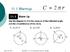
Odyssey Papers 11. A Note on the Wooden Carpenter s Rule from Odyssey Shipwreck Site 35F
|
|
|
- Buddy Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Odyssey Papers 11 A Note on the Wooden Carpenter s Rule from Odyssey Shipwreck Site 35F Stephen Johnston Museum of the History of Science, University of Oxford In 2006 Odyssey Marine Exploration recovered one half of a wooden folding rule from site T7a35f-5, a shipwreck heavily impacted by the offshore fishing industry and located at a depth of 110m in the Western Approaches to the English Channel. The 1ft-long object is one half of a distinctive type of carpenter s joint rule with a design that is characteristically English. The artifact is extremely rare and the earliest example found on a shipwreck. The very limited comparative examples on land suggest a possible date of manufacture for the instrument between the 1660s and 1690s. Odyssey Marine Exploration, Scale Identification The 1ft-long wooden artifact recovered by Odyssey Marine Exploration in 2006 from site 35F in the Western Approaches to the English Channel is a single arm from an originally 2ft-long folding rule (Figs. 1-3). It features a series of lines, numbers and letter abbreviations incised into three sides. These scales (Kingsley, 2008) are the key to identifying and dating the instrument. 1. Side A has three scales (Figs. 1, 3, 5-10): a. An inch scale [0]-12, divided to unit, half, quarter, eighth and numbered by 1. This would have continued to 24 on the missing leg. b. A pair of scales labelled C and D (Fig. 10), standing for Circumference and Diameter. The two scales share the same format: each begins with a subdivided segment and then a scale of equal parts from [0] to the limit imposed by the length of the rule. 2. Side B has three elements (Figs. 2, 3, 11-15): a. The end of a line of board measure running from 12 (at the hinge) to 36, each unit subdivided to half. The scale ends 4in from the end of the leg (4 x 36 = 144 = 1ft square). b. The beginning of a line of timber measure from 9 to 12 (at the hinge), each unit subdivided to quarter. c. A table of timber undermeasure. This is continuous with the timber line and supplies values for 1 to 8in, which the rule cannot accommodate on the scale line. 3. The edge carries a logarithmic line of numbers 1-10 (Fig. 4). The missing leg would have carried the same scale to make a double radius line Mathematical Formulas Side B for timber and board measure was designed to be used for measuring areas and volumes. This particular format was established during the 17th century as an adaptation of a design first published by Leonard Digges in 1556 (Knight, 1988; see Johnston, 1994 for the 16th-century development, and Johnston, 2006 for a detailed study of an unusual straight carpenter s rule of 1635). The complete instrument would have had a board line running from 7 to 36, with a table of undermeasure from 1 to 6in at the end of the missing leg. The timber line would have run on to 36 on the other leg, terminating 1 1/3in from the end. The logarithmic line of numbers on the edge was first published by Edmund Gunter in the 1620s. In the form found here, which appeared on a range of instruments in the 17th century, it would have been used with a pair of dividers or compasses as a general-purpose calculator in effect, a slide rule. The most distinctive scales are those marked C and D (Fig. 10). They would have been used with compasses or dividers and are interrelated. If the circumference of a log had been measured with string, the scales provided the diameter without calculation. These scales would have been matched by another pair on the missing leg, most likely labelled SE for Square Equal and SW for Square
2 Fig. 1. Site 35F wooden folding rule side A with an incised inch scale numbered [0]-12 inches and divided into half, quarter and eighth units. Fig. 2. Site 35F wooden folding rule side B incorporates three elements. Inner scale: the end of a line of board measure running from 12 to 36, each unit subdivided to half. Outer scale: beginning of a line of timber measure from 9 to 12, each unit subdivided to quarter. Far left: table of timber undermeasure. 2
3 Fig. 3. Drawing of the one arm of the wooden folding rule from site 35F (inv. no. 0010). Left: Side B. Centre: Side A.
4 Within. Given any one of these four dimensions, the others can be determined without arithmetic. For example, to find the diameter of a log with a circumference of 108in, first one foot of a pair of dividers would have been placed on the 100 mark of C, while the other foot would have been extended to the 8 division on the subdivided segment. Keeping the dividers separated, this length would have been transferred to the D scale so that one foot was on a numbered division and the other was in the subdivided segment: the rule would show about 34½in as the diameter. The C scale is simply the D scale multiplied by π (pi), since C = πd. The approximation used here is not the standard one of 2 2/7, but a less accurate one of about 3 1/8. (The disparity is easily seen from the scales. When 2 2/7 is used, the divisions for 100 and 30 coincide since, taking account of the subdivided segments, they actually represent 110 and 35.) The SE and SW scales would have been constructed in a similar way. The square equal provided the side of a square whose area equalled the circle defined by the circumference; squaring this value (easily done with the logarithmic line) provided the cross-sectional area of the circular log. The square within (also known as the inscribed square) gives the side of a square that fits within the circle and hence provided an indication of the usable timber that could be extracted from the log. 3. Historical Context & Chronology The presence of the C and D scales provides the best clue for dating the instrument. They were first referred to in print in 1661 by the mathematical instrument maker John Brown, who provided an explanatory diagram. Brown s discussion was introduced without fanfare as simply The use of four scales, called Circumfence [sic], Diameter, Square equal, Square inscribed. This brief account appeared in his The Description and Use of a Joynt-Rule (London, 1661: 87, 107-8) at the end of a chapter entitled The use of certain lines for the mensuration of superficial and solid bodies, usually inserted on Joynt-Rules for the use of Work-men, of several sorts and kindes, which suggests that the scales were already known by this date. There is some evidence, however, from surviving instruments that these scales were a relatively recent innovation. The Science Museum collection in London retains an instrument (inv ) to the same design as the 35F example, which is dated to 1659 (Fig. 16). The four scales are fully labelled as circumference, diameter, square equal and square within. This suggests a degree of unfamiliarity regarding terminology, which had evidently been overcome by the time the 35F example was manufactured and could use the abbreviations C and D. The Science Museum example remains the earliest currently known that features all four scales. A unique instrument, however, in the National Museums Scotland, Edinburgh (inv ), incorporates three of the scales found on the site 35F example. This is a 3ft, three-fold brass carpenter s rule, evidently made in London but inscribed 1655 Robert Trollap of yorke free mason (Fig. 17). Like the 35F example, it was designed for board and timber measure, and also has an inch scale and a double radius logarithmic line of numbers. It includes three unlabelled scales for circumference, diameter and square equal. There is space where a fourth scale for square within could have been inserted. Its absence suggests that the four-scale pattern, as exemplified on the site 35F wooden rule, was created in the later 1650s. Prior to their introduction as scales on rules, the problem of the interrelation of these four dimensions had been treated as a topic for the logarithmic line of numbers. When first announcing the logarithmic line in 1623, Edmund Gunter s De sectore & radio. The Description and Vse of the Sector in Three Bookes. The Description and Vse of the Cross- Staffe in other Three Bookes (London, 1623: 35-6) provided problems interrelating the circumference, diameter and square equal. Presumably Gunter was the inspiration for the scales on the 1655 instrument now in Edinburgh. In 1645 Edmund Wingate expanded Gunter s logarithmic problems in The Use of the Rule of Proportion in Arithmetique and Geometrie (London, 1645: 65-6) to include the inscribed square. He was followed in 1656 by John Brown s The Description and Use of the Carpenters-Rule together with the Use of the Line of Numbers (inscribed thereon) in Arithmatick and Geometry (London, 1656: 53-5), which described the function of the straight 2ft carpenter s rule. Brown, therefore, may have been responsible for the instrument pattern that the 35F example follows. How long-lived was this particular pattern of carpenter s rule? The characteristic set of four scales was mentioned as an optional extra for joint rules by John Brown in 1677 and they were still current in 1688 when he added their use to a new impression of his The Description and Use of the Carpenters-Rule. The latest dated example of such an instrument currently known is 1685 (Richard Knight, pers. comm. 22 February 2002). Therefore, it seems reasonable to place the 35F example in the period between the 1660s and the 1690s. Although no more than an educated hunch, the 1670s or 1680s might be considered most likely. The closest known
5 Fig. 4. Detail of the side edge of the folding rule incised with a logarithmic line of numbers (The missing leg would have carried the same scale to make a double radius line ) Fig. 5. Detail of the hinge end of side A. Fig. 6. Detail of the hinge mechanism at the folding end of side A.
6 Figs Detail of side A.
7 Fig. 9. The end section of side A. Fig. 10. Detail of the end section of side A with a pair of scales incised C and D, standing for Circumference and Diameter.
8 Figs Detail of side B.
9 Fig. 14. End section of side B with table of undermeasure at right. Fig. 15. Detail of table of undermeasure on side B. 9
10 Fig. 16. An intact wooden folding rule in the collections of the Science Museum, London, was crafted to the same design as the site 35F instrument, and is dated by an inscription to Its four central scales are fully labelled as circumference, diameter, square equal and square within. Photo: Science Museum, London (inv ). Fig. 17. A unique 3ft, three-fold brass carpenter s rule in the National Museums Scotland, Edinburgh. It shares scales with the site 35F example and appears to be a prototype for the overall design. Though crafted in London, it is inscribed 1655 Robert Trollap of yorke free mason. Photo: National Museums Scotland (inv ). 10
11 surviving example in the Science Museum, London, is dated to 1674 (inv ). Further surviving examples are currently being actively sought and a comparative study of the numeral forms would also be desirable. Acknowledgements Figs. 1-2 and 4-15 are by Lisa Payne. The drawing of the wooden folding rule (Fig. 3) is by Sean Kingsley. Bibliography Brown, J., The Description and Use of the Carpenters-Rule together with the Use of the Line of Numbers (inscribed thereon) in Arithmatick and Geometry (London, 1656). Brown, J., The Description and Use of a Joynt-Rule (London, 1661). Brown, J., A Supplement, Containing the Description and some Uses, of a convenient Two-foot Joynt-Rule: Upon which are inscribed divers Lines and Scales, sutable to all sort of Artificers occasions. In William Leybourn, The Line of Proportion, commonly called Gunter s Line, made easie. A Second Part (London, 1677). Brown, J., The Description and Use of the Carpenters-Rule: together with The Use of the Line of Numbers commonly called Gunter-Line (London, 1688). Gunter, E., De sectore & radio. The Description and Vse of the Sector in Three Bookes. The Description and Vse of the Cross-Staffe in other Three Bookes (London, 1623). Johnston, S., The Carpenter s Rule: Instruments, Practitioners and Artisans in 16th-century England. In G. Dragoni, A. McConnell and G.L E. Turner (eds.), Proceedings of the Eleventh International Scientific Instrument Symposium (Bologna, 1994), Johnston, S., Reading Rules: Artefactual Evidence for Mathematics and Craft in Early-modern England. In Liba Taub and Frances Willmoth (eds.), The Whipple Museum of the History of Science: Instruments and Interpretations (Cambridge, 2006), Kingsley, S., A Folding Rule from Odyssey Marine Exploration s Shipwreck Site 35F: a Preliminary Note (Odyssey Marine Exploration, unpublished, 2008). Knight, R., The Carpenter s Rule, Newsletter of the Tools and Trades Society 20 (Winter, 1988), Wingate, E., The Use of the Rule of Proportion in Arithmetique and Geometrie (London, 1645). 11
Displayed with permission The American Surveyor Charter Issue Copyright 2004 Cheves Media
 Jeff Lock 2004 Rowland Houghton s THEODOLATE theodolite is an instrument with which the angle viewed between two sighted points is to be read off the horizontal circle of the instrument, using the reading
Jeff Lock 2004 Rowland Houghton s THEODOLATE theodolite is an instrument with which the angle viewed between two sighted points is to be read off the horizontal circle of the instrument, using the reading
Circle Notes. Circumference and Area of Circles
 Love of Learning Educational Services Bringing Curiosity, Relevance, and Enjoyment to the Math Classroom Circle Notes Circumference and Area of Circles Guided note taking pages for calculating circumference
Love of Learning Educational Services Bringing Curiosity, Relevance, and Enjoyment to the Math Classroom Circle Notes Circumference and Area of Circles Guided note taking pages for calculating circumference
Pi: The Ultimate Ratio
 Pi: The Ultimate Ratio Exploring the Ratio of Circle Circumference to Diameter 1 WARM UP Scale up or down to determine an equivalent ratio. 1. 18 miles 3 hours 5? 1 hour 2. $750 4 days 3. 4. 12 in. 1 ft
Pi: The Ultimate Ratio Exploring the Ratio of Circle Circumference to Diameter 1 WARM UP Scale up or down to determine an equivalent ratio. 1. 18 miles 3 hours 5? 1 hour 2. $750 4 days 3. 4. 12 in. 1 ft
Curvaceous Circles BUT IT DOES WORK! Yep we can still relate the formula for the area of a circle to the formula for the area of a rectangle
 Curvaceous Circles So our running theme on our worksheets has been that all the formulas for calculating the area of various shapes comes back to relating that shape to a rectangle. But how can that possibly
Curvaceous Circles So our running theme on our worksheets has been that all the formulas for calculating the area of various shapes comes back to relating that shape to a rectangle. But how can that possibly
April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length
 11.1 Warmup April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length 1 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length mbhaub@mpsaz.org 11.1 Essential Question How can you find the length of a circular arc?
11.1 Warmup April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length 1 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length mbhaub@mpsaz.org 11.1 Essential Question How can you find the length of a circular arc?
Trades Math Practice Assessment Test
 Trades Math Practice Assessment Test Please leave 2 or 3 digits after the decimal point rounding is optional Calculators ARE allowed For full marks, you MUST include units in your answer e.g. 2 ft. or
Trades Math Practice Assessment Test Please leave 2 or 3 digits after the decimal point rounding is optional Calculators ARE allowed For full marks, you MUST include units in your answer e.g. 2 ft. or
F78SC2 Notes 2 RJRC. If the interest rate is 5%, we substitute x = 0.05 in the formula. This gives
 F78SC2 Notes 2 RJRC Algebra It is useful to use letters to represent numbers. We can use the rules of arithmetic to manipulate the formula and just substitute in the numbers at the end. Example: 100 invested
F78SC2 Notes 2 RJRC Algebra It is useful to use letters to represent numbers. We can use the rules of arithmetic to manipulate the formula and just substitute in the numbers at the end. Example: 100 invested
Chapter 7 Sect. 2. A pythagorean triple is a set of three nonzero whole numbers a, b, and c, that satisfy the equation a 2 + b 2 = c 2.
 Chapter 7 Sect. 2 The well-known right triangle relationship called the Pythagorean Theorem is named for Pythagoras, a Greek mathematician who lived in the sixth century b.c. We now know that the Babylonians,
Chapter 7 Sect. 2 The well-known right triangle relationship called the Pythagorean Theorem is named for Pythagoras, a Greek mathematician who lived in the sixth century b.c. We now know that the Babylonians,
How can you find decimal approximations of square roots that are not rational? ACTIVITY: Approximating Square Roots
 . Approximating Square Roots How can you find decimal approximations of square roots that are not rational? ACTIVITY: Approximating Square Roots Work with a partner. Archimedes was a Greek mathematician,
. Approximating Square Roots How can you find decimal approximations of square roots that are not rational? ACTIVITY: Approximating Square Roots Work with a partner. Archimedes was a Greek mathematician,
how to use ELIDE ULJLEB IC]GEL 000 LDD LDG PlclIcElu THE WORLD'S Nfour ACCUIRATE E RULES SUPPLEMENT TO MANUAL M-14
![how to use ELIDE ULJLEB IC]GEL 000 LDD LDG PlclIcElu THE WORLD'S Nfour ACCUIRATE E RULES SUPPLEMENT TO MANUAL M-14 how to use ELIDE ULJLEB IC]GEL 000 LDD LDG PlclIcElu THE WORLD'S Nfour ACCUIRATE E RULES SUPPLEMENT TO MANUAL M-14](/thumbs/74/70098340.jpg) SUPPLEMENT TO MANUAL M-14 0 how to use IC]GEL 000 LDD LDG ELIDE ULJLEB 43Y PROFESSOR MAURICE L. HARTUNG THE UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO. I PlclIcElu THE WORLD'S Nfour ACCUIRATE 91.117E RULES PICKETT, INC. PICKETT
SUPPLEMENT TO MANUAL M-14 0 how to use IC]GEL 000 LDD LDG ELIDE ULJLEB 43Y PROFESSOR MAURICE L. HARTUNG THE UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO. I PlclIcElu THE WORLD'S Nfour ACCUIRATE 91.117E RULES PICKETT, INC. PICKETT
Try It! 30 minutes Groups of 4. Geometry
 3 7.G.4 Objective Common Core State Standards Circumference of a Circle and π Students look at the ratio of circumference to diameter for various circles and develop both an approximation of the value
3 7.G.4 Objective Common Core State Standards Circumference of a Circle and π Students look at the ratio of circumference to diameter for various circles and develop both an approximation of the value
Module 3 Slabbing, Skimming, Dry Lining and Floors UNIT: 9 Panel Moulding on Wall
 TRADE OF PLASTERING PHASE 2 Module 3 Slabbing, Skimming, Dry Lining and Floors UNIT: 9 Produced by In cooperation with subject matter expert: Terry Egan Some images & text courtesy of Gypsum Industries
TRADE OF PLASTERING PHASE 2 Module 3 Slabbing, Skimming, Dry Lining and Floors UNIT: 9 Produced by In cooperation with subject matter expert: Terry Egan Some images & text courtesy of Gypsum Industries
UNIT 6. BELL WORK: Draw 3 different sized circles, 1 must be at LEAST 15cm across! Cut out each circle. The Circle
 UNIT 6 BELL WORK: Draw 3 different sized circles, 1 must be at LEAST 15cm across! Cut out each circle The Circle 1 Questions How are perimeter and area related? How are the areas of polygons and circles
UNIT 6 BELL WORK: Draw 3 different sized circles, 1 must be at LEAST 15cm across! Cut out each circle The Circle 1 Questions How are perimeter and area related? How are the areas of polygons and circles
HONORS GEOMETRY SUMMER REVIEW PACKET (2012)
 HONORS GEOMETRY SUMMER REVIEW PACKET (01) The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous mathematics courses that are important to your success in Honors Geometry. Please
HONORS GEOMETRY SUMMER REVIEW PACKET (01) The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous mathematics courses that are important to your success in Honors Geometry. Please
As you work through the computer exercises, you will be prompted to make notes in your notebook/math journal.
 Concept: The Circle COMPUTER COMPONENT Name: Instructions: In follow the Content Menu path: Measurement and Geometry > Circles Work through all Sub Lessons of the following Lessons in order: In This Topic
Concept: The Circle COMPUTER COMPONENT Name: Instructions: In follow the Content Menu path: Measurement and Geometry > Circles Work through all Sub Lessons of the following Lessons in order: In This Topic
I.31 Now given a circular field, the circumference is 30 bu and the diameter 10 bu. Question: What is the area? Answer:
 Chapter 9 Areas of circular regions 9.1 Problems I31 38 1 I.31 Now given a circular field, the circumference is 30 bu and the diameter 10 bu. I.3 Given another circular field, the circumference is 181
Chapter 9 Areas of circular regions 9.1 Problems I31 38 1 I.31 Now given a circular field, the circumference is 30 bu and the diameter 10 bu. I.3 Given another circular field, the circumference is 181
SAT & ACT Foundations
 E SAT & ACT Foundations SA M PL MATHEMATICS (800) MY TUTOR Focusing on the Individual Student MYTUTOR.COM Copyright Statement The ACT & SAT Skills Book, along with all Summit Educational Group Course Materials,
E SAT & ACT Foundations SA M PL MATHEMATICS (800) MY TUTOR Focusing on the Individual Student MYTUTOR.COM Copyright Statement The ACT & SAT Skills Book, along with all Summit Educational Group Course Materials,
Integrated Mathematics I, II, III 2016 Scope and Sequence
 Mathematics I, II, III 2016 Scope and Sequence I Big Ideas Math 2016 Mathematics I, II, and III Scope and Sequence Number and Quantity The Real Number System (N-RN) Properties of exponents to rational
Mathematics I, II, III 2016 Scope and Sequence I Big Ideas Math 2016 Mathematics I, II, and III Scope and Sequence Number and Quantity The Real Number System (N-RN) Properties of exponents to rational
OALCF Task Cover Sheet
 Learner Name: OALCF Task Cover Sheet Date Started: Date Completed: Successful Completion: Yes No Goal Path: Employment Apprenticeship Secondary School Post Secondary Independence Task Description: Carpenters
Learner Name: OALCF Task Cover Sheet Date Started: Date Completed: Successful Completion: Yes No Goal Path: Employment Apprenticeship Secondary School Post Secondary Independence Task Description: Carpenters
Circles Test Circumference/Area Calculator Active. Clearly label the following in the circle to the right.
 Circles Test Circumference/Area Calculator Active Clearly label the following in the circle to the right. 1. Point B as the center 2. Diameter AC 3. Radius BD 4. Chord EF 5. Arc FG Find the following.
Circles Test Circumference/Area Calculator Active Clearly label the following in the circle to the right. 1. Point B as the center 2. Diameter AC 3. Radius BD 4. Chord EF 5. Arc FG Find the following.
English Measurement Relationships
 Math 30 Prealgebra Sec 10.1: Using Unit Fractions with U.S. and Metric Units Defn A unit fraction is a fraction that shows the relationship between units and is equal to 1. Ex English Measurement Relationships
Math 30 Prealgebra Sec 10.1: Using Unit Fractions with U.S. and Metric Units Defn A unit fraction is a fraction that shows the relationship between units and is equal to 1. Ex English Measurement Relationships
Trigonometric Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 4 Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.1 Radian and Degree Measure Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Describe angles. Use radian
4 Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.1 Radian and Degree Measure Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Describe angles. Use radian
What is the longest chord?.
 Section: 7-6 Topic: ircles and rcs Standard: 7 & 21 ircle Naming a ircle Name: lass: Geometry 1 Period: Date: In a plane, a circle is equidistant from a given point called the. circle is named by its.
Section: 7-6 Topic: ircles and rcs Standard: 7 & 21 ircle Naming a ircle Name: lass: Geometry 1 Period: Date: In a plane, a circle is equidistant from a given point called the. circle is named by its.
Unit 3, Lesson 2: Exploring Circles
 Unit 3, Lesson 2: Exploring Circles Lesson Goals Describe the characteristics that make something a circle. Be introduced to the terms diameter, center, radius, and circumference. Required Materials rulers
Unit 3, Lesson 2: Exploring Circles Lesson Goals Describe the characteristics that make something a circle. Be introduced to the terms diameter, center, radius, and circumference. Required Materials rulers
2008 Cayley Contest. Solutions
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 19, 008
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Cayley Contest (Grade 10) Tuesday, February 19, 008
1998 Harvard/MIT Math Tournament GEOMETRY Answer Sheet
 1998 Harvard/MIT Math Tournament GEOMETRY Answer Sheet Name: School: Grade: 1 7 2 8 3 9 4 10a 5 10b 6 10c TOTAL: GEOMETRY Question One. [3 points] Quadrilateral ALEX, pictured below (but not necessarily
1998 Harvard/MIT Math Tournament GEOMETRY Answer Sheet Name: School: Grade: 1 7 2 8 3 9 4 10a 5 10b 6 10c TOTAL: GEOMETRY Question One. [3 points] Quadrilateral ALEX, pictured below (but not necessarily
hmhco.com Adaptive. Intuitive. Transformative. AGA Scope and Sequence
 hmhco.com Adaptive. Intuitive. Transformative. AGA Algebra 1 Geometry Algebra 2 Scope and Sequence Number and Quantity The Real Number System (N-RN) Properties of exponents to rational exponents Properties
hmhco.com Adaptive. Intuitive. Transformative. AGA Algebra 1 Geometry Algebra 2 Scope and Sequence Number and Quantity The Real Number System (N-RN) Properties of exponents to rational exponents Properties
Applications of Advanced Mathematics (C4) Paper B: Comprehension TUESDAY 22 JANUARY 2008 Time:Upto1hour
 ADVANCED GCE 4754/01B MATHEMATICS (MEI) Applications of Advanced Mathematics (C4) Paper B: Comprehension TUESDAY JANUARY 008 Afternoon Time:Upto1hour Additional materials: Rough paper MEI Examination Formulae
ADVANCED GCE 4754/01B MATHEMATICS (MEI) Applications of Advanced Mathematics (C4) Paper B: Comprehension TUESDAY JANUARY 008 Afternoon Time:Upto1hour Additional materials: Rough paper MEI Examination Formulae
1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle.
 Master 8.17 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1 Properties of Tangents to a Circle 1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle. 2. Point O is the centre of the circle. Points
Master 8.17 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1 Properties of Tangents to a Circle 1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle. 2. Point O is the centre of the circle. Points
Applications of Advanced Mathematics (C4) Paper B: Comprehension INSERT. TUESDAY 22 JANUARY 2008 Time:Upto1hour
 VNE GE 4754/01 MTHEMTIS (MEI) pplications of dvanced Mathematics (4) Paper : omprehension INSERT TUESY JNURY 008 fternoon Time:Upto1hour INSTRUTIONS TO NITES This insert contains the text for use with
VNE GE 4754/01 MTHEMTIS (MEI) pplications of dvanced Mathematics (4) Paper : omprehension INSERT TUESY JNURY 008 fternoon Time:Upto1hour INSTRUTIONS TO NITES This insert contains the text for use with
AREA. The Square Inch The Square Foot The Square Yard. 1 foot. 1 foot. The Square Mile The Square Meter The Square Centimeter. 1 meter.
 Tallahassee Community College 48 AREA The area of a figure measures the surface of the figure. The unit of measure for area cannot be a linear unit. To measure area we use square units such as: The Square
Tallahassee Community College 48 AREA The area of a figure measures the surface of the figure. The unit of measure for area cannot be a linear unit. To measure area we use square units such as: The Square
UNIVERSITY OF LONDON GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION
 UNIVERSITY OF LONDON GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION Ordinary Level SUMMER, 1957 P U R E M A T H E M A T I C S (a) ARITHMETIC AND TRIGONOMETRY TUESDAY, June 18. Morning, 9.0 to 11.0 All necessary working
UNIVERSITY OF LONDON GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION Ordinary Level SUMMER, 1957 P U R E M A T H E M A T I C S (a) ARITHMETIC AND TRIGONOMETRY TUESDAY, June 18. Morning, 9.0 to 11.0 All necessary working
Unit 1: Geography and Social Studies Skills
 Unit 1: Geography and Social Studies Skills Standard(s) of Learning: WHI.1 The student will improve skills in historical research and geographical analysis by a) Identifying, analyzing, and interpreting
Unit 1: Geography and Social Studies Skills Standard(s) of Learning: WHI.1 The student will improve skills in historical research and geographical analysis by a) Identifying, analyzing, and interpreting
Sect 10.1 Angles and Triangles
 175 Sect 10.1 Angles and Triangles Objective 1: Converting Angle Units Each degree can be divided into 60 minutes, denoted 60', and each minute can be divided into 60 seconds, denoted 60". Hence, 1 = 60'
175 Sect 10.1 Angles and Triangles Objective 1: Converting Angle Units Each degree can be divided into 60 minutes, denoted 60', and each minute can be divided into 60 seconds, denoted 60". Hence, 1 = 60'
Guide to the Gunflint Research and Comparative Collection
 Guide to the Gunflint Research and Comparative Collection Author: BL, JM; 4/30/2007 Encoder: Creator of Collection: Carlyle S. Smith Collection Dates: 1957 1975 Acquisition Number: 2007.1 Repository: Archaeological
Guide to the Gunflint Research and Comparative Collection Author: BL, JM; 4/30/2007 Encoder: Creator of Collection: Carlyle S. Smith Collection Dates: 1957 1975 Acquisition Number: 2007.1 Repository: Archaeological
Math 8 Notes Unit 8: Area and Perimeter
 Math 8 Notes Unit 8: Area and Perimeter Syllabus Objective: (6.) The student will compute the perimeter and area of rectangles and parallelograms. Perimeter is defined as the distance around the outside
Math 8 Notes Unit 8: Area and Perimeter Syllabus Objective: (6.) The student will compute the perimeter and area of rectangles and parallelograms. Perimeter is defined as the distance around the outside
Preliminary chapter: Review of previous coursework. Objectives
 Preliminary chapter: Review of previous coursework Objectives By the end of this chapter the student should be able to recall, from Books 1 and 2 of New General Mathematics, the facts and methods that
Preliminary chapter: Review of previous coursework Objectives By the end of this chapter the student should be able to recall, from Books 1 and 2 of New General Mathematics, the facts and methods that
Example 1 Give the degree measure of the angle shown on the circle.
 Section 5. Angles 307 Section 5. Angles Because many applications involving circles also involve q rotation of the circle, it is natural to introduce a measure for the rotation, or angle, between two rays
Section 5. Angles 307 Section 5. Angles Because many applications involving circles also involve q rotation of the circle, it is natural to introduce a measure for the rotation, or angle, between two rays
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere
 The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
Circles and Circumference
 Practice A Circles and Circumference Point G is the center of the circle. Use it to answer each question. 1. Name the circle. 2. Name the diameter. 3. Name three radii. Find each missing value to the nearest
Practice A Circles and Circumference Point G is the center of the circle. Use it to answer each question. 1. Name the circle. 2. Name the diameter. 3. Name three radii. Find each missing value to the nearest
English 3 rd Grade A-L Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: May 31, 2013
 English 3 rd Grade A-L Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: May 31, 2013 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah
English 3 rd Grade A-L Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Revised: May 31, 2013 Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file match the Common Core, the math curriculum adopted by the Utah
Activity Sheet 1: Constructions
 Name ctivity Sheet 1: Constructions Date 1. Constructing a line segment congruent to a given line segment: Given a line segment B, B a. Use a straightedge to draw a line, choose a point on the line, and
Name ctivity Sheet 1: Constructions Date 1. Constructing a line segment congruent to a given line segment: Given a line segment B, B a. Use a straightedge to draw a line, choose a point on the line, and
Circumference and Arc Length
 Circumference and Arc Length Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Circumference and Arc Length Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
New Rochelle High School Geometry Summer Assignment
 NAME - New Rochelle High School Geometry Summer Assignment To all Geometry students, This assignment will help you refresh some of the necessary math skills you will need to be successful in Geometry and
NAME - New Rochelle High School Geometry Summer Assignment To all Geometry students, This assignment will help you refresh some of the necessary math skills you will need to be successful in Geometry and
Dawood Public School Course Outline Math Class IV
 Dawood Public School Course Outline 2017-18 Math Class IV MONTHS CONTENTS DURATION Place value + Comparing and Ordering Rounding off to the nearest 10 s and 100 s AUGUST Divisibility rule Multiplication
Dawood Public School Course Outline 2017-18 Math Class IV MONTHS CONTENTS DURATION Place value + Comparing and Ordering Rounding off to the nearest 10 s and 100 s AUGUST Divisibility rule Multiplication
4R & 4A Math Pacing Guides
 GRADING PERIOD: 1st Nine Weeks Getting to Know You - Community Building 4.14- Data a. Collect data, using observations, surveys, measurement, polls, or questionnaires. b. Organize data into a chart or
GRADING PERIOD: 1st Nine Weeks Getting to Know You - Community Building 4.14- Data a. Collect data, using observations, surveys, measurement, polls, or questionnaires. b. Organize data into a chart or
Meet #4. Math League SCASD. Self-study Packet. Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets):
 Math League SCASD Meet #4 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets): 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. : Properties of Circles 3. Number Theory: Modular Arithmetic,
Math League SCASD Meet #4 Self-study Packet Problem Categories for this Meet (in addition to topics of earlier meets): 1. Mystery: Problem solving 2. : Properties of Circles 3. Number Theory: Modular Arithmetic,
(A) 20% (B) 25% (C) 30% (D) % (E) 50%
 ACT 2017 Name Date 1. The population of Green Valley, the largest suburb of Happyville, is 50% of the rest of the population of Happyville. The population of Green Valley is what percent of the entire
ACT 2017 Name Date 1. The population of Green Valley, the largest suburb of Happyville, is 50% of the rest of the population of Happyville. The population of Green Valley is what percent of the entire
Trigonometric ratios:
 0 Trigonometric ratios: The six trigonometric ratios of A are: Sine Cosine Tangent sin A = opposite leg hypotenuse adjacent leg cos A = hypotenuse tan A = opposite adjacent leg leg and their inverses:
0 Trigonometric ratios: The six trigonometric ratios of A are: Sine Cosine Tangent sin A = opposite leg hypotenuse adjacent leg cos A = hypotenuse tan A = opposite adjacent leg leg and their inverses:
Key competencies (student abilities)
 Year 9 Mathematics Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics is accepted by universities and employers as proof of mathematical knowledge and understanding. Successful Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics candidates gain lifelong
Year 9 Mathematics Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics is accepted by universities and employers as proof of mathematical knowledge and understanding. Successful Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics candidates gain lifelong
CK-12 Geometry: Circumference and Arc Length
 CK-12 Geometry: Circumference and Arc Length Learning Objectives Find the circumference of a circle. Define the length of an arc and find arc length. Review Queue a. Find a central angle in that intercepts
CK-12 Geometry: Circumference and Arc Length Learning Objectives Find the circumference of a circle. Define the length of an arc and find arc length. Review Queue a. Find a central angle in that intercepts
A. 180 B. 108 C. 360 D. 540
 Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C. eight D. ten 3. The sum of the interior
Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C. eight D. ten 3. The sum of the interior
Calculating methods. Addition. Multiplication. Th H T U Th H T U = Example
 1 Addition Calculating methods Example 534 + 2678 Place the digits in the correct place value columns with the numbers under each other. Th H T U Begin adding in the units column. 5 3 4 + 12 16 17 8 4+8
1 Addition Calculating methods Example 534 + 2678 Place the digits in the correct place value columns with the numbers under each other. Th H T U Begin adding in the units column. 5 3 4 + 12 16 17 8 4+8
CCE RR. Œ æ fl : V {}
 SL. No. : J Jlflo Æ ÀÊ-V MSÊ : 40 ] [ Jlflo» flfl } Æ lv MSÊ : 1 CCE RR Total No. of Questions : 40 ] [ Total No. of Printed Pages : 1 MOÊfi} MSÊ : 81-E Code No. : 81-E Œ æ fl : V {} Subject : MATHEMATICS
SL. No. : J Jlflo Æ ÀÊ-V MSÊ : 40 ] [ Jlflo» flfl } Æ lv MSÊ : 1 CCE RR Total No. of Questions : 40 ] [ Total No. of Printed Pages : 1 MOÊfi} MSÊ : 81-E Code No. : 81-E Œ æ fl : V {} Subject : MATHEMATICS
Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Paper 1 (Core) May/June minutes
 *2660893404* Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICS 0607/11 Paper 1 (Core) May/June 2014 45 minutes Candidates
*2660893404* Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICS 0607/11 Paper 1 (Core) May/June 2014 45 minutes Candidates
THIS IS HOW I SEE IT (1 HOUR)
 (1 HOUR) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: 3-5 (with 6th Grade Extentions) OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct interactive lunar cycle models to illustrate the phases of
(1 HOUR) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: 3-5 (with 6th Grade Extentions) OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct interactive lunar cycle models to illustrate the phases of
Around the corner. Mathematics B-day 2015, Friday November 13, 9:00h-16:00h
 Around the corner Mathematics B-day 2015, Friday November 13, 9:00h-16:00h Exploration 1 (Piano) You have to move a heavy piano through a 1 meter wide corridor with a right-angled corner in it. The figure
Around the corner Mathematics B-day 2015, Friday November 13, 9:00h-16:00h Exploration 1 (Piano) You have to move a heavy piano through a 1 meter wide corridor with a right-angled corner in it. The figure
Name Period Date. GEO2.2: Area of Circles Derive the area formula for circles. Solve application problems that involve areas of circles.
 Name Period Date GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT Student Pages for Packet 2: Circles GEO2.1 Circumference Use multiple representations to explore the relationship between the diameter and the circumference of
Name Period Date GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT Student Pages for Packet 2: Circles GEO2.1 Circumference Use multiple representations to explore the relationship between the diameter and the circumference of
KEY STANDARDS ADDRESSED: MM2G3. Students will understand the properties of circles.
 KEY STANDARDS ADDRESSED:. Students will understand the properties of circles. a. Understand and use properties of chords, tangents, and secants an application of triangle similarity. b. Understand and
KEY STANDARDS ADDRESSED:. Students will understand the properties of circles. a. Understand and use properties of chords, tangents, and secants an application of triangle similarity. b. Understand and
150 Lecture Notes - Section 6.1 Angle Measure
 c Marcia Drost, February, 008 Definition of Terms 50 Lecture Notes - Section 6. Angle Measure ray a line angle vertex two rays with a common endpoint the common endpoint initial side terminal side Standard
c Marcia Drost, February, 008 Definition of Terms 50 Lecture Notes - Section 6. Angle Measure ray a line angle vertex two rays with a common endpoint the common endpoint initial side terminal side Standard
MATHEMATICS Compulsory Part PAPER 1. Question-Answer Book. Please stick the barcode label here. 2017/18-ME MATH CP PAPER 1 HOK YAU CLUB
 2017/18-ME MATH CP PAPER 1 HOK YAU CLUB HONG KONG MOCK EXAMINATION 2017/18 Please stick the barcode label here. MATHEMATICS Compulsory Part PAPER 1 Question-Answer Book 9.00 am - 11.15 am (2¼ hours) Candidate
2017/18-ME MATH CP PAPER 1 HOK YAU CLUB HONG KONG MOCK EXAMINATION 2017/18 Please stick the barcode label here. MATHEMATICS Compulsory Part PAPER 1 Question-Answer Book 9.00 am - 11.15 am (2¼ hours) Candidate
3RD GRADE COMMON CORE VOCABULARY A-L
 o o o 3RD GRADE COMMON CORE VOCABULARY A-L For possible additions or corrections to the vocabulary cards, please contact the Granite School District Math Department at 385-646-4239. a.m. a.m. 12:00 A.M.
o o o 3RD GRADE COMMON CORE VOCABULARY A-L For possible additions or corrections to the vocabulary cards, please contact the Granite School District Math Department at 385-646-4239. a.m. a.m. 12:00 A.M.
Solutions to the Exercises of Chapter 5
 Solutions to the Eercises of Chapter 5 5A. Lines and Their Equations. The slope is 5 5. Since (, is a point on the line, y ( ( is an ( 6 8 8 equation of the line in point-slope form. This simplifies to
Solutions to the Eercises of Chapter 5 5A. Lines and Their Equations. The slope is 5 5. Since (, is a point on the line, y ( ( is an ( 6 8 8 equation of the line in point-slope form. This simplifies to
STUDY GUIDE Math 20. To accompany Intermediate Algebra for College Students By Robert Blitzer, Third Edition
 STUDY GUIDE Math 0 To the students: To accompany Intermediate Algebra for College Students By Robert Blitzer, Third Edition When you study Algebra, the material is presented to you in a logical sequence.
STUDY GUIDE Math 0 To the students: To accompany Intermediate Algebra for College Students By Robert Blitzer, Third Edition When you study Algebra, the material is presented to you in a logical sequence.
Physics 101. Hour Exam I Spring Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name:
 Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators may not be shared. Please keep your calculator on your own desk.
Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Calculators may not be shared. Please keep your calculator on your own desk.
SURNAME... FIRST NAME... (Block capitals, please) JUNIOR SCHOOL... SENIOR SCHOOL... COMMON ENTRANCE EXAMINATION AT 13+ MATHEMATICS PAPER 3
 SURNAME... FIRST NAME... (Block capitals, please) JUNIOR SCHOOL... SENIOR SCHOOL... COMMON ENTRANCE EXAMINATION AT 13+ MATHEMATICS PAPER 3 Calculator Paper Tuesday 28 February 2006 Please read this information
SURNAME... FIRST NAME... (Block capitals, please) JUNIOR SCHOOL... SENIOR SCHOOL... COMMON ENTRANCE EXAMINATION AT 13+ MATHEMATICS PAPER 3 Calculator Paper Tuesday 28 February 2006 Please read this information
Odd numbers 4 2 = 4 X 4 = 16
 Even numbers Square numbers 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 1 2 = 1 x 1 = 1 2 divides exactly into every even number. 2 2 = 2 x 2 = 4 3 2 = 3 x 3 = 9 Odd numbers 4 2 = 4 X 4 = 16 5 2 = 5 X 5 = 25 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 6
Even numbers Square numbers 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 1 2 = 1 x 1 = 1 2 divides exactly into every even number. 2 2 = 2 x 2 = 4 3 2 = 3 x 3 = 9 Odd numbers 4 2 = 4 X 4 = 16 5 2 = 5 X 5 = 25 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 6
Wheels Radius / Distance Traveled
 Mechanics Teacher Note to the teacher On these pages, students will learn about the relationships between wheel radius, diameter, circumference, revolutions and distance. Students will use formulas relating
Mechanics Teacher Note to the teacher On these pages, students will learn about the relationships between wheel radius, diameter, circumference, revolutions and distance. Students will use formulas relating
5.3 Multiplying Decimals
 370 CHAPTER 5. DECIMALS 5.3 Multiplying Decimals Multiplying decimal numbers involves two steps: (1) multiplying the numbers as whole numbers, ignoring the decimal point, and (2) placing the decimal point
370 CHAPTER 5. DECIMALS 5.3 Multiplying Decimals Multiplying decimal numbers involves two steps: (1) multiplying the numbers as whole numbers, ignoring the decimal point, and (2) placing the decimal point
PART 1 LINKS. The Cole Error, Duration of the Natural Second of Time and the Speed of Light.
 PART 1 LINKS The Cole Error, Duration of the Natural Second of Time and the Speed of Light. In 1925 the Egyptian government hired English surveyor J.H. Cole to determine the Great Pyramid s true orientation
PART 1 LINKS The Cole Error, Duration of the Natural Second of Time and the Speed of Light. In 1925 the Egyptian government hired English surveyor J.H. Cole to determine the Great Pyramid s true orientation
MENSURATION. Mensuration is the measurement of lines, areas, and volumes. Before, you start this pack, you need to know the following facts.
 MENSURATION Mensuration is the measurement of lines, areas, and volumes. Before, you start this pack, you need to know the following facts. When you see kilo, it indicates 000 in length, mass and capacity.
MENSURATION Mensuration is the measurement of lines, areas, and volumes. Before, you start this pack, you need to know the following facts. When you see kilo, it indicates 000 in length, mass and capacity.
Wednesday 3 June 2015 Morning
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Wednesday 3 June 015 Morning AS GCE MATHEMATICS (MEI) 475/01 Concepts for Advanced Mathematics (C) QUESTION PAPER * 3 6 7 4 8 0 7 8 7 * Candidates answer on the Printed Answer
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Wednesday 3 June 015 Morning AS GCE MATHEMATICS (MEI) 475/01 Concepts for Advanced Mathematics (C) QUESTION PAPER * 3 6 7 4 8 0 7 8 7 * Candidates answer on the Printed Answer
NOTE The book 'Eight Essays on Geometry for an Oral Tradition' will hopefully be available later in 2016, free online
 THREE BOOKS AND A PAPER: A GEOMETRY PROJECT Andrew Nicholas ABSTRACT The aim of the project was to produce a sort of miniature Vedic mathematics version of Euclid's 'Elements', covering much less ground
THREE BOOKS AND A PAPER: A GEOMETRY PROJECT Andrew Nicholas ABSTRACT The aim of the project was to produce a sort of miniature Vedic mathematics version of Euclid's 'Elements', covering much less ground
Complete E3. Copyright Mathster.com Licensed to Matthew Moss High School, Rochdale. 2) Round to 2 significant figures [7] g) 0.
![Complete E3. Copyright Mathster.com Licensed to Matthew Moss High School, Rochdale. 2) Round to 2 significant figures [7] g) 0. Complete E3. Copyright Mathster.com Licensed to Matthew Moss High School, Rochdale. 2) Round to 2 significant figures [7] g) 0.](/thumbs/83/88085963.jpg) Complete E Name: Class: Date: Mark ) Round to significant figure [] a) b) c) d). e) 0.0 f) 0. ) Round to significant figures [] a) b) c). d). e) 0. f) 0.0 g) 0.0 ) Estimate the answer by rounding each
Complete E Name: Class: Date: Mark ) Round to significant figure [] a) b) c) d). e) 0.0 f) 0. ) Round to significant figures [] a) b) c). d). e) 0. f) 0.0 g) 0.0 ) Estimate the answer by rounding each
Unit 3, Lesson 1: How Well Can You Measure?
 Unit 3, Lesson 1: How Well Can You Measure? 1. Estimate the side length of a square that has a 9 cm long diagonal. 2. Select all quantities that are proportional to the diagonal length of a square. A.
Unit 3, Lesson 1: How Well Can You Measure? 1. Estimate the side length of a square that has a 9 cm long diagonal. 2. Select all quantities that are proportional to the diagonal length of a square. A.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICS 0607/13 Paper 1 (Core) May/June 2017 5 minutes Candidates answer
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICS 0607/13 Paper 1 (Core) May/June 2017 5 minutes Candidates answer
Review Topics. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review Topics MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. On the real number line, label the points with the given coordinates. 1) 11,- 11 1)
Review Topics MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. On the real number line, label the points with the given coordinates. 1) 11,- 11 1)
UNC Charlotte Super Competition Comprehensive Test March 5, 2018
 Solutions. A survey of 60 graduate and undegraduate students attending a university found that 9 were living off campus and 36 were undergraduates. Also, 3 were undergraduates living off campus. How many
Solutions. A survey of 60 graduate and undegraduate students attending a university found that 9 were living off campus and 36 were undergraduates. Also, 3 were undergraduates living off campus. How many
Taking away works in exactly the same way as adding. The only difference is that the final answer has a take away sign in place of the add sign.
 Taking away works in exactly the same way as adding. The only difference is that the final answer has a take away sign in place of the add sign. Example Take away, giving your answer as a single fraction
Taking away works in exactly the same way as adding. The only difference is that the final answer has a take away sign in place of the add sign. Example Take away, giving your answer as a single fraction
Section 3.2 Applications of Radian Measure
 Section. Applications of Radian Measure 07 (continued) 88. 80 radians = = 0 5 5 80 radians = = 00 7 5 = 5 radian s 0 = 0 radian s = radian 80 89. (a) In hours, the hour hand will rotate twice around the
Section. Applications of Radian Measure 07 (continued) 88. 80 radians = = 0 5 5 80 radians = = 00 7 5 = 5 radian s 0 = 0 radian s = radian 80 89. (a) In hours, the hour hand will rotate twice around the
Circles Unit Test. Secondary Math II
 Circles Unit Test Secondary Math II 1. Which pair of circles described are congruent to each other? Circle M has a radius of 6 m; Circle N has a diameter of 10 m. Circle J has a circumference of in; Circle
Circles Unit Test Secondary Math II 1. Which pair of circles described are congruent to each other? Circle M has a radius of 6 m; Circle N has a diameter of 10 m. Circle J has a circumference of in; Circle
Write an equation and solve for x, then find the missing angle measures. Pictures are not drawn to scale. 1. Equation: Solution: Equation: Solution:
 6.1d Class Activity: Triangles and Circles In chapter 5, you worked with angle measures in triangles. Now, you are going to practice writing equations to solve for a missing angle measure. Recall from
6.1d Class Activity: Triangles and Circles In chapter 5, you worked with angle measures in triangles. Now, you are going to practice writing equations to solve for a missing angle measure. Recall from
Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts
 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #4 February, 2002 Category 1 Mystery You may use a calculator today! 1. Margie had a 3-by-3-by-3 cube, a 4-by-4-by-4 cube, and a 5-by-5-by-5
Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #4 February, 2002 Category 1 Mystery You may use a calculator today! 1. Margie had a 3-by-3-by-3 cube, a 4-by-4-by-4 cube, and a 5-by-5-by-5
11.2 Start Thinking Warm Up Cumulative Review Warm Up
 11.2 Start Thinking The circle in the diagram has a diameter of 14 inches. What is the area of the circle? Use the area of the circle to calculate the area of the sector created b the given measure of
11.2 Start Thinking The circle in the diagram has a diameter of 14 inches. What is the area of the circle? Use the area of the circle to calculate the area of the sector created b the given measure of
Algebra 2 End of Course Review
 1 Natural numbers are not just whole numbers. Integers are all whole numbers both positive and negative. Rational or fractional numbers are all fractional types and are considered ratios because they divide
1 Natural numbers are not just whole numbers. Integers are all whole numbers both positive and negative. Rational or fractional numbers are all fractional types and are considered ratios because they divide
. 7.9A STUDENT ACTIVITY #1
 . 7.9A STUDENT ACTIVITY #1 Problem #1: Morgan is designing a circular spirit sign to put in the front yard of the middle school athletes. The sign will have a circumference of 94 inches. What is the minimum
. 7.9A STUDENT ACTIVITY #1 Problem #1: Morgan is designing a circular spirit sign to put in the front yard of the middle school athletes. The sign will have a circumference of 94 inches. What is the minimum
Trigonometric Functions and Triangles
 Trigonometric Functions and Triangles Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw STate University Abstract This handout defines the trigonometric function of angles and discusses the relationship between trigonometric
Trigonometric Functions and Triangles Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw STate University Abstract This handout defines the trigonometric function of angles and discusses the relationship between trigonometric
NUMERACY TOOLKIT TOOLKIT NUMERACY
 NUMERACY TOOLKIT TOOLKIT NUMERACY Addition Calculating methods Example 534 + 2678 Place the digits in the correct place value columns with the numbers under each other. Th H T U Begin adding in the units
NUMERACY TOOLKIT TOOLKIT NUMERACY Addition Calculating methods Example 534 + 2678 Place the digits in the correct place value columns with the numbers under each other. Th H T U Begin adding in the units
Common Core State Standards for Mathematics Integrated Pathway: Mathematics I
 A CORRELATION OF TO THE Standards for Mathematics A Correlation of Table of Contents Unit 1: Relationships between Quantities... 1 Unit 2: Linear and Exponential Relationships... 4 Unit 3: Reasoning with
A CORRELATION OF TO THE Standards for Mathematics A Correlation of Table of Contents Unit 1: Relationships between Quantities... 1 Unit 2: Linear and Exponential Relationships... 4 Unit 3: Reasoning with
Finding a Percent of a Number (page 216)
 LESSON Name 1 Finding a Percent of a Number (page 216) You already know how to change a percent to a fraction. Rewrite the percent as a fraction with a denominator of 100 and reduce. 25% = 25 100 = 1 5%
LESSON Name 1 Finding a Percent of a Number (page 216) You already know how to change a percent to a fraction. Rewrite the percent as a fraction with a denominator of 100 and reduce. 25% = 25 100 = 1 5%
Chapter 8. Chapter 8 Opener. Section 8.1. Big Ideas Math Red Accelerated Worked-Out Solutions 4 7 = = 4 49 = = 39 = = 3 81 = 243
 Chapter 8 Opener Try It Yourself (p. 35). trapezoids. circles Large Perimeter Diameter Small Perimeter Diameter Average of Ratios 3. trapezoid, triangle. triangles 5. rectangle, triangle 6. rectangle,
Chapter 8 Opener Try It Yourself (p. 35). trapezoids. circles Large Perimeter Diameter Small Perimeter Diameter Average of Ratios 3. trapezoid, triangle. triangles 5. rectangle, triangle 6. rectangle,
Topics in Mathematics: Mathematics and Music Section 1.1: Musical Notation and a Geometric Property January 25, 2018
 Topics in Mathematics: Mathematics and Music Section.: Musical Notation and a Geometric Property January 5, 08 Duration: Geometric Sequences note head stem flag = Figure : Some basic symbols and terminology
Topics in Mathematics: Mathematics and Music Section.: Musical Notation and a Geometric Property January 5, 08 Duration: Geometric Sequences note head stem flag = Figure : Some basic symbols and terminology
ACCUPLACER Sample Questions for Students
 ACCUPLACER Sample Questions for Students 0 The College Board. College Board, ACCUPLACER, WritePlacer and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. All other products and services may
ACCUPLACER Sample Questions for Students 0 The College Board. College Board, ACCUPLACER, WritePlacer and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. All other products and services may
Mathematics 4306/2H (Specification A)
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Time allowed hours General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 011 Mathematics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Time allowed hours General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier June 011 Mathematics
Angle Measurement. By Myron Berg Dickinson State University
 Angle Measurement By Myron Berg Dickinson State University abstract This PowerPoint deck was created for a presentation. I discuss some ways other than degrees or radians in which angles are measured Instead
Angle Measurement By Myron Berg Dickinson State University abstract This PowerPoint deck was created for a presentation. I discuss some ways other than degrees or radians in which angles are measured Instead
EXPLAINING AREA AND CIRCUMFERENCE OF A CIRCLE
 1 EXPLAINING AREA AND CIRCUMFERENCE OF A CIRCLE INSTRUCTIONAL ACTIVITY Lesson 1 LEARNING GOAL Students will develop an understanding of diameter, radius, circumference, and pi and the relationships among
1 EXPLAINING AREA AND CIRCUMFERENCE OF A CIRCLE INSTRUCTIONAL ACTIVITY Lesson 1 LEARNING GOAL Students will develop an understanding of diameter, radius, circumference, and pi and the relationships among
Honors Geometry Circle Investigation - Instructions
 Honors Geometry ircle Investigation - Instructions 1. On the first circle a. onnect points and O with a line segment. b. onnect points O and also. c. Measure O. d. Estimate the degree measure of by using
Honors Geometry ircle Investigation - Instructions 1. On the first circle a. onnect points and O with a line segment. b. onnect points O and also. c. Measure O. d. Estimate the degree measure of by using
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning. Progressive Mathematics Initiative
 Slide 1 / 150 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
Slide 1 / 150 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
20th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Qualifying Stage, 28 October 2017
 0th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Qualifying Stage, 8 October 017 A project of the Mathematical Society of the Philippines (MSP) and the Department of Science and Technology - Science Education Institute
0th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Qualifying Stage, 8 October 017 A project of the Mathematical Society of the Philippines (MSP) and the Department of Science and Technology - Science Education Institute
