The IGM in simulations
|
|
|
- Stuart Bridges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The IGM in simulations Institute for Computational Cosmology Ogden Centre for Fundamental Physics Durham University, UK and University of Antwerp Belgium 1
2 Menu: Simulated DLAs: column density and dynamics The temperature-t relation (redux) 2
3 OWLS project Leiden: Wierma,Van de Voort Chicago HITS ICC-Durham MPE /IAC 3 ICC
4 Star formation Subgrid physics in OWLS Galactic winds AGN feedback Z+J(nu) dependent cooling Stellar evolution 4
5 Track 11 elements that dominate cooling/heating for in photo-ionisation equilibrium with optically thin UV-X-ray background 5
6 Subgrid: the star formation implementation Schaye & Dalla Vecchia, 08 d? dt = f(,t,z,h 2,...) d? dt d / 3/2 But code s density is averaged 6 on kilo-parsecs scales!
7 Subgrid: the star formation implementation (and the origin of the Kennicutt-Schmidt law) Σ SFR Σ n gas (n =1.4 ± 0.15) Local: same galaxy Global: different galaxies Calzetti et al Kennicutt 98
8 Star formation guarantees the simulated galaxies follow the imposed Kennicutt-Schmidt law Schaye 04
9 Subgrid: stellar evolution Assume: stellar initial initial mass function (Chabrier) Assume: stellar lifetimes Assume: luminosities (BC models) Assume: stellar yields Type I SNe Type II SNe AGB stars Few+12, Tornatore+07,Oppenheimer +06,Kawata+13,Scannapieco+09 9
10 Subgrid: SN feedback Supernova feedback expels gas out of galaxy/halo Dark halos (const M/L) galaxies GIMIC simulation 10 Crain+09
11 Galactic winds: stochastic kinetic feedback, no hydrodecoupling, no switching off of cooling At high z: Pettini et al 02 11
12 Z=2 reference model solar mass halo 12
13 Subgrid variations 13
14 Post-processing OWLS for self-shielding to identify DLAs: ray-tracing 14
15 Optically thick gas has tiny cross section. Ray-tracing inefficient 15
16 reverse-ray tracing: start from high density regions: good! Urchin Random sight lines will almost always miss high-density region: bad! Impose optically thin ionising 16 background
17 Urchin can take into account full spectral information. Since know optical depth, can switch from case-a to case-b recombination rate neutral fraction Different spectral shapes depth into 17 slice [kpc]
18 Urchin tests Analytical profile Urchin profile OWLS gas mass HI density total density Ray-tracing spherically-symmetric 18 (stacked) OWLS Tom haloes Theuns
19 Through Thick and Thin - Hi Absorption in Cosmological Simulations Gabriel Altay 1, 1,2, Joop Schaye 3, Neil H. M. Crighton 4,5 and Claudio Dalla Vecchia 3,6 Urchin 8 SPHRAY: A Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Ray Tracer for Radiative Transfer Gabriel Altay 1, Rupert A.C. Croft 1, and Inti Pelupessy 1 1 Carnegie Mellon University, Department of Physics, 5000 Forbes Avenue, Pittsburgh PA 15213, USA 19
20 Column-density distribution function co-moving number density of lines owls + urchin log HI column density 20
21 owls = hydrodynamical simulation (Schaye 2010)! urchin = reverse ray-tracer (Altay & TT, 2013) 21
22 22
23 DLAs 23
24 Dependence on physics/numerics (self-shielding, H2 formation, UV-bckg, ) ( ) - LLS and DLA range. In the left panel, we vary the amplitude of the UV ba 24
25 log ratio compared to Ref ISM log HI column 25
26 Outliers Millennium no reionisation no feedback other IMF AGN 26
27 LLS Incidence DLAs 27 cosmology
28 Menu: Simulated DLAs: column density and dynamics The temperature-t relation (redux) 28
29 Rob Perry DLA line widths small DLA big DLA 29
30 Sample DLA - but without the damping wing (!) Si abundance - from simulation SiII/Si = HI/H from Urchin 30
31 31
32 zoomed-in Si2 column density contours 32
33 w i d e l i n e s: velocity structure narrow lines: temperature 33
34 V90 statistics Neeleman (100 DLAs) Owls (1+2 sigma) 34
35 Si II components vs subfind TM structures typical unusual 35
36 Dissected cumulatively in FoF mass 36
37 ratio v90 compared to REF no feedback Millennium no reionisation V90 [km s -1 ] 37
38 Problem? 38
39 Sample DLA - but without the damping wing (!) Si abundance - from simulation SiII/Si = HI/H from Urchin 39
40 Maximum Si II extent ( v100 ) 40
41 Menu: WDM and satellites (to follow Lya WDM) Lya flux PDF (and inverted rho-t relation) Galactic winds Simulated DLAs and LLSs The rho-t relation (redux) 41
42 log temperature log density 42
43 OWLS temperature-density relation 43
44 Line-width Column density 44 b-n from Tom VPfit Theuns
45 1.even narrow lines are broader than (T/m) 1/2 2.what are broader lines: errors? 3.what are narrower lines: errors? metals? Antonella Garzilli thermal broadening 45
46 Don t use VPfit: single max is single absorber (no noise!) 46
47 transmission optical depth Temperature velocity [km s -1 ] 47
48 Use curvature of spectrum to obtain temperature Antonella Garzilli Obtain density from integrating optical depth over the line 48
49 T=100K: still lines have width. Jeans smoothing 49
50 Percentiles Thermal broadening + Jeans smoothing 50
51 ?? 51 line clustering
52 Summary 52
How feedback shapes the galaxy stellar mass function
 How feedback shapes the galaxy stellar mass function Eagle, owls and other Gimics Institute for Computational Cosmology Ogden Centre for Fundamental Physics Durham University, UK and University of Antwerp
How feedback shapes the galaxy stellar mass function Eagle, owls and other Gimics Institute for Computational Cosmology Ogden Centre for Fundamental Physics Durham University, UK and University of Antwerp
Joop Schaye (Leiden) (Yope Shea)
 Overview of sub-grid models in cosmological simulations Joop Schaye (Leiden) (Yope Shea) Length Scales (cm) Subgrid models Cosmological simulations 8 0 2 11 18 20 22 24 28 interparticle distance in stars
Overview of sub-grid models in cosmological simulations Joop Schaye (Leiden) (Yope Shea) Length Scales (cm) Subgrid models Cosmological simulations 8 0 2 11 18 20 22 24 28 interparticle distance in stars
Towards Understanding Simulations of Galaxy Formation. Nigel Mitchell. On the Origin of Cores in Simulated Galaxy Clusters
 Towards Understanding Simulations of Galaxy Formation Nigel Mitchell On the Origin of Cores in Simulated Galaxy Clusters Work published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomy Society Journal, 2009,
Towards Understanding Simulations of Galaxy Formation Nigel Mitchell On the Origin of Cores in Simulated Galaxy Clusters Work published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomy Society Journal, 2009,
Hunting for dark matter in the forest (astrophysical constraints on warm dark matter)
 Hunting for dark matter in the forest (astrophysical constraints on warm dark matter) ICC, Durham! with the Eagle collaboration: J Schaye (Leiden), R Crain (Liverpool), R Bower, C Frenk, & M Schaller (ICC)
Hunting for dark matter in the forest (astrophysical constraints on warm dark matter) ICC, Durham! with the Eagle collaboration: J Schaye (Leiden), R Crain (Liverpool), R Bower, C Frenk, & M Schaller (ICC)
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 26 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 26 Sep 2013 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 26 Sep 2013](/thumbs/96/127253459.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 20 (201?) Printed 24 September 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:1307.6879v2 [astro-ph.co] 26 Sep 2013 The impact of different physical processes on the statistics
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 20 (201?) Printed 24 September 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:1307.6879v2 [astro-ph.co] 26 Sep 2013 The impact of different physical processes on the statistics
Reverse Ray-Tracing in Urchin
 Reverse Ray-Tracing in Urchin Cosmological Radiative Transfer Comparison Project December - 2012 Gabriel Altay Tom Theuns, Joop Schaye Motivation Galaxy Formation in HI Hydrogen Revolution - I Westerbork
Reverse Ray-Tracing in Urchin Cosmological Radiative Transfer Comparison Project December - 2012 Gabriel Altay Tom Theuns, Joop Schaye Motivation Galaxy Formation in HI Hydrogen Revolution - I Westerbork
The Physical Properties of Low-z OVI Absorbers in the OverWhelmingly Large Simulations
 The Physical Properties of Low-z OVI Absorbers in the OverWhelmingly Large Simulations Thorsten Tepper García in collaboration with: Philipp Richter (Universität Potsdam) Joop Schaye (Sterrewacht Leiden)
The Physical Properties of Low-z OVI Absorbers in the OverWhelmingly Large Simulations Thorsten Tepper García in collaboration with: Philipp Richter (Universität Potsdam) Joop Schaye (Sterrewacht Leiden)
Superbubble Feedback in Galaxy Formation
 Superbubble Feedback in Galaxy Formation Ben Keller (McMaster University) James Wadsley, Samantha Benincasa, Hugh Couchman Paper: astro-ph/1405.2625 (Accepted MNRAS) Keller, Wadsley, Benincasa & Couchman
Superbubble Feedback in Galaxy Formation Ben Keller (McMaster University) James Wadsley, Samantha Benincasa, Hugh Couchman Paper: astro-ph/1405.2625 (Accepted MNRAS) Keller, Wadsley, Benincasa & Couchman
The distribution of neutral hydrogen around high-redshift galaxies and quasars in the EAGLE simulation
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1414 The distribution of neutral hydrogen around high-redshift galaxies and quasars in the EAGLE simulation Alireza Rahmati, 1,2 Joop Schaye, 3 Richard G. Bower, 4 Robert A. Crain,
doi:10.1093/mnras/stv1414 The distribution of neutral hydrogen around high-redshift galaxies and quasars in the EAGLE simulation Alireza Rahmati, 1,2 Joop Schaye, 3 Richard G. Bower, 4 Robert A. Crain,
High Redshift Universe
 High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau
 Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Black Hole Feedback. What is it? What does it do? Richard Bower Durham University
 Black Hole Feedback What is it? What does it do? GALFORM: RGB + Benson, Lagos, Fanidakis, Frenk, Lacey, Baugh & Cole +++ EAGLE: Booth, Dalla Vecchia, Crain, Furlong, Rosas- Guevara, Schaye, RGB, Theuns,
Black Hole Feedback What is it? What does it do? GALFORM: RGB + Benson, Lagos, Fanidakis, Frenk, Lacey, Baugh & Cole +++ EAGLE: Booth, Dalla Vecchia, Crain, Furlong, Rosas- Guevara, Schaye, RGB, Theuns,
Feedback and Galaxy Formation
 Heating and Cooling in Galaxies and Clusters Garching August 2006 Feedback and Galaxy Formation Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Cluster assembly in ΛCDM Gao et al 2004 'Concordance'
Heating and Cooling in Galaxies and Clusters Garching August 2006 Feedback and Galaxy Formation Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Cluster assembly in ΛCDM Gao et al 2004 'Concordance'
The enrichment history of cosmic metals
 CHAPTER 5 The enrichment history of cosmic metals Robert P. C. Wiersma, Joop Schaye, Claudio Dalla Vecchia, C. M. Booth, Tom Theuns, and Anthony Aguirre Accepted for publication in the Monthly Notices
CHAPTER 5 The enrichment history of cosmic metals Robert P. C. Wiersma, Joop Schaye, Claudio Dalla Vecchia, C. M. Booth, Tom Theuns, and Anthony Aguirre Accepted for publication in the Monthly Notices
The drop in the cosmic star formation rate below redshift 2 is caused by a change in the mode of gas accretion and by active galactic nucleus feedback
 3 The drop in the cosmic star formation rate below redshift 2 is caused by a change in the mode of gas accretion and by active galactic nucleus feedback The cosmic star formation rate is observed to drop
3 The drop in the cosmic star formation rate below redshift 2 is caused by a change in the mode of gas accretion and by active galactic nucleus feedback The cosmic star formation rate is observed to drop
Modelling star formation in galaxy formation simulations
 Modelling star formation in galaxy formation simulations Vadim Semenov (U.Chicago) Andrey Kravtsov University of Chicago Carving through the codes Davos, Switzerland 16 February, 2017 Nick Gnedin (Fermilab)
Modelling star formation in galaxy formation simulations Vadim Semenov (U.Chicago) Andrey Kravtsov University of Chicago Carving through the codes Davos, Switzerland 16 February, 2017 Nick Gnedin (Fermilab)
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation! Star Formation Efficiency!
 Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Simulations* in the radio waves regime for ASKAP *of galaxy formation. Claudia Lagos (ARC DECRA fellow) on behalf of ICRAR-theory group
 Simulations* in the radio waves regime for ASKAP *of galaxy formation Claudia Lagos (ARC DECRA fellow) on behalf of ICRAR-theory group Theory/computing group at ICRAR Preparing the theory for ASKAP...
Simulations* in the radio waves regime for ASKAP *of galaxy formation Claudia Lagos (ARC DECRA fellow) on behalf of ICRAR-theory group Theory/computing group at ICRAR Preparing the theory for ASKAP...
TRAPHIC TRAnsport of PHotons In Cones
 Cosmological RadiaCve Transfer Code Comparison Project IV AusCn, Dec. 2012 TRAPHIC TRAnsport of PHotons In Cones Current TRAPHIC team: Joop Schaye (Leiden) Ali RahmaC (Leiden) Milan Raicevic (Leiden) Myoungwon
Cosmological RadiaCve Transfer Code Comparison Project IV AusCn, Dec. 2012 TRAPHIC TRAnsport of PHotons In Cones Current TRAPHIC team: Joop Schaye (Leiden) Ali RahmaC (Leiden) Milan Raicevic (Leiden) Myoungwon
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 15 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 15 Dec 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 15 Dec 2008](/thumbs/84/91023869.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 5 () Printed 8 May 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Photo-heating and supernova feedback amplify each other s effect on the cosmic star formation rate arxiv:0812.2913v1
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 5 () Printed 8 May 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Photo-heating and supernova feedback amplify each other s effect on the cosmic star formation rate arxiv:0812.2913v1
The Iguaçu Lectures. Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures
 April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
Rupert Croft. QuickTime and a decompressor are needed to see this picture.
 Rupert Croft QuickTime and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. yesterday: Plan for lecture 1: History : -the first quasar spectra -first theoretical models (all wrong) -CDM cosmology meets the
Rupert Croft QuickTime and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. yesterday: Plan for lecture 1: History : -the first quasar spectra -first theoretical models (all wrong) -CDM cosmology meets the
Intergalactic Medium and Lyman-Alpha / Metal Absorbers
 Intergalactic Medium and Lyman-Alpha / Metal Absorbers Image credit: Tom Abel & Ralf Kaehler (Stanford) Ji-hoon Kim (TAPIR)! Slides provided by: Phil Hopkins and Ji-hoon Kim Today s Agenda What are there
Intergalactic Medium and Lyman-Alpha / Metal Absorbers Image credit: Tom Abel & Ralf Kaehler (Stanford) Ji-hoon Kim (TAPIR)! Slides provided by: Phil Hopkins and Ji-hoon Kim Today s Agenda What are there
Cold Clouds in Cool Cores
 Becky Canning NGC 1275, Perseus Cluster Cold Clouds in Cool Cores 1 Snowcluster 2015 Cold Clouds in Cool Cores Excitation mechanisms of the multi-phase cool/cold gas Why should we care? Heard that X-ray
Becky Canning NGC 1275, Perseus Cluster Cold Clouds in Cool Cores 1 Snowcluster 2015 Cold Clouds in Cool Cores Excitation mechanisms of the multi-phase cool/cold gas Why should we care? Heard that X-ray
Age-redshift relation. The time since the big bang depends on the cosmological parameters.
 Age-redshift relation The time since the big bang depends on the cosmological parameters. Lyman Break Galaxies High redshift galaxies are red or absent in blue filters because of attenuation from the neutral
Age-redshift relation The time since the big bang depends on the cosmological parameters. Lyman Break Galaxies High redshift galaxies are red or absent in blue filters because of attenuation from the neutral
Comparing l-galaxies, galform and eagle
 V. Gonzalez-Perez /9 Comparing l-galaxies, galform and eagle Violeta Gonzalez-Perez @violegp Quan Guo (Postdam), Qi Guo (Beijing), Matthieu Schaller (Durham), Michelle Furlong (Durham), Richard Bower (Durham),
V. Gonzalez-Perez /9 Comparing l-galaxies, galform and eagle Violeta Gonzalez-Perez @violegp Quan Guo (Postdam), Qi Guo (Beijing), Matthieu Schaller (Durham), Michelle Furlong (Durham), Richard Bower (Durham),
Coupling small and large scales: how massive and dying stars drive the formation of a galaxy
 Coupling small and large scales: how massive and dying stars drive the formation of a galaxy P. Monaco, Trieste University and INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste Micro-physics of star formation and
Coupling small and large scales: how massive and dying stars drive the formation of a galaxy P. Monaco, Trieste University and INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste Micro-physics of star formation and
Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges
 Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
Lecture 11: Ages and Metalicities from Observations A Quick Review
 Lecture 11: Ages and Metalicities from Observations A Quick Review Ages from main-sequence turn-off stars Main sequence lifetime: lifetime = fuel / burning rate $ M " MS = 7 #10 9 % & M $ L " MS = 7 #10
Lecture 11: Ages and Metalicities from Observations A Quick Review Ages from main-sequence turn-off stars Main sequence lifetime: lifetime = fuel / burning rate $ M " MS = 7 #10 9 % & M $ L " MS = 7 #10
On the relation between the Schmidt and Kennicutt-Schmidt star formation laws
 On the relation between the Schmidt and Kennicutt-Schmidt star formation laws Claudio Dalla Vecchia Leiden Observatory / Sterrewacht Leiden < Schaye & Dalla Vecchia 2007 - astro-ph 0709.0292 > Observed
On the relation between the Schmidt and Kennicutt-Schmidt star formation laws Claudio Dalla Vecchia Leiden Observatory / Sterrewacht Leiden < Schaye & Dalla Vecchia 2007 - astro-ph 0709.0292 > Observed
THE ROLE OF RADIATION PRESSURE IN HIGH-Z DWARF GALAXIES
 THE ROLE OF RADIATION PRESSURE IN HIGH-Z DWARF GALAXIES John Wise (Georgia Tech) Tom Abel (Stanford), Michael Norman (UC San Diego), Britton Smith (Michigan State), Matthew Turk (Columbia) 14 Dec 2012
THE ROLE OF RADIATION PRESSURE IN HIGH-Z DWARF GALAXIES John Wise (Georgia Tech) Tom Abel (Stanford), Michael Norman (UC San Diego), Britton Smith (Michigan State), Matthew Turk (Columbia) 14 Dec 2012
Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ M gas / dyn. Log SFR. Kennicutt Log. gas / dyn
 Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ 0.017 M gas / dyn Log SFR Kennicutt 1998 Log gas / dyn Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Moster 2009 No Feedback 10% of baryons Log(
Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ 0.017 M gas / dyn Log SFR Kennicutt 1998 Log gas / dyn Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Moster 2009 No Feedback 10% of baryons Log(
The Intergalactic Medium: Overview and Selected Aspects
 The Intergalactic Medium: Overview and Selected Aspects Draft Version Tristan Dederichs June 18, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 The IGM at high redshifts (z > 5) 2 2.1 Early Universe and Reionization......................................
The Intergalactic Medium: Overview and Selected Aspects Draft Version Tristan Dederichs June 18, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 The IGM at high redshifts (z > 5) 2 2.1 Early Universe and Reionization......................................
Physical properties of simulated galaxies from varying input physics
 2 Physical properties of simulated galaxies from varying input physics Abstract We investigate the baryonic properties, such as stellar mass, (specific) star formation rate, gas consumption time scale,
2 Physical properties of simulated galaxies from varying input physics Abstract We investigate the baryonic properties, such as stellar mass, (specific) star formation rate, gas consumption time scale,
Abundance Constraints on Early Chemical Evolution. Jim Truran
 Abundance Constraints on Early Chemical Evolution Jim Truran Astronomy and Astrophysics Enrico Fermi Institute University of Chicago Argonne National Laboratory MLC Workshop Probing Early Structure with
Abundance Constraints on Early Chemical Evolution Jim Truran Astronomy and Astrophysics Enrico Fermi Institute University of Chicago Argonne National Laboratory MLC Workshop Probing Early Structure with
Diffuse Interstellar Medium
 Diffuse Interstellar Medium Basics, velocity widths H I 21-cm radiation (emission) Interstellar absorption lines Radiative transfer Resolved Lines, column densities Unresolved lines, curve of growth Abundances,
Diffuse Interstellar Medium Basics, velocity widths H I 21-cm radiation (emission) Interstellar absorption lines Radiative transfer Resolved Lines, column densities Unresolved lines, curve of growth Abundances,
Physics and Chemistry of the Interstellar Medium
 Physics and Chemistry of the Interstellar Medium Sun Kwok The University of Hong Kong UNIVERSITY SCIENCE BOOKS Sausalito, California * Preface xi The Interstellar Medium.1.1 States of Matter in the ISM
Physics and Chemistry of the Interstellar Medium Sun Kwok The University of Hong Kong UNIVERSITY SCIENCE BOOKS Sausalito, California * Preface xi The Interstellar Medium.1.1 States of Matter in the ISM
high density low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) Springel (2010)
 GAS MIXES high density Springel (2010) low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) HOT HALO highest resolved density nth= 50x10
GAS MIXES high density Springel (2010) low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) HOT HALO highest resolved density nth= 50x10
Interstellar Medium and Star Birth
 Interstellar Medium and Star Birth Interstellar dust Lagoon nebula: dust + gas Interstellar Dust Extinction and scattering responsible for localized patches of darkness (dark clouds), as well as widespread
Interstellar Medium and Star Birth Interstellar dust Lagoon nebula: dust + gas Interstellar Dust Extinction and scattering responsible for localized patches of darkness (dark clouds), as well as widespread
Lecture 11: Ages and Metalicities from Observations. A Quick Review. Multiple Ages of stars in Omega Cen. Star Formation History.
 Ages from main-sequence turn-off stars Lecture 11: Main sequence lifetime: Ages and Metalicities from Observations R diagram lifetime = fuel / burning rate MV *1 M ' L ' MS = 7 10 9 ) ) M. ( L. ( A Quick
Ages from main-sequence turn-off stars Lecture 11: Main sequence lifetime: Ages and Metalicities from Observations R diagram lifetime = fuel / burning rate MV *1 M ' L ' MS = 7 10 9 ) ) M. ( L. ( A Quick
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Implementing sub-grid treatments of galactic outflows into cosmological simulations. Hugo Martel Université Laval
 Implementing sub-grid treatments of galactic outflows into cosmological simulations Hugo Martel Université Laval Leiden, June 19, 2013 GALACTIC OUTFLOWS Optical image of galaxy (Hubble Space Telescope)
Implementing sub-grid treatments of galactic outflows into cosmological simulations Hugo Martel Université Laval Leiden, June 19, 2013 GALACTIC OUTFLOWS Optical image of galaxy (Hubble Space Telescope)
Gas 1: Molecular clouds
 Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
The X-ray absorption in GRB afterglows
 The X-ray absorption in GRB afterglows Darach Watson DARK Cosmology Centre Niels Bohr Institute University of Copenhagen Overview Downturn at low energies deviating from a power-law Very similar to photoelectric
The X-ray absorption in GRB afterglows Darach Watson DARK Cosmology Centre Niels Bohr Institute University of Copenhagen Overview Downturn at low energies deviating from a power-law Very similar to photoelectric
Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem. Presented by: Michael Solway
 Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem Presented by: Michael Solway Papers 1. Vitvitska, M. et al. 2002, The origin of angular momentum in dark matter halos, ApJ 581: 799-809 2. D Onghia, E. 2008,
Disk Formation and the Angular Momentum Problem Presented by: Michael Solway Papers 1. Vitvitska, M. et al. 2002, The origin of angular momentum in dark matter halos, ApJ 581: 799-809 2. D Onghia, E. 2008,
Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation. Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan)
 Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) In current simulations, galaxies look like this: 10 kpc Disk galaxy at z=3: stars, molecular gas, atomic gas (Zemp,
Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) In current simulations, galaxies look like this: 10 kpc Disk galaxy at z=3: stars, molecular gas, atomic gas (Zemp,
Properties of gas in and around galaxy haloes
 4 Properties of gas in and around galaxy haloes We study the properties of gas inside and around galaxy haloes as a function of radius and halo mass, focusing mostly on z = 2, but also showing some results
4 Properties of gas in and around galaxy haloes We study the properties of gas inside and around galaxy haloes as a function of radius and halo mass, focusing mostly on z = 2, but also showing some results
Galaxy Formation: Overview
 Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Dust [12.1] Star clusters. Absorb and scatter light Effect strongest in blue, less in red, zero in radio.
![Dust [12.1] Star clusters. Absorb and scatter light Effect strongest in blue, less in red, zero in radio. Dust [12.1] Star clusters. Absorb and scatter light Effect strongest in blue, less in red, zero in radio.](/thumbs/94/121056697.jpg) More abs. Dust [1.1] kev V Wavelength Optical Infra-red More abs. Wilms et al. 000, ApJ, 54, 914 No grains Grains from http://www.astro.princeton.edu/~draine/dust/dustmix.html See DraineH 003a, column
More abs. Dust [1.1] kev V Wavelength Optical Infra-red More abs. Wilms et al. 000, ApJ, 54, 914 No grains Grains from http://www.astro.princeton.edu/~draine/dust/dustmix.html See DraineH 003a, column
Visible Matter. References: Ryden, Introduction to Cosmology - Par. 8.1 Liddle, Introduction to Modern Cosmology - Par. 9.1
 COSMOLOGY PHYS 30392 DENSITY OF THE UNIVERSE Part I Giampaolo Pisano - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics The University of Manchester - March 2013 http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~gp/ giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk
COSMOLOGY PHYS 30392 DENSITY OF THE UNIVERSE Part I Giampaolo Pisano - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics The University of Manchester - March 2013 http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~gp/ giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk
Dust. The four letter word in astrophysics. Interstellar Emission
 Dust The four letter word in astrophysics Interstellar Emission Why Dust Dust attenuates and scatters UV/optical/NIR Amount of attenuation and spectral shape depends on dust properties (grain size/type)
Dust The four letter word in astrophysics Interstellar Emission Why Dust Dust attenuates and scatters UV/optical/NIR Amount of attenuation and spectral shape depends on dust properties (grain size/type)
The Hot Gaseous Halos of Spiral Galaxies. Joel Bregman, Matthew Miller, Edmund Hodges Kluck, Michael Anderson, XinyuDai
 The Hot Gaseous Halos of Spiral Galaxies Joel Bregman, Matthew Miller, Edmund Hodges Kluck, Michael Anderson, XinyuDai Hot Galaxy Halos and Missing Baryons Dai et al. (2010) Rich clusters have nearly all
The Hot Gaseous Halos of Spiral Galaxies Joel Bregman, Matthew Miller, Edmund Hodges Kluck, Michael Anderson, XinyuDai Hot Galaxy Halos and Missing Baryons Dai et al. (2010) Rich clusters have nearly all
THE GALACTIC CORONA. In honor of. Jerry Ostriker. on his 80 th birthday. Chris McKee Princeton 5/13/2017. with Yakov Faerman Amiel Sternberg
 THE GALACTIC CORONA In honor of Jerry Ostriker on his 80 th birthday Chris McKee Princeton 5/13/2017 with Yakov Faerman Amiel Sternberg A collaboration that began over 40 years ago and resulted in a lifelong
THE GALACTIC CORONA In honor of Jerry Ostriker on his 80 th birthday Chris McKee Princeton 5/13/2017 with Yakov Faerman Amiel Sternberg A collaboration that began over 40 years ago and resulted in a lifelong
Swift: task-based hydrodynamics at Durham s IPCC. Bower
 Swift: task-based hydrodynamics at Durham s IPCC Gonnet Schaller Chalk movie: Richard Bower (Durham) For the cosmological simulations of the formation of galaxies Bower Institute for Computational Cosmology
Swift: task-based hydrodynamics at Durham s IPCC Gonnet Schaller Chalk movie: Richard Bower (Durham) For the cosmological simulations of the formation of galaxies Bower Institute for Computational Cosmology
Star Formation Indicators
 Star Formation Indicators Calzetti 2007 astro-ph/0707.0467 Brinchmann et al. 2004 MNRAS 351, 1151 SFR indicators in general! SFR indicators are defined from the X ray to the radio! All probe the MASSIVE
Star Formation Indicators Calzetti 2007 astro-ph/0707.0467 Brinchmann et al. 2004 MNRAS 351, 1151 SFR indicators in general! SFR indicators are defined from the X ray to the radio! All probe the MASSIVE
What Doesn t Quench Galaxy Formation?
 What Doesn t Quench Galaxy Formation? Phil Hopkins Dusan Keres, Claude Faucher-Giguere, Jose Onorbe, Freeke van de Voort, Sasha Muratov, Xiangcheng Ma, Lena Murchikova, Norm Murray, Eliot Quataert, James
What Doesn t Quench Galaxy Formation? Phil Hopkins Dusan Keres, Claude Faucher-Giguere, Jose Onorbe, Freeke van de Voort, Sasha Muratov, Xiangcheng Ma, Lena Murchikova, Norm Murray, Eliot Quataert, James
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Oct 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Oct 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 2 Oct 2014](/thumbs/75/72077021.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 3 October 2014 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The EAGLE project: Simulating the evolution and assembly of galaxies and their environments arxiv:1407.7040v2
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 3 October 2014 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The EAGLE project: Simulating the evolution and assembly of galaxies and their environments arxiv:1407.7040v2
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21949 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Rahmati, Alireza Title: Simulating the cosmic distribution of neutral hydrogen
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21949 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Rahmati, Alireza Title: Simulating the cosmic distribution of neutral hydrogen
Quasar Absorption Lines
 Tracing the Cosmic Web with Diffuse Gas DARK MATTER GAS STARS NEUTRAL HYDROGEN Quasar Absorption Lines use quasars as bright beacons for probing intervening gaseous material can study both galaxies and
Tracing the Cosmic Web with Diffuse Gas DARK MATTER GAS STARS NEUTRAL HYDROGEN Quasar Absorption Lines use quasars as bright beacons for probing intervening gaseous material can study both galaxies and
Lya as a Probe of the (High-z) Universe
 Lya as a Probe of the (High-z) Universe Mark Dijkstra (CfA) Main Collaborators: Adam Lidz, Avi Loeb (CfA) Stuart Wyithe (Melbourne), Zoltan Haiman (Columbia) Lya as a Probe of the (High-z) Universe Outline
Lya as a Probe of the (High-z) Universe Mark Dijkstra (CfA) Main Collaborators: Adam Lidz, Avi Loeb (CfA) Stuart Wyithe (Melbourne), Zoltan Haiman (Columbia) Lya as a Probe of the (High-z) Universe Outline
Soft X-ray and ultraviolet metal-line emission from the gas around galaxies
 MNRAS 430, 2688 2702 (2013) doi:10.1093/mnras/stt115 Soft X-ray and ultraviolet metal-line emission from the gas around galaxies Freeke van de Voort and Joop Schaye Leiden Observatory, Leiden University,
MNRAS 430, 2688 2702 (2013) doi:10.1093/mnras/stt115 Soft X-ray and ultraviolet metal-line emission from the gas around galaxies Freeke van de Voort and Joop Schaye Leiden Observatory, Leiden University,
Modelling the galaxy population
 Modelling the galaxy population Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik IAU 277 Ouagadougou 1 The standard model reproduces -- the linear initial conditions -- IGM structure during galaxy formation
Modelling the galaxy population Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik IAU 277 Ouagadougou 1 The standard model reproduces -- the linear initial conditions -- IGM structure during galaxy formation
The X-ray absorption in GRB afterglows
 The X-ray absorption in GRB afterglows Darach Watson DARK Cosmology Centre Niels Bohr Institute University of Copenhagen Overview Downturn at low energies deviating from a power-law Very similar to photoelectric
The X-ray absorption in GRB afterglows Darach Watson DARK Cosmology Centre Niels Bohr Institute University of Copenhagen Overview Downturn at low energies deviating from a power-law Very similar to photoelectric
X-ray ionization of the intergalactic medium by quasars
 X-ray ionization of the intergalactic medium by quasars Luca Graziani In collaboration with: CRASH4 IGM reionisation by QSOs GAMESH, QSOs evolution & QSOs impact on SF B. Ciardi (MPA, Munich) A. Ferrara
X-ray ionization of the intergalactic medium by quasars Luca Graziani In collaboration with: CRASH4 IGM reionisation by QSOs GAMESH, QSOs evolution & QSOs impact on SF B. Ciardi (MPA, Munich) A. Ferrara
Astr 5465 March 6, 2018 Abundances in Late-type Galaxies Spectra of HII Regions Offer a High-Precision Means for Measuring Abundance (of Gas)
 Astr 5465 March 6, 2018 Abundances in Late-type Galaxies Spectra of HII Regions Offer a High-Precision Means for Measuring Abundance (of Gas) Emission lines arise from permitted (recombination) and forbidden
Astr 5465 March 6, 2018 Abundances in Late-type Galaxies Spectra of HII Regions Offer a High-Precision Means for Measuring Abundance (of Gas) Emission lines arise from permitted (recombination) and forbidden
Astronomy 730. Evolution
 Astronomy 730 Evolution Outline } Evolution } Formation of structure } Processes on the galaxy scale } Gravitational collapse, merging, and infall } SF, feedback and chemical enrichment } Environment }
Astronomy 730 Evolution Outline } Evolution } Formation of structure } Processes on the galaxy scale } Gravitational collapse, merging, and infall } SF, feedback and chemical enrichment } Environment }
Simulating Feedback-Driven Galactic Chemical Evolution with Individual Stars
 Simulating Feedback-Driven Galactic Chemical Evolution with Individual Stars Andrew Emerick Blue Waters Fellow NSF Graduate Research Fellow Greg Bryan Mordecai-Mark Mac Low Emerick + 18a (submitted) Emerick
Simulating Feedback-Driven Galactic Chemical Evolution with Individual Stars Andrew Emerick Blue Waters Fellow NSF Graduate Research Fellow Greg Bryan Mordecai-Mark Mac Low Emerick + 18a (submitted) Emerick
Radiation-hydrodynamics from Mpc to sub-pc scales with RAMSES-RT
 Radiation-hydrodynamics from Mpc to sub-pc scales with RAMSES-RT Joki Rosdahl Centre de Recherche Astrophysique de Lyon With Aubert, Blaizot, Bieri, Biernacki, Commercon, Costa, Dubois, Geen, Katz, Kimm,
Radiation-hydrodynamics from Mpc to sub-pc scales with RAMSES-RT Joki Rosdahl Centre de Recherche Astrophysique de Lyon With Aubert, Blaizot, Bieri, Biernacki, Commercon, Costa, Dubois, Geen, Katz, Kimm,
Rotation rates, sizes and star formation efficiencies of a representative population of simulated disc galaxies
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 427, 379 392 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21951.x Rotation rates, sizes and star formation efficiencies of a representative population of simulated disc galaxies I. G.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 427, 379 392 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21951.x Rotation rates, sizes and star formation efficiencies of a representative population of simulated disc galaxies I. G.
Star formation and Galaxy evolution as traced through cosmic env. and time
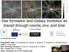 Star formation and Galaxy evolution as traced through cosmic env. and time Luca Graziani In collaboration with: First@INAF, Italy: R. Schneider, M. Ginolfi, S. Marassi, R. Valiante, M. de Bennassuti UniFI:
Star formation and Galaxy evolution as traced through cosmic env. and time Luca Graziani In collaboration with: First@INAF, Italy: R. Schneider, M. Ginolfi, S. Marassi, R. Valiante, M. de Bennassuti UniFI:
Cosmic Structure Formation on Supercomputers (and laptops)
 Cosmic Structure Formation on Supercomputers (and laptops) Lecture 4: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and baryonic sub-grid models Benjamin Moster! Ewald Puchwein 1 Outline of the lecture course Lecture
Cosmic Structure Formation on Supercomputers (and laptops) Lecture 4: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and baryonic sub-grid models Benjamin Moster! Ewald Puchwein 1 Outline of the lecture course Lecture
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines!
 Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Feedback from massive stars in dwarf galaxy formation
 Highlights of Spanish Astrophysics VII, Proceedings of the X Scientific Meeting of the Spanish Astronomical Society held on July 9-13, 2012, in Valencia, Spain. J. C. Guirado, L. M. Lara, V. Quilis, and
Highlights of Spanish Astrophysics VII, Proceedings of the X Scientific Meeting of the Spanish Astronomical Society held on July 9-13, 2012, in Valencia, Spain. J. C. Guirado, L. M. Lara, V. Quilis, and
The Universe of Galaxies: from large to small. Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 1 introduction
 The Universe of Galaxies: from large to small Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 1 introduction 1 Galaxies lie at the crossroads of astronomy The study of galaxies brings together nearly all astronomical disciplines:
The Universe of Galaxies: from large to small Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 1 introduction 1 Galaxies lie at the crossroads of astronomy The study of galaxies brings together nearly all astronomical disciplines:
GALAXIES 626. The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution:
 GALAXIES 626 The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution: Chemical evolution Observation of spiral and irregular galaxies show that the fraction of heavy elements varies with the fraction of the total mass which
GALAXIES 626 The Milky Way II. Chemical evolution: Chemical evolution Observation of spiral and irregular galaxies show that the fraction of heavy elements varies with the fraction of the total mass which
Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback
 1 1 Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback 1 1 Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback Geoff Bicknell & Alex Wagner Australian National University 1 1 High redshift radio
1 1 Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback 1 1 Black Holes in the Early Universe Accretion and Feedback Geoff Bicknell & Alex Wagner Australian National University 1 1 High redshift radio
Lecture 27 The Intergalactic Medium
 Lecture 27 The Intergalactic Medium 1. Cosmological Scenario 2. The Ly Forest 3. Ionization of the Forest 4. The Gunn-Peterson Effect 5. Comment on HeII Reionization References J Miralda-Escude, Science
Lecture 27 The Intergalactic Medium 1. Cosmological Scenario 2. The Ly Forest 3. Ionization of the Forest 4. The Gunn-Peterson Effect 5. Comment on HeII Reionization References J Miralda-Escude, Science
arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.co] 25 May 2015
![arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.co] 25 May 2015 arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.co] 25 May 2015](/thumbs/95/124135521.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 21 (2014) Printed 26 May 2015 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Baryon effects on the internal structure of ΛCDM halos in the EAGLE simulations arxiv:1409.8617v3 [astro-ph.co]
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 21 (2014) Printed 26 May 2015 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Baryon effects on the internal structure of ΛCDM halos in the EAGLE simulations arxiv:1409.8617v3 [astro-ph.co]
Two Phase Formation of Massive Galaxies
 Two Phase Formation of Massive Galaxies Focus: High Resolution Cosmological Zoom Simulation of Massive Galaxies ApJ.L.,658,710 (2007) ApJ.,697, 38 (2009) ApJ.L.,699,L178 (2009) ApJ.,725,2312 (2010) ApJ.,744,63(2012)
Two Phase Formation of Massive Galaxies Focus: High Resolution Cosmological Zoom Simulation of Massive Galaxies ApJ.L.,658,710 (2007) ApJ.,697, 38 (2009) ApJ.L.,699,L178 (2009) ApJ.,725,2312 (2010) ApJ.,744,63(2012)
Origin of Bi-modality
 Origin of Bi-modality and Downsizing Avishai Dekel HU Jerusalem Galaxies and Structures Through Cosmic Times Venice, March 2006 Summary Q: z
Origin of Bi-modality and Downsizing Avishai Dekel HU Jerusalem Galaxies and Structures Through Cosmic Times Venice, March 2006 Summary Q: z
telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us?
 The Milky Way From a dark site the Milky Way can be seen as a broad band across the sky What is it? telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us? that we live in a spiral
The Milky Way From a dark site the Milky Way can be seen as a broad band across the sky What is it? telescopes resolve it into many faint (i.e. distant) stars What does it tell us? that we live in a spiral
Age Dating A SSP. Quick quiz: please write down a 3 sentence explanation of why these plots look like they do.
 Color is only a weak function of age after ~3Gyrs (for a given metallicity) (See MBW pg 473) But there is a strong change in M/L V and weak change in M/L K Age Dating A SSP Quick quiz: please write down
Color is only a weak function of age after ~3Gyrs (for a given metallicity) (See MBW pg 473) But there is a strong change in M/L V and weak change in M/L K Age Dating A SSP Quick quiz: please write down
Durham Research Online
 Durham Research Online Deposited in DRO: 16 February 2016 Version of attached le: Published Version Peer-review status of attached le: Peer-reviewed Citation for published item: Furlong, M. and Bower,
Durham Research Online Deposited in DRO: 16 February 2016 Version of attached le: Published Version Peer-review status of attached le: Peer-reviewed Citation for published item: Furlong, M. and Bower,
THE GAS MASS AND STAR FORMATION RATE
 THE GAS MASS AND STAR FORMATION RATE OF STAR-FORMING GALAXIES AT z ~ 1.3 Nissim Kanekar National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, Pune Apurba Bera Shiv Sethi Ben Weiner K. Dwarakanath Image: B. Premkumar
THE GAS MASS AND STAR FORMATION RATE OF STAR-FORMING GALAXIES AT z ~ 1.3 Nissim Kanekar National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, Pune Apurba Bera Shiv Sethi Ben Weiner K. Dwarakanath Image: B. Premkumar
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009
 Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies. Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts
 X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts Chandra survey of diffuse X-ray emission from 53 edge-on galaxies i > 60 o, D < 30 Mpc (Li, J.-T. & Wang, Q.D.
X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts Chandra survey of diffuse X-ray emission from 53 edge-on galaxies i > 60 o, D < 30 Mpc (Li, J.-T. & Wang, Q.D.
AGN Feedback In an Isolated Elliptical Galaxy
 AGN Feedback In an Isolated Elliptical Galaxy Feng Yuan Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, CAS Collaborators: Zhaoming Gan (SHAO) Jerry Ostriker (Princeton) Luca Ciotti (Bologna) Greg Novak (Paris) 2014.9.10;
AGN Feedback In an Isolated Elliptical Galaxy Feng Yuan Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, CAS Collaborators: Zhaoming Gan (SHAO) Jerry Ostriker (Princeton) Luca Ciotti (Bologna) Greg Novak (Paris) 2014.9.10;
Bright Cluster Galaxy formation and the role of AGN feedback. Romain Teyssier
 Bright Cluster Galaxy formation and the role of AGN feedback Romain Teyssier KITP 2011: Monster Inc. Romain Teyssier 1 Outline - Feedback and galaxy formation - The role of AGN feedback in Milky Way halos
Bright Cluster Galaxy formation and the role of AGN feedback Romain Teyssier KITP 2011: Monster Inc. Romain Teyssier 1 Outline - Feedback and galaxy formation - The role of AGN feedback in Milky Way halos
Galaxies 626. Lecture 5
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 5 Galaxies 626 The epoch of reionization After Reionization After reionization, star formation was never the same: the first massive stars produce dust, which catalyzes H2 formation
Galaxies 626 Lecture 5 Galaxies 626 The epoch of reionization After Reionization After reionization, star formation was never the same: the first massive stars produce dust, which catalyzes H2 formation
Multiwavelength observation campaign of Mrk 509: UV spectra of the X-ray Outflow!!!!Gerard Kriss!! STScI!!! (with N. Arav, J. Kaastra & the Mrk 509
 Multiwavelength observation campaign of Mrk 509: UV spectra of the X-ray Outflow!!!!Gerard Kriss!! STScI!!! (with N. Arav, J. Kaastra & the Mrk 509 Team)!! The Influence of AGN Outflows! «They may affect
Multiwavelength observation campaign of Mrk 509: UV spectra of the X-ray Outflow!!!!Gerard Kriss!! STScI!!! (with N. Arav, J. Kaastra & the Mrk 509 Team)!! The Influence of AGN Outflows! «They may affect
A measurement of galaxy halo mass from the surrounding H I Lyα absorption
 MNRAS 433, 3103 3114 (2013) Advance Access publication 2013 June 29 doi:10.1093/mnras/stt950 A measurement of galaxy halo mass from the surrounding H I Lyα absorption Olivera Rakic, 1,2 Joop Schaye, 1
MNRAS 433, 3103 3114 (2013) Advance Access publication 2013 June 29 doi:10.1093/mnras/stt950 A measurement of galaxy halo mass from the surrounding H I Lyα absorption Olivera Rakic, 1,2 Joop Schaye, 1
Durham Research Online
 Durham Research Online Deposited in DRO: 01 November 2017 Version of attached le: Published Version Peer-review status of attached le: Peer-reviewed Citation for published item: De Rossi, Mar a Emilia
Durham Research Online Deposited in DRO: 01 November 2017 Version of attached le: Published Version Peer-review status of attached le: Peer-reviewed Citation for published item: De Rossi, Mar a Emilia
Illuminating the Dark Ages: Luminous Quasars in the Epoch of Reionisation. Bram Venemans MPIA Heidelberg
 Illuminating the Dark Ages: Luminous Quasars in the Epoch of Reionisation Bram Venemans MPIA Heidelberg Workshop The Reionization History of the Universe Bielefeld University, March 8-9 2018 History of
Illuminating the Dark Ages: Luminous Quasars in the Epoch of Reionisation Bram Venemans MPIA Heidelberg Workshop The Reionization History of the Universe Bielefeld University, March 8-9 2018 History of
Lecture 2 Interstellar Absorption Lines: Line Radiative Transfer
 Lecture 2 Interstellar Absorption Lines: Line Radiative Transfer 1. Atomic absorption lines 2. Application of radiative transfer to absorption & emission 3. Line broadening & curve of growth 4. Optical/UV
Lecture 2 Interstellar Absorption Lines: Line Radiative Transfer 1. Atomic absorption lines 2. Application of radiative transfer to absorption & emission 3. Line broadening & curve of growth 4. Optical/UV
Galaxy Simulators Star Formation for Dummies ^
 Galaxy Simulators Star Formation for Dummies ^ Mark Krumholz UC Santa Cruz HIPACC Summer School August 6, 2010 The Challenge of Star Formation ~10 pc ~10 pc ~10 pc Like stars, star formation involves impossibly
Galaxy Simulators Star Formation for Dummies ^ Mark Krumholz UC Santa Cruz HIPACC Summer School August 6, 2010 The Challenge of Star Formation ~10 pc ~10 pc ~10 pc Like stars, star formation involves impossibly
Galaxies 626. Lecture 9 Metals (2) and the history of star formation from optical/uv observations
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 9 Metals (2) and the history of star formation from optical/uv observations Measuring metals at high redshift Metals at 6 How can we measure the ultra high z star formation? One robust
Galaxies 626 Lecture 9 Metals (2) and the history of star formation from optical/uv observations Measuring metals at high redshift Metals at 6 How can we measure the ultra high z star formation? One robust
The effects of galaxy formation on the matter power spectrum: A challenge for precision cosmology
 2 The effects of galaxy formation on the matter power spectrum: A challenge for precision cosmology Upcoming weak lensing surveys, such as LSST, EUCLID, and WFIRST, aim to measure the matter power spectrum
2 The effects of galaxy formation on the matter power spectrum: A challenge for precision cosmology Upcoming weak lensing surveys, such as LSST, EUCLID, and WFIRST, aim to measure the matter power spectrum
Galaxy population simulations
 Aspen, February 2014 Galaxy population simulations Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics semi-analytic simulations provide a tool... To explore the statistics and interactions of the many processes
Aspen, February 2014 Galaxy population simulations Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics semi-analytic simulations provide a tool... To explore the statistics and interactions of the many processes
Outline. Walls, Filaments, Voids. Cosmic epochs. Jeans length I. Jeans length II. Cosmology AS7009, 2008 Lecture 10. λ =
 Cosmology AS7009, 2008 Lecture 10 Outline Structure formation Jeans length, Jeans mass Structure formation with and without dark matter Cold versus hot dark matter Dissipation The matter power spectrum
Cosmology AS7009, 2008 Lecture 10 Outline Structure formation Jeans length, Jeans mass Structure formation with and without dark matter Cold versus hot dark matter Dissipation The matter power spectrum
