Circulation and Vorticity. The tangential linear velocity of a parcel on a rotating body is related to angular velocity of the body by the relation
|
|
|
- John Norton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Circulation and Vorticity 1. Conservation of Absolute Angular Momentum The tangential linear velocity of a parcel on a rotating body is related to angular velocity of the body by the relation V = ωr (1) If equation (1) is applied to a point on the rotating earth, ω is the angular velocity of the earth and r is the radial distance to the axis of rotation, r = R cos ø where R is the radius of the earth and ø is latitude. 1 Angular momentum is defined as Vr and, in the absence of torques, absolute angular momentum (that is, angular momentum relative to a stationary observer in space) is conserved [ ] = constant (2) ( Vr) a = Vr + Vr ( ) e where V e is the tangential velocity of the earth surface. This is the quantitative basis for the ballet dancer effect. Equation (2) states that the absolute angular momentum of a parcel of air is the sum of the angular momentum imparted to the air parcel by the rotating surface of the earth and angular momentum due to the motion of the air parcel relative to the rotating surface of the earth (where the subscript r for relative to the earth is dropped. Put (1) into (2) ( ωr 2 ) a = constant (3) 1 The symbol ω is also used to denote the vertical velocity in the x, y, p coordinate system. 1
2 Example Problem: An air parcel at rest with respect to the surface of the earth at the equator in the upper troposphere moves northward to 30N because of the Hadley Cell circulation. Assuming that absolute angular momentum is conserved, what tangential velocity would the air parcel possess relative to the earth upon reaching 30N? ( ωr 2 ) = Vr a [ ] = constant (1) ( ) a = Vr + ( Vr) e Note that ω is positive if rotation is counterclockwise relative to North Pole. Thus, V is positive if the zonal motion vector is oriented west to east. [ ] = Vr + Vr f [ ] i (2) Vr + ( Vr) e ( ) e Solve for V f, the tangential velocity relative to the earth at the final latitude. ([ V f = Vr + ( Vr ) e ] i [( Vr) e ] ) f r f (3) r = radial distance to axis of rotation = Rcosϕ (4) V e = ΩRcosϕ (5) where is the angular velocity of the earth, X10-5 s -1. 2
3 Substitute (5) into (3) and simplify by inserting initial V i = 0 and remembering that the average radius of the earth is 6378 km we get V f = km h -1 Clearly, though such wind speeds are not observed at 30N in the upper troposphere, this exercise proves that there should be a belt of fast moving winds in the upper troposphere unrelated to baroclinic considerations (i.e., thermal wind) and only related to conservation of absolute angular momentum. In the real atmosphere, such speeds are not observed (the subtropical jet stream speeds are on the order of 200 km/hr) because of viscosity/frictional effects. 2. Circulation: General Circulation is the macroscopic measure of swirl in a fluid. It is a precise measure of the average flow of fluid along a given closed curve. Mathematically, horizontal (around a vertical axis) circulation is given by V d s VΔs ( ) (6) For an air column with circular cross-sectional area πr 2 turning with a constant angular velocity ω, where V = ω r, the distance s is given by the circumference 2πr, the circulation V s is given by C = 2πωr 2 (7a) or 3
4 C πr 2 = 2ω = ζ (7b) Note that the "omega" in equations (7a and b) represents the air parcel's angular velocity relative to an axis perpendicular to the surface of the earth. Equations (3) and (5a) tell us that circulation is directly proportional to angular momentum. The fundamental definition of vorticity is (2ω), that is, twice the local angular velocity. Thus, rearranging (7a) shows that circulation per unit area is the vorticity, and is directly proportional to (but not the same as) angular velocity of the fluid. Vorticity, then, is the microscopic measure of swirl and is the vector measure of the tendency of the fluid element to rotate around an axis through its center of mass. At the North Pole, an air column with circular cross sectional area at rest with respect to the surface of the earth would have a circulation relative to a stationary observer in space due to the rotation of the earth around the local vertical, Equation (7c). C e = 2πω e r 2 = 2πΩsinφr 2 = fπr 2 (8a) or C e πr 2 = 2Ωsinφ = f = ζ e (8b) Thus, the circulation imparted to a an air column by the rotation of the earth is just the Coriolis parameter times the area of the air column. Dividing both sides by the area shows that the Coriolis parameter is just the "earth's vorticity." 4
5 An observer in space would note that the total or absolute circulation experienced by the air column is due to the circulation imparted to the column by the rotating surface of the earth AND the circulation that the column possesses relative to the earth. C a = C e + C (9) Where C is the circulation the air column has relative to the earth. Thus, dividing (8) by the area of the air column yields # C & % ( $ πr 2 ' a # = f + C & % ( $ πr 2 ' or (10a,b) ζ a = f +ζ which states that absolute vorticity is the relative vorticity plus earth s vorticity (Coriolis parameter). 2. Real Torques In reality circulation can occur around the three coordinate axes (two for the natural coordinate system). In natural coordinates the wind components are V and w and absolute circulation can be written C a = Vds + wdz (12) The change in absolute circulation (assuming that ds and dz do not change) would be given by 5
6 dc a = dv ds + dw dz (13) Substitution of the horizontal and vertical equations of motion into (13) dc a = dp ρ (14) where dp is the variation of pressure along the length of the circuit being considered. The term to the right of the equals sign is known as the solenoid term. A solenoid is the trapezoidal figure created if isobars and isopycnics intersect. At a given pressure, density is inversely proportional to temperature. Hence, a solenoid is the trapezoidal figure created if isobars and isotherms intersect. Equation (14) states that circulation will develop (increase or decrease) only when isotherms are inclined with respect to isobars (known as a baroclinic state). When isotherms are parallel to isobars (known as a barotropic state), no circulation development can occur. (Remember, we are assuming no frictional torques.) 3. Simplified Vorticity Equation From the discussions above absolute circulation can be stated as C a = ζ a A (1) where ζ α is the absolute vorticity Taking the time derivative of both sides 6
7 dc a = d ( ζ a A) # da& # = ζ a % ( + A dζ a % $ ' $ & ( (2) ' Assuming no torques so that absolute circulation is conserved dc a / = 0, and 1 " da% A $ ' = # & 1 " ζ $ a # dζ a % ' (3) & Applying the fundamental definition of divergence DIV h = 1 $ ζ & a % dζ a ' ) (4) ( Equation (4) is the simplified vorticity equation. It states that the change in absolute vorticity (proportional to absolute angular velocity) experienced by an air parcel is due to divergence or convergence. This analgous to the principle of conservation of absolute angular momentum applied at a microscopic level. This is the so-called ballet dancer effect applied to a fluid parcel. Please remember that (4) is simplified. It applies only in extremely restrictive circumstances. Near fronts, sea-breeze boundaries, outflow boundaries etc., equation (4) will not work, since it does not contain the solenoidal effects discussed in class. 7
Circulation and Vorticity. The tangential linear velocity of a parcel on a rotating body is related to angular velocity of the body by the relation
 Circulation and Vticity 1. Conservation of Absolute Angular Momentum The tangential linear velocity of a parcel on a rotating body is related to angular velocity of the body by the relation V = ωr (1)
Circulation and Vticity 1. Conservation of Absolute Angular Momentum The tangential linear velocity of a parcel on a rotating body is related to angular velocity of the body by the relation V = ωr (1)
1/25/2010. Circulation and vorticity are the two primary
 Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
Circulation and Vorticity
 Circulation and Vorticity Example: Rotation in the atmosphere water vapor satellite animation Circulation a macroscopic measure of rotation for a finite area of a fluid Vorticity a microscopic measure
Circulation and Vorticity Example: Rotation in the atmosphere water vapor satellite animation Circulation a macroscopic measure of rotation for a finite area of a fluid Vorticity a microscopic measure
Measurement of Rotation. Circulation. Example. Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity 1/31/2017
 Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
By convention, C > 0 for counterclockwise flow, hence the contour must be counterclockwise.
 Chapter 4 4.1 The Circulation Theorem Circulation is a measure of rotation. It is calculated for a closed contour by taking the line integral of the velocity component tangent to the contour evaluated
Chapter 4 4.1 The Circulation Theorem Circulation is a measure of rotation. It is calculated for a closed contour by taking the line integral of the velocity component tangent to the contour evaluated
Using simplified vorticity equation,* by assumption 1 above: *Metr 430 handout on Circulation and Vorticity. Equations (4) and (5) on that handout
 Rossby Wave Equation A. Assumptions 1. Non-divergence 2. Initially, zonal flow, or nearly zonal flow in which u>>v>>w. 3. Initial westerly wind is geostrophic and does not vary along the x-axis and equations
Rossby Wave Equation A. Assumptions 1. Non-divergence 2. Initially, zonal flow, or nearly zonal flow in which u>>v>>w. 3. Initial westerly wind is geostrophic and does not vary along the x-axis and equations
Fixed Rossby Waves: Quasigeostrophic Explanations and Conservation of Potential Vorticity
 Fixed Rossby Waves: Quasigeostrophic Explanations and Conservation of Potential Vorticity 1. Observed Planetary Wave Patterns After upper air observations became routine, it became easy to produce contour
Fixed Rossby Waves: Quasigeostrophic Explanations and Conservation of Potential Vorticity 1. Observed Planetary Wave Patterns After upper air observations became routine, it became easy to produce contour
Chapter 7: Circulation and Vorticity
 Chapter 7: Circulation and Vorticity Circulation C = u ds Integration is performed in a counterclockwise direction C is positive for counterclockwise flow!!! Kelvin s Circulation Theorem The rate of change
Chapter 7: Circulation and Vorticity Circulation C = u ds Integration is performed in a counterclockwise direction C is positive for counterclockwise flow!!! Kelvin s Circulation Theorem The rate of change
Effective Depth of Ekman Layer.
 5.5: Ekman Pumping Effective Depth of Ekman Layer. 2 Effective Depth of Ekman Layer. Defining γ = f/2k, we derived the solution u = u g (1 e γz cos γz) v = u g e γz sin γz corresponding to the Ekman spiral.
5.5: Ekman Pumping Effective Depth of Ekman Layer. 2 Effective Depth of Ekman Layer. Defining γ = f/2k, we derived the solution u = u g (1 e γz cos γz) v = u g e γz sin γz corresponding to the Ekman spiral.
= vorticity dilution + tilting horizontal vortices + microscopic solenoid
 4.4 Vorticity Eq 4.4.1 Cartesian Coordinates Because ζ = ˆk V, gives D(ζ + f) x minus [v momentum eq. in Cartesian Coordinates] y [u momentum eq. in Cartesian Coordinates] = vorticity dilution + tilting
4.4 Vorticity Eq 4.4.1 Cartesian Coordinates Because ζ = ˆk V, gives D(ζ + f) x minus [v momentum eq. in Cartesian Coordinates] y [u momentum eq. in Cartesian Coordinates] = vorticity dilution + tilting
Dynamics Rotating Tank
 Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science - IACETH Atmospheric Physics Lab Work Dynamics Rotating Tank Large scale flows on different latitudes of the rotating Earth Abstract The large scale atmospheric
Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science - IACETH Atmospheric Physics Lab Work Dynamics Rotating Tank Large scale flows on different latitudes of the rotating Earth Abstract The large scale atmospheric
Part 4. Atmospheric Dynamics
 Part 4. Atmospheric Dynamics We apply Newton s Second Law: ma =Σ F i to the atmosphere. In Cartesian coordinates dx u = dt dy v = dt dz w = dt 1 ai = F m i i du dv dw a = ; ay = ; az = x dt dt dt 78 Coordinate
Part 4. Atmospheric Dynamics We apply Newton s Second Law: ma =Σ F i to the atmosphere. In Cartesian coordinates dx u = dt dy v = dt dz w = dt 1 ai = F m i i du dv dw a = ; ay = ; az = x dt dt dt 78 Coordinate
Mathematical Concepts & Notation
 Mathematical Concepts & Notation Appendix A: Notation x, δx: a small change in x t : the partial derivative with respect to t holding the other variables fixed d : the time derivative of a quantity that
Mathematical Concepts & Notation Appendix A: Notation x, δx: a small change in x t : the partial derivative with respect to t holding the other variables fixed d : the time derivative of a quantity that
t tendency advection convergence twisting baroclinicity
 RELATIVE VORTICITY EQUATION Newton s law in a rotating frame in z-coordinate (frictionless): U + U U = 2Ω U Φ α p U + U U 2 + ( U) U = 2Ω U Φ α p Applying to both sides, and noting ω U and using identities
RELATIVE VORTICITY EQUATION Newton s law in a rotating frame in z-coordinate (frictionless): U + U U = 2Ω U Φ α p U + U U 2 + ( U) U = 2Ω U Φ α p Applying to both sides, and noting ω U and using identities
A Summary of Some Important Points about the Coriolis Force/Mass. D a U a Dt. 1 ρ
 A Summary of Some Important Points about the Coriolis Force/Mass Introduction Newton s Second Law applied to fluids (also called the Navier-Stokes Equation) in an inertial, or absolute that is, unaccelerated,
A Summary of Some Important Points about the Coriolis Force/Mass Introduction Newton s Second Law applied to fluids (also called the Navier-Stokes Equation) in an inertial, or absolute that is, unaccelerated,
Part-8c Circulation (Cont)
 Part-8c Circulation (Cont) Global Circulation Means of Transfering Heat Easterlies /Westerlies Polar Front Planetary Waves Gravity Waves Mars Circulation Giant Planet Atmospheres Zones and Belts Global
Part-8c Circulation (Cont) Global Circulation Means of Transfering Heat Easterlies /Westerlies Polar Front Planetary Waves Gravity Waves Mars Circulation Giant Planet Atmospheres Zones and Belts Global
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
u g z = g T y (1) f T Margules Equation for Frontal Slope
 Margules Equation for Frontal Slope u g z = g f T T y (1) Equation (1) is the thermal wind relation for the west wind geostrophic component of the flow. For the purposes of this derivation, we assume that
Margules Equation for Frontal Slope u g z = g f T T y (1) Equation (1) is the thermal wind relation for the west wind geostrophic component of the flow. For the purposes of this derivation, we assume that
Models of ocean circulation are all based on the equations of motion.
 Equations of motion Models of ocean circulation are all based on the equations of motion. Only in simple cases the equations of motion can be solved analytically, usually they must be solved numerically.
Equations of motion Models of ocean circulation are all based on the equations of motion. Only in simple cases the equations of motion can be solved analytically, usually they must be solved numerically.
Dynamic Meteorology - Introduction
 Dynamic Meteorology - Introduction Atmospheric dynamics the study of atmospheric motions that are associated with weather and climate We will consider the atmosphere to be a continuous fluid medium, or
Dynamic Meteorology - Introduction Atmospheric dynamics the study of atmospheric motions that are associated with weather and climate We will consider the atmosphere to be a continuous fluid medium, or
Class exercises Chapter 3. Elementary Applications of the Basic Equations
 Class exercises Chapter 3. Elementary Applications of the Basic Equations Section 3.1 Basic Equations in Isobaric Coordinates 3.1 For some (in fact many) applications we assume that the change of the Coriolis
Class exercises Chapter 3. Elementary Applications of the Basic Equations Section 3.1 Basic Equations in Isobaric Coordinates 3.1 For some (in fact many) applications we assume that the change of the Coriolis
SIO 210: Dynamics VI: Potential vorticity
 SIO 210: Dynamics VI: Potential vorticity Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity Rossby waves READING: Review Section 7.2.3 Section 7.7.1 through 7.7.4 or Supplement S7.7
SIO 210: Dynamics VI: Potential vorticity Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity Rossby waves READING: Review Section 7.2.3 Section 7.7.1 through 7.7.4 or Supplement S7.7
The Equations of Motion in a Rotating Coordinate System. Chapter 3
 The Equations of Motion in a Rotating Coordinate System Chapter 3 Since the earth is rotating about its axis and since it is convenient to adopt a frame of reference fixed in the earth, we need to study
The Equations of Motion in a Rotating Coordinate System Chapter 3 Since the earth is rotating about its axis and since it is convenient to adopt a frame of reference fixed in the earth, we need to study
EESC V2100 The Climate System spring 2004 Lecture 4: Laws of Atmospheric Motion and Weather
 EESC V2100 The Climate System spring 2004 Lecture 4: Laws of Atmospheric Motion and Weather Yochanan Kushnir Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Palisades, NY 10964, USA kushnir@ldeo.columbia.edu
EESC V2100 The Climate System spring 2004 Lecture 4: Laws of Atmospheric Motion and Weather Yochanan Kushnir Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Palisades, NY 10964, USA kushnir@ldeo.columbia.edu
Examples of Pressure Gradient. Pressure Gradient Force. Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances. Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion 2/2/2015
 Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
SIO 210: Dynamics VI (Potential vorticity) L. Talley Fall, 2014 (Section 2: including some derivations) (this lecture was not given in 2015)
 SIO 210: Dynamics VI (Potential vorticity) L. Talley Fall, 2014 (Section 2: including some derivations) (this lecture was not given in 2015) Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity
SIO 210: Dynamics VI (Potential vorticity) L. Talley Fall, 2014 (Section 2: including some derivations) (this lecture was not given in 2015) Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity
Lecture 1. Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions. Pressure gradient + force force
 Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
Introduction to Atmospheric Circulation
 Introduction to Atmospheric Circulation Start rotating table Cloud Fraction Dice Results from http://eos.atmos.washington.edu/erbe/ from http://eos.atmos.washington.edu/erbe/ from http://eos.atmos.washington.edu/erbe/
Introduction to Atmospheric Circulation Start rotating table Cloud Fraction Dice Results from http://eos.atmos.washington.edu/erbe/ from http://eos.atmos.washington.edu/erbe/ from http://eos.atmos.washington.edu/erbe/
Dynamic Meteorology 1
 Dynamic Meteorology 1 Lecture 14 Sahraei Department of Physics, Razi University http://www.razi.ac.ir/sahraei Buys-Ballot rule (Northern Hemisphere) If the wind blows into your back, the Low will be to
Dynamic Meteorology 1 Lecture 14 Sahraei Department of Physics, Razi University http://www.razi.ac.ir/sahraei Buys-Ballot rule (Northern Hemisphere) If the wind blows into your back, the Low will be to
The Circulation of the Atmosphere:
 The Circulation of the Atmosphere: Laboratory Experiments (see next slide) Fluid held in an annular container is at rest and is subjected to a temperature gradient. The less dense fluid near the warm wall
The Circulation of the Atmosphere: Laboratory Experiments (see next slide) Fluid held in an annular container is at rest and is subjected to a temperature gradient. The less dense fluid near the warm wall
General Comment on Lab Reports: v. good + corresponds to a lab report that: has structure (Intro., Method, Results, Discussion, an Abstract would be
 General Comment on Lab Reports: v. good + corresponds to a lab report that: has structure (Intro., Method, Results, Discussion, an Abstract would be a bonus) is well written (take your time to edit) shows
General Comment on Lab Reports: v. good + corresponds to a lab report that: has structure (Intro., Method, Results, Discussion, an Abstract would be a bonus) is well written (take your time to edit) shows
4. Atmospheric transport. Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017
 4. Atmospheric transport Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 Forces in the atmosphere: Gravity g Pressure-gradient ap = ( 1/ ρ ) dp / dx for x-direction (also y, z directions)
4. Atmospheric transport Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 Forces in the atmosphere: Gravity g Pressure-gradient ap = ( 1/ ρ ) dp / dx for x-direction (also y, z directions)
Note that Rossby waves are tranverse waves, that is the particles move perpendicular to the direction of propagation. f up, down (clockwise)
 Ocean 423 Rossby waves 1 Rossby waves: Restoring force is the north-south gradient of background potential vorticity (f/h). That gradient can be due to either the variation in f with latitude, or to a
Ocean 423 Rossby waves 1 Rossby waves: Restoring force is the north-south gradient of background potential vorticity (f/h). That gradient can be due to either the variation in f with latitude, or to a
Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Answers to Chapter 8
 Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Answers to Chapter 8 1. Consider a zonally symmetric circulation (i.e., one with no longitudinal variations) in the atmosphere. In the inviscid upper troposphere,
Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Answers to Chapter 8 1. Consider a zonally symmetric circulation (i.e., one with no longitudinal variations) in the atmosphere. In the inviscid upper troposphere,
Lecture 12: Angular Momentum and the Hadley Circulation
 Lecture 12: Angular Momentum and the Hadley Circulation September 30, 2003 We learnt last time that there is a planetary radiative drive net warming in the tropics, cooling over the pole which induces
Lecture 12: Angular Momentum and the Hadley Circulation September 30, 2003 We learnt last time that there is a planetary radiative drive net warming in the tropics, cooling over the pole which induces
Control Volume. Dynamics and Kinematics. Basic Conservation Laws. Lecture 1: Introduction and Review 1/24/2017
 Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review
 Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Review of fundamental mathematical tools Fundamental and apparent forces Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Review of fundamental mathematical tools Fundamental and apparent forces Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study
g (z) = 1 (1 + z/a) = 1
 1.4.2 Gravitational Force g is the gravitational force. It always points towards the center of mass, and it is proportional to the inverse square of the distance above the center of mass: g (z) = GM (a
1.4.2 Gravitational Force g is the gravitational force. It always points towards the center of mass, and it is proportional to the inverse square of the distance above the center of mass: g (z) = GM (a
General Atmospheric Circulation
 General Atmospheric Circulation Take away Concepts and Ideas Global circulation: The mean meridional (N-S) circulation Trade winds and westerlies The Jet Stream Earth s climate zones Monsoonal climate
General Atmospheric Circulation Take away Concepts and Ideas Global circulation: The mean meridional (N-S) circulation Trade winds and westerlies The Jet Stream Earth s climate zones Monsoonal climate
The dynamics of high and low pressure systems
 The dynamics of high and low pressure systems Newton s second law for a parcel of air in an inertial coordinate system (a coordinate system in which the coordinate axes do not change direction and are
The dynamics of high and low pressure systems Newton s second law for a parcel of air in an inertial coordinate system (a coordinate system in which the coordinate axes do not change direction and are
Lecture 14. Equations of Motion Currents With Friction Sverdrup, Stommel, and Munk Solutions Remember that Ekman's solution for wind-induced transport
 Lecture 14. Equations of Motion Currents With Friction Sverdrup, Stommel, and Munk Solutions Remember that Ekman's solution for wind-induced transport is which can also be written as (14.1) i.e., #Q x,y
Lecture 14. Equations of Motion Currents With Friction Sverdrup, Stommel, and Munk Solutions Remember that Ekman's solution for wind-induced transport is which can also be written as (14.1) i.e., #Q x,y
1/3/2011. This course discusses the physical laws that govern atmosphere/ocean motions.
 Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 2. Lecture 1. Forces on a rotating planet. We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their:
 Lecture 2 Lecture 1 Forces on a rotating planet We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their: velocity u = (u,v,w) pressure P density ρ temperature T salinity S up For convenience, we will
Lecture 2 Lecture 1 Forces on a rotating planet We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their: velocity u = (u,v,w) pressure P density ρ temperature T salinity S up For convenience, we will
Dust devils, water spouts, tornados
 Balanced flow Things we know Primitive equations are very comprehensive, but there may be a number of vast simplifications that may be relevant (e.g., geostrophic balance). Seems that there are things
Balanced flow Things we know Primitive equations are very comprehensive, but there may be a number of vast simplifications that may be relevant (e.g., geostrophic balance). Seems that there are things
X Y. Equator. Question 1
 Question 1 The schematic below shows the Hadley circulation in the Earth s tropical atmosphere around the spring equinox. Air rises from the equator and moves poleward in both hemispheres before descending
Question 1 The schematic below shows the Hadley circulation in the Earth s tropical atmosphere around the spring equinox. Air rises from the equator and moves poleward in both hemispheres before descending
ESCI 342 Atmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 12 Vorticity
 ESCI 34 tmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 1 Vorticity Reference: n Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (4 rd edition), Holton n Informal Introduction to Theoretical Fluid Mechanics, Lighthill Reading: Martin,
ESCI 34 tmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 1 Vorticity Reference: n Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (4 rd edition), Holton n Informal Introduction to Theoretical Fluid Mechanics, Lighthill Reading: Martin,
F = ma. ATS 150 Global Climate Change Winds and Weather. Scott Denning CSU CMMAP 1. Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook
 Winds and Weather Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook Circulation of the atmosphere and oceans are driven by energy imbalances Energy Imbalances What Makes the Wind Blow? Three real forces (gravity,
Winds and Weather Please read Chapter 6 from Archer Textbook Circulation of the atmosphere and oceans are driven by energy imbalances Energy Imbalances What Makes the Wind Blow? Three real forces (gravity,
Lab Ten Introduction to General Circulation and Angular Momentum
 Question 1 (15 points) Lab Ten Introduction to General Circulation and Angular Momentum a.) (5 points) Examining the diagram above, between which latitudes is there net heating and between which latitudes
Question 1 (15 points) Lab Ten Introduction to General Circulation and Angular Momentum a.) (5 points) Examining the diagram above, between which latitudes is there net heating and between which latitudes
Quick Recapitulation of Fluid Mechanics
 Quick Recapitulation of Fluid Mechanics Amey Joshi 07-Feb-018 1 Equations of ideal fluids onsider a volume element of a fluid of density ρ. If there are no sources or sinks in, the mass in it will change
Quick Recapitulation of Fluid Mechanics Amey Joshi 07-Feb-018 1 Equations of ideal fluids onsider a volume element of a fluid of density ρ. If there are no sources or sinks in, the mass in it will change
warmest (coldest) temperatures at summer heat dispersed upward by vertical motion Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A heated by solar radiation at the base
 Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
Pole Eq Lecture 3: ATMOSPHERE (Outline) JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell Polar Cell (driven by eddies) L H L H Basic Structures and Dynamics General Circulation in the Troposphere General Circulation in the
g (z) = 1 (1 + z/a) = 1 1 ( km/10 4 km) 2
 1.4.2 Gravitational Force g is the gravitational force. It always points towards the center of mass, and it is proportional to the inverse square of the distance above the center of mass: g (z) = GM (a
1.4.2 Gravitational Force g is the gravitational force. It always points towards the center of mass, and it is proportional to the inverse square of the distance above the center of mass: g (z) = GM (a
ρ x + fv f 'w + F x ρ y fu + F y Fundamental Equation in z coordinate p = ρrt or pα = RT Du uv tanφ Dv Dt + u2 tanφ + vw a a = 1 p Dw Dt u2 + v 2
 Fundamental Equation in z coordinate p = ρrt or pα = RT Du uv tanφ + uw Dt a a = 1 p ρ x + fv f 'w + F x Dv Dt + u2 tanφ + vw a a = 1 p ρ y fu + F y Dw Dt u2 + v 2 = 1 p a ρ z g + f 'u + F z Dρ Dt + ρ
Fundamental Equation in z coordinate p = ρrt or pα = RT Du uv tanφ + uw Dt a a = 1 p ρ x + fv f 'w + F x Dv Dt + u2 tanφ + vw a a = 1 p ρ y fu + F y Dw Dt u2 + v 2 = 1 p a ρ z g + f 'u + F z Dρ Dt + ρ
Ocean dynamics: the wind-driven circulation
 Ocean dynamics: the wind-driven circulation Weston Anderson March 13, 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 The wind driven circulation (Ekman Transport) 3 3 Sverdrup flow 5 4 Western boundary currents (western
Ocean dynamics: the wind-driven circulation Weston Anderson March 13, 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 The wind driven circulation (Ekman Transport) 3 3 Sverdrup flow 5 4 Western boundary currents (western
Divergence, Spin, and Tilt. Convergence and Divergence. Midlatitude Cyclones. Large-Scale Setting
 Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Midlatitude Cyclones Equator-to-pole temperature gradient tilts pressure surfaces and produces westerly jets in midlatitudes Waves in the jet induce divergence and convergence aloft, leading to surface
Chapter 5. Sound Waves and Vortices. 5.1 Sound waves
 Chapter 5 Sound Waves and Vortices In this chapter we explore a set of characteristic solutions to the uid equations with the goal of familiarizing the reader with typical behaviors in uid dynamics. Sound
Chapter 5 Sound Waves and Vortices In this chapter we explore a set of characteristic solutions to the uid equations with the goal of familiarizing the reader with typical behaviors in uid dynamics. Sound
1/18/2011. From the hydrostatic equation, it is clear that a single. pressure and height in each vertical column of the atmosphere.
 Lecture 3: Applications of Basic Equations Pressure as Vertical Coordinate From the hydrostatic equation, it is clear that a single valued monotonic relationship exists between pressure and height in each
Lecture 3: Applications of Basic Equations Pressure as Vertical Coordinate From the hydrostatic equation, it is clear that a single valued monotonic relationship exists between pressure and height in each
The atmosphere in motion: forces and wind. AT350 Ahrens Chapter 9
 The atmosphere in motion: forces and wind AT350 Ahrens Chapter 9 Recall that Pressure is force per unit area Air pressure is determined by the weight of air above A change in pressure over some distance
The atmosphere in motion: forces and wind AT350 Ahrens Chapter 9 Recall that Pressure is force per unit area Air pressure is determined by the weight of air above A change in pressure over some distance
Model equations for planetary and synoptic scale atmospheric motions associated with different background stratification
 Model equations for planetary and synoptic scale atmospheric motions associated with different background stratification Stamen Dolaptchiev & Rupert Klein Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research
Model equations for planetary and synoptic scale atmospheric motions associated with different background stratification Stamen Dolaptchiev & Rupert Klein Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research
On side wall labeled A: we can express the pressure in a Taylor s series expansion: x 2. + higher order terms,
 Chapter 1 Notes A Note About Coordinates We nearly always use a coordinate system in this class where the vertical, ˆk, is normal to the Earth s surface and the x-direction, î, points to the east and the
Chapter 1 Notes A Note About Coordinates We nearly always use a coordinate system in this class where the vertical, ˆk, is normal to the Earth s surface and the x-direction, î, points to the east and the
d v 2 v = d v d t i n where "in" and "rot" denote the inertial (absolute) and rotating frames. Equation of motion F =
 Governing equations of fluid dynamics under the influence of Earth rotation (Navier-Stokes Equations in rotating frame) Recap: From kinematic consideration, d v i n d t i n = d v rot d t r o t 2 v rot
Governing equations of fluid dynamics under the influence of Earth rotation (Navier-Stokes Equations in rotating frame) Recap: From kinematic consideration, d v i n d t i n = d v rot d t r o t 2 v rot
Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates: a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations. Cristiana Stan
 Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates: a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations Cristiana Stan School and Conference on the General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Oceans: a Modern Perspective
Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates: a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations Cristiana Stan School and Conference on the General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Oceans: a Modern Perspective
Chapter 4: Fundamental Forces
 Chapter 4: Fundamental Forces Newton s Second Law: F=ma In atmospheric science it is typical to consider the force per unit mass acting on the atmosphere: Force mass = a In order to understand atmospheric
Chapter 4: Fundamental Forces Newton s Second Law: F=ma In atmospheric science it is typical to consider the force per unit mass acting on the atmosphere: Force mass = a In order to understand atmospheric
1/27/2010. With this method, all filed variables are separated into. from the basic state: Assumptions 1: : the basic state variables must
 Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method With this method, all filed variables are separated into two parts: (a) a basic state part and (b) a deviation from the basic state: Perturbation Method
Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method With this method, all filed variables are separated into two parts: (a) a basic state part and (b) a deviation from the basic state: Perturbation Method
TROPICAL CYCLONE MOTION
 Chapter 3 TROPICAL CYCLONE MOTION The prediction of tropical cyclone motion has improved dramatically during the last decade as has our understanding of the mechanisms involved. Some of the basic aspects
Chapter 3 TROPICAL CYCLONE MOTION The prediction of tropical cyclone motion has improved dramatically during the last decade as has our understanding of the mechanisms involved. Some of the basic aspects
Dynamics of the Earth
 Time Dynamics of the Earth Historically, a day is a time interval between successive upper transits of a given celestial reference point. upper transit the passage of a body across the celestial meridian
Time Dynamics of the Earth Historically, a day is a time interval between successive upper transits of a given celestial reference point. upper transit the passage of a body across the celestial meridian
Changes in Density Within An Air are Density Velocity Column Fixed due and/or With Respect to to Advection Divergence the Earth
 The Continuity Equation: Dines Compensation and the Pressure Tendency Equation 1. General The Continuity Equation is a restatement of the principle of Conservation of Mass applied to the atmosphere. The
The Continuity Equation: Dines Compensation and the Pressure Tendency Equation 1. General The Continuity Equation is a restatement of the principle of Conservation of Mass applied to the atmosphere. The
Introduction to Physical Oceanography Homework 3 - Solutions. 1. Volume transport in the Gulf Stream and Antarctic Circumpolar current (ACC):
 Laure Zanna 10/17/05 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Homework 3 - Solutions 1. Volume transport in the Gulf Stream and Antarctic Circumpolar current (ACC): (a) Looking on the web you can find a lot
Laure Zanna 10/17/05 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Homework 3 - Solutions 1. Volume transport in the Gulf Stream and Antarctic Circumpolar current (ACC): (a) Looking on the web you can find a lot
GFD 2 Spring 2010 P.B. Rhines Problem set 1-solns out: 5 April back: 12 April
 GFD 2 Spring 2010 P.B. Rhines Problem set 1-solns out: 5 April back: 12 April 1 The Gulf Stream has a dramatic thermal-wind signature : the sloping isotherms and isohalines (hence isopycnals) not only
GFD 2 Spring 2010 P.B. Rhines Problem set 1-solns out: 5 April back: 12 April 1 The Gulf Stream has a dramatic thermal-wind signature : the sloping isotherms and isohalines (hence isopycnals) not only
Dynamics of Upper-Level Waves
 Dynamics of Upper-Level Waves Atmos 5110 Synoptic Dynamic Meteorology I Instructor: Jim Steenburgh jim.steenburgh@utah.edu 801-581-8727 Suite 480/Office 488 INSCC Suggested reading: Lackman (2011) section
Dynamics of Upper-Level Waves Atmos 5110 Synoptic Dynamic Meteorology I Instructor: Jim Steenburgh jim.steenburgh@utah.edu 801-581-8727 Suite 480/Office 488 INSCC Suggested reading: Lackman (2011) section
Single Particle Motion
 Single Particle Motion C ontents Uniform E and B E = - guiding centers Definition of guiding center E gravitation Non Uniform B 'grad B' drift, B B Curvature drift Grad -B drift, B B invariance of µ. Magnetic
Single Particle Motion C ontents Uniform E and B E = - guiding centers Definition of guiding center E gravitation Non Uniform B 'grad B' drift, B B Curvature drift Grad -B drift, B B invariance of µ. Magnetic
Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates:! a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations" Cristiana Stan
 Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates:! a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations" Cristiana Stan School and Conference on the General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Oceans: a Modern Perspective!
Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates:! a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations" Cristiana Stan School and Conference on the General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Oceans: a Modern Perspective!
Aerodynamic Performance 1. Figure 1: Flowfield of a Wind Turbine and Actuator disc. Table 1: Properties of the actuator disk.
 Aerodynamic Performance 1 1 Momentum Theory Figure 1: Flowfield of a Wind Turbine and Actuator disc. Table 1: Properties of the actuator disk. 1. The flow is perfect fluid, steady, and incompressible.
Aerodynamic Performance 1 1 Momentum Theory Figure 1: Flowfield of a Wind Turbine and Actuator disc. Table 1: Properties of the actuator disk. 1. The flow is perfect fluid, steady, and incompressible.
Physical Oceanography, MSCI 3001 Oceanographic Processes, MSCI Dr. Katrin Meissner Week 5.
 Physical Oceanography, MSCI 3001 Oceanographic Processes, MSCI 5004 Dr. Katrin Meissner k.meissner@unsw.e.au Week 5 Ocean Dynamics Transport of Volume, Heat & Salt Flux: Amount of heat, salt or volume
Physical Oceanography, MSCI 3001 Oceanographic Processes, MSCI 5004 Dr. Katrin Meissner k.meissner@unsw.e.au Week 5 Ocean Dynamics Transport of Volume, Heat & Salt Flux: Amount of heat, salt or volume
Study Guide for Exam #2
 Physical Mechanics METR103 November, 000 Study Guide for Exam # The information even below is meant to serve as a guide to help you to prepare for the second hour exam. The absence of a topic or point
Physical Mechanics METR103 November, 000 Study Guide for Exam # The information even below is meant to serve as a guide to help you to prepare for the second hour exam. The absence of a topic or point
7 The General Circulation
 7 The General Circulation 7.1 The axisymmetric state At the beginning of the class, we discussed the nonlinear, inviscid, axisymmetric theory of the meridional structure of the atmosphere. The important
7 The General Circulation 7.1 The axisymmetric state At the beginning of the class, we discussed the nonlinear, inviscid, axisymmetric theory of the meridional structure of the atmosphere. The important
CHAPTER 4. THE HADLEY CIRCULATION 59 smaller than that in midlatitudes. This is illustrated in Fig. 4.2 which shows the departures from zonal symmetry
 Chapter 4 THE HADLEY CIRCULATION The early work on the mean meridional circulation of the tropics was motivated by observations of the trade winds. Halley (1686) and Hadley (1735) concluded that the trade
Chapter 4 THE HADLEY CIRCULATION The early work on the mean meridional circulation of the tropics was motivated by observations of the trade winds. Halley (1686) and Hadley (1735) concluded that the trade
1/18/2011. Conservation of Momentum Conservation of Mass Conservation of Energy Scaling Analysis ESS227 Prof. Jin-Yi Yu
 Lecture 2: Basic Conservation Laws Conservation Law of Momentum Newton s 2 nd Law of Momentum = absolute velocity viewed in an inertial system = rate of change of Ua following the motion in an inertial
Lecture 2: Basic Conservation Laws Conservation Law of Momentum Newton s 2 nd Law of Momentum = absolute velocity viewed in an inertial system = rate of change of Ua following the motion in an inertial
Kepler s Law of Areal Velocity in Cyclones
 Kepler s Law of Areal Velocity in Cyclones Frederick David Tombe, Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom, Formerly a Physics Teacher at College of Technology Belfast, and Royal Belfast Academical Institution,
Kepler s Law of Areal Velocity in Cyclones Frederick David Tombe, Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom, Formerly a Physics Teacher at College of Technology Belfast, and Royal Belfast Academical Institution,
1. The vertical structure of the atmosphere. Temperature profile.
 Lecture 4. The structure of the atmosphere. Air in motion. Objectives: 1. The vertical structure of the atmosphere. Temperature profile. 2. Temperature in the lower atmosphere: dry adiabatic lapse rate.
Lecture 4. The structure of the atmosphere. Air in motion. Objectives: 1. The vertical structure of the atmosphere. Temperature profile. 2. Temperature in the lower atmosphere: dry adiabatic lapse rate.
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week Radiative Transfer Black body radiation, Planck function, Wien s law Absorption, emission, opacity, optical depth Intensity, flux Radiative diffusion,
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week Radiative Transfer Black body radiation, Planck function, Wien s law Absorption, emission, opacity, optical depth Intensity, flux Radiative diffusion,
( u,v). For simplicity, the density is considered to be a constant, denoted by ρ 0
 ! Revised Friday, April 19, 2013! 1 Inertial Stability and Instability David Randall Introduction Inertial stability and instability are relevant to the atmosphere and ocean, and also in other contexts
! Revised Friday, April 19, 2013! 1 Inertial Stability and Instability David Randall Introduction Inertial stability and instability are relevant to the atmosphere and ocean, and also in other contexts
Eliassen-Palm Cross Sections Edmon et al. (1980)
 Eliassen-Palm Cross Sections Edmon et al. (1980) Cecily Keppel November 14 2014 Eliassen-Palm Flux For β-plane Coordinates (y, p) in northward, vertical directions Zonal means F = v u f (y) v θ θ p F will
Eliassen-Palm Cross Sections Edmon et al. (1980) Cecily Keppel November 14 2014 Eliassen-Palm Flux For β-plane Coordinates (y, p) in northward, vertical directions Zonal means F = v u f (y) v θ θ p F will
6 Two-layer shallow water theory.
 6 Two-layer shallow water theory. Wewillnowgoontolookatashallowwatersystemthathastwolayersofdifferent density. This is the next level of complexity and a simple starting point for understanding the behaviour
6 Two-layer shallow water theory. Wewillnowgoontolookatashallowwatersystemthathastwolayersofdifferent density. This is the next level of complexity and a simple starting point for understanding the behaviour
The Behaviour of the Atmosphere
 3 The Behaviour of the Atmosphere Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: apply the ideal gas law and the concept of hydrostatic balance to the atmosphere (pp. 49 54); apply
3 The Behaviour of the Atmosphere Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: apply the ideal gas law and the concept of hydrostatic balance to the atmosphere (pp. 49 54); apply
V (r,t) = i ˆ u( x, y,z,t) + ˆ j v( x, y,z,t) + k ˆ w( x, y, z,t)
 IV. DIFFERENTIAL RELATIONS FOR A FLUID PARTICLE This chapter presents the development and application of the basic differential equations of fluid motion. Simplifications in the general equations and common
IV. DIFFERENTIAL RELATIONS FOR A FLUID PARTICLE This chapter presents the development and application of the basic differential equations of fluid motion. Simplifications in the general equations and common
x+ y = 50 Dividing both sides by 2 : ( ) dx By (7.2), x = 25m gives maximum area. Substituting this value into (*):
 Solutions 7(b 1 Complete solutions to Exercise 7(b 1. Since the perimeter 100 we have x+ y 100 [ ] ( x+ y 50 ividing both sides by : y 50 x * The area A xy, substituting y 50 x gives: A x( 50 x A 50x x
Solutions 7(b 1 Complete solutions to Exercise 7(b 1. Since the perimeter 100 we have x+ y 100 [ ] ( x+ y 50 ividing both sides by : y 50 x * The area A xy, substituting y 50 x gives: A x( 50 x A 50x x
ATMOSPHERIC MOTION I (ATM S 441/503 )
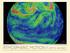 http://earth.nullschool.net/ ATMOSPHERIC MOTION I (ATM S 441/503 ) INSTRUCTOR Daehyun Kim Born in 1980 B.S. 2003 Ph.D. 2010 2010-2013 2014- Assistant Professor at Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences Office:
http://earth.nullschool.net/ ATMOSPHERIC MOTION I (ATM S 441/503 ) INSTRUCTOR Daehyun Kim Born in 1980 B.S. 2003 Ph.D. 2010 2010-2013 2014- Assistant Professor at Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences Office:
The dynamics of a simple troposphere-stratosphere model
 The dynamics of a simple troposphere-stratosphere model by Jessica Duin under supervision of Prof. Dr. A. Doelman, UvA Dr. W.T.M. Verkley, KNMI August 31, 25 Universiteit van Amsterdam Korteweg-de vries
The dynamics of a simple troposphere-stratosphere model by Jessica Duin under supervision of Prof. Dr. A. Doelman, UvA Dr. W.T.M. Verkley, KNMI August 31, 25 Universiteit van Amsterdam Korteweg-de vries
The general circulation: midlatitude storms
 The general circulation: midlatitude storms Motivation for this class Provide understanding basic motions of the atmosphere: Ability to diagnose individual weather systems, and predict how they will change
The general circulation: midlatitude storms Motivation for this class Provide understanding basic motions of the atmosphere: Ability to diagnose individual weather systems, and predict how they will change
4 Mechanics of Fluids (I)
 1. The x and y components of velocity for a two-dimensional flow are u = 3.0 ft/s and v = 9.0x ft/s where x is in feet. Determine the equation for the streamlines and graph representative streamlines in
1. The x and y components of velocity for a two-dimensional flow are u = 3.0 ft/s and v = 9.0x ft/s where x is in feet. Determine the equation for the streamlines and graph representative streamlines in
EATS Notes 1. Some course material will be online at
 EATS 3040-2015 Notes 1 14 Aug 2015 Some course material will be online at http://www.yorku.ca/pat/esse3040/ HH = Holton and Hakim. An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, 5th Edition. Most of the images
EATS 3040-2015 Notes 1 14 Aug 2015 Some course material will be online at http://www.yorku.ca/pat/esse3040/ HH = Holton and Hakim. An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, 5th Edition. Most of the images
OCN/ATM/ESS 587. The wind-driven ocean circulation. Friction and stress. The Ekman layer, top and bottom. Ekman pumping, Ekman suction
 OCN/ATM/ESS 587 The wind-driven ocean circulation. Friction and stress The Ekman layer, top and bottom Ekman pumping, Ekman suction Westward intensification The wind-driven ocean. The major ocean gyres
OCN/ATM/ESS 587 The wind-driven ocean circulation. Friction and stress The Ekman layer, top and bottom Ekman pumping, Ekman suction Westward intensification The wind-driven ocean. The major ocean gyres
Introduction to Atmospheric Circulation
 Introduction to Atmospheric Circulation Start rotating table Start heated bottle experiment Scientific Practice Observe nature Develop a model*/hypothesis for what is happening Carry out experiments Make
Introduction to Atmospheric Circulation Start rotating table Start heated bottle experiment Scientific Practice Observe nature Develop a model*/hypothesis for what is happening Carry out experiments Make
Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton
 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each & Q. 10 Q. 22 carry two marks each. Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton Q.2 The pair of variables that
Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each & Q. 10 Q. 22 carry two marks each. Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton Q.2 The pair of variables that
Conservation of Mass Conservation of Energy Scaling Analysis. ESS227 Prof. Jin-Yi Yu
 Lecture 2: Basic Conservation Laws Conservation of Momentum Conservation of Mass Conservation of Energy Scaling Analysis Conservation Law of Momentum Newton s 2 nd Law of Momentum = absolute velocity viewed
Lecture 2: Basic Conservation Laws Conservation of Momentum Conservation of Mass Conservation of Energy Scaling Analysis Conservation Law of Momentum Newton s 2 nd Law of Momentum = absolute velocity viewed
Vortex motion. Wasilij Barsukow, July 1, 2016
 The concept of vorticity We call Vortex motion Wasilij Barsukow, mail@sturzhang.de July, 206 ω = v vorticity. It is a measure of the swirlyness of the flow, but is also present in shear flows where the
The concept of vorticity We call Vortex motion Wasilij Barsukow, mail@sturzhang.de July, 206 ω = v vorticity. It is a measure of the swirlyness of the flow, but is also present in shear flows where the
ATS 421/521. Climate Modeling. Spring 2015
 ATS 421/521 Climate Modeling Spring 2015 Lecture 9 Hadley Circulation (Held and Hou, 1980) General Circulation Models (tetbook chapter 3.2.3; course notes chapter 5.3) The Primitive Equations (tetbook
ATS 421/521 Climate Modeling Spring 2015 Lecture 9 Hadley Circulation (Held and Hou, 1980) General Circulation Models (tetbook chapter 3.2.3; course notes chapter 5.3) The Primitive Equations (tetbook
Dynamics of the Zonal-Mean, Time-Mean Tropical Circulation
 Dynamics of the Zonal-Mean, Time-Mean Tropical Circulation First consider a hypothetical planet like Earth, but with no continents and no seasons and for which the only friction acting on the atmosphere
Dynamics of the Zonal-Mean, Time-Mean Tropical Circulation First consider a hypothetical planet like Earth, but with no continents and no seasons and for which the only friction acting on the atmosphere
Chapter 9 [ Edit ] Ladybugs on a Rotating Disk. v = ωr, where r is the distance between the object and the axis of rotation. Chapter 9. Part A.
![Chapter 9 [ Edit ] Ladybugs on a Rotating Disk. v = ωr, where r is the distance between the object and the axis of rotation. Chapter 9. Part A. Chapter 9 [ Edit ] Ladybugs on a Rotating Disk. v = ωr, where r is the distance between the object and the axis of rotation. Chapter 9. Part A.](/thumbs/77/75060038.jpg) Chapter 9 [ Edit ] Chapter 9 Overview Summary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Due: 11:59pm on Sunday, October 30, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this
Chapter 9 [ Edit ] Chapter 9 Overview Summary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Due: 11:59pm on Sunday, October 30, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this
Physical Oceanography, MSCI 3001 Oceanographic Processes, MSCI Dr. Katrin Meissner Ocean Dynamics.
 Physical Oceanography, MSCI 3001 Oceanographic Processes, MSCI 5004 Dr. Katrin Meissner k.meissner@unsw.e.au Ocean Dynamics The Equations of Motion d u dt = 1 ρ Σ F dt = 1 ρ ΣF x dt = 1 ρ ΣF y dw dt =
Physical Oceanography, MSCI 3001 Oceanographic Processes, MSCI 5004 Dr. Katrin Meissner k.meissner@unsw.e.au Ocean Dynamics The Equations of Motion d u dt = 1 ρ Σ F dt = 1 ρ ΣF x dt = 1 ρ ΣF y dw dt =
