Probing the formation mechanism of prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF: First results from Herschel
|
|
|
- Cory York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Probing the formation mechanism of prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF: First results from Herschel Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Herschel GB survey Ophiuchus 70/250/500 µm composite With: A. Menshchikov, V. Könyves, N. Schneider, D. Arzoumanian, S. Bontemps, F. Motte,P.Didelon, N. Peretto, D. Ward-Thompson, J. Di Francesco, P. Martin, P. Saraceno, P. Palmeirim, J. Kirk & the Herschel Gould Belt KP Consortium Ph. André - The millimeter and submillimeter sky in the Planck mission era - Paris 12 Jan 2011
2 The Herschel Gould Belt Survey SPIRE/PACS µm imaging of the bulk of nearby (d < 0.5 kpc) molecular clouds (~ 160 deg 2 ), mostly located in Gould s Belt. Complete census of prestellar cores and Class 0 protostars. Taurus Perseus Cepheus Serpens Aquila Ophiuchus Lupus Gould Belt Chamaeleon CrA Orion IRAS 100 µm ~ 15 resolution at λ ~ 200 µm ~ 0.02 pc < Jeans d = 300 pc Motivation: Key issues on the early stages of star formation Nature of the relationship between the CMF and the IMF? What generates prestellar cores and what governs their evolution to protostars and proto-brown dwarfs?
3 Outline: First images from the Herschel Gould Belt survey Preliminary results on cores (e.g. CMF vs. IMF) The role of filaments in the core formation process Implications/Speculations Herschel GB survey L /250/500 µm composite Ph. André - Planck 2011 Conference - Paris 12 Jan 2011 PACS
4 First images from the Gould Belt Survey PACS/SPIRE // mode 70/160/250/350/500 µm 1) Aquila Rift star-forming cloud (d ~ 260 pc) cf. Red : SPIRE 500 µm Green : PACS 160 µm Blue : PACS 70 µm ~ 3.3 o x 3.3 o field André et al Könyves et al Bontemps et al Men shchikov et al A&A special issue (vol. 518)
5 First images from the Gould Belt Survey PACS/SPIRE // mode SPIRE 250 µm image 2) Polaris flare translucent cloud (d ~ 150 pc) ~ 5500 M (CO+HI) Heithausen & Thaddeus 90 ~ 13 deg 2 field Miville-Deschênes et al Ward-Thompson et al Men shchikov et al André et al A&A special issue
6 Revealing the structure of one of the nearest infrared dark clouds (Aquila Main: d ~ 260 pc) Herschel (SPIRE+PACS) Dust temperature map (K) Herschel (SPIRE+PACS) Column density map (H 2 /cm 2 ) W40 1 deg ~ 4.5 pc
7 Dense cores form primarily in filaments Cores Morphological Component Analysis: Wavelet component (H 2 /cm 2 ) Herschel Column density map = + (P. Didelon based on Starck et al. 2003) Filaments Curvelet component (H 2 /cm 2 )
8 Aquila: `Compact Source Extraction (using getsources A. Menshchikov et al. 2010) Herschel (SPIRE+PACS) Aquila entire field: N H2 (cm -2 ) Spatial distribution of extracted cores 541 starless 201 YSOs Starless = no PACS 70 µ emission (F 70µ < > L proto cf. Dunham, Crapsi, Evans e.a c2d) Könyves et al deg ~ 14 pc 5σ level: ~ cm -2 70/160/500 µm composite image
9 Core: Examples of starless cores in Aquila-East local column density peak simple (convex) shape no substructure at Herschel resol. potential single star-forming entity Herschel N H2 map (cm -2 ) Radial intensity profiles Including background Background subtracted Ellipses: FWHM sizes of 24 starless cores at 250 µm Könyves et al. 2010, A&A special issue
10 Most of the Herschel starless cores in Aquila are bound Motte et al. (1998,2001) Mass, M (M ) T = 20 K T = 7 K Cirrus noise limit in Aquila > 60% are likely prestellar in nature Könyves et al Deconvolved FWHM size, R (pc) (at 250 µm) Positions in mass vs. size diagram, consistent with ~ critical Bonnor-Ebert spheroids: M BE = 2.4 R BE c s 2 /G for T ~ 7-20 K
11 Most of the ~300 Polaris starless cores are unbound Motte et al. (1998,2001) Mass, M (M ) T = 20 K T = 7 K Cirrus noise limit in Polaris not (yet?) prestellar André et al Ward-Thompson et al Deconvolved FWHM size, R (pc) (at 250 µm) Locations in mass vs. size diagram: 2 orders of magnitude below the density of self-gravitating Bonnor-Ebert isothermal spheres
12 Confirming the link between the prestellar CMF & the IMF Könyves et al André et al A&A special issue prestellar cores in Aquila Factor ~ 2-9 better statistics than earlier CMF studies: e.g. Motte, André, Neri 1998; Johnstone et al. 2000; Stanke et al. 2006; Enoch et al. 2006; Alves et al. 2007; Nutter & Ward-Thompson 07 Number of objects per mass bin: ΔN/ΔlogM Core Mass Function (CMF) in Aquila Complex Good (~ one-to-one) correspondence between core mass and stellar system mass: M * = ε M core with ε ~ in Aquila The IMF is at least partly determined by pre-collapse cloud fragmentation (cf. models by Padoan & Nordlund 2002, Hennebelle & Chabrier 2008) IMF CMF 0.3 M Mass (M ) CO clumps (Kramer et al. 1998) ε Salpeter s IMF
13 Prestellar cores form out of a filamentary background : Class 0 protostars : Aquila N H2 map (cm -2 ) Prestellar cores Aquila curvelet N H2 map (cm -2 )
14 Herschel reveals a network of filaments in every cloud Polaris A characteristic width ~ 0.1 pc? (deconvolved FWHM) Distribution of widths for 90 filaments Number of filaments per bin 0.1 pc Distribution of Jeans lengths [λ J ~ c s2 /(GΣ)] Aquila Polaris IC5146 IC5146 Filament width (FWHM) [pc] Using the skeleton or DisPerSE algorithm (Sousbie, Pichon et al. 2008, 2010) to trace the ridge of each filament D. Arzoumanian et al. 2011
15 Prestellar cores form out of a filamentary background : Class 0 protostars : Prestellar cores - 90% found at A v (back) > 7 Aquila N H2 map (cm -2 ) Aquila curvelet N H2 map (cm -2 ) Unstable 0.1Mline/Mline,crit Stable
16 Number of cores per extinction bin: ΔN/ΔA V Confirmation of an extinction threshold for the formation of prestellar cores Distribution of background extinctions for the Aquila prestellar cores A v ~ 7 Background cloud extinction, A V In Aquila, ~ 90% of the prestellar cores identified with Herschel are found above A v ~ 7 Σ ~ 150 M pc -2 cf. Onishi et al (Taurus) Johnstone, Di Francesco, Kirk 04 (Ophiuchus) See also (for YSOs): Heiderman, Evans et al. 2010
17 Only the densest filaments are gravitationally unstable and contain prestellar cores ( ) Aquila curvelet N H2 map (cm -2 ) André et al. 2010, A&A Special issue 1 Unstable Mline/M line,crit 0.1 Stable The gravitational instability of filaments is controlled by the mass per unit length M line (cf. Ostriker 1964, Inutsuka & Miyama 1997): unstable if M line > M line, crit unbound if M line < M line, crit M line, crit = 2 c s 2 /G ~ 15 M /pc for T ~ 10K A V threshold Simple estimate: M line N H2 x Width (~ 0.1 pc) Unstable filaments highlighted in white in the N H2 map
18 Importance of the star formation threshold on (extra)galactic scales Star formation rate vs. Gas surface density Σ SFR Σ gas for Σ gas > Σ threshold Σ th ~ 150 M pc -2 A V ~ 7-8 Heiderman et al Lada et al See also Gao & Solomon 2004 for external galaxies Heiderman, Evans et al. 2010
19 Origin of the filaments: Large-scale turbulence? Numerical simulations including large-scale turbulence: Padoan, Juvela, Goodman, Nordlund (2001) Klessen & Burkert (2000) Li & Nakamura (2004) Also: Bate, Bonnell, Bromm (2003) Basu, Ciolek et al. (2009) Hennebelle, Banerjee, Vazquez-Semadeni et al. (2008) Duffin, Pudritz et al. 2010
20 Turbulence dissipation and filament formation In Polaris, one of the most tenuous filaments detected by SPIRE coincides with a CO(2-1) structure of intense velocity shear (~ 40 km/s/pc) found at IRAM 30m (Hily-Blant & Falgarone 2009) SPIRE 250 µm 0.8 Jy/b SPIRE 250 µm + CO(2-1) CVI 0.1 Jy/b 1 deg ~ 2.6 pc 10 ~ 0.45 pc
21 Filaments permeate the ISM on all scales Herschel SPIRE 500 µm + PACS 160/70 µm (from ~0.1 pc to > 50 pc) Planck HFI 540/350 µm + IRAS 100 µm Aquila ESA and the Gould Belt KP ESA and the HFI Consortium
22 Conclusions First results from Herschel on prestellar cores are very promising: Confirm the close link between the prestellar CMF and the IMF, although the whole survey will be required to fully characterize the nature of this link. Suggest that prestellar core formation occurs in 2 main steps: 1) Filaments form first in the cold ISM, probably as a result of the dissipation of MHD turbulence; 2) The densest filaments then fragment into prestellar cores via gravitational instability above a critical column density threshold Σ th ~ 150 M pc -2 Spectroscopic and polarimetric observations required to clarify the roles of turbulence, B fields, gravity in forming the filaments.
!From the filamentary structure of the ISM! to prestellar cores to the IMF:!! Results from the Herschel Gould Belt survey!
 !From the filamentary structure of the ISM! to prestellar cores to the IMF:!! Results from the Herschel Gould Belt survey! Philippe André CEA Lab. AIM Paris- Saclay PACS! Part of Orion B! 70/250/500 µm!
!From the filamentary structure of the ISM! to prestellar cores to the IMF:!! Results from the Herschel Gould Belt survey! Philippe André CEA Lab. AIM Paris- Saclay PACS! Part of Orion B! 70/250/500 µm!
The Herschel View of Star Formation
 Near The Herschel View of Star Formation Philippe André CEA Laboratoire AIM Paris-Saclay Far PACS Alpbach 2011 Summer School Star Formation Across the Universe 19/07/2011 Outline: Submm observations as
Near The Herschel View of Star Formation Philippe André CEA Laboratoire AIM Paris-Saclay Far PACS Alpbach 2011 Summer School Star Formation Across the Universe 19/07/2011 Outline: Submm observations as
Star Formation in GMCs: Lessons from Herschel Observations of the Aquila Complex
 Herschel PACS/SPIRE map of Aquila (Gould Belt survey) ORISTARS erc project Lab. AIM, Paris-Saclay, France Ph. André, A. Men'shchikov, N. Schneider, S. Bontemps, D. Arzoumanian, N. Peretto, P. Didelon,
Herschel PACS/SPIRE map of Aquila (Gould Belt survey) ORISTARS erc project Lab. AIM, Paris-Saclay, France Ph. André, A. Men'shchikov, N. Schneider, S. Bontemps, D. Arzoumanian, N. Peretto, P. Didelon,
Observed Relationships between Filaments and Star Formation
 Observed Relationships between Filaments and Star Formation James Di Francesco (Ph. André, J. Pineda, R. Pudritz, D. Ward-Thompson, S.Inutsuka & the Herschel GBS, JCMT GBS and HOBYS Teams Herschel Gould
Observed Relationships between Filaments and Star Formation James Di Francesco (Ph. André, J. Pineda, R. Pudritz, D. Ward-Thompson, S.Inutsuka & the Herschel GBS, JCMT GBS and HOBYS Teams Herschel Gould
Properties of interstellar filaments as derived from Herschel Gould Belt observations
 Properties of interstellar filaments as derived from Herschel Gould Belt observations Doris Arzoumanian PhD student at CEA Saclay, France with Ph. André, V. Könyves, N. Schneider, N. Peretto, A. Men shchikov,
Properties of interstellar filaments as derived from Herschel Gould Belt observations Doris Arzoumanian PhD student at CEA Saclay, France with Ph. André, V. Könyves, N. Schneider, N. Peretto, A. Men shchikov,
Recent results from Herschel on the filamentary structure of the cold interstellar medium
 Recent results from Herschel on the filamentary structure of the cold interstellar medium Laboratoire d Astrophysique (AIM) de Paris-Saclay, CEA Saclay, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France E-mail: pandre@cea.fr
Recent results from Herschel on the filamentary structure of the cold interstellar medium Laboratoire d Astrophysique (AIM) de Paris-Saclay, CEA Saclay, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France E-mail: pandre@cea.fr
Molecular Clouds and Star Formation. James Di Francesco September 21, 2015 NRC Herzberg Programs in Astronomy & Astrophysics
 James Di Francesco September 21, 2015 NRC Herzberg Programs in Astronomy & Astrophysics 2 Hubble image of M51 (NASA/ESA) Five Star Formation Regimes Local (Low-mass) Star Formation o
James Di Francesco September 21, 2015 NRC Herzberg Programs in Astronomy & Astrophysics 2 Hubble image of M51 (NASA/ESA) Five Star Formation Regimes Local (Low-mass) Star Formation o
Early Phases of Star Formation
 Early Phases of Star Formation Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: The earliest stages of the star formation process Probing the formation and evolution of prestellar cores with Herschel
Early Phases of Star Formation Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: The earliest stages of the star formation process Probing the formation and evolution of prestellar cores with Herschel
Early Stages of (Low-Mass) Star Formation: The ALMA Promise
 Early Stages of (Low-Mass) Star Formation: The ALMA Promise Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: Prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF Identifying proto-brown dwarfs Bate et al. 1995
Early Stages of (Low-Mass) Star Formation: The ALMA Promise Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: Prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF Identifying proto-brown dwarfs Bate et al. 1995
From Filamentary Networks to Dense Cores in Molecular Clouds: Toward a New Paradigm for Star Formation
 From Filamentary Networks to Dense Cores in Molecular Clouds: Toward a New Paradigm for Star Formation Philippe André Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Paris-Saclay James Di Francesco National Research Council
From Filamentary Networks to Dense Cores in Molecular Clouds: Toward a New Paradigm for Star Formation Philippe André Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Paris-Saclay James Di Francesco National Research Council
the Solar Neighborhood
 Click to edit Master title style Star Formation at High A V in the Solar Neighborhood Amanda Heiderman NSF Fellow UVa/NRAO (w/ Neal Evans, UT Austin) Filaments 2014, October, 11, 2014 10/13/2014 1 Click
Click to edit Master title style Star Formation at High A V in the Solar Neighborhood Amanda Heiderman NSF Fellow UVa/NRAO (w/ Neal Evans, UT Austin) Filaments 2014, October, 11, 2014 10/13/2014 1 Click
The Herschel view of molecular cloud structure and star- forma6on
 The Herschel view of molecular cloud structure and star- forma6on Nicola S chneider LAB/Observatoire de Bordeaux (France) Image: Cygnus X (HOBYS) (ESA press release: 3- color image from Herschel PACS/SPIRE)
The Herschel view of molecular cloud structure and star- forma6on Nicola S chneider LAB/Observatoire de Bordeaux (France) Image: Cygnus X (HOBYS) (ESA press release: 3- color image from Herschel PACS/SPIRE)
Origin of the stellar Initial Mass Function (IMF) in the W43-MM1 ridge
 Origin of the stellar Initial Mass Function (IMF) in the W43-MM1 ridge Fabien Louvet (Universidad de Chile & IPAG Grenoble) Special credits to: F. Motte, T. Nony, S. Bontemps, A. Gusdorf, P. Didelon, P.
Origin of the stellar Initial Mass Function (IMF) in the W43-MM1 ridge Fabien Louvet (Universidad de Chile & IPAG Grenoble) Special credits to: F. Motte, T. Nony, S. Bontemps, A. Gusdorf, P. Didelon, P.
Frédérique Motte and Nicola Schneider (AIM Paris-Saclay, Obs. Bordeaux) Coordinated by Frédérique Motte, Annie Zavagno, and Sylvain Bontemps
 Cloud structure and high-mass star formation in HOBYS, the Herschel imaging survey of OB Young Stellar objects Frédérique Motte and Nicola Schneider (AIM Paris-Saclay, Obs. Bordeaux) http://hobys-herschel.cea.fr
Cloud structure and high-mass star formation in HOBYS, the Herschel imaging survey of OB Young Stellar objects Frédérique Motte and Nicola Schneider (AIM Paris-Saclay, Obs. Bordeaux) http://hobys-herschel.cea.fr
Cold Cores on Planck1,
 Cold Cores on Planck1, 2 and Herschel 1 on behalf of the Planck collaboration M. Juvela, I. Ristorcelli (coord.) Planck Desert, Dupac, Giard, Harju, Harrison, Joncas, Jones, Lagache, Lamarre, Laureijs,
Cold Cores on Planck1, 2 and Herschel 1 on behalf of the Planck collaboration M. Juvela, I. Ristorcelli (coord.) Planck Desert, Dupac, Giard, Harju, Harrison, Joncas, Jones, Lagache, Lamarre, Laureijs,
How do protostars get their mass?
 How do protostars get their mass? Phil Myers Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Origin of Stellar Masses Tenerife, Spain October 18, 2010 Introduction How does nature make a star? a star of particular
How do protostars get their mass? Phil Myers Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Origin of Stellar Masses Tenerife, Spain October 18, 2010 Introduction How does nature make a star? a star of particular
The Formation and Evolution of Prestellar Cores
 The Formation and Evolution of Prestellar Cores Formation of Prestellar Cores: Observations and Theory Edited by PHILIPPE ANDRE 1, SHANTANU BASU 2, and SHU-ICHIRO INUTSUKA 3 (1) Service d Astrophysique,
The Formation and Evolution of Prestellar Cores Formation of Prestellar Cores: Observations and Theory Edited by PHILIPPE ANDRE 1, SHANTANU BASU 2, and SHU-ICHIRO INUTSUKA 3 (1) Service d Astrophysique,
Origin of the dense core mass function in contracting filaments
 Origin of the dense core mass function in contracting filaments Philip C. Myers Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge MA 02138 USA pmyers@cfa.harvard.edu Abstract. Mass
Origin of the dense core mass function in contracting filaments Philip C. Myers Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge MA 02138 USA pmyers@cfa.harvard.edu Abstract. Mass
Cold Cores of Molecular Clouds. Mika Juvela, Department of physics, University of Helsinki
 Cold Cores of Molecular Clouds Mika Juvela, Department of physics, University of Helsinki Juvela - IAU August 2012 on cold cores On behalfmika of the Planck andxxviii, Herschel projects Content Molecular
Cold Cores of Molecular Clouds Mika Juvela, Department of physics, University of Helsinki Juvela - IAU August 2012 on cold cores On behalfmika of the Planck andxxviii, Herschel projects Content Molecular
Galactic Cold Cores. M.Juvela On behalf of the Galactic Cold Cores project
 Galactic Cold Cores M.Juvela On behalf of the Galactic Cold Cores project M. Juvela, I. Ristorcelli (coord.) Desert, Dupac, Giard, Harju, Harrison, Joncas, Jones, Lagache, Lamarre, Laureijs, Lehtinen,
Galactic Cold Cores M.Juvela On behalf of the Galactic Cold Cores project M. Juvela, I. Ristorcelli (coord.) Desert, Dupac, Giard, Harju, Harrison, Joncas, Jones, Lagache, Lamarre, Laureijs, Lehtinen,
within entire molecular cloud complexes
 The earliest phases of high-mass stars within entire molecular cloud complexes Frédérique Motte (CEA-Saclay, AIM) Collaborators: S. Bontemps (Obs Bordeaux), N. Schneider, J. Grac (CEA-Saclay), P. Schilke,
The earliest phases of high-mass stars within entire molecular cloud complexes Frédérique Motte (CEA-Saclay, AIM) Collaborators: S. Bontemps (Obs Bordeaux), N. Schneider, J. Grac (CEA-Saclay), P. Schilke,
Frédérique Motte (AIM Paris-Saclay)
 Clusters of high-mass protostars: From extreme clouds to minibursts of star formation Frédérique Motte (AIM Paris-Saclay) Special thanks to S. Bontemps, T. Csengeri, P. Didelon, M. Hennemann, T. Hill,
Clusters of high-mass protostars: From extreme clouds to minibursts of star formation Frédérique Motte (AIM Paris-Saclay) Special thanks to S. Bontemps, T. Csengeri, P. Didelon, M. Hennemann, T. Hill,
The formation of high-mass stars: new insights from Herschel, IRAM, and ALMA imaging
 The formation of high-mass stars: new insights from Herschel, IRAM, and ALMA imaging Frédérique Motte (IPAG Grenoble & AIM Paris-Saclay) Special credits to S. Bontemps, T. Csengeri, P. Didelon, A. Gusdorf,
The formation of high-mass stars: new insights from Herschel, IRAM, and ALMA imaging Frédérique Motte (IPAG Grenoble & AIM Paris-Saclay) Special credits to S. Bontemps, T. Csengeri, P. Didelon, A. Gusdorf,
Theory of star formation
 Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
High mass star formation in the Herschel era: highlights of the HOBYS key program
 Recent Advances in Star Formation ASI Conference Series, 2012, Vol. 4, pp 55 62 Edited by Annapurni Subramaniam & Sumedh Anathpindika High mass star formation in the Herschel era: highlights of the HOBYS
Recent Advances in Star Formation ASI Conference Series, 2012, Vol. 4, pp 55 62 Edited by Annapurni Subramaniam & Sumedh Anathpindika High mass star formation in the Herschel era: highlights of the HOBYS
The Role of Magnetic Field in Star Formation in the Disk of Milky Way Galaxy Shu-ichiro Inutsuka (Nagoya University)
 Role of Magnetic Field in Star Formation & Galactic Structure (Dec 20 22, 2017) The Role of Magnetic Field in Star Formation in the Disk of Milky Way Galaxy Shu-ichiro Inutsuka (Nagoya University) Main
Role of Magnetic Field in Star Formation & Galactic Structure (Dec 20 22, 2017) The Role of Magnetic Field in Star Formation in the Disk of Milky Way Galaxy Shu-ichiro Inutsuka (Nagoya University) Main
Low mass star formation. Mark Thompson (with contributions from Jennifer Hatchell, Derek Ward-Thompson, Jane Greaves, Larry Morgan...
 Low mass star formation Mark Thompson (with contributions from Jennifer Hatchell, Derek Ward-Thompson, Jane Greaves, Larry Morgan...) The observational state of play Multiwavelength surveys are bringing
Low mass star formation Mark Thompson (with contributions from Jennifer Hatchell, Derek Ward-Thompson, Jane Greaves, Larry Morgan...) The observational state of play Multiwavelength surveys are bringing
From Filaments to Stars: a Theoretical Perspective
 From Filaments to Stars: a Theoretical Perspective NRAO Filaments. Oct. 10-11, 2014 Ralph E. Pudritz Origins Institute, McMaster U. Collaborators McMaster: Mikhail Klassen, Corey Howard, (Ph.D.s) Helen
From Filaments to Stars: a Theoretical Perspective NRAO Filaments. Oct. 10-11, 2014 Ralph E. Pudritz Origins Institute, McMaster U. Collaborators McMaster: Mikhail Klassen, Corey Howard, (Ph.D.s) Helen
igure 4 of McMullin et al McMullin et al Testi & Sargent 1998 Figure 1 of Testi & Sargent 1998:
 igure 4 of McMullin et al. 1994. Figure 1 of Testi & Sargent 1998: McMullin et al. 1994 BIMA with (only!) three elements Eight configurationsàcoverage of 2 kλ to 30 kλ Naturally wtd. Beam of 11" x 6" (for
igure 4 of McMullin et al. 1994. Figure 1 of Testi & Sargent 1998: McMullin et al. 1994 BIMA with (only!) three elements Eight configurationsàcoverage of 2 kλ to 30 kλ Naturally wtd. Beam of 11" x 6" (for
II- Molecular clouds
 2. II- Molecular clouds 3. Introduction 4. Observations of MC Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 218 / 290 3. Introduction 3. Introduction Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 219 /
2. II- Molecular clouds 3. Introduction 4. Observations of MC Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 218 / 290 3. Introduction 3. Introduction Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 219 /
Thermal physics, cloud geometry and the stellar initial mass function
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 359, 211 222 (2005) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.08881.x Thermal physics, cloud geometry and the stellar initial mass function Richard B. Larson Yale Astronomy Department, Box
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 359, 211 222 (2005) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.08881.x Thermal physics, cloud geometry and the stellar initial mass function Richard B. Larson Yale Astronomy Department, Box
The Star Formation Rate of Molecular Clouds
 The Star Formation Rate of Molecular Clouds Paolo Padoan University of Barcelona Christoph Federrath Monash University Gilles Chabrier Ecole Normale Suprieure de Lyon Neal J. Evans II The University of
The Star Formation Rate of Molecular Clouds Paolo Padoan University of Barcelona Christoph Federrath Monash University Gilles Chabrier Ecole Normale Suprieure de Lyon Neal J. Evans II The University of
The role of the magnetic field in the formation of structure in molecular clouds
 The role of the magnetic field in the formation of structure in molecular clouds Juan Diego Soler Institute d Astrophysique Spatiale (France) on behalf of the Planck collaboration IAU General Assembly.
The role of the magnetic field in the formation of structure in molecular clouds Juan Diego Soler Institute d Astrophysique Spatiale (France) on behalf of the Planck collaboration IAU General Assembly.
Star-forming filament models
 Star-forming filament models Philip C. Myers Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge MA 02138 USA pmyers@cfa.harvard.edu Abstract. New models of star-forming filamentary
Star-forming filament models Philip C. Myers Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge MA 02138 USA pmyers@cfa.harvard.edu Abstract. New models of star-forming filamentary
Filamentary Structures in the Galactic Plane Morphology, Physical conditions and relation with star formation
 Background: Column Density Map from Herschel Observation of Galactic Plane Hi-GAL project - field centered at (l,b) )=(224,0 ) Filamentary Structures in the Galactic Plane Morphology, Physical conditions
Background: Column Density Map from Herschel Observation of Galactic Plane Hi-GAL project - field centered at (l,b) )=(224,0 ) Filamentary Structures in the Galactic Plane Morphology, Physical conditions
Astronomy. Astrophysics. Fragmentation and mass segregation in the massive dense cores of Cygnus X
 A&A 524, A18 (2010) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/200913286 c ESO 2010 Astronomy & Astrophysics Fragmentation and mass segregation in the massive dense cores of Cygnus X S. Bontemps 1,F.Motte 2,T.Csengeri 2,
A&A 524, A18 (2010) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/200913286 c ESO 2010 Astronomy & Astrophysics Fragmentation and mass segregation in the massive dense cores of Cygnus X S. Bontemps 1,F.Motte 2,T.Csengeri 2,
Filamentary structure of star-forming complexes
 Filamentary structure of star-forming complexes Philip C. Myers Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge MA 02138 USA pmyers@cfa.harvard.edu Abstract. The nearest young
Filamentary structure of star-forming complexes Philip C. Myers Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge MA 02138 USA pmyers@cfa.harvard.edu Abstract. The nearest young
UNDERSTANDING THE IMF
 UNDERSTANDING THE IMF Richard B. Larson Department of Astronomy, Yale University Box 208101, New Haven, CT 06520-8101, USA larson@astro.yale.edu Abstract It is suggested that the thermal physics of star-forming
UNDERSTANDING THE IMF Richard B. Larson Department of Astronomy, Yale University Box 208101, New Haven, CT 06520-8101, USA larson@astro.yale.edu Abstract It is suggested that the thermal physics of star-forming
How do high line-mass filaments fragment? Towards an evolutionary sequence with ALMA
 How do high line-mass filaments fragment? Towards an evolutionary sequence with ALMA Jouni Kainulainen Max-Planck-Institute for Astronomy Kainulainen+2017 (A&A accepted; arxiv:1603.05688) With: Amelia
How do high line-mass filaments fragment? Towards an evolutionary sequence with ALMA Jouni Kainulainen Max-Planck-Institute for Astronomy Kainulainen+2017 (A&A accepted; arxiv:1603.05688) With: Amelia
Characteristic structure of star-forming clouds
 Characteristic structure of star-forming clouds Philip C. Myers Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge MA 02138 USA pmyers@cfa.harvard.edu Abstract. This paper gives a
Characteristic structure of star-forming clouds Philip C. Myers Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge MA 02138 USA pmyers@cfa.harvard.edu Abstract. This paper gives a
Collapse of magnetized dense cores. Is there a fragmentation crisis?
 Collapse of magnetized dense cores Is there a fragmentation crisis? Patrick Hennebelle (ENS-Observatoire de Paris) Collaborators: Benoît Commerçon, Andréa Ciardi, Sébastien Fromang, Romain Teyssier, Philippe
Collapse of magnetized dense cores Is there a fragmentation crisis? Patrick Hennebelle (ENS-Observatoire de Paris) Collaborators: Benoît Commerçon, Andréa Ciardi, Sébastien Fromang, Romain Teyssier, Philippe
THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS. η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith)
 THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith) THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS Christopher F. McKee HIPACC, UCSC August 8, 2013 with Andrew Cunningham Richard Klein Mark Krumholz Andrew Myers
THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith) THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS Christopher F. McKee HIPACC, UCSC August 8, 2013 with Andrew Cunningham Richard Klein Mark Krumholz Andrew Myers
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 15 Oct 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 15 Oct 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 15 Oct 2018](/thumbs/89/98754926.jpg) Star-forming Filaments and Cores on a Galactic Scale arxiv:1810.06701v1 [astro-ph.sr] 15 Oct 2018 James Di Francesco 1, Jared Keown 2, Rachel Friesen 3, Tyler Bourke 4, and Paola Caselli 5 1 National Research
Star-forming Filaments and Cores on a Galactic Scale arxiv:1810.06701v1 [astro-ph.sr] 15 Oct 2018 James Di Francesco 1, Jared Keown 2, Rachel Friesen 3, Tyler Bourke 4, and Paola Caselli 5 1 National Research
Revealing and understanding the low-mass end of the IMF. Low-mass part of the Initial Mass Function Star, brown dwarf formation. G.
 Revealing and understanding the low-mass end of the IMF Low-mass part of the Initial Mass Function Star, brown dwarf formation G. Chabrier Field: Resolved objects IMF down to the HB limit Salpeter Kroupa
Revealing and understanding the low-mass end of the IMF Low-mass part of the Initial Mass Function Star, brown dwarf formation G. Chabrier Field: Resolved objects IMF down to the HB limit Salpeter Kroupa
The Formation of Star Clusters
 The Formation of Star Clusters Orion Nebula Cluster (JHK) - McCaughrean Jonathan Tan University of Florida & KITP In collaboration with: Brent Buckalew (ERAU), Michael Butler (UF u-grad), Jayce Dowell
The Formation of Star Clusters Orion Nebula Cluster (JHK) - McCaughrean Jonathan Tan University of Florida & KITP In collaboration with: Brent Buckalew (ERAU), Michael Butler (UF u-grad), Jayce Dowell
Summary and Future work
 299 Chapter 7 Summary and Future work 7.1 Summary In this thesis I have utilized large-scale millimeter and mid- to far-infrared surveys to address a number of outstanding questions regarding the formation
299 Chapter 7 Summary and Future work 7.1 Summary In this thesis I have utilized large-scale millimeter and mid- to far-infrared surveys to address a number of outstanding questions regarding the formation
Brown dwarf & star formation and the bottom of the IMF: a critical look
 Brown dwarf & star formation and the bottom of the IMF: a critical look Gilles Chabrier ENS-Lyon U. Exeter Origin of stars and their planetary systems Mac Master University, June 2012 Field: Resolved objects
Brown dwarf & star formation and the bottom of the IMF: a critical look Gilles Chabrier ENS-Lyon U. Exeter Origin of stars and their planetary systems Mac Master University, June 2012 Field: Resolved objects
Where, Exactly, do Stars Form? (and how can SOFIA help with the answer)
 Where, Exactly, do Stars Form? (and how can SOFIA help with the answer) Alyssa A. Goodman Harvard University Astronomy Department photo credit: Alves, Lada & Lada On a galactic scale Star Formation=Column
Where, Exactly, do Stars Form? (and how can SOFIA help with the answer) Alyssa A. Goodman Harvard University Astronomy Department photo credit: Alves, Lada & Lada On a galactic scale Star Formation=Column
The JCMT and Herschel Gould Belt Surveys: a comparison of SCUBA-2 and Herschel data of dense cores in the Taurus dark cloud L1495
 Advance Access publication 2016 August 16 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw1978 The JCMT and Herschel Gould Belt Surveys: a comparison of SCUBA-2 and Herschel data of dense cores in the Taurus dark cloud L1495 D.
Advance Access publication 2016 August 16 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw1978 The JCMT and Herschel Gould Belt Surveys: a comparison of SCUBA-2 and Herschel data of dense cores in the Taurus dark cloud L1495 D.
Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud
 Red: CO from Mini survey Orion B Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud Spitzer Orion Cloud Survey: 10 sq. degrees in Orion A and Orion B mapped between 2004-2009 Orion A Green
Red: CO from Mini survey Orion B Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud Spitzer Orion Cloud Survey: 10 sq. degrees in Orion A and Orion B mapped between 2004-2009 Orion A Green
Low-Mass Star Formation
 Low-Mass Star Formation Neal J. Evans II with credit to Mike Dunham, Lori Allen, Hyo Jeong Kim, Amy Stutz Star Formation Questions What determines the IMF? How long do various stages of the process take?
Low-Mass Star Formation Neal J. Evans II with credit to Mike Dunham, Lori Allen, Hyo Jeong Kim, Amy Stutz Star Formation Questions What determines the IMF? How long do various stages of the process take?
The Competitive Accretion Debate
 The Competitive Accretion Debate 1,2 Paul C. Clark 2 Ralf S. Klessen 3 Ian A. Bonnell 3 Rowan J. Smith 1 KITP 2 University of Heidelberg 3 University of St Andrews What is CA and how does it work? Theory
The Competitive Accretion Debate 1,2 Paul C. Clark 2 Ralf S. Klessen 3 Ian A. Bonnell 3 Rowan J. Smith 1 KITP 2 University of Heidelberg 3 University of St Andrews What is CA and how does it work? Theory
Astronomy. Astrophysics. The Pipe Nebula as seen with Herschel: formation of filamentary structures by large-scale compression?,
 A&A 541, A63 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201118663 c ESO 2012 Astronomy & Astrophysics The Pipe Nebula as seen with Herschel: formation of filamentary structures by large-scale compression?, N. Peretto
A&A 541, A63 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201118663 c ESO 2012 Astronomy & Astrophysics The Pipe Nebula as seen with Herschel: formation of filamentary structures by large-scale compression?, N. Peretto
Physics of Star and Planet Formation Towards a Unified Picture
 Thomas Henning Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg Physics of Star and Planet Formation Towards a Unified Picture ISOSS 22164+6003 (Distance = 6 kpc L=20 000 L sun ) Deep NIR CAHA Image + Herschel/PACS
Thomas Henning Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg Physics of Star and Planet Formation Towards a Unified Picture ISOSS 22164+6003 (Distance = 6 kpc L=20 000 L sun ) Deep NIR CAHA Image + Herschel/PACS
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2013
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2013 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2013](/thumbs/94/119654252.jpg) Two Mass Distributions in the L 1641 Molecular Clouds: The Herschel connection of Dense Cores and Filaments in Orion A 1 arxiv:1309.2332v2 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2013 D. Polychroni 1,3, E. Schisano 2,3, D.
Two Mass Distributions in the L 1641 Molecular Clouds: The Herschel connection of Dense Cores and Filaments in Orion A 1 arxiv:1309.2332v2 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2013 D. Polychroni 1,3, E. Schisano 2,3, D.
THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS. η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith)
 THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith) THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS Christopher F. McKee Institute for Astronomy November 2, 2011 with Andrew Cunningham Edith Falgarone Richard
THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith) THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS Christopher F. McKee Institute for Astronomy November 2, 2011 with Andrew Cunningham Edith Falgarone Richard
A SCUBA survey of the NGC 2068/2071 protoclusters
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) A SCUBA survey of the NGC 2068/2071 protoclusters F. Motte 1, P. André 2, D. Ward-Thompson 3, and S. Bontemps 4 1 Max-Planck-Institut
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. (will be inserted by hand later) A SCUBA survey of the NGC 2068/2071 protoclusters F. Motte 1, P. André 2, D. Ward-Thompson 3, and S. Bontemps 4 1 Max-Planck-Institut
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
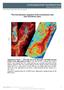 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0158 The link between magnetic field orientations and star formation rates Supplementary Figure 1 - YSOs (blue dots in the
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0158 The link between magnetic field orientations and star formation rates Supplementary Figure 1 - YSOs (blue dots in the
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 23 Jan 2018](/thumbs/74/71085467.jpg) Astronomy& Astrophysics manuscript no. HGBS_craNS_paper c ESO 2018 January 25, 2018 The dense cores and filamentary structure of the molecular cloud in Corona Australis: Herschel SPIRE and PACS observations
Astronomy& Astrophysics manuscript no. HGBS_craNS_paper c ESO 2018 January 25, 2018 The dense cores and filamentary structure of the molecular cloud in Corona Australis: Herschel SPIRE and PACS observations
Brown Dwarf Formation from Disk Fragmentation and Ejection
 Brown Dwarf Formation from Disk Fragmentation and Ejection Shantanu Basu Western University, London, Ontario, Canada Collaborator: Eduard Vorobyov (University of Vienna) 50 years of Brown Dwarfs Ringberg
Brown Dwarf Formation from Disk Fragmentation and Ejection Shantanu Basu Western University, London, Ontario, Canada Collaborator: Eduard Vorobyov (University of Vienna) 50 years of Brown Dwarfs Ringberg
Fragmentation and mass segregation in the massive dense cores of Cygnus X
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. irquiet-frag c ESO 2018 April 14, 2018 Fragmentation and mass segregation in the massive dense cores of Cygnus X S. Bontemps, 1,2,3 F. Motte, 3 T. Csengeri, 3 N.
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. irquiet-frag c ESO 2018 April 14, 2018 Fragmentation and mass segregation in the massive dense cores of Cygnus X S. Bontemps, 1,2,3 F. Motte, 3 T. Csengeri, 3 N.
Turbulence in the (Cold) ISM
 Turbulence in the (Cold) ISM P. Hily-Blant IPAG April 14th, 2011 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Introduction to turbulence 3 Turbulent Cascade 4 Structures 5 Dissipation 6 Flavors 7 Perspectives failed to catch
Turbulence in the (Cold) ISM P. Hily-Blant IPAG April 14th, 2011 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Introduction to turbulence 3 Turbulent Cascade 4 Structures 5 Dissipation 6 Flavors 7 Perspectives failed to catch
Star Formation: How my knowledge has been shaped by observations taken by the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope
 Star Formation: How my knowledge has been shaped by observations taken by the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope With: J. Di Francesco, H. Kirk (NRC); S. Mairs, M. Chen (UVic); A. Pon (Leeds); R. Friesen (DI);
Star Formation: How my knowledge has been shaped by observations taken by the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope With: J. Di Francesco, H. Kirk (NRC); S. Mairs, M. Chen (UVic); A. Pon (Leeds); R. Friesen (DI);
Searching for the dominant mode of galaxy growth! from deep extragalactic Herschel surveys! D.Elbaz (CEA Saclay)
 Searching for the dominant mode of galaxy growth! from deep extragalactic Herschel surveys! D.Elbaz (CEA Saclay) Star formation = local process (~pc scale)! How sensitive is SF to larger scales inside
Searching for the dominant mode of galaxy growth! from deep extragalactic Herschel surveys! D.Elbaz (CEA Saclay) Star formation = local process (~pc scale)! How sensitive is SF to larger scales inside
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 7 May 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 7 May 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 7 May 2008](/thumbs/77/74833557.jpg) Draft version January 23, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 08/22/09 THE MASS DISTRIBUTION AND LIFETIME OF PRESTELLAR CORES IN PERSEUS, SERPENS, AND OPHIUCHUS Melissa L. Enoch 1,3,
Draft version January 23, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 08/22/09 THE MASS DISTRIBUTION AND LIFETIME OF PRESTELLAR CORES IN PERSEUS, SERPENS, AND OPHIUCHUS Melissa L. Enoch 1,3,
N-body Dynamics in Stellar Clusters Embedded in Gas
 N-body Dynamics in Stellar Clusters Embedded in Gas Matthew Bate, University of Exeter Kurosawa, Harries, Bate & Symington (2004) Collaborators: Ian Bonnell, St Andrews Volker Bromm, Texas Star Formation
N-body Dynamics in Stellar Clusters Embedded in Gas Matthew Bate, University of Exeter Kurosawa, Harries, Bate & Symington (2004) Collaborators: Ian Bonnell, St Andrews Volker Bromm, Texas Star Formation
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Jul 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Jul 2018](/thumbs/82/86636680.jpg) Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan (2014) 00(0), 1 15 doi: 10.1093/pasj/xxx000 1 arxiv:1807.08968v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Jul 2018 Molecular filament formation and filament-cloud interaction: Hints from Nobeyama 45m
Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan (2014) 00(0), 1 15 doi: 10.1093/pasj/xxx000 1 arxiv:1807.08968v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 Jul 2018 Molecular filament formation and filament-cloud interaction: Hints from Nobeyama 45m
The dependence of star cluster formation on initial conditions. Matthew Bate University of Exeter
 The dependence of star cluster formation on initial conditions Matthew Bate University of Exeter Stellar properties do not greatly depend on initial conditions constellation Little evidence for variation
The dependence of star cluster formation on initial conditions Matthew Bate University of Exeter Stellar properties do not greatly depend on initial conditions constellation Little evidence for variation
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 May 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 May 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 May 2016](/thumbs/91/106884719.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ngc6334_artemis_aa c ESO 2018 November 6, 2018 arxiv:1605.07434v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 May 2016 Characterizing filaments in regions of high-mass star formation: High-resolution
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ngc6334_artemis_aa c ESO 2018 November 6, 2018 arxiv:1605.07434v1 [astro-ph.ga] 24 May 2016 Characterizing filaments in regions of high-mass star formation: High-resolution
The physics of star formation
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Rep. Prog. Phys. 66 (2003) 1651 1697 REPORTS ON PROGRESS IN PHYSICS PII: S0034-4885(03)07916-8 The physics of star formation Richard B Larson Department of Astronomy, Yale
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Rep. Prog. Phys. 66 (2003) 1651 1697 REPORTS ON PROGRESS IN PHYSICS PII: S0034-4885(03)07916-8 The physics of star formation Richard B Larson Department of Astronomy, Yale
Molecular Cloud Turbulence and Star Formation
 Molecular Cloud Turbulence and Star Formation Javier Ballesteros-Paredes1, Ralf Klessen2, MordecaiMark Mac Low3, Enrique Vazquez-Semadeni1 1UNAM Morelia, Mexico, 2AIP, Potsdam, Germany, 3AMNH New York,
Molecular Cloud Turbulence and Star Formation Javier Ballesteros-Paredes1, Ralf Klessen2, MordecaiMark Mac Low3, Enrique Vazquez-Semadeni1 1UNAM Morelia, Mexico, 2AIP, Potsdam, Germany, 3AMNH New York,
The Schmidt Law at Sixty. Robert Kennicutt University of Arizona Texas A&M University
 The Schmidt Law at Sixty Robert Kennicutt University of Arizona Texas A&M University Log (SFR surface density) Maarten Schmidt conjecture (1959, 1963): - volume/surface densities of star formation scale
The Schmidt Law at Sixty Robert Kennicutt University of Arizona Texas A&M University Log (SFR surface density) Maarten Schmidt conjecture (1959, 1963): - volume/surface densities of star formation scale
The dust temperatures of the pre-stellar cores in the ρ Oph main cloud and in other star-forming regions: consequences for the core mass function
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 379, 1390 1400 (2007) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.11999.x The dust temperatures of the pre-stellar cores in the ρ Oph main cloud and in other star-forming regions: consequences
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 379, 1390 1400 (2007) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.11999.x The dust temperatures of the pre-stellar cores in the ρ Oph main cloud and in other star-forming regions: consequences
Hierarchical structure of the interstellar molecular clouds and star formation
 Open Astron. 2017; 26: 285 292 Research Article Alexander E. Dudorov* and Sergey A. Khaibrakhmanov Hierarchical structure of the interstellar molecular clouds and star formation https://doi.org/10.1515/astro-2017-0428
Open Astron. 2017; 26: 285 292 Research Article Alexander E. Dudorov* and Sergey A. Khaibrakhmanov Hierarchical structure of the interstellar molecular clouds and star formation https://doi.org/10.1515/astro-2017-0428
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Sep 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Sep 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Sep 2018](/thumbs/88/115895832.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper ESO 2018 September 13, 2018 A catalogue of dense cores and young stellar objects in the Lupus complex based on Herschel Gould Belt Survey observations M. Benedettini
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper ESO 2018 September 13, 2018 A catalogue of dense cores and young stellar objects in the Lupus complex based on Herschel Gould Belt Survey observations M. Benedettini
Brown Dwarf Formation and Jet Propagation in Core Collapse Simulations
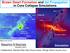 Brown Dwarf Formation and Jet Propagation in Core Collapse Simulations Knot Knot Cavity (proto-b.d) Observation Riaz et al. (2017) Masahiro N Machida (Kyushu Univ.) Clumps B.D mass object Simulation Collaborators:
Brown Dwarf Formation and Jet Propagation in Core Collapse Simulations Knot Knot Cavity (proto-b.d) Observation Riaz et al. (2017) Masahiro N Machida (Kyushu Univ.) Clumps B.D mass object Simulation Collaborators:
The Initial Mass Function Elisa Chisari
 The Initial Mass Function AST 541 Dec 4 2012 Outline The form of the IMF Summary of observations Ingredients of a complete model A Press Schechter model Numerical simulations Conclusions The form of the
The Initial Mass Function AST 541 Dec 4 2012 Outline The form of the IMF Summary of observations Ingredients of a complete model A Press Schechter model Numerical simulations Conclusions The form of the
Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era. François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale
 Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Motivation Dust emission Dust models Dust life cycle Planck early results Dust polarisation Outline Dust
Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Motivation Dust emission Dust models Dust life cycle Planck early results Dust polarisation Outline Dust
Herschel Mission Status Star and Planet Formation Over the Most Recent 12 GigaYears
 Herschel Mission Status Star and Planet Formation Over the Most Recent 12 GigaYears From Atoms Pebbles: Herschel s View of Star and Planet Formation Grenoble, 20-23/03/2012 Göran Pilbratt, Herschel Project
Herschel Mission Status Star and Planet Formation Over the Most Recent 12 GigaYears From Atoms Pebbles: Herschel s View of Star and Planet Formation Grenoble, 20-23/03/2012 Göran Pilbratt, Herschel Project
SAM GEEN (ITA/ZAH HEIDELBERG)
 SAM GEEN (ITA/ZAH HEIDELBERG) WITH PATRICK HENNEBELLE JUAN SOLER AND RALF KLESSEN Credit: Lost Valley Observatory Star formation is self regulating HII HII regions, regions, supernovae supernovae Molecular
SAM GEEN (ITA/ZAH HEIDELBERG) WITH PATRICK HENNEBELLE JUAN SOLER AND RALF KLESSEN Credit: Lost Valley Observatory Star formation is self regulating HII HII regions, regions, supernovae supernovae Molecular
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 7 Sep 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 7 Sep 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 7 Sep 2007](/thumbs/82/86576840.jpg) To appear in the Astrophysical Journal The Nature of the Dense Core Population in the Pipe Nebula: Thermal Cores Under Pressure arxiv:0709.1164v1 [astro-ph] 7 Sep 2007 Charles J. Lada 1, A.A. Muench 1,
To appear in the Astrophysical Journal The Nature of the Dense Core Population in the Pipe Nebula: Thermal Cores Under Pressure arxiv:0709.1164v1 [astro-ph] 7 Sep 2007 Charles J. Lada 1, A.A. Muench 1,
Fragmentation of the Integral Shaped Filament as viewed by ALMA
 Fragmentation of the Integral Shaped Filament as viewed by ALMA Jouni Kainulainen Max-Planck-Institute for Astronomy Kainulainen et al. (submitted; arxiv:1603.05688) With: Amelia Stutz, Thomas Stanke,
Fragmentation of the Integral Shaped Filament as viewed by ALMA Jouni Kainulainen Max-Planck-Institute for Astronomy Kainulainen et al. (submitted; arxiv:1603.05688) With: Amelia Stutz, Thomas Stanke,
An analytic column density profile to fit prestellar cores
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 395, 109 1098 (009) doi:10.1111/j.1365-966.009.14616.x An analytic column density profile to fit prestellar cores Wolf B. Dapp and Shantanu Basu Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 395, 109 1098 (009) doi:10.1111/j.1365-966.009.14616.x An analytic column density profile to fit prestellar cores Wolf B. Dapp and Shantanu Basu Department of Physics and Astronomy,
An analytic column density profile to fit prestellar cores
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 23 March 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) An analytic column density profile to fit prestellar cores Wolf B. Dapp 1 and Shantanu Basu 1, 1 Department
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 23 March 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) An analytic column density profile to fit prestellar cores Wolf B. Dapp 1 and Shantanu Basu 1, 1 Department
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 25 May 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 25 May 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 25 May 2007](/thumbs/76/73809998.jpg) Cold Dark Clouds 1 COLD DARK CLOUDS: The Initial Conditions for Star Formation arxiv:0705.3765v1 [astro-ph] 25 May 2007 Edwin A. Bergin Department of Astronomy, University of Michigan, 500 Church St. Ann
Cold Dark Clouds 1 COLD DARK CLOUDS: The Initial Conditions for Star Formation arxiv:0705.3765v1 [astro-ph] 25 May 2007 Edwin A. Bergin Department of Astronomy, University of Michigan, 500 Church St. Ann
The structure of molecular clouds II. Column density and mass distributions
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 406, 1350 1357 (2010) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16769.x The structure of molecular clouds II. Column density and mass distributions Dirk Froebrich and Jonathan Rowles Centre
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 406, 1350 1357 (2010) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16769.x The structure of molecular clouds II. Column density and mass distributions Dirk Froebrich and Jonathan Rowles Centre
21. The Green Bank Ammonia Survey: Dense Cores Under Pressure in Orion A Kirk+ ApJ in press GAS Herschel YSO
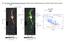 21. The Green Bank Ammonia Survey: Dense Cores Under Pressure in Orion A Kirk+ ApJ in press GAS Herschel YSO Spitzer YSO JCMT prestellar core prestellar core JCMT protostellar core protostellar core surface
21. The Green Bank Ammonia Survey: Dense Cores Under Pressure in Orion A Kirk+ ApJ in press GAS Herschel YSO Spitzer YSO JCMT prestellar core prestellar core JCMT protostellar core protostellar core surface
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 30 Nov 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 30 Nov 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 30 Nov 2009](/thumbs/75/71957006.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Kainulainen c ESO 2013 December 25, 2013 Letter to the Editor Probing the evolution of molecular cloud structure: From quiescence to birth arxiv:0911.5648v1 [astro-ph.ga]
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Kainulainen c ESO 2013 December 25, 2013 Letter to the Editor Probing the evolution of molecular cloud structure: From quiescence to birth arxiv:0911.5648v1 [astro-ph.ga]
Impact of magnetic fields on molecular cloud formation and evolution
 MNRAS 51, 33 3353 (15) doi:1.193/mnras/stv1 Impact of magnetic fields on molecular cloud formation and evolution Bastian Körtgen and Robi Banerjee Hamburger Sternwarte, Universität Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg
MNRAS 51, 33 3353 (15) doi:1.193/mnras/stv1 Impact of magnetic fields on molecular cloud formation and evolution Bastian Körtgen and Robi Banerjee Hamburger Sternwarte, Universität Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg
Formation Mechanisms of Brown Dwarfs: Observations & Theories. Dan Li April 2009
 Formation Mechanisms of Brown Dwarfs: Observations & Theories Dan Li April 2009 What is brown dwarf (BD)? BD Mass : upper-limit ~ 0.075 M lower-limit ~ 0.013 M (?) Differences between BD and giant planet:
Formation Mechanisms of Brown Dwarfs: Observations & Theories Dan Li April 2009 What is brown dwarf (BD)? BD Mass : upper-limit ~ 0.075 M lower-limit ~ 0.013 M (?) Differences between BD and giant planet:
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Apr 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Apr 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 25 Apr 2014](/thumbs/88/115453127.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. AlvesDeOliveira_Chamaeleon_accepted c ESO 2018 September 24, 2018 Herschel s view of the large-scale structure in the Chamaeleon dark clouds C. Alves de Oliveira
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. AlvesDeOliveira_Chamaeleon_accepted c ESO 2018 September 24, 2018 Herschel s view of the large-scale structure in the Chamaeleon dark clouds C. Alves de Oliveira
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Mar 2006
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 21 January 2014 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) The Jeans mass and the origin of the knee in the IMF arxiv:astro-ph/0603444v1 17 Mar 2006 I. A. Bonnell
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 21 January 2014 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) The Jeans mass and the origin of the knee in the IMF arxiv:astro-ph/0603444v1 17 Mar 2006 I. A. Bonnell
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Mar 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 12 Mar 2014](/thumbs/83/88559072.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. pdf bg 04022014 c ESO 2014 March 13, 2014 Understanding star formation in molecular clouds I. A universal probability distribution of column densities? N. Schneider
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. pdf bg 04022014 c ESO 2014 March 13, 2014 Understanding star formation in molecular clouds I. A universal probability distribution of column densities? N. Schneider
The Origin of the Initial Mass Function
 The Origin of the Initial Mass Function Ian A. Bonnell University of St Andrews Richard B. Larson Yale University Hans Zinnecker Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam Bonnell et al.: Origin of the Initial
The Origin of the Initial Mass Function Ian A. Bonnell University of St Andrews Richard B. Larson Yale University Hans Zinnecker Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam Bonnell et al.: Origin of the Initial
Molecular Tracers of Embedded Star Formation in Ophiuchus
 PUBLICATIONS OF THE ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC, 120:1193 1206, 2008 November 2008. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Molecular Tracers of Embedded
PUBLICATIONS OF THE ASTRONOMICAL SOCIETY OF THE PACIFIC, 120:1193 1206, 2008 November 2008. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. Molecular Tracers of Embedded
Possible link between the power spectrum of interstellar filaments and the origin of the prestellar core mass function ABSTRACT
 DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201526431 c ESO 2015 Astronomy & Astrophysics Possible link between the power spectrum of interstellar filaments and the origin of the prestellar core mass function A. Roy 1, Ph.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201526431 c ESO 2015 Astronomy & Astrophysics Possible link between the power spectrum of interstellar filaments and the origin of the prestellar core mass function A. Roy 1, Ph.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Mar 2006
 The Origin of the Initial Mass Function Ian A. Bonnell University of St Andrews Richard B. Larson Yale University Hans Zinnecker Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam arxiv:astro-ph/0603447v1 17 Mar 2006
The Origin of the Initial Mass Function Ian A. Bonnell University of St Andrews Richard B. Larson Yale University Hans Zinnecker Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam arxiv:astro-ph/0603447v1 17 Mar 2006
The Jeans mass and the origin of the knee in the IMF
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 368, 1296 1300 (2006) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10214.x The Jeans mass and the origin of the knee in the IMF I. A. Bonnell, 1 C. J. Clarke 2 and M. R. Bate 3 1 School of Physics
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 368, 1296 1300 (2006) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10214.x The Jeans mass and the origin of the knee in the IMF I. A. Bonnell, 1 C. J. Clarke 2 and M. R. Bate 3 1 School of Physics
STARLESS CORES. Mario Tafalla. (Observatorio Astronómico Nacional, Spain)
 STARLESS CORES Mario Tafalla (Observatorio Astronómico Nacional, Spain) Outline: 1. Internal Structure a. Introduction b. How to characterize the internal strcuture of starless cores c. L1498 & L1517B:
STARLESS CORES Mario Tafalla (Observatorio Astronómico Nacional, Spain) Outline: 1. Internal Structure a. Introduction b. How to characterize the internal strcuture of starless cores c. L1498 & L1517B:
Astronomy. Astrophysics. SDC13 infrared dark clouds: Longitudinally collapsing filaments?,,
 DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201322172 c ESO 2014 Astronomy & Astrophysics SDC13 infrared dark clouds: Longitudinally collapsing filaments?,, N. Peretto 1,2, G. A. Fuller 3, Ph. André 2, D. Arzoumanian 4, V.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201322172 c ESO 2014 Astronomy & Astrophysics SDC13 infrared dark clouds: Longitudinally collapsing filaments?,, N. Peretto 1,2, G. A. Fuller 3, Ph. André 2, D. Arzoumanian 4, V.
