has, for instance, gained one second on the the front of the dial G'. other hand, H, secured to the shaft H, carry The pendulum F of the regulator or clock ing the said gear-wheel K, then the second
6 O SO ,306 hand Q will move forward one second, there by showing the difference which has occurred between the two hands J' and H or the two gear-wheels Kamd K. On the shaft Q is secured the pinion T, mesh ing into the gear-wheel T, secured on the shaft T, carrying the pinion T, meshing into the gear-wheel T, fastened on the shaft U, carry ing on its outer end the minute-hand U", indi cating minutes on the main dial R. On the shaft U is also secured the pinion V, meshing into the gear-wheel V', having a pinion, V', meshing into the gear-wheel. V, formed on the sleeve V, held loosely on the shaft U, and carrying on its outer end the hour-hand V, indicating hours on the main dial R. On the sleeve V* is secured the gear-wheel W, meshing into the pinion W, held on the gear-wheel W', meshing into the gear-wheel W", formed on the sleeve W, held loosely on the sleeve V, and carrying on its outer end the moon-hand W, indicating position of the moon on the dial R. The latter is divided into twenty-four hours, each hour of which is in dicated by the hour-hand V, the hours being Subdivided into minutes, indicated by the min ute-lhand U", and on the dial is also formed the Zodiac R', by which the moon s place is indi cated by the moon-hand W, giving the re spective position of the moon in right ascen Sl(O. The operation is as follows: The two regu lators or clocks C and D are connected with the differential-motion mechanism on the shaft Q by the gear-wheels O and O', which revolve in opposite directions at a different rate of Speed, according to the mean Solar time and the sidereal time indicated by the said regul lators or clocks C and D. The gear-wheels O and O' impart their motion and speed to the bevel gear-wheels PP and PP, and as both bevel gear-wheels act on the planetary gear-wheel S, but in opposite directions and at a differential rate of speed, the gear wheel will consequently turn with its cross piece S in the direction of the bevel gear wheel, PP or P P', which travels the fast est; but the wheel S travels at a differential rate of Speed in relation to the said double gear-wheels P. P. and P. P. The planetary gear-wheel S and its cross-piece S thus cause the shaft Q to travel at a differential rate of speed between the regulator or clock C and the regulator or clock D, and as the shaft Q oper. ates by its direct connections the hands U, V, and W on the main dial R it necessarily fol lows that the time indicated by these hands is the time of the mean right ascension of the Sll. To illustrate the action of the instrument more clearly it is Supposed that the hands of all these dials are set exactly at noon-that is, the Solar clock points exactly at mean solar noon, the sidereal clock to sidereal noon, and the upper or right ascension dial to the vernal equinox or twenty-four hours. This, it will be understood, is Zeroposition, and both clocks are properly adjusted and regulated to lilean Solar and sidereal time, respectively, as indicated. Now let the sidereal clock be started and run exactly one hour, while the mean solar re mains stationary. The hands on right-ascen sion dial R will move forward exactly at the same rate, because it must record the difference between the time by the sidereal and mean so lar clocks, so that at the end of one hour the second and minute hands of the sidereal and right-ascension dials will point to zero, and the hour-hands at one hour, showing that the side real clock has gained one hour over the mean solar clock exactly. Now suppose the sidereal clock to be stopped at this point and the so lar clock started and run exactly one hour. Now, if the hands of the right-ascension dial always show the difference in time of the two clocks, it is evident that they must move back ward, as every second that the solar clock makes reduces the recorded difference. This it does so faithfully that at the end of the hour the hands of the right-ascension dial are all moved back to the hour of 24 and zero, as at first. This shows that there is no difference in the time of the mean solar or sidereal clocks. It will be evident from this that whatever the sidereal clock gains over the solar clock will be the measure of the movement of the hands on the right ascension on the large dial R, and it is evident also that the daily gain of the si dereal over solar time is the daily progress of those hands, and also the mean Sun in right ascension, so that the time indicated at any instant by the hands of that dial is the record in hours, minutes, and seconds of the sun's progress and his position at that instant, and the time required for these hands to perform the complete record of twenty-four hours, and which is the time required for the sidereal clock to gain twenty-four hours or one whole day and again overtake the Solar clock, is ex actly the measure of a tropical year, and the instant that the sidereal time is exactly with mean solar time and its pendulums tick simul taneously, that is the instant of the vernal equinox, and in whatever longitude the mean sun crosses the equator on that meridian the vernal equinox takes place and sidereal and solar noon occur simultaneously, and this in strument, if there, would take the exact posi tion first given to all dials indicating noon and ZeO. The moon-hand W is to represent approxi mately the position of that planet in right as cension, and as its motions will be regular it will be a mean moon just as the hour-hand of this dial represents the mean and not the true sun. This hand W makesin its cycle of nine teen years two hundred and fifty-four revolu tions about the earth, and will make two hun dred and thirty-five conjunctions with the sun, each representing a new moon, and its appo sition a full moon, so that the dial will always show approximately the noon s position in the heavens, the center of the dial representing the north pole and also the earth's axis. 75 ICO IO5 IO IIS
7 371,306 3 it will be seen that the clock is differential, be indicated on a third dial, in the manner sub- 25 as the hands on the main dial R are indebted stantially as set forth. for their motion to the difference between the 3. The combination, in one instrument, of a two regulators or clocks C and D, the mean solar and sidereal clock and a third train con right ascension of the sun being always the dif. nected therewith by a differential motion, the ference between mean solar and sidereal time. whole forming an astronomical clock, showing 3o Having thus described my invention, what at a glance mean solar time, sidereal time, and I claim as new, and desire to secure by Letters the right ascension of the mean Sun in hours, Patent, is- - minutes, and seconds, and approximately the 1. The combination, in one instrument, of two positions of other heavenly bodies-as the moon clock or time-measuring movements or mech or fixed stars, as may be desired-in the man- 35 anisms regulated to sidereal and solar time, ner substantially as described. respectively, and a third train or mechanism 4. In an astronomical time-keeping instru which is actuated by the difference in speed of ment, the combination, with two regulators or said clocks or time-measuring mechanisms, and clocks set, respectively, to mean solar time and indicates said difference by means of moving sidereal time, of means, substantially as de- 4o hands over the face of a third dial, substan scribed, for indicating the absolute difference tially as set forth and described. between the movements of the two regulators 2. The combination of a solar and sidereal or clocks on a separate dial by hour and min clock or time-keeping movement or mechan ute hands, as set forth. anism with a differential device or mechanism, HEZEKIAH CON ANT. substantially as described, by means of which Witnesses: the progress of the mean sun in right ascen THEO. G. HOSTER, sion, and other heavenly bodies as well, may C. SEDG WICR. IO 15
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
Chapter S1 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter S1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. S1.1 Astronomical
Chapter S1 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. S1.1 Astronomical
PHSC 1053: Astronomy Time and Coordinates
 PHSC 1053: Astronomy Time and Coordinates Astronomical Clocks Earth s Rotation on its Axis Time between two successive meridian transits of the sun 1 solar day (our adopted clock time) 24 hours (86,400
PHSC 1053: Astronomy Time and Coordinates Astronomical Clocks Earth s Rotation on its Axis Time between two successive meridian transits of the sun 1 solar day (our adopted clock time) 24 hours (86,400
Sept. 29, S. W. BOGGS 2,056,089
 Sept. 29, 1936. S. W. BOGGS 2,06,089 HOROLOGICAL INSTRUMENT AND RELATED DEVICES Filed Feb. 11, 1932 2. Sheets-Sheet l NSS A. ATTORNEY. Sept. 29, 1936. S. W. BOGGS 2,06,089 HOROLOGICAL INSTRUMENT AND RELATED
Sept. 29, 1936. S. W. BOGGS 2,06,089 HOROLOGICAL INSTRUMENT AND RELATED DEVICES Filed Feb. 11, 1932 2. Sheets-Sheet l NSS A. ATTORNEY. Sept. 29, 1936. S. W. BOGGS 2,06,089 HOROLOGICAL INSTRUMENT AND RELATED
Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation. How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?
 Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation S1.1 Astronomical Time Periods Our goals for learning:! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?! How do we tell the time of day?!
Chapter S1 Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation S1.1 Astronomical Time Periods Our goals for learning:! How do we define the day, month, year, and planetary time periods?! How do we tell the time of day?!
Knowing the Heavens. Goals: Constellations in the Sky
 Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Knowing the Heavens. Goals: Constellations in the Sky
 Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
Goals: Knowing the Heavens To see how the sky changes during a night and from night to night. To measure the positions of stars in celestial coordinates. To understand the cause of the seasons. Constellations
LAW WOODEN CLOCK 5 SHT 1 OF 9 SHTS. General Assembly 1 NTS FEB Designed by: BRLAW
 2 43 31 42 4 32 39 14 29 21 2 21 22 40 23 22 20 18 1 17 1 4 8 7 9 15 20 29 40 ITEM NO. QTY. PART NO. 1 1 back 2 1 front 4 1 Pendulum hanger 4 Dial spacer 7 1 Pendulum head 8 1 Pendulum pivot 9 1 Pendulum
2 43 31 42 4 32 39 14 29 21 2 21 22 40 23 22 20 18 1 17 1 4 8 7 9 15 20 29 40 ITEM NO. QTY. PART NO. 1 1 back 2 1 front 4 1 Pendulum hanger 4 Dial spacer 7 1 Pendulum head 8 1 Pendulum pivot 9 1 Pendulum
UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES
 UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES Structure 6.1 Introduction Objectives 6.2 References 6.3 Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun and the Concept of the Ecliptic and the Obliquity
UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES Structure 6.1 Introduction Objectives 6.2 References 6.3 Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun and the Concept of the Ecliptic and the Obliquity
LAW WOODEN CLOCK 1 GENERAL ASSEMBLY SHT 1 OF 10 SHTS. Designed by: BRLAW
 Woodenclocks Clock1 The drawings on the following pages contain plans to build the wooden clock shown above. For further information and more detailed rendered images visit SHT 1 OF 10 SHTS GENERAL ASSEMBLY
Woodenclocks Clock1 The drawings on the following pages contain plans to build the wooden clock shown above. For further information and more detailed rendered images visit SHT 1 OF 10 SHTS GENERAL ASSEMBLY
Dial removed for clarity
 8 7 4 1 18 19 15 1 9 24 21 24 29 17 14 20 21 29 23 22 3 40 22 25 2 44 41 39 2 32 12 33 13 12 31 43 42 ITEM QTY PART NO. DESCRIPTION 1 1 Back 2 1 Front 3 3 Spacer top 4 1 Pendulum hanger 5 1 Clock dial
8 7 4 1 18 19 15 1 9 24 21 24 29 17 14 20 21 29 23 22 3 40 22 25 2 44 41 39 2 32 12 33 13 12 31 43 42 ITEM QTY PART NO. DESCRIPTION 1 1 Back 2 1 Front 3 3 Spacer top 4 1 Pendulum hanger 5 1 Clock dial
The Measurement of Time
 CHAPTER TWO The Measurement of Time Solar Time In antiquity the time of day was measured by the direction of a shadow cast in sunlight. This resulted in the development of a wide variety of sophisticated
CHAPTER TWO The Measurement of Time Solar Time In antiquity the time of day was measured by the direction of a shadow cast in sunlight. This resulted in the development of a wide variety of sophisticated
April 26, J. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604
 April 26, 1932- J. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604 Filed Aug. 9, 1929 2 Sheets-Sheet l 43 00009600 2/ 22 ' April 26, 1932. J'. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604 Filed Aug. 9, 1929 2 Sheets-Sheet 2 46 l? wag Patented Apr. 26,
April 26, 1932- J. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604 Filed Aug. 9, 1929 2 Sheets-Sheet l 43 00009600 2/ 22 ' April 26, 1932. J'. G. LINDEMAN 1,855,604 Filed Aug. 9, 1929 2 Sheets-Sheet 2 46 l? wag Patented Apr. 26,
LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME. a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system.
 UNIT 2 UNIT 2 LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME Goals After mastery of this unit, you should: a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system. b. understand
UNIT 2 UNIT 2 LOCATING CELESTIAL OBJECTS: COORDINATES AND TIME Goals After mastery of this unit, you should: a. understand the basic concepts needed for any astronomical coordinate system. b. understand
Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 02 Sep. 10, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15) Chap. 16: Our Sun Chap. 28: Search for
Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin. 43 North 89 West. September Daylight
 Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin 43 North 89 West 7 32 September 21 2005 Daylight Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin September 21,2005 7:32 43 North 89 West Names & Planetary Character Luminaries Symbols
Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin 43 North 89 West 7 32 September 21 2005 Daylight Astrology Class Madison, Wisconsin September 21,2005 7:32 43 North 89 West Names & Planetary Character Luminaries Symbols
Knowing the Heavens. Chapter Two. Guiding Questions. Naked-eye (unaided-eye) astronomy had an important place in ancient civilizations
 Knowing the Heavens Chapter Two Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same
Knowing the Heavens Chapter Two Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same
Exercise 7.0 THE CHANGING DIURNAL CIRCLES OF THE SUN
 Exercise 7.0 THE CHANGING DIURNAL CIRCLES OF THE SUN I. The Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun A star always rises and sets at the same place on the horizon and, hence, it is above the horizon for the same
Exercise 7.0 THE CHANGING DIURNAL CIRCLES OF THE SUN I. The Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun A star always rises and sets at the same place on the horizon and, hence, it is above the horizon for the same
2. Knowing the Heavens
 2. Knowing the Heavens Ancient naked-eye astronomy Eighty-eight constellations The sky s ever-changing appearance The celestial sphere Celestial coordinates Seasons: Earth s axial tilt Precession of Earth
2. Knowing the Heavens Ancient naked-eye astronomy Eighty-eight constellations The sky s ever-changing appearance The celestial sphere Celestial coordinates Seasons: Earth s axial tilt Precession of Earth
Summary Sheet #1 for Astronomy Main Lesson
 Summary Sheet #1 for Astronomy Main Lesson From our perspective on earth The earth appears flat. We can see half the celestial sphere at any time. The earth s axis is always perpendicular to the equator.
Summary Sheet #1 for Astronomy Main Lesson From our perspective on earth The earth appears flat. We can see half the celestial sphere at any time. The earth s axis is always perpendicular to the equator.
Discovering the Night Sky
 Discovering the Night Sky Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Discovering the Night Sky Guiding Questions 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Discovering the Night Sky
 Guiding Questions Discovering the Night Sky 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Guiding Questions Discovering the Night Sky 1. What role did astronomy play in ancient civilizations? 2. Are the stars that make up a constellation actually close to one another? 3. Are the same stars
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Origins of Modern Astronomy Earth Science, 13e Chapter 21 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Origins of Modern Astronomy Earth Science, 13e Chapter 21 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical
Zoë 2%lvy Arafa, BY Ace. Aig. / May 28, ,793,758. Aewe// A. Ai//lings/ey. Filed March 28, 1956 MUD AND SAND SEPARATOR FOR WELL, DRILLING
 May 28, 1957 Filed March 28, 1956 Aig. / L. E. BLINGSLEY MUD AND SAND SEPARATOR FOR WELL, DRILLING 26 3 Sheets-Sheet l Aewe// A. Ai//lings/ey INVENTOR. Zoë 2%lvy Arafa, BY Ace May 28, 1957 E, BILLINGSLEY
May 28, 1957 Filed March 28, 1956 Aig. / L. E. BLINGSLEY MUD AND SAND SEPARATOR FOR WELL, DRILLING 26 3 Sheets-Sheet l Aewe// A. Ai//lings/ey INVENTOR. Zoë 2%lvy Arafa, BY Ace May 28, 1957 E, BILLINGSLEY
Earth Science, 11e. Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21. Early history of astronomy. Early history of astronomy. Early history of astronomy
 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 21 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
2006 Pearson Prentice Hall Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 21 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21
 Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21 Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical arguments to explain natural phenomena Also used some observa:onal data (looking at the night sky) Ancient
Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21 Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical arguments to explain natural phenomena Also used some observa:onal data (looking at the night sky) Ancient
Chapter 0 2/19/2014. Lecture Outline. 0.1 The Obvious View. Charting the Heavens. 0.1 The Obvious View. 0.1 The Obvious View. Units of Chapter 0
 Lecture Outline Chapter 0 Charting the Heavens Earth is average we don t occupy any special place in the universe Universe: Totality of all space, time, matter, and energy Astronomy: Study of the universe
Lecture Outline Chapter 0 Charting the Heavens Earth is average we don t occupy any special place in the universe Universe: Totality of all space, time, matter, and energy Astronomy: Study of the universe
Cartesian Coordinates Need two dimensional system 2 number lines perpendicular to each other X-axis is horizontal Y-axis is vertical Position relative
 General Physical Science Chapter 15 Place and Time Space and Time Einstein Space and time related Single entity Time is the 4 th dimension! Cartesian Coordinates Need some system to tell us where something
General Physical Science Chapter 15 Place and Time Space and Time Einstein Space and time related Single entity Time is the 4 th dimension! Cartesian Coordinates Need some system to tell us where something
3) During retrograde motion a planet appears to be A) dimmer than usual. B) the same brightness as usual C) brighter than usual.
 Descriptive Astronomy (ASTR 108) Exam 1 B February 17, 2010 Name: In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best possible answer. In the line on the scan sheet corresponding to the
Descriptive Astronomy (ASTR 108) Exam 1 B February 17, 2010 Name: In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best possible answer. In the line on the scan sheet corresponding to the
1) Kepler's third law allows us to find the average distance to a planet from observing its period of rotation on its axis.
 Descriptive Astronomy (ASTR 108) Exam 1 A February 17, 2010 Name: In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best possible answer. In the line on the scan sheet corresponding to the
Descriptive Astronomy (ASTR 108) Exam 1 A February 17, 2010 Name: In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best possible answer. In the line on the scan sheet corresponding to the
Astronomy 291. Professor Bradley M. Peterson
 Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
Fundamentals of Satellite technology
 Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky. The sky is divided into 88 unequal areas that we call constellations.
 Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
(12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
Meridian Circle through Zenith, North Celestial Pole, Zenith Direction Straight Up from Observer. South Celestial Pole
 Chapter 3 How Earth and Sky Work- Effects of Latitude In chapters 3 and 4we will learn why our view of the heavens depends on our position on the Earth, the time of day, and the day of the year. We will
Chapter 3 How Earth and Sky Work- Effects of Latitude In chapters 3 and 4we will learn why our view of the heavens depends on our position on the Earth, the time of day, and the day of the year. We will
The simultaneity of the planets and the simultaneity of time
 Eric Kraeghbod The simultaneity of the planets and the simultaneity of time [ Simultaneity Theory - SIMT ] April 2009 Copyright Eric Kraeghbod 2008-2009 The present English version is an approximative
Eric Kraeghbod The simultaneity of the planets and the simultaneity of time [ Simultaneity Theory - SIMT ] April 2009 Copyright Eric Kraeghbod 2008-2009 The present English version is an approximative
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
The Earth, Moon, and Sky. Lecture 5 1/31/2017
 The Earth, Moon, and Sky Lecture 5 1/31/2017 From Last Time: Stable Orbits The type of orbit depends on the initial speed of the object Stable orbits are either circular or elliptical. Too slow and gravity
The Earth, Moon, and Sky Lecture 5 1/31/2017 From Last Time: Stable Orbits The type of orbit depends on the initial speed of the object Stable orbits are either circular or elliptical. Too slow and gravity
A Warm Up Exercise. The Motion of the Sun. A Warm Up Exercise. A Warm Up Exercise. A Warm Up Exercise
 A Warm Up Exercise The Motion of the Sun Which of the following is NOT true of a circumpolar star? a) It rises and sets from my latitude b) Its direction can be far North c) Its direction can be far South
A Warm Up Exercise The Motion of the Sun Which of the following is NOT true of a circumpolar star? a) It rises and sets from my latitude b) Its direction can be far North c) Its direction can be far South
Topic Guide: The Celestial Sphere. GCSE (9-1) Astronomy. Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Astronomy (1AS0)
 Topic Guide: The Celestial Sphere GCSE (9-1) Astronomy Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Astronomy (1AS0) The Celestial Sphere Contents Specification Points 1 The Astronomy 2 Equatorial coordinates
Topic Guide: The Celestial Sphere GCSE (9-1) Astronomy Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Astronomy (1AS0) The Celestial Sphere Contents Specification Points 1 The Astronomy 2 Equatorial coordinates
Oberth: Energy vs. Momentum
 1 2 The Oberth Effect 3 Oberth: Energy vs. Momentum 4 The Celestial Sphere From our perspective on Earth the stars appear embedded on a distant 2-dimensional surface the Celestial Sphere. 5 The Celestial
1 2 The Oberth Effect 3 Oberth: Energy vs. Momentum 4 The Celestial Sphere From our perspective on Earth the stars appear embedded on a distant 2-dimensional surface the Celestial Sphere. 5 The Celestial
Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008
 Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008 Announcements Pick up a golf ball at the front of the class or get one from Alex; you will need it for an in-class activity today. You will also need the question sheet from Alex.
Astronomy 101: 9/18/2008 Announcements Pick up a golf ball at the front of the class or get one from Alex; you will need it for an in-class activity today. You will also need the question sheet from Alex.
Guiding Questions. Discovering the Night Sky. iclicker Qustion
 Guiding Questions Discovering the Night Sky 1 1. What methods do scientists use to expand our understanding of the universe? 2. What makes up our solar system? 3. What are the stars? Do they last forever?
Guiding Questions Discovering the Night Sky 1 1. What methods do scientists use to expand our understanding of the universe? 2. What makes up our solar system? 3. What are the stars? Do they last forever?
If Earth had no tilt, what else would happen?
 A more in depth explanation from last week: If Earth had no tilt, what else would happen? The equator would be much hotter due to the direct sunlight which would lead to a lower survival rate and little
A more in depth explanation from last week: If Earth had no tilt, what else would happen? The equator would be much hotter due to the direct sunlight which would lead to a lower survival rate and little
The. Astronomy is full of cycles. Like the day, the month, & the year In this section we will try to understand these cycles.
 Understanding The Sky Astronomy is full of cycles Like the day, the month, & the year In this section we will try to understand these cycles. For Example Why do we think of stars as nighttime objects?
Understanding The Sky Astronomy is full of cycles Like the day, the month, & the year In this section we will try to understand these cycles. For Example Why do we think of stars as nighttime objects?
The Nature of Stars. The Nature of Stars
 The Nature of Stars The total number of stars is beyond our ability to count Only a few stars have been studied in detail. To understand the nature of stars, we will compare and catalog the stars by: Physical
The Nature of Stars The total number of stars is beyond our ability to count Only a few stars have been studied in detail. To understand the nature of stars, we will compare and catalog the stars by: Physical
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
10/17/2012. Observing the Sky. Lecture 8. Chapter 2 Opener
 Observing the Sky Lecture 8 Chapter 2 Opener 1 Figure 2.1 Figure 2.2 2 Figure 2.6 Figure 2.4 Annotated 3 The Celestial Sphere The celestial sphere is the vast hollow sphere on which the stars appear fixed.
Observing the Sky Lecture 8 Chapter 2 Opener 1 Figure 2.1 Figure 2.2 2 Figure 2.6 Figure 2.4 Annotated 3 The Celestial Sphere The celestial sphere is the vast hollow sphere on which the stars appear fixed.
Astronomy 101 Lab Manual. Victor Andersen Community College of Aurora
 Astronomy 101 Lab Manual Victor Andersen Community College of Aurora victor.andersen@ccaurora.edu January 8, 2013 2 Contents 1 Angular Measures 5 1.1 Introduction............................ 5 1.1.1 Degrees,
Astronomy 101 Lab Manual Victor Andersen Community College of Aurora victor.andersen@ccaurora.edu January 8, 2013 2 Contents 1 Angular Measures 5 1.1 Introduction............................ 5 1.1.1 Degrees,
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
43&SS756) A. as S-AL.S /2. 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. a 2 Y3 ( Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA 3,333,762 ATTORNEY JOHN C. WRANA O4.0.44,- INVEVTOR.
 Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
Time, Seasons, and Tides
 Time, Seasons, and Tides Celestial Sphere Imagine the sky as a great, hollow, sphere surrounding the Earth. The stars are attached to this sphere--- some bigger and brighter than others--- which rotates
Time, Seasons, and Tides Celestial Sphere Imagine the sky as a great, hollow, sphere surrounding the Earth. The stars are attached to this sphere--- some bigger and brighter than others--- which rotates
(os) SSO. (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 (12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
Chapter 2 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Discovering the Universe for Yourself
 Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
Daily Motions. Daily Motions. Solar and Sidereal Days. Annual Motions of the Sun. Coordinate system on Earth. Annual Motion of the Stars.
 Sun: rises in the east sets in the west travels on an arc across the sky 24 hours Daily Motions Solar Day = 24 hours Stars: stars travel on arcs in the sky moving from east to west. some stars rise and
Sun: rises in the east sets in the west travels on an arc across the sky 24 hours Daily Motions Solar Day = 24 hours Stars: stars travel on arcs in the sky moving from east to west. some stars rise and
PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy
 PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy Dr Roger Wesson Research interests: deaths of stars. Planetary nebulae, novae and supernovae. Astronomy: some maths You can see that distances in astronomy are huge.
PHAS 1511: Foundations of Astronomy Dr Roger Wesson Research interests: deaths of stars. Planetary nebulae, novae and supernovae. Astronomy: some maths You can see that distances in astronomy are huge.
Aileen A. O Donoghue Priest Associate Professor of Physics
 SOAR: The Sky in Motion Life on the Tilted Teacup Ride Celestial Coordinates and the Day Aileen A. O Donoghue Priest Associate Professor of Physics Reference Points Poles Equator Prime Meridian Greenwich,
SOAR: The Sky in Motion Life on the Tilted Teacup Ride Celestial Coordinates and the Day Aileen A. O Donoghue Priest Associate Professor of Physics Reference Points Poles Equator Prime Meridian Greenwich,
N. TESLA. No. 613,735. Patented Nov. 8, ELECTRIC CIRCUIT CONTROLLER. 2 Sheets-Sheet I. (No Model.) (Application filed Apr. 19, 1898.
 No. 613,735. (No Model.) Patented Nov. 8, 1898. N. TESLA. ELECTRIC CIRCUIT CONTROLLER. (Application filed Apr. 19, 1898.) 2 Sheets-Sheet I. HIE NORRIS PETERS co.. PHOTO-LITHO.. Wlt.SHINGTON. O. C. No.
No. 613,735. (No Model.) Patented Nov. 8, 1898. N. TESLA. ELECTRIC CIRCUIT CONTROLLER. (Application filed Apr. 19, 1898.) 2 Sheets-Sheet I. HIE NORRIS PETERS co.. PHOTO-LITHO.. Wlt.SHINGTON. O. C. No.
1 11 A3. Designed by: Brian law All dimensions in mm and (inchs) 3rd Angle projection. Not to Scale Unless otherwise stated
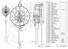 B 2 11 12 37 17 6 2 44 36 43 1 20 3 35 7 18 22 18 16 30 3 6 5 2 18 41 19 26 25 27 42 17 SECTION B-B SCALE 1 : 2 24 21 31 29 1 23 4 9 14 10 11 33 15 37 40 38 32 39 45 28 ITEM NO. PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION
B 2 11 12 37 17 6 2 44 36 43 1 20 3 35 7 18 22 18 16 30 3 6 5 2 18 41 19 26 25 27 42 17 SECTION B-B SCALE 1 : 2 24 21 31 29 1 23 4 9 14 10 11 33 15 37 40 38 32 39 45 28 ITEM NO. PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
A2 Principi di Astrofisica. Coordinate Celesti
 A2 Principi di Astrofisica Coordinate Celesti ESO La Silla Tel. 3.6m Celestial Sphere Our lack of depth perception when we look into space creates the illusion that Earth is surrounded by a celestial sphere.
A2 Principi di Astrofisica Coordinate Celesti ESO La Silla Tel. 3.6m Celestial Sphere Our lack of depth perception when we look into space creates the illusion that Earth is surrounded by a celestial sphere.
The Earth and its representation
 GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 The Earth and its representation THE SOLAR SYSTEM AND THE EARTH THE SOLAR SYSTEM The solar system is a planetary system. Is a group of astronomical objects who surround a star, in this
GEOGRAPHY UNIT 1 The Earth and its representation THE SOLAR SYSTEM AND THE EARTH THE SOLAR SYSTEM The solar system is a planetary system. Is a group of astronomical objects who surround a star, in this
Problem Set I Observing the Sky: The Birth of Astronomy
 Problem Set I Observing the Sky: The Birth of Astronomy Problem 1.1 The ideal terrestrial locations from which one can observe all the stars over the course of a year lie along the Earth s equator, which,
Problem Set I Observing the Sky: The Birth of Astronomy Problem 1.1 The ideal terrestrial locations from which one can observe all the stars over the course of a year lie along the Earth s equator, which,
The sky and the celestial sphere
 Chapter 1 The sky and the celestial sphere The Sun, and sometimes the Moon are, by and large, the only astronomical objects visible in the day sky. Traditionally, astronomy has been a nocturnal activity.
Chapter 1 The sky and the celestial sphere The Sun, and sometimes the Moon are, by and large, the only astronomical objects visible in the day sky. Traditionally, astronomy has been a nocturnal activity.
100-N. (12) United States Patent N 2 Q US 7,234,334 B1. Jun. 26, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: SZZ
 USOO7234,334B1 (12) United States Patent Pfabe (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,234,334 B1 Jun. 26, 2007 (54) SADDLE FOR BACKING ASSEMBLIES IN A ROLLING MILL (75) Inventor: Dennis P. Pfabe, Canton,
USOO7234,334B1 (12) United States Patent Pfabe (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,234,334 B1 Jun. 26, 2007 (54) SADDLE FOR BACKING ASSEMBLIES IN A ROLLING MILL (75) Inventor: Dennis P. Pfabe, Canton,
FRIOT'S EXPLANATION OF THE TIP OF THE EARTH'S CONTRIBUTION TO THE EQUATION OF TIME
 FRIOT'S EXPLANATION OF THE TIP OF THE EARTH'S CONTRIBUTION TO THE EQUATION OF TIME For this explanation it has been assumed that the reader is knowledgeable of certain facts and scientific understandings.
FRIOT'S EXPLANATION OF THE TIP OF THE EARTH'S CONTRIBUTION TO THE EQUATION OF TIME For this explanation it has been assumed that the reader is knowledgeable of certain facts and scientific understandings.
2. Modern: A constellation is a region in the sky. Every object in the sky, whether we can see it or not, is part of a constellation.
 6/14 10. Star Cluster size about 10 14 to 10 17 m importance: where stars are born composed of stars. 11. Galaxy size about 10 21 m importance: provide a stable environment for stars. Composed of stars.
6/14 10. Star Cluster size about 10 14 to 10 17 m importance: where stars are born composed of stars. 11. Galaxy size about 10 21 m importance: provide a stable environment for stars. Composed of stars.
UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS
 UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS After Unit 3 you should be able to: o Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the Earth o Apply the rates of rotation and revolution to basic problems o Recall the evidence
UNIT 3: EARTH S MOTIONS After Unit 3 you should be able to: o Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the Earth o Apply the rates of rotation and revolution to basic problems o Recall the evidence
The following terms are some of the vocabulary that students should be familiar with in order to fully master this lesson.
 Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
Lesson 211: EARTH'S SEASONS Students learn the complex geometry and planetary motions that cause Earth to have four distinct seasons. Fundamental Questions Attempting to give thorough and reasonable answers
A Chronicle of Timekeeping
 Reading Practice A A Chronicle of Timekeeping Our conception of time depends on the way we measure it According to archaeological evidence, at least 5,000 years ago, and long before the advent of the Roman
Reading Practice A A Chronicle of Timekeeping Our conception of time depends on the way we measure it According to archaeological evidence, at least 5,000 years ago, and long before the advent of the Roman
Satellite Communications
 Satellite Communications Lecture (3) Chapter 2.1 1 Gravitational Force Newton s 2nd Law: r r F = m a Newton s Law Of Universal Gravitation (assuming point masses or spheres): Putting these together: r
Satellite Communications Lecture (3) Chapter 2.1 1 Gravitational Force Newton s 2nd Law: r r F = m a Newton s Law Of Universal Gravitation (assuming point masses or spheres): Putting these together: r
is a revolution relative to a fixed celestial position. is the instant of transit of mean equinox relative to a fixed meridian position.
 PERIODICITY FORMULAS: Sidereal Orbit Tropical Year Eclipse Year Anomalistic Year Sidereal Lunar Orbit Lunar Mean Daily Sidereal Motion Lunar Synodical Period Centenial General Precession Longitude (365.25636042
PERIODICITY FORMULAS: Sidereal Orbit Tropical Year Eclipse Year Anomalistic Year Sidereal Lunar Orbit Lunar Mean Daily Sidereal Motion Lunar Synodical Period Centenial General Precession Longitude (365.25636042
Mounts and Coordinate Systems
 Mounts and Coordinate Systems Part 3: Some Advanced Techniques For Mounts Last month we looked at the basic mount types and methods for aligning them. This month s article, and the last for this series
Mounts and Coordinate Systems Part 3: Some Advanced Techniques For Mounts Last month we looked at the basic mount types and methods for aligning them. This month s article, and the last for this series
May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,765 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING. Filed Aug. 19, 1965 (,,,,, SR-33-R-N
 May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,7 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING Filed Aug. 19, 19 FG- SR-33-R-N FIG-4 (,,,,, S-CONSTANT CURRENT SOURCE FG-2 INVENTORS HAROY W. TROLANDER 8 By RAY
May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,7 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING Filed Aug. 19, 19 FG- SR-33-R-N FIG-4 (,,,,, S-CONSTANT CURRENT SOURCE FG-2 INVENTORS HAROY W. TROLANDER 8 By RAY
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY
 ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Fall 2018 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 2 Number of students: 1300 Examination date: 29 September 2018 Time limit: 50 min
ASTR 1P01 Test 1, September 2018 Page 1 BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: Fall 2018 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 2 Number of students: 1300 Examination date: 29 September 2018 Time limit: 50 min
United States Patent (19) Tanaka
 United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,194,815 B1
 USOO6194815B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Carroll (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 27, 2001 (54) PIEZOELECTRIC ROTARY ELECTRICAL 4,387,318 : 6/1983 Kolm et al.... 3.10/330 ENERGY GENERATOR FOREIGN
USOO6194815B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Carroll (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 27, 2001 (54) PIEZOELECTRIC ROTARY ELECTRICAL 4,387,318 : 6/1983 Kolm et al.... 3.10/330 ENERGY GENERATOR FOREIGN
Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016
 (12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
1.4j interpret simple shadow stick data to determine local noon and observer s longitude
 1.4j interpret simple shadow stick data to determine local noon and observer s longitude There are many opportunities for making observations of shadows cast with a vertical stick and the Sun. Observations
1.4j interpret simple shadow stick data to determine local noon and observer s longitude There are many opportunities for making observations of shadows cast with a vertical stick and the Sun. Observations
The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
chapter 7 The Earth-Moon-Sun System section 2 Time and Seasons What You ll Learn how to calculate time and date in different time zones how to distinguish rotation and revolution what causes seasons Before
It is obviously illogical. What
 Illogical: What Else Would You Call It? by Dr. Clayton Boyer (CA) Author s Note: The beautiful mechanisms shown in this article were all imaginatively crafted through the artistry of Forrest Burnett. The
Illogical: What Else Would You Call It? by Dr. Clayton Boyer (CA) Author s Note: The beautiful mechanisms shown in this article were all imaginatively crafted through the artistry of Forrest Burnett. The
vulcanhammer.info the website about Vulcan Iron Works Inc. and the pile driving equipment it manufactured Terms and Conditions of Use:
 this document downloaded from vulcanhammer.info the website about Vulcan Iron Works Inc. and the pile driving equipment it manufactured Terms and Conditions of Use: All of the information, data and computer
this document downloaded from vulcanhammer.info the website about Vulcan Iron Works Inc. and the pile driving equipment it manufactured Terms and Conditions of Use: All of the information, data and computer
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION
 Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 0 Charting the Heavens Lecture Presentation 0.0 Astronmy a why is that subject! Q. What rare astronomical event happened in late summer
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 0 Charting the Heavens Lecture Presentation 0.0 Astronmy a why is that subject! Q. What rare astronomical event happened in late summer
A GEOCENTRIC ORRERY. What is an orrery?
 Biblical Astronomer, number 94 5 A GEOCENTRIC ORRERY Last spring, a gentle lady wrote asking about the possibility that the shadow of the moon during a solar eclipse could prove geocentricity. Part of
Biblical Astronomer, number 94 5 A GEOCENTRIC ORRERY Last spring, a gentle lady wrote asking about the possibility that the shadow of the moon during a solar eclipse could prove geocentricity. Part of
Jacob & Co. Astronomia Sky Press Release
 Jacob & Co. Astronomia Sky Press Release JACOB & CO. ASTRONOMIA SKY CELESTIAL PANORAMA GRAVITATIONAL TRIPLE AXIS TOURBILLON The Triple Axis Tourbillon Goes Sidereal As a sailor heading toward the seas
Jacob & Co. Astronomia Sky Press Release JACOB & CO. ASTRONOMIA SKY CELESTIAL PANORAMA GRAVITATIONAL TRIPLE AXIS TOURBILLON The Triple Axis Tourbillon Goes Sidereal As a sailor heading toward the seas
s % RN N N 2. United States Patent (19) Barriac 11) 4,238, Dec. 16, 1980 slope of a drilling line includes a gyroscope and an
 United States Patent (19) Barriac 54) DEVICES FOR THE AZIMUTH AD SLOPE SCAIG OF A DRILLIG LIE (75) Inventor: Jacques Barriac, Plaisir, France 73 Assignee: Societe d'applications Generales d'electricite
United States Patent (19) Barriac 54) DEVICES FOR THE AZIMUTH AD SLOPE SCAIG OF A DRILLIG LIE (75) Inventor: Jacques Barriac, Plaisir, France 73 Assignee: Societe d'applications Generales d'electricite
4 Solar System and Time
 4 olar ystem and Time 4.1 The Universe 4.1.1 Introduction The Universe consists of countless galaxies distributed throughout space. The bodies used in astro navigation belong to the Galaxy known as the
4 olar ystem and Time 4.1 The Universe 4.1.1 Introduction The Universe consists of countless galaxies distributed throughout space. The bodies used in astro navigation belong to the Galaxy known as the
Yr1 Lesson 1. The Great Circles of Astrology, the Angles, Precession,
 Yr1 Lesson 1 The Great Circles of Astrology, the Angles, Precession, Cosmic Intelligence Agency 2015 Astro Lesson 1! Signs, Symbols, Glyphs and Charts! The Celestial Sphere Great Circles of Astrology -
Yr1 Lesson 1 The Great Circles of Astrology, the Angles, Precession, Cosmic Intelligence Agency 2015 Astro Lesson 1! Signs, Symbols, Glyphs and Charts! The Celestial Sphere Great Circles of Astrology -
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, Nanjing (CN) (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20120307356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0307356 A1 Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TECHNIQUE FOR TELESCOPE POLAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/428; 359/430
US 20120307356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0307356 A1 Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TECHNIQUE FOR TELESCOPE POLAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 359/428; 359/430
ZZZZZZZZZZYZZZZZZZZZZZZZz6
 USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
Celestial Sphere Spectroscopy (Something interesting; e.g., advanced data analyses with IDL)
 AST326, 2010 Winter Semester Celestial Sphere Spectroscopy (Something interesting; e.g., advanced data analyses with IDL) Practical Assignment: analyses of Keck spectroscopic data from the instructor (can
AST326, 2010 Winter Semester Celestial Sphere Spectroscopy (Something interesting; e.g., advanced data analyses with IDL) Practical Assignment: analyses of Keck spectroscopic data from the instructor (can
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time
 James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time Place & Time Read sections 15.5 and 15.6, but ignore the math. Concentrate on those sections that help explain the slides.
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Chapter 15 Place and Time Place & Time Read sections 15.5 and 15.6, but ignore the math. Concentrate on those sections that help explain the slides.
2. Descriptive Astronomy ( Astronomy Without a Telescope )
 How do we locate stars in the heavens? 2. Descriptive Astronomy ( Astronomy Without a Telescope ) What stars are visible from a given location? Where is the sun in the sky at any given time? Where are
How do we locate stars in the heavens? 2. Descriptive Astronomy ( Astronomy Without a Telescope ) What stars are visible from a given location? Where is the sun in the sky at any given time? Where are
CELESTIAL COORDINATES
 ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 27 Celestial Coordinates CELESTIAL COORDINATES GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATES The Earth's geographic coordinate system is familiar to everyone - the north and south poles are defined by
ASTR 1030 Astronomy Lab 27 Celestial Coordinates CELESTIAL COORDINATES GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATES The Earth's geographic coordinate system is familiar to everyone - the north and south poles are defined by
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
These notes may contain copyrighted material! They are for your own use only during this course.
 Licensed for Personal Use Only DO NOT DISTRIBUTE These notes may contain copyrighted material! They are for your own use only during this course. Distributing them in anyway will be considered a breach
Licensed for Personal Use Only DO NOT DISTRIBUTE These notes may contain copyrighted material! They are for your own use only during this course. Distributing them in anyway will be considered a breach
Exercise 2: The UW planetarium
 Astronomy 100, Fall 2008 Name(s): Exercise 2: The UW planetarium The University of Washington Physics and Astronomy Building houses a wonderful planetarium, in addition to some other interesting displays.
Astronomy 100, Fall 2008 Name(s): Exercise 2: The UW planetarium The University of Washington Physics and Astronomy Building houses a wonderful planetarium, in addition to some other interesting displays.
Orbit Definition. Reference Vector. Vernal (March) Equinox Vector. Sun Vector
 Simulation: TMG Thermal Analysis User's Guide Orbit Definition TMG can model three types of orbits: Beta Angle, Geostationary and Classical. For Earth, three special classical orbits are already partially
Simulation: TMG Thermal Analysis User's Guide Orbit Definition TMG can model three types of orbits: Beta Angle, Geostationary and Classical. For Earth, three special classical orbits are already partially
