The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds
|
|
|
- Blanche Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Dance of Stars MODEST-14 The Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Eva K. Grebel Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds! All Local Group galaxies with M V < 13 contain star clusters, regardless of morphological galaxy type. (Grebel 2002, IAU Symp. 207 review) What makes the Magellanic Clouds special? Proximity - deep resolved CMDs and spectroscopy of individual stars possible. Richness of their cluster systems. Age range Existence of clusters of all ages, including large numbers of rich, massive young and intermediate- age clusters. Populous star clusters(hodge 1961) Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 1
2 Census of Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds! Numerous searches for star clusters in the Magellanic Clouds were conducted over the years. Earlier: photographic plates. Now: CCD imaging surveys such as the Magellanic Clouds Photometric Survey (MCPS, Zaritsky et al. 2002, 2004) or the time-domain Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment (OGLE, e.g., Udalski et al. 2008, 2009). Most recent, most comprehensive catalog of LMC, SMC, and Bridge clusters: Bica et al. 2008, MNRAS 389, 678 A general catalog of extended objects in the Magellanic System LMC: 3103 clusters, 2944 associations. Bridge: 91 clusters, 148 associations. SMC: 546 clusters, 234 associations Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 2 Distribution of Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds! All Local Group galaxies with M V < 13 contain star clusters, regardless of morphological galaxy type. [Beware: observational incompleteness in eastern part of Bridge] Bica et al. 2008, MNRAS 389, 678 Here old means age > 4 Gyr Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 3
3 Distribution of Star Clusters in the Magellanic Clouds! Old LMC clusters trace bar-like structure, slightly rotated against younger star cluster distribution. SMC disk and Bridge better traced by associations. LMC associations also trace leading edge, but its outer clusters form loose ring around entire LMC (not seen in associations). Old LMC clusters also in outer parts (not only in bar). Old SMC clusters preferentially found in outer parts. Associations Clusters Bica et al. 2008, MNRAS 389, Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 4 Recent Star Formation History of the LMC! Ages of 1193 populous LMC star clusters from resolved CMDs of the MCPS (Glatt, Grebel, & Koch 2010, A&A 517, 50). Age < 20 Myr 20 Myr age < 50 Myr Ellipses show approximate location of supergiant shells. Glatt et al. 2010, A&A 517, Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 5
4 Recent Star Formation History of the LMC! Ages of 1193 populous LMC star clusters from resolved CMDs of the MCPS (Glatt, Grebel, & Koch 2010, A&A 517, 50). 50 Myr age < 100 Myr 100 Myr age < 250 Myr Glatt et al. 2010, A&A 517, Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 6 Recent Star Formation History of the LMC! Ages of 1193 populous LMC star clusters from resolved CMDs of the MCPS (Glatt, Grebel, & Koch 2010, A&A 517, 50). 250 Myr age < 500 Myr age > 500 Myr Glatt et al. 2010, A&A 517, Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 7
5 Recent Star Formation History of the SMC! Ages of 324 populous SMC star clusters from resolved CMDs of the MCPS (Glatt, Grebel, & Koch 2010, A&A 517, 50). 250 Myr age < 500 Myr age > 500 Myr Black open circles: No resolved CMDs. Glatt et al. 2010, A&A 517, Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 8 Diameters and Ellipticities as Function of Distance! Apparent diameter [] Ellipticity Larger D app with increasing galactocentric distance More circular with increasing galactocentric distance Bica et al. 2008, MNRAS 389, Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 9
6 Bica et al. 2008, MNRAS 389, 678 [Beware: D app typically 4x smaller than tidal radii R t.] Cluster Size Distributions! Numbers of MC clusters fall off towards large diameters faster than associations. Likely due to dynamical evolution & disruption. In Bridge slopes are similar, possibly due to weaker tidal field. MW GCs: drop off both towards small & large radii drop-off at small radii in MCs may be real, not incomplete- ness. MW GCs Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Peak ~ 4 6 pc. SMC associations on average larger than LMC associations. D app [arcmin] Peak tidal radii: ~16 ~30 pc. R t [pc] Associations can have larger D than clusters. 10 Magellanic Cloud Cluster Core Radii vs. Ages! Mackey et al. 2008, MNRAS 386, 65 Glatt et al. 2009, AJ, 138, 138 Spread in cluster core radii (r c ) increases with age. Young massive (> 10 4 M ) clusters: r c ~ 1 2 pc; oldest clusters: up to 8 pc. GCs in Fornax & Sgr dsphs also fit this trend, as do MW GCs (esp. young halo GCs). r c [pc] log (age) [yr] Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 11
7 Magellanic Cloud Cluster Core Radii vs. Ages! Mackey et al. 2008, MNRAS 386, 65 Galactic young halo GCs mainly at Galactocentric distances > ~ 15 kpc. Progression of cluster structural properties with time? Internal dynamical evolution or Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 12 Magellanic Cloud Cluster Core Radii vs. Ages! Hurley & Mackey 2010, MNRAS 408, 2353 Differences in initial cluster size may play important role (Hurley & Mackey 2010). Extended clusters (ECs) also in outer regions of other massive galaxies (M31; Huxor et al. 2005) and other dwarfs. 2 modes of GC formation, one with typical half-light radii of ~ 3 pc, and extended mode with r 1/2 ~ 10 pc? (Da Costa et al. 2009, see also Baumgardt et al. 2010) Diffuse star clusters can form directly in regions where tidal forces are low (Elmegreen 2008). ECs with r 1/2 up to 30 pc (depending on galactic tidal field) can form from standard cluster evolution if clusters are close to filling their tidal radii initially (Hurley & Mackey 2010). ECs such as some Galactic outer halo GCs probably formed in dwarfs (like the MCs) and were later accreted Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 13
8 Star Cluster Survivability! Baumgardt et al. 2013, MNRAS, 430, 676 LMC cluster masses vs. age: Note lack of low- mass clusters for ages > 1 Gyr. Due to dissolution or difficulty of detecting older, sparse clusters? Consider age (dissolution) bias. Dotted line: 50% completeness. Dashed line: Present analysis; ages > 10 7 yr; masses > 5000 M, M V > Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 14 Star Cluster Survivability! No. of clusters formed per unit stellar mass ~ constant up to 200 Myr. Then sharp drop onset of dissolution. Cluster frequency divided by field SFH. LMC Primordial gas expulsion either has little effect, or is only effective during first 10 Myr, or only affects clusters with M < 5000 M. Characteristic lifetime of a 10 4 M cluster: 200 Myr (1/2 the value for same mass in solar neighborhood; Lamers et al. 05) For t > 200 Myr ~ 90% of clusters destroyed per 1 dex in log t Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 15 Baumgardt et al. 2013, MNRAS, 430, 676
9 Clusters with multiple MS TOPs?! LMC, SMC: Multiple main-sequence turn- offs and/or red clumps. Suggested explanations: Extended or multiple SF episodes; age spreads of Myr? Cluster mergers? Interacting binaries? Stellar rotation? Not seen in younger ( Myr) clusters. (e.g., Girardi et al. 2011; Yang et al. 2012, 2013; Bastian & de Mink 2009, Bastian et al. 2013) Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds Yang et al Glatt et al. 2008, AJ 136, Differences between LMC/SMC Clusters! LMC: at least 15 old globular clusters. Variety of abundances and horizontal branch types. Oldest LMC GCs as old as oldest Galactic GCs. (e.g., Johnson et al. 1999). Belong kinematically to disk; no kinematic halo GCs. LMC: Extended hiatus in star cluster formation at intermediate ages; the famous age gap. SMC: Only one genuine, old GC; NGC121; 2-3 Gyr younger than old Galactic halo clusters. SMC: fairly continuous age sequence of clusters. Difference not understood. Puzzling if Clouds were long-term bound, interacting pair Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 17 (e.g., Glatt et al. 2008)
10 LMC: Field and Cluster Age-Metallicity Relation! Field stars seem to trace cluster AMR rather well. Initial rapid enrichment. Cluster age gap appears to coincide with low field SFR; enrichment mainly via SNe Ia. But be aware of caveats in deriving field AMR from either photometry or spectra! Note the gap in the age distribution between ~ 4 and ~ 9 Gyr. Note the large scatter in metallicity at a given age. Harris & Zaritsky 2009, AJ 138, Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 18 SMC Field and Cluster Age-Metallicity Relation! Field AMR overall traces cluster AMR. At any given age: range of [Fe/H]; SMC not well mixed. Clusters formed and survived even while field SFR was low. Large symbols: Clusters with spectroscopic [Fe/H]. Small symbols: Clusters with photometric [Fe/H]. Thick lines: Field AMR from HST CMDs. Cignoni et al. 2013, ApJ 775, Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 19
11 Summary! Clusters found in LMC, SMC, Bridge. Young clusters/field stars: irregular distribution, different activity centers (incl. bar), loci change with time. Recent age distribution peaks may coincide with times of close encounters between Clouds and/or Milky Way. Cluster-to-field-star ratio ~ constant for Myr. Characteristic cluster life time ~ 200 Myr (LMC). Main dissolution mechanism probably two-body relaxation. SMC cluster age-metallicity relation: Not well mixed in metallicity at any given age! (Apparently also in LMC) Differences LMC/SMC clusters (reasons unclear): LMC age gap (~4 ~9 Gyr) vs. continuous age range. Many old GCs vs. 1 GC 2 3 Gyr younger than old GCs. Multiple stellar populations under debate Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 20 Coming soon:! HTTP The Hubble Tarantula Treasury Survey (ACS & WFC3) Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 21
12 SMC Clusters with HST! Glatt et al. 2008, AJ 136, 1703 and AJ, 135, 1106 NGC 121 Kron 3 NGC Gyr 11 Gyr 6.5 Gyr Grebel: Star Clusters of the Magellanic Clouds 22
Stellar Populations in the Local Group
 Stellar Populations in the Local Group Recall what we ve learned from the Milky Way: Age and metallicity tend to be correlated: older -> lower heavy element content younger -> greater heavy element content
Stellar Populations in the Local Group Recall what we ve learned from the Milky Way: Age and metallicity tend to be correlated: older -> lower heavy element content younger -> greater heavy element content
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a preprint version which may differ from the publisher's version. For additional information about this
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a preprint version which may differ from the publisher's version. For additional information about this
The star cluster formation history of the LMC
 MNRAS 430, 676 685 (2013) doi:10.1093/mnras/sts667 The star cluster formation history of the LMC H. Baumgardt, 1 G. Parmentier, 2,3 P. Anders 4 ande.k.grebel 5 1 School of Mathematics and Physics, University
MNRAS 430, 676 685 (2013) doi:10.1093/mnras/sts667 The star cluster formation history of the LMC H. Baumgardt, 1 G. Parmentier, 2,3 P. Anders 4 ande.k.grebel 5 1 School of Mathematics and Physics, University
Using the HR Diagram to Measure the Star Formation Histories of Galaxies. Tammy Smecker-Hane University of California, Irvine
 Using the HR Diagram to Measure the Star Formation Histories of Galaxies Tammy Smecker-Hane University of California, Irvine tsmecker@uci.edu Irvine, California 1 Outline 1. Stellar Evolution Hertzsprung-Russell
Using the HR Diagram to Measure the Star Formation Histories of Galaxies Tammy Smecker-Hane University of California, Irvine tsmecker@uci.edu Irvine, California 1 Outline 1. Stellar Evolution Hertzsprung-Russell
Rupali Chandar University of Toledo
 Star Formation in Clusters Rupali Chandar University of Toledo Star Clusters: Near and Far. Very Near: ONC (400 pc) ~103 Msun Near: NGC 3603 (7 kpc) ~104 Msun Star Clusters: Near and Far. Kinda Near: R136
Star Formation in Clusters Rupali Chandar University of Toledo Star Clusters: Near and Far. Very Near: ONC (400 pc) ~103 Msun Near: NGC 3603 (7 kpc) ~104 Msun Star Clusters: Near and Far. Kinda Near: R136
Zoccali et al. 2003, A&A, 399, 931. Overview of (old) Galactic components. bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo. metallicity & age distribution
 Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Globular Clusters in LSB Dwarf Galaxies
 Globular Clusters in LSB Dwarf Galaxies New results from HST photometry and VLT spectroscopy Thomas H. Puzia Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics in collaboration with Margarita E. Sharina SAO, Russian Academy
Globular Clusters in LSB Dwarf Galaxies New results from HST photometry and VLT spectroscopy Thomas H. Puzia Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics in collaboration with Margarita E. Sharina SAO, Russian Academy
II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies
 II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies Ferguson & Binggeli 1994, A&ARev 6, 67 1 1. Properties low mass : 10 6 10 10 M slow rotators : 10 100 km s -1 low luminosity : 10 6 10 10 L low surface brightness
II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies Ferguson & Binggeli 1994, A&ARev 6, 67 1 1. Properties low mass : 10 6 10 10 M slow rotators : 10 100 km s -1 low luminosity : 10 6 10 10 L low surface brightness
The star cluster frequency throughout the Large Magellanic Cloud
 MNRAS 437, 1646 1661 (2014) Advance Access publication 2013 November 26 doi:10.1093/mnras/stt1998 The star cluster frequency throughout the Large Magellanic Cloud Andrés E. Piatti Observatorio Astronómico,
MNRAS 437, 1646 1661 (2014) Advance Access publication 2013 November 26 doi:10.1093/mnras/stt1998 The star cluster frequency throughout the Large Magellanic Cloud Andrés E. Piatti Observatorio Astronómico,
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies
 Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
SMASHing the LMC. Yumi Choi. Montana State University/University of Arizona. Collaborator
 SMASHing the LMC Montana State University/University of Arizona Collaborator David Nidever, Knut Olsen, Gurtina Besla, Robert Blum, Dennis Zaritsky, Roeland van der Marel, Eric Bell, Carme Gallart, Maria-Rosa
SMASHing the LMC Montana State University/University of Arizona Collaborator David Nidever, Knut Olsen, Gurtina Besla, Robert Blum, Dennis Zaritsky, Roeland van der Marel, Eric Bell, Carme Gallart, Maria-Rosa
Reddening map of the Large Magellanic Cloud bar region. A. Subramaniam
 A&A 430, 421 426 (2005) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20041279 c ESO 2005 Astronomy & Astrophysics Reddening map of the Large Magellanic Cloud bar region A. Subramaniam Indian Institute of Astrophysics, II Block,
A&A 430, 421 426 (2005) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20041279 c ESO 2005 Astronomy & Astrophysics Reddening map of the Large Magellanic Cloud bar region A. Subramaniam Indian Institute of Astrophysics, II Block,
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
THE GALACTIC BULGE AND ITS GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: MOS. B. Barbuy
 THE GALACTIC BULGE AND ITS GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: MOS B. Barbuy IAG - Universidade de São Paulo Outline: Interest of studies on Galactic bulge and globulars Data available on metallicity,, kinematics in field
THE GALACTIC BULGE AND ITS GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: MOS B. Barbuy IAG - Universidade de São Paulo Outline: Interest of studies on Galactic bulge and globulars Data available on metallicity,, kinematics in field
Stellar Populations: Resolved vs. unresolved
 Outline Stellar Populations: Resolved vs. unresolved Individual stars can be analyzed Applicable for Milky Way star clusters and the most nearby galaxies Integrated spectroscopy / photometry only The most
Outline Stellar Populations: Resolved vs. unresolved Individual stars can be analyzed Applicable for Milky Way star clusters and the most nearby galaxies Integrated spectroscopy / photometry only The most
Astr 5465 Feb. 13, 2018 Distribution & Classification of Galaxies Distribution of Galaxies
 Astr 5465 Feb. 13, 2018 Distribution & Classification of Galaxies Distribution of Galaxies Faintest galaxies are distributed ~ uniformly over the sky except for the Galactic plane (zone of avoidance) Brighter
Astr 5465 Feb. 13, 2018 Distribution & Classification of Galaxies Distribution of Galaxies Faintest galaxies are distributed ~ uniformly over the sky except for the Galactic plane (zone of avoidance) Brighter
Milky Way S&G Ch 2. Milky Way in near 1 IR H-W Rixhttp://online.kitp.ucsb.edu/online/galarcheo-c15/rix/
 Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
The M31 Globular Cluster System
 The M31 Globular Cluster System How alike are the GC systems of the Milky Way and M31? Jean Brodie UCO/Lick Observatory UCSC 1 GCs trace the star formation and assembly GC formation occurs early Accompanies
The M31 Globular Cluster System How alike are the GC systems of the Milky Way and M31? Jean Brodie UCO/Lick Observatory UCSC 1 GCs trace the star formation and assembly GC formation occurs early Accompanies
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
GALAXIES 626. The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution:
 GALAXIES 626 The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution: Chemical evolution Observation of spiral and irregular galaxies show that the fraction of heavy elements varies with the fraction of the total mass which
GALAXIES 626 The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution: Chemical evolution Observation of spiral and irregular galaxies show that the fraction of heavy elements varies with the fraction of the total mass which
Review of stellar evolution and color-magnitude diagrams
 Review of stellar evolution and color-magnitude diagrams The evolution of stars can be used to study the properties of galaxies Very characteristic features pinpoint at the age (chemistry) of the stars
Review of stellar evolution and color-magnitude diagrams The evolution of stars can be used to study the properties of galaxies Very characteristic features pinpoint at the age (chemistry) of the stars
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
The effect of primordial mass segregation on the size scale of the star clusters
 The effect of primordial mass segregation on the size scale of the star clusters Hosein Haghi In collaboration with: HoseiniRad, Zonoozi, Kuepper Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences (IASBS),Zanjan
The effect of primordial mass segregation on the size scale of the star clusters Hosein Haghi In collaboration with: HoseiniRad, Zonoozi, Kuepper Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences (IASBS),Zanjan
Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology:
 Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology: Looking more deeply at the Hubble Sequence Galaxy Morphology How do you quantify the properties of galaxies? and how do you put them in groups which allow you to study physically
Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology: Looking more deeply at the Hubble Sequence Galaxy Morphology How do you quantify the properties of galaxies? and how do you put them in groups which allow you to study physically
The Star Cluster Systems of the Magellanic Clouds
 Extragalactic Star Clusters IAU Symposium Series, Vol. 207, 2001 Eva K. Grebel, Doug Geisler, and Dante Minniti, eds. The Star Cluster Systems of the Magellanic Clouds G. S. Da Costa Research School of
Extragalactic Star Clusters IAU Symposium Series, Vol. 207, 2001 Eva K. Grebel, Doug Geisler, and Dante Minniti, eds. The Star Cluster Systems of the Magellanic Clouds G. S. Da Costa Research School of
Stellar Populations in the Galaxy
 Stellar Populations in the Galaxy Stars are fish in the sea of the galaxy, and like fish they often travel in schools. Star clusters are relatively small groupings, the true schools are stellar populations.
Stellar Populations in the Galaxy Stars are fish in the sea of the galaxy, and like fish they often travel in schools. Star clusters are relatively small groupings, the true schools are stellar populations.
Direct N-body simulations of distant halo globular clusters
 Direct N-body simulations of distant halo globular clusters Hosein Haghi Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences (IASBS) Zanjan, IRAN in collaboration with Akram Hasani Zonoozi (IASBS), Holger
Direct N-body simulations of distant halo globular clusters Hosein Haghi Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences (IASBS) Zanjan, IRAN in collaboration with Akram Hasani Zonoozi (IASBS), Holger
Co-Evolution of Central Black Holes and Nuclear Star Clusters
 Co-Evolution of Central Black Holes and Nuclear Star Clusters Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) Globular clusters in the Galaxy median distance from the center is 5 kpc Resolved star cluster highest
Co-Evolution of Central Black Holes and Nuclear Star Clusters Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) Globular clusters in the Galaxy median distance from the center is 5 kpc Resolved star cluster highest
1924: Hubble classification scheme 1925: Hubble measures Cepheids (Period-Luminosity) in Andromeda case closed
 Galaxies 1920 - Curtis-Shapley debate on nature of spiral nebulae - distribution in the sky: zone of avoidance Curtis: extinction Shapley:? - apparent brightness of stars(?) observed in some nebulae Shapley:
Galaxies 1920 - Curtis-Shapley debate on nature of spiral nebulae - distribution in the sky: zone of avoidance Curtis: extinction Shapley:? - apparent brightness of stars(?) observed in some nebulae Shapley:
Dust [12.1] Star clusters. Absorb and scatter light Effect strongest in blue, less in red, zero in radio.
![Dust [12.1] Star clusters. Absorb and scatter light Effect strongest in blue, less in red, zero in radio. Dust [12.1] Star clusters. Absorb and scatter light Effect strongest in blue, less in red, zero in radio.](/thumbs/94/121056697.jpg) More abs. Dust [1.1] kev V Wavelength Optical Infra-red More abs. Wilms et al. 000, ApJ, 54, 914 No grains Grains from http://www.astro.princeton.edu/~draine/dust/dustmix.html See DraineH 003a, column
More abs. Dust [1.1] kev V Wavelength Optical Infra-red More abs. Wilms et al. 000, ApJ, 54, 914 No grains Grains from http://www.astro.princeton.edu/~draine/dust/dustmix.html See DraineH 003a, column
The physical properties of galaxies in Universe
 The physical properties of galaxies in Universe Iurii Babyk, Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Dublin City University, Main Astronomical Observatory of the NAS of Ukraine. Introduction Large-Scale
The physical properties of galaxies in Universe Iurii Babyk, Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Dublin City University, Main Astronomical Observatory of the NAS of Ukraine. Introduction Large-Scale
Galaxies -- Introduction. Classification -- Feb 13, 2014
 Galaxies -- Introduction Classification -- Feb 13, 2014 Why Begin with Classification? The Hubble system forms the basic vocabulary of the subject. The sequence of galaxy types reflects an underlying physical
Galaxies -- Introduction Classification -- Feb 13, 2014 Why Begin with Classification? The Hubble system forms the basic vocabulary of the subject. The sequence of galaxy types reflects an underlying physical
Astronomy. Astrophysics. Ages and luminosities of young SMC/LMC star clusters and the recent star formation history of the Clouds
 A&A 517, A5 (21) DOI: 1.151/4-6361/217 c ESO 21 Astronomy & Astrophysics Ages and luminosities of young /LMC star clusters and the recent star formation history of the Clouds K. Glatt 1,2,E.K.Grebel 1,2,andA.Koch
A&A 517, A5 (21) DOI: 1.151/4-6361/217 c ESO 21 Astronomy & Astrophysics Ages and luminosities of young /LMC star clusters and the recent star formation history of the Clouds K. Glatt 1,2,E.K.Grebel 1,2,andA.Koch
The HERMES project. Reconstructing Galaxy Formation. Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU. The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012
 The HERMES project Reconstructing Galaxy Formation Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012 HERMES is a new high-resolution fiber-fed multi-object spectrometer
The HERMES project Reconstructing Galaxy Formation Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012 HERMES is a new high-resolution fiber-fed multi-object spectrometer
Tidal Remnants and Intergalactic H II Regions
 Recycling intergalactic and interstellar matter IAU Symposium Series, Vol. 217, 2004 Pierre-Alain Duc, Jonathan Braine and Elias Brinks, eds. Tidal Remnants and Intergalactic H II Regions Tom Oosterloo,
Recycling intergalactic and interstellar matter IAU Symposium Series, Vol. 217, 2004 Pierre-Alain Duc, Jonathan Braine and Elias Brinks, eds. Tidal Remnants and Intergalactic H II Regions Tom Oosterloo,
Upcoming class schedule
 Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
Dwarf spheroidal satellites of M31: Variable stars and stellar populations
 Dwarf spheroidal satellites of M31: Variable stars and stellar populations Felice Cusano INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna LBT Team Italy collaborators: Gisella Clementini, Alessia Garofalo, Michele
Dwarf spheroidal satellites of M31: Variable stars and stellar populations Felice Cusano INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna LBT Team Italy collaborators: Gisella Clementini, Alessia Garofalo, Michele
University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli. Lecture 16
 University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year 2011-2012 Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli Lecture 16 Stellar populations Walter Baade (1893-1960) Learning outcomes The student
University of Naples Federico II, Academic Year 2011-2012 Istituzioni di Astrofisica, read by prof. Massimo Capaccioli Lecture 16 Stellar populations Walter Baade (1893-1960) Learning outcomes The student
Galaxies. Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations
 Galaxies Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations Cepheids in M31 Up to 1920s, the Milky Way was thought by
Galaxies Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations Cepheids in M31 Up to 1920s, the Milky Way was thought by
Multiple stellar populations in star clusters: an observational (incomplete) overview
 Multiple stellar populations in star clusters: an observational (incomplete) overview Giampaolo Piotto Dipartimento di Astronomia Universita di Padova Collaborators: J. Anderson, L.R. Bedin, I.R. King,
Multiple stellar populations in star clusters: an observational (incomplete) overview Giampaolo Piotto Dipartimento di Astronomia Universita di Padova Collaborators: J. Anderson, L.R. Bedin, I.R. King,
CN Variations in Globular Clusters
 CN Variations in Globular Clusters Jason Smolinski originally presented 08/11/2010 encore presentation 08/25/2010 Outline I. What Are We Talking About? a) Cluster Environment b) Expectations from Theory
CN Variations in Globular Clusters Jason Smolinski originally presented 08/11/2010 encore presentation 08/25/2010 Outline I. What Are We Talking About? a) Cluster Environment b) Expectations from Theory
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies
 Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
The Milky Way Formation Timescale
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 13 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della The Milky Way Formation Timescale A. Aparicio 1,2, A. Rosenberg 2, G. Piotto 3, I. Saviane 4 and A. Recio-Blanco 3 1 Departamento de Astrofisica, Universidad
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 13 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della The Milky Way Formation Timescale A. Aparicio 1,2, A. Rosenberg 2, G. Piotto 3, I. Saviane 4 and A. Recio-Blanco 3 1 Departamento de Astrofisica, Universidad
Young Stellar Structures in the Magellanic Clouds as Revealed by the VMC Survey
 Young Stellar Structures in the Magellanic Clouds as Revealed by the VMC Survey SFDE17, Aug.11, 2017 Speaker: Ning-Chen Sun (KIAA-PKU) Advisor: Prof. Richard de Grijs in collaboration with the VMC team
Young Stellar Structures in the Magellanic Clouds as Revealed by the VMC Survey SFDE17, Aug.11, 2017 Speaker: Ning-Chen Sun (KIAA-PKU) Advisor: Prof. Richard de Grijs in collaboration with the VMC team
What is an ultra-faint Galaxy?
 What is an ultra-faint Galaxy? UCSB KITP Feb 16 2012 Beth Willman (Haverford College) Large Magellanic Cloud, M V = -18 ~ 1/10 Milky Way luminosity image credit: Yuri Beletsky (ESO) and APOD NGC 205, M
What is an ultra-faint Galaxy? UCSB KITP Feb 16 2012 Beth Willman (Haverford College) Large Magellanic Cloud, M V = -18 ~ 1/10 Milky Way luminosity image credit: Yuri Beletsky (ESO) and APOD NGC 205, M
Mapping the Galactic halo with main-sequence and RR Lyrae stars
 EPJ Web of Conferences 19, 02002 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/20121902002 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2012 Mapping the Galactic halo with main-sequence and RR Lyrae stars B. Sesar
EPJ Web of Conferences 19, 02002 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/20121902002 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2012 Mapping the Galactic halo with main-sequence and RR Lyrae stars B. Sesar
SUPER STAR CLUSTERS: High Resolution Observations. James R. Graham (UCB) Nate McCrady (UCLA) & Andrea Gilbert (LLNL) KIPT
 SUPER STAR CLUSTERS: High Resolution Observations James R. Graham (UCB) Nate McCrady (UCLA) & Andrea Gilbert (LLNL) KIPT 2007-8-16 M82 N 100 pc McCrady & Graham 2007 ACS F814W & NICMOS F160W/F222M images
SUPER STAR CLUSTERS: High Resolution Observations James R. Graham (UCB) Nate McCrady (UCLA) & Andrea Gilbert (LLNL) KIPT 2007-8-16 M82 N 100 pc McCrady & Graham 2007 ACS F814W & NICMOS F160W/F222M images
The Milky Way. Overview: Number of Stars Mass Shape Size Age Sun s location. First ideas about MW structure. Wide-angle photo of the Milky Way
 Figure 70.01 The Milky Way Wide-angle photo of the Milky Way Overview: Number of Stars Mass Shape Size Age Sun s location First ideas about MW structure Figure 70.03 Shapely (~1900): The system of globular
Figure 70.01 The Milky Way Wide-angle photo of the Milky Way Overview: Number of Stars Mass Shape Size Age Sun s location First ideas about MW structure Figure 70.03 Shapely (~1900): The system of globular
Stellar Population Synthesis: The Role of Adaptive Optics
 Stellar Population Synthesis: The Role of Adaptive Optics Jason Melbourne (Caltech) Nearby (2.5 Mpc) Dwarf Irregular Galaxy KKH 98 HST F475W (Blue), HST F814W (Green), Keck AO K-band (red) Melbourne et
Stellar Population Synthesis: The Role of Adaptive Optics Jason Melbourne (Caltech) Nearby (2.5 Mpc) Dwarf Irregular Galaxy KKH 98 HST F475W (Blue), HST F814W (Green), Keck AO K-band (red) Melbourne et
Astro2010 Science White Paper: The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN)
 Astro2010 Science White Paper: The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN) Thomas M. Brown (tbrown@stsci.edu) and Marc Postman (postman@stsci.edu) Space Telescope Science Institute Daniela Calzetti (calzetti@astro.umass.edu)
Astro2010 Science White Paper: The Galactic Neighborhood (GAN) Thomas M. Brown (tbrown@stsci.edu) and Marc Postman (postman@stsci.edu) Space Telescope Science Institute Daniela Calzetti (calzetti@astro.umass.edu)
4 Star Formation Relations
 The Wonders of Star Formation - Edinburgh - 7.9.2018 4 Star Formation Relations (+ Strengthened Cluster Survival) With One Single Model Geneviève Parmentier Astronomisches-Rechen Institut Zentrum für Astronomie
The Wonders of Star Formation - Edinburgh - 7.9.2018 4 Star Formation Relations (+ Strengthened Cluster Survival) With One Single Model Geneviève Parmentier Astronomisches-Rechen Institut Zentrum für Astronomie
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2015](/thumbs/94/118561873.jpg) Baltic Astronomy, vol. 23, 221 229, 2014 MODELS OF LATE-TYPE DISK GALAXIES: 1-D VERSUS 2-D arxiv:1502.00232v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2015 T. Mineikis 1,2 and V. Vansevičius 1,2 1 Vilnius University Observatory,
Baltic Astronomy, vol. 23, 221 229, 2014 MODELS OF LATE-TYPE DISK GALAXIES: 1-D VERSUS 2-D arxiv:1502.00232v1 [astro-ph.ga] 1 Feb 2015 T. Mineikis 1,2 and V. Vansevičius 1,2 1 Vilnius University Observatory,
Our Milky Way (MW) Galaxy L*, M* but not SFR*
 Our Milky Way (MW) Galaxy L*, M* but not SFR* (Our galaxy is revered as Galaxy and others are merely galaxy ;-).) (SFR is less than 5 solar mass per year) MW Structure Diagram Midplane molecular layer
Our Milky Way (MW) Galaxy L*, M* but not SFR* (Our galaxy is revered as Galaxy and others are merely galaxy ;-).) (SFR is less than 5 solar mass per year) MW Structure Diagram Midplane molecular layer
The Great Debate: The Size of the Universe (1920)
 The Great Debate: The Size of the Universe (1920) Heber Curtis Our Galaxy is rather small, with Sun near the center. 30,000 LY diameter. Universe composed of many separate galaxies Spiral nebulae = island
The Great Debate: The Size of the Universe (1920) Heber Curtis Our Galaxy is rather small, with Sun near the center. 30,000 LY diameter. Universe composed of many separate galaxies Spiral nebulae = island
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Apr 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Apr 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Apr 2018](/thumbs/77/74866091.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper2_smc_31march2018 ESO 2018 April 3, 2018 STAR CLUSTERS IN THE MAGELLANIC CLOUDS - II. AGE-DATING, CLASSIFICATION AND SPATIO-TEMPORAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE SMC
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper2_smc_31march2018 ESO 2018 April 3, 2018 STAR CLUSTERS IN THE MAGELLANIC CLOUDS - II. AGE-DATING, CLASSIFICATION AND SPATIO-TEMPORAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE SMC
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 31 Jul 1998
 Cosmic Star Formation from the Milky Way and its Satellites arxiv:astro-ph/973v1 31 Jul 199 F.D.A. Hartwick Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada, VW 3P Abstract.
Cosmic Star Formation from the Milky Way and its Satellites arxiv:astro-ph/973v1 31 Jul 199 F.D.A. Hartwick Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada, VW 3P Abstract.
THE QUEST RR LYRAE SURVEY AND HALO SUB-STRUCTURE
 THE QUEST RR LYRAE SURVEY AND HALO SUB-STRUCTURE Kathy Vivas (CIDA, Venezuela), Bob Zinn (Yale U., USA), Sonia Duffau (U. de Chile), Yara Jaffé, Jesús Hernández, Yolimar Subero (CIDA, Venezuela), G. Carraro
THE QUEST RR LYRAE SURVEY AND HALO SUB-STRUCTURE Kathy Vivas (CIDA, Venezuela), Bob Zinn (Yale U., USA), Sonia Duffau (U. de Chile), Yara Jaffé, Jesús Hernández, Yolimar Subero (CIDA, Venezuela), G. Carraro
The origin of lopsidedness in galaxies
 The Galaxy Disk in Cosmological Context Proceedings IAU Symposium No. xxx, 2008 c 2008 International Astronomical Union J. Andersen (Chief Editor), J. Bland-Hawthorn & B. Nordström, eds. The origin of
The Galaxy Disk in Cosmological Context Proceedings IAU Symposium No. xxx, 2008 c 2008 International Astronomical Union J. Andersen (Chief Editor), J. Bland-Hawthorn & B. Nordström, eds. The origin of
A wide-field view of the Phoenix transition type dwarf galaxy (Battaglia et al., MNRAS accepted, airxv/ )
 A wide-field view of the Phoenix transition type dwarf galaxy (Battaglia et al., MNRAS accepted, airxv/1205.2704) Giuseppina Battaglia INAF Astronomical Observatory of Bologna With thanks to M.Rejkuba,
A wide-field view of the Phoenix transition type dwarf galaxy (Battaglia et al., MNRAS accepted, airxv/1205.2704) Giuseppina Battaglia INAF Astronomical Observatory of Bologna With thanks to M.Rejkuba,
Deriving Star Formation Histories of Galaxies from their Most-Massive Star-Cluster Distributions
 Deriving Star Formation Histories of Galaxies from their Most-Massive Star-Cluster Distributions Thomas Maschberger Pavel Kroupa Argelander-Institut für Astronomie Universität Bonn RSDN Hoher List December
Deriving Star Formation Histories of Galaxies from their Most-Massive Star-Cluster Distributions Thomas Maschberger Pavel Kroupa Argelander-Institut für Astronomie Universität Bonn RSDN Hoher List December
Age Dating A SSP. Quick quiz: please write down a 3 sentence explanation of why these plots look like they do.
 Color is only a weak function of age after ~3Gyrs (for a given metallicity) (See MBW pg 473) But there is a strong change in M/L V and weak change in M/L K Age Dating A SSP Quick quiz: please write down
Color is only a weak function of age after ~3Gyrs (for a given metallicity) (See MBW pg 473) But there is a strong change in M/L V and weak change in M/L K Age Dating A SSP Quick quiz: please write down
Knut Olsen DECam Community Workshop August 2011
 Knut Olsen DECam Community Workshop August 2011 Motivation The Magellanic Clouds are rich laboratories of astrophysical phenomena Their structure and stellar populations allow us to explore their evolution
Knut Olsen DECam Community Workshop August 2011 Motivation The Magellanic Clouds are rich laboratories of astrophysical phenomena Their structure and stellar populations allow us to explore their evolution
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way
 Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way Almost everything we see in the night sky belongs to the Milky Way We see most of the Milky Way as a faint band of light across the sky From the outside, our
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way Almost everything we see in the night sky belongs to the Milky Way We see most of the Milky Way as a faint band of light across the sky From the outside, our
Structure of Merger Remnants:
 Structure of Merger Remnants: Lessons from Spectral Line Observations John E. Hibbard NRAO-CV Merger Hypothesis: Two gas-rich Spirals Merge into One Elliptical Toomre Sequence of On-going Mergers (Toomre
Structure of Merger Remnants: Lessons from Spectral Line Observations John E. Hibbard NRAO-CV Merger Hypothesis: Two gas-rich Spirals Merge into One Elliptical Toomre Sequence of On-going Mergers (Toomre
Stellar Systems with HST
 Stellar Systems with HST (With European Impact) Topics: Surprizing Globular Clusters in the Milky Way The MW Bulge and its Globulars The Bulge, Halo, Stream and Disk of Andromeda Bulges at high redshifts
Stellar Systems with HST (With European Impact) Topics: Surprizing Globular Clusters in the Milky Way The MW Bulge and its Globulars The Bulge, Halo, Stream and Disk of Andromeda Bulges at high redshifts
Galaxies The Hubble Sequence Different Types of Galaxies 4 broad Morphological Types created by Edwin Hubble Galaxies come is a variety of shapes and
 Galaxies The Hubble Sequence Different Types of Galaxies 4 broad Morphological Types created by Edwin Hubble Galaxies come is a variety of shapes and sizes Edwin Hubble classified the galaxies into four
Galaxies The Hubble Sequence Different Types of Galaxies 4 broad Morphological Types created by Edwin Hubble Galaxies come is a variety of shapes and sizes Edwin Hubble classified the galaxies into four
The Origin of Multiple Populations within Stellar Clusters An Unsolved Problem
 The Origin of Multiple Populations within Stellar Clusters An Unsolved Problem Nate Bastian (Liverpool, LJMU) Ivan Cabrera-Ziri (LJMU), Katie Hollyhead (LJMU), Florian Niederhofer (LMU/ESO) V (brightness)
The Origin of Multiple Populations within Stellar Clusters An Unsolved Problem Nate Bastian (Liverpool, LJMU) Ivan Cabrera-Ziri (LJMU), Katie Hollyhead (LJMU), Florian Niederhofer (LMU/ESO) V (brightness)
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
 Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Massive star clusters
 Massive star clusters as a host of compact binaries Michiko Fujii ( 藤井通子 ) The University of Tokyo Outline Massive star clusters and compact binaries Dynamical evolution of star clusters Distribution of
Massive star clusters as a host of compact binaries Michiko Fujii ( 藤井通子 ) The University of Tokyo Outline Massive star clusters and compact binaries Dynamical evolution of star clusters Distribution of
Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy
 Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy Raja Guhathakurta University of California Observatories (Lick, Keck, TMT) University of California at Santa Cruz M31 s extended stellar
Substructure in the Stellar Halo of the Andromeda Spiral Galaxy Raja Guhathakurta University of California Observatories (Lick, Keck, TMT) University of California at Santa Cruz M31 s extended stellar
The separate formation of different galaxy components
 The separate formation of different galaxy components Alfonso Aragón-Salamanca School of Physics and Astronomy University of Nottingham Overview: Galaxy properties and morphologies Main galaxy components:
The separate formation of different galaxy components Alfonso Aragón-Salamanca School of Physics and Astronomy University of Nottingham Overview: Galaxy properties and morphologies Main galaxy components:
Galaxies and Hubble s Law
 Galaxies and Hubble s Law Some Important History: Charles Messier In the early 19 th century, Charles Messier was hunting for comets, but in the telescopes of the time, identifying comets was difficult
Galaxies and Hubble s Law Some Important History: Charles Messier In the early 19 th century, Charles Messier was hunting for comets, but in the telescopes of the time, identifying comets was difficult
Star systems like our Milky Way. Galaxies
 Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
Using Globular Clusters to. Study Elliptical Galaxies. The View Isn t Bad... Omega Centauri. Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office M13
 Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
Studying stars in M31 GCs using NIRI and GNIRS
 Studying stars in M31 GCs using NIRI and GNIRS Ricardo Schiavon Gemini Observatory GSM 2012 San Francisco July 19, 2012 Collaborators Andy Stephens (Gemini) Nelson Caldwell (SAO) Matthew Shetrone (HET)
Studying stars in M31 GCs using NIRI and GNIRS Ricardo Schiavon Gemini Observatory GSM 2012 San Francisco July 19, 2012 Collaborators Andy Stephens (Gemini) Nelson Caldwell (SAO) Matthew Shetrone (HET)
Measuring the Hubble Constant through Cepheid Distances
 Measuring the Hubble Constant through Cepheid Distances Final Results from the Hubble Space Telescope Key Project to Measure the Hubble Constant Freedman, Madore, Gibson, et al., Astrophysical Journal
Measuring the Hubble Constant through Cepheid Distances Final Results from the Hubble Space Telescope Key Project to Measure the Hubble Constant Freedman, Madore, Gibson, et al., Astrophysical Journal
Local Group See S&G ch 4
 Our galactic neighborhood consists of one more 'giant' spiral (M31, Andromeda), a smaller spiral M33 and lots of (>35 galaxies), most of which are dwarf ellipticals and irregulars with low mass; most are
Our galactic neighborhood consists of one more 'giant' spiral (M31, Andromeda), a smaller spiral M33 and lots of (>35 galaxies), most of which are dwarf ellipticals and irregulars with low mass; most are
Age and abundance structure of the central sub-kpc of the Milky Way
 Age and abundance structure of the central sub-kpc of the Milky Way Thomas Bensby Department of Astronomy and THeoretical Physics Sweden MBD collaboration (Microlensed Bulge Dwarf) Sofia Feltzing Thomas
Age and abundance structure of the central sub-kpc of the Milky Way Thomas Bensby Department of Astronomy and THeoretical Physics Sweden MBD collaboration (Microlensed Bulge Dwarf) Sofia Feltzing Thomas
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 14 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 14 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ep] 14 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/113680790.jpg) Origins: from the Protosun to the First Steps of Life Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 345, 2019 Bruce G. Elmegreen, L. Viktor Tóth, Manuel Güdel, eds. c 2019 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X
Origins: from the Protosun to the First Steps of Life Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 345, 2019 Bruce G. Elmegreen, L. Viktor Tóth, Manuel Güdel, eds. c 2019 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X
Figure 69.01a. Formation of Stars
 1. One cloud many clumps 2. Up to 1000 cores can form within 1 clump 3. Core: begins to build a star by attracting material from the cloud 4. Protostar, MS star 5. Up to 1000 stars 6. Stars usually form
1. One cloud many clumps 2. Up to 1000 cores can form within 1 clump 3. Core: begins to build a star by attracting material from the cloud 4. Protostar, MS star 5. Up to 1000 stars 6. Stars usually form
IV. Interacting Galaxies
 IV. Interacting Galaxies Examples of galaxies in interaction: Pairs of galaxies (NGC 4038/39) M 51 type (satellites) Arp 220 type Compact galaxy groups 2 1 B.A. Vorontsov-Velyaminov: Atlas and Catalog
IV. Interacting Galaxies Examples of galaxies in interaction: Pairs of galaxies (NGC 4038/39) M 51 type (satellites) Arp 220 type Compact galaxy groups 2 1 B.A. Vorontsov-Velyaminov: Atlas and Catalog
The Detailed Chemical Abundance Patterns of M31 Globular Clusters
 The Detailed Chemical Abundance Patterns of M31 Globular Clusters University of California Santa Cruz E-mail: jcolucci@ucolick.org Rebecca A. Bernstein University of California Santa Cruz E-mail: rab@ucolick.org
The Detailed Chemical Abundance Patterns of M31 Globular Clusters University of California Santa Cruz E-mail: jcolucci@ucolick.org Rebecca A. Bernstein University of California Santa Cruz E-mail: rab@ucolick.org
Globular Clusters in Massive Galaxies
 Globular Clusters in Massive Galaxies Patrick Durrell (Youngstown State University) + Pat Côté, John Blakeslee, Laura Ferrarese (Herzberg-Victoria), Eric Peng (Peking Univ) Chris Mihos (CWRU) + NGVS Team
Globular Clusters in Massive Galaxies Patrick Durrell (Youngstown State University) + Pat Côté, John Blakeslee, Laura Ferrarese (Herzberg-Victoria), Eric Peng (Peking Univ) Chris Mihos (CWRU) + NGVS Team
The Stellar Populations of Galaxies H. W. Rix IMPRS Galaxies Course March 11, 2011
 The Stellar Populations of Galaxies H. W. Rix IMPRS Galaxies Course March 11, 2011 Goal: Determine n * (M *,t age,[fe/h],r) for a population of galaxies How many stars of what mass and metallicity formed
The Stellar Populations of Galaxies H. W. Rix IMPRS Galaxies Course March 11, 2011 Goal: Determine n * (M *,t age,[fe/h],r) for a population of galaxies How many stars of what mass and metallicity formed
The Accretion History of the Milky Way
 The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
An analogy. "Galaxies" can be compared to "cities" What would you like to know about cities? What would you need to be able to answer these questions?
 An analogy "Galaxies" can be compared to "cities" What would you like to know about cities? how does your own city look like? how big is it? what is its population? history? how did it develop? how does
An analogy "Galaxies" can be compared to "cities" What would you like to know about cities? how does your own city look like? how big is it? what is its population? history? how did it develop? how does
Chapter 8: Simple Stellar Populations
 Chapter 8: Simple Stellar Populations Simple Stellar Population consists of stars born at the same time and having the same initial element composition. Stars of different masses follow different evolutionary
Chapter 8: Simple Stellar Populations Simple Stellar Population consists of stars born at the same time and having the same initial element composition. Stars of different masses follow different evolutionary
Building the cosmic distance scale: from Hipparcos to Gaia
 The Fundamental Distance Scale: state of the art and the Gaia perspectives 3-6 May 2011 Building the cosmic distance scale: from Hipparcos to Gaia Catherine TURON and Xavier LURI 1 ESA / ESO-H. Heyer Fundamental
The Fundamental Distance Scale: state of the art and the Gaia perspectives 3-6 May 2011 Building the cosmic distance scale: from Hipparcos to Gaia Catherine TURON and Xavier LURI 1 ESA / ESO-H. Heyer Fundamental
Population synthesis models
 Population synthesis models From stellar evolution models to synthetic populations in the Milky Way Léo Girardi OAPadova INAF Italy LIneA Rio de Janeiro Brazil GAIA/ITN School, Tenerife, Sep 2013 Léo Girardi
Population synthesis models From stellar evolution models to synthetic populations in the Milky Way Léo Girardi OAPadova INAF Italy LIneA Rio de Janeiro Brazil GAIA/ITN School, Tenerife, Sep 2013 Léo Girardi
The formation and evolution of globular cluster systems. Joel Pfeffer, Nate Bastian (Liverpool, LJMU)
 The formation and evolution of globular cluster systems Joel Pfeffer, Nate Bastian (Liverpool, LJMU) Introduction to stellar clusters Open clusters: few - 10 4 M few Myr - few Gyr solar metallicity disk
The formation and evolution of globular cluster systems Joel Pfeffer, Nate Bastian (Liverpool, LJMU) Introduction to stellar clusters Open clusters: few - 10 4 M few Myr - few Gyr solar metallicity disk
Myung Gyoon Lee ( 李明均 )
 Myung Gyoon Lee ( 李明均 ) With Observational Cosmology Team Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Nov 1-4, 2011, The 3 rd Subaru Conference/The 1 st NAOJ Symposium, Galactic
Myung Gyoon Lee ( 李明均 ) With Observational Cosmology Team Department of Physics & Astronomy Seoul National University, Korea Nov 1-4, 2011, The 3 rd Subaru Conference/The 1 st NAOJ Symposium, Galactic
Formation of Galactic Halo Globular Clusters through Self-Enrichment
 12 June 2003, Uppsala Astronomical Observatory Formation of Galactic Halo Globular Clusters through Self-Enrichment Parmentier Geneviève Institute of Astrophysics and Geophysics Liège University Peer-reviewed
12 June 2003, Uppsala Astronomical Observatory Formation of Galactic Halo Globular Clusters through Self-Enrichment Parmentier Geneviève Institute of Astrophysics and Geophysics Liège University Peer-reviewed
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies
 Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 5 Jul 2006
 THE DWARF SATELLITES OF M31 AND THE GALAXY Sidney van den Bergh Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, National Research Council of Canada, 5071 West Saanich Road, Victoria,
THE DWARF SATELLITES OF M31 AND THE GALAXY Sidney van den Bergh Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, National Research Council of Canada, 5071 West Saanich Road, Victoria,
Astr 5465 Feb. 6, 2018 Characteristics of Color-Magnitude Diagrams
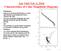 Astr 5465 Feb. 6, 2018 Characteristics of Color-Magnitude Diagrams Preliminaries: Shape of an Isochrone (Distribution at a Given Age) Depends on the Bandpasses Used to Construct the CMD The Turn-off Absolute
Astr 5465 Feb. 6, 2018 Characteristics of Color-Magnitude Diagrams Preliminaries: Shape of an Isochrone (Distribution at a Given Age) Depends on the Bandpasses Used to Construct the CMD The Turn-off Absolute
Galaxy classification
 Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
ASTRO504 Extragalactic Astronomy. 2. Classification
 ASTRO504 Extragalactic Astronomy 2. Classification Morphological classification Elliptical (E) galaxies Lenticular (SO) galaxies Spiral (S) galaxies Irregular (Im) galaxies The realm of nebulae Hubble
ASTRO504 Extragalactic Astronomy 2. Classification Morphological classification Elliptical (E) galaxies Lenticular (SO) galaxies Spiral (S) galaxies Irregular (Im) galaxies The realm of nebulae Hubble
Clicker Question: Galaxy Classification. What type of galaxy do we live in? The Variety of Galaxy Morphologies Another barred galaxy
 Galaxies Galaxies First spiral nebula found in 1845 by the Earl of Rosse. Speculated it was beyond our Galaxy. 1920 - "Great Debate" between Shapley and Curtis on whether spiral nebulae were galaxies beyond
Galaxies Galaxies First spiral nebula found in 1845 by the Earl of Rosse. Speculated it was beyond our Galaxy. 1920 - "Great Debate" between Shapley and Curtis on whether spiral nebulae were galaxies beyond
SPACE MOTIONS OF GALACTIC GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: NEW RESULTS AND HALO-FORMATION IMPLICATIONS
 SPACE MOTIONS OF GALACTIC GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: NEW RESULTS AND HALO-FORMATION IMPLICATIONS Dana I. Casetti-Dinescu, Terrence M. Girard, David Herrera, William F. van Altena, Young-Wook Lee, Carlos Lopez
SPACE MOTIONS OF GALACTIC GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: NEW RESULTS AND HALO-FORMATION IMPLICATIONS Dana I. Casetti-Dinescu, Terrence M. Girard, David Herrera, William F. van Altena, Young-Wook Lee, Carlos Lopez
Veilleux! see MBW ! 23! 24!
 Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
