THE INFLUENCE OF LENS HAZE ON HEADLAMP BEAM PATTERNS
|
|
|
- Gilbert Flynn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UMTRI TE INFLUENCE OF LENS AZE ON EADLAMP BEAM PATTERNS Michael Sivak Michael J. Flannagan Shinichi Kojima Eric C. Traube April 1998
2 TE INFLUENCE OF LENS AZE ON EADLAMP BEAM PATTERNS Michael Sivak Michael J. Flannagan Shinichi Kojima Eric C. Traube The University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute Ann Arbor, Michigan U.S.A. Report No. UMTRI April 1998
3 1. Report No. UMTRI Technical Report Documentation Page 2. Government Accession No. 3. Recipient s Catalog No. 4. Title and Subtitle The Influence of Lens aze on eadlamp Beam Patterns 7. Author(s) Sivak, M., Flannagan, M.J., Kojima, S., and Traube, E.C. 9. Performing Organization Name and Address The University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute 2901 Baxter Road Ann Arbor, Michigan U.S.A. 12. Sponsoring Agency Name and Address 5. Report Date April Performing Organization Code Performing Organization Report No. UMTRI Work Unit no. (TRAIS) 11. Contract or Grant No. 13. Type of Report and Period Covered The University of Michigan Industry Affiliation Program for 14. Sponsoring Agency Code uman Factors in Transportation Safety 15. Supplementary Notes The Affiliation Program currently includes Adac Plastics, BMW, Bosch, Britax International, Chrysler, Corning, Delphi Interior and Lighting Systems, Denso, GE, GM NAO Safety Center, ella, ewlett-packard, Ichikoh Industries, Koito Manufacturing, LESCOA, Libbey-Owens-Ford, Magneti Marelli, North American Lighting, Osram Sylvania, Philips Lighting, PPG Industries, Reflexite, Stanley Electric, Stimsonite, TEXTRON Automotive, Valeo, Visteon, Wagner Lighting, 3M Personal Safety Products, and 3M Traffic Control Materials. Information about the Affiliation Program is available at: Abstract This study investigated changes in headlamp beam patterns as a function of the level of haze in sheets of plastic materials that were inserted in front of either a U.S. or a European low-beam headlamp. The level of haze was measured according to the method required by the U.S. National ighway Traffic Safety Administration. This method (ASTM Standard D ) measures the percentage of transmitted light that deviates from the incident beam through forward scatter by more than 2.5.The actual effects on the beam pattern were then compared with predictions based on modeling the effects by assuming Gaussian distributions of the scattered light. The main finding is that the predictions for the four different plastic materials tested were neither uniformly accurate nor uniformly inaccurate. This lack of consistency is in agreement with the fact that the ASTM definition of haze does not uniquely specify the distribution of the scattered light. This problem with using the ASTM definition was confirmed by measuring the distributions of light scattering by two materials that had essentially the same ASTM index of haze. The implication of this research is that establishing a justifiable maximum haze level for headlamp lens materials would require using a definition of haze that uniquely defines the resultant distribution of the light scatter. Consequently, it is recommended that future research should evaluate the distribution of scattered light using actual materials for headlamp lenses after different lengths of weathering exposure. 17. Key Words 18. Distribution Statement headlighting, headlamps, low beams, haze, Unlimited simulation, visibility, glare, plastics, lenses 19. Security Classification (of this report) None 20. Security Classification (of this page) None 21. No. of Pages Price i
4 Acknowledgments Appreciation is extended to the members of the University of Michigan Industry Affiliation Program for uman Factors in Transportation Safety for support of this research. The current members of the Program are: Adac Plastics BMW Bosch Britax International Chrysler Corning Delphi Interior and Lighting Systems Denso GE GM NAO Safety Center ella ewlett-packard Ichikoh Industries Koito Manufacturing LESCOA Libbey-Owens-Ford Magneti Marelli North American Lighting Osram Sylvania Philips Lighting PPG Industries Reflexite Stanley Electric Stimsonite TEXTRON Automotive Valeo Visteon Wagner Lighting 3M Personal Safety Products 3M Traffic Control Materials ii
5 Contents Acknowledgments...ii Introduction...1 Method...3 Results...6 Discussion...23 Conclusions...26 References...27 iii
6 Introduction aze is a word used in the general sense to describe light scattering by particles suspended in an otherwise nonscattering or transparent medium. The medium may be gas, liquid, or solid. In determining haze, the measured value is given in terms of a collimated light beam which is scattered when the light beam passes through the specified medium. Only that portion of the scattered light that is scattered in the forward direction, as the beam exits from the specimen, is considered in measuring the percentage haze. Backscattering is not included, nor is the angular distribution of the scattered light derived from haze measurements. aze, or light scattering, degrades image quality and therefore affects visual perception (Weidner and sia, 1979, p. 1619) The current U.S. vehicle lighting regulations state that "after the outdoor exposure test, the haze and loss of surface luster of plastic materials (other than those incorporating reflex reflectors) used for outer lenses shall not be greater than 30 percent haze" (FMVSS, 1997, p. 224) using the method of ASTM (1992). In turn, ASTM (1992) defines haze as "the percent of total transmitted light, which, in passing through the specimen, deviates from the incident beam through forward scatter by more than rad (2.5 ) on the average" (p. 1). 1 On the other hand, SAE recommends that "plastic materials used for forward road illumination devices, excluding cornering lamps, shall show no deterioration" (SAE, 1991, p. 1). The usual discussion concerning haze deals with the appropriate haze limits for different vehicle-lighting applications. owever, there is a more fundamental issue: Is the ASTM method applicable to vehicle lighting? If not, the issue of what should be the limit of haze as defined by the ASTM method is not relevant. As pointed out by Weidner and sia (1979) and Sivak, Flannagan, ashimoto, and Kojima (1997), there are two major problems with the ASTM definition of haze. First, this definition does not describe the angular distribution of the scattered light. Second, the definition disregards the amount of light that is either backscattered or absorbed. Consequently, a given level of haze, as defined by ASTM, does not uniquely describe what will happen to the emitted light. 1 There is a newer version of the ASTM standard (ASTM, 1995). owever, it is essentially the same as ASTM (1992). Furthermore, the current U.S. regulations explicitly reference ASTM (1992). 1
7 In our previous study on this topic (Sivak et al., 1997), we simulated the effects of haze by applying Gaussian (normal) spread functions to each point of a beam pattern. That simulation used actual photometry from a U.S. low-beam headlamp and a European low-beam headlamp. The measure of interest was the percentage change, at each point in the beam pattern, of the luminous intensity with haze compared to the luminous intensity without haze. Seven levels of haze were simulated: 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, and 30% (as defined by ASTM). The results indicated that even the smallest amount of haze tested may produce major changes in both the visibility and glare illumination provided by lowbeam headlamps. The results in Sivak et al. (1997) are based on the assumption that the effects of haze are well described by Gaussian distributions. owever, we are not aware of any information on the distribution of the light scatter in actual materials used for headlamp lenses. To obtain such information, a flat piece of the lens material (to comply with the specifications provided by hazemeter manufacturers) would have to be exposed to outdoor weathering for three years; accelerated weathering is not permitted (FMVSS, 1997, p. 224). The present study investigated changes in headlamp beam patterns as a function of the level of haze in sheets of plastic materials that were inserted in front of the lamp. These actual effects were then compared with the predictions based on modeling the effects by assuming Gaussian distributions of haze. Consequently, this research can be viewed as a test of the validity of the simulation in Sivak et al. (1997). 2
8 Method Approach The beam pattern of each of two low-beam headlamps was measured with and without sheets of plastic material with known ASTM indexes of haze inserted in front of the lamp. The resultant changes in light output due to the presence of the plastic materials in front of the lamp were then compared with predictions based on modeling the effects by assuming Gaussian distributions of haze. Simulation Gaussian spread functions, corresponding to particular levels of haze, were applied to each individual point in the original (without haze) beam pattern (Sivak et al., 1997). Given the assumption that the effect of haze is Gaussian, the haze values defined by ASTM (1992) completely specify the effects of haze on the distribution of the transmitted light. For example, if haze is specified as 10%, there will be a unique corresponding Gaussian function with 10% of its area beyond ±2.5. (This is the case because haze is defined as the percentage of the transmitted light that is scattered more than 2.5 from the intended direction.) In this manner, a unique function was derived for each of the four levels of haze, corresponding to the haze levels of our four plastic materials (see below). In addition to being Gaussian, these functions were further constrained as follows: (1) The width of the spread was set at ± 5. Thus, the effects of haze were truncated at ±5. This constraint is unlikely to affect the results noticeably, because the area outside of ±5 is relatively small (especially for the low levels of simulated haze). (2) The sum of the values for all points of the function (i.e., from -5 to +5 ) was set equal to 1. (The step size was 0.5.) These Gaussian haze functions were then used as multiplicative functions at each point of the beam pattern. Thus, each original (without haze) value of luminous intensity was distributed within ±5, according to the particular haze function under consideration. (The same Gaussian function was applied to each original intensity, and thus each intensity was distributed within ±5 of its original location.) After the same Gaussian function was applied to each original luminous intensity, a sum of all luminous intensities at each point produced the after-haze luminous intensity pattern. This sum consisted of a reduction of the original value, with additions from the neighboring points. Finally, adjustments due to transmittance losses (see Table 1) were made. 3
9 Photometry The photometry for each lamp was performed in 0.5 steps from 10 down to 10 up, and from 25 left to 25 right. owever, the results will be presented only from 5 down to 5 up, and from 20 left to 20 right. This is because the effects on the outlying 5 in each direction of the original photometric matrix from even more peripheral parts of the beam pattern could not be calculated. For example, the haze effects for a location at 24 left should be simulated by considering the influence from points located between 19 left and 29 left, but we did not have the photometry for the area extending beyond 25 left. The photometry was performed five times for each lamp: without any plastic material in front of the lamp, and with each of the four materials in front of the lamp. The measurements were made in a photometry laboratory. The voltage was set at 12.8 V. Plastic materials Four sheets of plastic materials were used. The ASTM haze index and transmittance of each material are listed in Table 1. These measurements were made using a BYK Gardner XL-211 azegard azemeter. Table 1. The ASTM haze indexes and transmittances of the plastic materials used in the study. No. Type aze (%) Transmittance (%) 1 Acrylic Polyester Polyester Acrylic Beam patterns Two low-beam headlamps were used, one manufactured for sale in the U.S., and one for sale in Europe. Figure 1 presents the original photometry, obtained without any plastic material in front of the lamps. 4
10 U.S. low beam 20L 10L V 10R 20R Luminous intensity (cd) European low beam 20L 10L V 10R 20R Figure 1. Photometry of the U.S. and European low beams tested. 5
11 Results Figure 2 shows the predicted changes (top panel) and the actual changes (bottom panel) in luminous intensities for the U.S. lamp in the 0.2% haze condition. Figure 3 presents the corresponding predictions and actual changes for the European lamp. The results for the haze conditions of 3.3, 5.0, and 10.5% are shown in Figures 4 through 9. Figures 10 through 17 present correlations of the actual changes with the predictions. 6
12 Simulation U.S. low beam, 0.2% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L % -25% 0% +25% +100% +250% +750% 0 Actual measurements U.S. low beam, 0.2% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L Figure 2. The predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the U.S. low beam and the 0.2% haze material. 7
13 Simulation European low beam, 0.2% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L % -25% 0% +25% +100% +250% +750% 0 Actual measurements European low beam, 0.2% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L Figure 3. The predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the European low beam and the 0.2% haze material. 8
14 Simulation U.S. low beam, 3.3% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L % -25% 0% +25% +100% +250% +750% 0 Actual measurements U.S. low beam, 3.3% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L Figure 4. The predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the U.S. low beam and the 3.3% haze material. 9
15 Simulation European low beam, 3.3% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L % -25% 0% +25% +100% +250% +750% 0 Actual measurements European low beam, 3.3% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L Figure 5. The predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the European low beam and the 3.3% haze material. 10
16 Simulation U.S. low beam, 5.0% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L % -25% 0% +25% +100% +250% +750% 0 Actual measurements U.S. low beam, 5.0% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L Figure 6. The predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the U.S. low beam and the 5.0% haze material. 11
17 Simulation European low beam, 5.0% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L % -25% 0% +25% +100% +250% +750% 0 Actual measurements European low beam, 5.0% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L Figure 7. The predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the European low beam and the 5.0% haze material. 12
18 Simulation U.S. low beam, 10.5% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L % -25% 0% +25% +100% +250% +750% 0 Actual measurements U.S. low beam, 10.5% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L Figure 8. The predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the U.S. low beam and the 10.5% haze material. 13
19 Simulation European low beam, 10.5% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L % -25% 0% +25% +100% +250% +750% Actual measurements European low beam, 10.5% haze 20R 10R V 10L 20L Figure 9. The predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the European low beam and the 10.5% haze material. 14
20 Figure 10. The relationship between the predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the U.S. low beam and the 0.2% haze material. The solid line is the best-fitting linear model. For comparison, the dashed line shows where points would fall if the predicted and actual changes were the same. 15
21 Figure 11. The relationship between the predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the European low beam and the 0.2% haze material. The solid line is the best-fitting linear model. For comparison, the dashed line shows where points would fall if the predicted and actual changes were the same. 16
22 Figure 12. The relationship between the predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the U.S. low beam and the 3.3% haze material. The solid line is the best-fitting linear model. For comparison, the dashed line shows where points would fall if the predicted and actual changes were the same. 17
23 Figure 13. The relationship between the predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the European low beam and the 3.3% haze material. The solid line is the best-fitting linear model. For comparison, the dashed line shows where points would fall if the predicted and actual changes were the same. 18
24 Figure 14. The relationship between the predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the U.S. low beam and the 5.0% haze material. The solid line is the best-fitting linear model. For comparison, the dashed line shows where points would fall if the predicted and actual changes were the same. 19
25 Figure 15. The relationship between the predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the European low beam and the 5.0% haze material. The solid line is the best-fitting linear model. For comparison, the dashed line shows where points would fall if the predicted and actual changes were the same 20
26 Figure 16. The relationship between the predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the U.S. low beam and the 10.5% haze material. The solid line is the best-fitting linear model. For comparison, the dashed line shows where points would fall if the predicted and actual changes were the same. 21
27 Figure 17. The relationship between the predicted and actual percentage changes in luminous intensities for the European low beam and 10.5% haze material. The solid line is the best-fitting linear model. For comparison, the dashed line shows where points would fall if the predicted and actual changes were the same. 22
28 Discussion The data in Figures 2 through 17 indicate that the simulation yielded reasonably accurate predictions for the 10.5% haze material, but inaccurate predictions for the other three materials. This pattern of results was obtained for both the U.S. and European low beams. In general, the predictions were more extreme than the actual effects. In other words, the simulation predicted greater reductions and greater increases than proved to be the case. In Figures 2 through 7, this is most evident when one examines the parts of the beam pattern just above the horizontal and near the vertical: ere the predictions call for greater increases than were obtained with the actual materials. Substantial numbers of points in both beam patterns, which were predicted to be affected by the materials with 0.2, 3.3, or 5.0% haze, were relatively unaffected. In Figures 10 through 15, these points lie in the horizontal groups of points near 0% actual change. Consistent with the results of the simulation, the actual effects of haze were greater for the European than the U.S. beam pattern. This is a consequence of a sharper vertical gradient for the European beam pattern. The most intriguing finding is the fact that the predictions for the four materials were neither uniformly accurate nor uniformly inaccurate. This finding brings us back to an observation we made in the Introduction: The ASTM definition of haze does not uniquely specify the distribution of the scattered light. We believe that differences in the distributions are responsible for the differences in the fit of the predictions. To illustrate that the ASTM definition does not uniquely define the distribution of the scatter, we measured the scattering properties of two materials with nominally the same haze index. One material was the 10.5% haze material used in the main study. The other material was a calibrated haze standard purchased from BYK Gardner. According to the manufacturer, the haze index of this particular standard was 10.1% virtually identical to the haze index of our 10.5% sample. In order to make a rough assessment of the overall distribution of scatter from the two materials, a laser was aimed through each sample at a CCD array, and the resulting scatter was measured. Figure 18 shows the relative amount of scatter as a function of angle from the axis of the laser for the two materials in question. 23
29 Luminous intensity (arbitrary units) Our sample (10.5%) 50 Calibrated standard (10.1%) Angle (degrees) Figure 18. Scattering functions for a test material with an ASTM haze index of 10.5%, and for a calibrated haze standard with an ASTM haze index of 10.1%. 24
30 Because of the extreme differences in luminous intensity between the center and periphery of the scatter patterns, these measurements do not provide the complete scattering functions. owever, even the partial functions in Figure 18 are sufficient to show that under these conditions, the patterns of scattering by the two materials are not the same. Note that the functions cross over, so that no adjustment in the vertical axis units (to compensate, for example, for possible differences in transmittance) will bring them into alignment. Although these measurements cannot be used to establish whether either of the scattering functions is Gaussian, together with the haze index results (which indicate that for both functions about 10% is scattered beyond 2.5%), they indicate that they cannot both be Gaussian. Because of the success of the Gaussian model in the case of our 10.5% material, it is tempting to speculate that the scattering function for that material is Gaussian. There are several straightforward ways in which these measurements would need to be extended (e.g., using white light rather than a laser, and using a wider range of receptor sensitivity) in order to characterize the scattering functions well enough to make useful predictions about visual performance. The purpose here is simply to raise the issue of the need for such measurements. 25
31 Conclusions This study investigated changes in headlamp beam patterns as a function of the level of haze in sheets of plastic materials that were inserted in front of either a U.S. or a European low-beam headlamp. The level of haze was measured according to the method required by the U.S. National ighway Traffic Safety Administration. This method (ASTM Standard D ) measures the percentage of transmitted light that deviates from the incident beam through forward scatter by more than 2.5.The actual effects on the beam pattern were then compared with predictions based on modeling the effects by assuming Gaussian distributions of the scattered light. The main finding is that the predictions for the four different plastic materials tested were neither uniformly accurate nor uniformly inaccurate. This lack of consistency is in agreement with the fact that the ASTM definition of haze does not uniquely specify the distribution of the scattered light. This problem with using the ASTM definition was confirmed by measuring the distributions of light scattering by two materials that had essentially the same ASTM index of haze. The implication of this research is that establishing a justifiable maximum haze level for headlamp lens materials would require using a definition of haze that uniquely defines the resultant distribution of the light scatter. Consequently, it is recommended that future research should evaluate the distribution of scattered light using actual materials for headlamp lenses after different lengths of weathering exposure. 26
32 References ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials). (1992). Standard test method for haze and luminous transmittance of transparent plastic (Standard D ). Philadelphia, PA: Author. ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials). (1995). Standard test method for haze and luminous transmittance of transparent plastic (Standard D ). Philadelphia, PA: Author. FMVSS (Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard). (1997). Standard No. 108: Lamps, reflective devices, and associated equipment. In, Code of Federal Regulations, [Title] 49. Washington, D.C.: Office of the Federal Register. Sivak, M., Flannagan, M.J., ashimoto,., and Kojima, S. (1997). A simulation of the effects of haze in headlamp lenses on beam Patterns: A preliminary study (Report No. UMTRI-97-1). Ann Arbor, MI: The University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute. SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers). (1991). Plastic materials for use in optical parts as lenses and reflex reflectors of motor vehicle lighting devices (SAE Standard J576). Warrendale, PA: Author. Weidner, V.C. and sia, J.J. (1979). NBS reference hazemeter: Its development and testing. Applied Optics, 18,
Revision of GRE/2017/05
 Transmitted by the experts from The International Automotive Lighting and Light Signalling Expert Group (GTB) Informal document GRE-77-12 (77th GRE, 4-7 April 2017 agenda item 5 ) Revision of GRE/2017/05
Transmitted by the experts from The International Automotive Lighting and Light Signalling Expert Group (GTB) Informal document GRE-77-12 (77th GRE, 4-7 April 2017 agenda item 5 ) Revision of GRE/2017/05
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/TRANS/WP.29/GRE/2017/20 Distr.: General 7 August 2017 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee World Forum for Harmonization
United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/TRANS/WP.29/GRE/2017/20 Distr.: General 7 August 2017 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee World Forum for Harmonization
THE IMPORTANCE OF ACTIVE AND INTELLIGENT TIRES FOR AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES
 SWT-2017-2 JANUARY 2017 THE IMPORTANCE OF ACTIVE AND INTELLIGENT TIRES FOR AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES BRANDON SCHOETTLE MICHAEL SIVAK SUSTAINABLE WORLDWIDE TRANSPORTATION THE IMPORTANCE OF ACTIVE AND INTELLIGENT
SWT-2017-2 JANUARY 2017 THE IMPORTANCE OF ACTIVE AND INTELLIGENT TIRES FOR AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES BRANDON SCHOETTLE MICHAEL SIVAK SUSTAINABLE WORLDWIDE TRANSPORTATION THE IMPORTANCE OF ACTIVE AND INTELLIGENT
A conventional approach to nighttime visibility in adverse weather conditions
 A conventional approach to nighttime visibility in adverse weather conditions Romain Gallen, Eric Dumont and Nicolas Hautière Keywords: target visibility, headlight, fog 1 Introduction This paper presents
A conventional approach to nighttime visibility in adverse weather conditions Romain Gallen, Eric Dumont and Nicolas Hautière Keywords: target visibility, headlight, fog 1 Introduction This paper presents
The official directions are written in Chinese, this English edition is for your reference only -1-
 Refer to: R128 00-S2 74.1 Effective Date and Scope: 74.1.1 Effective date from 2017/1/1, the new types of LED replaceable light sources and from 2019/1/1 the all types of LED replaceable light sources
Refer to: R128 00-S2 74.1 Effective Date and Scope: 74.1.1 Effective date from 2017/1/1, the new types of LED replaceable light sources and from 2019/1/1 the all types of LED replaceable light sources
Optics. Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer. LD Physics Leaflets P
 Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
D DAVID PUBLISHING. Simulation of Accelerated Ageing of UV-Radiation for Photodegradable Geotextiles/Geomembranes. 1. Introduction
 Journal of Geological Resource and Engineering 1 (2016) 44-50 doi:10.17265/2328-2193/2016.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Simulation of Accelerated Ageing of UV-Radiation for Photodegradable Geotextiles/Geomembranes
Journal of Geological Resource and Engineering 1 (2016) 44-50 doi:10.17265/2328-2193/2016.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Simulation of Accelerated Ageing of UV-Radiation for Photodegradable Geotextiles/Geomembranes
A Thesis Proposal. Agrawal, Ravi. Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University
 Using Finite Element Structural Analysis of Retroreflective Raised Pavement Markers (RRPMs) to Recommend Testing Procedures for Simulating Field Performance of RRPMs A Thesis Proposal By Agrawal, Ravi
Using Finite Element Structural Analysis of Retroreflective Raised Pavement Markers (RRPMs) to Recommend Testing Procedures for Simulating Field Performance of RRPMs A Thesis Proposal By Agrawal, Ravi
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
CZECH TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE FACULTY OF TRANSPORTATION SCIENCES
 CZECH TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE FACULTY OF TRANSPORTATION SCIENCES Bc. Lenka Žaludová THE HEADLIGHT ILLUMINANCE IN FRONT OF THE CAR Master thesis 2012 2 Acknowledgement Hereby I would like to thank
CZECH TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE FACULTY OF TRANSPORTATION SCIENCES Bc. Lenka Žaludová THE HEADLIGHT ILLUMINANCE IN FRONT OF THE CAR Master thesis 2012 2 Acknowledgement Hereby I would like to thank
BRE Client Report. Aging of light pipe materials (4000 hours artificial ageing) Prepared for: James McGowan Monodraught. BRE Watford, Herts WD25 9XX
 BRE Client Report Aging of light pipe materials (4000 hours artificial ageing) Prepared for: James McGowan Date: 24 February 2015 Report Number: 298-109 Issue: 4 BRE Watford, Herts WD25 9XX Prepared for:
BRE Client Report Aging of light pipe materials (4000 hours artificial ageing) Prepared for: James McGowan Date: 24 February 2015 Report Number: 298-109 Issue: 4 BRE Watford, Herts WD25 9XX Prepared for:
White Paper Luminance & Illuminance. Brief explanation of photometry for the application of tunnel lighting control
 White Paper Luminance & Illuminance Brief explanation of photometry for the application of tunnel lighting control 1 General This document gives a brief explanation of photometry, the basics of tunnel
White Paper Luminance & Illuminance Brief explanation of photometry for the application of tunnel lighting control 1 General This document gives a brief explanation of photometry, the basics of tunnel
AN INSTRUMENT FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF ROAD SURFACE REFLECTION PROPERTIES
 AN INSTRUMENT FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF ROAD SURFACE REFLECTION PROPERTIES Corell, D. D 1, Sørensen, K. 2 1 Technical University of Denmark, DTU Fotonik, 4000 Roskilde, DENMARK, 2 Johnsen Consult, 2100 København
AN INSTRUMENT FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF ROAD SURFACE REFLECTION PROPERTIES Corell, D. D 1, Sørensen, K. 2 1 Technical University of Denmark, DTU Fotonik, 4000 Roskilde, DENMARK, 2 Johnsen Consult, 2100 København
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/TRANS/WP.29/GRE/2014/20 Distr.: General 7 August 2014 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee World Forum for Harmonization
United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/TRANS/WP.29/GRE/2014/20 Distr.: General 7 August 2014 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee World Forum for Harmonization
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
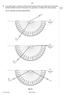 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
A Case Study: Fallacies in ANSI/ISEA 107, 2010 High Visibility Safety Clothing Standard
 A Case Study: Fallacies in ANSI/ISEA 107, 2010 High Visibility Safety Clothing Standard By Tom King Chairman, Photometric Subcommittee, High Visibility Products Group, ISEA Date: September 15, 2010 Introduction
A Case Study: Fallacies in ANSI/ISEA 107, 2010 High Visibility Safety Clothing Standard By Tom King Chairman, Photometric Subcommittee, High Visibility Products Group, ISEA Date: September 15, 2010 Introduction
The Control of Glare by the AS1680 Systems
 Lab Notes Issue The Control of Glare by the AS1680 Systems 8 1.00 Introduction : This Lab Note is one of several which discusses the matter of glare in the workplace. They have been issued as a series
Lab Notes Issue The Control of Glare by the AS1680 Systems 8 1.00 Introduction : This Lab Note is one of several which discusses the matter of glare in the workplace. They have been issued as a series
MODELING PERIPHERAL VISIBILITY UNDER HEADLAMP ILLUMINATION
 Bullough 1 MODELING PERIPHERAL VISIBILITY UNDER HEADLAMP ILLUMINATION Transportation Research Board 16th Biennial Symposium on Visibility and Simulation Iowa City, IA, June 2-4, 2002 John D. Bullough Lighting
Bullough 1 MODELING PERIPHERAL VISIBILITY UNDER HEADLAMP ILLUMINATION Transportation Research Board 16th Biennial Symposium on Visibility and Simulation Iowa City, IA, June 2-4, 2002 John D. Bullough Lighting
Introduction to atmospheric visibility estimation
 BRISTOL INDUSTRIAL AND RESEARCH ASSOCIATES LIMITED PO Box, Harbour Road, Portishead, Bristol, BS0 7BL, UK Telephone : +44 (0)175 847787 Facsimile : +44(0)175 847303 E-mail: info@biral.com Home Page at
BRISTOL INDUSTRIAL AND RESEARCH ASSOCIATES LIMITED PO Box, Harbour Road, Portishead, Bristol, BS0 7BL, UK Telephone : +44 (0)175 847787 Facsimile : +44(0)175 847303 E-mail: info@biral.com Home Page at
A Study of Mesopic Adaptation conditions for Night Drivers using an approximation for Oncoming headlight glare
 A Study of Mesopic Adaptation conditions for Night Drivers using an approximation for Oncoming headlight glare Robert L. Donofrio www.displayconsultants.com 1 This presentation is in part a review of our
A Study of Mesopic Adaptation conditions for Night Drivers using an approximation for Oncoming headlight glare Robert L. Donofrio www.displayconsultants.com 1 This presentation is in part a review of our
Optical Properties of Binoculars and Telescopes Relevant to Laser Safety
 ILSC 2001 Conference Proceedings Optical Properties of Binoculars and Telescopes Relevant to Laser Safety Karl Schulmeister, Herbert Hödlmoser, Helmut Schön and Volker Stübler Please register to receive
ILSC 2001 Conference Proceedings Optical Properties of Binoculars and Telescopes Relevant to Laser Safety Karl Schulmeister, Herbert Hödlmoser, Helmut Schön and Volker Stübler Please register to receive
object objective lens eyepiece lens
 Advancing Physics G495 June 2015 SET #1 ANSWERS Field and Particle Pictures Seeing with electrons The compound optical microscope Q1. Before attempting this question it may be helpful to review ray diagram
Advancing Physics G495 June 2015 SET #1 ANSWERS Field and Particle Pictures Seeing with electrons The compound optical microscope Q1. Before attempting this question it may be helpful to review ray diagram
Report No.: EASZF Page 2 of 14
 Report No.: EASZF01050007 age 2 of 14 Test item particulars... : Tested lamp... : continuous wave lamps pulsed lamps Tested lamp system... : Lamp classification group... : exempt risk 1 risk 2 risk 3 Lamp
Report No.: EASZF01050007 age 2 of 14 Test item particulars... : Tested lamp... : continuous wave lamps pulsed lamps Tested lamp system... : Lamp classification group... : exempt risk 1 risk 2 risk 3 Lamp
MEMS Metrology. Prof. Tianhong Cui ME 8254
 MEMS Metrology Prof. Tianhong Cui ME 8254 What is metrology? Metrology It is the science of weights and measures Refers primarily to the measurements of length, weight, time, etc. Mensuration- A branch
MEMS Metrology Prof. Tianhong Cui ME 8254 What is metrology? Metrology It is the science of weights and measures Refers primarily to the measurements of length, weight, time, etc. Mensuration- A branch
KULTIWAVELENGTH LASER PROPAGATION STUDY ~ III. Quarterly Progress Report No. h March 16, June 15, J. Richard Kerr
 CO o KULTIWAVELENGTH LASER PROPAGATION STUDY ~ III i> Quarterly Progress Report No. h March 16, 1971 - June 15, 1971 J. Richard Kerr Oregon Graduate Center for Study and Research Portland, Oregon July,
CO o KULTIWAVELENGTH LASER PROPAGATION STUDY ~ III i> Quarterly Progress Report No. h March 16, 1971 - June 15, 1971 J. Richard Kerr Oregon Graduate Center for Study and Research Portland, Oregon July,
IALA Recommendation E On Marine Signal Lights Part 2 - Calculation, Definition and Notation of Luminous Range. Edition 1 December 2008
 International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities AISM Association of Internationale de Signalisation Maritime IALA IALA Recommendation E-200-2 On Marine Signal Lights Part
International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities AISM Association of Internationale de Signalisation Maritime IALA IALA Recommendation E-200-2 On Marine Signal Lights Part
Lednium Series Optimal X OVTL09LG3x Series
 (10-watts,120 Viewing Angle) x x x x x Revolutionary 3-dimensional packaged LED source Robust energy-efficient design with long operating life Low thermal resistance (2.5 C/W) Exceptional spatial uniformity
(10-watts,120 Viewing Angle) x x x x x Revolutionary 3-dimensional packaged LED source Robust energy-efficient design with long operating life Low thermal resistance (2.5 C/W) Exceptional spatial uniformity
Measuring Laser Diode Optical Power with an Integrating Sphere
 Measuring Laser Diode Optical Power with an Integrating Sphere Introduction Characterizing radiant sources like laser diodes accurately depends on the ability to measure their optical power output accurately.
Measuring Laser Diode Optical Power with an Integrating Sphere Introduction Characterizing radiant sources like laser diodes accurately depends on the ability to measure their optical power output accurately.
A SELF-INDICATING MODE I INTERLAMINAR TOUGHNESS TEST
 A SELF-INDICATING MODE I INTERLAMINAR TOUGHNESS TEST P. Robinson The Composites Centre, Department of Aeronautics, Imperial College London South Kensington, London, SW7 2AZ, UK p.robinson@imperial.ac.uk
A SELF-INDICATING MODE I INTERLAMINAR TOUGHNESS TEST P. Robinson The Composites Centre, Department of Aeronautics, Imperial College London South Kensington, London, SW7 2AZ, UK p.robinson@imperial.ac.uk
Department of Transportation. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. [Docket No. NHTSA ; Notice 2]
![Department of Transportation. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. [Docket No. NHTSA ; Notice 2] Department of Transportation. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. [Docket No. NHTSA ; Notice 2]](/thumbs/89/99595080.jpg) This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 04/12/2016 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2016-08362, and on FDsys.gov Department of Transportation National
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 04/12/2016 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2016-08362, and on FDsys.gov Department of Transportation National
Eye Safety With LED Components
 technical article CLD-AP34 rev 20 Eye Safety With LED Components www.cree.com/xlamp Table of Contents Introduction...2 Photobiological Standards and Regulations for LED Components...3 Summary Test Results...4...5
technical article CLD-AP34 rev 20 Eye Safety With LED Components www.cree.com/xlamp Table of Contents Introduction...2 Photobiological Standards and Regulations for LED Components...3 Summary Test Results...4...5
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/TRANS/WP.9/GRE/010/53 Distr.: General 3 July 010 Original: English English and French only Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee World
United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/TRANS/WP.9/GRE/010/53 Distr.: General 3 July 010 Original: English English and French only Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee World
E/ECE/324/Rev.2/Add.127/Amend.7 E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.2/Add.127/Amend.7
 2 November 2018 Agreement Concerning the Adoption of Harmonized Technical United Nations Regulations for Wheeled Vehicles, Equipment and Parts which can be Fitted and/or be Used on Wheeled Vehicles and
2 November 2018 Agreement Concerning the Adoption of Harmonized Technical United Nations Regulations for Wheeled Vehicles, Equipment and Parts which can be Fitted and/or be Used on Wheeled Vehicles and
EXPERIMENTAL DETERMINATION OF SPECTRAL AND ANGULAR DEPENDENT OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF INSULATING GLASSES
 CISBAT 2005, Proceedings, EPFL 2005, p. 441-446 EXPERIMENTAL DETERMINATION OF SPECTRAL AND ANGULAR DEPENDENT OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF INSULATING GLASSES R. Steiner, P. Oelhafen, G. Reber and A. Romanyuk Institute
CISBAT 2005, Proceedings, EPFL 2005, p. 441-446 EXPERIMENTAL DETERMINATION OF SPECTRAL AND ANGULAR DEPENDENT OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF INSULATING GLASSES R. Steiner, P. Oelhafen, G. Reber and A. Romanyuk Institute
Motor vehicle and pedal cycle conspicuity - part 3: retroflective and fluorescent materials, disability glare of red markings.
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Motor vehicle and pedal cycle conspicuity - part 3: retroflective and fluorescent materials, disability glare of red markings. This item was submitted to
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Motor vehicle and pedal cycle conspicuity - part 3: retroflective and fluorescent materials, disability glare of red markings. This item was submitted to
Table of Contents. DS133 LUXEON TX Product Datasheet Lumileds Holding B.V. All rights reserved.
 Illumination LUXEON TX Extreme efficacy and best performance with compatibility to LUXEON T LUXEON TX is designed to deliver high efficacy with high flux density to enable tight beam control in directional
Illumination LUXEON TX Extreme efficacy and best performance with compatibility to LUXEON T LUXEON TX is designed to deliver high efficacy with high flux density to enable tight beam control in directional
Prüf-, Überwachungs- und Zertifizierungsgemeinschaft
 rüf-, berwachungs- und ertifizierungsgemeinschaft Construction roducts Regulation Berlin, 17 th July 2015 Test Certificate No. 0913-2015-02 regarding the suitability of the RetroTek-M Mobile avement Retroreflectometer
rüf-, berwachungs- und ertifizierungsgemeinschaft Construction roducts Regulation Berlin, 17 th July 2015 Test Certificate No. 0913-2015-02 regarding the suitability of the RetroTek-M Mobile avement Retroreflectometer
HONOURTEK Delux Array Series HRA0303 Preliminary
 HONOURTEK Delux Array Series HRA0303 Preliminary Product Data Sheet HRA0303 Product Introduction The Delux Series LED Array products deliver high quality light with Delux lighting-class reliability. This
HONOURTEK Delux Array Series HRA0303 Preliminary Product Data Sheet HRA0303 Product Introduction The Delux Series LED Array products deliver high quality light with Delux lighting-class reliability. This
Book 14 Edition 1.1 March Socketable Flat LED Module and LED Light Engine
 Book 14 Edition 1.1 March 2017 Socketable Flat LED Module and LED Light Engine Book 14 Summary (informative) Background The Zhaga Consortium is a global lighting-industry organization that aims to standardize
Book 14 Edition 1.1 March 2017 Socketable Flat LED Module and LED Light Engine Book 14 Summary (informative) Background The Zhaga Consortium is a global lighting-industry organization that aims to standardize
Brewster's angle (3)
 Aim: Subjects: Diagram: To investigate the reflection and transmission of p- and s-polarized light at different angles of incidence at the surface of an acrylic block. Also the critical angle is shown.
Aim: Subjects: Diagram: To investigate the reflection and transmission of p- and s-polarized light at different angles of incidence at the surface of an acrylic block. Also the critical angle is shown.
E/ECE/324/Rev.2/Add.127/Amend.4 E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.2/Add.127/Amend.4
 9 November 2015 Agreement oncerning the Adoption of Uniform Technical Prescriptions for Wheeled Vehicles, Equipment and Parts which can be Fitted and/or be Used on Wheeled Vehicles and the onditions for
9 November 2015 Agreement oncerning the Adoption of Uniform Technical Prescriptions for Wheeled Vehicles, Equipment and Parts which can be Fitted and/or be Used on Wheeled Vehicles and the onditions for
Satellite Type Estination from Ground-based Photometric Observation
 Satellite Type Estination from Ground-based Photometric Observation Takao Endo, HItomi Ono, Jiro Suzuki and Toshiyuki Ando Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Information Technology R&D Center Takashi Takanezawa
Satellite Type Estination from Ground-based Photometric Observation Takao Endo, HItomi Ono, Jiro Suzuki and Toshiyuki Ando Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Information Technology R&D Center Takashi Takanezawa
Stereoscopic Programmable Automotive Headlights for Improved Safety Road
 Stereoscopic Programmable Automotive Headlights for Improved Safety Road Project ID: 30 Srinivasa Narasimhan (PI), Associate Professor Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0389-1921
Stereoscopic Programmable Automotive Headlights for Improved Safety Road Project ID: 30 Srinivasa Narasimhan (PI), Associate Professor Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0389-1921
ISOFOOTCANDLE LINES OF HORIZONTAL ILLUMINATION
 Transverse Distance in Units of Mounting Heights Street Side House Side 2 1 0 1 1 5 2 ISOFOOTCANDLE LINES OF HORIZONTAL ILLUMINATION Values based on 8 foot mounting height. 7 3/4 1 3/4 3 1/8.02 0 3 1/2.01.005
Transverse Distance in Units of Mounting Heights Street Side House Side 2 1 0 1 1 5 2 ISOFOOTCANDLE LINES OF HORIZONTAL ILLUMINATION Values based on 8 foot mounting height. 7 3/4 1 3/4 3 1/8.02 0 3 1/2.01.005
GA A22722 CENTRAL THOMSON SCATTERING UPGRADE ON DIII D
 GA A22722 CENTRAL THOMSON SCATTERING UPGRADE ON DIII D by D.G. NILSON, T.N. CARLSTROM, C.L. HSIEH, B.W. STALLARD, and R.E. STOCKDALE NOVEMBER 1997 DISCLAIMER This report was prepared as an account of work
GA A22722 CENTRAL THOMSON SCATTERING UPGRADE ON DIII D by D.G. NILSON, T.N. CARLSTROM, C.L. HSIEH, B.W. STALLARD, and R.E. STOCKDALE NOVEMBER 1997 DISCLAIMER This report was prepared as an account of work
Transvision: a Light Transmission Measurement System for Greenhouse Covering Materials
 Transvision: a Light Transmission Measurement System for Greenhouse Covering Materials G.L.A.M. Swinkels Wageningen UR Greenhouse Horticulture Wageningen The Netherlands Keywords: hemispherical, light
Transvision: a Light Transmission Measurement System for Greenhouse Covering Materials G.L.A.M. Swinkels Wageningen UR Greenhouse Horticulture Wageningen The Netherlands Keywords: hemispherical, light
LED Retrofit. Fast-track proposal and feedback. W. Schlager Karlsruhe, 23-July-2015
 LED Retrofit Fast-track proposal and feedback W. Schlager Karlsruhe, 23-July-2015 Introduction = Motivation ECE R37-compliant light source ECE compliant device True LED retrofit Pseudo non-approved LED
LED Retrofit Fast-track proposal and feedback W. Schlager Karlsruhe, 23-July-2015 Introduction = Motivation ECE R37-compliant light source ECE compliant device True LED retrofit Pseudo non-approved LED
Test Report No.: GZHL HM Date: Aug 08, 2016 Page 1 of 10
 Test Report No.: GZHL1607032559HM Date: Aug 08, 2016 Page 1 of 10 ZHEJIANG BIO INDUSTRY&TRADE CO.,LTD NUM 1269,BADA ROAD,QIUBIN INDUSTRY PARK,JINHUA,CITY,ZHEJIANG PTOVINCE,CHINA. The following sample(s)
Test Report No.: GZHL1607032559HM Date: Aug 08, 2016 Page 1 of 10 ZHEJIANG BIO INDUSTRY&TRADE CO.,LTD NUM 1269,BADA ROAD,QIUBIN INDUSTRY PARK,JINHUA,CITY,ZHEJIANG PTOVINCE,CHINA. The following sample(s)
L ight color influence on obstacle recognition in road lighting. 1. Introduction
 Computer Applications in Electrical Engineering L ight color influence on obstacle recognition in road lighting Małgorzata Górczewska, Sandra Mroczkowska, Przemysław Skrzypczak Poznań University of Technology
Computer Applications in Electrical Engineering L ight color influence on obstacle recognition in road lighting Małgorzata Górczewska, Sandra Mroczkowska, Przemysław Skrzypczak Poznań University of Technology
Fundamentals of light
 Fundamentals of light CHAPTER 1 Introduction Environmental issues Limited resources. Consumption. Sustainability Environmental damage will result in environmental changes (climate change, global warming,
Fundamentals of light CHAPTER 1 Introduction Environmental issues Limited resources. Consumption. Sustainability Environmental damage will result in environmental changes (climate change, global warming,
Fundamentals of light
 Fundamentals of light CHAPTER 1 Introduction Environmental issues Limited resources. Consumption. Sustainability Environmental damage will result in environmental changes (climate change, global warming,
Fundamentals of light CHAPTER 1 Introduction Environmental issues Limited resources. Consumption. Sustainability Environmental damage will result in environmental changes (climate change, global warming,
Applications Automotive Exterior Lighting Electronic Signs and Signals
 Super Flux LEDs Technical Data HP SunPower Series HPWA-MH HPWT-RH HPWA-DH HPWT-MH HPWA-ML HPWT-DH HPWA-DL HPWT-BH HPWT-RD HPWT-RL HPWT-MD HPWT-ML HPWT-DD HPWT-DL HPWT-BD HPWT-BL Benefits Fewer LEDs Required
Super Flux LEDs Technical Data HP SunPower Series HPWA-MH HPWT-RH HPWA-DH HPWT-MH HPWA-ML HPWT-DH HPWA-DL HPWT-BH HPWT-RD HPWT-RL HPWT-MD HPWT-ML HPWT-DD HPWT-DL HPWT-BD HPWT-BL Benefits Fewer LEDs Required
Calibrating the Thermal Camera
 1 of 5 4/19/2012 5:33 AM from photonics.com: 12/01/2009 http://www.photonics.com/article.aspx?aid=40679 Calibrating the Thermal Camera As thermal cameras gain ground in the commercial market, testing becomes
1 of 5 4/19/2012 5:33 AM from photonics.com: 12/01/2009 http://www.photonics.com/article.aspx?aid=40679 Calibrating the Thermal Camera As thermal cameras gain ground in the commercial market, testing becomes
Test Report No.: GZHL HM-01 Date: Aug 16, 2016 Page 1 of 10
 Test Report No.: GZHL1608034628HM-01 Date: Aug 16, 2016 Page 1 of 10 ZHEJIANG BIO INDUSTRY&TRADE CO.,LTD NUM 1269,BADA ROAD,QIUBIN INDUSTRY PARK,JINHUA,CITY,ZHEJIANG PTOVINCE,CHINA. The following sample(s)
Test Report No.: GZHL1608034628HM-01 Date: Aug 16, 2016 Page 1 of 10 ZHEJIANG BIO INDUSTRY&TRADE CO.,LTD NUM 1269,BADA ROAD,QIUBIN INDUSTRY PARK,JINHUA,CITY,ZHEJIANG PTOVINCE,CHINA. The following sample(s)
Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report
 Report Number: Model: PL07611-001A BXSPR-HO-HT-3ME-60W-57K-UL Date: 04/08/2016 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report Prepared For: Christopher
Report Number: Model: PL07611-001A BXSPR-HO-HT-3ME-60W-57K-UL Date: 04/08/2016 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report Prepared For: Christopher
PREDICTION OF HIGH TEMPERATURE GREASE LIFE USING A DECOMPOSITION KINETIC MODEL
 PREDICTION OF HIGH TEMPERATURE GREASE LIFE USING A DECOMPOSITION KINETIC MODEL In-Sik Rhee, Ph.D., U.S. Army Tank-Automotive Research, Development and Engineering Center, Warren, MI, 48397-5000 76th NLGI
PREDICTION OF HIGH TEMPERATURE GREASE LIFE USING A DECOMPOSITION KINETIC MODEL In-Sik Rhee, Ph.D., U.S. Army Tank-Automotive Research, Development and Engineering Center, Warren, MI, 48397-5000 76th NLGI
Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report
 Report Number: Model: PL07609-001B BXSPR-HO-HT-3ME-60W-30K-UL Date: 03/28/2016 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report Prepared For: Christopher
Report Number: Model: PL07609-001B BXSPR-HO-HT-3ME-60W-30K-UL Date: 03/28/2016 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report Prepared For: Christopher
HONOURTEK Delux Array Series HRA0407 Preliminary
 Copyright 2018 HONOURTEK,INC.ALL RIGH TS RESERVED HONOURTEK Delux Array Series HRA0407 Preliminary Product Data Sheet HRA0407 Product Introduction The Delux Series LED Array products deliver high quality
Copyright 2018 HONOURTEK,INC.ALL RIGH TS RESERVED HONOURTEK Delux Array Series HRA0407 Preliminary Product Data Sheet HRA0407 Product Introduction The Delux Series LED Array products deliver high quality
High Intensity LED, ø 5 mm Untinted Non-Diffused
 High Intensity LED, ø 5 mm Untinted Non-Diffused Color Type Technology Angle of Half Intensity ± TLHK5.. AlInGaP on GaAs 9 Yellow TLHE5.. AlInGaP on GaAs 9 TLHG5.. GaP on GaP 9 Pure green TLHP5.. GaP on
High Intensity LED, ø 5 mm Untinted Non-Diffused Color Type Technology Angle of Half Intensity ± TLHK5.. AlInGaP on GaAs 9 Yellow TLHE5.. AlInGaP on GaAs 9 TLHG5.. GaP on GaP 9 Pure green TLHP5.. GaP on
Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report
 Report Number: Model: PL07860-001B BXSPR-HO-xx-5SH-60W-40K-UL Date: 03/28/2016 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report Prepared For: Christopher
Report Number: Model: PL07860-001B BXSPR-HO-xx-5SH-60W-40K-UL Date: 03/28/2016 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report Prepared For: Christopher
TLCW5100. Ultrabright White LED, 5 mm Untinted Non-Diffused VISHAY. Vishay Semiconductors
 Ultrabright White LED, 5 mm Untinted Non-Diffused Description The series is a clear, non diffused 5 mm LED for high end applications where supreme luminous intensity required. These lamps with clear untinted
Ultrabright White LED, 5 mm Untinted Non-Diffused Description The series is a clear, non diffused 5 mm LED for high end applications where supreme luminous intensity required. These lamps with clear untinted
Lednium Series Optimal X (10-watts,120 Viewing Angle)
 (10-watts,120 Viewing Angle) Revolutionary 3-dimensional packaged LED source Robust energy-efficient design with long operating life Low thermal resistance (2.5 C/W) Exceptional spatial uniformity Available
(10-watts,120 Viewing Angle) Revolutionary 3-dimensional packaged LED source Robust energy-efficient design with long operating life Low thermal resistance (2.5 C/W) Exceptional spatial uniformity Available
National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program
 SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Sapphire Technical Solutions, L.L.C. 10230 Rodney St. Pineville, NC 28134 Mr. Ron Wathan Phone: 704-561-3100 x106 Fax: 866-829-1502 E-mail: rwathan@sapphirests.com
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Sapphire Technical Solutions, L.L.C. 10230 Rodney St. Pineville, NC 28134 Mr. Ron Wathan Phone: 704-561-3100 x106 Fax: 866-829-1502 E-mail: rwathan@sapphirests.com
ASSESSMENT OF THE LATEST PROPOSAL BY THE NETHERLANDS AS PRESENTED DURING THE LAST 66 th SESSION OF GRB
 Transmitted by the expert from ETRTO Informal document GRB-67-08 (67th GRB, 24-26 January 2018, agenda item 6) ASSESSMENT OF THE LATEST PROPOSAL BY THE NETHERLANDS AS PRESENTED DURING THE LAST 66 th SESSION
Transmitted by the expert from ETRTO Informal document GRB-67-08 (67th GRB, 24-26 January 2018, agenda item 6) ASSESSMENT OF THE LATEST PROPOSAL BY THE NETHERLANDS AS PRESENTED DURING THE LAST 66 th SESSION
Basic Optical Concepts. Oliver Dross, LPI Europe
 Basic Optical Concepts Oliver Dross, LPI Europe 1 Refraction- Snell's Law Snell s Law: Sin( φi ) Sin( φ ) f = n n f i n i Media Boundary φ i n f φ φ f angle of exitance 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 internal
Basic Optical Concepts Oliver Dross, LPI Europe 1 Refraction- Snell's Law Snell s Law: Sin( φi ) Sin( φ ) f = n n f i n i Media Boundary φ i n f φ φ f angle of exitance 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 internal
Two-Dimensional simulation of thermal blooming effects in ring pattern laser beam propagating into absorbing CO2 gas
 Two-Dimensional simulation of thermal blooming effects in ring pattern laser beam propagating into absorbing CO gas M. H. Mahdieh 1, and B. Lotfi Department of Physics, Iran University of Science and Technology,
Two-Dimensional simulation of thermal blooming effects in ring pattern laser beam propagating into absorbing CO gas M. H. Mahdieh 1, and B. Lotfi Department of Physics, Iran University of Science and Technology,
Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report
 Report Number: Model: PL08270-001A BXSPR-HO-HT-3ME-60W-57K-UL w/ XA-SPR3BLS Date: 05/07/2016 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report Prepared
Report Number: Model: PL08270-001A BXSPR-HO-HT-3ME-60W-57K-UL w/ XA-SPR3BLS Date: 05/07/2016 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report Prepared
Indoor Testing of Solar Systems: A Solar Simulator for Multidisciplinary Research on Solar Technologies
 A publication of VOL. 39, 2014 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
A publication of VOL. 39, 2014 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
Test report of IES LM Approved Method: Electrical and Photometric
 NVLAP LAB CODE 600102-0 Test report of IES LM-79-08 Approved Method: Electrical and Photometric Measurements of Solid-State Lighting Products Date of issue 2016-05-17 Version 1.0 Total pages 16 Applicant:
NVLAP LAB CODE 600102-0 Test report of IES LM-79-08 Approved Method: Electrical and Photometric Measurements of Solid-State Lighting Products Date of issue 2016-05-17 Version 1.0 Total pages 16 Applicant:
FUNDAMENTAL STUDIES OF THE CATALYTIC IGNITION PROCESS
 FUNDAMENTAL STUDIES OF THE CATALYTIC IGNITION PROCESS Final Report KLK411 N08-03 National Institute for Advanced Transportation Technology University of Idaho Robert Lounsbury; Katrina Leichliter; and
FUNDAMENTAL STUDIES OF THE CATALYTIC IGNITION PROCESS Final Report KLK411 N08-03 National Institute for Advanced Transportation Technology University of Idaho Robert Lounsbury; Katrina Leichliter; and
Product family data sheet
 Cree XLamp XR-C LEDs Product family data sheet CLD-DS1 Rev 12 Product Description FEATURES Table of contents www.cree.com/xlamp The XLamp XR-C LED gives lighting designers the flexibility and performance
Cree XLamp XR-C LEDs Product family data sheet CLD-DS1 Rev 12 Product Description FEATURES Table of contents www.cree.com/xlamp The XLamp XR-C LED gives lighting designers the flexibility and performance
Texas Transportation Institute The Texas A&M University System College Station, Texas
 1. Report No. FHWA/TX-03/4150-1 4. Title and Subtitle ANALYSIS OF TXDOT THICKNESS MEASUREMENT PROCEDURES FOR THERMOPLASTIC PAVEMENT MARKINGS Technical Report Documentation Page 2. Government Accession
1. Report No. FHWA/TX-03/4150-1 4. Title and Subtitle ANALYSIS OF TXDOT THICKNESS MEASUREMENT PROCEDURES FOR THERMOPLASTIC PAVEMENT MARKINGS Technical Report Documentation Page 2. Government Accession
Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report
 NVLAP Lab Code 500089-0 Report Number: Model: PL10023-003B ARE-EDG-2MB-xx-06-E-UL-xx-525-xxxx-40K Date: 02/28/2017 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation
NVLAP Lab Code 500089-0 Report Number: Model: PL10023-003B ARE-EDG-2MB-xx-06-E-UL-xx-525-xxxx-40K Date: 02/28/2017 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation
Computer Aided Modeling of Soil Mix Designs to Predict Characteristics and Properties of Stabilized Road Bases
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Final Reports & Technical Briefs from Mid-America Transportation Center Mid-America Transportation Center 2009 Computer
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Final Reports & Technical Briefs from Mid-America Transportation Center Mid-America Transportation Center 2009 Computer
Photobiological Safety of Luminaires: Refining the New Approach
 Photobiological Safety of Luminaires: Refining the New Approach Leslie Lyons Bentham Instruments Limited Reading, UK llyons@bentham.co.uk We are all familiar with the visual characteristics of lighting
Photobiological Safety of Luminaires: Refining the New Approach Leslie Lyons Bentham Instruments Limited Reading, UK llyons@bentham.co.uk We are all familiar with the visual characteristics of lighting
LUXEON Z. Industry s smallest high power emitter for use in close-packed applications requiring an undomed solution ILLUMINATION
 ILLUMINATION LUXEON Z Industry s smallest high power emitter for use in close-packed applications requiring an undomed solution LUXEON Z is a high power 1.3mm x 1.7mm LED that enables never before seen
ILLUMINATION LUXEON Z Industry s smallest high power emitter for use in close-packed applications requiring an undomed solution LUXEON Z is a high power 1.3mm x 1.7mm LED that enables never before seen
: Imaging Systems Laboratory II. Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 2002
 151-232: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 22 Abstract. In this lab, we will investigate linear and circular polarization of light. Linearly polarized
151-232: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 22 Abstract. In this lab, we will investigate linear and circular polarization of light. Linearly polarized
A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth.
 Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report
 Report Number: Model: PL03375-001 CPY250-A-xx-D-C-UL-xx-40K or Date: 03/24/2014 BXCCAxD04-UW7 or XCCAxD04-UW7 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation
Report Number: Model: PL03375-001 CPY250-A-xx-D-C-UL-xx-40K or Date: 03/24/2014 BXCCAxD04-UW7 or XCCAxD04-UW7 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation
TEST REPORT IES LM For Signlite Opto-electronics Co.,Ltd.
 NVLAP LAB CODE:201045-0 TEST REPORT IES LM-79-08 For Signlite Opto-electronics Co.,Ltd. 6F, Weixing industry park, No.268-3 Baoshi East Road, Shiyan subdistrict, Bao an District, Shenzhe, China. Report
NVLAP LAB CODE:201045-0 TEST REPORT IES LM-79-08 For Signlite Opto-electronics Co.,Ltd. 6F, Weixing industry park, No.268-3 Baoshi East Road, Shiyan subdistrict, Bao an District, Shenzhe, China. Report
SYSTEMATIC EVALUATION OF RUN OFF ROAD CRASH LOCATIONS IN WISCONSIN FINAL REPORT
 SYSTEMATIC EVALUATION OF RUN OFF ROAD CRASH LOCATIONS IN WISCONSIN FINAL REPORT DECEMBER 2004 DISCLAIMER This research was funded by the Wisconsin Department of Transportation. The contents of this report
SYSTEMATIC EVALUATION OF RUN OFF ROAD CRASH LOCATIONS IN WISCONSIN FINAL REPORT DECEMBER 2004 DISCLAIMER This research was funded by the Wisconsin Department of Transportation. The contents of this report
Cree XLamp XR-C LEDs. CLD-DS10 Rev 12H. Product family data sheet
 Cree XLamp XR-C LEDs Product family data sheet CLD-DS1 Rev 12H Product Description The XLamp XR-C LED gives lighting designers the flexibility and performance to create the next generation of LED lighting
Cree XLamp XR-C LEDs Product family data sheet CLD-DS1 Rev 12H Product Description The XLamp XR-C LED gives lighting designers the flexibility and performance to create the next generation of LED lighting
A Driving Simulation Based Study on the Effects of. Road Marking Luminance Contrast on Driving Safety. Yong Cao, Jyh-Hone Wang
 A Driving Simulation Based Study on the Effects of Road Marking Luminance Contrast on Driving Safety Yong Cao, Jyh-Hone Wang Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering University of Rhode Island,
A Driving Simulation Based Study on the Effects of Road Marking Luminance Contrast on Driving Safety Yong Cao, Jyh-Hone Wang Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering University of Rhode Island,
Name Date Class _. Please turn to the section titled The Nature of Light.
 Please turn to the section titled The Nature of Light. In this section, you will learn that light has both wave and particle characteristics. You will also see that visible light is just part of a wide
Please turn to the section titled The Nature of Light. In this section, you will learn that light has both wave and particle characteristics. You will also see that visible light is just part of a wide
Cree Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (CESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report
 Report Number: Model: PL04023-001 CXBAxxM40K8 CXBA16N Date: 7/27/2014 Cree Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (CESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report Prepared For: Jonathan Vollers Cree,
Report Number: Model: PL04023-001 CXBAxxM40K8 CXBA16N Date: 7/27/2014 Cree Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (CESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report Prepared For: Jonathan Vollers Cree,
LUXEON Flash. power light source. Introduction
 Technical Datasheet DS49 power light source LUXEON Flash Introduction LUXEON Flash is a family of ultra-compact light sources specifically designed and tested for use as a camera flash in space-constrained,
Technical Datasheet DS49 power light source LUXEON Flash Introduction LUXEON Flash is a family of ultra-compact light sources specifically designed and tested for use as a camera flash in space-constrained,
Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report
 Report Number: Model: RESTL-2013-0012 E-HL6S11CSZ Date: 11/08/2013 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report Prepared For: Joshua Krohn Cree,
Report Number: Model: RESTL-2013-0012 E-HL6S11CSZ Date: 11/08/2013 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report Prepared For: Joshua Krohn Cree,
Photometric Report. 42 Partners Limited 21 Woden Road Wolverhampton WV10 0AU UK
 42 Partners Limited 21 Woden Road Wolverhampton WV10 0AU UK www.42partners.com 42@42partners.com T +44 (0) 1902 453650 F +44 (0) 8721 153400 Registered in England: Company Number 3021552 VAT Registration
42 Partners Limited 21 Woden Road Wolverhampton WV10 0AU UK www.42partners.com 42@42partners.com T +44 (0) 1902 453650 F +44 (0) 8721 153400 Registered in England: Company Number 3021552 VAT Registration
Flocculation, Optics and Turbulence in the Community Sediment Transport Model System: Application of OASIS Results
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Flocculation, Optics and Turbulence in the Community Sediment Transport Model System: Application of OASIS Results Emmanuel
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Flocculation, Optics and Turbulence in the Community Sediment Transport Model System: Application of OASIS Results Emmanuel
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION SPECTRAFLOW ON LINE ANALYZER for BELT CONVEYOR APPLICATION
 TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION SPECTRAFLOW ON LINE ANALYZER for BELT CONVEYOR APPLICATION TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION SPECTRAFLOW ON LINE ANALYZER FOR BELT CONVEYOR CONTENTS 1. SpectraFlow Technical Description...
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION SPECTRAFLOW ON LINE ANALYZER for BELT CONVEYOR APPLICATION TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION SPECTRAFLOW ON LINE ANALYZER FOR BELT CONVEYOR CONTENTS 1. SpectraFlow Technical Description...
Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report
 Report Number: Model: PL06411-001A CPY250-A-xx-F-D-UL-40K-xxxx or BXCCAxA17-Ux7xxxx Date: 07/17/2015 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report
Report Number: Model: PL06411-001A CPY250-A-xx-F-D-UL-40K-xxxx or BXCCAxA17-Ux7xxxx Date: 07/17/2015 Cree Racine Engineering Services Testing Laboratory (RESTL) Photometric Testing and Evaluation Report
TEST REPORT IEC and/or EN Photobiological safety of lamps and lamp systems
 Test Report issued under the responsibility of: TEST REORT and/or EN 62471 hotobiological safety of lamps and lamp systems Report Reference No.... : GZES160200176431 Tested by (name + signature)... : Jack
Test Report issued under the responsibility of: TEST REORT and/or EN 62471 hotobiological safety of lamps and lamp systems Report Reference No.... : GZES160200176431 Tested by (name + signature)... : Jack
PoS(PhotoDet 2012)010
 Study on Large Area Photomultipliers with Super Bialkali Photocathode 1 Sebastiano Aiello Domenico Lo Presti, Dipartimento di Fisica ed Astronomia di Catania Valentina Giordano Fabio Longhitano Cristina
Study on Large Area Photomultipliers with Super Bialkali Photocathode 1 Sebastiano Aiello Domenico Lo Presti, Dipartimento di Fisica ed Astronomia di Catania Valentina Giordano Fabio Longhitano Cristina
OPERATIONS SUPPLEMENT FOR THE COMPARISON AUTOCOLLIMATOR, D600
 STANFORD UNIVERSITY W.W. HANSEN EXPERIMENTAL PHYSICS LABORATORY GRAVITY PROBE B, RELATIVITY GYROSCOPE EXPERIMENT STANFORD, CALIFORNIA 94305-4085 P0354 SU/GP-B P0354 OPERATIONS SUPPLEMENT FOR THE COMPARISON
STANFORD UNIVERSITY W.W. HANSEN EXPERIMENTAL PHYSICS LABORATORY GRAVITY PROBE B, RELATIVITY GYROSCOPE EXPERIMENT STANFORD, CALIFORNIA 94305-4085 P0354 SU/GP-B P0354 OPERATIONS SUPPLEMENT FOR THE COMPARISON
Module Optical Analyzer: Identification Of Defects On The Production Line
 Module Optical Analyzer: Identification Of Defects On The Production Line Rebeca Herrero, Stephen Askins, Ignacio Antón, Gabriel Sala, Kenji Araki Hirokazu Nagai Abstract. The usefulness of the module
Module Optical Analyzer: Identification Of Defects On The Production Line Rebeca Herrero, Stephen Askins, Ignacio Antón, Gabriel Sala, Kenji Araki Hirokazu Nagai Abstract. The usefulness of the module
ISOFOOTCANDLE LINES OF HORIZONTAL ILLUMINATION
 2.02.05 ISOFOOTCANDLE LINES OF HORIZONTAL ILLUMINATION Values based on 12 foot mounting height..01.005.002 REPORT NUMBER: RAB02670 ISSUE DATE: 11/08/16 PAGE: 1 OF 9 DATE SAMPLE TESTED: 11/08/16 CATALOG
2.02.05 ISOFOOTCANDLE LINES OF HORIZONTAL ILLUMINATION Values based on 12 foot mounting height..01.005.002 REPORT NUMBER: RAB02670 ISSUE DATE: 11/08/16 PAGE: 1 OF 9 DATE SAMPLE TESTED: 11/08/16 CATALOG
HYDROBETA: A NEW INSTRUMENT FOR MEASURING IN-SITU PROFILES OF THE VOLUME SCATTERING FUNCTION FROM 10 TO 170 DEGREES
 HYDROBETA: A NEW INSTRUMENT FOR MEASURING IN-SITU PROFILES OF THE VOLUME SCATTERING FUNCTION FROM 10 TO 170 DEGREES David R. Dana, Robert A. Maffione Hydro-Optics, Biology and Instrumentation Laboratories,
HYDROBETA: A NEW INSTRUMENT FOR MEASURING IN-SITU PROFILES OF THE VOLUME SCATTERING FUNCTION FROM 10 TO 170 DEGREES David R. Dana, Robert A. Maffione Hydro-Optics, Biology and Instrumentation Laboratories,
Fundamental Concepts of Radiometry p. 1 Electromagnetic Radiation p. 1 Terminology Conventions p. 3 Wavelength Notations and Solid Angle p.
 Preface p. xiii Fundamental Concepts of Radiometry p. 1 Electromagnetic Radiation p. 1 Terminology Conventions p. 3 Wavelength Notations and Solid Angle p. 4 Fundamental Definitions p. 7 Lambertian Radiators
Preface p. xiii Fundamental Concepts of Radiometry p. 1 Electromagnetic Radiation p. 1 Terminology Conventions p. 3 Wavelength Notations and Solid Angle p. 4 Fundamental Definitions p. 7 Lambertian Radiators
AERODROMES PANEL (AP) VISUAL AIDS WORKING GROUP (VAWG) FIFTH MEETING. Montréal, Canada, 25 to 27 June 2008
 VAWG/5-DP/18 25/6/08 AERODROMES PANEL (AP) VISUAL AIDS WORKING GROUP (VAWG) FIFTH MEETING Montréal, Canada, 25 to 27 June 2008 Agenda Item 11: Any other business NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR HIGH PRECISION PAPI
VAWG/5-DP/18 25/6/08 AERODROMES PANEL (AP) VISUAL AIDS WORKING GROUP (VAWG) FIFTH MEETING Montréal, Canada, 25 to 27 June 2008 Agenda Item 11: Any other business NEW TECHNOLOGIES FOR HIGH PRECISION PAPI
Order No. G Date: September 8, 2010 REPORT NO CRT-001 TEST OF SMF/PAPI SYSTEM RENDERED TO
 REPORT 3933 US ROUTE 11 CORTLAND, NEW YORK 13045 Order No. G100147381 Date: September 8, 2010 INTRODUCTION REPORT NO. 100147381CRT-001 TEST OF SMF/PAPI SYSTEM RENDERED TO ARGOS INGEGNERIA SpA VIA TIBURTINA,
REPORT 3933 US ROUTE 11 CORTLAND, NEW YORK 13045 Order No. G100147381 Date: September 8, 2010 INTRODUCTION REPORT NO. 100147381CRT-001 TEST OF SMF/PAPI SYSTEM RENDERED TO ARGOS INGEGNERIA SpA VIA TIBURTINA,
