Reionization constraints post Planck-15
|
|
|
- Ernest Crawford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reionization constraints post Planck-15 Tirthankar Roy Choudhury National Centre for Radio Astrophysics Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Pune CMB Spectral Distortions from Cosmic Baryon Evolution RRI, Bangalore, India 12 July
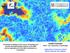
2 Studying the epoch of reionization 3 Figure courtesy Raghunath Ghara universe getting ionized by the first stars aim is to study the neutral hydrogen fraction x HI (x,z) as it decreases from 1 to 0 get insights on the nature of the first stars 1
3 Quasar absorption spectra at z 6 Fan, Carilli & Keating (2006) ( F obs = F cont e τ xhi ) GP, τ GP
4 Thomson scattering τ el from CMBR Planck Collaboration (2016) τ el = σ T c z[t] 0 dt n e (1+z) 3 3
5 Thomson scattering τ el from CMBR Planck Collaboration (2016) τ el = σ T c z[t] 0 dt n e (1+z) 3 3
6 Quasar absorption + CMBR Quasar absorption spectra measure e τgp, not straightforward to convert into x HI CMBR measures the integrated effect Need theoretical models to interpret the two data set simultaneously 4
7 Reionization models Formation of (dark matter) haloes: Analytical: Press-Schechter/Sheth-Tormen formalism: dn(m, z) 2 dm = ρ m δ c(z) dσ(m) π M σ 2 (M) dm Simulations: DM only N-body codes e δ2 c (z)/2σ2 (M) 5
8 Reionization models Formation of (dark matter) haloes: Analytical: Press-Schechter/Sheth-Tormen formalism: dn(m, z) 2 dm = ρ m δ c(z) dσ(m) π M σ 2 (M) dm Simulations: DM only N-body codes Photon production ṅ γ e δ2 c (z)/2σ2 (M) 5
9 Reionization models Formation of (dark matter) haloes: Analytical: Press-Schechter/Sheth-Tormen formalism: dn(m, z) 2 dm = ρ m δ c(z) dσ(m) π M σ 2 (M) dm Simulations: DM only N-body codes e δ2 c (z)/2σ2 (M) Photon production ṅ γ Galaxy/star formation: cooling, fragmentation, feedback (radiative, mechanical, chemical) 5
10 Reionization models Formation of (dark matter) haloes: Analytical: Press-Schechter/Sheth-Tormen formalism: dn(m, z) 2 dm = ρ m δ c(z) dσ(m) π M σ 2 (M) dm Simulations: DM only N-body codes e δ2 c (z)/2σ2 (M) Photon production ṅ γ Galaxy/star formation: cooling, fragmentation, feedback (radiative, mechanical, chemical) Radiation from stars: population synthesis. 5
11 Reionization models Formation of (dark matter) haloes: Analytical: Press-Schechter/Sheth-Tormen formalism: dn(m, z) 2 dm = ρ m δ c(z) dσ(m) π M σ 2 (M) dm Simulations: DM only N-body codes e δ2 c (z)/2σ2 (M) Photon production ṅ γ Galaxy/star formation: cooling, fragmentation, feedback (radiative, mechanical, chemical) Radiation from stars: population synthesis. Escape of photons f esc: neutral hydrogen within the host galaxy 5
12 Reionization models Formation of (dark matter) haloes: Analytical: Press-Schechter/Sheth-Tormen formalism: dn(m, z) 2 dm = ρ m δ c(z) dσ(m) π M σ 2 (M) dm Simulations: DM only N-body codes e δ2 c (z)/2σ2 (M) Photon production ṅ γ Galaxy/star formation: cooling, fragmentation, feedback (radiative, mechanical, chemical) Radiation from stars: population synthesis. Escape of photons f esc: neutral hydrogen within the host galaxy Radiative transfer in the IGM: evolution of ionization fronts Simulations, semi-numerical, analytical 5
13 Analytical models: basic formalism Choudhury & Ferrara (2005, 2006) Average the radiative transfer equation over large volumes = evolution of volume filling factor of ionized regions dq HII dt = ṅγ n H Q HII C HII n e a 3α R(T) can be extended to account for density-dependent reionization Miralda-Escúde, Haehnelt & Rees (2000) 6
14 Analytical models: basic formalism Choudhury & Ferrara (2005, 2006) Average the radiative transfer equation over large volumes = evolution of volume filling factor of ionized regions dq HII dt = ṅγ n H Q HII C HII n e a 3α R(T) can be extended to account for density-dependent reionization Miralda-Escúde, Haehnelt & Rees (2000) Supplemented by temperature and species evolution equations 6
15 Analytical models: sources Choudhury & Ferrara (2005, 2006) dq HII dt = ṅγ n H Q HII C HII n e a 3α R(T) Assumption: reionization driven primarily by galaxies. Photon production rate: ṅ γ = N ion ( Ωb Ω m ) df coll dt Number of ionizing photons in the IGM per baryons Collapse rate of dark matter haloes N ion = f esc ǫ number of photons per baryons in stars 7
16 Analytical models: sources Choudhury & Ferrara (2005, 2006) dq HII dt = ṅγ n H Q HII C HII n e a 3α R(T) Assumption: reionization driven primarily by galaxies. Photon production rate: ṅ γ = N ion ( Ωb Ω m ) df coll dt Number of ionizing photons in the IGM per baryons Collapse rate of dark matter haloes N ion = f esc ǫ number of photons per baryons in stars Predict observables, e.g., τ el (or C l ), photoionization rate (or mean transmitted flux),... 7
17 Analytical models: sources Choudhury & Ferrara (2005, 2006) dq HII dt = ṅγ n H Q HII C HII n e a 3α R(T) Assumption: reionization driven primarily by galaxies. Photon production rate: ṅ γ = N ion ( Ωb Ω m ) df coll dt Number of ionizing photons in the IGM per baryons Collapse rate of dark matter haloes N ion = f esc ǫ number of photons per baryons in stars Predict observables, e.g., τ el (or C l ), photoionization rate (or mean transmitted flux),... full MCMC analysis accounting for N ion (z) and other free parameters 7
18 Data constrained models Mitra, Choudhury & Ferrara (2015) Constraints based on Planck15 data on τ el quasar absorption line measurements at z 6 (either Γ HI or τ eff ) prior on x HI at z based on dark pixel fraction McGreer, Mesinger & D Odorico (2015) 8
19 Data constrained models Mitra, Choudhury & Ferrara (2015) reionization starts at z % ionized at z 6 10 large uncertainties at 7 z 10 8
20 How to constrain reionization at z 7? Galaxy luminosity function: uncertain escape fraction Quasar absorption spectra (damping wings/near zones) IGM temperature Lyman-α emitters (number density, also clustering) Future: 21 cm experiments 9
21 How to constrain reionization at z 7? Galaxy luminosity function: uncertain escape fraction Quasar absorption spectra (damping wings/near zones) IGM temperature Lyman-α emitters (number density, also clustering) Future: 21 cm experiments 9
22 Lyα emitters and reionization Dijkstra, Mesinger & Wyithe (2011) 10
23 Fraction of galaxies having Lyα emission Lyα emitter fraction x Lyα, M UV > This work M UV < Stark et al. (2011) A Redshift Sharp change in behaviour at z > 6. Schenker et al (2014) 11
24 Fraction of galaxies having Lyα emission 11
25 Uncertainties and challenges decrease in the space density of Lyα emitters at z > 6. intrinsic, or damping wing of the surrounding neutral medium? modelling challenges: reionization topology, optically thick (super-) Lyman-limit systems use high (effective) dynamic range numerical simulations Choudhury, Puchwein, Haehnelt & Bolton (2015), Mesinger et al (2015), Kakiichi et al (2015) 12
26 Calibrating the reionization simulations Early (τ = 0.084) Late (τ = 0.068) Very Late (τ = 0.055) 13
27 Matching the data default model late model late reionization seems to explain the decrease in Lyα visibility consistent with other studies Choudhury, Puchwein, Haehnelt & Bolton (2015) 14
28 21 cm maps ν (MHz) ν [MHz] cmpc/h Early (0.084) cmpc/h log10 (Tb /mk) cmpc/h Late (0.068) Very Late (0.055) z redshift Kulkarni, Choudhury, Puchwein & Haehnelt (in prep) 15
29 21 cm power spectra 10 5 Early HM12 (0.084) Late/Default (0.068) Very Very Late Late (0.055) GMRT (k) [mk 2 ] PAPER k [h/cmpc] k [h/cmpc] z = 7 z = 8 z = 10 z = 7 z = 8 z = 10 (dashed: no self-shielding) k [h/cmpc] Kulkarni, Choudhury, Puchwein & Haehnelt (in prep) 16
30 Summary Good progress in modelling the reionization, possible to construct models consistent with available data Uncertainties at z 7, the Lyα emitters could put some constraints Future lies in the 21 cm experiments Currently operating telescopes (e.g., LOFAR) may be able to detect the statistical signal, else have to wait till the SKA1-low 17
31 Summary Good progress in modelling the reionization, possible to construct models consistent with available data Uncertainties at z 7, the Lyα emitters could put some constraints Future lies in the 21 cm experiments Currently operating telescopes (e.g., LOFAR) may be able to detect the statistical signal, else have to wait till the SKA1-low Thank you 17
32 UV luminosity function at z > 6 18
33 Self-consistent reionization from simulations Assume Q(z) to be given. Choose a z: mean free path λ mfp emissivity ṅ ion trial photoionization rate Γ HI dq/dt clumping factor C ionization field, self-shielding invert Γ HI ṅ ion λ mfp solve dq/dt = ṅ ion /n H Cn H α rec 19
34 Galaxy luminosity function N ion = f esc ǫ number of photons per baryons in stars Φ(M AB,z) [mag -1 Mpc -3 ] ϵ = * z = ϵ = * z = ϵ = * z = M AB ϵ = * z = max ϵ = * z = Mitra, Choudhury & Ferrara (2015) 20
35 Constraints on f esc N ion = f esc ǫ number of photons per baryons in stars best-fit 0.3 f esc z Mitra, Choudhury & Ferrara (2015) 21
36 f esc at lower redshifts Escape fraction (f esc) σ upper limits Grazian et al Vanzella et al Siana et al Cowie et al HM z Γ HI in s Becker+2013 Wyithe+2011 Bolton+2007 Calverley+2011 HM12 with f esc = z Planck Collaboration Q H II Schenker McGreer z τ el f esc = 0.14 f esc = 0.18 f esc = 0.22 f esc = z f esc z Khaire, Srianand, Choudhury & Gaikwad (2016) 22
37 Reionization driven by quasars? ϵ 912 (erg s -1 Hz -1 Mpc -3 ) Hopkins+07 Madau+15 Giallongo z 22 faint quasar candidates detected through multi-wavelength observations Giallongo et al (2015) leads to higher number of ionizing photons contributed by quasars 23
38 Constraints on the galaxy contribution τ el Hopkins+07 Madau+15 Giallongo z dn LL /dz z Parameters best-fit with 2-σ errors H07 MH15 G15 ǫ II < f esc < x HI τ el z what about helium reionization? 24
The Probes and Sources of Cosmic Reionization Francesco Haardt University of Como INFN, Milano-Bicocca
 1 The Probes and Sources of Cosmic Reionization Francesco Haardt University of Insubria@Lake Como INFN, Milano-Bicocca 2 TALK OUTLINE 1. Dark Ages and Reionization 2. Observations: QSO Absorption Lines
1 The Probes and Sources of Cosmic Reionization Francesco Haardt University of Insubria@Lake Como INFN, Milano-Bicocca 2 TALK OUTLINE 1. Dark Ages and Reionization 2. Observations: QSO Absorption Lines
Illuminating the Dark Ages: Luminous Quasars in the Epoch of Reionisation. Bram Venemans MPIA Heidelberg
 Illuminating the Dark Ages: Luminous Quasars in the Epoch of Reionisation Bram Venemans MPIA Heidelberg Workshop The Reionization History of the Universe Bielefeld University, March 8-9 2018 History of
Illuminating the Dark Ages: Luminous Quasars in the Epoch of Reionisation Bram Venemans MPIA Heidelberg Workshop The Reionization History of the Universe Bielefeld University, March 8-9 2018 History of
Probing dark matter and the physical state of the IGM with the Lyα forest
 Probing dark matter and the physical state of the IGM with the Lyα forest Martin Haehnelt in collaboration with: George Becker, James Bolton, Jonathan Chardin, Laura Keating, Ewald Puchwein, Debora Sijacki,
Probing dark matter and the physical state of the IGM with the Lyα forest Martin Haehnelt in collaboration with: George Becker, James Bolton, Jonathan Chardin, Laura Keating, Ewald Puchwein, Debora Sijacki,
- Motivation - New measurements of IGM Lyα Opacity & - Implications for Reionization & High-z Galaxies with Jamie Bolton (Nottingham)
 Galaxy Evolution in the Reionization Era Probed Using the UV Background - Motivation - New measurements of IGM Lyα Opacity & Temperature - UVB Results George Becker Cambridge IoA & KICC GalEvol2013 - Implications
Galaxy Evolution in the Reionization Era Probed Using the UV Background - Motivation - New measurements of IGM Lyα Opacity & Temperature - UVB Results George Becker Cambridge IoA & KICC GalEvol2013 - Implications
Models of the cosmological 21 cm signal from the epoch of reionization calibrated with Ly α and CMB data
 Advance Access publication 2016 August 30 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw2168 Models of the cosmological 21 cm signal from the epoch of reionization calibrated with Ly α and CMB data Girish Kulkarni, 1 Tirthankar
Advance Access publication 2016 August 30 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw2168 Models of the cosmological 21 cm signal from the epoch of reionization calibrated with Ly α and CMB data Girish Kulkarni, 1 Tirthankar
COBE/DIRBE Satellite. Black Body T=2.725 K. Tuesday, November 27, 12
 COBE/DIRBE Satellite Black Body T=2.725 K COBE/DIRBE Satellite Thermal component subtracted, ΔT=3.353 mk COBE/DIRBE Satellite Dipole component subtracted, ΔT = 18 μk Origin of Structure WMAP image Fluctuations
COBE/DIRBE Satellite Black Body T=2.725 K COBE/DIRBE Satellite Thermal component subtracted, ΔT=3.353 mk COBE/DIRBE Satellite Dipole component subtracted, ΔT = 18 μk Origin of Structure WMAP image Fluctuations
The Nottingham eprints service makes this work by researchers of the University of Nottingham available open access under the following conditions.
 Choudhury, Tirthankar Roy and Puchwein, Ewald and Haehnelt, Martin G. and Bolton, James S. (2015) Lyman α emitters gone missing: evidence for late reionization? Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical
Choudhury, Tirthankar Roy and Puchwein, Ewald and Haehnelt, Martin G. and Bolton, James S. (2015) Lyman α emitters gone missing: evidence for late reionization? Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical
Probing the End of Dark Ages with High-redshift Quasars. Xiaohui Fan University of Arizona Dec 14, 2004
 Probing the End of Dark Ages with High-redshift Quasars Xiaohui Fan University of Arizona Dec 14, 2004 High-redshift Quasars and the End of Cosmic Dark Ages Existence of SBHs at the end of Dark Ages BH
Probing the End of Dark Ages with High-redshift Quasars Xiaohui Fan University of Arizona Dec 14, 2004 High-redshift Quasars and the End of Cosmic Dark Ages Existence of SBHs at the end of Dark Ages BH
Lecture 27 The Intergalactic Medium
 Lecture 27 The Intergalactic Medium 1. Cosmological Scenario 2. The Ly Forest 3. Ionization of the Forest 4. The Gunn-Peterson Effect 5. Comment on HeII Reionization References J Miralda-Escude, Science
Lecture 27 The Intergalactic Medium 1. Cosmological Scenario 2. The Ly Forest 3. Ionization of the Forest 4. The Gunn-Peterson Effect 5. Comment on HeII Reionization References J Miralda-Escude, Science
V2'#$0D*:$0()%"*,-.!/ K'(B5*2#*0D; T2&3B5U
 V2'#$0D*:$0()%"*,-.!/ K'(B5*2#*0D; T2&3B5U 2 S-Cam NB101 Observations KONNO ET AL. tion. The previous studies suggest that the fraction of strong LAEs in Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) decreases from z 6
V2'#$0D*:$0()%"*,-.!/ K'(B5*2#*0D; T2&3B5U 2 S-Cam NB101 Observations KONNO ET AL. tion. The previous studies suggest that the fraction of strong LAEs in Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) decreases from z 6
Lyman-alpha intensity mapping during the Epoch of Reionization
 Lyman-alpha intensity mapping during the Epoch of Reionization Mário G. Santos CENTRA IST (Austin, May 15, 2012) Marta Silva, Mario G. Santos, Yan Gong, Asantha Cooray (2012), arxiv:1205.1493 Intensity
Lyman-alpha intensity mapping during the Epoch of Reionization Mário G. Santos CENTRA IST (Austin, May 15, 2012) Marta Silva, Mario G. Santos, Yan Gong, Asantha Cooray (2012), arxiv:1205.1493 Intensity
The Epoch of Reionization: Observational & Theoretical Topics
 The Epoch of Reionization: Observational & Theoretical Topics Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Lecture 3 Lecture 4 Current constraints on Reionization Physics of the 21cm probe EoR radio experiments Expected Scientific
The Epoch of Reionization: Observational & Theoretical Topics Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Lecture 3 Lecture 4 Current constraints on Reionization Physics of the 21cm probe EoR radio experiments Expected Scientific
Galaxies 626. Lecture 5
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 5 Galaxies 626 The epoch of reionization After Reionization After reionization, star formation was never the same: the first massive stars produce dust, which catalyzes H2 formation
Galaxies 626 Lecture 5 Galaxies 626 The epoch of reionization After Reionization After reionization, star formation was never the same: the first massive stars produce dust, which catalyzes H2 formation
On the Detectability of Lyman Alpha Emission by Galaxies from the Epoch of Reionization. Mark Dijkstra (MPA, Garching)
 On the Detectability of Lyman Alpha Emission by Galaxies from the Epoch of Reionization Mark Dijkstra (MPA, Garching) Outline Why we care about the HI Lya line. Lya transfer basics. Why direct detection
On the Detectability of Lyman Alpha Emission by Galaxies from the Epoch of Reionization Mark Dijkstra (MPA, Garching) Outline Why we care about the HI Lya line. Lya transfer basics. Why direct detection
Simulating HI 21-cm Signal from EoR and Cosmic Dawn. Kanan K. Datta Presidency University, Kolkata
 Simulating HI 21-cm Signal from EoR and Cosmic Dawn Kanan K. Datta Presidency University, Kolkata Plan of the talk Why simulations?! Dynamic ranges of simulations! Basic flowchart for simulation! Various
Simulating HI 21-cm Signal from EoR and Cosmic Dawn Kanan K. Datta Presidency University, Kolkata Plan of the talk Why simulations?! Dynamic ranges of simulations! Basic flowchart for simulation! Various
What can we learn about reionization from the ksz
 What can we learn about reionization from the ksz Andrei Mesinger Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa IGM effect on CMB primary temperature anisotropies ionized IGM damps CMB temperature anisotropies through
What can we learn about reionization from the ksz Andrei Mesinger Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa IGM effect on CMB primary temperature anisotropies ionized IGM damps CMB temperature anisotropies through
PoS(Cosmology2009)022
 and 21cm Observations Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics E-mail: ciardi@mpa-garching.mpg.de With the advent in the near future of radio telescopes as LOFAR, a new window on the highredshift universe
and 21cm Observations Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics E-mail: ciardi@mpa-garching.mpg.de With the advent in the near future of radio telescopes as LOFAR, a new window on the highredshift universe
The First Cosmic Billion Years. Andrea Ferrara Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa, Italy
 The First Cosmic Billion Years Andrea Ferrara Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa, Italy DAVID The Dark Ages VIrtual Department http://www.arcetri.astro.it/twiki/bin/view/david/webhome S. Bianchi INAF/Arcetri
The First Cosmic Billion Years Andrea Ferrara Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa, Italy DAVID The Dark Ages VIrtual Department http://www.arcetri.astro.it/twiki/bin/view/david/webhome S. Bianchi INAF/Arcetri
Rupert Croft. QuickTime and a decompressor are needed to see this picture.
 Rupert Croft QuickTime and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. yesterday: Plan for lecture 1: History : -the first quasar spectra -first theoretical models (all wrong) -CDM cosmology meets the
Rupert Croft QuickTime and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. yesterday: Plan for lecture 1: History : -the first quasar spectra -first theoretical models (all wrong) -CDM cosmology meets the
Cross-correlations of CMB lensing as tools for cosmology and astrophysics. Alberto Vallinotto Los Alamos National Laboratory
 Cross-correlations of CMB lensing as tools for cosmology and astrophysics Alberto Vallinotto Los Alamos National Laboratory Dark matter, large scales Structure forms through gravitational collapse......
Cross-correlations of CMB lensing as tools for cosmology and astrophysics Alberto Vallinotto Los Alamos National Laboratory Dark matter, large scales Structure forms through gravitational collapse......
Reionization by Galaxies and QSOs and the Thermal State of the IGM What drives reionization?
 Reionization by Galaxies and QSOs and the Thermal State of the IGM What drives reionization? Koki Kakiichi MPA with thanks to Luca Graziani, Benedetta Ciardi, Avery Meiksin, Michele Compostella, Marius
Reionization by Galaxies and QSOs and the Thermal State of the IGM What drives reionization? Koki Kakiichi MPA with thanks to Luca Graziani, Benedetta Ciardi, Avery Meiksin, Michele Compostella, Marius
Simulating cosmic reionization at large scales
 Simulating cosmic reionization at large scales I.T. Iliev, G. Mellema, U. L. Pen, H. Merz, P.R. Shapiro and M.A. Alvarez Presentation by Mike Pagano Nov. 30th 2007 Simulating cosmic reionization at large
Simulating cosmic reionization at large scales I.T. Iliev, G. Mellema, U. L. Pen, H. Merz, P.R. Shapiro and M.A. Alvarez Presentation by Mike Pagano Nov. 30th 2007 Simulating cosmic reionization at large
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 12 Aug 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 12 Aug 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 12 Aug 2015](/thumbs/75/72220413.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 5 (?) Printed 3 January 8 (MN LATEX style file v.) -cm signal from cosmic dawn - II: Imprints of the light-cone effects arxiv:54.56v [astro-ph.co] Aug 5 Raghunath Ghara, Kanan
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 5 (?) Printed 3 January 8 (MN LATEX style file v.) -cm signal from cosmic dawn - II: Imprints of the light-cone effects arxiv:54.56v [astro-ph.co] Aug 5 Raghunath Ghara, Kanan
Lyα Galaxies as a Probe of the High-z Universe. Mark Dijkstra
 Lyα Galaxies as a Probe of the High-z Universe Mark Dijkstra Credit: Andrew Chung (MPA) Credit: Max Gronke (Oslo) The Suppressed Lyα flux from galaxies at z>6 `Lyα fraction Stark et al., Pentericci et
Lyα Galaxies as a Probe of the High-z Universe Mark Dijkstra Credit: Andrew Chung (MPA) Credit: Max Gronke (Oslo) The Suppressed Lyα flux from galaxies at z>6 `Lyα fraction Stark et al., Pentericci et
First Light And Reionization. Nick Gnedin
 First Light And Reionization Nick Gnedin Reionization and 5-Year Plans Sovier leaders would love reionization it is a field where every 5 years something interesting happens. SDSS Quasars ~ 2005 z=5.7
First Light And Reionization Nick Gnedin Reionization and 5-Year Plans Sovier leaders would love reionization it is a field where every 5 years something interesting happens. SDSS Quasars ~ 2005 z=5.7
The First Galaxies: Evolution drivers via luminosity functions and spectroscopy through a magnifying GLASS
 Charlotte Mason (UCLA) Aspen, 7 Feb 2016 The First Galaxies: Evolution drivers via luminosity functions and spectroscopy through a magnifying GLASS with Tommaso Treu (UCLA), Michele Trenti (U. Melbourne),
Charlotte Mason (UCLA) Aspen, 7 Feb 2016 The First Galaxies: Evolution drivers via luminosity functions and spectroscopy through a magnifying GLASS with Tommaso Treu (UCLA), Michele Trenti (U. Melbourne),
Radiative Transfer in a Clumpy Universe: the UVB. Piero Madau UC Santa Cruz
 Radiative Transfer in a Clumpy Universe: the UVB Piero Madau UC Santa Cruz The cosmic UVB originates from the integrated emission of starforming galaxies and QSOs. It determines the thermal and ionization
Radiative Transfer in a Clumpy Universe: the UVB Piero Madau UC Santa Cruz The cosmic UVB originates from the integrated emission of starforming galaxies and QSOs. It determines the thermal and ionization
Ewald Puchwein KICC / IoA, University of Cambridge
 Constent modelling of cosmic UV background and rmal/ioniation htory of IGM and its implications for AGN contribution to reioniation Ewald Puchwein KICC / IoA University of Cambridge collaborators: Francesco
Constent modelling of cosmic UV background and rmal/ioniation htory of IGM and its implications for AGN contribution to reioniation Ewald Puchwein KICC / IoA University of Cambridge collaborators: Francesco
The Intergalactic Medium: Overview and Selected Aspects
 The Intergalactic Medium: Overview and Selected Aspects Draft Version Tristan Dederichs June 18, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 The IGM at high redshifts (z > 5) 2 2.1 Early Universe and Reionization......................................
The Intergalactic Medium: Overview and Selected Aspects Draft Version Tristan Dederichs June 18, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 The IGM at high redshifts (z > 5) 2 2.1 Early Universe and Reionization......................................
Seeing Through the Trough: Detecting Lyman Alpha from Early Generations of Galaxies
 Seeing Through the Trough: Detecting Lyman Alpha from Early Generations of Galaxies Mark Dijkstra (ITC) collaborators: Stuart Wyithe, Avi Loeb, Adam Lidz, Zoltan Haiman Schematic History of the Universe
Seeing Through the Trough: Detecting Lyman Alpha from Early Generations of Galaxies Mark Dijkstra (ITC) collaborators: Stuart Wyithe, Avi Loeb, Adam Lidz, Zoltan Haiman Schematic History of the Universe
Galaxies 626. Lecture 8 The universal metals
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 8 The universal metals The Spectra of Distant Galaxies Distant Galaxy Stellar Continuum Emission Observer Scattering by clouds of HI in the IGM at λline* (1+zcloud) Forest of absorption
Galaxies 626 Lecture 8 The universal metals The Spectra of Distant Galaxies Distant Galaxy Stellar Continuum Emission Observer Scattering by clouds of HI in the IGM at λline* (1+zcloud) Forest of absorption
Cosmological observables and the nature of dark matter
 Cosmological observables and the nature of dark matter Shiv Sethi Raman Research Institute March 18, 2018 SDSS results: power... SDSS results: BAO at... Planck results:... Planck-SDSS comparison Summary
Cosmological observables and the nature of dark matter Shiv Sethi Raman Research Institute March 18, 2018 SDSS results: power... SDSS results: BAO at... Planck results:... Planck-SDSS comparison Summary
Gamma-Ray Absorption in High-Redshift Objects and Cosmic Reionization
 Gamma-Ray Absorption in High-Redshift Objects and Cosmic Reionization Susumu Inoue (MPI Munich/ICRR U.Tokyo) - Model 1: SI, Salvaterra, Choudhury, Ferrara, Ciardi, Schneider - Model 2: Yoshiyuki Inoue,
Gamma-Ray Absorption in High-Redshift Objects and Cosmic Reionization Susumu Inoue (MPI Munich/ICRR U.Tokyo) - Model 1: SI, Salvaterra, Choudhury, Ferrara, Ciardi, Schneider - Model 2: Yoshiyuki Inoue,
The First Galaxies. Erik Zackrisson. Department of Astronomy Stockholm University
 The First Galaxies Erik Zackrisson Department of Astronomy Stockholm University Outline The first galaxies what, when, why? What s so special about them? Why are they important for cosmology? How can we
The First Galaxies Erik Zackrisson Department of Astronomy Stockholm University Outline The first galaxies what, when, why? What s so special about them? Why are they important for cosmology? How can we
ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY TEMPE, ARIZONA Obtaining a Cold IGM through Modification of the Residual Ionization Fraction Following Recombination
 ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY TEMPE, ARIZONA 85287 LOCO EDGES REPORT #098 Obtaining a Cold IGM through Modification of the Residual Ionization Fraction Following Recombination Judd Bowman July 16, 2017 1. Calculation
ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY TEMPE, ARIZONA 85287 LOCO EDGES REPORT #098 Obtaining a Cold IGM through Modification of the Residual Ionization Fraction Following Recombination Judd Bowman July 16, 2017 1. Calculation
An analytical model of the neutral islands during the late stage of reionization
 An analytical model of the neutral islands during the late stage of reionization Yidong Xu (NAOC), Bin Yue (SNS), Meng Su (MIT), Zuhui Fan (PKU), Xuelei Chen (NAOC) 2014-01-08 NAOC lunch talk Analytical
An analytical model of the neutral islands during the late stage of reionization Yidong Xu (NAOC), Bin Yue (SNS), Meng Su (MIT), Zuhui Fan (PKU), Xuelei Chen (NAOC) 2014-01-08 NAOC lunch talk Analytical
arxiv:astro-ph/ v4 8 Jan 2003
 1 Spectral signature of cosmological infall of gas around the first quasars Rennan Barkana and Abraham Loeb arxiv:astro-ph/0209515v4 8 Jan 2003 School of Physics and Astronomy, Tel Aviv University, Tel
1 Spectral signature of cosmological infall of gas around the first quasars Rennan Barkana and Abraham Loeb arxiv:astro-ph/0209515v4 8 Jan 2003 School of Physics and Astronomy, Tel Aviv University, Tel
Planck was conceived to confirm the robustness of the ΛCDM concordance model when the relevant quantities are measured with much higher accuracy
 12-14 April 2006, Rome, Italy Francesco Melchiorri Memorial Conference Planck was conceived to confirm the robustness of the ΛCDM concordance model when the relevant quantities are measured with much higher
12-14 April 2006, Rome, Italy Francesco Melchiorri Memorial Conference Planck was conceived to confirm the robustness of the ΛCDM concordance model when the relevant quantities are measured with much higher
HI across cosmic time
 HI across cosmic time Hubble-ITC Fellow CfA Avi Loeb (CfA) Steve Furlanetto (UCLA) Stuart Wyithe (Melbourne) Mario Santos (Portugal) Hy Trac (CMU) Alex Amblard (Ames) Renyue Cen (Princeton) Asanthe Cooray
HI across cosmic time Hubble-ITC Fellow CfA Avi Loeb (CfA) Steve Furlanetto (UCLA) Stuart Wyithe (Melbourne) Mario Santos (Portugal) Hy Trac (CMU) Alex Amblard (Ames) Renyue Cen (Princeton) Asanthe Cooray
Emission lines from galaxies in the Epoch of Reioniza5on
 Emission lines from galaxies in the Epoch of Reioniza5on Simona Gallerani Emanuele Sobacchi, Andrea Ferrara, Livia Vallini, Andrea PalloBni, CarloDa Gruppioni, Andrei Mesinger Monte Mario, Roma, SPICA
Emission lines from galaxies in the Epoch of Reioniza5on Simona Gallerani Emanuele Sobacchi, Andrea Ferrara, Livia Vallini, Andrea PalloBni, CarloDa Gruppioni, Andrei Mesinger Monte Mario, Roma, SPICA
High-Redshift Galaxies at the Epoch of Cosmic Reionization
 High-Redshift Galaxies at the Epoch of Cosmic Reionization Linhua Jiang ( 江林华 ) (KIAA, Peking University) 2014 KIAA-PKU Astrophysics Forum Collaborators: F. Bian, B. Clement, S. Cohen, R. Dave, E. Egami,
High-Redshift Galaxies at the Epoch of Cosmic Reionization Linhua Jiang ( 江林华 ) (KIAA, Peking University) 2014 KIAA-PKU Astrophysics Forum Collaborators: F. Bian, B. Clement, S. Cohen, R. Dave, E. Egami,
Really, what universe do we live in? White dwarfs Supernova type Ia Accelerating universe Cosmic shear Lyman α forest
 Really, what universe do we live in? White dwarfs Supernova type Ia Accelerating universe Cosmic shear Lyman α forest White dwarf Core of solar mass star No energy from fusion or gravitational contraction
Really, what universe do we live in? White dwarfs Supernova type Ia Accelerating universe Cosmic shear Lyman α forest White dwarf Core of solar mass star No energy from fusion or gravitational contraction
Research Collection. How will we determine the reionization history of the universe?: introduction to session 2. Other Conference Item.
 Research Collection Other Conference Item How will we determine the reionization history of the universe?: introduction to session 2 Author(s): Haiman, Zoltàn Publication Date: 2003 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004584667
Research Collection Other Conference Item How will we determine the reionization history of the universe?: introduction to session 2 Author(s): Haiman, Zoltàn Publication Date: 2003 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004584667
Galaxies are not distributed randomly in space. 800 Mpc. 400 Mpc
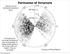 Formation Origin of of Structure Galaxies are not distributed randomly in space. 800 Mpc 400 Mpc If one galaxy has comoving coordinate, x, then the probability of finding another galaxy in the vicinity
Formation Origin of of Structure Galaxies are not distributed randomly in space. 800 Mpc 400 Mpc If one galaxy has comoving coordinate, x, then the probability of finding another galaxy in the vicinity
Quasars in the epoch of reioniza1on
 Big Bang Dark Ages Quasars in the epoch of reioniza1on Carnegie-Princeton Fellow Illumina9ng the Dark Ages June 27, Heidelberg, Germany Universe Today Quasars and galaxies in the reioniza1on epoch Quasars
Big Bang Dark Ages Quasars in the epoch of reioniza1on Carnegie-Princeton Fellow Illumina9ng the Dark Ages June 27, Heidelberg, Germany Universe Today Quasars and galaxies in the reioniza1on epoch Quasars
SELF-CONSISTENT MODELING OF REIONIZATION IN COSMOLOGICAL HYDRODYNAMICAL SIMULATIONS
 Draft version March 0, 017 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 1/16/11 Immediately after the reioniation of H i ( 6) or He ii ( 3), T 0 is likely to be around 10 4 K and γ 1 (Bolton et al.
Draft version March 0, 017 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 1/16/11 Immediately after the reioniation of H i ( 6) or He ii ( 3), T 0 is likely to be around 10 4 K and γ 1 (Bolton et al.
The Growth and Radiative Signatures of High Redshift Black Holes
 The Growth and Radiative Signatures of High Redshift Black Holes Jarrett Johnson (LANL) with Bhaskar Agarwal (Yale) Joe Smidt (LANL) Brandon Wiggins (LANL, BYU) Dan Whalen (Heidelberg, Portsmouth) Erik
The Growth and Radiative Signatures of High Redshift Black Holes Jarrett Johnson (LANL) with Bhaskar Agarwal (Yale) Joe Smidt (LANL) Brandon Wiggins (LANL, BYU) Dan Whalen (Heidelberg, Portsmouth) Erik
PoS(MCCT-SKADS)010. Epoch of Reionization. Benedetta Ciardi Max Planck Institute ...
 Max Planck Institute E-mail: ciardi@mpa-garching.mpg.de...... First MCCT-SKADS Training School September 23-29, 2007 Medicina, Bologna Italy Speaker. A footnote may follow. c Copyright owned by the author(s)
Max Planck Institute E-mail: ciardi@mpa-garching.mpg.de...... First MCCT-SKADS Training School September 23-29, 2007 Medicina, Bologna Italy Speaker. A footnote may follow. c Copyright owned by the author(s)
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 12 Feb 2007
 Optical Depth of the Cosmic Microwave Background and Reionization of the Intergalactic Medium J. Michael Shull & Aparna Venkatesan 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0702323v1 12 Feb 2007 University of Colorado, Department
Optical Depth of the Cosmic Microwave Background and Reionization of the Intergalactic Medium J. Michael Shull & Aparna Venkatesan 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0702323v1 12 Feb 2007 University of Colorado, Department
Physics of the Intergalactic Medium During the Epoch of Reionization
 Physics of the Intergalactic Medium During the Epoch of Reionization Adam Lidz 1 Introduction Most of the volume of the universe, and much of the matter within it, lies in between the galaxies; this space
Physics of the Intergalactic Medium During the Epoch of Reionization Adam Lidz 1 Introduction Most of the volume of the universe, and much of the matter within it, lies in between the galaxies; this space
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 29 May 2007
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 8 (2006) Printed 5 February 2008 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) Luminosity Functions of Lyα Emitting Galaxies and Cosmic Reionization of Hydrogen Mark Dijkstra 1, J. Stuart
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 8 (2006) Printed 5 February 2008 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) Luminosity Functions of Lyα Emitting Galaxies and Cosmic Reionization of Hydrogen Mark Dijkstra 1, J. Stuart
Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges
 Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
Quasar Absorption Lines
 Tracing the Cosmic Web with Diffuse Gas DARK MATTER GAS STARS NEUTRAL HYDROGEN Quasar Absorption Lines use quasars as bright beacons for probing intervening gaseous material can study both galaxies and
Tracing the Cosmic Web with Diffuse Gas DARK MATTER GAS STARS NEUTRAL HYDROGEN Quasar Absorption Lines use quasars as bright beacons for probing intervening gaseous material can study both galaxies and
National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China xuyd at nao.cas.cn
 Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics, Garching, Germany E-mail: ciardi at mpa-garching.mpg.de Susumu Inoue Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan E-mail: sinoue at icrr.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics, Garching, Germany E-mail: ciardi at mpa-garching.mpg.de Susumu Inoue Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan E-mail: sinoue at icrr.u-tokyo.ac.jp
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 27 Mar 2018
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 27 Mar 2018 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 27 Mar 2018](/thumbs/77/75862162.jpg) Preprint 28 March 2018 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3.0 The duration of reionization constrains the ionizing sources Mahavir Sharma, Tom Theuns, Carlos Frenk Institute for Computational Cosmology,
Preprint 28 March 2018 Compiled using MNRAS LATEX style file v3.0 The duration of reionization constrains the ionizing sources Mahavir Sharma, Tom Theuns, Carlos Frenk Institute for Computational Cosmology,
Feedback and Galaxy Formation
 Heating and Cooling in Galaxies and Clusters Garching August 2006 Feedback and Galaxy Formation Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Cluster assembly in ΛCDM Gao et al 2004 'Concordance'
Heating and Cooling in Galaxies and Clusters Garching August 2006 Feedback and Galaxy Formation Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Cluster assembly in ΛCDM Gao et al 2004 'Concordance'
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 24 Mar 2017
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 24 Mar 2017 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 24 Mar 2017](/thumbs/80/81813475.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 27 March 2017 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Epoch of Reionisation 21cm Forecasting From MCMC-Constrained Semi-Numerical Models Sultan Hassan 1, Romeel
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 27 March 2017 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Epoch of Reionisation 21cm Forecasting From MCMC-Constrained Semi-Numerical Models Sultan Hassan 1, Romeel
Probing the Dark Ages with 21 cm Absorption
 May 13, 2008 Probing the Dark Ages with 21 cm Absorption Emil Polisensky (UMD/NRL) ABSTRACT A brief overview of detecting neutral hydrogen gas during the cosmic Dark Ages in absorption against the background
May 13, 2008 Probing the Dark Ages with 21 cm Absorption Emil Polisensky (UMD/NRL) ABSTRACT A brief overview of detecting neutral hydrogen gas during the cosmic Dark Ages in absorption against the background
Galaxies 626. Lecture 9 Metals (2) and the history of star formation from optical/uv observations
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 9 Metals (2) and the history of star formation from optical/uv observations Measuring metals at high redshift Metals at 6 How can we measure the ultra high z star formation? One robust
Galaxies 626 Lecture 9 Metals (2) and the history of star formation from optical/uv observations Measuring metals at high redshift Metals at 6 How can we measure the ultra high z star formation? One robust
Intergalactic Medium Piero Madau. Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin
 eaa.iop.org DOI: 10.1888/0333750888/1821 Intergalactic Medium Piero Madau From Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin IOP Publishing Ltd 2006 ISBN: 0333750888 Institute of Physics Publishing
eaa.iop.org DOI: 10.1888/0333750888/1821 Intergalactic Medium Piero Madau From Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin IOP Publishing Ltd 2006 ISBN: 0333750888 Institute of Physics Publishing
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Nov 2015
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Nov 2015 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Nov 2015](/thumbs/93/111211081.jpg) High-Redshift Galaxy Surveys and the Reionization of the Universe Rychard Bouwens arxiv:1511.01133v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Nov 2015 Abstract Star-forming galaxies in the early universe provide us with perhaps
High-Redshift Galaxy Surveys and the Reionization of the Universe Rychard Bouwens arxiv:1511.01133v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Nov 2015 Abstract Star-forming galaxies in the early universe provide us with perhaps
Observations of First Light
 Image from Space Telescope Science Institute Observations of First Light Betsy Barton (UC Irvine) Member, TMT SAC Project Scientist, IRIS on TMT Microwave Background What reionized the universe? The End
Image from Space Telescope Science Institute Observations of First Light Betsy Barton (UC Irvine) Member, TMT SAC Project Scientist, IRIS on TMT Microwave Background What reionized the universe? The End
Reionization of the Intergalactic Medium: What Is it and When Did it Occur?
 Hannah Krug ASTR 688R Spring 2008 Final Project Due 5/13/08 Reionization of the Intergalactic Medium: What Is it and When Did it Occur? In the time following the Big Bang, there are two epochs which astronomers
Hannah Krug ASTR 688R Spring 2008 Final Project Due 5/13/08 Reionization of the Intergalactic Medium: What Is it and When Did it Occur? In the time following the Big Bang, there are two epochs which astronomers
The effect of fluctuations on the helium-ionizing background
 MNRAS 437, 1141 1154 (2014) Advance Access publication 2013 November 15 doi:10.1093/mnras/stt1911 The effect of fluctuations on the helium-ionizing background Frederick B. Davies and Steven R. Furlanetto
MNRAS 437, 1141 1154 (2014) Advance Access publication 2013 November 15 doi:10.1093/mnras/stt1911 The effect of fluctuations on the helium-ionizing background Frederick B. Davies and Steven R. Furlanetto
Dark-ages reionization and galaxy formation simulation V: morphology and statistical signatures of reionization
 Advance Access publication 2016 July 18 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw1718 Dark-ages reionization and galaxy formation simulation V: morphology and statistical signatures of reionization Paul M. Geil, 1 Simon J.
Advance Access publication 2016 July 18 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw1718 Dark-ages reionization and galaxy formation simulation V: morphology and statistical signatures of reionization Paul M. Geil, 1 Simon J.
University of Groningen. Exploring 21CM - Lyman Alpha Emitter Synergies for SKA Dayal, Pratika; Hutter, Anne; Müller, Volker; Trott, C. M.
 University of Groningen Exploring 21CM - Lyman Alpha Emitter Synergies for SKA Dayal, Pratika; Hutter, Anne; Müller, Volker; Trott, C. M. Published in: Astrophysical Journal DOI: 1.3847/1538-4357/836/2/176
University of Groningen Exploring 21CM - Lyman Alpha Emitter Synergies for SKA Dayal, Pratika; Hutter, Anne; Müller, Volker; Trott, C. M. Published in: Astrophysical Journal DOI: 1.3847/1538-4357/836/2/176
Reionization. High-Redshift Galaxy UV Luminosity Function. Axion Dark Matter. Rosemary Wyse
 Reionization and the High-Redshift Galaxy UV Luminosity Function with Axion Dark Matter Rosemary Wyse Johns Hopkins University and University of Edinburgh Brandon Bozek, Doddy Marsh & Joe Silk Galaxy-scale
Reionization and the High-Redshift Galaxy UV Luminosity Function with Axion Dark Matter Rosemary Wyse Johns Hopkins University and University of Edinburgh Brandon Bozek, Doddy Marsh & Joe Silk Galaxy-scale
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 5 Feb 2016
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 5 Feb 2016 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 5 Feb 2016](/thumbs/86/94573710.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 8 February 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Simulating the 21-cm signal from reionisation including non-linear ionisations and inhomogeneous recombinations
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 8 February 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Simulating the 21-cm signal from reionisation including non-linear ionisations and inhomogeneous recombinations
On the Direct Detectability of the Cosmic Dark Ages: 21-cm Emission from Minihalos
 On the Direct Detectability of the Cosmic Dark Ages: 21-cm Emission from Minihalos Ilian T. Iliev 1, Paul R. Shapiro 2, Andrea Ferrara 1, and Hugo Martel 2 iliev@arcetri.astro.it, shapiro@astro.as.utexas.edu
On the Direct Detectability of the Cosmic Dark Ages: 21-cm Emission from Minihalos Ilian T. Iliev 1, Paul R. Shapiro 2, Andrea Ferrara 1, and Hugo Martel 2 iliev@arcetri.astro.it, shapiro@astro.as.utexas.edu
How to cheat with maps. perfectly sensible, honest version
 How to cheat with maps watch out for weasel maps : logarithmic (favors solar system) conformal (blows up BB singularity into something significant, popular with CMB types) comoving (makes the local universe
How to cheat with maps watch out for weasel maps : logarithmic (favors solar system) conformal (blows up BB singularity into something significant, popular with CMB types) comoving (makes the local universe
Constraining the IGM thermal state and Cosmology
 Constraining the IGM thermal state and Cosmology Antonella Garzilli IEU, Ewha Womans University 29th November, 2013 with: Prof. Tom Theuns Dr. James Bolton Dr. Tae-Sun Kim Dr. Samuel Leach Dr. Matteo Viel
Constraining the IGM thermal state and Cosmology Antonella Garzilli IEU, Ewha Womans University 29th November, 2013 with: Prof. Tom Theuns Dr. James Bolton Dr. Tae-Sun Kim Dr. Samuel Leach Dr. Matteo Viel
HII regions. Massive (hot) stars produce large numbers of ionizing photons (energy above 13.6 ev) which ionize hydrogen in the vicinity.
 HII regions Massive (hot) stars produce large numbers of ionizing photons (energy above 13.6 ev) which ionize hydrogen in the vicinity. Detailed nebular structure depends on density distribution of surrounding
HII regions Massive (hot) stars produce large numbers of ionizing photons (energy above 13.6 ev) which ionize hydrogen in the vicinity. Detailed nebular structure depends on density distribution of surrounding
The intergalactic medium! and! the epoch of reionization! Cristiano Porciani! AIfA, Uni-Bonn!
 The intergalactic medium! and! the epoch of reionization! Cristiano Porciani! AIfA, Uni-Bonn! Questions?! C. Porciani! IGM & EoR! 2! Gunn-Peterson effect! In 1965 Gunn and Peterson pointed out that any
The intergalactic medium! and! the epoch of reionization! Cristiano Porciani! AIfA, Uni-Bonn! Questions?! C. Porciani! IGM & EoR! 2! Gunn-Peterson effect! In 1965 Gunn and Peterson pointed out that any
The first black holes
 The first black holes Marta Volonteri Institut d Astrophysique de Paris M. Habouzit, Y. Dubois, M. Latif (IAP) A. Reines (NOAO) M. Tremmel (University of Washington) F. Pacucci (SNS) High-redshift quasars
The first black holes Marta Volonteri Institut d Astrophysique de Paris M. Habouzit, Y. Dubois, M. Latif (IAP) A. Reines (NOAO) M. Tremmel (University of Washington) F. Pacucci (SNS) High-redshift quasars
Outline: Part II. The end of the dark ages. Structure formation. Merging cold dark matter halos. First stars z t Univ Myr.
 Outline: Part I Outline: Part II The end of the dark ages Dark ages First stars z 20 30 t Univ 100 200 Myr First galaxies z 10 15 t Univ 300 500 Myr Current observational limit: HST and 8 10 m telescopes
Outline: Part I Outline: Part II The end of the dark ages Dark ages First stars z 20 30 t Univ 100 200 Myr First galaxies z 10 15 t Univ 300 500 Myr Current observational limit: HST and 8 10 m telescopes
Observing the Reionization Epoch Through 21 Centimeter Radiation
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 7 May 2003 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Observing the Reionization Epoch Through 21 Centimeter Radiation Steven R. Furlanetto, Aaron Sokasian, and Lars
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 7 May 2003 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Observing the Reionization Epoch Through 21 Centimeter Radiation Steven R. Furlanetto, Aaron Sokasian, and Lars
HeII reionization: observational implications
 HeII reionization: observational implications Michele Compostella (Argelander Institute, Bonn) Cristiano Porciani (AIfA, Bonn), Sebastiano Cantalupo (UCSC, Santa Cruz) Intergalactic Matters Heidelberg,
HeII reionization: observational implications Michele Compostella (Argelander Institute, Bonn) Cristiano Porciani (AIfA, Bonn), Sebastiano Cantalupo (UCSC, Santa Cruz) Intergalactic Matters Heidelberg,
Cross-Correlation of Cosmic Shear and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Background
 Cross-Correlation of Cosmic Shear and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Background Masato Shirasaki (Univ. of Tokyo) with Shunsaku Horiuchi (UCI), Naoki Yoshida (Univ. of Tokyo, IPMU) Extragalactic Gamma-Ray Background
Cross-Correlation of Cosmic Shear and Extragalactic Gamma-ray Background Masato Shirasaki (Univ. of Tokyo) with Shunsaku Horiuchi (UCI), Naoki Yoshida (Univ. of Tokyo, IPMU) Extragalactic Gamma-Ray Background
Galaxy formation and evolution. Astro 850
 Galaxy formation and evolution Astro 850 Introduction What are galaxies? Systems containing many galaxies, e.g. 10 11 stars in the Milky Way. But galaxies have different properties. Properties of individual
Galaxy formation and evolution Astro 850 Introduction What are galaxies? Systems containing many galaxies, e.g. 10 11 stars in the Milky Way. But galaxies have different properties. Properties of individual
Measuring the dark universe. Luca Amendola University of Heidelberg
 Measuring the dark universe Luca Amendola University of Heidelberg 1 In search of the dark Searching with new probes Searching in new domains Or: a short overview of what I have been doing in the last
Measuring the dark universe Luca Amendola University of Heidelberg 1 In search of the dark Searching with new probes Searching in new domains Or: a short overview of what I have been doing in the last
Star Formation at the End of the Dark Ages
 Star Formation at the End of the Dark Ages...or when (rest-frame) UV becomes (observed) IR Piero Madau University of California Santa Cruz Distant Star Formation: what who came first? neanderthal Outline
Star Formation at the End of the Dark Ages...or when (rest-frame) UV becomes (observed) IR Piero Madau University of California Santa Cruz Distant Star Formation: what who came first? neanderthal Outline
Lya as a Probe of the (High-z) Universe
 Lya as a Probe of the (High-z) Universe Mark Dijkstra (CfA) Main Collaborators: Adam Lidz, Avi Loeb (CfA) Stuart Wyithe (Melbourne), Zoltan Haiman (Columbia) Lya as a Probe of the (High-z) Universe Outline
Lya as a Probe of the (High-z) Universe Mark Dijkstra (CfA) Main Collaborators: Adam Lidz, Avi Loeb (CfA) Stuart Wyithe (Melbourne), Zoltan Haiman (Columbia) Lya as a Probe of the (High-z) Universe Outline
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 1 Oct 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 1 Oct 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 1 Oct 2007](/thumbs/92/109436815.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 25 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Lyα damping wing constraints on inhomogeneous reionization Andrei Mesinger & Steven R. Furlanetto Yale Center
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 25 October 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Lyα damping wing constraints on inhomogeneous reionization Andrei Mesinger & Steven R. Furlanetto Yale Center
How extinction correction influences the estimate of Lyα escape fraction?
 How extinction correction influences the estimate of Lyα escape fraction? Speaker: Fangxia An (Purple Mountain Observatory; Durham University) fangxiaan@pmo.ac.cn Supervisor: Xianzhong Zheng; Ian Smail;
How extinction correction influences the estimate of Lyα escape fraction? Speaker: Fangxia An (Purple Mountain Observatory; Durham University) fangxiaan@pmo.ac.cn Supervisor: Xianzhong Zheng; Ian Smail;
Planck meets the Lyman-α forest
 Planck meets the Lyman-α forest Jose Oñorbe Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (onorbe@mpia.de) Collaborators: J. Hennawi (MPIA), Z. Lukić (LBNL), A. Rorai (IoA), G. Kulkarni (IoA) June 15, 2016 Meeting
Planck meets the Lyman-α forest Jose Oñorbe Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (onorbe@mpia.de) Collaborators: J. Hennawi (MPIA), Z. Lukić (LBNL), A. Rorai (IoA), G. Kulkarni (IoA) June 15, 2016 Meeting
M. Dijkstra (UiO) Aspen, Mark Dijkstra. with: Shiv Sethi (RRI), Abraham Loeb (CfA), Max Gronke (UiO) & David Sobral (Lancaster)
 Mark Dijkstra with: Shiv Sethi (RRI), Abraham Loeb (CfA), Max Gronke (UiO) & David Sobral (Lancaster) arxiv:1601.04712 (ApJ accepted), Dijkstra, Sethi & Loeb arxiv:1602.07695 (resubmitted to ApJ), Dijkstra,
Mark Dijkstra with: Shiv Sethi (RRI), Abraham Loeb (CfA), Max Gronke (UiO) & David Sobral (Lancaster) arxiv:1601.04712 (ApJ accepted), Dijkstra, Sethi & Loeb arxiv:1602.07695 (resubmitted to ApJ), Dijkstra,
Problem Set 5 - Solution
 Problem Set 5 - Solution E.S. Phinney, and J. Sebastian Pineda March 4, 212 1. a) We consider a source at rest in comoving coordinates at redshift z = a(t )/a(t e ) 1. We want to find out how this redshift
Problem Set 5 - Solution E.S. Phinney, and J. Sebastian Pineda March 4, 212 1. a) We consider a source at rest in comoving coordinates at redshift z = a(t )/a(t e ) 1. We want to find out how this redshift
Observational Cosmology
 (C. Porciani / K. Basu) Lecture 7 Cosmology with galaxy clusters (Mass function, clusters surveys) Course website: http://www.astro.uni-bonn.de/~kbasu/astro845.html Outline of the two lecture Galaxy clusters
(C. Porciani / K. Basu) Lecture 7 Cosmology with galaxy clusters (Mass function, clusters surveys) Course website: http://www.astro.uni-bonn.de/~kbasu/astro845.html Outline of the two lecture Galaxy clusters
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 3 June, 2004 9 to 12 PAPER 67 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start to
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 3 June, 2004 9 to 12 PAPER 67 PHYSICAL COSMOLOGY Attempt THREE questions. There are four questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. You may not start to
Studying 21cm power spectrum with one-point statistics
 doi:10.1093/mnras/stv965 Studying 21cm power spectrum with one-point statistics Hayato Shimabukuro, 1,2 Shintaro Yoshiura, 2 Keitaro Takahashi, 2 Shuichiro Yokoyama 3 and Kiyotomo Ichiki 1 1 Department
doi:10.1093/mnras/stv965 Studying 21cm power spectrum with one-point statistics Hayato Shimabukuro, 1,2 Shintaro Yoshiura, 2 Keitaro Takahashi, 2 Shuichiro Yokoyama 3 and Kiyotomo Ichiki 1 1 Department
Michael Shull (University of Colorado)
 Early Galaxies, Stars, Metals, and the Epoch of Reionization Michael Shull (University of Colorado) Far-IR Workshop (Pasadena, CA) May 29, 2008 Submillimeter Galaxies: only the brightest? How long? [dust
Early Galaxies, Stars, Metals, and the Epoch of Reionization Michael Shull (University of Colorado) Far-IR Workshop (Pasadena, CA) May 29, 2008 Submillimeter Galaxies: only the brightest? How long? [dust
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11177 S1. Description of the simulation code We developed our own code that implements a hybrid method to produce instances of the expected three-dimensional distribution of the first
doi:10.1038/nature11177 S1. Description of the simulation code We developed our own code that implements a hybrid method to produce instances of the expected three-dimensional distribution of the first
80 2 Observational Cosmology L and the mean energy
 80 2 Observational Cosmology fluctuations, short-wavelength modes have amplitudes that are suppressed because these modes oscillated as acoustic waves during the radiation epoch whereas the amplitude of
80 2 Observational Cosmology fluctuations, short-wavelength modes have amplitudes that are suppressed because these modes oscillated as acoustic waves during the radiation epoch whereas the amplitude of
Simulation of Cosmic Reionization: small things matter. Kyungjin Ahn Chosun University UCSD (visiting) SKA Science Workshop, Jodrell Bank Mar 2013
 Simulation of Cosmic Reionization: small things matter Kyungjin Ahn Chosun University UCSD (visiting) SKA Science Workshop, Jodrell Bank Mar 2013 (Some of) Observational constraints on Reionization When
Simulation of Cosmic Reionization: small things matter Kyungjin Ahn Chosun University UCSD (visiting) SKA Science Workshop, Jodrell Bank Mar 2013 (Some of) Observational constraints on Reionization When
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays. UHECRs from Mildly Relativistic Supernovae
 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays from Mildly Relativistic Supernovae Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai, India March 13, 2012 Outline UHECRS Chakraborti, Ray, Soderberg, Loeb, Chandra 2011 Nature
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays from Mildly Relativistic Supernovae Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai, India March 13, 2012 Outline UHECRS Chakraborti, Ray, Soderberg, Loeb, Chandra 2011 Nature
Electromagnetic Spectra. AST443, Lecture 13 Stanimir Metchev
 Electromagnetic Spectra AST443, Lecture 13 Stanimir Metchev Administrative Homework 2: problem 5.4 extension: until Mon, Nov 2 Reading: Bradt, chapter 11 Howell, chapter 6 Tenagra data: see bottom of Assignments
Electromagnetic Spectra AST443, Lecture 13 Stanimir Metchev Administrative Homework 2: problem 5.4 extension: until Mon, Nov 2 Reading: Bradt, chapter 11 Howell, chapter 6 Tenagra data: see bottom of Assignments
Intergalactic UV Background Radiation Field. Snigdha Das and Pushpa Khare, Physics Department, Utkal University Bhubaneswar, , India
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (1997) 18, 133 143 Intergalactic UV Background Radiation Field Snigdha Das and Pushpa Khare, Physics Department, Utkal University Bhubaneswar, 751004, India Received 1997 May 13; accepted
J. Astrophys. Astr. (1997) 18, 133 143 Intergalactic UV Background Radiation Field Snigdha Das and Pushpa Khare, Physics Department, Utkal University Bhubaneswar, 751004, India Received 1997 May 13; accepted
Galaxies 626. Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star
 Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
Galaxies 626 Lecture 3: From the CMBR to the first star Galaxies 626 Firstly, some very brief cosmology for background and notation: Summary: Foundations of Cosmology 1. Universe is homogenous and isotropic
The simulated 21 cm signal during the EoR : Ly-α and X-ray fluctuations
 The simulated 21 cm signal during the EoR : Ly-α and X-ray fluctuations Sunghye BAEK Collaborators : B. Semelin, P. Di Matteo, F. Combes, Y. Revaz LERMA - Observatoire de Paris 9 Dec 2008 Physics of the
The simulated 21 cm signal during the EoR : Ly-α and X-ray fluctuations Sunghye BAEK Collaborators : B. Semelin, P. Di Matteo, F. Combes, Y. Revaz LERMA - Observatoire de Paris 9 Dec 2008 Physics of the
Cosmology. Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick.
 Cosmology Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick http://astro.uni-tuebingen.de/~wilms/teach/cosmo Contents 2 Old Cosmology Space and Time Friedmann Equations World Models Modern Cosmology
Cosmology Jörn Wilms Department of Physics University of Warwick http://astro.uni-tuebingen.de/~wilms/teach/cosmo Contents 2 Old Cosmology Space and Time Friedmann Equations World Models Modern Cosmology
