Formation Mechanisms of Brown Dwarfs: Observations & Theories. Dan Li April 2009
|
|
|
- Frederick Alexander
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Formation Mechanisms of Brown Dwarfs: Observations & Theories Dan Li April 2009
2 What is brown dwarf (BD)? BD Mass : upper-limit ~ M lower-limit ~ M (?) Differences between BD and giant planet: 1) Formation mechanism 2) Elemental composition
3 Continuity between BDs and lowmass stars: IMF (Initial mass function) Clustering properties Binary statistics (multiplicity) Discs, accretion and outflows (Whitworth & Goodwin 2006)
4 IMF IMF of young cluster NGC 6611 (Oliveira et al. 2008)
5 IMF Can be better characterized in starforming regions and young clusters, in which BDs are brighter. Two constraints from observed IMF: Star to BD ratio normal stars outnumber BDs by a factor of 5~8 (Luhman et al. 2007) Minimum mass of BDs 10~20 M Jup (Luhman et al. 2007)
6 Clustering properties Spatial distributions of BDs (red crosses) and H-burning stars (blue circles) in Taurus starforming region The velocity dispersions are not distinguishable between BDs and H- burning stars, either (Luhman 2006)
7 Multiplicity properties Frequency, separation, mass radio distribution, etc. Sun-like star BD binary systems lack of close (separation < 3 AU) system - BD Desert more common at larger separations (semimajor > 100 A.U.) BD BD binary systems
8 Disks, accretion and outflows Disks (Luhman et al. 2005e)
9 Disks, accretion and outflows Accretion (Muzerolle et al. 1998, 2005)
10 Disks, accretion and outflows Jets and outflows Indicated by photometric and line profile variability, H 2 emission in UV, UV continuum excesses, and blue-shifted absorption and forbidden emission (see Luhman et al for references).
11 Formation mechanisms of BDs: (copyright by Don Dixon / cosmographica.com)
12 Formation by turbulent fragmentation Explored by Padona & Nordlund 2002: Strong, magnetic shocks produce high density post-shock gas which will have low Jeans masses and therefore form brown dwarfs directly from the turbulence Revised by Boyd & Whitworth 2005: 2-D one-shot fragmentation Star formation occurs in molecular clouds where two or more turbulent flows of sufficient density collide with sufficient ram pressure to produce a shock-compressed layer
13 Formation by turbulent fragmentation 2-D one-shot fragmentation Minimum stellar mass: solar mass (for shocked gas with temperature T ~ 10K) or even solar mass (for T ~ 6K) Cons: two or more coincident shocks are required to produce the high-density layer; not efficient enough to produce all BDs
14 Formation by disk fragmentation Bate, Bonnell & Bromm 2002; Whitworth & Stamatellos 2006; Stamatellos et al. 2007, etc. Disk fragmentation occurs when i) Disk is massive enough to be gravitational unstable, and ii) Compressional energy from condensation can radiate away efficiently
15 Formation by disk fragmentation Is convection efficient enough for cooling (for inner regions of disks around Sun-like stars, R ~ 3 to 30 A.U.)? Reason for BD Desert? Not a problem for outer regions (R > 100 A.U.) (Whitworth & Stamatellos 2006)
16 Formation by disk fragmentation Numerical simulations (Stamatellos & Whitworth 2007)
17 Formation by disk fragmentation Numerical simulations predictions: Low-mass H-burning stars forms close to the central star, while BDs form farther out in the disk a possible explanation of BD desert Most BDs forms with disk, however, most ejected BDs cannot retain their disks BDs that are companions to Sun-like stars are more likely to have discs than BDs in the field Binary properties. BD HS (H-burning star) and BD-BD binaries can exist even after ejection Existence of free-floating planetary-mass objects
18 Formation by ejection More than one protostars are formed in the collapse of a prestellar core grow by competitive accretion and interact dynamically protostars which get ejected from the core before they have time to grow to solar mass end up as BDs (Reipurth & Clarke, 2001) Even quite modest levels of turbulence are sufficient to ensure the fragmentation of the prestellar core; N-body dynamics will then almost inevitably eject one of the protostars, usually the least massive one.
19 Formation by ejection Numerical simulations (Bate, Bonnell & Bromm, 2002a, b, 2003; Delgado Donate, Clarke & Bate, 2003, 2004; Godwin, Whitworth & Ward-Thompson, 2004a,b) Low-mass disk (M DISK < 0.01 solar-mass, R DISK < 40AU) can be retained after ejection (but difficult to explain massive disks); Radial velocity distribution of ejected BDs is similar to that of the H-burning stars; Difficult to produce close BD-BD binaries
20 Formation by photo-erosion A pre-existing core of standard mass is overrun by an HII region photoerosion (Hester et al. 1996; Whitworth & Zinnecker 2004) Very inefficient one massive pre-existing prestellar core forms only one low-mass star or BD finally Can only work in the immediate vicinity of an OB star
21 Formation by binary disruption Goodwin & Whitworth 2008 BDs are initially binary companions, formed around low-mass H-burning stars. Most of these binaries are then gently disrupted by passing stars to create a largely single population of BDs and low-mass hydrogen-burning stars BDs will have velocity dispersions and spatial distributions very similar to higher-mass stars, and they will be able to retain discs, and thereby to sustain accretion and outflows. Formation by gravitational fragmentation of infalling gas into stellar clusters Bonnell et al. 2008
22 References Bate. M. R., Bonnell, I. A., Bromm, V., 2002a, MNRAS, 332, 65 Bate. M. R., Bonnell, I. A., Bromm, V., 2002b, MNRAS, 336, 705 Bate. M. R., Bonnell, I. A., Bromm, V., 2003, MNRAS, 339, 577 Bonnell, I. A., Clark, P., Bate, M. R.,2008, MNRAS, 389, 1556 Boyd, D. F. A., Whitworth, A. P., 2005, A&A, 430, 1059 Delgado Donate E. J., Clarke, C. J., Bate, M. R., 2003, MNRAS, 342, 926 Delgado Donate E. J., Clarke, C. J., Bate, M. R., 2004, MNRAS, 347, 759 Goodwin, S. P., Whitworth, A. P., 2007, A&A, 466, 943 Goodwin, S. P., Whitworth, A. P., Ward-Thompson, D., 2004a, A&A, 414, 633 Goodwin, S. P., Whitworth, A. P., Ward-Thompson, D., 2004b, A&A, 423, 169 Hester, J. J., et al. 1996, AJ, 111, 2349 Luhman, K. L., 2006, ApJ, 645, 676 Luhman, K. L., et al., 2005, ApJ, 635, 93 Luhman, K. L. et al., Protostars and Planets V (University of Arizona Press, Tucson; Eds. B. Reipurth, D. Jewitt, K. Keil), 443 Muzerolle, J., Hartmann, L., & Calvet, N., 1998, AJ, 116, 455 Muzerolle, J., et al. 2005, ApJ, 625, 906 Oliveira, J. M., Jeffries, R. D., & van Loon, J. T. 2009, MNRAS, 392, 1034 Padoan, P., Nordlund, A., 2002, ApJ, 576, 870 Reipurth, B., Clark, C. J., 2001, AJ, 122, 432 Stamatellos, D., Hubber, D. A., Whitworth, A. P., 2007, MNRAS, 328, 30 Whitworth, A. P., Goodwin, S. P., 2005, AN, 326, 899 Whitworth, A. P., Stamatellos, D., 2006, A&A, 458, 817 Whitworth, A. P., Zinnecker, H., 2004, A&A, 427, 299
Gravitational fragmentation of discs can form stars with masses
 Gravitational fragmentation of discs can form stars with masses from ~3 M J to ~200 M J (0.2M ) Defining stars, brown dwarfs Stars and planets Objects formed by gravitational instability on a dynamical
Gravitational fragmentation of discs can form stars with masses from ~3 M J to ~200 M J (0.2M ) Defining stars, brown dwarfs Stars and planets Objects formed by gravitational instability on a dynamical
The formation of brown dwarfs
 Star clusters: basic galactic building blocks Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 266, 2009 R. degrijs& J. R. D. Lépine, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s174392130999113x The formation
Star clusters: basic galactic building blocks Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 266, 2009 R. degrijs& J. R. D. Lépine, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s174392130999113x The formation
Brown dwarf formation by gravitational fragmentation of massive, extended protostellar discs
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 382, L30 L34 (2007) doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2007.00383.x Brown dwarf formation by gravitational fragmentation of massive, extended protostellar discs Dimitris Stamatellos, David
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 382, L30 L34 (2007) doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2007.00383.x Brown dwarf formation by gravitational fragmentation of massive, extended protostellar discs Dimitris Stamatellos, David
BROWN DWARF FORMATION BY DISC FRAGMENTATION
 BROWN DWARF FORMATION BY DISC FRAGMENTATION Ant Whitworth, Cardiff Dimitri Stamatellos, Cardiff plus Steffi Walch, Cardiff Murat Kaplan, Cardiff Simon Goodwin, Sheffield David Hubber, Sheffield Richard
BROWN DWARF FORMATION BY DISC FRAGMENTATION Ant Whitworth, Cardiff Dimitri Stamatellos, Cardiff plus Steffi Walch, Cardiff Murat Kaplan, Cardiff Simon Goodwin, Sheffield David Hubber, Sheffield Richard
Article: Whitworth, A.P. and Goodwin, S.P. (2005) The formation of brown dwarfs. Astronomische Nachrichten, 326 (10). pp
 This is a repository copy of The formation of brown dwarfs. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/127498/ Version: Accepted Version Article: Whitworth, A.P. and
This is a repository copy of The formation of brown dwarfs. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/127498/ Version: Accepted Version Article: Whitworth, A.P. and
The Initial Mass Function Elisa Chisari
 The Initial Mass Function AST 541 Dec 4 2012 Outline The form of the IMF Summary of observations Ingredients of a complete model A Press Schechter model Numerical simulations Conclusions The form of the
The Initial Mass Function AST 541 Dec 4 2012 Outline The form of the IMF Summary of observations Ingredients of a complete model A Press Schechter model Numerical simulations Conclusions The form of the
The dependence of star cluster formation on initial conditions. Matthew Bate University of Exeter
 The dependence of star cluster formation on initial conditions Matthew Bate University of Exeter Stellar properties do not greatly depend on initial conditions constellation Little evidence for variation
The dependence of star cluster formation on initial conditions Matthew Bate University of Exeter Stellar properties do not greatly depend on initial conditions constellation Little evidence for variation
Revealing and understanding the low-mass end of the IMF. Low-mass part of the Initial Mass Function Star, brown dwarf formation. G.
 Revealing and understanding the low-mass end of the IMF Low-mass part of the Initial Mass Function Star, brown dwarf formation G. Chabrier Field: Resolved objects IMF down to the HB limit Salpeter Kroupa
Revealing and understanding the low-mass end of the IMF Low-mass part of the Initial Mass Function Star, brown dwarf formation G. Chabrier Field: Resolved objects IMF down to the HB limit Salpeter Kroupa
Early Phases of Star Formation
 Early Phases of Star Formation Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: The earliest stages of the star formation process Probing the formation and evolution of prestellar cores with Herschel
Early Phases of Star Formation Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: The earliest stages of the star formation process Probing the formation and evolution of prestellar cores with Herschel
Numerical Simulations of Star Cluster Formation. Matthew Bate
 Numerical Simulations of Star Cluster Formation Matthew Bate http://www.astro.ex.ac.uk/people/mbate Typical molecular cloud Jeans mass 1 M, Opacity limit 3 MJ, P(k) k -4 Denser cloud Jeans mass 1/3 M Lower
Numerical Simulations of Star Cluster Formation Matthew Bate http://www.astro.ex.ac.uk/people/mbate Typical molecular cloud Jeans mass 1 M, Opacity limit 3 MJ, P(k) k -4 Denser cloud Jeans mass 1/3 M Lower
N-body Dynamics in Stellar Clusters Embedded in Gas
 N-body Dynamics in Stellar Clusters Embedded in Gas Matthew Bate, University of Exeter Kurosawa, Harries, Bate & Symington (2004) Collaborators: Ian Bonnell, St Andrews Volker Bromm, Texas Star Formation
N-body Dynamics in Stellar Clusters Embedded in Gas Matthew Bate, University of Exeter Kurosawa, Harries, Bate & Symington (2004) Collaborators: Ian Bonnell, St Andrews Volker Bromm, Texas Star Formation
OBSERVATIONAL CONSTRAINTS on the FORMATION of VERY LOW MASS STARS & BROWN DWARFS
 OBSERVATIONAL CONSTRAINTS on the FORMATION of VERY LOW MASS STARS & BROWN DWARFS Subhanjoy Mohanty (Spitzer Fellow, Harvard University) Gibor Basri, Ray Jayawardhana, Antonella Natta David Barrado y Navascués,
OBSERVATIONAL CONSTRAINTS on the FORMATION of VERY LOW MASS STARS & BROWN DWARFS Subhanjoy Mohanty (Spitzer Fellow, Harvard University) Gibor Basri, Ray Jayawardhana, Antonella Natta David Barrado y Navascués,
How do protostars get their mass?
 How do protostars get their mass? Phil Myers Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Origin of Stellar Masses Tenerife, Spain October 18, 2010 Introduction How does nature make a star? a star of particular
How do protostars get their mass? Phil Myers Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Origin of Stellar Masses Tenerife, Spain October 18, 2010 Introduction How does nature make a star? a star of particular
Implications of protostellar disk fragmentation
 Implications of protostellar disk fragmentation Eduard Vorobyov: The Institute of Astronomy, The University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Collaborators: Shantanu Basu, The University of Western Ontario, Canada
Implications of protostellar disk fragmentation Eduard Vorobyov: The Institute of Astronomy, The University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Collaborators: Shantanu Basu, The University of Western Ontario, Canada
Observa6ons of Brown Dwarfs
 Observa6ons of Brown Dwarfs Image credit: Don Dixon Kevin L. Luhman Penn State University 0 2 211 M J Log 10 (L/L sun ) 4 6 1 M J 13 M J 73 M J 0.3 M J 8 Burrows et al. 1997 10 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10
Observa6ons of Brown Dwarfs Image credit: Don Dixon Kevin L. Luhman Penn State University 0 2 211 M J Log 10 (L/L sun ) 4 6 1 M J 13 M J 73 M J 0.3 M J 8 Burrows et al. 1997 10 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10
18. Stellar Birth. Initiation of Star Formation. The Orion Nebula: A Close-Up View. Interstellar Gas & Dust in Our Galaxy
 18. Stellar Birth Star observations & theories aid understanding Interstellar gas & dust in our galaxy Protostars form in cold, dark nebulae Protostars evolve into main-sequence stars Protostars both gain
18. Stellar Birth Star observations & theories aid understanding Interstellar gas & dust in our galaxy Protostars form in cold, dark nebulae Protostars evolve into main-sequence stars Protostars both gain
Limits on the primordial stellar multiplicity
 A&A 439, 565 569 (2005) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20052654 c ESO 2005 Astronomy & Astrophysics Limits on the primordial stellar multiplicity S. P. Goodwin 1 and P. Kroupa 2,3 1 School of Physics & Astronomy,
A&A 439, 565 569 (2005) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20052654 c ESO 2005 Astronomy & Astrophysics Limits on the primordial stellar multiplicity S. P. Goodwin 1 and P. Kroupa 2,3 1 School of Physics & Astronomy,
Early Stages of (Low-Mass) Star Formation: The ALMA Promise
 Early Stages of (Low-Mass) Star Formation: The ALMA Promise Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: Prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF Identifying proto-brown dwarfs Bate et al. 1995
Early Stages of (Low-Mass) Star Formation: The ALMA Promise Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: Prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF Identifying proto-brown dwarfs Bate et al. 1995
Brown Dwarf Formation from Disk Fragmentation and Ejection
 Brown Dwarf Formation from Disk Fragmentation and Ejection Shantanu Basu Western University, London, Ontario, Canada Collaborator: Eduard Vorobyov (University of Vienna) 50 years of Brown Dwarfs Ringberg
Brown Dwarf Formation from Disk Fragmentation and Ejection Shantanu Basu Western University, London, Ontario, Canada Collaborator: Eduard Vorobyov (University of Vienna) 50 years of Brown Dwarfs Ringberg
An overview of star formation
 An overview of star formation Paul Clark ITA: Ralf Klessen Robi Banerjee Simon Glover Ian Bonnell Clare Dobbs Jim Dale Why study star formation? Stars chemically the enrich the Universe, so star formation
An overview of star formation Paul Clark ITA: Ralf Klessen Robi Banerjee Simon Glover Ian Bonnell Clare Dobbs Jim Dale Why study star formation? Stars chemically the enrich the Universe, so star formation
Stellar Birth. Stellar Formation. A. Interstellar Clouds. 1b. What is the stuff. Astrophysics: Stellar Evolution. A. Interstellar Clouds (Nebulae)
 Astrophysics: Stellar Evolution 1 Stellar Birth Stellar Formation A. Interstellar Clouds (Nebulae) B. Protostellar Clouds 2 C. Protostars Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Updated: 10/02/2006 A. Interstellar Clouds 1.
Astrophysics: Stellar Evolution 1 Stellar Birth Stellar Formation A. Interstellar Clouds (Nebulae) B. Protostellar Clouds 2 C. Protostars Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Updated: 10/02/2006 A. Interstellar Clouds 1.
Lecture 21 Formation of Stars November 15, 2017
 Lecture 21 Formation of Stars November 15, 2017 1 2 Birth of Stars Stars originally condense out of a COLD, interstellar cloud composed of H and He + trace elements. cloud breaks into clumps (gravity)
Lecture 21 Formation of Stars November 15, 2017 1 2 Birth of Stars Stars originally condense out of a COLD, interstellar cloud composed of H and He + trace elements. cloud breaks into clumps (gravity)
Stellar Evolution: Outline
 Stellar Evolution: Outline Interstellar Medium (dust) Hydrogen and Helium Small amounts of Carbon Dioxide (makes it easier to detect) Massive amounts of material between 100,000 and 10,000,000 solar masses
Stellar Evolution: Outline Interstellar Medium (dust) Hydrogen and Helium Small amounts of Carbon Dioxide (makes it easier to detect) Massive amounts of material between 100,000 and 10,000,000 solar masses
Gravitational collapse of gas
 Gravitational collapse of gas Assume a gas cloud of mass M and diameter D Sound speed for ideal gas is c s = γ P ρ = γ nkt ρ = γ kt m Time for sound wave to cross the cloud t sound = D == D m c s γ kt
Gravitational collapse of gas Assume a gas cloud of mass M and diameter D Sound speed for ideal gas is c s = γ P ρ = γ nkt ρ = γ kt m Time for sound wave to cross the cloud t sound = D == D m c s γ kt
29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Second Hour Exam November 10, 2010 Form A
 29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Second Hour Exam November 10, 2010 Form A There are 20 questions (Note: There will be 32 on the real thing). Read each question and all of the choices before choosing.
29:50 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Second Hour Exam November 10, 2010 Form A There are 20 questions (Note: There will be 32 on the real thing). Read each question and all of the choices before choosing.
Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud
 Red: CO from Mini survey Orion B Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud Spitzer Orion Cloud Survey: 10 sq. degrees in Orion A and Orion B mapped between 2004-2009 Orion A Green
Red: CO from Mini survey Orion B Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud Spitzer Orion Cloud Survey: 10 sq. degrees in Orion A and Orion B mapped between 2004-2009 Orion A Green
Star Formation. Stellar Birth
 Star Formation Lecture 12 Stellar Birth Since stars don t live forever, then they must be born somewhere and at some time in the past. How does this happen? And when stars are born, so are planets! 1 Molecular
Star Formation Lecture 12 Stellar Birth Since stars don t live forever, then they must be born somewhere and at some time in the past. How does this happen? And when stars are born, so are planets! 1 Molecular
The Life Cycles of Stars. Modified from Information provided by: Dr. Jim Lochner, NASA/GSFC
 The Life Cycles of Stars Modified from Information provided by: Dr. Jim Lochner, NASA/GSFC Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star... What do you see? How I Wonder What You Are... Stars have: Different Colors -
The Life Cycles of Stars Modified from Information provided by: Dr. Jim Lochner, NASA/GSFC Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star... What do you see? How I Wonder What You Are... Stars have: Different Colors -
Brown Dwarf Formation and Jet Propagation in Core Collapse Simulations
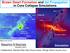 Brown Dwarf Formation and Jet Propagation in Core Collapse Simulations Knot Knot Cavity (proto-b.d) Observation Riaz et al. (2017) Masahiro N Machida (Kyushu Univ.) Clumps B.D mass object Simulation Collaborators:
Brown Dwarf Formation and Jet Propagation in Core Collapse Simulations Knot Knot Cavity (proto-b.d) Observation Riaz et al. (2017) Masahiro N Machida (Kyushu Univ.) Clumps B.D mass object Simulation Collaborators:
Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars
 Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars Guidepost The last chapter introduced you to the gas and dust between the stars that are raw material for new stars. Here you will begin putting together
Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars Guidepost The last chapter introduced you to the gas and dust between the stars that are raw material for new stars. Here you will begin putting together
THE INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM
 THE INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM An IR view of dust clouds In particular, light from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH s) Little bit of carbon out there, forms hydrocarbons like car exhaust Associated with
THE INTERSTELLAR MEDIUM An IR view of dust clouds In particular, light from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH s) Little bit of carbon out there, forms hydrocarbons like car exhaust Associated with
The Birth Of Stars. How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation
 Goals: The Birth Of Stars How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation Interstellar Medium Gas and dust between stars is the interstellar
Goals: The Birth Of Stars How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation Interstellar Medium Gas and dust between stars is the interstellar
10/29/2009. The Lives And Deaths of Stars. My Office Hours: Tuesday 3:30 PM - 4:30 PM 206 Keen Building. Stellar Evolution
 of s Like s of Other Stellar The Lives And Deaths of s a Sun-like s More 10/29/2009 My Office Hours: Tuesday 3:30 PM - 4:30 PM 206 Keen Building Test 2: 11/05/2009 of s Like s of Other a Sun-like s More
of s Like s of Other Stellar The Lives And Deaths of s a Sun-like s More 10/29/2009 My Office Hours: Tuesday 3:30 PM - 4:30 PM 206 Keen Building Test 2: 11/05/2009 of s Like s of Other a Sun-like s More
The Formation of Brown Dwarfs: Observations
 Luhman et al.: The Formation of Brown Dwarfs 443 The Formation of Brown Dwarfs: Observations Kevin L. Luhman The Pennsylvania State University Viki Joergens The University of Leiden Charles Lada Smithsonian
Luhman et al.: The Formation of Brown Dwarfs 443 The Formation of Brown Dwarfs: Observations Kevin L. Luhman The Pennsylvania State University Viki Joergens The University of Leiden Charles Lada Smithsonian
Star Cluster Formation and the Origin of Stellar Properties. Matthew Bate University of Exeter
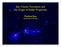 Star Cluster Formation and the Origin of Stellar Properties Matthew Bate University of Exeter Typical molecular cloud (Bate et al. 2003) Denser cloud (Bate & Bonnell 2005) Jeans mass 1 M, Opacity limit
Star Cluster Formation and the Origin of Stellar Properties Matthew Bate University of Exeter Typical molecular cloud (Bate et al. 2003) Denser cloud (Bate & Bonnell 2005) Jeans mass 1 M, Opacity limit
Accretion disks in the sub-stellar regime
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 76, 295 c SAIt 2005 Memorie della Accretion disks in the sub-stellar regime Ray Jayawardhana 1, Subhanjoy Mohanty 2 and Gibor Basri 3 1 Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, University
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 76, 295 c SAIt 2005 Memorie della Accretion disks in the sub-stellar regime Ray Jayawardhana 1, Subhanjoy Mohanty 2 and Gibor Basri 3 1 Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, University
Planet-like Companion to a Brown Dwarf
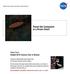 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Planet-like Companion to a Brown Dwarf Taken from: Hubble 2010: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Planet-like Companion to a Brown Dwarf Taken from: Hubble 2010: Science Year in Review Produced by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope
AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies The H-R Diagram review So far: Stars on Main Sequence (MS) Next: - Pre MS (Star Birth) - Post MS: Giants, Super Giants, White dwarfs Star Birth We start
AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies The H-R Diagram review So far: Stars on Main Sequence (MS) Next: - Pre MS (Star Birth) - Post MS: Giants, Super Giants, White dwarfs Star Birth We start
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015
 Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015 Today: Continue Ch. 13: Star Stuff Reading in Bennett: For Monday: Finish Chapter 13 Star Stuff Reminders: Ch. 12 HW now on Mastering Astronomy, due Monday. Ch. 13 will be
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015 Today: Continue Ch. 13: Star Stuff Reading in Bennett: For Monday: Finish Chapter 13 Star Stuff Reminders: Ch. 12 HW now on Mastering Astronomy, due Monday. Ch. 13 will be
Chapter 16 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Birth Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Stellar Evolution. Stars are chemical factories The Earth and all life on the Earth are made of elements forged in stars
 Lecture 11 Stellar Evolution Stars are chemical factories The Earth and all life on the Earth are made of elements forged in stars A Spiral Galaxy (Milky Way Type) 120,000 ly A few hundred billion stars
Lecture 11 Stellar Evolution Stars are chemical factories The Earth and all life on the Earth are made of elements forged in stars A Spiral Galaxy (Milky Way Type) 120,000 ly A few hundred billion stars
The physics of stars. A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure.
 Lecture 4 Stars The physics of stars A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure. X-ray ultraviolet infrared radio To understand
Lecture 4 Stars The physics of stars A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure. X-ray ultraviolet infrared radio To understand
THE STAR FORMATION NEWSLETTER No February /5/29
 THE STAR FORMATION NEWSLETTER No.266-12 February 2015 2015/5/29 46-50 Understanding star formation in molecular clouds II. Signatures of gravitational collapse of IRDCs to Cloud-cloud collision as a trigger
THE STAR FORMATION NEWSLETTER No.266-12 February 2015 2015/5/29 46-50 Understanding star formation in molecular clouds II. Signatures of gravitational collapse of IRDCs to Cloud-cloud collision as a trigger
IV From cores to stars
 IV From cores to stars 4.0 The Jeans condition When the supporting pressure in a region is not able to hold that region up against gravitational collapse it is said to be Jeans unstable. The Jeans length
IV From cores to stars 4.0 The Jeans condition When the supporting pressure in a region is not able to hold that region up against gravitational collapse it is said to be Jeans unstable. The Jeans length
From Massive Cores to Massive Stars
 From Massive Cores to Massive Stars Mark Krumholz Princeton University / UC Santa Cruz Collaborators: Richard Klein, Christopher McKee (UC Berkeley) Kaitlin Kratter, Christopher Matzner (U. Toronto) Jonathan
From Massive Cores to Massive Stars Mark Krumholz Princeton University / UC Santa Cruz Collaborators: Richard Klein, Christopher McKee (UC Berkeley) Kaitlin Kratter, Christopher Matzner (U. Toronto) Jonathan
AST 6336, Interstellar Medium, Spring 2015
 AST 6336, Interstellar Medium, Spring 2015 Young stellar clusters (lectures by Nicola Da Rio ndario@ufl.edu) January 2, 4, 2015 Star formation A molecular cloud may become unsupported gas pressure + magnetic
AST 6336, Interstellar Medium, Spring 2015 Young stellar clusters (lectures by Nicola Da Rio ndario@ufl.edu) January 2, 4, 2015 Star formation A molecular cloud may become unsupported gas pressure + magnetic
The Formation of Brown Dwarfs: Observations
 The Formation of Brown Dwarfs: Observations Kevin L. Luhman The Pennsylvania State University Viki Joergens The University of Leiden Charles Lada Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory James Muzerolle and
The Formation of Brown Dwarfs: Observations Kevin L. Luhman The Pennsylvania State University Viki Joergens The University of Leiden Charles Lada Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory James Muzerolle and
Chapter 12: The Lives of Stars. How do we know it s there? Three Kinds of Nebulae 11/7/11. 1) Emission Nebulae 2) Reflection Nebulae 3) Dark Nebulae
 11/7/11 Chapter 12: The Lives of Stars Space is Not Empty The Constellation Orion The Orion Nebula This material between the stars is called the Interstellar Medium It is very diffuse and thin. In fact
11/7/11 Chapter 12: The Lives of Stars Space is Not Empty The Constellation Orion The Orion Nebula This material between the stars is called the Interstellar Medium It is very diffuse and thin. In fact
Recall what you know about the Big Bang.
 What is this? Recall what you know about the Big Bang. Most of the normal matter in the universe is made of what elements? Where do we find most of this normal matter? Interstellar medium (ISM) The universe
What is this? Recall what you know about the Big Bang. Most of the normal matter in the universe is made of what elements? Where do we find most of this normal matter? Interstellar medium (ISM) The universe
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics
 Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 16: The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation Interstellar Dust and Dark Nebulae Interstellar Dust Dark Nebulae Interstellar Reddening Interstellar
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 16: The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation Interstellar Dust and Dark Nebulae Interstellar Dust Dark Nebulae Interstellar Reddening Interstellar
SPH simulations of star/planet formation triggered by cloud-cloud collisions
 Exoplanets: Detection, Formation and Dynamics Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 249, 2008 Y.-S. Sun, S. Ferraz-Mello & J.-L. Zhou, eds. c 2008 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X
Exoplanets: Detection, Formation and Dynamics Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 249, 2008 Y.-S. Sun, S. Ferraz-Mello & J.-L. Zhou, eds. c 2008 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X
A Tale of Star and Planet Formation. Lynne Hillenbrand Caltech
 A Tale of Star and Planet Formation Lynne Hillenbrand Caltech Vermeer s The Astronomer (1688) Mauna Kea (last week) photos by: Sarah Anderson and Bill Bates Context: Our Sun The Sun is a completely average
A Tale of Star and Planet Formation Lynne Hillenbrand Caltech Vermeer s The Astronomer (1688) Mauna Kea (last week) photos by: Sarah Anderson and Bill Bates Context: Our Sun The Sun is a completely average
Star Cluster Formation
 Star Cluster Formation HST Colin Hill Princeton Astrophysics 4 December 2012 Trapezium VLT Outline Star Clusters: Background + Observations The Life of a Cluster - Fragmentation - Feedback Effects - Mass
Star Cluster Formation HST Colin Hill Princeton Astrophysics 4 December 2012 Trapezium VLT Outline Star Clusters: Background + Observations The Life of a Cluster - Fragmentation - Feedback Effects - Mass
Topics for Today s Class
 Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 11 Formation of Stars and Structure of Stars Topics for Today s Class 1. Making Stars from the Interstellar Medium 2. Evidence of Star Formation: The Orion Nebula
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 11 Formation of Stars and Structure of Stars Topics for Today s Class 1. Making Stars from the Interstellar Medium 2. Evidence of Star Formation: The Orion Nebula
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 31 Aug 2002
 Brown Dwarfs IAU Symposium, Vol. 211, 2003 E. L. Martín, ed. Brown Dwarfs as Ejected Stellar Embryos: Observational Perspectives arxiv:astro-ph/0209005v1 31 Aug 2002 Bo Reipurth Institute for Astronomy,
Brown Dwarfs IAU Symposium, Vol. 211, 2003 E. L. Martín, ed. Brown Dwarfs as Ejected Stellar Embryos: Observational Perspectives arxiv:astro-ph/0209005v1 31 Aug 2002 Bo Reipurth Institute for Astronomy,
Chapter 9. The Formation and Structure of Stars
 Chapter 9 The Formation and Structure of Stars The Interstellar Medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
Chapter 9 The Formation and Structure of Stars The Interstellar Medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
Chapter 11 The Formation of Stars
 Chapter 11 The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky.
Chapter 11 The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky.
M42 (The Orion Nebula) and M43
 3.4b demonstrate an understanding that emission nebulae, absorption nebulae and open clusters are associated with the birth of stars 3.4c demonstrate an understanding that planetary nebulae and supernovae
3.4b demonstrate an understanding that emission nebulae, absorption nebulae and open clusters are associated with the birth of stars 3.4c demonstrate an understanding that planetary nebulae and supernovae
IX. Star and planet formation. h"p://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html
 IX. Star and planet formation h"p://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html 1. The ISM Most of the volume of space around us contains the diffuse ISM at 10 4-10 6 K with densities of only a few atoms per
IX. Star and planet formation h"p://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy111.html 1. The ISM Most of the volume of space around us contains the diffuse ISM at 10 4-10 6 K with densities of only a few atoms per
Discs or Disks? A review of circumstellar discs. Ken Rice Institute for Astronomy University of Edinburgh. 6/18/12 Labyrinth of Star Formation
 Discs or Disks? A review of circumstellar discs Ken Rice Institute for Astronomy University of Edinburgh Circumstellar accretion discs Formed during the gravitational collapse of a gaseous molecular cloud
Discs or Disks? A review of circumstellar discs Ken Rice Institute for Astronomy University of Edinburgh Circumstellar accretion discs Formed during the gravitational collapse of a gaseous molecular cloud
Chapter 16: Star Birth
 Chapter 16 Lecture Chapter 16: Star Birth Star Birth 16.1 Stellar Nurseries Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Where do stars form? Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds
Chapter 16 Lecture Chapter 16: Star Birth Star Birth 16.1 Stellar Nurseries Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Where do stars form? Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds
Fragmentation and collapse the road to star formation
 Chapter 5 Fragmentation and collapse the road to star formation 5.1 The road to star formation Thus far we have studied the places where stars form molecular clouds. We have discussed the ways in which
Chapter 5 Fragmentation and collapse the road to star formation 5.1 The road to star formation Thus far we have studied the places where stars form molecular clouds. We have discussed the ways in which
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 22 Oct 2001
 A Dynamical Origin for Brown Dwarfs Bo Reipurth 1,2, Cathie Clarke 3, & Eduardo Delgado-Donate 3 arxiv:astro-ph/0110481v1 22 Oct 2001 Abstract. Brown dwarfs may have such low masses because they are prematurely
A Dynamical Origin for Brown Dwarfs Bo Reipurth 1,2, Cathie Clarke 3, & Eduardo Delgado-Donate 3 arxiv:astro-ph/0110481v1 22 Oct 2001 Abstract. Brown dwarfs may have such low masses because they are prematurely
Guiding Questions. Stellar Evolution. Stars Evolve. Interstellar Medium and Nebulae
 Guiding Questions Stellar Evolution 1. Why do astronomers think that stars evolve? 2. What kind of matter exists in the spaces between the stars? 3. What steps are involved in forming a star like the Sun?
Guiding Questions Stellar Evolution 1. Why do astronomers think that stars evolve? 2. What kind of matter exists in the spaces between the stars? 3. What steps are involved in forming a star like the Sun?
AST4930: Star and Planet Formation. Syllabus. AST4930: Star and Planet Formation, Spring 2014
 AST4930: Star and Planet Formation Lecture 1: Overview Assoc. Prof. Jonathan C. Tan jt@astro.ufl.edu Bryant 302 Syllabus AST4930: Star and Planet Formation, Spring 2014 Assoc. Prof. Jonathan C. Tan (jt
AST4930: Star and Planet Formation Lecture 1: Overview Assoc. Prof. Jonathan C. Tan jt@astro.ufl.edu Bryant 302 Syllabus AST4930: Star and Planet Formation, Spring 2014 Assoc. Prof. Jonathan C. Tan (jt
Chapter 12 Review. 2) About 90% of the star's total life is spent on the main sequence. 2)
 Chapter 12 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) As a main-sequence star, the Sun's hydrogen supply should last about 10 billion years from the zero-age
Chapter 12 Review TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) As a main-sequence star, the Sun's hydrogen supply should last about 10 billion years from the zero-age
Chapter 17: Stellar Evolution
 Astr 2310 Thurs. Mar. 30, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 17: Stellar Evolution Birth of Stars and Pre Main Sequence Evolution Evolution on and off the Main Sequence Solar Mass Stars Massive Stars Low Mass
Astr 2310 Thurs. Mar. 30, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 17: Stellar Evolution Birth of Stars and Pre Main Sequence Evolution Evolution on and off the Main Sequence Solar Mass Stars Massive Stars Low Mass
The Competitive Accretion Debate
 The Competitive Accretion Debate 1,2 Paul C. Clark 2 Ralf S. Klessen 3 Ian A. Bonnell 3 Rowan J. Smith 1 KITP 2 University of Heidelberg 3 University of St Andrews What is CA and how does it work? Theory
The Competitive Accretion Debate 1,2 Paul C. Clark 2 Ralf S. Klessen 3 Ian A. Bonnell 3 Rowan J. Smith 1 KITP 2 University of Heidelberg 3 University of St Andrews What is CA and how does it work? Theory
Astronomy 122 Midterm
 Astronomy 122 Midterm This Class (Lecture 15): Stellar Evolution: The Main Sequence Next Class: Stellar Evolution: Post-Main Sequence Midterm on Thursday! Last week for Nightlabs 1 hour exam in this classroom
Astronomy 122 Midterm This Class (Lecture 15): Stellar Evolution: The Main Sequence Next Class: Stellar Evolution: Post-Main Sequence Midterm on Thursday! Last week for Nightlabs 1 hour exam in this classroom
Clicker Question: Clicker Question: Clicker Question: Clicker Question: What is the remnant left over from a Type Ia (carbon detonation) supernova:
 Test 3 results D C Grades posted in cabinet and Grades posted on-line B A F If you are not properly registered then come see me for your grade What is the ultimate origin of the elements heavier than helium
Test 3 results D C Grades posted in cabinet and Grades posted on-line B A F If you are not properly registered then come see me for your grade What is the ultimate origin of the elements heavier than helium
Brown dwarfs in their infancy and some other remaining bits
 Brown dwarfs in their infancy and some other remaining bits Brown dwarf disks Observed photometry Dereddened photometry December 11, 2006 field M dwarfs without disk! different photometric systems! Jayawardhana
Brown dwarfs in their infancy and some other remaining bits Brown dwarf disks Observed photometry Dereddened photometry December 11, 2006 field M dwarfs without disk! different photometric systems! Jayawardhana
Stellar, brown dwarf and multiple star properties from a radiation hydrodynamical simulation of star cluster formation
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 419, 3115 3146 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19955.x Stellar, brown dwarf and multiple star properties from a radiation hydrodynamical simulation of star cluster formation
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 419, 3115 3146 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19955.x Stellar, brown dwarf and multiple star properties from a radiation hydrodynamical simulation of star cluster formation
The Jeans mass and the origin of the knee in the IMF
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 368, 1296 1300 (2006) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10214.x The Jeans mass and the origin of the knee in the IMF I. A. Bonnell, 1 C. J. Clarke 2 and M. R. Bate 3 1 School of Physics
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 368, 1296 1300 (2006) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10214.x The Jeans mass and the origin of the knee in the IMF I. A. Bonnell, 1 C. J. Clarke 2 and M. R. Bate 3 1 School of Physics
10/26/ Star Birth. Chapter 13: Star Stuff. How do stars form? Star-Forming Clouds. Mass of a Star-Forming Cloud. Gravity Versus Pressure
 10/26/16 Lecture Outline 13.1 Star Birth Chapter 13: Star Stuff How do stars form? Our goals for learning: How do stars form? How massive are newborn stars? Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds
10/26/16 Lecture Outline 13.1 Star Birth Chapter 13: Star Stuff How do stars form? Our goals for learning: How do stars form? How massive are newborn stars? Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds
The formation of free-floating brown dwarves and planetary-mass objects by photo-erosion of prestellar cores
 A&A 47, 99 06 004) DOI: 10.1051/0004-661:004111 c ESO 004 Astronomy & Astrophysics The formation of free-floating brown dwarves and planetary-mass objects by photo-erosion of prestellar cores A. P. Whitworth
A&A 47, 99 06 004) DOI: 10.1051/0004-661:004111 c ESO 004 Astronomy & Astrophysics The formation of free-floating brown dwarves and planetary-mass objects by photo-erosion of prestellar cores A. P. Whitworth
Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 9
 Phys 0 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 9 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. We know that giant stars are larger in diameter than the sun because * a. they are more luminous but have about the
Phys 0 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 9 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. We know that giant stars are larger in diameter than the sun because * a. they are more luminous but have about the
Astronomy 104: Stellar Astronomy
 Astronomy 104: Stellar Astronomy Lecture 16: A Star is Born Spring Semester 2013 Dr. Matt Craig 1 1 Goals By the end of the next two to three lectures you should be able to: Describe the life cycle of
Astronomy 104: Stellar Astronomy Lecture 16: A Star is Born Spring Semester 2013 Dr. Matt Craig 1 1 Goals By the end of the next two to three lectures you should be able to: Describe the life cycle of
Physics Homework Set 2 Sp 2015
 1) A large gas cloud in the interstellar medium that contains several type O and B stars would appear to us as 1) A) a reflection nebula. B) a dark patch against a bright background. C) a dark nebula.
1) A large gas cloud in the interstellar medium that contains several type O and B stars would appear to us as 1) A) a reflection nebula. B) a dark patch against a bright background. C) a dark nebula.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Mar 2006
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 21 January 2014 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) The Jeans mass and the origin of the knee in the IMF arxiv:astro-ph/0603444v1 17 Mar 2006 I. A. Bonnell
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 21 January 2014 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) The Jeans mass and the origin of the knee in the IMF arxiv:astro-ph/0603444v1 17 Mar 2006 I. A. Bonnell
The Early Evolution of low mass stars and Brown Dwarfs. I. Baraffe University of Exeter
 The Early Evolution of low mass stars and Brown Dwarfs I. Baraffe University of Exeter 1. Some observational/theoretical facts Spread in the HRD Lithium depletion Evidence for episodic accretion - Embedded
The Early Evolution of low mass stars and Brown Dwarfs I. Baraffe University of Exeter 1. Some observational/theoretical facts Spread in the HRD Lithium depletion Evidence for episodic accretion - Embedded
Star formation Part III
 Lecture 4 Star formation Part III Lecture Universität Heidelberg WS 11/12 Dr. C. Mordasini Based partially on script of Prof. W. Benz Matthew R. Bate Mentor Prof. T. Henning Lecture 4 overview 1. Heating
Lecture 4 Star formation Part III Lecture Universität Heidelberg WS 11/12 Dr. C. Mordasini Based partially on script of Prof. W. Benz Matthew R. Bate Mentor Prof. T. Henning Lecture 4 overview 1. Heating
Cassiopeia A: Supernova Remnant
 Crab Nebula: Pulsar During a supernova, the core of a massive star can be compressed to form a rapidly rotating ball composed mostly of neutrons that is only twelve miles in diameter. A teaspoon of such
Crab Nebula: Pulsar During a supernova, the core of a massive star can be compressed to form a rapidly rotating ball composed mostly of neutrons that is only twelve miles in diameter. A teaspoon of such
Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A star (no matter what its mass) spends
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A star (no matter what its mass) spends
Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A star (no matter what its mass) spends
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 20 Stellar Evolution MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A star (no matter what its mass) spends
Giant Planet Formation
 Giant Planet Formation Overview Observations: Meteorites to Extrasolar Planets Our Solar System Dynamics Meteorites Geology Planetary composition & structure Other Stars Circumstellar disks Extrasolar
Giant Planet Formation Overview Observations: Meteorites to Extrasolar Planets Our Solar System Dynamics Meteorites Geology Planetary composition & structure Other Stars Circumstellar disks Extrasolar
Abundance of Elements. Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System
 Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
Abundance of Elements Relative abundance of elements in the Solar System What is the origin of elements in the universe? Three elements formed in the first minutes after the big bang (hydrogen, helium
Astronomy 104: Second Exam
 Astronomy 104: Second Exam Stephen Lepp October 29, 2014 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer A The Sun is powered by converting hydrogen to what?
Astronomy 104: Second Exam Stephen Lepp October 29, 2014 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. Short Answer A The Sun is powered by converting hydrogen to what?
AST 248, Lecture 5. James Lattimer. Department of Physics & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook University. February 6, 2015
 AST 248, Lecture 5 James Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook University February 6, 2015 The Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe james.lattimer@stonybrook.edu Star
AST 248, Lecture 5 James Lattimer Department of Physics & Astronomy 449 ESS Bldg. Stony Brook University February 6, 2015 The Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe james.lattimer@stonybrook.edu Star
Guiding Questions. The Birth of Stars
 Guiding Questions The Birth of Stars 1 1. Why do astronomers think that stars evolve (bad use of term this is about the birth, life and death of stars and that is NOT evolution)? 2. What kind of matter
Guiding Questions The Birth of Stars 1 1. Why do astronomers think that stars evolve (bad use of term this is about the birth, life and death of stars and that is NOT evolution)? 2. What kind of matter
Chapters 12 and 13 Review: The Life Cycle and Death of Stars. How are stars born, and how do they die? 4/1/2009 Habbal Astro Lecture 27 1
 Chapters 12 and 13 Review: The Life Cycle and Death of Stars How are stars born, and how do they die? 4/1/2009 Habbal Astro 110-01 Lecture 27 1 Stars are born in molecular clouds Clouds are very cold:
Chapters 12 and 13 Review: The Life Cycle and Death of Stars How are stars born, and how do they die? 4/1/2009 Habbal Astro 110-01 Lecture 27 1 Stars are born in molecular clouds Clouds are very cold:
Brown dwarf & star formation and the bottom of the IMF: a critical look
 Brown dwarf & star formation and the bottom of the IMF: a critical look Gilles Chabrier ENS-Lyon U. Exeter Origin of stars and their planetary systems Mac Master University, June 2012 Field: Resolved objects
Brown dwarf & star formation and the bottom of the IMF: a critical look Gilles Chabrier ENS-Lyon U. Exeter Origin of stars and their planetary systems Mac Master University, June 2012 Field: Resolved objects
Accretion Mechanisms
 Massive Protostars Accretion Mechanism Debate Protostellar Evolution: - Radiative stability - Deuterium shell burning - Contraction and Hydrogen Ignition Stahler & Palla (2004): Section 11.4 Accretion
Massive Protostars Accretion Mechanism Debate Protostellar Evolution: - Radiative stability - Deuterium shell burning - Contraction and Hydrogen Ignition Stahler & Palla (2004): Section 11.4 Accretion
Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation
 Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation Thomas Peters Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Ralf Klessen, Robi Banerjee (ITA, Heidelberg) Mordecai-Mark
Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation Thomas Peters Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Ralf Klessen, Robi Banerjee (ITA, Heidelberg) Mordecai-Mark
The Life and Death of Stars
 The Life and Death of Stars A Star Is Born Not everyone agrees, but it is generally thought that stars originate from nebulae (clouds of dust and gas). Almost inevitably, a nebula will "collapse" into
The Life and Death of Stars A Star Is Born Not everyone agrees, but it is generally thought that stars originate from nebulae (clouds of dust and gas). Almost inevitably, a nebula will "collapse" into
Remember from Stefan-Boltzmann that 4 2 4
 Lecture 17 Review Most stars lie on the Main sequence of an H&R diagram including the Sun, Sirius, Procyon, Spica, and Proxima Centauri. This figure is a plot of logl versus logt. The main sequence is
Lecture 17 Review Most stars lie on the Main sequence of an H&R diagram including the Sun, Sirius, Procyon, Spica, and Proxima Centauri. This figure is a plot of logl versus logt. The main sequence is
Chapter 16 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Birth Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth Star Birth 16.1 Stellar Nurseries Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Where do stars form? Star-Forming
Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth Star Birth 16.1 Stellar Nurseries Our goals for learning: Where do stars form? Why do stars form? Where do stars form? Star-Forming
AST 101 INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY SPRING MIDTERM EXAM 2 TEST VERSION 1 ANSWERS
 AST 101 INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY SPRING 2008 - MIDTERM EXAM 2 TEST VERSION 1 ANSWERS Multiple Choice. In the blanks provided before each question write the letter for the phrase that best answers the
AST 101 INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY SPRING 2008 - MIDTERM EXAM 2 TEST VERSION 1 ANSWERS Multiple Choice. In the blanks provided before each question write the letter for the phrase that best answers the
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Nov 2006
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 4 December 2013 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) On the relative motions of dense cores and envelopes in star-forming molecular clouds arxiv:astro-ph/0611421v1
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 4 December 2013 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) On the relative motions of dense cores and envelopes in star-forming molecular clouds arxiv:astro-ph/0611421v1
The Interstellar Medium. Papillon Nebula. Neutral Hydrogen Clouds. Interstellar Gas. The remaining 1% exists as interstellar grains or
 The Interstellar Medium About 99% of the material between the stars is in the form of a gas The remaining 1% exists as interstellar grains or interstellar dust If all the interstellar gas were spread evenly,
The Interstellar Medium About 99% of the material between the stars is in the form of a gas The remaining 1% exists as interstellar grains or interstellar dust If all the interstellar gas were spread evenly,
Midterm Results. The Milky Way in the Infrared. The Milk Way from Above (artist conception) 3/2/10
 Lecture 13 : The Interstellar Medium and Cosmic Recycling Midterm Results A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath The Milky Way in the Infrared View from the Earth: Edge On Infrared light penetrates the clouds and shows
Lecture 13 : The Interstellar Medium and Cosmic Recycling Midterm Results A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath The Milky Way in the Infrared View from the Earth: Edge On Infrared light penetrates the clouds and shows
