Astro 6590: Dwarf galaxies
|
|
|
- Veronica Wells
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Astro 6590: Dwarf galaxies Overview of dwarf galaxies Distinctive features of dwarfs Dwarfs vs giants Dwarfs vs globular clusters Dwarfs: challenges to CDM Missing satellite problem: how many dwarfs? The core-cusp problem: dark matter halos Morphological sequence of dwarfs: de, dsph, di Morphological segregation Local Group dwarfs Perseus dwarfs Virgo dwarfs Transition dwarfs Star formation history Metallicity-luminosity relation Blowout in dwarfs Stellar streams and disrupted satellites near the Milky Way DDO 154: an almost dark galaxy HST Survey of the Perseus Cluster core 12 Orbits centered around the core of Perseus (Conselice (PI), Held, DeRijke) 1
2 Dwarf ellipticals exist in clusters and morphologically appear similar to Local Group dwarf ellipticals Discovered in 1950s by G. Reaves through a Virgo cluster imaging survey There are however 5-10 as many low-mass cluster galaxies per giant galaxy as there are in Looser groups Low-Mass Galaxies in the Perseus Cluster (Conselice, Ringberg conf.) Perseus Cluster HST survey (Conselice, Gallagher & Wyse 03 sample) Real Dwarfs Compact dwarfs Background Spirals? Ambiguous cases 2
3 Cluster des deviate from the color-magnitude relation Clues for this deviation are old (e.g., Held & Mould 1994) Low L galaxies in clusters are a heterogenous population Color-Magnitude diagram for Perseus galaxies with Local Group des plotted. Both 'blue' and 'red des Conselice, Gallagher & Wyse (2003) Cluster des likely have a mix of stellar populations some might be metal rich Three stellar synthesis-modeled age tracts at constant metallicity (3 different ones) for different age populations. Conselice et al. (2003) 3
4 Kinematics of des Kinematics of dwarfs 4
5 Kinematics of dwarfs Internal Dynamics of NGC 205 CFHT12K mosaic imag (Demers et al. 2003) Keck/ DEIMOS slitmasks chosen to lie along tidal extensions. Spectroscopic targets chosen to be likely RGB stars in NGC
6 NGC 205 Inner rotation = 15 km s -1 velocity (km/s) radius (arcmin) Geha, Guhathakurta, Rich & Cooper (2006) Local Group rotation curves NGC 205 Geha et al. (2006) velocity (km/s) NGC 147 Geha et al. in prep vrot = 17 km/s NGC 185 Bender et al (1991) radius (arcmin) 6
7 dsphs in the LG Rotation of des in Virgo Unlike des in the Local Group, some des in Virgo are rotationdominated. Long slit stellar absorption line spectroscopy from Palomar 5m Rotation curve Velocity dispersion van Zee et al
8 de s as stripped di s? Rotationdominated des appear to avoid the cluster center Non-rotating des are found in the core van Zee et al 2004 Velocity distribution of des is large, with more substructure than giant cluster galaxies Conselice et al. (2001) A sign of their formation mechanism? 8
9 des in Virgo des are widely distributed in Virgo. Do not cluster around giants Different dynamics from Es des versus de,ns At the faint end, M B ~ -12, only 10% of des are nucleated. At the bright end, M B -16, almost 100% are. A significant fraction of des in Virgo are rotation dominated. Binggeli et al. 2000, A&A, 359, 447 Conselice et al. 2001, ApJ 559, 791. Oh & lin 2000, ApJ 543, 620 van Zee et al. 2004, AJ Fornax dsph 9
10 Fornax CMD Carina Dwarf: Episodic SF Plots from Smecker-Hane
11 Observational Constraints All dwarfs so studied have ancient stars (> 10 Gyr) IC1613 Dolphin et al. LeoA Dolphin et al. M32 Alonso et al. LG dwarfs: wide range of SFH 11
12 Substructure in the Local Group Galaxies mainly clustered around the two principal galaxies MW & M31 Giant spirals dsph (+dell) dirr dirr/dsph Diagram from Eva Grebel Transformations?? Different types of dwarfs: de dsph di } different scaling relations in r, M, L, SB, etc (Kormendy 1985; Kormendy and Freeman 2004). Hybrid/Transition cases (eg, LGS3, Phoenix) What are the evolutionary relationships? 12
13 Characteristics of the satellite systems (Some) simulations suggest that: abundance and dynamics of the satallites depend on the host halo predictions accurate for satellites with v>50 km/s VDF significantly different at low v the Milky Way should have ~50 satellites with v>20km/s with M>3E8 and within 570kpc Issues: Resolution in the simulations Gastrophysics Reionization Transition type dwarfs Grebel, Gallagher & Hardbeck 2003 dsphs: Filled circles des: Open circles dirr/dsph: Filled diamonds dirr: Open diamonds General trend for HI masses to increase with increasing D dsphs typically < 10 5 M dirrs typically > 10 7 M Transition types intermediate Distance to nearest massive galaxy 13
14 Transition type dwarfs Grebel, Gallagher & Hardbeck 2003 dsphs & dirrs Show similar exponential radial surface brightness profiles Different versions of the same? dsphs vs dirrs dsphs are more metal-rich at same L Evident both in PNe and stellar Z Gas poor Different histories? Phoenix, DDO 210, LGS 3, Antlia, KKR 25, Leo T Locus in L-Z diagram is consistent with dsphs Have mixed dirr/dsph morphologies Low stellar mass Low angular momentum Small HI mass Would closely resemble dsphs if gas were removed Progenitors of dsphs? The case of Leo T Discovered by Irwin et al MNRAS 384, 535 D = 420 kpc V = +35 km/s M T,V = -7.1 R plummer ~ 170pc R HI ~ 300 pc CMD has both RGB (6-8 Gyr) and young blue *s (200 Myr) Morphologically dsph but SF transition dwarf Two phase HI(500/6000K) Stellar mass: 1.2 x 10 5 M HI mass: 2.8 x 10 5 M Peak N HI = 7 x cm -2 M dyn (R<R HI ) = 3.3 x 10 6 M M/L > 50 Kopylov et al
15 The case of Leo T Ryan-Weber et al. 2008, MNRAS 384, 535 Outer contour 2 x cm -2 HI radius = 2.5 = 300 pc Cold and warm components seen but no organized rotation The case of Leo T Discovered by Irwin et al MNRAS 384, 535 D = 420 kpc V = +35 km/s M T,V = -7.1 R plummer ~ 170pc R HI /R plummer ~ 1.8 CMD has both RGB (6-8 Gyr) and young blue *s (200 Myr) Morphologically dsph but SF transition dwarf Two phase HI(500/6000K) Stellar mass: 1.2 x 10 5 M HI mass: 2.8 x 10 5 M Peak N HI = 7 x cm -2 M dyn (R<R HI ) = 3.3 x 10 6 M M/L > 50 Forming stars at slow rate x 10-5 M /yr Gas consumption time ~ 5 x 10 9 yr Low N H but also low central σ ~2 km/s => form *s Ryan-Weber et al. 2008, MNRAS 384,
16 Environmental effects Astro-ph/ Morphological Segregation Grebel 2005 Gas-poor, low-mass dwarfs (dsphs) tend to cluster around massive galaxies (Cetus & Tucana are exceptions) Gas-rich, high-mass dwarfs (dis) are found to be widely distributed Observed in nearby groups and clusters as well as the Local Group Do these trends result from morphological transformations due to the influence of the massive primary galaxy? (i.e. tidal or ram pressure stripping) info on orbits of satellites would help 16
17 1) Not a single dwarf galaxy studied lacked an old population although how dominant that population was varied. 2) Evidence was found for a common episode of star formation (ancient Pop II stars found in Galactic halo and galactic dsphs to be same age within 1 Gyr). 3) Even the least massive dsphs showed evidence of some kind of continuous star formation (but with decreasing intensity) over several Gyr - no cessation of star formation during or after reionization. 4) No two histories look the same. Grebel & Gallagher Dwarf galaxies & metallicity 17
18 Blow out in Holmberg II Bureau & Carignan 2002, AJ 123, 1316 Blow out in Holmberg II Rhode et al AJ 118,
19 Blow out in Holmberg II Rhode et al AJ 118, 323 Extremely low mass galaxies may lose most or all of their ISM after a vigorous star formation episode. Starbursting and Blue Compact Dwarfs (BCDs) Small size Very blue Optical light dominated by line emission Young stellar population (and old stars?) Low metallicity => 1/40 th solar 19
20 IZw 18: A Young Galaxy? Small size Very blue Optical light dominated by line emission Young stellar population (and old stars?) Low metallicity => 1/40 th solar Not a young galaxy just one which did not form many/any stars until recently I Zw 18 van Zee et al The Magellanic Clouds LMC SMC The Magellanic Clouds are contained within a common HI envelope. The Magellanic Stream traces their interaction with the MW. Best fit by tidal encounter with MW (but parameters still uncertain) 20
21 The Sagittarius Dwarf Discovered in 1994 by Ibata et al. Small, relatively metal rich About 14 kpc away Being deformed by the Milky Way In MASS shows that stream circles whole sky David Martinez-Delgado (MPIA) & Gabriel Perez (IAC), The Sagittarius Dwarf Tidal Stream Drawing. From: nasa.gov/apod/ap html Sagittarius streams in 2MASS Used M-Giant Stars from the 2MASS database Computer modeling: N-body simulations Mass and morphology of the Milky Way, mass and location of Sgr Used physical constraints to rule out certain models with out a full trial Picked the best fitting oblate, prolate, and spherical models Law, Johnston, Majewski,
22 Tidal debris in the Milky Way? Tidal Tidal debris is usually assumed to contribute to the spheroidal component of the galaxy like the Sagittarius stream but it may also contribute to the Galactic disk(s Tidal debris in the disk of the Milky Way ω Cen The J z distribution of metal poor stars in the vicinity of the Sun suggests the presence of distinct kinematical groups. 22
23 The Milky Way Field of Streams SDSS SEGUE and other surveys designed to measure spectrum of millions of stars in MW to get velocities, metallicities => fossil record of MW history Ring around the Galaxy: its progenitor? Ibata et al
24 Tidal Remnants Durrell & DeCesar; +Yun 1994 HI traces event history even in absence of stellar debris. HI in the M81/M82 system Yun et al 1994 VLA-D De Mello et al. 2007, astro-ph/ : GALEX +ACS => modest SF intermediate between low levels in Magellanic Bridge and SF tails in major mergers like Antennae. 24
25 HI in the M81/M82 system 5 previously unidentified clouds M HI = ( ) x 10 7 M Chynoweth et al 2008 astro-ph/ A few examples of TDGs These are young, massive, gaseous, TDG candidates Duc et al., 1996,1997, 1998,1999; Hibbard etal., 1996; Malphrus et al.,
26 Tidal Dwarf Galaxies Hibbard et al Expected to form in dynamically cool, gas-rich tidal tails Should be a mix of pre-existing stars from tidally disrupted material and a new generation of young stars produced as HI gas condenses => fall off the metallicity-luminosity relation Should contain little dark matter (assuming no DM in galaxy disks) Although young TDGs may be prominent due to the burst of star formation, their long-term fate remains unclear Other types of tidal objects Giant star-forming regions along tidal tails Detached «intergalactic» star forming regions A Gavazzi et al. 2003, Sakai et al., 2003 Tadpole galaxy (HST/ACS) All called «Tidal Dwarf Galaxies candidates» 26
27 VCC 2062: an old tidal dwarf? Faint, low SB dwarf Kinematically detached rotating condensation within HI tail Linked to disturbed N4694 (SB0 pec) VCC 2062 has strong CO and high O/H => deviates from metallicity - luminosity relation VLA map (blue) superposed on true color (BVR) image of N4694 (left) and VCC 2062 (right) with GALEX (red) overlaid. Duc et al. 2007, A&A 475, 187 Ultracompact Dwarf Galaxies Cluster UCD s(hilker et al. 1999; Drinkwater et al. 1999, 2000) First identified by spectroscopic survey of Fornax; also found in Virgo To date, found only in cluster centers (but see last slide) < M B < (intermediate between GCs and de/dsph) Unresolved in ground-based images so r ½ 50 pc versus normal dwarfs (r ½ ~ 300pc) or typical MW GCs (r ½ ~3 pc) Formation scenarios: Massive (intra-cluster) GCs Remnant nuclei of stripped ( threshed ) de,n Evolved products of YMGCs, massive superstar clusters formed in galaxy interactions Ultracompact BCDs identified in SDSS (Corbin et al. 2006) D(r band) < 6 => D < 1 kpc z < 0.01 (to allow for high resolution imaging) Only 9 in SDSS DR2 (rare!) Reside in voids Very metal poor 27
28 UltraCompact BlueDwarf Galaxies Color images (U, V narrow, I) Composite populations Starburst regions embedded in envelopes of red stars Corbin et al. 2006, ApJ 651, 861 Sample identified from SDSS UltraCompact BlueDwarf Galaxies Young massive cluster at its center Number of red supergiants Underlying, low surface brightness component UM 463 M = D = 27 Mpc D(neigh) ~ 2.4 Mpc Corbin et al. 2006, ApJ 651, 861 Sample identified from SDSS 28
29 Ultracompact BlueDwarf Galaxies Left: fraction of light at 4020Å from stellar components by age Right: fraction of mass contained in different stellar population components All UBCDscontain significant population of stars ~10 Gyr old. HI content shows no clear pattern; some rich, some not Corbin et al. 2006, ApJ 651, 861 Sample identified from SDSS Compact objects near M87 Hasegan et al 2005, ApJ 627, 203 : HST-ACS Virgo Survey 10 compact, high-l (-11.8<M V <-10.8) dwarf globular transition objects 29
30 Compact objects near M87 Hasegan et al 2005, ApJ 627, 203 : HST-ACS Virgo Survey 10 compact, high-l (-11.8<M V <-10.8) dwarf globular transition objects Circles indicated inferred tidal radii Compact objects near M87 Hasegan et al 2005, ApJ 627, 203 : HST-ACS Virgo Survey 10 compact, high-l (-11.8<M V <-10.8) dwarf globular transition objects Get r ½, σ, M/L => 2 objects like predictions of population synthesis models for old, metal-rich, high L GCs 3 are much larger with r ½ ~ 20 pc and 6 < M/L V < 9. Resemble nuclei of nucleated des in Virgo 1 uncertain: stellar supercluster? 30
31 Compact objects near M87 Hasegan et al 2005, ApJ 627, 203 : HST-ACS Virgo Survey 10 compact, high-l (-11.8<M V <-10.8) dwarf globular transition objects Half-light radius r ½ vs magnitude for 2000 sources in M87 field. DGTO s near M87 Hasegan et al 2005, ApJ 627, 203 : HST-ACS Virgo Survey 10 compact, high-l (-11.8<M V <-10.8) dwarf globular transition objects Central velocity dispersion σ vs M for hot stellar systems 31
32 DGTO s near M87 Hasegan et al 2005, ApJ 627, 203 : HST-ACS Virgo Survey 10 compact, high-l (-11.8<M V <-10.8) dwarf globular transition objects Representation of the Virial Theorem for hot stellar systems Lower dashed line shows VT for M/L V =1.45. Upper line shows VT for M/L V =5 Compact objects near M87 Hasegan et al 2005, ApJ 627, 203 : HST-ACS Virgo Survey 10 compact, high-l (-11.8<M V <-10.8) dwarf globular transition objects Scaling relations for low-mass hot stellar systems 32
33 Compact objects near M87 Hasegan et al 2005, ApJ 627, 203 : HST-ACS Virgo Survey 10 compact, high-l (-11.8<M V <-10.8) dwarf globular transition objects DGTOs: Some similar to old, metal-rich, high L globular clusters Some are larger: ultra compact dwarfs Transition in scaling relations between two types ~ 2 X 10 6 M Three are embedded in low surface brightness envelopes. Presence of DM is fundamental property distinguishing globular clusters from UCDs 5/13 DGTOs in Virgo are associated with M87 Proximity to Virgo center may be critical UCDs form through tidal stripping of nucleated dwarfs? But Mieske et al AJ 131, 244 found that Fornax de nuclei have lower metallicity than UCD s Fornax vs Virgo UltraCompact Dwarf Galaxies Most luminous UCDs: -14<M V <-12 Most/all have shallow or steep cusps; only 1 shows flat King core None show tidal cutoffs (to limit) ACS images and residuals from fits Evstigneeva et al. 2007, A.J. 133, 1722 Virgo and Fornax images+spectra 33
34 Comparison of internal dynamics of UCDs and GCs UltraCompact Dwarf Galaxies No gap between bright GCs and UCDs Virgo UCDs have velocity dispersions and luminosities similar to those of Fornax UCDs Evstigneeva et al. 2007, A.J. 133, 1722 Virgo and Fornax images+spectra Fundamental plane for dynamically hot stellar systems κ-space: axes are combination of central velocity dispersion, effective radius and mean intensity within r eff κ 1 log Mass κ 2 log SB 3 x M/L κ 3 log M/L Top: UCDs lie on same line as bright GCs but fainter GCs show large spread Bottom: UCDs not on main GC relation UltraCompact Dwarf Galaxies Evstigneeva et al. 2007, A.J. 133, 1722 Virgo and Fornax images+spectra 34
35 Comparison of data with model grids for different samples. UltraCompact Dwarf Galaxies Majority of de nuclei are consistent with solar [α/fe] ~ 0.0 Majority of UCDs have supersolar ratios (+0.3 to +0.5) Evstigneeva et al. 2007, A.J. 133, 1722 Virgo and Fornax images+spectra Comparison of data with model grids Hβ index: age sensitive [MgFe] index: total metallicity UltraCompact Dwarf Galaxies Virgo UCDs are old Stellar pops older than present-day de,n nuclei Evstigneeva et al. 2007, A.J. 133, 1722 Virgo and Fornax images+spectra 35
36 Ultra Compact Dwarf Galaxies Keck Echelle spectroscopy: v(helio), σ, Lick indices (stellar pops) Virgo UCDs are old (older than 8 Gyr) and have [Z/H] = to dex. 5 Virgo UCDs have supersolar [α/fe] abundances 1 Virgo UCD has a solar abundance ratio Virgo UCDs have structural and dynamical properties similar to Fornax UCDs Masses ~ (2 to 9) x 10 7 M M/L V ~ (3 to 5) Virgo UCD s M/L consistent with simple stellar model predictions => do NOT require dark matter Origin? Could be M/L extreme of known globular cluster population Couldresult from simple removal of halo from the nuclei of nucleated dwarf galaxies => But ages/metallicities argue against simple stripping Evstigneeva et al. 2007, A.J. 133, 1722 Virgo and Fornax images+spectra Ultra Compact Dwarf Galaxies Previous studies have found UCDs only in the centers of rich clusters; do they exist elsewhere? Survey of 6 galaxy groups using 2dF spectrograph on AAT: Dorado, N1400, N681, N4038 (Antennae), N4697, N5084 Only 1 UCD candidate found; 2 others maybe. Compare to simulations of Kravtsov & Gnedin (2005, ApJ623, 650) who give relation between total mass of the cluster population and mass of the host galaxy: M max = 2.9 x 10 6 M (M h /10 11 M ) 1.29 ±0.12 Find that this relation works for Fornax UCDs/N1399 and Virgo UCDs/M87 What about dominant galaxies in these groups? Would expect to find UCDs in Dorado, N1400 and N5084 group but not others Need deeper observations to provide firm test Evstigneeva et al
37 DDO 154 Are there totally dark galaxies? Arecibo map outer extent [Hoffman et al. 1993] DDO154 M H M stars M Dyn = 3.0 x 10 8 M = 5.0 x 10 7 M = 4.0 x 10 9 M Extent of Optical image Carignan & Beaulieu 1989 VLA D HI 37
38 HI Optical galaxy M L > 200 Giovanelli, Williams & Haynes 1989 Dwarf galaxies: summary Dwarf galaxies of the Local Group : Mateo 1998 ARAA 36, 435 Dwarf galaxies exist in large numbers, especially in large clusters The Local Group contains a mix of dirr and dsph/de s among its low L galaxies; they are distributed very differently. Low L dwarfs tend to be metal poor; the lowest L dwarfs are still composed largely of primordial material. Dwarfs are the simplest galactic systems known. But the dwarfs in the LG show complex star formation and chemical enrichment histories. Dwarf galaxies may be among the darkest single galaxies known; they provide important constraints on the distribution and nature of DM. Tides/interactions are important to the evolution of dwarfs and, possibly, their formation. 38
II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies
 II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies Ferguson & Binggeli 1994, A&ARev 6, 67 1 1. Properties low mass : 10 6 10 10 M slow rotators : 10 100 km s -1 low luminosity : 10 6 10 10 L low surface brightness
II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies Ferguson & Binggeli 1994, A&ARev 6, 67 1 1. Properties low mass : 10 6 10 10 M slow rotators : 10 100 km s -1 low luminosity : 10 6 10 10 L low surface brightness
Astro 590: next 3 classes
 Astro 590: next 3 classes Dwarf galaxies as probes of evolution Distribution Kinematics The star formation history of the universe Star formation indicators Nebular abundances Starburst populations The
Astro 590: next 3 classes Dwarf galaxies as probes of evolution Distribution Kinematics The star formation history of the universe Star formation indicators Nebular abundances Starburst populations The
Stellar Populations in the Local Group
 Stellar Populations in the Local Group Recall what we ve learned from the Milky Way: Age and metallicity tend to be correlated: older -> lower heavy element content younger -> greater heavy element content
Stellar Populations in the Local Group Recall what we ve learned from the Milky Way: Age and metallicity tend to be correlated: older -> lower heavy element content younger -> greater heavy element content
This week at Astro 3303
 This week at Astro 3303 HW #8-10 deal with your final project! (HW#8 is posted already) The project counts 20% of the grade and is expected to be a significant piece of work. HW#8 for next Wed: prepare
This week at Astro 3303 HW #8-10 deal with your final project! (HW#8 is posted already) The project counts 20% of the grade and is expected to be a significant piece of work. HW#8 for next Wed: prepare
The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds
 The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds!
Extreme Galaxies: Part I
 M87, giant elliptical in the Virgo Cluster Extreme Galaxies: Part I Looking at the extremes in galaxy properties may tell us much about the systematics of galaxy formation and evolution and can provide
M87, giant elliptical in the Virgo Cluster Extreme Galaxies: Part I Looking at the extremes in galaxy properties may tell us much about the systematics of galaxy formation and evolution and can provide
1924: Hubble classification scheme 1925: Hubble measures Cepheids (Period-Luminosity) in Andromeda case closed
 Galaxies 1920 - Curtis-Shapley debate on nature of spiral nebulae - distribution in the sky: zone of avoidance Curtis: extinction Shapley:? - apparent brightness of stars(?) observed in some nebulae Shapley:
Galaxies 1920 - Curtis-Shapley debate on nature of spiral nebulae - distribution in the sky: zone of avoidance Curtis: extinction Shapley:? - apparent brightness of stars(?) observed in some nebulae Shapley:
Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy
 Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy Raja Guhathakurta University of California Observatories (Lick, Keck, TMT) University of California at Santa Cruz M31 s extended stellar
Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy Raja Guhathakurta University of California Observatories (Lick, Keck, TMT) University of California at Santa Cruz M31 s extended stellar
Using Globular Clusters to. Study Elliptical Galaxies. The View Isn t Bad... Omega Centauri. Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office M13
 Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
Galaxies -- Introduction. Classification -- Feb 13, 2014
 Galaxies -- Introduction Classification -- Feb 13, 2014 Why Begin with Classification? The Hubble system forms the basic vocabulary of the subject. The sequence of galaxy types reflects an underlying physical
Galaxies -- Introduction Classification -- Feb 13, 2014 Why Begin with Classification? The Hubble system forms the basic vocabulary of the subject. The sequence of galaxy types reflects an underlying physical
Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology:
 Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology: Looking more deeply at the Hubble Sequence Galaxy Morphology How do you quantify the properties of galaxies? and how do you put them in groups which allow you to study physically
Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology: Looking more deeply at the Hubble Sequence Galaxy Morphology How do you quantify the properties of galaxies? and how do you put them in groups which allow you to study physically
Zoccali et al. 2003, A&A, 399, 931. Overview of (old) Galactic components. bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo. metallicity & age distribution
 Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Large-Scale Structure
 Large-Scale Structure Evidence for Dark Matter Dark Halos in Ellipticals Hot Gas in Ellipticals Clusters Hot Gas in Clusters Cluster Galaxy Velocities and Masses Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies 1
Large-Scale Structure Evidence for Dark Matter Dark Halos in Ellipticals Hot Gas in Ellipticals Clusters Hot Gas in Clusters Cluster Galaxy Velocities and Masses Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies 1
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Oct 2003
 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Galaxy threshing and the origin of intracluster stellar objects arxiv:astro-ph/0310350v1 14 Oct 2003 Kenji
**TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Galaxy threshing and the origin of intracluster stellar objects arxiv:astro-ph/0310350v1 14 Oct 2003 Kenji
Globular Clusters in LSB Dwarf Galaxies
 Globular Clusters in LSB Dwarf Galaxies New results from HST photometry and VLT spectroscopy Thomas H. Puzia Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics in collaboration with Margarita E. Sharina SAO, Russian Academy
Globular Clusters in LSB Dwarf Galaxies New results from HST photometry and VLT spectroscopy Thomas H. Puzia Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics in collaboration with Margarita E. Sharina SAO, Russian Academy
A wide-field view of the Phoenix transition type dwarf galaxy (Battaglia et al., MNRAS accepted, airxv/ )
 A wide-field view of the Phoenix transition type dwarf galaxy (Battaglia et al., MNRAS accepted, airxv/1205.2704) Giuseppina Battaglia INAF Astronomical Observatory of Bologna With thanks to M.Rejkuba,
A wide-field view of the Phoenix transition type dwarf galaxy (Battaglia et al., MNRAS accepted, airxv/1205.2704) Giuseppina Battaglia INAF Astronomical Observatory of Bologna With thanks to M.Rejkuba,
The M31 Dwarf Galaxy Population
 The M31 Dwarf Galaxy Population Marla Geha (Yale) Google Sky IRAS map Raja Guhathakurta (UCSC) Jason Kalirai (STScI) Steve Majewski (UVa) Roeland van der Marel (STScI) Racheal Beaton (UVa) Kirsten Howley
The M31 Dwarf Galaxy Population Marla Geha (Yale) Google Sky IRAS map Raja Guhathakurta (UCSC) Jason Kalirai (STScI) Steve Majewski (UVa) Roeland van der Marel (STScI) Racheal Beaton (UVa) Kirsten Howley
Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters
 Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters in this lecture we move up in scale, to explore typical clusters of galaxies the Local Group is an example of a not very rich cluster interesting topics include:
Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters in this lecture we move up in scale, to explore typical clusters of galaxies the Local Group is an example of a not very rich cluster interesting topics include:
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Stellar Populations in the Galaxy
 Stellar Populations in the Galaxy Stars are fish in the sea of the galaxy, and like fish they often travel in schools. Star clusters are relatively small groupings, the true schools are stellar populations.
Stellar Populations in the Galaxy Stars are fish in the sea of the galaxy, and like fish they often travel in schools. Star clusters are relatively small groupings, the true schools are stellar populations.
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies
 Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Myung Gyoon LEE Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea
 Myung Gyoon LEE Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Cosmology and Structure Formation (The 4 th KIAS workshop), Nov 4-6, 2010, KIAS, Korea 1 M.G. Lee, Sungsoon Lim (SNU)
Myung Gyoon LEE Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Cosmology and Structure Formation (The 4 th KIAS workshop), Nov 4-6, 2010, KIAS, Korea 1 M.G. Lee, Sungsoon Lim (SNU)
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints
 Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Properties of Dark Matter: What is it? And what isn t it? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley Stanford July 31, 2007 How much is there? WMAP results Rotation curves of Galaxies
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Properties of Dark Matter: What is it? And what isn t it? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley Stanford July 31, 2007 How much is there? WMAP results Rotation curves of Galaxies
Myung Gyoon Lee ( 李明均 )
 Myung Gyoon Lee ( 李明均 ) With Observational Cosmology Team Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Nov 1-4, 2011, The 3 rd Subaru Conference/The 1 st NAOJ Symposium, Galactic
Myung Gyoon Lee ( 李明均 ) With Observational Cosmology Team Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Nov 1-4, 2011, The 3 rd Subaru Conference/The 1 st NAOJ Symposium, Galactic
The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf
 The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf Ewa L. Łokas Copernicus Center, Warsaw Stelios Kazantzidis (Ohio State) Lucio Mayer (University of Zurich) Collaborators: Steven Majewski
The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf Ewa L. Łokas Copernicus Center, Warsaw Stelios Kazantzidis (Ohio State) Lucio Mayer (University of Zurich) Collaborators: Steven Majewski
Using the HR Diagram to Measure the Star Formation Histories of Galaxies. Tammy Smecker-Hane University of California, Irvine
 Using the HR Diagram to Measure the Star Formation Histories of Galaxies Tammy Smecker-Hane University of California, Irvine tsmecker@uci.edu Irvine, California 1 Outline 1. Stellar Evolution Hertzsprung-Russell
Using the HR Diagram to Measure the Star Formation Histories of Galaxies Tammy Smecker-Hane University of California, Irvine tsmecker@uci.edu Irvine, California 1 Outline 1. Stellar Evolution Hertzsprung-Russell
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 31 Jul 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 31 Jul 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 31 Jul 2007](/thumbs/81/84026065.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (1994) Printed 1 February 8 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Origin of lower velocity dispersions of ultra-compact dwarf galaxy populations in clusters of galaxies K. Bekki
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1?? (1994) Printed 1 February 8 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) Origin of lower velocity dispersions of ultra-compact dwarf galaxy populations in clusters of galaxies K. Bekki
Starburst Dwarf Galaxies
 Starburst Dwarf Galaxies 1 Starburst Dwarf Galaxies The star-formation history does in general not show a continuous evolution but preferably an episoidal behaviour. 2 1 Definition: Starburst ( t0) 10....100
Starburst Dwarf Galaxies 1 Starburst Dwarf Galaxies The star-formation history does in general not show a continuous evolution but preferably an episoidal behaviour. 2 1 Definition: Starburst ( t0) 10....100
Observations of Globular Cluster Systems of Giant Galaxies
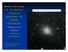 Observations of Globular Cluster Systems of Giant Galaxies Katherine Rhode Indiana University 38 x 38 R image of Virgo elliptical NGC 4472 KITP Conference January 2009 Observations of Globular Cluster
Observations of Globular Cluster Systems of Giant Galaxies Katherine Rhode Indiana University 38 x 38 R image of Virgo elliptical NGC 4472 KITP Conference January 2009 Observations of Globular Cluster
HW#6 is due; please pass it in. HW#7 is posted; it requires you to write out answers clearly and completely explaining your logic.
 Oct 21, 2015 Basic properties of groups and clusters of galaxies Number density, structure X-ray emission from hot ICM Estimating cluster masses Cluster scaling relations Impact of environment on galaxies
Oct 21, 2015 Basic properties of groups and clusters of galaxies Number density, structure X-ray emission from hot ICM Estimating cluster masses Cluster scaling relations Impact of environment on galaxies
2 Galaxy morphology and classification
 2 Galaxy morphology and classification Galaxy classification is an important first step towards a physical understanding of the nature of these objects. For a detailed description of classification systems
2 Galaxy morphology and classification Galaxy classification is an important first step towards a physical understanding of the nature of these objects. For a detailed description of classification systems
2. Galaxy Evolution and Environment
 Topics in Extragalactic Astronomy 2. Galaxy Evolution and Environment Laerte Sodré Jr. IAG USP Vitória, February 2019 outline What is environment Physical process Environmental effects in groups and clusters
Topics in Extragalactic Astronomy 2. Galaxy Evolution and Environment Laerte Sodré Jr. IAG USP Vitória, February 2019 outline What is environment Physical process Environmental effects in groups and clusters
Kinematic Properties and Dark Matter Halos of Dwarf Early-Type Galaxies in the Virgo Cluster
 Kinematic Properties and Dark Matter Halos of Dwarf Early-Type Galaxies in the Virgo Cluster Elisa Toloba (Fulbright Fellow at UCO/Lick & Carnegie Observatories) Collaborators: Alessandro Boselli (LAM-Marseille)
Kinematic Properties and Dark Matter Halos of Dwarf Early-Type Galaxies in the Virgo Cluster Elisa Toloba (Fulbright Fellow at UCO/Lick & Carnegie Observatories) Collaborators: Alessandro Boselli (LAM-Marseille)
Lecture 30. The Galactic Center
 Lecture 30 History of the Galaxy Populations and Enrichment Galactic Evolution Spiral Arms Galactic Types Apr 5, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 30 1 The Galactic Center The nature of the center of the Galaxy is
Lecture 30 History of the Galaxy Populations and Enrichment Galactic Evolution Spiral Arms Galactic Types Apr 5, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 30 1 The Galactic Center The nature of the center of the Galaxy is
Veilleux! see MBW ! 23! 24!
 Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
Chap.6 Formation and evolution of Local Group galaxies
 Chap.6 Formation and evolution of Local Group galaxies Properties of LG galaxies Formation history of LG galaxies Models to solve missing satellites problem Formation of Andromeda galaxy Future prospects
Chap.6 Formation and evolution of Local Group galaxies Properties of LG galaxies Formation history of LG galaxies Models to solve missing satellites problem Formation of Andromeda galaxy Future prospects
Fossils of the First Galaxies in the Local Group: True Fossils and Ghost Halos
 Fossils of the First Galaxies in the Local Group: True Fossils and Ghost Halos Mia S. Bovill with Massimo Ricotti University of Maryland The Smallest Galaxies Minihalos DO NOT initiate gas condensation
Fossils of the First Galaxies in the Local Group: True Fossils and Ghost Halos Mia S. Bovill with Massimo Ricotti University of Maryland The Smallest Galaxies Minihalos DO NOT initiate gas condensation
The Accretion History of the Milky Way
 The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Aug 2001
 HOW DID GLOBULAR CLUSTERS FORM? Sidney van den Bergh Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, National arxiv:astro-ph/0108298v1 17 Aug 2001 Research Council of Canada, 5071
HOW DID GLOBULAR CLUSTERS FORM? Sidney van den Bergh Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, National arxiv:astro-ph/0108298v1 17 Aug 2001 Research Council of Canada, 5071
What is an ultra-faint Galaxy?
 What is an ultra-faint Galaxy? UCSB KITP Feb 16 2012 Beth Willman (Haverford College) Large Magellanic Cloud, M V = -18 ~ 1/10 Milky Way luminosity image credit: Yuri Beletsky (ESO) and APOD NGC 205, M
What is an ultra-faint Galaxy? UCSB KITP Feb 16 2012 Beth Willman (Haverford College) Large Magellanic Cloud, M V = -18 ~ 1/10 Milky Way luminosity image credit: Yuri Beletsky (ESO) and APOD NGC 205, M
Galaxies. Lecture Topics. Lecture 23. Discovering Galaxies. Galaxy properties. Local Group. History Cepheid variable stars. Classifying galaxies
 Galaxies Lecture 23 APOD: NGC 3628 (The Hamburger Galaxy) 1 Lecture Topics Discovering Galaxies History Cepheid variable stars Galaxy properties Classifying galaxies Local Group 2 23-1 Discovering Galaxies
Galaxies Lecture 23 APOD: NGC 3628 (The Hamburger Galaxy) 1 Lecture Topics Discovering Galaxies History Cepheid variable stars Galaxy properties Classifying galaxies Local Group 2 23-1 Discovering Galaxies
Milky Way S&G Ch 2. Milky Way in near 1 IR H-W Rixhttp://online.kitp.ucsb.edu/online/galarcheo-c15/rix/
 Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
This week at Astro Lecture 06, Sep 13, Pick up PE#6. Please turn in HW#2. HW#3 is posted
 This week at Astro 3303 Lecture 06, Sep 13, 2017 Pick up PE#6 Please turn in HW#2 HW#3 is posted Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading: Continue reading
This week at Astro 3303 Lecture 06, Sep 13, 2017 Pick up PE#6 Please turn in HW#2 HW#3 is posted Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading: Continue reading
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies
 Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
View of the Galaxy from within. Lecture 12: Galaxies. Comparison to an external disk galaxy. Where do we lie in our Galaxy?
 Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
Astronomy 330 Lecture Dec 2010
 Astronomy 330 Lecture 26 10 Dec 2010 Outline Clusters Evolution of cluster populations The state of HI sensitivity Large Scale Structure Cluster Evolution Why might we expect it? What does density determine?
Astronomy 330 Lecture 26 10 Dec 2010 Outline Clusters Evolution of cluster populations The state of HI sensitivity Large Scale Structure Cluster Evolution Why might we expect it? What does density determine?
Dwarf Elliptical Galaxies Nelson Caldwell. Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin
 eaa.iop.org DOI: 10.1888/0333750888/2615 Dwarf Elliptical Galaxies Nelson Caldwell From Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin IOP Publishing Ltd 2006 ISBN: 0333750888 Institute of Physics
eaa.iop.org DOI: 10.1888/0333750888/2615 Dwarf Elliptical Galaxies Nelson Caldwell From Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin IOP Publishing Ltd 2006 ISBN: 0333750888 Institute of Physics
Galaxy classification
 Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Theorem : Proof... Pavel Kroupa. Pavel Kroupa: AIfA, University of Bonn
 Theorem : dsph = TDG = LCDM Proof... Pavel Kroupa 1 Two Zwicky Conjectures of fundamental importance : 1. Zwicky (1937) galaxies are about 500 times heavier in the Coma galaxy cluster than judged from
Theorem : dsph = TDG = LCDM Proof... Pavel Kroupa 1 Two Zwicky Conjectures of fundamental importance : 1. Zwicky (1937) galaxies are about 500 times heavier in the Coma galaxy cluster than judged from
Lecture 15: Galaxy morphology and environment
 GALAXIES 626 Lecture 15: Galaxy morphology and environment Why classify galaxies? The Hubble system gives us our basic description of galaxies. The sequence of galaxy types may reflect an underlying physical
GALAXIES 626 Lecture 15: Galaxy morphology and environment Why classify galaxies? The Hubble system gives us our basic description of galaxies. The sequence of galaxy types may reflect an underlying physical
Survey of Astrophysics A110
 Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Dwarf Galaxies - ideal Laboratories to study astrophysical Processes
 Dwarf Galaxies - ideal Laboratories to study astrophysical Processes Gerhard Hensler University of Vienna Lecture 1 Lecture "Dwarf Galaxies",, Thursday 11:30 am Content/Presenter 7.3. Organization 14.3.
Dwarf Galaxies - ideal Laboratories to study astrophysical Processes Gerhard Hensler University of Vienna Lecture 1 Lecture "Dwarf Galaxies",, Thursday 11:30 am Content/Presenter 7.3. Organization 14.3.
Astro2010 Science White Paper: The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN)
 Astro2010 Science White Paper: The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN) Thomas M. Brown (tbrown@stsci.edu) and Marc Postman (postman@stsci.edu) Space Telescope Science Institute Daniela Calzetti (calzetti@astro.umass.edu)
Astro2010 Science White Paper: The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN) Thomas M. Brown (tbrown@stsci.edu) and Marc Postman (postman@stsci.edu) Space Telescope Science Institute Daniela Calzetti (calzetti@astro.umass.edu)
The Nearest Giant Ellipticals: Rosetta Stones or Fool s Gold?
 The Nearest Giant Ellipticals: Rosetta Stones or Fool s Gold? A hypothesis or theory is clear, decisive, and positive, but it is believed by no one but the man who created it. Experimental findings, on
The Nearest Giant Ellipticals: Rosetta Stones or Fool s Gold? A hypothesis or theory is clear, decisive, and positive, but it is believed by no one but the man who created it. Experimental findings, on
Looking into a nucleus with unprecedented detail (structure & kinematics): the case of the Sgr dsph. Results from:
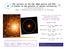 The nucleus of the Sgr dsph galaxy and M54: A window on the process of galaxy nucleation by Michele Bellazzini INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna Looking into a nucleus with unprecedented detail
The nucleus of the Sgr dsph galaxy and M54: A window on the process of galaxy nucleation by Michele Bellazzini INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna Looking into a nucleus with unprecedented detail
Lecture Three: Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Hubble Sequence. Environment! Globular Clusters in Milky Way. kpc
 Hubble Sequence Lecture Three: Fundamental difference between Elliptical galaxies and galaxies with disks, and variations of disk type & importance of bulges Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Monday
Hubble Sequence Lecture Three: Fundamental difference between Elliptical galaxies and galaxies with disks, and variations of disk type & importance of bulges Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Monday
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs
 A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
Lecture Two: Observed Properties of Galaxies
 Lecture Two: Observed Properties of Galaxies http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/gfe14/index.html Longair, chapter 3 Wednesday 5th Feb Binney & Merrifield, chapter 4 1 From pretty picture to science 2 Galaxies
Lecture Two: Observed Properties of Galaxies http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/gfe14/index.html Longair, chapter 3 Wednesday 5th Feb Binney & Merrifield, chapter 4 1 From pretty picture to science 2 Galaxies
Our Galaxy. We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky.
 Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
Galaxy clusters. Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems April 6, 2018
 Galaxy clusters László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 April 6, 2018 Satellite galaxies Large galaxies are surrounded by orbiting dwarfs approx. 14-16 satellites
Galaxy clusters László Dobos Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems dobos@complex.elte.hu É 5.60 April 6, 2018 Satellite galaxies Large galaxies are surrounded by orbiting dwarfs approx. 14-16 satellites
The VPOS: a vast polar structure of satellite galaxies, globular clusters and streams around the MW
 The VPOS: a vast polar structure of satellite galaxies, globular clusters and streams around the MW Marcel S. Pawlowski (mpawlow@astro.uni-bonn.de) Supervisor: Pavel Kroupa (Bonn) Collaborators: Jan Pflamm-Altenburg
The VPOS: a vast polar structure of satellite galaxies, globular clusters and streams around the MW Marcel S. Pawlowski (mpawlow@astro.uni-bonn.de) Supervisor: Pavel Kroupa (Bonn) Collaborators: Jan Pflamm-Altenburg
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes
 Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Astr 5465 Feb. 13, 2018 Distribution & Classification of Galaxies Distribution of Galaxies
 Astr 5465 Feb. 13, 2018 Distribution & Classification of Galaxies Distribution of Galaxies Faintest galaxies are distributed ~ uniformly over the sky except for the Galactic plane (zone of avoidance) Brighter
Astr 5465 Feb. 13, 2018 Distribution & Classification of Galaxies Distribution of Galaxies Faintest galaxies are distributed ~ uniformly over the sky except for the Galactic plane (zone of avoidance) Brighter
The HERMES project. Reconstructing Galaxy Formation. Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU. The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012
 The HERMES project Reconstructing Galaxy Formation Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012 HERMES is a new high-resolution fiber-fed multi-object spectrometer
The HERMES project Reconstructing Galaxy Formation Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012 HERMES is a new high-resolution fiber-fed multi-object spectrometer
Upcoming class schedule
 Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
Dwarf Galaxies in the nearby Universe
 Blue Compact Dwarf Galaxies: born to be wild Polychronis Papaderos Centro de Astrofísica da Universidade do Porto & Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço Estallidos Workshop 2015 Granada May 2015
Blue Compact Dwarf Galaxies: born to be wild Polychronis Papaderos Centro de Astrofísica da Universidade do Porto & Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço Estallidos Workshop 2015 Granada May 2015
Three Major Components
 The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
Two Main Techniques. I: Star-forming Galaxies
 p.1/24 The high redshift universe has been opened up to direct observation in the last few years, but most emphasis has been placed on finding the progenitors of today s massive ellipticals. p.2/24 Two
p.1/24 The high redshift universe has been opened up to direct observation in the last few years, but most emphasis has been placed on finding the progenitors of today s massive ellipticals. p.2/24 Two
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies
 Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Mass modelling of dwarf spheroidals. Jorge Peñarrubia
 Mass modelling of dwarf spheroidals Jorge Peñarrubia Santiago de Chile 13 April 2015 Universe Composition Assumption: GR is correct WMAP7 DM particle models: Constraints 63 orders 51 orders DM particle
Mass modelling of dwarf spheroidals Jorge Peñarrubia Santiago de Chile 13 April 2015 Universe Composition Assumption: GR is correct WMAP7 DM particle models: Constraints 63 orders 51 orders DM particle
Using radial metallicity gradients in dwarf galaxies to study environmental processing
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 85, 504 c SAIt 2014 Memorie della Using radial metallicity gradients in dwarf galaxies to study environmental processing R. Leaman 1,2,3, K. Venn 3, A. Brooks 4,5,6, G. Battaglia 7, A.
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 85, 504 c SAIt 2014 Memorie della Using radial metallicity gradients in dwarf galaxies to study environmental processing R. Leaman 1,2,3, K. Venn 3, A. Brooks 4,5,6, G. Battaglia 7, A.
IV. Interacting Galaxies
 IV. Interacting Galaxies Examples of galaxies in interaction: Pairs of galaxies (NGC 4038/39) M 51 type (satellites) Arp 220 type Compact galaxy groups 2 1 B.A. Vorontsov-Velyaminov: Atlas and Catalog
IV. Interacting Galaxies Examples of galaxies in interaction: Pairs of galaxies (NGC 4038/39) M 51 type (satellites) Arp 220 type Compact galaxy groups 2 1 B.A. Vorontsov-Velyaminov: Atlas and Catalog
ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney
 ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 3 January 23, 2017 The Milky Way Galaxy: Vertical Distributions of Stars & the Stellar Disk disks exist in many astrophysical systems
ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 3 January 23, 2017 The Milky Way Galaxy: Vertical Distributions of Stars & the Stellar Disk disks exist in many astrophysical systems
The Combined effects of ram pressure stripping, and tidal influences on Virgo cluster dwarf galaxies, using N body/ SPH simulation
 The Combined effects of ram pressure stripping, and tidal influences on Virgo cluster dwarf galaxies, using N body/ SPH simulation Author: Rory Smith, Cardiff University Collaborators: Jonathon Davies,
The Combined effects of ram pressure stripping, and tidal influences on Virgo cluster dwarf galaxies, using N body/ SPH simulation Author: Rory Smith, Cardiff University Collaborators: Jonathon Davies,
Probing Gravity in the Low Acceleration Regime with Globular Clusters
 Probing Gravity in the Low Acceleration Regime with Globular Clusters By Riccardo Scarpa Instituto de astrofisica de Canarias Gran Telescopio Canarias The idea for this study sparked from the desire of
Probing Gravity in the Low Acceleration Regime with Globular Clusters By Riccardo Scarpa Instituto de astrofisica de Canarias Gran Telescopio Canarias The idea for this study sparked from the desire of
This week at Astro 3303
 This week at Astro 3303 HW #8-10 deal with your final project! (HW#8 is posted already) The project counts 20% of the grade and is expected to be a significant piece of work. HW#8 for next Wed: prepare
This week at Astro 3303 HW #8-10 deal with your final project! (HW#8 is posted already) The project counts 20% of the grade and is expected to be a significant piece of work. HW#8 for next Wed: prepare
The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology
 The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology Kathryn V Johnston (Columbia University) Collaborators (theorists): James S Bullock (Irvine), Andreea Font (Durham), Brant Robertson (Chicago), Sanjib Sharma (Columbia),
The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology Kathryn V Johnston (Columbia University) Collaborators (theorists): James S Bullock (Irvine), Andreea Font (Durham), Brant Robertson (Chicago), Sanjib Sharma (Columbia),
The effects of the environment on the evolution of late-type galaxies
 The effects of the environment on the evolution of late-type galaxies Alessandro BOSELLI Samuel BOISSIER, Luca CORTESE, Giuseppe GAVAZZI, Elisa TOLOBA Boselli et al 2006, ApJ, 651, 811 Boselli et al 2008,
The effects of the environment on the evolution of late-type galaxies Alessandro BOSELLI Samuel BOISSIER, Luca CORTESE, Giuseppe GAVAZZI, Elisa TOLOBA Boselli et al 2006, ApJ, 651, 811 Boselli et al 2008,
 http://www.eso.org/sci/activities/santiago/personnel/visitors.html Morphological transformation in galaxy clusters > interpreted as the result of galaxy harassment (Moore et al. 1996). Harassment = 1
http://www.eso.org/sci/activities/santiago/personnel/visitors.html Morphological transformation in galaxy clusters > interpreted as the result of galaxy harassment (Moore et al. 1996). Harassment = 1
Halo Tidal Star Streams with DECAM. Brian Yanny Fermilab. DECam Community Workshop NOAO Tucson Aug
 Halo Tidal Star Streams with DECAM Brian Yanny Fermilab DECam Community Workshop NOAO Tucson Aug 19 2011 M31 (Andromeda) Our Local Group neighbors: Spiral galaxies similar to The Milky Way 150 kpc M33
Halo Tidal Star Streams with DECAM Brian Yanny Fermilab DECam Community Workshop NOAO Tucson Aug 19 2011 M31 (Andromeda) Our Local Group neighbors: Spiral galaxies similar to The Milky Way 150 kpc M33
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Dec 1998
 Spectroscopy of red giants of the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy arxiv:astro-ph/9812267v1 14 Dec 1998 G. Marconi Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma P. Bonifacio Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste L. Pasquini
Spectroscopy of red giants of the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy arxiv:astro-ph/9812267v1 14 Dec 1998 G. Marconi Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma P. Bonifacio Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste L. Pasquini
ASTR 200 : Lecture 25. Galaxies: internal and cluster dynamics
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 25 Galaxies: internal and cluster dynamics 1 Galaxy interactions Isolated galaxies are often spirals One can find small galaxy `groups' (like the Local group) with only a few large spiral
ASTR 200 : Lecture 25 Galaxies: internal and cluster dynamics 1 Galaxy interactions Isolated galaxies are often spirals One can find small galaxy `groups' (like the Local group) with only a few large spiral
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
 Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Clusters and Groups of Galaxies
 Clusters and Groups of Galaxies Groups and clusters The Local Group Clusters: spatial distribution and dynamics Clusters: other components Clusters versus groups Morphology versus density Groups and Clusters
Clusters and Groups of Galaxies Groups and clusters The Local Group Clusters: spatial distribution and dynamics Clusters: other components Clusters versus groups Morphology versus density Groups and Clusters
THE QUEST RR LYRAE SURVEY AND HALO SUB-STRUCTURE
 THE QUEST RR LYRAE SURVEY AND HALO SUB-STRUCTURE Kathy Vivas (CIDA, Venezuela), Bob Zinn (Yale U., USA), Sonia Duffau (U. de Chile), Yara Jaffé, Jesús Hernández, Yolimar Subero (CIDA, Venezuela), G. Carraro
THE QUEST RR LYRAE SURVEY AND HALO SUB-STRUCTURE Kathy Vivas (CIDA, Venezuela), Bob Zinn (Yale U., USA), Sonia Duffau (U. de Chile), Yara Jaffé, Jesús Hernández, Yolimar Subero (CIDA, Venezuela), G. Carraro
Planetary Nebulae beyond the Milky Way historical overview
 Planetary Nebulae beyond the Milky Way historical overview M. J. Barlow Dept. of Physics & Astronomy University College London Outline (a) Surveys for planetary nebulae in other galaxies, PN luminosity
Planetary Nebulae beyond the Milky Way historical overview M. J. Barlow Dept. of Physics & Astronomy University College London Outline (a) Surveys for planetary nebulae in other galaxies, PN luminosity
Evolution of second generation stars in stellar disks of globular and nuclear clusters: ω Centauri as a test case
 Evolution of second generation stars in stellar disks of globular and nuclear clusters: ω Centauri as a test case Alessandra Mastrobuono-Battisti & Hagai Perets Outline Dense stellar clusters: Nuclear
Evolution of second generation stars in stellar disks of globular and nuclear clusters: ω Centauri as a test case Alessandra Mastrobuono-Battisti & Hagai Perets Outline Dense stellar clusters: Nuclear
Demographics of radio galaxies nearby and at z~0.55. Are radio galaxies signposts to black-hole mergers?
 Elaine M. Sadler Black holes in massive galaxies Demographics of radio galaxies nearby and at z~0.55 Are radio galaxies signposts to black-hole mergers? Work done with Russell Cannon, Scott Croom, Helen
Elaine M. Sadler Black holes in massive galaxies Demographics of radio galaxies nearby and at z~0.55 Are radio galaxies signposts to black-hole mergers? Work done with Russell Cannon, Scott Croom, Helen
Structure of Merger Remnants:
 Structure of Merger Remnants: Lessons from Spectral Line Observations John E. Hibbard NRAO-CV Merger Hypothesis: Two gas-rich Spirals Merge into One Elliptical Toomre Sequence of On-going Mergers (Toomre
Structure of Merger Remnants: Lessons from Spectral Line Observations John E. Hibbard NRAO-CV Merger Hypothesis: Two gas-rich Spirals Merge into One Elliptical Toomre Sequence of On-going Mergers (Toomre
IMPACT OF A MAJOR MERGER IN THE LOCAL GROUP
 SF2A 2013 L. Cambrésy, F. Martins, E. Nuss and A. Palacios (eds) IMPACT OF A MAJOR MERGER IN THE LOCAL GROUP S. Fouquet 1, F. Hammer 1,, Y. Yang 1, 2, M. Puech 1 and H. Flores 1 Abstract. The Local Group
SF2A 2013 L. Cambrésy, F. Martins, E. Nuss and A. Palacios (eds) IMPACT OF A MAJOR MERGER IN THE LOCAL GROUP S. Fouquet 1, F. Hammer 1,, Y. Yang 1, 2, M. Puech 1 and H. Flores 1 Abstract. The Local Group
Thesis defence Friday 11:00
 Thesis defence Friday 11:00 Promotors: Marc Verheijen Filippo Fraternali In collaboration with: Renzo Sancisi Outline: Introduction on (starbursting) dwarfs (Chap. 1) I. Large-scale HI morphology (Chaps.
Thesis defence Friday 11:00 Promotors: Marc Verheijen Filippo Fraternali In collaboration with: Renzo Sancisi Outline: Introduction on (starbursting) dwarfs (Chap. 1) I. Large-scale HI morphology (Chaps.
New insights into the Sagittarius stream
 New insights into the Sagittarius stream EWASS, Turku July 8th, 213 Martin C. Smith Shanghai Astronomical Observatory http://hubble.shao.ac.cn/~msmith/ Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal(ish) Since its discovery
New insights into the Sagittarius stream EWASS, Turku July 8th, 213 Martin C. Smith Shanghai Astronomical Observatory http://hubble.shao.ac.cn/~msmith/ Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal(ish) Since its discovery
Galaxy Luminosity Function. Galaxy Luminosity Function. Schechter Function. Schechter Function by environment. Schechter (1976) found that
 Galaxy Luminosity Function Count the number of galaxies as a function of luminosity (or absolute magnitude) Useful for: Understanding galaxy formation (distribution by luminosity implies distribution by
Galaxy Luminosity Function Count the number of galaxies as a function of luminosity (or absolute magnitude) Useful for: Understanding galaxy formation (distribution by luminosity implies distribution by
The Milky Way - Chapter 23
 The Milky Way - Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy A galaxy: huge collection of stars (10 7-10 13 ) and interstellar matter (gas & dust). Held together by gravity. Much bigger than any star cluster we have
The Milky Way - Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy A galaxy: huge collection of stars (10 7-10 13 ) and interstellar matter (gas & dust). Held together by gravity. Much bigger than any star cluster we have
Clicker Question: Galaxy Classification. What type of galaxy do we live in? The Variety of Galaxy Morphologies Another barred galaxy
 Galaxies Galaxies First spiral nebula found in 1845 by the Earl of Rosse. Speculated it was beyond our Galaxy. 1920 - "Great Debate" between Shapley and Curtis on whether spiral nebulae were galaxies beyond
Galaxies Galaxies First spiral nebula found in 1845 by the Earl of Rosse. Speculated it was beyond our Galaxy. 1920 - "Great Debate" between Shapley and Curtis on whether spiral nebulae were galaxies beyond
John E. Hibbard NRAO-CV
 John E. Hibbard NRAO-CV A Range of Substructures are found in Tidal Tails Outstanding Questions: On what scales (if any) are these structures bound? Is this an evolutionary sequence? Are these Tidal Dwarf
John E. Hibbard NRAO-CV A Range of Substructures are found in Tidal Tails Outstanding Questions: On what scales (if any) are these structures bound? Is this an evolutionary sequence? Are these Tidal Dwarf
This week at Astro 3303
 This week at Astro 3303 Pick up PE#9 I am handing back HW#3 Please turn in HW#4 Usual collaboration rules apply Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading:
This week at Astro 3303 Pick up PE#9 I am handing back HW#3 Please turn in HW#4 Usual collaboration rules apply Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading:
Number of Stars: 100 billion (10 11 ) Mass : 5 x Solar masses. Size of Disk: 100,000 Light Years (30 kpc)
 THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
Galaxies. Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations
 Galaxies Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations Cepheids in M31 Up to 1920s, the Milky Way was thought by
Galaxies Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations Cepheids in M31 Up to 1920s, the Milky Way was thought by
