The Theory of the Lunar Motion
|
|
|
- Phoebe Douglas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Theory of the Lunar Motion (Lunar cycles) V. D. Krasnov Abstract Continuous attempts to create theories of the Moon's motion have been made since the time of Isaac Newton. The theory of the Moon's motion which would take into account the influence of the Sun, Earth and other planets proved to be one of the most complicated tasks in astronomy. In this article, a physical model of the lunar motion built on the basis of the statements of the "Comprehensive Law of Motion of Objects in Planetary Type Systems" is presented. It is shown that the Moon's motion is formed by a complex combination of the gravitational attraction from the Earth and the Sun, acting on the Moon in the direction of the planetary system's motion. In accordance with the physical model presented, a calculation of the Moon's motion is performed. The results of the calculations of the Moon's motion in the field of mutual interaction of the Earth, Sun, and Moon, agree with the motion observed and confirm the Theory of Lunar Motion set forth here. Any quantity of bodies (planets) affecting the Moon's motion could be included in the the calculations. The results of the calculations verify the "Comprehensive Law of Motion of Objects in Planetary Type Systems". Contents Introduction (Modern representations) Theory of Lunar Motion Conclusions References
2 Introduction (Modern representations) The Moon's motion around the Earth is considered today as a combination of several motions: revolution around the Earth along the elliptical orbit; rotation of the lunar orbit plane. Its nodes shift to the west, making complete turn during the period of 18.6 years; rotation of the lunar orbit's major axis with the period of 8.8 years (in the direction opposite to the nodes' movement); periodical changes in the lunar orbit's inclination to the ecliptic in the range of 9 59' to 9 19'; periodical change of the lunar orbit's size: the perigee changes in the range of to thousand km, and the apogee in the range of to thousand km; gradual movement of the Moon from the Earth as a result of tidal acceleration (about 4 cm per year). Some investigators add several other motions to this list. Because of the fact that each orbital element experiences a great number of perturbations with different periods and amplitudes, the actual motion of the Moon is immensely complicated, and its study constitutes one of the most difficult tasks of celestial mechanics [1]. Expressions including tens of thousands members (coefficients and arguments in the trigonometrical functions) are used in the calculations of the motion of the Moon, and there is no limit in their number if a more high precision is required. Theory of Lunar Motion The above-listed motions of the Moon are not independent ones, combination of which determines the resulting lunar motion. These motions themselves are the effects of some hidden interactions unexplored for today. In the article [2], [3] (Comprehensive Law of Motion of Objects in Planetary Type Systems), a description of physical interactions not previously known, which form the planets' orbits observed and allow to explain the complex character of the Moon's motion, is presented. According to the article [2], the Moon relative to the Earth (likewise the Earth relative to the Sun) performs its motion in two planes: revolution around the Earth in the plane of equator, and in the form of periodical oscillations in the direction of motion of the Earth-Moon planetary system (Fig. 9). At the same time, the Moon along with the Earth similarly performs the motion relative to the Sun in two planes: rotation in equatorial plane and in the form of periodical oscillations in the direction of movement of the Solar System (Fig. 9).
3 Plane of celestial equator Earth Vn Moon Equatorial plane V C ±F з ± F c ±F c Fig. 9. Physical model of the planets' motion. The Earth relative to the Sun and the Moon relative to the Earth are shown on one side for clarity. The combination of these two motions just forms the observed orbits of planets. It is safe to assume the planets' rotation in the equatorial plane as uniform. As it was shown in [2], the cyclic oscillations of the planets along the direction of the motion of the planetary system, taking place under the influence of the gravitation force F of the central body, play a major role in the shaping of the observed orbit. The calculation of this motion gives an estimate of the declination, dynamics of the declination change, and inclination of the plane of the planet's rotation at any instant of time. It also gives the duration of the planetary cycles and the speed of motion in the direction of the planetary system's motion. The superposition of the cyclic oscillations of the planet along the direction of the planetary system's motion in the equatorial plane allows to build the observed orbit of the planet, determine the orbital speed of the planet's motion along the observed orbit at any time and the dynamics of the change of its movement. The calculation of the oscillatory movement of the Moon along the direction of the planetary system's motion shall be performed with simultaneous taking into account of the oscillatory motions of the Earth relative to the Sun, of the Moon relative to the Sun, and of the Moon relative to the Earth. The calculation of the oscillatory motion of the Moon along the direction of the planetary system's motion and the Moon's inclination formed by this motion, is performed using the same methods as in the calculation of the Earth's inclination (see [2]). The total acceleration of the Moon (in the system Sun-Earth-Moon) consists of the acceleration caused by the gravitational force F E of the Earth, and gravitational force F S of the Sun, acting in the direction of the planetary system's motion, Fig. 10. And the vectors of these forces become alternatively parallel and anti-parallel. At a certain moments, one or both these forces can be equal to zero.
4 The complex combination of these forces, permanently changing both in amount and direction, determines the complicated character of the Moon's motion. Vn F E +F S +B F E F S B V S F S F S F S F S F E F S +B F E +F S B Fig. 10. Complex combination of gravitational forces acting on the Moon. In the table below is presented a fragment of the calculation of the inclination (motion) of the Moon, determined by the gravitational force components FS and FE of the attraction of the Sun and Earth. The calculation was performed with the time intervals of 3600 s. In this period of time, the parameters which determine the Moon's motion are assumed as constant. (All the presented calculations are not final, they are given for estimation. More precise calculations must include changing the distances of the planets from the central body, acceleration of the Earth under the action of the Moon's gravitation, gravitational interaction with the other planets, and some other perturbations).
5 Table. The fragment of the calculation of the inclination (motion) of the Moon, changing under the action of the components of gravitational force F S and F E from the Sun and the Earth. In this calculation, the accelerations of the Moon and the Earth caused by the component FS of the Sun's gravitational force are assumed equal. The accelerations ΔV E were taken from the table with the calculation of the cyclic oscillations of the Earth performed in-parallel. Lunar cycles *[4] Diagram 1 shows the calculation of the Moon's inclination (motion) determined by the cyclic oscillations of the Moon along the direction of the planetary system's motion, occurring under the action of only the components F S and F E of the gravitational force from the Sun and the Earth (row 1). The values of inclinations (motions) of the Moon from the published sources [4] are superimposed on this diagram (row 2).
6 Inclination δ degrees 01/09/ /09/ /09/ /09/ /09/ /10/ /10/ /10/ /10/ /11/ /11/ /11/ /11/ /12/ /12/ /12/ /12/ /12/2014 Inclination δ degrees 01/05/ /05/ /05/ /05/ /05/ /06/ /06/ /06/ /06/ /07/ /07/ /07/ /07/ /07/ /08/ /08/ /08/ /08/2014 Inclination δ degrees 21/12/ /12/ /01/ /01/ /01/ /01/ /02/ /02/ /02/ /02/ /03/ /03/ /03/ /03/ /03/ /04/ /04/ /04/ /04/2014 Diagram 1. Moon's cycles under the influence of the components F S and F E of the gravitational force from the Sun and the Earth, acting along the direction of the planetary system's motion. Lunar cycles years Ряд1 Ряд Lunar cycles, year 2014 (continuation) Ряд1 Ряд Lunar cycles, year 2014 (continuation) Ряд1 Ряд
7 21/12/ /01/ /02/ /03/ /04/ /05/ /06/ /07/ /08/ /09/ /10/ /11/ /12/2014 Speed, km/s It can be seen from the diagram that the sinusoid of the lunar motion built on the basis of the Theory of Lunar Motion repeats the one built on the data from the published sources. The calculations demonstrate and confirm that the lunar motion and its observed orbit are formed by the cyclic oscillations of the Moon, occurring along the direction of the planetary system's motion under the action of the components of gravitational attraction of the Sun and the Earth. It was noted in the Introduction that tens of thousands of members (coefficients and arguments in trigonometrical functions) are used in the modern calculations of the lunar motion. The calculation presented here was performed using actually two variables gravitational components F S and F E of the attraction of the Sun and the Earth, acting on the Moon along the direction of the planetary system's motion. The calculated Moon's inclination, the dynamics of its changing, and duration of the lunar cycles, determined by the oscillatory motion of the Moon along the direction of the planetary system's motion, agree with the observed values and the data from the published sources. Diagram 2 presents the graph of the changing of the speed Vn of the lunar motion in the direction of the Solar System's motion. Diagram 2. The diagram shows a non-uniform character of the Moon's motion along the direction of the planetary system's motion. This motion forms the non-uniform motion of the Moon along the observed orbit. Diagram of the lunar motion along the direction of the planetary system's motion Ряд1 Conclusions The calculations of the Moon's cycles confirm the "Theory of Lunar Motion" presented here and verify the "Comprehensive Law of Motion of Objects in Planetary Type Systems".
8 The Theory of Lunar Motion and the used methods of calculations allow to take into consideration an influence of any number of objects on the character of the motion of the Moon. References: 1. А. Рой, «Движение по орбитам» (гл.9, М,: Мир, 1981) 2. V. Krasnov, The Papers of Independent Authors, ISSN , Lulu Inc., publ. DNA, volume 37, 2016, ID , ISBN vixra: ; vixra: Александрович. Эфемериды Солнца, Луны г.г.
Resonant Cosmos. Resume. planet's rotation around a central body (star) in the plane of celestial equator and
 V.D. Krasnov Email: apeyron7@yandex.ru Resonant Cosmos (Oscillatory motion and forming of the inclination of the planets' rotation plane) Resume A mechanism of originating and forming of the inclination
V.D. Krasnov Email: apeyron7@yandex.ru Resonant Cosmos (Oscillatory motion and forming of the inclination of the planets' rotation plane) Resume A mechanism of originating and forming of the inclination
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 4 Orbits, Motions, Kepler s and Newton s Laws
 Observational Astronomy - Lecture 4 Orbits, Motions, Kepler s and Newton s Laws Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu February 24, 2014 1 / 21 Tycho Brahe s Equatorial
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 4 Orbits, Motions, Kepler s and Newton s Laws Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu February 24, 2014 1 / 21 Tycho Brahe s Equatorial
Chapter 3 The Cycles of the Moon
 Chapter 3 The Cycles of the Moon Goals: To understand the phases of the moon To understand how the moon affects tides To understand lunar and solar eclipses To learn some of the history associated with
Chapter 3 The Cycles of the Moon Goals: To understand the phases of the moon To understand how the moon affects tides To understand lunar and solar eclipses To learn some of the history associated with
Chapter 3: Cycles of the Sky
 Chapter 3: Cycles of the Sky Motions of the Planets Mercury Venus Earth All planets in almost circular (elliptical) orbits around the sun, in approx. the same plane, the ecliptic plane. The Moon is orbiting
Chapter 3: Cycles of the Sky Motions of the Planets Mercury Venus Earth All planets in almost circular (elliptical) orbits around the sun, in approx. the same plane, the ecliptic plane. The Moon is orbiting
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Origins of Modern Astronomy Earth Science, 13e Chapter 21 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical
Earth Science, 13e Tarbuck & Lutgens Origins of Modern Astronomy Earth Science, 13e Chapter 21 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Early history of astronomy Ancient Greeks Used philosophical
Chapter. Origin of Modern Astronomy
 Chapter Origin of Modern Astronomy 22.1 Early Astronomy Ancient Greeks Astronomy is the science that studies the universe. It includes the observation and interpretation of celestial bodies and phenomena.
Chapter Origin of Modern Astronomy 22.1 Early Astronomy Ancient Greeks Astronomy is the science that studies the universe. It includes the observation and interpretation of celestial bodies and phenomena.
Fundamentals of Satellite technology
 Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Science Level 1. Demonstrate understanding of the effects of astronomical cycles on planet Earth.
 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Science Level 1 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard 90954 Demonstrate understanding of the effects of astronomical cycles on planet
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Science Level 1 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard 90954 Demonstrate understanding of the effects of astronomical cycles on planet
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 5 The Motion of the Earth and Moon Time, Precession, Eclipses, Tides
 Observational Astronomy - Lecture 5 The Motion of the Earth and Moon Time, Precession, Eclipses, Tides Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu March 2, 2014 1 / 29 Geosynchronous
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 5 The Motion of the Earth and Moon Time, Precession, Eclipses, Tides Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu March 2, 2014 1 / 29 Geosynchronous
Earth Science, 11e. Origin of Modern Astronomy Chapter 21. Early history of astronomy. Early history of astronomy. Early history of astronomy
 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 21 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
2006 Pearson Prentice Hall Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 21 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Chapter 3 Cycles of the Moon
 Chapter 3 Cycles of the Moon Guidepost In the previous chapter, you studied the cycle of day and night and the cycle of the seasons. Now you are ready to study the brightest object in the night sky. The
Chapter 3 Cycles of the Moon Guidepost In the previous chapter, you studied the cycle of day and night and the cycle of the seasons. Now you are ready to study the brightest object in the night sky. The
Test 1 Review Chapter 1 Our place in the universe
 Test 1 Review Bring Gator 1 ID card Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the scantrons Formulas will be projected on the screen You can use
Test 1 Review Bring Gator 1 ID card Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the scantrons Formulas will be projected on the screen You can use
Name Period Date Earth and Space Science. Solar System Review
 Name Period Date Earth and Space Science Solar System Review 1. is the spinning a planetary object on its axis. 2. is the backward motion of planets. 3. The is a unit less number between 0 and 1 that describes
Name Period Date Earth and Space Science Solar System Review 1. is the spinning a planetary object on its axis. 2. is the backward motion of planets. 3. The is a unit less number between 0 and 1 that describes
Some remarks concerning solar eclipse data predictions
 Some remarks concerning solar eclipse data predictions Robert Nufer, Switzerland (Robert.Nufer@Bluewin.ch) Computing solar eclipse predictions consists of two main "steps": 1.) Accurate computing of the
Some remarks concerning solar eclipse data predictions Robert Nufer, Switzerland (Robert.Nufer@Bluewin.ch) Computing solar eclipse predictions consists of two main "steps": 1.) Accurate computing of the
THIRD-BODY PERTURBATION USING A SINGLE AVERAGED MODEL
 INPE-1183-PRE/67 THIRD-BODY PERTURBATION USING A SINGLE AVERAGED MODEL Carlos Renato Huaura Solórzano Antonio Fernando Bertachini de Almeida Prado ADVANCES IN SPACE DYNAMICS : CELESTIAL MECHANICS AND ASTRONAUTICS,
INPE-1183-PRE/67 THIRD-BODY PERTURBATION USING A SINGLE AVERAGED MODEL Carlos Renato Huaura Solórzano Antonio Fernando Bertachini de Almeida Prado ADVANCES IN SPACE DYNAMICS : CELESTIAL MECHANICS AND ASTRONAUTICS,
CALCULATION OF POSITION AND VELOCITY OF GLONASS SATELLITE BASED ON ANALYTICAL THEORY OF MOTION
 ARTIFICIAL SATELLITES, Vol. 50, No. 3 2015 DOI: 10.1515/arsa-2015-0008 CALCULATION OF POSITION AND VELOCITY OF GLONASS SATELLITE BASED ON ANALYTICAL THEORY OF MOTION W. Góral, B. Skorupa AGH University
ARTIFICIAL SATELLITES, Vol. 50, No. 3 2015 DOI: 10.1515/arsa-2015-0008 CALCULATION OF POSITION AND VELOCITY OF GLONASS SATELLITE BASED ON ANALYTICAL THEORY OF MOTION W. Góral, B. Skorupa AGH University
Introduction To Modern Astronomy II
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 03 Sep. 18, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy II Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch1: Astronomy and the Universe Ch2: Knowing the Heavens
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 03 Sep. 18, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy II Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch1: Astronomy and the Universe Ch2: Knowing the Heavens
ANNEX 1. DEFINITION OF ORBITAL PARAMETERS AND IMPORTANT CONCEPTS OF CELESTIAL MECHANICS
 ANNEX 1. DEFINITION OF ORBITAL PARAMETERS AND IMPORTANT CONCEPTS OF CELESTIAL MECHANICS A1.1. Kepler s laws Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) discovered the laws of orbital motion, now called Kepler's laws.
ANNEX 1. DEFINITION OF ORBITAL PARAMETERS AND IMPORTANT CONCEPTS OF CELESTIAL MECHANICS A1.1. Kepler s laws Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) discovered the laws of orbital motion, now called Kepler's laws.
Abstract. Solomon I. Khmelnik Unsupported Motion Without Violating the Laws of Physics
 Solomon I. Khmelnik Unsupported Motion Without iolating the Laws of Physics Abstract We are considering some speculative experiments with charges and currents, which demonstrate a breach of Newton's third
Solomon I. Khmelnik Unsupported Motion Without iolating the Laws of Physics Abstract We are considering some speculative experiments with charges and currents, which demonstrate a breach of Newton's third
The History of Astronomy. Please pick up your assigned transmitter.
 The History of Astronomy Please pick up your assigned transmitter. When did mankind first become interested in the science of astronomy? 1. With the advent of modern computer technology (mid-20 th century)
The History of Astronomy Please pick up your assigned transmitter. When did mankind first become interested in the science of astronomy? 1. With the advent of modern computer technology (mid-20 th century)
AST Section 2: Test 1
 AST1002 - Section 2: Test 1 Date: 10/06/2009 Name: Equations: c = λ f, λ peak = Question 1: A star with a declination of +40.0 degrees will be 1. east of the vernal equinox. 2. west of the vernal equinox.
AST1002 - Section 2: Test 1 Date: 10/06/2009 Name: Equations: c = λ f, λ peak = Question 1: A star with a declination of +40.0 degrees will be 1. east of the vernal equinox. 2. west of the vernal equinox.
Exam #1 Covers material from first day of class, all the way through Tides and Nature of Light Supporting reading chapters 1-5 Some questions are
 Exam #1 Covers material from first day of class, all the way through Tides and Nature of Light Supporting reading chapters 1-5 Some questions are concept questions, some involve working with equations,
Exam #1 Covers material from first day of class, all the way through Tides and Nature of Light Supporting reading chapters 1-5 Some questions are concept questions, some involve working with equations,
Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications
 Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications Third Edition David A. Vallado with technical contributions by Wayne D. McClain Space Technology Library Published Jointly by Microcosm Press Hawthorne, CA
Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications Third Edition David A. Vallado with technical contributions by Wayne D. McClain Space Technology Library Published Jointly by Microcosm Press Hawthorne, CA
Space Notes Covers Objectives 1 & 2
 Space Notes Covers Objectives 1 & 2 Space Introduction Space Introduction Video Celestial Bodies Refers to a natural object out in space 1) Stars 2) Comets 3) Moons 4) Planets 5) Asteroids Constellations
Space Notes Covers Objectives 1 & 2 Space Introduction Space Introduction Video Celestial Bodies Refers to a natural object out in space 1) Stars 2) Comets 3) Moons 4) Planets 5) Asteroids Constellations
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. GRAVITY. Chapter 12
 GRAVITY Chapter 12 Units of Chapter 12 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Gravitational Attraction of Spherical Bodies Kepler s Laws of Orbital Motion Gravitational Potential Energy Energy Conservation
GRAVITY Chapter 12 Units of Chapter 12 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Gravitational Attraction of Spherical Bodies Kepler s Laws of Orbital Motion Gravitational Potential Energy Energy Conservation
Basics of Kepler and Newton. Orbits of the planets, moons,
 Basics of Kepler and Newton Orbits of the planets, moons, Kepler s Laws, as derived by Newton. Kepler s Laws Universal Law of Gravity Three Laws of Motion Deriving Kepler s Laws Recall: The Copernican
Basics of Kepler and Newton Orbits of the planets, moons, Kepler s Laws, as derived by Newton. Kepler s Laws Universal Law of Gravity Three Laws of Motion Deriving Kepler s Laws Recall: The Copernican
Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017
 Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017 Finish Ch. 2: Eclipses & Planetary Motion Seasons Angular Size formula Eclipses Planetary Motion Reading: For Today: Finish Chapter 2 For Monday: Start Chapter 3 Homework on
Astr 1050 Mon. Jan. 31, 2017 Finish Ch. 2: Eclipses & Planetary Motion Seasons Angular Size formula Eclipses Planetary Motion Reading: For Today: Finish Chapter 2 For Monday: Start Chapter 3 Homework on
The in-plane Motion of a Geosynchronous Satellite under the Gravitational Attraction of the Sun, the Moon and the Oblate Earth
 J Astrophys Astr (1990) 11, 1 10 The in-plane Motion of a Geosynchronous Satellite under the Gravitational Attraction of the Sun, the Moon and the Oblate Earth Κ Β Bhatnagar Department of Mathematics,
J Astrophys Astr (1990) 11, 1 10 The in-plane Motion of a Geosynchronous Satellite under the Gravitational Attraction of the Sun, the Moon and the Oblate Earth Κ Β Bhatnagar Department of Mathematics,
Astronomy Regents Review
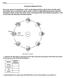 Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
PAP Eighth Grade Science Year-at-a-Glance ARKANSAS STATE SCIENCE STANDARDS
 PAP Eighth Grade Science Year-at-a-Glance ARKANSAS STATE SCIENCE STANDARDS FIRST SEMESTER SECOND SEMESTER Unit 1 Motion Unit 2 Waves Unit 3 Space Unit 4 Genetics 9 weeks 8 weeks 7 weeks 8 weeks 8-PS2-1
PAP Eighth Grade Science Year-at-a-Glance ARKANSAS STATE SCIENCE STANDARDS FIRST SEMESTER SECOND SEMESTER Unit 1 Motion Unit 2 Waves Unit 3 Space Unit 4 Genetics 9 weeks 8 weeks 7 weeks 8 weeks 8-PS2-1
A) M D) The Moon s distance from Earth varies in a cyclic manner.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M 1, M 2, M 3, and M 4 indicate positions of the Moon in its
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows Earth in orbit around the Sun, and the Moon in orbit around Earth. M 1, M 2, M 3, and M 4 indicate positions of the Moon in its
Satellite Communications
 Satellite Communications Lecture (3) Chapter 2.1 1 Gravitational Force Newton s 2nd Law: r r F = m a Newton s Law Of Universal Gravitation (assuming point masses or spheres): Putting these together: r
Satellite Communications Lecture (3) Chapter 2.1 1 Gravitational Force Newton s 2nd Law: r r F = m a Newton s Law Of Universal Gravitation (assuming point masses or spheres): Putting these together: r
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy AST0111-3 (Astronomía) Semester 2014B Prof. Thomas H. Puzia Theme Our Sky 1. Celestial Sphere 2. Diurnal Movement 3. Annual Movement 4. Lunar Movement 5. The Seasons 6. Eclipses
Introduction to Astronomy AST0111-3 (Astronomía) Semester 2014B Prof. Thomas H. Puzia Theme Our Sky 1. Celestial Sphere 2. Diurnal Movement 3. Annual Movement 4. Lunar Movement 5. The Seasons 6. Eclipses
Chapter 12 Gravity. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 12 Gravity Units of Chapter 12 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Gravitational Attraction of Spherical Bodies Kepler s Laws of Orbital Motion Gravitational Potential Energy Energy Conservation
Chapter 12 Gravity Units of Chapter 12 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Gravitational Attraction of Spherical Bodies Kepler s Laws of Orbital Motion Gravitational Potential Energy Energy Conservation
UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES
 UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES Structure 6.1 Introduction Objectives 6.2 References 6.3 Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun and the Concept of the Ecliptic and the Obliquity
UNIT 6 CELESTIAL SPHERE AND EQUINOCTIAL SYSTEM OF COORDINATES Structure 6.1 Introduction Objectives 6.2 References 6.3 Apparent Annual Motion of the Sun and the Concept of the Ecliptic and the Obliquity
Gravity Investigation
 Gravity Investigation Name: Learning Target #14: I am able to use evidence to support the claim that gravitational interactions are attractive and depend on the masses of objects. From acorns to apples,
Gravity Investigation Name: Learning Target #14: I am able to use evidence to support the claim that gravitational interactions are attractive and depend on the masses of objects. From acorns to apples,
7 th Grade Science. Name: Date: Friday, November 4, Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon. Homeroom: Lesson: ESM 14_ Tides Review
 7 th Grade Science Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon Lesson: ESM 14_ Tides Review Name: Date: Friday, November 4, 2016 Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT demonstrate
7 th Grade Science Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon Lesson: ESM 14_ Tides Review Name: Date: Friday, November 4, 2016 Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT demonstrate
Guided Notes Astronomy. Earth s Moon Formation Orbit Craters Motions Phases Tides Eclipses
 Guided Notes Astronomy Earth s Moon Formation Orbit Craters Motions Phases Tides Eclipses K. Coder 2015 1. What is the Moon? The Moon: the Earth's only natural satellite. See ESRT page 15 for data on Earth
Guided Notes Astronomy Earth s Moon Formation Orbit Craters Motions Phases Tides Eclipses K. Coder 2015 1. What is the Moon? The Moon: the Earth's only natural satellite. See ESRT page 15 for data on Earth
1UNIT. The Universe. What do you remember? Key language. Content objectives
 1UNIT The Universe What do you remember? What are the points of light in this photo? What is the difference between a star and a planet? a moon and a comet? Content objectives In this unit, you will Learn
1UNIT The Universe What do you remember? What are the points of light in this photo? What is the difference between a star and a planet? a moon and a comet? Content objectives In this unit, you will Learn
AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology
 AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology L E C T U R E S 8-9 Part B, Lectures 8-9 23 March, 2017 C O N T E N T S In this lecture, we will look at factors that cause an orbit to change over time orbital
AS3010: Introduction to Space Technology L E C T U R E S 8-9 Part B, Lectures 8-9 23 March, 2017 C O N T E N T S In this lecture, we will look at factors that cause an orbit to change over time orbital
Ay 1 Lecture 2. Starting the Exploration
 Ay 1 Lecture 2 Starting the Exploration 2.1 Distances and Scales Some Commonly Used Units Distance: Astronomical unit: the distance from the Earth to the Sun, 1 au = 1.496 10 13 cm ~ 1.5 10 13 cm Light
Ay 1 Lecture 2 Starting the Exploration 2.1 Distances and Scales Some Commonly Used Units Distance: Astronomical unit: the distance from the Earth to the Sun, 1 au = 1.496 10 13 cm ~ 1.5 10 13 cm Light
The Earth-Moon-Sun System. I. Lunar Rotation and Revolution II. Phases of the Moon III. Lunar Eclipses IV. Solar Eclipses
 The Earth-Moon-Sun System I. Lunar Rotation and Revolution II. Phases of the Moon III. Lunar Eclipses IV. Solar Eclipses I. Lunar Rotation and Revolution The Moon rotates on its axis as it circles the
The Earth-Moon-Sun System I. Lunar Rotation and Revolution II. Phases of the Moon III. Lunar Eclipses IV. Solar Eclipses I. Lunar Rotation and Revolution The Moon rotates on its axis as it circles the
Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to. SWBAT explain how the gravity of the moon causes tides in Earth s oceans.
 7 th Grade Science Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon Lesson: ESM 9_ Tides 1 Name: Date: Thursday, October 27, 2016 Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT explain how the
7 th Grade Science Unit: Earth, Sun, and Moon Lesson: ESM 9_ Tides 1 Name: Date: Thursday, October 27, 2016 Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of today s lesson, you will be able to SWBAT explain how the
The Moon s Orbit. Practical and computational project
 The Moon s Orbit. Practical and computational project Ederlinda Viñuales Gavín Grupo de Mecánica Espacial. Universidad de Zaragoza Abstract In this workshop we ll tray to calculate the Moon s orbital elements.
The Moon s Orbit. Practical and computational project Ederlinda Viñuales Gavín Grupo de Mecánica Espacial. Universidad de Zaragoza Abstract In this workshop we ll tray to calculate the Moon s orbital elements.
Ch. 22 Origin of Modern Astronomy Pretest
 Ch. 22 Origin of Modern Astronomy Pretest Ch. 22 Origin of Modern Astronomy Pretest 1. True or False: Early Greek astronomers (600 B.C. A.D. 150) used telescopes to observe the stars. Ch. 22 Origin of
Ch. 22 Origin of Modern Astronomy Pretest Ch. 22 Origin of Modern Astronomy Pretest 1. True or False: Early Greek astronomers (600 B.C. A.D. 150) used telescopes to observe the stars. Ch. 22 Origin of
THE LUNAR LIBRATION: COMPARISONS BETWEEN VARIOUS MODELS- A MODEL FITTED TO LLR OBSERVATIONS
 THE LUNAR LIBRATION: COMPARISONS BETWEEN VARIOUS MODELS- A MODEL FITTED TO LLR OBSERVATIONS J. CHAPRONT, G. FRANCOU SYRTE - Observatoire de Paris - UMR 8630/CNRS 61, avenue de l Observatoire 75014 Paris
THE LUNAR LIBRATION: COMPARISONS BETWEEN VARIOUS MODELS- A MODEL FITTED TO LLR OBSERVATIONS J. CHAPRONT, G. FRANCOU SYRTE - Observatoire de Paris - UMR 8630/CNRS 61, avenue de l Observatoire 75014 Paris
APPLICATIONS OF LAPLACE SPHERICAL FUNCTIONS IN METEOROLOGY. Ion Isaia 1
 PRESENT ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT, VOL. 5, no. 1, 2011 APPLICATIONS OF LAPLACE SPHERICAL FUNCTIONS IN METEOROLOGY Ion Isaia 1 Key words: Laplace spherical functions, tidal potential, tidal
PRESENT ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT, VOL. 5, no. 1, 2011 APPLICATIONS OF LAPLACE SPHERICAL FUNCTIONS IN METEOROLOGY Ion Isaia 1 Key words: Laplace spherical functions, tidal potential, tidal
Trajectories of the planets - impact of parameters on the shape of orbit (Translated from Polish into English by Maksymilian Miklasz)
 Trajectories of the planets - impact of parameters on the shape of orbit (Translated from Polish into English by Maksymilian Miklasz) Abstract: This article contains presentation of mathematical function,
Trajectories of the planets - impact of parameters on the shape of orbit (Translated from Polish into English by Maksymilian Miklasz) Abstract: This article contains presentation of mathematical function,
Satellite meteorology
 GPHS 422 Satellite meteorology GPHS 422 Satellite meteorology Lecture 1 6 July 2012 Course outline 2012 2 Course outline 2012 - continued 10:00 to 12:00 3 Course outline 2012 - continued 4 Some reading
GPHS 422 Satellite meteorology GPHS 422 Satellite meteorology Lecture 1 6 July 2012 Course outline 2012 2 Course outline 2012 - continued 10:00 to 12:00 3 Course outline 2012 - continued 4 Some reading
Lesson 2 - The Copernican Revolution
 Lesson 2 - The Copernican Revolution READING ASSIGNMENT Chapter 2.1: Ancient Astronomy Chapter 2.2: The Geocentric Universe Chapter 2.3: The Heliocentric Model of the Solar System Discovery 2-1: The Foundations
Lesson 2 - The Copernican Revolution READING ASSIGNMENT Chapter 2.1: Ancient Astronomy Chapter 2.2: The Geocentric Universe Chapter 2.3: The Heliocentric Model of the Solar System Discovery 2-1: The Foundations
Astronomy 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 1
 Astronomy 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 1 Chapter 1 1. A scientific hypothesis is a) a wild, baseless guess about how something works. b) a collection of ideas that seems to explain
Astronomy 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 1 Chapter 1 1. A scientific hypothesis is a) a wild, baseless guess about how something works. b) a collection of ideas that seems to explain
Chapter 22 Exam Study Guide
 Chapter 22 Exam Study Guide Name: Hour: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write the letter that best answers the question or completes
Chapter 22 Exam Study Guide Name: Hour: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write the letter that best answers the question or completes
Dynamical properties of the Solar System. Second Kepler s Law. Dynamics of planetary orbits. ν: true anomaly
 First Kepler s Law The secondary body moves in an elliptical orbit, with the primary body at the focus Valid for bound orbits with E < 0 The conservation of the total energy E yields a constant semi-major
First Kepler s Law The secondary body moves in an elliptical orbit, with the primary body at the focus Valid for bound orbits with E < 0 The conservation of the total energy E yields a constant semi-major
is a revolution relative to a fixed celestial position. is the instant of transit of mean equinox relative to a fixed meridian position.
 PERIODICITY FORMULAS: Sidereal Orbit Tropical Year Eclipse Year Anomalistic Year Sidereal Lunar Orbit Lunar Mean Daily Sidereal Motion Lunar Synodical Period Centenial General Precession Longitude (365.25636042
PERIODICITY FORMULAS: Sidereal Orbit Tropical Year Eclipse Year Anomalistic Year Sidereal Lunar Orbit Lunar Mean Daily Sidereal Motion Lunar Synodical Period Centenial General Precession Longitude (365.25636042
Topics for Today s Class. The Phases of the Moon. Why we see Phases of Moon. PHYS 1403 Stars and Galaxies
 PHYS 1403 Stars and Galaxies Topics for Today s Class Chapter 3: Lunar Phases Chapter 3: Lunar Eclipse Chapter 3: Solar Eclipse The Phases of the Moon Why we see Phases of Moon From Earth, we see different
PHYS 1403 Stars and Galaxies Topics for Today s Class Chapter 3: Lunar Phases Chapter 3: Lunar Eclipse Chapter 3: Solar Eclipse The Phases of the Moon Why we see Phases of Moon From Earth, we see different
History. Geocentric model (Ptolemy) Heliocentric model (Aristarchus of Samos)
 Orbital Mechanics History Geocentric model (Ptolemy) Heliocentric model (Aristarchus of Samos) Nicholas Copernicus (1473-1543) In De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium ("On the Revolutions of the Celestial
Orbital Mechanics History Geocentric model (Ptolemy) Heliocentric model (Aristarchus of Samos) Nicholas Copernicus (1473-1543) In De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium ("On the Revolutions of the Celestial
Chapter 12 Gravity. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 12 Gravity Units of Chapter 12 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Gravitational Attraction of Spherical Bodies Kepler s Laws of Orbital Motion Gravitational Potential Energy Energy Conservation
Chapter 12 Gravity Units of Chapter 12 Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Gravitational Attraction of Spherical Bodies Kepler s Laws of Orbital Motion Gravitational Potential Energy Energy Conservation
Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test
 is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
An Introduction to Celestial Mechanics
 An Introduction to Celestial Mechanics This accessible text on classical celestial mechanics the principles governing the motions of bodies in the solar system provides a clear and concise treatment of
An Introduction to Celestial Mechanics This accessible text on classical celestial mechanics the principles governing the motions of bodies in the solar system provides a clear and concise treatment of
Analytical Method for Space Debris propagation under perturbations in the geostationary ring
 Analytical Method for Space Debris propagation under perturbations in the geostationary ring July 21-23, 2016 Berlin, Germany 2nd International Conference and Exhibition on Satellite & Space Missions Daniel
Analytical Method for Space Debris propagation under perturbations in the geostationary ring July 21-23, 2016 Berlin, Germany 2nd International Conference and Exhibition on Satellite & Space Missions Daniel
2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky
 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What are constellations? How do we locate objects in the sky? Why do stars rise and set? Why don t we see the same constellations throughout the year?
2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What are constellations? How do we locate objects in the sky? Why do stars rise and set? Why don t we see the same constellations throughout the year?
Newton s Laws and the Nature of Matter
 Newton s Laws and the Nature of Matter The Nature of Matter Democritus (c. 470-380 BCE) posited that matter was composed of atoms Atoms: particles that can not be further subdivided 4 kinds of atoms: earth,
Newton s Laws and the Nature of Matter The Nature of Matter Democritus (c. 470-380 BCE) posited that matter was composed of atoms Atoms: particles that can not be further subdivided 4 kinds of atoms: earth,
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe
 Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
SHAPE OF ORBITAL PATH
 SHAPE OF ORBITAL PATH According to MATTER (Re-examined) Nainan K. Varghese, matterdoc@gmail.com http://www.matterdoc.info Abstract: In any system of macro bodies, relative considerations can provide only
SHAPE OF ORBITAL PATH According to MATTER (Re-examined) Nainan K. Varghese, matterdoc@gmail.com http://www.matterdoc.info Abstract: In any system of macro bodies, relative considerations can provide only
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky. The sky is divided into 88 unequal areas that we call constellations.
 Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Interface: Planetary Nodes
 1 Interface Planetary Nodes By Michael Erlewine 2 An ebook from Startypes.com 315 Marion Avenue Big Rapids, Michigan 49307 First published 1976 2007 Michael Erlewine ISBN 978-0-9798328-5-7 All rights reserved.
1 Interface Planetary Nodes By Michael Erlewine 2 An ebook from Startypes.com 315 Marion Avenue Big Rapids, Michigan 49307 First published 1976 2007 Michael Erlewine ISBN 978-0-9798328-5-7 All rights reserved.
1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface.
 1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. 2. The graph below shows the change in tide heights of the
1. The diagram below represents Earth and the Moon as viewed from above the North Pole. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on Earth's surface. 2. The graph below shows the change in tide heights of the
Lecture Module 2: Spherical Geometry, Various Axes Systems
 1 Lecture Module 2: Spherical Geometry, Various Axes Systems Satellites in space need inertial frame of reference for attitude determination. In a true sense, all bodies in universe are in motion and inertial
1 Lecture Module 2: Spherical Geometry, Various Axes Systems Satellites in space need inertial frame of reference for attitude determination. In a true sense, all bodies in universe are in motion and inertial
astronomy A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times.
 astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
astronomy 2008 1. A planet was viewed from Earth for several hours. The diagrams below represent the appearance of the planet at four different times. 5. If the distance between the Earth and the Sun were
Milford Public Schools Curriculum
 Milford Public Schools Curriculum Department: SCIENCE Course Name: Grade 8 Course Description Physical Science UNIT 1 - Motion LEARNING GOALS Enduring Understanding(s): Motion is relative to a reference
Milford Public Schools Curriculum Department: SCIENCE Course Name: Grade 8 Course Description Physical Science UNIT 1 - Motion LEARNING GOALS Enduring Understanding(s): Motion is relative to a reference
orbits Moon, Planets Spacecrafts Calculating the and by Dr. Shiu-Sing TONG
 A Science Enrichment Programme for Secondary 3-4 Students : Teaching and Learning Resources the and Spacecrafts orbits Moon, Planets Calculating the 171 of by Dr. Shiu-Sing TONG 172 Calculating the orbits
A Science Enrichment Programme for Secondary 3-4 Students : Teaching and Learning Resources the and Spacecrafts orbits Moon, Planets Calculating the 171 of by Dr. Shiu-Sing TONG 172 Calculating the orbits
Chapter 5 Centripetal Force and Gravity. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 Centripetal Force and Gravity v Centripetal Acceleration v Velocity is a Vector v It has Magnitude and Direction v If either changes, the velocity vector changes. Tumble Buggy Demo v Centripetal
Chapter 5 Centripetal Force and Gravity v Centripetal Acceleration v Velocity is a Vector v It has Magnitude and Direction v If either changes, the velocity vector changes. Tumble Buggy Demo v Centripetal
Unit 2: Celestial Mechanics
 Unit 2: Celestial Mechanics The position of the Earth Ptolemy (90 168 AD) Made tables that allowed a user to locate the position of a planet at any past, present, or future date. In order to maintain circular
Unit 2: Celestial Mechanics The position of the Earth Ptolemy (90 168 AD) Made tables that allowed a user to locate the position of a planet at any past, present, or future date. In order to maintain circular
The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity. Chapter 4 Lecture
 Chapter 4 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding
Chapter 4 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion, Energy, and Gravity 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding
Analysis of Lunisolar Resonances. in an Artificial Satellite Orbits
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol., 008, no., 0 0 Analysis of Lunisolar Resonances in an Artificial Satellite Orbits F. A. Abd El-Salam, Yehia A. Abdel-Aziz,*, M. El-Saftawy, and M. Radwan Cairo university,
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol., 008, no., 0 0 Analysis of Lunisolar Resonances in an Artificial Satellite Orbits F. A. Abd El-Salam, Yehia A. Abdel-Aziz,*, M. El-Saftawy, and M. Radwan Cairo university,
Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 2
 Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 2 Chapter 4 1. The Universal Law of Gravitation says that every particle of matter in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that
Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 2 Chapter 4 1. The Universal Law of Gravitation says that every particle of matter in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that
MOTION IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM ENGAGE, EXPLORE, EXPLAIN
 MOTION IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM ENGAGE, EXPLORE, EXPLAIN ENGAGE THE ATTRACTION TANGO THE ATTRACTION TANGO In your science journal, on the next clean page, title the page with The Attraction Tango. In your group,
MOTION IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM ENGAGE, EXPLORE, EXPLAIN ENGAGE THE ATTRACTION TANGO THE ATTRACTION TANGO In your science journal, on the next clean page, title the page with The Attraction Tango. In your group,
1. The diagram below represents a Foucault pendulum that is swinging back and forth.
 1. The diagram below represents a Foucault pendulum that is swinging back and forth. Which diagram best represents the change in the motion of a Foucault pendulum that provides evidence of Earth's rotation?
1. The diagram below represents a Foucault pendulum that is swinging back and forth. Which diagram best represents the change in the motion of a Foucault pendulum that provides evidence of Earth's rotation?
Chapter 13. Gravitation
 Chapter 13 Gravitation e = c/a A note about eccentricity For a circle c = 0 à e = 0 a Orbit Examples Mercury has the highest eccentricity of any planet (a) e Mercury = 0.21 Halley s comet has an orbit
Chapter 13 Gravitation e = c/a A note about eccentricity For a circle c = 0 à e = 0 a Orbit Examples Mercury has the highest eccentricity of any planet (a) e Mercury = 0.21 Halley s comet has an orbit
ASTRONOMY LECTURE NOTES MIDTERM REVIEW. ASTRONOMY LECTURE NOTES Chapter 1 Charting the Heavens
 ASTRONOMY LECTURE NOTES MIDTERM REVIEW ASTRONOMY LECTURE NOTES Chapter 1 Charting the Heavens How Do We Locate Objects in the Sky? Local-Sky Coordinates versus Celestial-Sphere Coordinates When the sky
ASTRONOMY LECTURE NOTES MIDTERM REVIEW ASTRONOMY LECTURE NOTES Chapter 1 Charting the Heavens How Do We Locate Objects in the Sky? Local-Sky Coordinates versus Celestial-Sphere Coordinates When the sky
Lecture 13. Gravity in the Solar System
 Lecture 13 Gravity in the Solar System Guiding Questions 1. How was the heliocentric model established? What are monumental steps in the history of the heliocentric model? 2. How do Kepler s three laws
Lecture 13 Gravity in the Solar System Guiding Questions 1. How was the heliocentric model established? What are monumental steps in the history of the heliocentric model? 2. How do Kepler s three laws
Copernican revolution Review
 opernican revolution Review Score: 1. How long does it take a planet to orbit the sun exactly once? Sidereal period Synodic period One rotation One day 2. Which of Kepler's laws is illustrated in the diagram?
opernican revolution Review Score: 1. How long does it take a planet to orbit the sun exactly once? Sidereal period Synodic period One rotation One day 2. Which of Kepler's laws is illustrated in the diagram?
Astronomy. Today: Eclipses and the Motion of the Moon. First homework on WebAssign is due Thursday at 11:00pm
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Today: Eclipses and the Motion of the Moon > > > Office hours: MTWR 10-11am First homework on WebAssign is due Thursday at 11:00pm > > > Phases of
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Today: Eclipses and the Motion of the Moon > > > Office hours: MTWR 10-11am First homework on WebAssign is due Thursday at 11:00pm > > > Phases of
Chapter 2: Orbits and Launching Methods
 9/20/ Chapter 2: Orbits and Launching Methods Prepared by Dr. Mohammed Taha El Astal EELE 6335 Telecom. System Part I: Satellite Communic ations Winter Content Kepler s First, Second, and Third Law Definitions
9/20/ Chapter 2: Orbits and Launching Methods Prepared by Dr. Mohammed Taha El Astal EELE 6335 Telecom. System Part I: Satellite Communic ations Winter Content Kepler s First, Second, and Third Law Definitions
CH 8. Universal Gravitation Planetary and Satellite Motion
 CH 8 Universal Gravitation Planetary and Satellite Motion Sir Isaac Newton UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION Newton: Universal Gravitation Newton concluded that earthly objects and heavenly objects obey the same physical
CH 8 Universal Gravitation Planetary and Satellite Motion Sir Isaac Newton UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION Newton: Universal Gravitation Newton concluded that earthly objects and heavenly objects obey the same physical
Key Points: Learn the relationship between gravitational attractive force, mass and distance. Understand that gravity can act as a centripetal force.
 Lesson 9: Universal Gravitation and Circular Motion Key Points: Learn the relationship between gravitational attractive force, mass and distance. Understand that gravity can act as a centripetal force.
Lesson 9: Universal Gravitation and Circular Motion Key Points: Learn the relationship between gravitational attractive force, mass and distance. Understand that gravity can act as a centripetal force.
a. 0.5 AU b. 5 AU c. 50 AU d.* AU e AU
 1 AST104 Sp04: WELCOME TO EXAM 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice. Read all answer choices before making selection. (No credit given when multiple answers are marked.) 1. A galaxy
1 AST104 Sp04: WELCOME TO EXAM 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice. Read all answer choices before making selection. (No credit given when multiple answers are marked.) 1. A galaxy
Intro to Astronomy. Looking at Our Space Neighborhood
 Intro to Astronomy Looking at Our Space Neighborhood Astronomy: The Original Science Ancient cultures used the movement of stars, planets and the moon to mark time Astronomy: the study of the universe
Intro to Astronomy Looking at Our Space Neighborhood Astronomy: The Original Science Ancient cultures used the movement of stars, planets and the moon to mark time Astronomy: the study of the universe
Astronomy 100 Section 2 MWF Greg Hall. Outline. Total Lunar Eclipse Time Lapse. Homework #1 is due Friday, 11:50 a.m.!!!!!
 Astronomy 100 Section 2 MWF 1200-1300 100 Greg Hall Leslie Looney Phone: 217-244-3615 Email: lwl @ uiuc. edu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: MTF 10:30-11:30 a.m. or by appointment Homework #1
Astronomy 100 Section 2 MWF 1200-1300 100 Greg Hall Leslie Looney Phone: 217-244-3615 Email: lwl @ uiuc. edu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: MTF 10:30-11:30 a.m. or by appointment Homework #1
Experimental Analysis of Low Earth Orbit Satellites due to Atmospheric Perturbations
 Experimental Analysis of Low Earth Orbit Satellites due to Atmospheric Perturbations Aman Saluja #1, Manish Bansal #2, M Raja #3, Mohd Maaz #4 #Aerospace Department, University of Petroleum and Energy
Experimental Analysis of Low Earth Orbit Satellites due to Atmospheric Perturbations Aman Saluja #1, Manish Bansal #2, M Raja #3, Mohd Maaz #4 #Aerospace Department, University of Petroleum and Energy
because you asked for it just one more set of MOON REVIEW questions
 because you asked for it just one more set of MOON REVIEW questions 1. The diagram below shows the Moon as it revolves around Earth. The numbered locations represent different positions of the Moon in
because you asked for it just one more set of MOON REVIEW questions 1. The diagram below shows the Moon as it revolves around Earth. The numbered locations represent different positions of the Moon in
Astronomy- The Original Science
 Astronomy- The Original Science Imagine that it is 5,000 years ago. Clocks and modern calendars have not been invented. How would you tell time or know what day it is? One way to tell the time is to study
Astronomy- The Original Science Imagine that it is 5,000 years ago. Clocks and modern calendars have not been invented. How would you tell time or know what day it is? One way to tell the time is to study
Solar System Glossary. The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting
 Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Day, Night & the Seasons. Lecture 2 1/21/2014
 Day, Night & the Seasons Lecture 2 1/21/2014 Logistics The following students see me after class: A. Gonzalez, Chen Anyone who was not here on first day see me after class Pin Numbers - if you have not
Day, Night & the Seasons Lecture 2 1/21/2014 Logistics The following students see me after class: A. Gonzalez, Chen Anyone who was not here on first day see me after class Pin Numbers - if you have not
Tides The Largest Waves in the Ocean
 Tides Tides The Largest Waves in the Ocean Understanding Tides Understanding Tides You will study several topics: Why Earth has tides Why tides vary daily Why tides vary monthly Tide Generation Tide Generation
Tides Tides The Largest Waves in the Ocean Understanding Tides Understanding Tides You will study several topics: Why Earth has tides Why tides vary daily Why tides vary monthly Tide Generation Tide Generation
Chapter 2 Case Studies and Study Guide: Energy Sources of Earth Processes and Disasters
 Chapter 2 Case Studies and Study Guide: Energy Sources of Earth Processes and Disasters Key Concepts The four principal types of energy relevant to natural disasters are kinetic, potential, rotational
Chapter 2 Case Studies and Study Guide: Energy Sources of Earth Processes and Disasters Key Concepts The four principal types of energy relevant to natural disasters are kinetic, potential, rotational
Newton s Gravitational Law
 1 Newton s Gravitational Law Gravity exists because bodies have masses. Newton s Gravitational Law states that the force of attraction between two point masses is directly proportional to the product of
1 Newton s Gravitational Law Gravity exists because bodies have masses. Newton s Gravitational Law states that the force of attraction between two point masses is directly proportional to the product of
The sky and the celestial sphere
 Chapter 1 The sky and the celestial sphere The Sun, and sometimes the Moon are, by and large, the only astronomical objects visible in the day sky. Traditionally, astronomy has been a nocturnal activity.
Chapter 1 The sky and the celestial sphere The Sun, and sometimes the Moon are, by and large, the only astronomical objects visible in the day sky. Traditionally, astronomy has been a nocturnal activity.
Unit 5 Gravitation. Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion
 Unit 5 Gravitation Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion Into to Gravity Phet Simulation Today: Make sure to collect all data. Finished lab due tomorrow!! Universal Law
Unit 5 Gravitation Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion Into to Gravity Phet Simulation Today: Make sure to collect all data. Finished lab due tomorrow!! Universal Law
Astronomy. The Seasons
 Astronomy The Seasons The seasons are caused by the inclination of the Earth s axis: when a hemisphere is tipped toward the Sun, the Sun is more directly above it. At the Summer Solstice the tilt is most
Astronomy The Seasons The seasons are caused by the inclination of the Earth s axis: when a hemisphere is tipped toward the Sun, the Sun is more directly above it. At the Summer Solstice the tilt is most
