HUNTING CORESHINE WITH SPITZER: FROM GRAIN GROWTH TO PLANET FORMATION
|
|
|
- Emmeline Cole
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HUNTING CORESHINE WITH SPITZER: FROM GRAIN GROWTH TO PLANET FORMATION Roberta Paladini & The Hunting Coreshine Team 1
2 Outline of the Talk CORESHINE EFFECT: brief recap SPITZER CYCLE 8/9 SURVEY (PI. ): rationale & observations PRELIMINARY RESULTS FROM CYCLE 8 /9: à Andersen et al. 13 à Lefevre et al. 14 à Steinacker et al. 15 2
3 The Team Roberta Paladini (P.-I.) IPAC/Caltech (USA) Laurent Pagani Observatoire de Paris (France) Jurgen Steinacker IPAG/Grenoble (France) Sean Carey IPAC/Caltech (USA) Mika Juvela University of Helsinki (Finland) Charlene Lefevre* Observatoire de Paris (France) Morten Andersen* IPAG/Grenoble (France) Veli-Matti Pelkonen FINCA (Finland) Alberto Noriega-Crespo IPAC/Caltech (USA) Aurore Bacmann IPAG/Grenoble (France) Isabelle Ristorcelli IRAP/Toulouse (France) Ludovic Montier IRAP/Toulouse (France) Doug Marshall CEA (France) * Cycle 9 only 3
4 Coreshine Effect: what is it? Coreshine (Pagani et al. 2010, Steinacker et al. 2010): scattering of MIR light by micron-size (> 0.25 µm) dust grains Cloudshine (Lehtinen & Mattila 1996; Foster & Goodman 2006): scattering of NIR light by micron-size (> 0.25 µm) dust grains 3.6 µm 4.5 µm 8 µm L 183 d ~ 110 pc M ~ 80 M sol Pagani et al. 2004, Steinacker et al
5 Coreshine Effect: why do we care? ISM PROTOPLANETARY SYSTEMS e.g. MRN 1977: n(a) ~ a -3/5 For silicates: a max ~ 0.25 µm likely not by collision probably from secking (if enough turbulent velocity is provided) a ~ from a few µm to ~1 mm: µm silicate feature β from sub-mm/mm observations 5
6 No dust reprocessing after cloud collapse Ricci et al
7 Spitzer Cycle 8 Survey u The survey consists in hr of observing time with Warm IRAC (3.6 µm, 4.5 µm) u It is the largest Galactic program of Cycle 8 u Observations were executed between August 11 and May 12 u The survey reaches a sensitivity of MJy/sr in both ch1 and ch2, with a substantial improvement with respect to archival data (e.g. 3 X c2d and Gould Belt Survey, 10 X WISE w1 and w2) 7
8 Cycle 8 Survey: Rationale Ø Is grain growth universal in cold, dense environments? Ø What are the observational biases? Ø What are the dust models that are able to reconcile the observations? 8
9 Cycle 8 Survey: Observations Sample of 90 sources from Planck Early Release Cold Clumps Catalog (ECC) Planck ECC: 915 cold clumps T D < 14 K S/N > 15 distance for ~50% sources (mostly < 1 kpc) Planck CollaboraEon (2011r) Monte Carlo source selection: longitude latitude mass 9
10 Cycle 8 Detections Coreshine is detected in ~ 50% of the sources (50/90) Very high # of new detections (86%) 3.6 µm 4.5 µm 4.5 µm 8 µm 4.5 µm 8 µm ecc469 ecc µm 3.6 µm 8 µm 4.5 µm 8 µm 3.6 µm ecc806 ecc µm 4.5 µm 8 µm ecc815 R. Paladini ExEP Science Briefing May 23rd
11 Spitzer Cycle 9 Survey u The survey consists in 42.5 hr of observing time with Warm IRAC (3.6 µm, 4.5 µm) u Observations were executed between January and June 13 u The survey reaches a sensitivity of MJy/sr in both ch1 and ch2 11
12 Cycle 9 Survey: Rationale d ~ 150 pc M ~ 1 M sol Model by J. Steinecker 12
13 Cycle 9 Survey: Observations 10 sources selected from all known coreshine cases showing no or weak coreshine emission at 4.5 µm all the selected sources had been already observed during either the Spitzer cryogenic (e.g c2d, etc.) or the warm mission L 1512 d ~ 140 pc M ~ 2.4 M sol 3.6 µm 4.5 µm 8 µm 13
14 Cycle 9 Detections > 70% detections L 1512 d ~ 140 pc M ~ 2.4 M sol 3.6 µm 4.5 µm 8 µm 14
15 Radiative Transfer Modeling (Lefevre et al. 2014, Steinacker et al. 2015) Ø ConEnuum RadiaEve Transfer (CRT) model (Juvela & Padoan 2003; Juvela 2005): Ø Incident ISRF: DIRBE J, K, 3.5 µm, 4.9 µm, 12 µm rescaled to Spitzer IRAC bands Ø Molecular Clump model: inclined 3D ellipsoid + Plummer- like profile: α = 2.5 Ø several dust models (see next slide..) 15
16 Dust Models Ø Is coagulaeon (hence suppression of the smallest grains) required to explain coreshine? Ø Is there a size limit for the size distribueon? Ø Can the size distribueon be different from standard MRN distribueon? Ø What is the role of ice mantles? Ø What is the role of fluffly grains? 16
17 Coreshine Universality and Relation with Environment Ø Some GalacEc regions seem to be favored: Taurus, Perseus, Aquila, Cepheus, Chameleon. Perhaps large grains already exist in the diffuse medium before cloud formaeon, or coagulaeon happens fast aler cloud formaeon and before turbulence dissipaeon Ø Coreshine is a constrast problem: scatered light > background field. Cannot be seen towards GalacEc Plane and GalacEc Center Ø Coreshine increases in the presence of protostars, due to increase of local radiaeon field Cryo + Warm: ~ 200 sources Lefevre et al
18 Grain Growth & Constraints on Dust Models Ø grains larger than 0.25 µm are mandatory Ø Classical compact/bare diffuse medium grains (e.g., WD01) are not able to reproduce coreshine observaeons Ø small grains have no influence in the modelling of coreshine Ø Porosity has no impact on coreshine modelling, while a fractal structure is favored Ø We know grains have ice mantles at A V > 3 mag. However, current models of grains with ice mantles do not explain the observed coreshine 18
19 Future Challenge Ø treating simultaneously: emission, extinction and scattering through 3D RT 19
Galactic Cold Cores. M.Juvela On behalf of the Galactic Cold Cores project
 Galactic Cold Cores M.Juvela On behalf of the Galactic Cold Cores project M. Juvela, I. Ristorcelli (coord.) Desert, Dupac, Giard, Harju, Harrison, Joncas, Jones, Lagache, Lamarre, Laureijs, Lehtinen,
Galactic Cold Cores M.Juvela On behalf of the Galactic Cold Cores project M. Juvela, I. Ristorcelli (coord.) Desert, Dupac, Giard, Harju, Harrison, Joncas, Jones, Lagache, Lamarre, Laureijs, Lehtinen,
Cold Cores of Molecular Clouds. Mika Juvela, Department of physics, University of Helsinki
 Cold Cores of Molecular Clouds Mika Juvela, Department of physics, University of Helsinki Juvela - IAU August 2012 on cold cores On behalfmika of the Planck andxxviii, Herschel projects Content Molecular
Cold Cores of Molecular Clouds Mika Juvela, Department of physics, University of Helsinki Juvela - IAU August 2012 on cold cores On behalfmika of the Planck andxxviii, Herschel projects Content Molecular
Polarization simulations of cloud cores
 Polarization simulations of cloud cores Veli-Matti Pelkonen 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Grain alignment by radiative torques (RATs) 3. Observational evidence for RATs 4. Radiative transfer modelling,
Polarization simulations of cloud cores Veli-Matti Pelkonen 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Grain alignment by radiative torques (RATs) 3. Observational evidence for RATs 4. Radiative transfer modelling,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 22 Jul 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 22 Jul 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 22 Jul 2014](/thumbs/71/66235938.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Coreshine paper Lefevre vfinal c ESO 2014 July 25, 2014 Dust properties inside molecular clouds from coreshine modeling and observations C. Lefèvre 1, L. Pagani
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Coreshine paper Lefevre vfinal c ESO 2014 July 25, 2014 Dust properties inside molecular clouds from coreshine modeling and observations C. Lefèvre 1, L. Pagani
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Aug 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Aug 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 17 Aug 2015](/thumbs/93/117983950.jpg) stronomy & strophysics manuscript no. dot c ESO ugust, Grain size limits derived from.µm and.µm coreshine J. Steinacker,,, M. ndersen, W.-F. Thi, R. Paladini, M. Juvela 7,. Bacmann,, V.-M. Pelkonen 7,8,
stronomy & strophysics manuscript no. dot c ESO ugust, Grain size limits derived from.µm and.µm coreshine J. Steinacker,,, M. ndersen, W.-F. Thi, R. Paladini, M. Juvela 7,. Bacmann,, V.-M. Pelkonen 7,8,
Cold Cores on Planck1,
 Cold Cores on Planck1, 2 and Herschel 1 on behalf of the Planck collaboration M. Juvela, I. Ristorcelli (coord.) Planck Desert, Dupac, Giard, Harju, Harrison, Joncas, Jones, Lagache, Lamarre, Laureijs,
Cold Cores on Planck1, 2 and Herschel 1 on behalf of the Planck collaboration M. Juvela, I. Ristorcelli (coord.) Planck Desert, Dupac, Giard, Harju, Harrison, Joncas, Jones, Lagache, Lamarre, Laureijs,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Feb 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Feb 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Feb 2018](/thumbs/91/106951870.jpg) stronomy & strophysics manuscript no. Near-infrared_scattering_as_a_dust_diagnostic c SO 1 ebruary, 1 Near-infrared scattering as a dust diagnostic Mika Saajasto 1, Mika Juvela 1, and Johanna Malinen 1,
stronomy & strophysics manuscript no. Near-infrared_scattering_as_a_dust_diagnostic c SO 1 ebruary, 1 Near-infrared scattering as a dust diagnostic Mika Saajasto 1, Mika Juvela 1, and Johanna Malinen 1,
Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era. François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale
 Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Motivation Dust emission Dust models Dust life cycle Planck early results Dust polarisation Outline Dust
Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Motivation Dust emission Dust models Dust life cycle Planck early results Dust polarisation Outline Dust
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Feb 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Feb 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Feb 2012](/thumbs/90/102863927.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paperiii astroph c ESO 218 September 9, 218 Galactic cold cores III. General cloud properties M. Juvela 1, I. Ristorcelli 2,3, L. Pagani 4, Y. Doi 6, V.-M. Pelkonen
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paperiii astroph c ESO 218 September 9, 218 Galactic cold cores III. General cloud properties M. Juvela 1, I. Ristorcelli 2,3, L. Pagani 4, Y. Doi 6, V.-M. Pelkonen
Probing the formation mechanism of prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF: First results from Herschel
 Probing the formation mechanism of prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF: First results from Herschel Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Herschel GB survey Ophiuchus 70/250/500 µm composite With: A. Menshchikov,
Probing the formation mechanism of prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF: First results from Herschel Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Herschel GB survey Ophiuchus 70/250/500 µm composite With: A. Menshchikov,
Transition Disk Chemistry in the Eye of ALMA
 COURTESY NASA/JPL-CALTECH Spectroscopy2011 January 16, 2011 Transition Disk Chemistry in the Eye of ALMA Ilse Cleeves Univ. of Michigan ADVISOR: Edwin Bergin Outline I. Transition Disks: Introduction II.
COURTESY NASA/JPL-CALTECH Spectroscopy2011 January 16, 2011 Transition Disk Chemistry in the Eye of ALMA Ilse Cleeves Univ. of Michigan ADVISOR: Edwin Bergin Outline I. Transition Disks: Introduction II.
The Planck Catalogue of Galactic Cold Clumps
 The Planck Catalogue of Galactic Cold Clumps L. Montier on behalf of the Cold Core Project I Overview History of the PGCC 2007: First meeting about the detection method 2009: First internal release with
The Planck Catalogue of Galactic Cold Clumps L. Montier on behalf of the Cold Core Project I Overview History of the PGCC 2007: First meeting about the detection method 2009: First internal release with
Earliest phases of high mass star formation in the Galactic Plane
 Earliest phases of high mass star formation in the Galactic Plane Sarolta Zahorecz Konkoly Observatory PhD student at ELTE, Hungary + at ESO, Germany In collaboration with: Viktor Toth (ELTE) Izaskun Jimenez-Serra
Earliest phases of high mass star formation in the Galactic Plane Sarolta Zahorecz Konkoly Observatory PhD student at ELTE, Hungary + at ESO, Germany In collaboration with: Viktor Toth (ELTE) Izaskun Jimenez-Serra
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2016](/thumbs/75/72558899.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ach cloud core shine I FINAL c ESO 2018 February 7, 2018 Mantle formation, coagulation and the origin of cloud/core shine: I. Modelling dust scattering and absorption
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ach cloud core shine I FINAL c ESO 2018 February 7, 2018 Mantle formation, coagulation and the origin of cloud/core shine: I. Modelling dust scattering and absorption
!From the filamentary structure of the ISM! to prestellar cores to the IMF:!! Results from the Herschel Gould Belt survey!
 !From the filamentary structure of the ISM! to prestellar cores to the IMF:!! Results from the Herschel Gould Belt survey! Philippe André CEA Lab. AIM Paris- Saclay PACS! Part of Orion B! 70/250/500 µm!
!From the filamentary structure of the ISM! to prestellar cores to the IMF:!! Results from the Herschel Gould Belt survey! Philippe André CEA Lab. AIM Paris- Saclay PACS! Part of Orion B! 70/250/500 µm!
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Oct 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Oct 2015](/thumbs/72/66711686.jpg) Draft version October 4, 205 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 04/7/3 SPECTROSCOPIC INFRARED EXTINCTION MAPPING AS A PROBE OF GRAIN GROWTH IN IRDCS Wanggi Lim Depatment of Astronomy, University
Draft version October 4, 205 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 04/7/3 SPECTROSCOPIC INFRARED EXTINCTION MAPPING AS A PROBE OF GRAIN GROWTH IN IRDCS Wanggi Lim Depatment of Astronomy, University
Dust properties in the ionized gas of the Large Magellanic Cloud
 Dust properties in the ionized gas of the Large Magellanic Cloud Déborah Paradis, SSC/CESR Roberta Paladini, SSC Alberto Noriega-Crespo, SSC Guilaine Lagache, IAS Context Detection of dust emission associated
Dust properties in the ionized gas of the Large Magellanic Cloud Déborah Paradis, SSC/CESR Roberta Paladini, SSC Alberto Noriega-Crespo, SSC Guilaine Lagache, IAS Context Detection of dust emission associated
Physics 224 The Interstellar Medium
 Physics 224 The Interstellar Medium Lecture #11: Dust Composition, Photoelectric Heating, Neutral Gas Outline Part I: Dust Heating & Cooling continued Part III: Dust Emission & Photoelectric Heating Part
Physics 224 The Interstellar Medium Lecture #11: Dust Composition, Photoelectric Heating, Neutral Gas Outline Part I: Dust Heating & Cooling continued Part III: Dust Emission & Photoelectric Heating Part
Modeling interactions between a debris disc and planet: which initial conditions?
 Modeling interactions between a debris disc and planet: which initial conditions? Elodie Thilliez @ET_astro Supervisors : Prof Sarah Maddison (Swinburne) Prof Jarrod Hurley (Swinburne) Crédit : NASA/JPL-Caltech
Modeling interactions between a debris disc and planet: which initial conditions? Elodie Thilliez @ET_astro Supervisors : Prof Sarah Maddison (Swinburne) Prof Jarrod Hurley (Swinburne) Crédit : NASA/JPL-Caltech
Star Formation Taste Tests. Alyssa A. Goodman Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics & Initiative for Innovative Computing at Harvard
 Star Formation Taste Tests Alyssa A. Goodman Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics & Initiative for Innovative Computing at Harvard Taste Tests? Taste Tests? We frame this project by analogy. How
Star Formation Taste Tests Alyssa A. Goodman Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics & Initiative for Innovative Computing at Harvard Taste Tests? Taste Tests? We frame this project by analogy. How
Reflections on Modern Work Simulated Zeeman Measurements and Magnetic Equilibrium in Molecular Clouds
 Reflections on Modern Work Simulated Zeeman Measurements and Magnetic Equilibrium in Molecular Clouds Paolo Padoan University of California, San Diego ICREA - University of Barcelona (Spring 2010) Collaborators:
Reflections on Modern Work Simulated Zeeman Measurements and Magnetic Equilibrium in Molecular Clouds Paolo Padoan University of California, San Diego ICREA - University of Barcelona (Spring 2010) Collaborators:
A Radio Jet Drives a Molecular & Atomic Gas Outflow in Multiple Regions within 1 kpc 2 of the Nucleus of IC5063
 A Radio Jet Drives a Molecular & Atomic Gas Outflow in Multiple Regions within 1 kpc 2 of the Nucleus of IC5063 K. M. Dasyra (University of Athens) F. Combes (College de France; Observatoire de Paris)
A Radio Jet Drives a Molecular & Atomic Gas Outflow in Multiple Regions within 1 kpc 2 of the Nucleus of IC5063 K. M. Dasyra (University of Athens) F. Combes (College de France; Observatoire de Paris)
Lecture 26 Clouds, Clumps and Cores. Review of Molecular Clouds
 Lecture 26 Clouds, Clumps and Cores 1. Review of Dense Gas Observations 2. Atomic Hydrogen and GMCs 3. Formation of Molecular Clouds 4. Internal Structure 5. Observing Cores 6. Preliminary Comments on
Lecture 26 Clouds, Clumps and Cores 1. Review of Dense Gas Observations 2. Atomic Hydrogen and GMCs 3. Formation of Molecular Clouds 4. Internal Structure 5. Observing Cores 6. Preliminary Comments on
Astrochemical Models. Eric Herbst Departments of Chemistry and Astronomy University of Virginia
 Astrochemical Models Eric Herbst Departments of Chemistry and Astronomy University of Virginia Chemical Models Gas-phase reactions 1000 s of reactions Grain-surface reactions Abundances, columns, spectra
Astrochemical Models Eric Herbst Departments of Chemistry and Astronomy University of Virginia Chemical Models Gas-phase reactions 1000 s of reactions Grain-surface reactions Abundances, columns, spectra
the Solar Neighborhood
 Click to edit Master title style Star Formation at High A V in the Solar Neighborhood Amanda Heiderman NSF Fellow UVa/NRAO (w/ Neal Evans, UT Austin) Filaments 2014, October, 11, 2014 10/13/2014 1 Click
Click to edit Master title style Star Formation at High A V in the Solar Neighborhood Amanda Heiderman NSF Fellow UVa/NRAO (w/ Neal Evans, UT Austin) Filaments 2014, October, 11, 2014 10/13/2014 1 Click
Interstellar Dust and Extinction
 University of Oxford, Astrophysics November 12, 2007 Outline Extinction Spectral Features Emission Scattering Polarization Grain Models & Evolution Conclusions What and Why? Dust covers a range of compound
University of Oxford, Astrophysics November 12, 2007 Outline Extinction Spectral Features Emission Scattering Polarization Grain Models & Evolution Conclusions What and Why? Dust covers a range of compound
Properties of interstellar filaments as derived from Herschel Gould Belt observations
 Properties of interstellar filaments as derived from Herschel Gould Belt observations Doris Arzoumanian PhD student at CEA Saclay, France with Ph. André, V. Könyves, N. Schneider, N. Peretto, A. Men shchikov,
Properties of interstellar filaments as derived from Herschel Gould Belt observations Doris Arzoumanian PhD student at CEA Saclay, France with Ph. André, V. Könyves, N. Schneider, N. Peretto, A. Men shchikov,
A Far-ultraviolet Fluorescent Molecular Hydrogen Emission Map of the Milky Way Galaxy
 A Far-ultraviolet Fluorescent Molecular Hydrogen Emission Map of the Milky Way Galaxy (The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 231:21 (16pp), 2017 August) November 14, 2017 Young-Soo Jo Young-Soo
A Far-ultraviolet Fluorescent Molecular Hydrogen Emission Map of the Milky Way Galaxy (The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 231:21 (16pp), 2017 August) November 14, 2017 Young-Soo Jo Young-Soo
Astrochemistry (2) Interstellar extinction. Measurement of the reddening
 Measurement of the reddening The reddening of stellar colours casts light on the properties of interstellar dust Astrochemistry (2) Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo The reddening is measured
Measurement of the reddening The reddening of stellar colours casts light on the properties of interstellar dust Astrochemistry (2) Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo The reddening is measured
Dust Polarization. J.Ph. Bernard Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planetologie (IRAP) Toulouse
 Dust Polarization J.Ph. Bernard Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planetologie (IRAP) Toulouse 1 Layout - Dust polarization (Extinction) - Dust polarization (Emission) - Dust polarization observational
Dust Polarization J.Ph. Bernard Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planetologie (IRAP) Toulouse 1 Layout - Dust polarization (Extinction) - Dust polarization (Emission) - Dust polarization observational
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Clicker Question: Clicker Question: What is the expected lifetime for a G2 star (one just like our Sun)?
 How Long do Stars Live (as Main Sequence Stars)? A star on Main Sequence has fusion of H to He in its core. How fast depends on mass of H available and rate of fusion. Mass of H in core depends on mass
How Long do Stars Live (as Main Sequence Stars)? A star on Main Sequence has fusion of H to He in its core. How fast depends on mass of H available and rate of fusion. Mass of H in core depends on mass
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 23 Mar 2003
 Photoelectric heating and [CII] cooling in translucent clouds: results for cloud models based on simulations of compressible MHD turbulence arxiv:astro-ph/0302365v2 23 Mar 2003 M. Juvela Helsinki University
Photoelectric heating and [CII] cooling in translucent clouds: results for cloud models based on simulations of compressible MHD turbulence arxiv:astro-ph/0302365v2 23 Mar 2003 M. Juvela Helsinki University
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Jun 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Jun 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Jun 2012](/thumbs/91/105406239.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. crah c ESO 2018 June 15, 2018 A Corona Australis cloud filament seen in NIR scattered light III. Modelling and comparison with Herschel sub-millimetre data M. Juvela
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. crah c ESO 2018 June 15, 2018 A Corona Australis cloud filament seen in NIR scattered light III. Modelling and comparison with Herschel sub-millimetre data M. Juvela
Observed Relationships between Filaments and Star Formation
 Observed Relationships between Filaments and Star Formation James Di Francesco (Ph. André, J. Pineda, R. Pudritz, D. Ward-Thompson, S.Inutsuka & the Herschel GBS, JCMT GBS and HOBYS Teams Herschel Gould
Observed Relationships between Filaments and Star Formation James Di Francesco (Ph. André, J. Pineda, R. Pudritz, D. Ward-Thompson, S.Inutsuka & the Herschel GBS, JCMT GBS and HOBYS Teams Herschel Gould
Exploring ISM dust with IRSIS. Emmanuel DARTOIS IAS-CNRS
 Exploring ISM dust with IRSIS Emmanuel DARTOIS IAS-CNRS IRSIS meeting 05-12-2007 Overview Intestellar ice mantles Hydrocarbons in the galaxy and outside Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Interstellar
Exploring ISM dust with IRSIS Emmanuel DARTOIS IAS-CNRS IRSIS meeting 05-12-2007 Overview Intestellar ice mantles Hydrocarbons in the galaxy and outside Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Interstellar
Dark gas contribution to diffuse gamma-ray emission
 Dark gas contribution to diffuse gamma-ray emission Masaki Mori ICRR CANGAROO group internal seminar, November 7, 2005 Adrian Cho S. Hunter, GLAST meeting, Oct.2004 The Galactic Diffuse Gamma-ray Emission...
Dark gas contribution to diffuse gamma-ray emission Masaki Mori ICRR CANGAROO group internal seminar, November 7, 2005 Adrian Cho S. Hunter, GLAST meeting, Oct.2004 The Galactic Diffuse Gamma-ray Emission...
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 19 Nov 2002
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. mjuvela October 29, 2018 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Dust emission from inhomogeneous interstellar clouds: radiative transfer in 3D with transiently heated
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. mjuvela October 29, 2018 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Dust emission from inhomogeneous interstellar clouds: radiative transfer in 3D with transiently heated
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 7 Sep 2006
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. polarization v9 c ESO 2018 January 1, 2018 Simulations of polarized dust emission arxiv:astro-ph/0609143v2 7 Sep 2006 V.-M. Pelkonen 1, M. Juvela 2, and P. Padoan
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. polarization v9 c ESO 2018 January 1, 2018 Simulations of polarized dust emission arxiv:astro-ph/0609143v2 7 Sep 2006 V.-M. Pelkonen 1, M. Juvela 2, and P. Padoan
Early Phases of Star Formation
 Early Phases of Star Formation Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: The earliest stages of the star formation process Probing the formation and evolution of prestellar cores with Herschel
Early Phases of Star Formation Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: The earliest stages of the star formation process Probing the formation and evolution of prestellar cores with Herschel
NRAO Instruments Provide Unique Windows On Star Formation
 NRAO Instruments Provide Unique Windows On Star Formation Crystal Brogan North American ALMA Science Center Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank
NRAO Instruments Provide Unique Windows On Star Formation Crystal Brogan North American ALMA Science Center Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array Expanded Very Large Array Robert C. Byrd Green Bank
DUST EMISSION FROM THE PERSEUS MOLECULAR CLOUD
 The Astrophysical Journal, 684:1228Y1239, 2008 September 10 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A DUST EMISSION FROM THE PERSEUS MOLECULAR CLOUD S. Schnee,
The Astrophysical Journal, 684:1228Y1239, 2008 September 10 # 2008. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A DUST EMISSION FROM THE PERSEUS MOLECULAR CLOUD S. Schnee,
Lecture 23 Internal Structure of Molecular Clouds
 Lecture 23 Internal Structure of Molecular Clouds 1. Location of the Molecular Gas 2. The Atomic Hydrogen Content 3. Formation of Clouds 4. Clouds, Clumps and Cores 5. Observing Molecular Cloud Cores References
Lecture 23 Internal Structure of Molecular Clouds 1. Location of the Molecular Gas 2. The Atomic Hydrogen Content 3. Formation of Clouds 4. Clouds, Clumps and Cores 5. Observing Molecular Cloud Cores References
Observations of exozodiacal disks. Jean-Charles Augereau LAOG, Grenoble, France. ISSI team: Exozodiacal dust diks and Darwin. Cambridge, August 2009
 + Olivier Absil Emmanuel Di Folco Hervé Beust Rémy Reche Alexander Krivov Philippe Thébault Torsten Loehne Vincent Coudé du Foresto Bertrand Menesson Pierre Kervella ISSI team: Exozodiacal dust diks and
+ Olivier Absil Emmanuel Di Folco Hervé Beust Rémy Reche Alexander Krivov Philippe Thébault Torsten Loehne Vincent Coudé du Foresto Bertrand Menesson Pierre Kervella ISSI team: Exozodiacal dust diks and
Filamentary Structures in the Galactic Plane Morphology, Physical conditions and relation with star formation
 Background: Column Density Map from Herschel Observation of Galactic Plane Hi-GAL project - field centered at (l,b) )=(224,0 ) Filamentary Structures in the Galactic Plane Morphology, Physical conditions
Background: Column Density Map from Herschel Observation of Galactic Plane Hi-GAL project - field centered at (l,b) )=(224,0 ) Filamentary Structures in the Galactic Plane Morphology, Physical conditions
Energy. mosquito lands on your arm = 1 erg. Firecracker = 5 x 10 9 ergs. 1 stick of dynamite = 2 x ergs. 1 ton of TNT = 4 x ergs
 Energy mosquito lands on your arm = 1 erg Firecracker = 5 x 10 9 ergs 1 stick of dynamite = 2 x 10 13 ergs 1 ton of TNT = 4 x 10 16 ergs 1 atomic bomb = 1 x 10 21 ergs Magnitude 8 earthquake = 1 x 10 26
Energy mosquito lands on your arm = 1 erg Firecracker = 5 x 10 9 ergs 1 stick of dynamite = 2 x 10 13 ergs 1 ton of TNT = 4 x 10 16 ergs 1 atomic bomb = 1 x 10 21 ergs Magnitude 8 earthquake = 1 x 10 26
The role of the magnetic field in the formation of structure in molecular clouds
 The role of the magnetic field in the formation of structure in molecular clouds Juan Diego Soler Institute d Astrophysique Spatiale (France) on behalf of the Planck collaboration IAU General Assembly.
The role of the magnetic field in the formation of structure in molecular clouds Juan Diego Soler Institute d Astrophysique Spatiale (France) on behalf of the Planck collaboration IAU General Assembly.
The Protostellar Luminosity Function
 Design Reference Mission Case Study Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy Science Steering Committee Program contacts: Lynne Hillenbrand, Tom Greene, Paul Harvey Scientific category: STAR FORMATION
Design Reference Mission Case Study Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy Science Steering Committee Program contacts: Lynne Hillenbrand, Tom Greene, Paul Harvey Scientific category: STAR FORMATION
II- Molecular clouds
 2. II- Molecular clouds 3. Introduction 4. Observations of MC Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 218 / 290 3. Introduction 3. Introduction Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 219 /
2. II- Molecular clouds 3. Introduction 4. Observations of MC Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 218 / 290 3. Introduction 3. Introduction Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 219 /
Nearby Universe: Rapporteur
 Nearby Universe: Rapporteur Margaret Meixner (STScI) SAGE: Tracing the Lifecycle of Baryonic Matter: Intermediate mass stars High mass stars credit: http://hea-www.cfa.harvard.edu/champ/education/public/icons/
Nearby Universe: Rapporteur Margaret Meixner (STScI) SAGE: Tracing the Lifecycle of Baryonic Matter: Intermediate mass stars High mass stars credit: http://hea-www.cfa.harvard.edu/champ/education/public/icons/
H 2 O and CO Ices in Protostellar Environments Recent Keck Telescope Results. Adwin Boogert California Inst. of Technology. Interstellar Ices-I
 Interstellar Ices-1 H 2 O and CO Ices in Protostellar Environments Recent Keck Telescope Results Adwin Boogert California Inst. of Technology Jan/2005 Interstellar Ices-I Contents Infrared spectra of highly
Interstellar Ices-1 H 2 O and CO Ices in Protostellar Environments Recent Keck Telescope Results Adwin Boogert California Inst. of Technology Jan/2005 Interstellar Ices-I Contents Infrared spectra of highly
The Ṁass- loss of Red Supergiants
 The Ṁass- loss of Red Supergiants Dr. Donald F. Figer Director, Center for Detectors Speaker: Yuanhao (Harry) Zhang RIT 9/12/13 1 9/12/13 2 Outline IntroducJon MoJvaJon Objects Method Need for SOFIA/FORCAST
The Ṁass- loss of Red Supergiants Dr. Donald F. Figer Director, Center for Detectors Speaker: Yuanhao (Harry) Zhang RIT 9/12/13 1 9/12/13 2 Outline IntroducJon MoJvaJon Objects Method Need for SOFIA/FORCAST
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 31 Jul 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 31 Jul 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 31 Jul 2017](/thumbs/93/113385460.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. feher_sample_herschel c ESO 2018 November 16, 2018 A CO survey on a sample of Herschel cold clumps O. Fehér 1, 2, M. Juvela 3, 4, T. Lunttila 5, J. Montillaud 4,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. feher_sample_herschel c ESO 2018 November 16, 2018 A CO survey on a sample of Herschel cold clumps O. Fehér 1, 2, M. Juvela 3, 4, T. Lunttila 5, J. Montillaud 4,
The Dusty Universe. Joe Weingartner George Mason University Dept of Physics and Astronomy
 The Dusty Universe Joe Weingartner George Mason University Dept of Physics and Astronomy To astronomers, dust means: sub micron solid grains (1 micron = 1 m = 10 6 m = one millionth of a meter) Typical
The Dusty Universe Joe Weingartner George Mason University Dept of Physics and Astronomy To astronomers, dust means: sub micron solid grains (1 micron = 1 m = 10 6 m = one millionth of a meter) Typical
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines!
 Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
The Universe o. Galaxies. The Universe of. Galaxies. Ajit Kembhavi IUCAA
 Hello! The Universe of Galaxies The Universe o Galaxies Ajit Kembhavi IUCAA Galaxies: Stars: ~10 11 Mass: ~10 11 M Sun Contain stars, gas and dust, possibly a supermassive black hole at the centre. Much
Hello! The Universe of Galaxies The Universe o Galaxies Ajit Kembhavi IUCAA Galaxies: Stars: ~10 11 Mass: ~10 11 M Sun Contain stars, gas and dust, possibly a supermassive black hole at the centre. Much
Star Formation. Spitzer Key Contributions to Date
 Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Astronomy 106, Fall September 2015
 Today in Astronomy 106: molecules to molecular clouds to stars Aromatic (benzene-ring) molecules in space Formation of molecules, on dust-grain surfaces and in the gas phase Interstellar molecular clouds
Today in Astronomy 106: molecules to molecular clouds to stars Aromatic (benzene-ring) molecules in space Formation of molecules, on dust-grain surfaces and in the gas phase Interstellar molecular clouds
Near-Infrared Spectroscopic Study of Supernova Ejecta and Supernova Dust in Cassiopeia A
 Supernova Remnants: An Odyssey in Space after Stellar Death 2016 June Near-Infrared Spectroscopic Study of Supernova Ejecta and Supernova Dust in Cassiopeia A Yong Hyun Lee 1 Supervisor: Bon-Chul Koo 1
Supernova Remnants: An Odyssey in Space after Stellar Death 2016 June Near-Infrared Spectroscopic Study of Supernova Ejecta and Supernova Dust in Cassiopeia A Yong Hyun Lee 1 Supervisor: Bon-Chul Koo 1
The influence of cosmic rays on the chemistry in Sagittarius B2(N)
 The influence of cosmic rays on the chemistry in Sagittarius B2(N) Mélisse Bonfand A. Belloche, K. M. Menten, R. Garrod Sagittarius B2 APEX Telescope Large Area Survey of the Galaxy Sgr B2 Sgr B2(N) Galactic
The influence of cosmic rays on the chemistry in Sagittarius B2(N) Mélisse Bonfand A. Belloche, K. M. Menten, R. Garrod Sagittarius B2 APEX Telescope Large Area Survey of the Galaxy Sgr B2 Sgr B2(N) Galactic
Ionized Hydrogen (HII)
 Ionized Hydrogen (HII) While ionized hydrogen (protons, electrons) forms the majority of the ionized phase of the ISM, it also contains ionized forms of other elements: e.g., OII, OIII, CIV, MgII. Highest
Ionized Hydrogen (HII) While ionized hydrogen (protons, electrons) forms the majority of the ionized phase of the ISM, it also contains ionized forms of other elements: e.g., OII, OIII, CIV, MgII. Highest
Dust in dwarf galaxies: The case of NGC 4214
 Dust in dwarf galaxies: The case of NGC 4214 Ute Lisenfeld Israel Hermelo Monica Relaño Richard Tuffs Cristina Popescu Joerg Fischera Brent Grove Image from HST WFC3 (Image: NASA/ESA/Hubble Heritage) Dust
Dust in dwarf galaxies: The case of NGC 4214 Ute Lisenfeld Israel Hermelo Monica Relaño Richard Tuffs Cristina Popescu Joerg Fischera Brent Grove Image from HST WFC3 (Image: NASA/ESA/Hubble Heritage) Dust
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
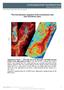 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0158 The link between magnetic field orientations and star formation rates Supplementary Figure 1 - YSOs (blue dots in the
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0158 The link between magnetic field orientations and star formation rates Supplementary Figure 1 - YSOs (blue dots in the
8: Composition and Physical state of Interstellar Dust
 8: Composition and Physical state of Interstellar Dust James Graham UC, Berkeley 1 Reading Tielens, Interstellar Medium, Ch. 5 Mathis, J. S. 1990, AARA, 28, 37 Draine, B. T., 2003, AARA, 41, 241 2 Nature
8: Composition and Physical state of Interstellar Dust James Graham UC, Berkeley 1 Reading Tielens, Interstellar Medium, Ch. 5 Mathis, J. S. 1990, AARA, 28, 37 Draine, B. T., 2003, AARA, 41, 241 2 Nature
Formation and Evolution of Planetary Systems
 Formation and Evolution of Planetary Systems Meyer, Hillenbrand et al., Formation and Evolution of Planetary Systems (FEPS): First Results from a Spitzer Legacy Science Program ApJ S 154: 422 427 (2004).
Formation and Evolution of Planetary Systems Meyer, Hillenbrand et al., Formation and Evolution of Planetary Systems (FEPS): First Results from a Spitzer Legacy Science Program ApJ S 154: 422 427 (2004).
Unscrambling the Egg. Yvonne Pendleton NASA Ames Research Center. JWST Workshop Nov. 14, 2017
 Unscrambling the Egg Yvonne Pendleton NASA Ames Research Center JWST Workshop Nov. 14, 2017 From interstellar dust to new stars and planets Comparisons between material forming new planetary systems and
Unscrambling the Egg Yvonne Pendleton NASA Ames Research Center JWST Workshop Nov. 14, 2017 From interstellar dust to new stars and planets Comparisons between material forming new planetary systems and
Mapping the column density and dust temperature structure of IRDCs with Herschel
 Mapping the column density and dust temperature structure of IRDCs with Herschel N. Pere=o 1,2, G.A. Fuller 2, R. Plume 3, L. Anderson, J. Bally, C. Ba=ersby, M. Beltran, J. Kirk, C. Lenfestey, D. Marshall,
Mapping the column density and dust temperature structure of IRDCs with Herschel N. Pere=o 1,2, G.A. Fuller 2, R. Plume 3, L. Anderson, J. Bally, C. Ba=ersby, M. Beltran, J. Kirk, C. Lenfestey, D. Marshall,
Anatomy of the S255-S257 complex - Triggered high-mass star formation
 Proceedings Title IAU Symposium Proceedings IAU Symposium No. IAUS237, 2006 A.C. Editor, B.D. Editor & C.E. Editor, eds. c 2006 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Anatomy of
Proceedings Title IAU Symposium Proceedings IAU Symposium No. IAUS237, 2006 A.C. Editor, B.D. Editor & C.E. Editor, eds. c 2006 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Anatomy of
Substellar Atmospheres II. Dust, Clouds, Meteorology. PHY 688, Lecture 19 Mar 11, 2009
 Substellar Atmospheres II. Dust, Clouds, Meteorology PHY 688, Lecture 19 Mar 11, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture substellar atmospheres: opacity, LTE, chemical species, metallicity Dust, Clouds,
Substellar Atmospheres II. Dust, Clouds, Meteorology PHY 688, Lecture 19 Mar 11, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture substellar atmospheres: opacity, LTE, chemical species, metallicity Dust, Clouds,
Where, Exactly, do Stars Form? (and how can SOFIA help with the answer)
 Where, Exactly, do Stars Form? (and how can SOFIA help with the answer) Alyssa A. Goodman Harvard University Astronomy Department photo credit: Alves, Lada & Lada On a galactic scale Star Formation=Column
Where, Exactly, do Stars Form? (and how can SOFIA help with the answer) Alyssa A. Goodman Harvard University Astronomy Department photo credit: Alves, Lada & Lada On a galactic scale Star Formation=Column
The dust temperatures of the pre-stellar cores in the ρ Oph main cloud and in other star-forming regions: consequences for the core mass function
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 379, 1390 1400 (2007) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.11999.x The dust temperatures of the pre-stellar cores in the ρ Oph main cloud and in other star-forming regions: consequences
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 379, 1390 1400 (2007) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.11999.x The dust temperatures of the pre-stellar cores in the ρ Oph main cloud and in other star-forming regions: consequences
Lecture 5. Interstellar Dust: Chemical & Thermal Properties
 Lecture 5. Interstellar Dust: Chemical & Thermal Properties!. Spectral Features 2. Grain populations and Models 3. Thermal Properties 4. Small Grains and Large Molecules -------------------------------------------------
Lecture 5. Interstellar Dust: Chemical & Thermal Properties!. Spectral Features 2. Grain populations and Models 3. Thermal Properties 4. Small Grains and Large Molecules -------------------------------------------------
Andromeda in all colours
 Andromeda in all colours Sébastien Viaene and the HELGA team: J. Fritz, M. Baes, G.J. Bendo, J.A.D.L. Blommaert, M. Boquien, A. Boselli, L. Ciesla, L. Cortese, I. De Looze, W.K. Gear, G. Gentile, T.M.
Andromeda in all colours Sébastien Viaene and the HELGA team: J. Fritz, M. Baes, G.J. Bendo, J.A.D.L. Blommaert, M. Boquien, A. Boselli, L. Ciesla, L. Cortese, I. De Looze, W.K. Gear, G. Gentile, T.M.
Revealing the Large Scale Distribution of Star Formation in the Milky Way with WISE
 Revealing the Large Scale Distribution of Star Formation in the Milky Way with WISE Xavier Koenig Yale University WISE @ 5 Conference Feb 11 2015 Collaborators: David Leisawitz Debbie Padgett Luisa Rebull
Revealing the Large Scale Distribution of Star Formation in the Milky Way with WISE Xavier Koenig Yale University WISE @ 5 Conference Feb 11 2015 Collaborators: David Leisawitz Debbie Padgett Luisa Rebull
Spinning Dust and the 3mm Excess
 Spinning Dust and the 3mm Excess 8th October 2010 Spinning dust 1996: COBE DMR-DIRBE (Kogut et al.) observe correlated microwave and 100 µm emission. 1997: Saskatoon 30 & 40 GHz observations; OVRO 14.5
Spinning Dust and the 3mm Excess 8th October 2010 Spinning dust 1996: COBE DMR-DIRBE (Kogut et al.) observe correlated microwave and 100 µm emission. 1997: Saskatoon 30 & 40 GHz observations; OVRO 14.5
Habitable exoplanets: modeling & characterization
 Habitable exoplanets: modeling & characterization F. Selsis CNRS, Bordeaux, France flux at 10 pc (photons m -2 hr -1 µm -1 ) R. Wordsworth, F. Forget Laboratoire de Meteorologie Dynamique (LMD), Paris
Habitable exoplanets: modeling & characterization F. Selsis CNRS, Bordeaux, France flux at 10 pc (photons m -2 hr -1 µm -1 ) R. Wordsworth, F. Forget Laboratoire de Meteorologie Dynamique (LMD), Paris
X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies. Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts
 X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts Chandra survey of diffuse X-ray emission from 53 edge-on galaxies i > 60 o, D < 30 Mpc (Li, J.-T. & Wang, Q.D.
X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts Chandra survey of diffuse X-ray emission from 53 edge-on galaxies i > 60 o, D < 30 Mpc (Li, J.-T. & Wang, Q.D.
INTRODUCTION TO SPACE
 INTRODUCTION TO SPACE 25.3.2019 The Galaxy II: Stars: Classification and evolution Various types of stars Interstellar matter: dust, gas Dark matter ELEC-E4530 Radio astronomy: the Sun, pulsars, microquasars,
INTRODUCTION TO SPACE 25.3.2019 The Galaxy II: Stars: Classification and evolution Various types of stars Interstellar matter: dust, gas Dark matter ELEC-E4530 Radio astronomy: the Sun, pulsars, microquasars,
Dust polarization observations towards interstellar filaments as seen by Planck: Signature of the magnetic field geometry
 Dust (total) emission of the ISM as seen by Planck Dust polarization observations towards interstellar filaments as seen by Planck: Signature of the magnetic field geometry Doris Arzoumanian (IAS, Orsay)
Dust (total) emission of the ISM as seen by Planck Dust polarization observations towards interstellar filaments as seen by Planck: Signature of the magnetic field geometry Doris Arzoumanian (IAS, Orsay)
The Physics of the Interstellar Medium
 The Physics of the Interstellar Medium Ulrike Heiter Contact: 471 5970 ulrike@astro.uu.se www.astro.uu.se Matter between stars Average distance between stars in solar neighbourhood: 1 pc = 3 x 1013 km,
The Physics of the Interstellar Medium Ulrike Heiter Contact: 471 5970 ulrike@astro.uu.se www.astro.uu.se Matter between stars Average distance between stars in solar neighbourhood: 1 pc = 3 x 1013 km,
Low mass star formation. Mark Thompson (with contributions from Jennifer Hatchell, Derek Ward-Thompson, Jane Greaves, Larry Morgan...
 Low mass star formation Mark Thompson (with contributions from Jennifer Hatchell, Derek Ward-Thompson, Jane Greaves, Larry Morgan...) The observational state of play Multiwavelength surveys are bringing
Low mass star formation Mark Thompson (with contributions from Jennifer Hatchell, Derek Ward-Thompson, Jane Greaves, Larry Morgan...) The observational state of play Multiwavelength surveys are bringing
Star Formation. Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase
 Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Star Formation Answering Fundamental Questions During the Spitzer Warm Mission Phase Lori Allen CfA John Carpenter, Caltech Lee Hartmann, University of Michigan Michael Liu, University of Hawaii Tom Megeath,
Galactic Dust Properties. Déborah Paradis CNES Post-doc IRAP, Toulouse
 Galactic Dust Properties Déborah Paradis CNES Post-doc IRAP, Toulouse BG emissivity λ I ν (λ) = Q abs (λ 0 ) λ 0 β emissivity = τ/n H β : spectral index B ν ( T eq,λ)n H Conventionally admitted : β = 2
Galactic Dust Properties Déborah Paradis CNES Post-doc IRAP, Toulouse BG emissivity λ I ν (λ) = Q abs (λ 0 ) λ 0 β emissivity = τ/n H β : spectral index B ν ( T eq,λ)n H Conventionally admitted : β = 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion In this Supplementary Discussion, we give more detailed derivations of several of the results in our letter. First, we describe in detail our method of calculating the temperature
Supplementary Discussion In this Supplementary Discussion, we give more detailed derivations of several of the results in our letter. First, we describe in detail our method of calculating the temperature
Remote sensing of ice clouds
 Remote sensing of ice clouds Carlos Jimenez LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France GDR microondes, Paris, 09/09/2008 Outline : ice clouds and the climate system : VIS-NIR, IR, mm/sub-mm, active 3. Observing
Remote sensing of ice clouds Carlos Jimenez LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France GDR microondes, Paris, 09/09/2008 Outline : ice clouds and the climate system : VIS-NIR, IR, mm/sub-mm, active 3. Observing
The Interstellar Medium
 The Interstellar Medium Fall 2014 Lecturer: Dr. Paul van der Werf Oortgebouw 565, ext 5883 pvdwerf@strw.leidenuniv.nl Assistant: Kirstin Doney Huygenslaboratorium 528 doney@strw.leidenuniv.nl Class Schedule
The Interstellar Medium Fall 2014 Lecturer: Dr. Paul van der Werf Oortgebouw 565, ext 5883 pvdwerf@strw.leidenuniv.nl Assistant: Kirstin Doney Huygenslaboratorium 528 doney@strw.leidenuniv.nl Class Schedule
Towards the Galactic Distribution of Exoplanets
 Towards the Galactic Distribution of Exoplanets Spitzer and the Microlensing Parallax May 23, 2016 ExEP Science Briefing, JPL, Pasadena Sebastiano Calchi Novati IPAC/NExScI, Caltech credit: NASA/JPL OUTLINE
Towards the Galactic Distribution of Exoplanets Spitzer and the Microlensing Parallax May 23, 2016 ExEP Science Briefing, JPL, Pasadena Sebastiano Calchi Novati IPAC/NExScI, Caltech credit: NASA/JPL OUTLINE
Chapter 16 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Birth Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Galactic plane surveys: What have/will we learn(ed)? Henrik Beuther
 Galactic plane surveys: What have/will we learn(ed)? Henrik Beuther M51 The Whirlpool Galaxy Blue: PAWS CO Red: THINGS HI Colors: multi-color HST Courtesy: T.A. Rector High-mass stars: Strong impact on
Galactic plane surveys: What have/will we learn(ed)? Henrik Beuther M51 The Whirlpool Galaxy Blue: PAWS CO Red: THINGS HI Colors: multi-color HST Courtesy: T.A. Rector High-mass stars: Strong impact on
AST4930: Star and Planet Formation. Syllabus. AST4930: Star and Planet Formation, Spring 2014
 AST4930: Star and Planet Formation Lecture 1: Overview Assoc. Prof. Jonathan C. Tan jt@astro.ufl.edu Bryant 302 Syllabus AST4930: Star and Planet Formation, Spring 2014 Assoc. Prof. Jonathan C. Tan (jt
AST4930: Star and Planet Formation Lecture 1: Overview Assoc. Prof. Jonathan C. Tan jt@astro.ufl.edu Bryant 302 Syllabus AST4930: Star and Planet Formation, Spring 2014 Assoc. Prof. Jonathan C. Tan (jt
Gas and Star Formation in the Circinus Galaxy
 Gas and Star Formation in the Circinus Galaxy Bi-Qing For PhD student University of Texas, Austin, USA Baerbel Koribalski (CASS) & Tom Jarrett (SSC) Outline The Circinus galaxy Why the need for Spitzer?
Gas and Star Formation in the Circinus Galaxy Bi-Qing For PhD student University of Texas, Austin, USA Baerbel Koribalski (CASS) & Tom Jarrett (SSC) Outline The Circinus galaxy Why the need for Spitzer?
within entire molecular cloud complexes
 The earliest phases of high-mass stars within entire molecular cloud complexes Frédérique Motte (CEA-Saclay, AIM) Collaborators: S. Bontemps (Obs Bordeaux), N. Schneider, J. Grac (CEA-Saclay), P. Schilke,
The earliest phases of high-mass stars within entire molecular cloud complexes Frédérique Motte (CEA-Saclay, AIM) Collaborators: S. Bontemps (Obs Bordeaux), N. Schneider, J. Grac (CEA-Saclay), P. Schilke,
Magnetic Fields over all Scales
 Magnetic Fields over all Scales Patrick Koch (ASIAA) 1 pc with: Hsuan-Gu Chou, Paul Ho, Ya-Wen Tang, Hsi-Wei Yen 30 mpc (CSO / Hertz @ 350µm, ~20 ) (JCMT / SCUPOL @850µm, ~10 ) (SMA@ 345 GHz: ~ 3 to 0.7
Magnetic Fields over all Scales Patrick Koch (ASIAA) 1 pc with: Hsuan-Gu Chou, Paul Ho, Ya-Wen Tang, Hsi-Wei Yen 30 mpc (CSO / Hertz @ 350µm, ~20 ) (JCMT / SCUPOL @850µm, ~10 ) (SMA@ 345 GHz: ~ 3 to 0.7
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline A galaxy is a collection of 100 billion stars! Our Milky Way Galaxy (1)Components - HII regions, Dust Nebulae, Atomic Gas (2) Shape & Size (3) Rotation of
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline A galaxy is a collection of 100 billion stars! Our Milky Way Galaxy (1)Components - HII regions, Dust Nebulae, Atomic Gas (2) Shape & Size (3) Rotation of
PMS OBJECTS IN THE STAR FORMATION REGION Cep OB3. II. YOUNG STELLAR OBJECTS IN THE Ha NEBULA Cep B
 Astrophysics, Vol. 56, No. 2, June, 2013 PMS OBJECTS IN THE STAR FORMATION REGION Cep OB3. II. YOUNG STELLAR OBJECTS IN THE Ha NEBULA Cep B E. H. Nikoghosyan Models for the spectral energy distributions
Astrophysics, Vol. 56, No. 2, June, 2013 PMS OBJECTS IN THE STAR FORMATION REGION Cep OB3. II. YOUNG STELLAR OBJECTS IN THE Ha NEBULA Cep B E. H. Nikoghosyan Models for the spectral energy distributions
The CO-H2 conversion factor of diffuse ISM: Bright 12CO emission also traces diffuse gas
 The CO-H2 conversion factor of diffuse ISM: Bright 12CO emission also traces diffuse gas Jérôme Pety, Harvey Liszt, Robert Lucas To cite this version: Jérôme Pety, Harvey Liszt, Robert Lucas. The CO-H2
The CO-H2 conversion factor of diffuse ISM: Bright 12CO emission also traces diffuse gas Jérôme Pety, Harvey Liszt, Robert Lucas To cite this version: Jérôme Pety, Harvey Liszt, Robert Lucas. The CO-H2
Taurus Spitzer Survey: Taking the Bull by the Horns. With apologies and thanks to Chuck Jones!
 Taurus Spitzer Survey: Taking the Bull by the Horns With apologies and thanks to Chuck Jones! Team Members D. Padgett - SSC A. Noriega-Crespo - SSC L. Rebull - SSC S. Carey SSC M. Fukagawa - Nagoya U.
Taurus Spitzer Survey: Taking the Bull by the Horns With apologies and thanks to Chuck Jones! Team Members D. Padgett - SSC A. Noriega-Crespo - SSC L. Rebull - SSC S. Carey SSC M. Fukagawa - Nagoya U.
3D Tomography of the Local Interstellar Medium
 3D Tomography of the Local Interstellar Medium supervised by Isabelle GRENIER DDays IRFU phds presentations days - 2 July 2015 1 Introduction Nom - Prénom : REMY Quentin Cursus : Licence physique fondamentale,
3D Tomography of the Local Interstellar Medium supervised by Isabelle GRENIER DDays IRFU phds presentations days - 2 July 2015 1 Introduction Nom - Prénom : REMY Quentin Cursus : Licence physique fondamentale,
Using Spitzer to Observe the Solar System
 Using Spitzer to Observe the Solar System Sean Carey Spitzer Science Center 47 th DPS meeting 09 November 2015 SJC - 1 Spitzer Space Telescope NASA s Infrared Great Observatory Launched on 25 August 2003
Using Spitzer to Observe the Solar System Sean Carey Spitzer Science Center 47 th DPS meeting 09 November 2015 SJC - 1 Spitzer Space Telescope NASA s Infrared Great Observatory Launched on 25 August 2003
Time-variable phenomena in Herbig Ae/Be stars
 Time-variable phenomena in Herbig Ae/Be stars! Péter Ábrahám Konkoly Observatory, Budapest, Hungary! Á. Kóspál, R. Szakáts! Santiago, 2014 April 7 Variability - and why it is interesting Herbig Ae/Be stars
Time-variable phenomena in Herbig Ae/Be stars! Péter Ábrahám Konkoly Observatory, Budapest, Hungary! Á. Kóspál, R. Szakáts! Santiago, 2014 April 7 Variability - and why it is interesting Herbig Ae/Be stars
