Ocean dynamics: the wind-driven circulation
|
|
|
- Moris Bell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ocean dynamics: the wind-driven circulation Weston Anderson March 13, 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 The wind driven circulation (Ekman Transport) 3 3 Sverdrup flow 5 4 Western boundary currents (western intensification) 7 1 Introduction In this set of notes we ll describe wind-driven circulations of the ocean, why we see western intensification of those currents (western boundary currents). For information on the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) see the separate notes on climate in the Atlantic. For information on ENSO, see the separate set of notes devoted solely to ENSO and its teleconnections. To begin with, let s remind ourselves of some of the momentum equation, which we ll be invoking throughout this section: Du p fv = Dt x + ν 2 u Dv p + fu = Dt y + ν 2 v Where the first term on the LHS is the advective term, the second term is the Coriolis force, the first term on the RHS is the pressure gradient force, and the final term is the wind stress (friction) term In general we ll be talking about the balance between dominant terms in the momentum equation in three situations. The first is geostrophic balance, in which is the Coriolis force and pressure gradient terms balance against one another. The second is Ekman transport, which is the balance between the friction terms and the Coriolis force. The final balance is sverdrup transport, which refers to a balance between advection of planetary vorticity and the wind 1
2 stress curl. This final balance is derived by transforming the momentum equation into a vorticity equation by taking the curl and applying continuity. We ll generally take geostrophic flow as a given, as we do in the atmosphere. Figure 1 briefly reviews the balance of forces in geostrophic flow around a high pressure system in the ocean. As stated earlier, we re balancing the Coriolis force against the pressure gradient force: fv = p x fu = p y Figure 1: Figure credit: (Talley, 2011) 2
3 2 The wind driven circulation (Ekman Transport) The Ekman layer refers to the upper 50m of the ocean that is affected by the surface wind stress. So to understand how surface wind stress affects ocean currents, we think about the depth-integrated transport over the entire Ekman layer (i.e. Ekman transport). The effect of Earth s rotation imparts two distinct features on Ekman transport: 1) the flow spirals to the right with depth and 2) the net mass-transport is perpendicular to the right (in the NH) of the surface wind stress. Figure 2 demonstrates these two properties. In the southern hemisphere the spiral is reversed and the Ekman transport is to the left. Figure 2: Figure credit: (Talley, 2011) We can apply the concept of Ekman transport in conjunction with equatorial trade winds to explain equatorial shoaling of the thermocline. When the trade winds blow along the equator, they force Ekman transport to the right in the NH and to the left in the SH, forcing divergence of surface water right along 3
4 the equator, which creates upwelling (i.e. Ekman pumping ). When applied to along-shore flow, Ekman transport explains upwelling because it similarly creates divergence of surface waters. These features demonstrate both why eastern boundary currents are cold and nutrient rich, and why we have an equatorial cold tongue. Figure 3: Figure credit: (Talley, 2011) 4
5 3 Sverdrup flow In the interior of the ocean (or right near the equator) we consider the importance of Sverdrup transport, which refers to a flow resulting from a large-scale vorticity balance between the wind-stress curl and advection of planetary vorticity. To understand this balance we need to first consider potential vorticity: Q = ζ + f H Where H is the thickness of the fluid layer, ζ is the vertical component of the relative vorticity and f is the vertical component of the planetary vorticity (i.e. the Coriolis parameter). f is zero near the equator and maximum near the poles. Now consider a fluid parcel that begins with no relative vorticity at a low latitude, and moves poleward. Because f increases as we move poleward the parcel must act to maintain constant potential vorticity (Q) by either: 1) inducing relative vorticity (i.e. change ζ) or 2) changing the height of the parcel (H). Relative vorticity is often small in the ocean interior, so parcels generally change H, as depicted below in Figure 4. This means that poleward-moving parcel tend to stretch (increase H), while equatorward-moving parcels tend to compress. Alternatively, if a parcel is stretched by an outside force (e.g. Ekman pumping), then it will tend to move poleward and if it is compressed it will move equatorward. Figure 4: Figure credit: (Talley, 2011) Now if we take the geostrophic equations for the x- and y- momentum equa- 5
6 tions are used to forma. vorticity equation with β = df/dy: ( u f x + v ) + βv = 0 y Then using the continuity equation to substitute into the parentheses: ( f w ) + βv = 0 z We could alternately substitute in the wind stress curl for w in the above equation, which would demonstrate how divergent wind-stress curls create vortex stretching, which forces parcels of water to move to higher latitudes as a means of maintaining PV. Alternatively, when Ekman pumping forces compression of the water column (due to convergence) the parcels move equatorward. This is referred to as Sverdrup transport. Figure 5 conceptually ties together Ekman transport, the wind-driven gyres and Sverdrup transport. Figure 5: Figure credit: (Talley, 2011) 6
7 4 Western boundary currents (western intensification) To understand why wind-driven currents are more intense on the western boundary of the ocean basin rather than the eastern boundary (see Figure 6), we again need to consider the conservation of potential vorticity. Figure 6: Figure credit: (Talley, 2011) In the subtropical gyres we have Sverdrup transport to the south in the interior of the ocean, which is only partially compensated for (in a PV sense) by vortex stretching/compression. So there must be an alternative source of postive PV input into the system to balance the negative βv term of Sverdrup transport. This input is vorticity induced by boundary friction. Figure 7 demonstrates how a northward flow and a western boundary imparts positive vorticity to the 7
8 system, while a northward flow and eastern boundary would impart negative vorticity. Because we need to add positive vorticity, the flow along the western boundary must intensify (as we see in western boundary currents such as the Gulf Stream and Kuroshio Current). Figure 7: Figure credit: (Talley, 2011) 8
9 References Lynne D Talley. Descriptive physical oceanography: an introduction. Academic press,
Lecture 8. Lecture 1. Wind-driven gyres. Ekman transport and Ekman pumping in a typical ocean basin. VEk
 Lecture 8 Lecture 1 Wind-driven gyres Ekman transport and Ekman pumping in a typical ocean basin. VEk wek > 0 VEk wek < 0 VEk 1 8.1 Vorticity and circulation The vorticity of a parcel is a measure of its
Lecture 8 Lecture 1 Wind-driven gyres Ekman transport and Ekman pumping in a typical ocean basin. VEk wek > 0 VEk wek < 0 VEk 1 8.1 Vorticity and circulation The vorticity of a parcel is a measure of its
SIO 210: Dynamics VI (Potential vorticity) L. Talley Fall, 2014 (Section 2: including some derivations) (this lecture was not given in 2015)
 SIO 210: Dynamics VI (Potential vorticity) L. Talley Fall, 2014 (Section 2: including some derivations) (this lecture was not given in 2015) Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity
SIO 210: Dynamics VI (Potential vorticity) L. Talley Fall, 2014 (Section 2: including some derivations) (this lecture was not given in 2015) Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity
Lecture 14. Equations of Motion Currents With Friction Sverdrup, Stommel, and Munk Solutions Remember that Ekman's solution for wind-induced transport
 Lecture 14. Equations of Motion Currents With Friction Sverdrup, Stommel, and Munk Solutions Remember that Ekman's solution for wind-induced transport is which can also be written as (14.1) i.e., #Q x,y
Lecture 14. Equations of Motion Currents With Friction Sverdrup, Stommel, and Munk Solutions Remember that Ekman's solution for wind-induced transport is which can also be written as (14.1) i.e., #Q x,y
Ocean Mixing and Climate Change
 Ocean Mixing and Climate Change Factors inducing seawater mixing Different densities Wind stirring Internal waves breaking Tidal Bottom topography Biogenic Mixing (??) In general, any motion favoring turbulent
Ocean Mixing and Climate Change Factors inducing seawater mixing Different densities Wind stirring Internal waves breaking Tidal Bottom topography Biogenic Mixing (??) In general, any motion favoring turbulent
Ocean surface circulation
 Ocean surface circulation Recall from Last Time The three drivers of atmospheric circulation we discussed: Differential heating Pressure gradients Earth s rotation (Coriolis) Last two show up as direct
Ocean surface circulation Recall from Last Time The three drivers of atmospheric circulation we discussed: Differential heating Pressure gradients Earth s rotation (Coriolis) Last two show up as direct
I. Ocean Layers and circulation types
 OCEAN CIRCULATION I. Ocean Layers and circulation types 1) Ocean Layers Ocean is strongly Stratified Consists of distinct LAYERS controlled by density takes huge amounts of energy to mix up the stable
OCEAN CIRCULATION I. Ocean Layers and circulation types 1) Ocean Layers Ocean is strongly Stratified Consists of distinct LAYERS controlled by density takes huge amounts of energy to mix up the stable
OCN/ATM/ESS 587. The wind-driven ocean circulation. Friction and stress. The Ekman layer, top and bottom. Ekman pumping, Ekman suction
 OCN/ATM/ESS 587 The wind-driven ocean circulation. Friction and stress The Ekman layer, top and bottom Ekman pumping, Ekman suction Westward intensification The wind-driven ocean. The major ocean gyres
OCN/ATM/ESS 587 The wind-driven ocean circulation. Friction and stress The Ekman layer, top and bottom Ekman pumping, Ekman suction Westward intensification The wind-driven ocean. The major ocean gyres
General Comment on Lab Reports: v. good + corresponds to a lab report that: has structure (Intro., Method, Results, Discussion, an Abstract would be
 General Comment on Lab Reports: v. good + corresponds to a lab report that: has structure (Intro., Method, Results, Discussion, an Abstract would be a bonus) is well written (take your time to edit) shows
General Comment on Lab Reports: v. good + corresponds to a lab report that: has structure (Intro., Method, Results, Discussion, an Abstract would be a bonus) is well written (take your time to edit) shows
I. Ocean Layers and circulation types
 OCEAN Title CIRCULATION slide I. Ocean Layers and circulation types 1) Ocean Layers Ocean is strongly Stratified Consists of distinct LAYERS controlled by density takes huge amounts of energy to mix up
OCEAN Title CIRCULATION slide I. Ocean Layers and circulation types 1) Ocean Layers Ocean is strongly Stratified Consists of distinct LAYERS controlled by density takes huge amounts of energy to mix up
Surface Circulation. Key Ideas
 Surface Circulation The westerlies and the trade winds are two of the winds that drive the ocean s surface currents. 1 Key Ideas Ocean water circulates in currents. Surface currents are caused mainly by
Surface Circulation The westerlies and the trade winds are two of the winds that drive the ocean s surface currents. 1 Key Ideas Ocean water circulates in currents. Surface currents are caused mainly by
Note that Rossby waves are tranverse waves, that is the particles move perpendicular to the direction of propagation. f up, down (clockwise)
 Ocean 423 Rossby waves 1 Rossby waves: Restoring force is the north-south gradient of background potential vorticity (f/h). That gradient can be due to either the variation in f with latitude, or to a
Ocean 423 Rossby waves 1 Rossby waves: Restoring force is the north-south gradient of background potential vorticity (f/h). That gradient can be due to either the variation in f with latitude, or to a
SIO 210 Final Exam Dec Name:
 SIO 210 Final Exam Dec 8 2006 Name: Turn off all phones, pagers, etc... You may use a calculator. This exam is 9 pages with 19 questions. Please mark initials or name on each page. Check which you prefer
SIO 210 Final Exam Dec 8 2006 Name: Turn off all phones, pagers, etc... You may use a calculator. This exam is 9 pages with 19 questions. Please mark initials or name on each page. Check which you prefer
Internal boundary layers in the ocean circulation
 Internal boundary layers in the ocean circulation Lecture 9 by Andrew Wells We have so far considered boundary layers adjacent to physical boundaries. However, it is also possible to find boundary layers
Internal boundary layers in the ocean circulation Lecture 9 by Andrew Wells We have so far considered boundary layers adjacent to physical boundaries. However, it is also possible to find boundary layers
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
Actual bathymetry (with vertical exaggeration) Geometry of the ocean 1/17/2018. Patterns and observations? Patterns and observations?
 Patterns and observations? Patterns and observations? Observations? Patterns? Observations? Patterns? Geometry of the ocean Actual bathymetry (with vertical exaggeration) Continental Continental Basin
Patterns and observations? Patterns and observations? Observations? Patterns? Observations? Patterns? Geometry of the ocean Actual bathymetry (with vertical exaggeration) Continental Continental Basin
Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.003 Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Problem
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.003 Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Problem
Basic Ocean Current Systems. Basic Ocean Structures. The State of Oceans. Lecture 6: The Ocean General Circulation and Climate. Temperature.
 Lecture 6: The Ocean General Circulation and Climate Basic Ocean Current Systems Upper Ocean surface circulation Basic Structures Mixed Layer Wind-Driven Circulation Theories Thermohaline Circulation Ocean
Lecture 6: The Ocean General Circulation and Climate Basic Ocean Current Systems Upper Ocean surface circulation Basic Structures Mixed Layer Wind-Driven Circulation Theories Thermohaline Circulation Ocean
Answer the following questions using letters A through H :
 SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 10, 2014 Due Nov. 24, 2014 Answer key 1. 10 total 6 points (a) The following kinds of wave motion were mentioned in class A. light 3 x 10 9 m/sec B. sound in air (340 m/sec)
SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 10, 2014 Due Nov. 24, 2014 Answer key 1. 10 total 6 points (a) The following kinds of wave motion were mentioned in class A. light 3 x 10 9 m/sec B. sound in air (340 m/sec)
CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation Pearson Education, Inc.
 CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Types of Ocean Currents Surface currents Deep currents 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Measuring Surface Currents Direct methods Floating device tracked
CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Types of Ocean Currents Surface currents Deep currents 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Measuring Surface Currents Direct methods Floating device tracked
General Atmospheric Circulation
 General Atmospheric Circulation Take away Concepts and Ideas Global circulation: The mean meridional (N-S) circulation Trade winds and westerlies The Jet Stream Earth s climate zones Monsoonal climate
General Atmospheric Circulation Take away Concepts and Ideas Global circulation: The mean meridional (N-S) circulation Trade winds and westerlies The Jet Stream Earth s climate zones Monsoonal climate
Thermohaline and wind-driven circulation
 Thermohaline and wind-driven circulation Annalisa Bracco Georgia Institute of Technology School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences NCAR ASP Colloquium: Carbon climate connections in the Earth System Tracer
Thermohaline and wind-driven circulation Annalisa Bracco Georgia Institute of Technology School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences NCAR ASP Colloquium: Carbon climate connections in the Earth System Tracer
SIO 210 Final examination Wednesday, December 12, :30-2:30 Eckart 227 Name:
 SIO 210 Final examination Wednesday, December 12, 2018 11:30-2:30 Eckart 227 Name: Please put your initials or name on each page, especially if you pull pages apart. Turn off all phones, ipods, etc. and
SIO 210 Final examination Wednesday, December 12, 2018 11:30-2:30 Eckart 227 Name: Please put your initials or name on each page, especially if you pull pages apart. Turn off all phones, ipods, etc. and
Ocean Dynamics. The Great Wave off Kanagawa Hokusai
 Ocean Dynamics The Great Wave off Kanagawa Hokusai LO: integrate relevant oceanographic processes with factors influencing survival and growth of fish larvae Physics Determining Ocean Dynamics 1. Conservation
Ocean Dynamics The Great Wave off Kanagawa Hokusai LO: integrate relevant oceanographic processes with factors influencing survival and growth of fish larvae Physics Determining Ocean Dynamics 1. Conservation
Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B
 Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B Instructor: Leif Thomas TA: Gonçalo Zo Zo Gil http://pangea.stanford.edu/courses/eess146bweb/ Course Objectives Identify and characterize
Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B Instructor: Leif Thomas TA: Gonçalo Zo Zo Gil http://pangea.stanford.edu/courses/eess146bweb/ Course Objectives Identify and characterize
BALANCED FLOW: EXAMPLES (PHH lecture 3) Potential Vorticity in the real atmosphere. Potential temperature θ. Rossby Ertel potential vorticity
 BALANCED FLOW: EXAMPLES (PHH lecture 3) Potential Vorticity in the real atmosphere Need to introduce a new measure of the buoyancy Potential temperature θ In a compressible fluid, the relevant measure
BALANCED FLOW: EXAMPLES (PHH lecture 3) Potential Vorticity in the real atmosphere Need to introduce a new measure of the buoyancy Potential temperature θ In a compressible fluid, the relevant measure
PAPER 333 FLUID DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Wednesday, 1 June, 2016 1:30 pm to 4:30 pm Draft 21 June, 2016 PAPER 333 FLUID DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE Attempt no more than THREE questions. There are FOUR questions in total.
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Wednesday, 1 June, 2016 1:30 pm to 4:30 pm Draft 21 June, 2016 PAPER 333 FLUID DYNAMICS OF CLIMATE Attempt no more than THREE questions. There are FOUR questions in total.
Ocean currents: some misconceptions and some dynamics
 Ocean currents: some misconceptions and some dynamics Joe LaCasce Dept. Geosciences October 30, 2012 Where is the Gulf Stream? BBC Weather Center Where is the Gulf Stream? Univ. Bergen news website (2011)
Ocean currents: some misconceptions and some dynamics Joe LaCasce Dept. Geosciences October 30, 2012 Where is the Gulf Stream? BBC Weather Center Where is the Gulf Stream? Univ. Bergen news website (2011)
2/15/2012. Earth System Science II EES 717 Spring 2012
 Earth System Science II EES 717 Spring 2012 1. The Earth Interior Mantle Convection & Plate Tectonics 2. The Atmosphere - Climate Models, Climate Change and Feedback Processes 3. The Oceans Circulation;
Earth System Science II EES 717 Spring 2012 1. The Earth Interior Mantle Convection & Plate Tectonics 2. The Atmosphere - Climate Models, Climate Change and Feedback Processes 3. The Oceans Circulation;
Upper Ocean Circulation
 Upper Ocean Circulation C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth 1 MAR555 Lecture 4: The Upper Oceanic Circulation The Oceanic Circulation
Upper Ocean Circulation C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth 1 MAR555 Lecture 4: The Upper Oceanic Circulation The Oceanic Circulation
C
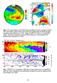 C 0.8 0.4 0.2 0.0-0.2-0.6 Fig. 1. SST-wind relation in the North Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Left panel: COADS SST (color shade), surface wind vectors, and SLP regressed upon the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
C 0.8 0.4 0.2 0.0-0.2-0.6 Fig. 1. SST-wind relation in the North Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Left panel: COADS SST (color shade), surface wind vectors, and SLP regressed upon the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
The General Circulation of the Oceans
 The General Circulation of the Oceans In previous classes we discussed local balances (Inertial otion, Ekman Transport, Geostrophic Flows, etc.), but can we eplain the large-scale general circulation of
The General Circulation of the Oceans In previous classes we discussed local balances (Inertial otion, Ekman Transport, Geostrophic Flows, etc.), but can we eplain the large-scale general circulation of
Wind-Driven Circulation: Stommel s gyre & Sverdrup s balance
 Wind-Driven Circulation: Stommel s gyre & Sverdrup s balance We begin by returning to our system o equations or low o a layer o uniorm density on a rotating earth. du dv h + [ u( H + h)] + [ v( H t y d
Wind-Driven Circulation: Stommel s gyre & Sverdrup s balance We begin by returning to our system o equations or low o a layer o uniorm density on a rotating earth. du dv h + [ u( H + h)] + [ v( H t y d
SIO 210 Final Exam December 10, :30 2:30 NTV 330 No books, no notes. Calculators can be used.
 SIO 210 Final Exam December 10, 2003 11:30 2:30 NTV 330 No books, no notes. Calculators can be used. There are three sections to the exam: multiple choice, short answer, and long problems. Points are given
SIO 210 Final Exam December 10, 2003 11:30 2:30 NTV 330 No books, no notes. Calculators can be used. There are three sections to the exam: multiple choice, short answer, and long problems. Points are given
isopycnal outcrop w < 0 (downwelling), v < 0 L.I. V. P.
 Ocean 423 Vertical circulation 1 When we are thinking about how the density, temperature and salinity structure is set in the ocean, there are different processes at work depending on where in the water
Ocean 423 Vertical circulation 1 When we are thinking about how the density, temperature and salinity structure is set in the ocean, there are different processes at work depending on where in the water
Lecture 28: A laboratory model of wind-driven ocean circulation
 Lecture 28: A laboratory model of wind-driven ocean circulation November 16, 2003 1 GFD Lab XIII: Wind-driven ocean gyres It is relatively straightforward to demonstrate the essential mechanism behind
Lecture 28: A laboratory model of wind-driven ocean circulation November 16, 2003 1 GFD Lab XIII: Wind-driven ocean gyres It is relatively straightforward to demonstrate the essential mechanism behind
SIO 210 Final examination Answer Key for all questions except Daisyworld. Wednesday, December 10, PM Name:
 SIO 210 Final examination Answer Key for all questions except Daisyworld. Wednesday, December 10, 2008 3-6 PM Name: This is a closed book exam. You may use a calculator. There are two parts: Talley (weighted
SIO 210 Final examination Answer Key for all questions except Daisyworld. Wednesday, December 10, 2008 3-6 PM Name: This is a closed book exam. You may use a calculator. There are two parts: Talley (weighted
1. The figure shows sea surface height (SSH) anomaly at 24 S (southern hemisphere), from a satellite altimeter.
 SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 16, 2015 1. The figure shows sea surface height (SSH) anomaly at 24 S (southern hemisphere), from a satellite altimeter. (a) What is the name of this type of data display?_hovmöller
SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 16, 2015 1. The figure shows sea surface height (SSH) anomaly at 24 S (southern hemisphere), from a satellite altimeter. (a) What is the name of this type of data display?_hovmöller
CANER SERTKAN ( ) WIND DRIVEN OCEAN CIRCULATION
 CANER SERTKAN (517101005) WIND DRIVEN OCEAN CIRCULATION INTRODUCTION The waters of the ocean are continually moving in powerful currents like the Gulf Stream, in large gyres, in feautures visible from
CANER SERTKAN (517101005) WIND DRIVEN OCEAN CIRCULATION INTRODUCTION The waters of the ocean are continually moving in powerful currents like the Gulf Stream, in large gyres, in feautures visible from
Atmospheric Sciences 321. Science of Climate. Lecture 20: More Ocean: Chapter 7
 Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 20: More Ocean: Chapter 7 Community Business Quiz discussion Next Topic will be Chapter 8, Natural Climate variability in the instrumental record. Homework
Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 20: More Ocean: Chapter 7 Community Business Quiz discussion Next Topic will be Chapter 8, Natural Climate variability in the instrumental record. Homework
Lecture 12: Angular Momentum and the Hadley Circulation
 Lecture 12: Angular Momentum and the Hadley Circulation September 30, 2003 We learnt last time that there is a planetary radiative drive net warming in the tropics, cooling over the pole which induces
Lecture 12: Angular Momentum and the Hadley Circulation September 30, 2003 We learnt last time that there is a planetary radiative drive net warming in the tropics, cooling over the pole which induces
Winds and Global Circulation
 Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.003 Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Contents
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.003 Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Contents
Module Contact: Dr Xiaoming Zhai, ENV Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 2
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-2018 OCEAN CIRCULATION ENV-5016A Time allowed: 2 hours Answer THREE questions Write each answer in a SEPARATE
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-2018 OCEAN CIRCULATION ENV-5016A Time allowed: 2 hours Answer THREE questions Write each answer in a SEPARATE
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10
 Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Instructions, Instructor Notes and Answer Key for Ocean Gyre Circulation and Patterns of Global Primary Productivity
 Instructions, Instructor Notes and Answer Key for Ocean Gyre Circulation and Patterns of Global Primary Productivity Instructions for activity: The instructions below are described for individual student
Instructions, Instructor Notes and Answer Key for Ocean Gyre Circulation and Patterns of Global Primary Productivity Instructions for activity: The instructions below are described for individual student
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination Wednesday, November 2, :00 2:50 PM
 SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination Wednesday, November 2, 2005 2:00 2:50 PM This is a closed book exam. Calculators are allowed. (101 total points.) MULTIPLE CHOICE (3 points
SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination Wednesday, November 2, 2005 2:00 2:50 PM This is a closed book exam. Calculators are allowed. (101 total points.) MULTIPLE CHOICE (3 points
Boundary Layers: Homogeneous Ocean Circulation
 Boundary Layers: Homogeneous Ocean irculation Lecture 7 by Angel Ruiz-Angulo The first explanation for the western intensification of the wind-driven ocean circulation was provided by Henry Stommel (948).
Boundary Layers: Homogeneous Ocean irculation Lecture 7 by Angel Ruiz-Angulo The first explanation for the western intensification of the wind-driven ocean circulation was provided by Henry Stommel (948).
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week Radiative Transfer Black body radiation, Planck function, Wien s law Absorption, emission, opacity, optical depth Intensity, flux Radiative diffusion,
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week Radiative Transfer Black body radiation, Planck function, Wien s law Absorption, emission, opacity, optical depth Intensity, flux Radiative diffusion,
Wind Gyres. curl[τ s τ b ]. (1) We choose the simple, linear bottom stress law derived by linear Ekman theory with constant κ v, viz.
![Wind Gyres. curl[τ s τ b ]. (1) We choose the simple, linear bottom stress law derived by linear Ekman theory with constant κ v, viz. Wind Gyres. curl[τ s τ b ]. (1) We choose the simple, linear bottom stress law derived by linear Ekman theory with constant κ v, viz.](/thumbs/88/117265944.jpg) Wind Gyres Here we derive the simplest (and oldest; Stommel, 1948) theory to explain western boundary currents like the Gulf Stream, and then discuss the relation of the theory to more realistic gyres.
Wind Gyres Here we derive the simplest (and oldest; Stommel, 1948) theory to explain western boundary currents like the Gulf Stream, and then discuss the relation of the theory to more realistic gyres.
Internal boundary layers in the ocean circulation
 Internal boundary layers in the ocean circulation Lecture 10 by Jan Zika This section follows on from Andy s Internal boundary layers in the ocean circulation. 1 Equations of motion in the equatorial region
Internal boundary layers in the ocean circulation Lecture 10 by Jan Zika This section follows on from Andy s Internal boundary layers in the ocean circulation. 1 Equations of motion in the equatorial region
Lecture 25: Ocean circulation: inferences from geostrophic and thermal wind balance
 Lecture 25: Ocean circulation: inferences from geostrophic and thermal wind balance November 5, 2003 Today we are going to study vertical sections through the ocean and discuss what we can learn about
Lecture 25: Ocean circulation: inferences from geostrophic and thermal wind balance November 5, 2003 Today we are going to study vertical sections through the ocean and discuss what we can learn about
CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds about a subtropical high blow a. clockwise and inward. b. counterclockwise.
CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds about a subtropical high blow a. clockwise and inward. b. counterclockwise.
Model equations for planetary and synoptic scale atmospheric motions associated with different background stratification
 Model equations for planetary and synoptic scale atmospheric motions associated with different background stratification Stamen Dolaptchiev & Rupert Klein Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research
Model equations for planetary and synoptic scale atmospheric motions associated with different background stratification Stamen Dolaptchiev & Rupert Klein Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research
ESCI 485 Air/sea Interaction Lesson 5 Oceanic Boundary Layer
 ESCI 485 Air/sea Interaction Lesson 5 Oceanic Boundar Laer References: Descriptive Phsical Oceanograph, Pickard and Emer Introductor Dnamical Oceanograph, Pond and Pickard Principles of Ocean Phsics, Apel
ESCI 485 Air/sea Interaction Lesson 5 Oceanic Boundar Laer References: Descriptive Phsical Oceanograph, Pickard and Emer Introductor Dnamical Oceanograph, Pond and Pickard Principles of Ocean Phsics, Apel
SIO 210: Dynamics VI: Potential vorticity
 SIO 210: Dynamics VI: Potential vorticity Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity Rossby waves READING: Review Section 7.2.3 Section 7.7.1 through 7.7.4 or Supplement S7.7
SIO 210: Dynamics VI: Potential vorticity Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity Rossby waves READING: Review Section 7.2.3 Section 7.7.1 through 7.7.4 or Supplement S7.7
climate system and its subcomponents: the atmosphere, ocean, land surface, Prof. Jin-Yi Yu ESS200A A general description of the Earth
 Earth System Climate () Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 9:30-10:20 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book The Earth System, Kump, Kasting, and Crane, Prentice-Hall Global Physical Climatology, Hartmann; Academic
Earth System Climate () Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 9:30-10:20 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book The Earth System, Kump, Kasting, and Crane, Prentice-Hall Global Physical Climatology, Hartmann; Academic
MAR 110 LECTURE #10 The Oceanic Conveyor Belt Oceanic Thermohaline Circulation
 1 MAR 110 LECTURE #10 The Oceanic Conveyor Belt Oceanic Thermohaline Circulation Ocean Climate Temperature Zones The pattern of approximately parallel oceanic surface isotherms (lines of constant temperature)
1 MAR 110 LECTURE #10 The Oceanic Conveyor Belt Oceanic Thermohaline Circulation Ocean Climate Temperature Zones The pattern of approximately parallel oceanic surface isotherms (lines of constant temperature)
Earth s Environmental System: Climate V2100. Midterm Exam. Wednesday March 12, 2003
 Earth s Environmental System: Climate V2100 Midterm Exam Wednesday March 12, 2003 Please put your name at the top of each page If you sketch something, make it big and clear and label your axes Explain
Earth s Environmental System: Climate V2100 Midterm Exam Wednesday March 12, 2003 Please put your name at the top of each page If you sketch something, make it big and clear and label your axes Explain
Winds and Currents in the Oceans
 Winds and Currents in the Oceans Atmospheric Processes Density of air is controlled by temperature, pressure, and moisture content. 1. Warm air is less dense than cold air and moist air is less dense than
Winds and Currents in the Oceans Atmospheric Processes Density of air is controlled by temperature, pressure, and moisture content. 1. Warm air is less dense than cold air and moist air is less dense than
Models of ocean circulation are all based on the equations of motion.
 Equations of motion Models of ocean circulation are all based on the equations of motion. Only in simple cases the equations of motion can be solved analytically, usually they must be solved numerically.
Equations of motion Models of ocean circulation are all based on the equations of motion. Only in simple cases the equations of motion can be solved analytically, usually they must be solved numerically.
1. tangential stresses at the ocean s surface due to the prevailing wind systems - the wind-driven circulation and
 Chapter 9 The wind-driven circulation [Hartmann, Ch. 7 (7.4-7.5)] There are two causes of the circulation of the ocean: 1. tangential stresses at the ocean s surface due to the prevailing wind systems
Chapter 9 The wind-driven circulation [Hartmann, Ch. 7 (7.4-7.5)] There are two causes of the circulation of the ocean: 1. tangential stresses at the ocean s surface due to the prevailing wind systems
SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 3, 2014; 1 hour 20 minutes
 NAME: SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 3, 2014; 1 hour 20 minutes Closed book; one sheet of your own notes is allowed. A calculator is allowed. (100 total points.)
NAME: SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 3, 2014; 1 hour 20 minutes Closed book; one sheet of your own notes is allowed. A calculator is allowed. (100 total points.)
Lecture 17 ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY. Learning objectives: understand the concepts & physics of
 ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 17 Learning objectives: understand the concepts & physics of 1. Ekman layer 2. Ekman transport 3. Ekman pumping 1. The Ekman Layer Scale analyses
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 17 Learning objectives: understand the concepts & physics of 1. Ekman layer 2. Ekman transport 3. Ekman pumping 1. The Ekman Layer Scale analyses
Reduced models of large-scale ocean circulation
 Reduced models of large-scale ocean circulation R. M. Samelson College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University rsamelson@coas.oregonstate.edu NCAR, 11 February 2010 Sea-surface Temperature
Reduced models of large-scale ocean circulation R. M. Samelson College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University rsamelson@coas.oregonstate.edu NCAR, 11 February 2010 Sea-surface Temperature
Currents & Gyres Notes
 Currents & Gyres Notes Current A river of water flowing in the ocean. 2 Types of Currents Surface Currents wind-driven currents that occur in the top 100m or less Deep Currents density-driven currents
Currents & Gyres Notes Current A river of water flowing in the ocean. 2 Types of Currents Surface Currents wind-driven currents that occur in the top 100m or less Deep Currents density-driven currents
t tendency advection convergence twisting baroclinicity
 RELATIVE VORTICITY EQUATION Newton s law in a rotating frame in z-coordinate (frictionless): U + U U = 2Ω U Φ α p U + U U 2 + ( U) U = 2Ω U Φ α p Applying to both sides, and noting ω U and using identities
RELATIVE VORTICITY EQUATION Newton s law in a rotating frame in z-coordinate (frictionless): U + U U = 2Ω U Φ α p U + U U 2 + ( U) U = 2Ω U Φ α p Applying to both sides, and noting ω U and using identities
Climate Variability Inferred from a Layered Model of the Ventilated Thermocline*
 APRIL 1999 HUANG AND PEDLOSKY 779 Climate Variability Inferred from a Layered Model of the Ventilated Thermocline* RUI XIN HUANG AND JOSEPH PEDLOSKY Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic
APRIL 1999 HUANG AND PEDLOSKY 779 Climate Variability Inferred from a Layered Model of the Ventilated Thermocline* RUI XIN HUANG AND JOSEPH PEDLOSKY Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic
Large-Scale Circulation with Locally Enhanced Vertical Mixing*
 712 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Large-Scale Circulation with Locally Enhanced Vertical Mixing* R. M. SAMELSON Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts (Manuscript received 15
712 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Large-Scale Circulation with Locally Enhanced Vertical Mixing* R. M. SAMELSON Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts (Manuscript received 15
Chapter 2. Quasi-Geostrophic Theory: Formulation (review) ε =U f o L <<1, β = 2Ω cosθ o R. 2.1 Introduction
 Chapter 2. Quasi-Geostrophic Theory: Formulation (review) 2.1 Introduction For most of the course we will be concerned with instabilities that an be analyzed by the quasi-geostrophic equations. These are
Chapter 2. Quasi-Geostrophic Theory: Formulation (review) 2.1 Introduction For most of the course we will be concerned with instabilities that an be analyzed by the quasi-geostrophic equations. These are
Fig. 1. Structure of the equatorial thermocline and circulation (Wyrtki and Kilonsky, 1984).
 Lecture 18. Equatorial thermocline 4/5/006 11:40 AM 1. Introduction We have discussed dynamics of western boundary layers in the subtropical and subpolar basin. In particular, inertial boundary layer plays
Lecture 18. Equatorial thermocline 4/5/006 11:40 AM 1. Introduction We have discussed dynamics of western boundary layers in the subtropical and subpolar basin. In particular, inertial boundary layer plays
Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity?
 Name: Date: TEACHER VERSION: Suggested Student Responses Included Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity? Introduction The circulation
Name: Date: TEACHER VERSION: Suggested Student Responses Included Ocean Boundary Currents Guiding Question: How do western boundary currents influence climate and ocean productivity? Introduction The circulation
Lecture 2. Lecture 1. Forces on a rotating planet. We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their:
 Lecture 2 Lecture 1 Forces on a rotating planet We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their: velocity u = (u,v,w) pressure P density ρ temperature T salinity S up For convenience, we will
Lecture 2 Lecture 1 Forces on a rotating planet We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their: velocity u = (u,v,w) pressure P density ρ temperature T salinity S up For convenience, we will
Lecture 5: Atmospheric General Circulation and Climate
 Lecture 5: Atmospheric General Circulation and Climate Geostrophic balance Zonal-mean circulation Transients and eddies Meridional energy transport Moist static energy Angular momentum balance Atmosphere
Lecture 5: Atmospheric General Circulation and Climate Geostrophic balance Zonal-mean circulation Transients and eddies Meridional energy transport Moist static energy Angular momentum balance Atmosphere
The dynamics of high and low pressure systems
 The dynamics of high and low pressure systems Newton s second law for a parcel of air in an inertial coordinate system (a coordinate system in which the coordinate axes do not change direction and are
The dynamics of high and low pressure systems Newton s second law for a parcel of air in an inertial coordinate system (a coordinate system in which the coordinate axes do not change direction and are
Lecture 1. Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions. Pressure gradient + force force
 Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
Lecture 9: General Circulation Explains Why There are Tropical Easterlies
 Lecture 9: General Circulation Single-Cell Model: Explains Why There are Tropical Easterlies JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell (driven by eddies) Polar Cell Without Earth Rotation With Earth Rotation L H L
Lecture 9: General Circulation Single-Cell Model: Explains Why There are Tropical Easterlies JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell (driven by eddies) Polar Cell Without Earth Rotation With Earth Rotation L H L
Lecture 9: General Circulation
 Lecture 9: General Circulation JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell (driven by eddies) Polar Cell L H L H Three-Cell Circulation in the Atmosphere Gyres in the Oceans Single-Cell Model: Explains Why There are
Lecture 9: General Circulation JS JP Hadley Cell Ferrel Cell (driven by eddies) Polar Cell L H L H Three-Cell Circulation in the Atmosphere Gyres in the Oceans Single-Cell Model: Explains Why There are
a Coriolis tutorial, Part 4: wind-driven circulation and the Sverdrup relation
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 a Coriolis tutorial, Part 4: wind-driven circulation and the Sverdrup relation James F. Price Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts, 2543 https://www2.whoi.edu/staff/jprice
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 a Coriolis tutorial, Part 4: wind-driven circulation and the Sverdrup relation James F. Price Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts, 2543 https://www2.whoi.edu/staff/jprice
4. Atmospheric transport. Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017
 4. Atmospheric transport Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 Forces in the atmosphere: Gravity g Pressure-gradient ap = ( 1/ ρ ) dp / dx for x-direction (also y, z directions)
4. Atmospheric transport Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 Forces in the atmosphere: Gravity g Pressure-gradient ap = ( 1/ ρ ) dp / dx for x-direction (also y, z directions)
The General Circulation of the Atmosphere: A Numerical Experiment
 The General Circulation of the Atmosphere: A Numerical Experiment Norman A. Phillips (1956) Presentation by Lukas Strebel and Fabian Thüring Goal of the Model Numerically predict the mean state of the
The General Circulation of the Atmosphere: A Numerical Experiment Norman A. Phillips (1956) Presentation by Lukas Strebel and Fabian Thüring Goal of the Model Numerically predict the mean state of the
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY
 MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 15, 2013 Due Nov. 22, 2013 Answerkey
 SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 15, 2013 Due Nov. 22, 2013 Answerkey 1. Dynamics: rotation (a) Draw the direction of an inertial current in (i) the northern hemisphere and (ii) the southern hemisphere and
SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 15, 2013 Due Nov. 22, 2013 Answerkey 1. Dynamics: rotation (a) Draw the direction of an inertial current in (i) the northern hemisphere and (ii) the southern hemisphere and
Please be ready for today by:
 Please be ready for today by: 1. HW out for a stamp 2. Paper and pencil/pen for notes 3. Be ready to discuss what you know about El Nino after you view the video clip What is El Nino? El Nino Basics El
Please be ready for today by: 1. HW out for a stamp 2. Paper and pencil/pen for notes 3. Be ready to discuss what you know about El Nino after you view the video clip What is El Nino? El Nino Basics El
Oceanography Quiz 2. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Oceanography Quiz 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The highest and lowest tides are known as the spring tides. When do these occur? a.
Oceanography Quiz 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The highest and lowest tides are known as the spring tides. When do these occur? a.
Abyssal Ocean Circulation. Raffaele Ferrari Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, MIT Les Houches, August 2017
 Abyssal Ocean Circulation Raffaele Ferrari Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, MIT Les Houches, August 2017 Outline The deep ocean The deep circulation The sinking branch: deep convection The upwelling
Abyssal Ocean Circulation Raffaele Ferrari Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, MIT Les Houches, August 2017 Outline The deep ocean The deep circulation The sinking branch: deep convection The upwelling
Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation. Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B
 Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B The observed mean circulation Lateral structure of the surface circulation Vertical structure of the circulation
Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B The observed mean circulation Lateral structure of the surface circulation Vertical structure of the circulation
Quasi-geostrophic ocean models
 Quasi-geostrophic ocean models March 19, 2002 1 Introduction The starting point for theoretical and numerical study of the three dimensional large-scale circulation of the atmosphere and ocean is a vorticity
Quasi-geostrophic ocean models March 19, 2002 1 Introduction The starting point for theoretical and numerical study of the three dimensional large-scale circulation of the atmosphere and ocean is a vorticity
I. Variability of off-shore thermocline depth and western boundary current. Rui Xin Huang *+ & Qinyan Liu +$
 Meridional circulation in the western coastal zone: I. Variability of off-shore thermocline depth and western boundary current transport on interannual and decadal time scales Rui Xin Huang *+ & Qinyan
Meridional circulation in the western coastal zone: I. Variability of off-shore thermocline depth and western boundary current transport on interannual and decadal time scales Rui Xin Huang *+ & Qinyan
Biome type of plant and animal community that covers large geographic areas
 1 Physical Environment: Atmosphere and Oceans - Circulation EVPP 110 Lecture Fall 2003 Dr. Largen 2 Global Environments 3 Biome type of plant and animal community that covers large geographic areas Global
1 Physical Environment: Atmosphere and Oceans - Circulation EVPP 110 Lecture Fall 2003 Dr. Largen 2 Global Environments 3 Biome type of plant and animal community that covers large geographic areas Global
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC FLUID DYNAMICS
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC FLUID DYNAMICS Fundamentals and Large-scale Circulation G E O F F R E Y K. V A L L I S Princeton University, New Jersey CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS An asterisk indicates more advanced
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC FLUID DYNAMICS Fundamentals and Large-scale Circulation G E O F F R E Y K. V A L L I S Princeton University, New Jersey CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS An asterisk indicates more advanced
Ocean Circulation- PART- I: In Class. Must be done inclass, and turned in before you leave for credit.
 Name: Section/ TA: Ocean Circulation- PART- I: In Class. Must be done inclass, and turned in before you leave for credit. Activity 1: The Sverdrup In our homes, we are used to calculating water volumes
Name: Section/ TA: Ocean Circulation- PART- I: In Class. Must be done inclass, and turned in before you leave for credit. Activity 1: The Sverdrup In our homes, we are used to calculating water volumes
Destruction of Potential Vorticity by Winds
 DECEMBER 2005 THOMAS 2457 Destruction of Potential Vorticity by Winds LEIF N. THOMAS* School of Oceanography, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington (Manuscript received 10 January 2005, in final
DECEMBER 2005 THOMAS 2457 Destruction of Potential Vorticity by Winds LEIF N. THOMAS* School of Oceanography, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington (Manuscript received 10 January 2005, in final
Wind-driven Western Boundary Ocean Currents in Terran and Superterran Exoplanets
 Wind-driven Western Boundary Ocean Currents in Terran and Superterran Exoplanets By Edwin Alfonso-Sosa, Ph.D. Ocean Physics Education, Inc. 10-Jul-2014 Introduction Simple models of oceanic general circulation
Wind-driven Western Boundary Ocean Currents in Terran and Superterran Exoplanets By Edwin Alfonso-Sosa, Ph.D. Ocean Physics Education, Inc. 10-Jul-2014 Introduction Simple models of oceanic general circulation
Introduction to Physical Oceanography Homework 3 - Solutions. 1. Volume transport in the Gulf Stream and Antarctic Circumpolar current (ACC):
 Laure Zanna 10/17/05 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Homework 3 - Solutions 1. Volume transport in the Gulf Stream and Antarctic Circumpolar current (ACC): (a) Looking on the web you can find a lot
Laure Zanna 10/17/05 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Homework 3 - Solutions 1. Volume transport in the Gulf Stream and Antarctic Circumpolar current (ACC): (a) Looking on the web you can find a lot
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY. Lecture 19. Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes
 ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
ATOC 5051 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY Lecture 19 Learning objectives: develop a physical understanding of ocean thermodynamic processes 1. Ocean surface heat fluxes; 2. Mixed layer temperature
Stationary Rossby Waves and Shocks on the Sverdrup Coordinate
 Journal of Oceanography Vol. 51, pp. 207 to 224. 1995 Stationary Rossby Waves and Shocks on the Sverdrup Coordinate ATSUSHI KUBOKAWA Graduate School of Environmental Earth Science, Hokkaido University,
Journal of Oceanography Vol. 51, pp. 207 to 224. 1995 Stationary Rossby Waves and Shocks on the Sverdrup Coordinate ATSUSHI KUBOKAWA Graduate School of Environmental Earth Science, Hokkaido University,
Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates: a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations. Cristiana Stan
 Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates: a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations Cristiana Stan School and Conference on the General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Oceans: a Modern Perspective
Introduction to Isentropic Coordinates: a new view of mean meridional & eddy circulations Cristiana Stan School and Conference on the General Circulation of the Atmosphere and Oceans: a Modern Perspective
Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Answers to Chapter 8
 Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Answers to Chapter 8 1. Consider a zonally symmetric circulation (i.e., one with no longitudinal variations) in the atmosphere. In the inviscid upper troposphere,
Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Answers to Chapter 8 1. Consider a zonally symmetric circulation (i.e., one with no longitudinal variations) in the atmosphere. In the inviscid upper troposphere,
CLIMATE VARIABILITY AND PREDICTABILITY
 CLIMATE VARIABILITY AND PREDICTABILITY Workshop on Tropical Atlantic Variability 3-6 September 2001, Paris, France Working Groups Reports January 2002 Working Group 1: Coupled Ocean-Atmospheric Systems
CLIMATE VARIABILITY AND PREDICTABILITY Workshop on Tropical Atlantic Variability 3-6 September 2001, Paris, France Working Groups Reports January 2002 Working Group 1: Coupled Ocean-Atmospheric Systems
