2.5. Infinite Limits and Vertical Asymptotes. Infinite Limits
|
|
|
- Ruby Parks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 . Infinite Limits and Vertical Asmptotes. Infinite Limits and Vertical Asmptotes In this section we etend the concept of it to infinite its, which are not its as before, but rather an entirel new use of the term it. Infinite its provide useful smbols and language for describing the behavior of functions whose values become arbitraril large, positive or negative. We continue our analsis of graphs of rational functions from the last section, using vertical asmptotes and dominant terms for numericall large values of. You can get as low as ou want b taking close enough to. FIGURE.7 B You can get as high as ou want b taking close enough to. No matter how high B is, the graph goes higher. B No matter how low B is, the graph goes lower. One-sided infinite its: : + = q and : - = -q Infinite Limits Let us look again at the function ƒsd = >. As : +, the values of ƒ grow without bound, eventuall reaching and surpassing ever positive real number. That is, given an positive real number B, however large, the values of ƒ become larger still (Figure.7). Thus, ƒ has no it as : +. It is nevertheless convenient to describe the behavior of ƒ b saing that ƒ() approaches q as : +. We write ƒsd = + : : = q. + In writing this, we are not saing that the it eists. Nor are we saing that there is a real number q, for there is no such number. Rather, we are saing that : + s>d does not eist because > becomes arbitraril large and positive as : +. As : -, the values of ƒsd = > become arbitraril large and negative. Given an negative real number -B, the values of ƒ eventuall lie below -B. (See Figure.7.) We write ƒsd = - : : = -q. - Again, we are not saing that the it eists and equals the number - q. There is no real number - q. We are describing the behavior of a function whose it as : - does not eist because its values become arbitraril large and negative. EXAMPLE One-Sided Infinite Limits Find : + - and : - -. Geometric Solution The graph of = >s - d is the graph of = > shifted unit to the right (Figure.8). Therefore, = >s - d behaves near eactl the wa = > behaves near : FIGURE.8 Near =, the function = >s - d behaves the wa the function = > behaves near =. Its graph is the graph of = > shifted unit to the right (Eample ). : + - = q and : - - = - q. Analtic Solution Think about the number - and its reciprocal. As : +, we have s - d : + and >s - d : q. As : -, we have s - d : - and >s - d : - q.
2 6 Chapter : Limits and Continuit B No matter how high B is, the graph goes higher. EXAMPLE Discuss the behavior of ƒsd = near =, Two-Sided Infinite Limits f() gsd = near = -. s + d Solution As approaches zero from either side, the values of > are positive and become arbitraril large (Figure.9a): g() ( ) FIGURE.9 The graphs of the functions in Eample. ƒ() approaches infinit as :. g() approaches infinit as : -. The graph of gsd = >s + d is the graph of ƒsd = > shifted units to the left (Figure.9b). Therefore, g behaves near - eactl the wa ƒ behaves near. The function = > shows no consistent behavior as :. We have > : q if : +, but > : - q if : -. All we can sa about : s>d is that it does not eist. The function = > is different. Its values approach infinit as approaches zero from either side, so we can sa that : s> d = q. EXAMPLE (c) (d) (e) : : - : + - = - : - - = : s - d - Rational Functions Can Behave in Various Was Near Zeros of Their Denominators = : - - = : - - = : ƒsd = : : = q. gsd = : - : - s + d = q. s - d s - ds + d = : - s - ds + d = : - : + s - ds + d = - q - : - s - ds + d = q - s - ds + d + = does not eist. - + = The values are negative for 7, near. The values are positive for 6, near. See parts (c) and (d). - (f) : s - d = -s - d - : s - d = : s - d = - q In parts and the effect of the zero in the denominator at = is canceled because the numerator is zero there also. Thus a finite it eists. This is not true in part (f), where cancellation still leaves a zero in the denominator. Precise Definitions of Infinite Limits Instead of requiring ƒ() to lie arbitraril close to a finite number L for all sufficientl close to, the definitions of infinite its require ƒ() to lie arbitraril far from the ori-
3 . Infinite Limits and Vertical Asmptotes 7 f() gin. Ecept for this change, the language is identical with what we have seen before. Figures. and. accompan these definitions. DEFINITIONS Infinit, Negative Infinit as Limits B. We sa that ƒ() approaches infinit as approaches, and write ƒsd = q, : if for ever positive real number B there eists a corresponding d 7 such that for all 6 ƒ - ƒ 6 d Q ƒsd 7 B. FIGURE. :. ƒ() approaches infinit as. We sa that ƒ() approaches negative infinit as approaches, and write ƒsd = -q, : if for ever negative real number -B there eists a corresponding d 7 such that for all 6 ƒ - ƒ 6 d Q ƒsd 6 -B. The precise definitions of one-sided infinite its at eercises. are similar and are stated in the B EXAMPLE Using the Definition of Infinite Limits f() Prove that : = q. Solution Given B 7, we want to find d 7 such that FIGURE. ƒ() approaches negative infinit as :. Now, or, equivalentl, 6 ƒ - ƒ 6 d implies 7 B. 7 B if and onl if 6 B ƒ ƒ 6 B. Thus, choosing d = > B (or an smaller positive number), we see that ƒ ƒ 6 d implies 7 d Ú B. Therefore, b definition, : = q.
4 8 Chapter : Limits and Continuit Vertical asmptote Vertical Asmptotes Notice that the distance between a point on the graph of = > and the -ais approaches zero as the point moves verticall along the graph and awa from the origin (Figure.). This behavior occurs because asmptote asmptote, : + = q and : - = -q. We sa that the line = (the -ais) is a vertical asmptote of the graph of = >. Observe that the denominator is zero at = and the function is undefined there. Vertical asmptote, FIGURE. The coordinate aes are asmptotes of both branches of the hperbola = >. asmptote, Vertical asmptote, 6 FIGURE. The lines = and = - are asmptotes of the curve = s + d>s + d (Eample ). DEFINITION Vertical Asmptote A line = a is a vertical asmptote of the graph of a function = ƒsd if either ƒsd = ; q or ƒsd = ; q. :a + :a - EXAMPLE Looking for Asmptotes Find the horizontal and vertical asmptotes of the curve Solution We are interested in the behavior as : ; q and as : -, where the denominator is zero. The asmptotes are quickl revealed if we recast the rational function as a polnomial with a remainder, b dividing s + d into s + d. This result enables us to rewrite : We now see that the curve in question is the graph of = > shifted unit up and units left (Figure.). The asmptotes, instead of being the coordinate aes, are now the lines = and = -. EXAMPLE 6 = = + Asmptotes Need Not Be Two-Sided Find the horizontal and vertical asmptotes of the graph of ƒsd = Solution We are interested in the behavior as : ; q and as : ;, where the denominator is zero. Notice that ƒ is an even function of, so its graph is smmetric with respect to the -ais. The behavior as : ; q. Since :q ƒsd =, the line = is a horizontal asmptote of the graph to the right. B smmetr it is an asmptote to the left as well
5 . Infinite Limits and Vertical Asmptotes 9 Vertical asmptote, Vertical asmptote, asmptote, FIGURE. Graph of = -8>s - d. Notice that the curve approaches the -ais from onl one side. Asmptotes do not have to be two-sided (Eample 6). (Figure.). Notice that the curve approaches the -ais from onl the negative side (or from below). The behavior as : ;. Since the line = is a vertical asmptote both from the right and from the left. B smmetr, the same holds for the line = -. There are no other asmptotes because ƒ has a finite it at ever other point. EXAMPLE 7 The curves ƒsd = - q and ƒsd = q, : + : - Curves with Infinitel Man Asmptotes = sec = cos and = tan = cos sin both have vertical asmptotes at odd-integer multiples of p>, where cos = (Figure.). sec tan FIGURE. The graphs of sec and tan have infinitel man vertical asmptotes (Eample 7). The graphs of = csc = and = cot = cos sin sin have vertical asmptotes at integer multiples of p, where sin = (Figure.6). csc cot FIGURE.6 The graphs of csc and cot (Eample 7).
6 Chapter : Limits and Continuit EXAMPLE 8 A Rational Function with Degree of Numerator Greater than Degree of Denominator Find the asmptotes of the graph of 6 Vertical asmptote, The vertical distance between curve and line goes to zero as Oblique asmptote FIGURE.7 The graph of ƒsd = s - d>s - d has a vertical asmptote and an oblique asmptote (Eample 8). Solution We are interested in the behavior as : ; q and also as :, where the denominator is zero. We divide s - d into s - d: This tells us that ƒsd = ƒsd = - - = + + linear -. remainder Since : + ƒsd = q and : - ƒsd = -q, the line = is a two-sided vertical asmptote. As : ; q, the remainder approaches and ƒsd : s>d +. The line = s>d + is an oblique asmptote both to the right and to the left (Figure.7). Notice in Eample 8, that if the degree of the numerator in a rational function is greater than the degree of the denominator, then the it is + q or - q, depending on the signs assumed b the numerator and denominator as ƒ ƒ becomes large. Dominant Terms Of all the observations we can make quickl about the function in Eample 8, probabl the most useful is that This tells us immediatel that ƒsd = - - ƒsd = ƒsd L + ƒsd L - For numericall large For near If we want to know how ƒ behaves, this is the wa to find out. It behaves like = s>d + when is numericall large and the contribution of >s - d to the total
7 . Infinite Limits and Vertical Asmptotes value of ƒ is insignificant. It behaves like >s - d when is so close to that >s - d makes the dominant contribution. We sa that s>d + dominates when is numericall large, and we sa that >s - d dominates when is near. Dominant terms like these are the ke to predicting a function s behavior. Here s another eample. EXAMPLE 9 Two Graphs Appearing Identical on a Large Scale Let ƒsd = and gsd =. Show that although ƒ and g are quite different for numericall small values of, the are virtuall identical for ƒ ƒ ver large. Solution The graphs of ƒ and g behave quite differentl near the origin (Figure.8a), but appear as virtuall identical on a larger scale (Figure.8b).,, f() g(),, FIGURE.8 The graphs of ƒ and g, are distinct for ƒ ƒ small, and nearl identical for ƒ ƒ large (Eample 9). We can test that the term in ƒ, represented graphicall b g, dominates the polnomial ƒ for numericall large values of b eamining the ratio of the two functions as : ; q. We find that ƒsd : ;q gsd = so that ƒ and g are nearl identical for ƒ ƒ large : ;q = a - : ;q b =,
Limits and Continuous Functions. 2.2 Introduction to Limits. We first interpret limits loosely. We write. lim f(x) = L
 2 Limits and Continuous Functions 2.2 Introduction to Limits We first interpret limits loosel. We write lim f() = L and sa the limit of f() as approaches c, equals L if we can make the values of f() arbitraril
2 Limits and Continuous Functions 2.2 Introduction to Limits We first interpret limits loosel. We write lim f() = L and sa the limit of f() as approaches c, equals L if we can make the values of f() arbitraril
7.7. Inverse Trigonometric Functions. Defining the Inverses
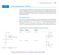 7.7 Inverse Trigonometric Functions 57 7.7 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse trigonometric functions arise when we want to calculate angles from side measurements in triangles. The also provide useful
7.7 Inverse Trigonometric Functions 57 7.7 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse trigonometric functions arise when we want to calculate angles from side measurements in triangles. The also provide useful
1.3 LIMITS AT INFINITY; END BEHAVIOR OF A FUNCTION
 . Limits at Infinit; End Behavior of a Function 89. LIMITS AT INFINITY; END BEHAVIOR OF A FUNCTION Up to now we have been concerned with its that describe the behavior of a function f) as approaches some
. Limits at Infinit; End Behavior of a Function 89. LIMITS AT INFINITY; END BEHAVIOR OF A FUNCTION Up to now we have been concerned with its that describe the behavior of a function f) as approaches some
2.5 CONTINUITY. a x. Notice that Definition l implicitly requires three things if f is continuous at a:
 SECTION.5 CONTINUITY 9.5 CONTINUITY We noticed in Section.3 that the it of a function as approaches a can often be found simpl b calculating the value of the function at a. Functions with this propert
SECTION.5 CONTINUITY 9.5 CONTINUITY We noticed in Section.3 that the it of a function as approaches a can often be found simpl b calculating the value of the function at a. Functions with this propert
Infinite Limits. Let f be the function given by. f x 3 x 2.
 0_005.qd //0 :07 PM Page 8 SECTION.5 Infinite Limits 8, as Section.5, as + f() = f increases and decreases without bound as approaches. Figure.9 Infinite Limits Determine infinite its from the left and
0_005.qd //0 :07 PM Page 8 SECTION.5 Infinite Limits 8, as Section.5, as + f() = f increases and decreases without bound as approaches. Figure.9 Infinite Limits Determine infinite its from the left and
1.2 Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus
 1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
1.2 Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus
 1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
Coordinate geometry. + bx + c. Vertical asymptote. Sketch graphs of hyperbolas (including asymptotic behaviour) from the general
 A Sketch graphs of = a m b n c where m = or and n = or B Reciprocal graphs C Graphs of circles and ellipses D Graphs of hperbolas E Partial fractions F Sketch graphs using partial fractions Coordinate
A Sketch graphs of = a m b n c where m = or and n = or B Reciprocal graphs C Graphs of circles and ellipses D Graphs of hperbolas E Partial fractions F Sketch graphs using partial fractions Coordinate
5.6 RATIOnAl FUnCTIOnS. Using Arrow notation. learning ObjeCTIveS
 CHAPTER PolNomiAl ANd rational functions learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Use arrow notation. Solve applied problems involving rational functions. Find the domains of rational functions. Identif
CHAPTER PolNomiAl ANd rational functions learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Use arrow notation. Solve applied problems involving rational functions. Find the domains of rational functions. Identif
In everyday speech, a continuous. Limits and Continuity. Critical Thinking Exercises
 062 Chapter Introduction to Calculus Critical Thinking Eercises Make Sense? In Eercises 74 77, determine whether each statement makes sense or does not make sense, and eplain our reasoning. 74. I evaluated
062 Chapter Introduction to Calculus Critical Thinking Eercises Make Sense? In Eercises 74 77, determine whether each statement makes sense or does not make sense, and eplain our reasoning. 74. I evaluated
3 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 3 Polnomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 3.2 Polnomial Functions and Their Graphs 3.3 Dividing Polnomials 3.4 Real Zeros of Polnomials 3.5 Comple Zeros and the Fundamental
3 Polnomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 3.2 Polnomial Functions and Their Graphs 3.3 Dividing Polnomials 3.4 Real Zeros of Polnomials 3.5 Comple Zeros and the Fundamental
Section 2.5: Graphs of Functions
 Section.5: Graphs of Functions Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, ou will be able to: Sketch the graph of a piecewise function containing an of the librar functions. o Polnomial functions of degree
Section.5: Graphs of Functions Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, ou will be able to: Sketch the graph of a piecewise function containing an of the librar functions. o Polnomial functions of degree
In this note we will evaluate the limits of some indeterminate forms using L Hôpital s Rule. Indeterminate Forms and 0 0. f(x)
 L Hôpital s Rule In this note we will evaluate the its of some indeterminate forms using L Hôpital s Rule. Indeterminate Forms and 0 0 f() Suppose a f() = 0 and a g() = 0. Then a g() the indeterminate
L Hôpital s Rule In this note we will evaluate the its of some indeterminate forms using L Hôpital s Rule. Indeterminate Forms and 0 0 f() Suppose a f() = 0 and a g() = 0. Then a g() the indeterminate
Properties of Limits
 33460_003qd //04 :3 PM Page 59 SECTION 3 Evaluating Limits Analticall 59 Section 3 Evaluating Limits Analticall Evaluate a it using properties of its Develop and use a strateg for finding its Evaluate
33460_003qd //04 :3 PM Page 59 SECTION 3 Evaluating Limits Analticall 59 Section 3 Evaluating Limits Analticall Evaluate a it using properties of its Develop and use a strateg for finding its Evaluate
L 8.6 L 10.6 L 13.3 L Psud = u 3-4u 2 + 5u; [1, 2]
![L 8.6 L 10.6 L 13.3 L Psud = u 3-4u 2 + 5u; [1, 2] L 8.6 L 10.6 L 13.3 L Psud = u 3-4u 2 + 5u; [1, 2]](/thumbs/80/82149634.jpg) . Rates of Change and Tangents to Curves 6 p Q (5, ) (, ) (5, ) (, 65) Slope of PQ p/ t (flies/ da) - 5 5 - - 5 - - 5 5-65 - 5 - L 8.6 L.6 L. L 6. Number of flies 5 B(5, 5) Q(5, ) 5 5 P(, 5) 5 5 A(, )
. Rates of Change and Tangents to Curves 6 p Q (5, ) (, ) (5, ) (, 65) Slope of PQ p/ t (flies/ da) - 5 5 - - 5 - - 5 5-65 - 5 - L 8.6 L.6 L. L 6. Number of flies 5 B(5, 5) Q(5, ) 5 5 P(, 5) 5 5 A(, )
MAT 1275: Introduction to Mathematical Analysis. Graphs and Simplest Equations for Basic Trigonometric Functions. y=sin( x) Function
 MAT 275: Introduction to Mathematical Analsis Dr. A. Rozenblum Graphs and Simplest Equations for Basic Trigonometric Functions We consider here three basic functions: sine, cosine and tangent. For them,
MAT 275: Introduction to Mathematical Analsis Dr. A. Rozenblum Graphs and Simplest Equations for Basic Trigonometric Functions We consider here three basic functions: sine, cosine and tangent. For them,
c) Words: The cost of a taxicab is $2.00 for the first 1/4 of a mile and $1.00 for each additional 1/8 of a mile.
 Functions Definition: A function f, defined from a set A to a set B, is a rule that associates with each element of the set A one, and onl one, element of the set B. Eamples: a) Graphs: b) Tables: 0 50
Functions Definition: A function f, defined from a set A to a set B, is a rule that associates with each element of the set A one, and onl one, element of the set B. Eamples: a) Graphs: b) Tables: 0 50
2.2. Calculating Limits Using the Limit Laws. 84 Chapter 2: Limits and Continuity. The Limit Laws. THEOREM 1 Limit Laws
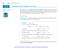 84 Chapter : Limits and Continuit. HISTORICAL ESSAY* Limits Calculating Limits Using the Limit Laws In Section. we used graphs and calculators to guess the values of its. This section presents theorems
84 Chapter : Limits and Continuit. HISTORICAL ESSAY* Limits Calculating Limits Using the Limit Laws In Section. we used graphs and calculators to guess the values of its. This section presents theorems
Rolle s Theorem. THEOREM 3 Rolle s Theorem. x x. then there is at least one number c in (a, b) at which ƒ scd = 0.
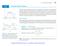 4.2 The Mean Value Theorem 255 4.2 The Mean Value Theorem f '(c) 0 f() We know that constant functions have zero derivatives, ut could there e a complicated function, with man terms, the derivatives of
4.2 The Mean Value Theorem 255 4.2 The Mean Value Theorem f '(c) 0 f() We know that constant functions have zero derivatives, ut could there e a complicated function, with man terms, the derivatives of
Math 111 Lecture Notes
 A rational function is of the form R() = p() q() where p and q are polnomial functions. The zeros of a rational function are the values of for which p() = 0, as the function s value is zero where the value
A rational function is of the form R() = p() q() where p and q are polnomial functions. The zeros of a rational function are the values of for which p() = 0, as the function s value is zero where the value
McKinney High School AP Calculus Summer Packet
 McKinne High School AP Calculus Summer Packet (for students entering AP Calculus AB or AP Calculus BC) Name:. This packet is to be handed in to our Calculus teacher the first week of school.. ALL work
McKinne High School AP Calculus Summer Packet (for students entering AP Calculus AB or AP Calculus BC) Name:. This packet is to be handed in to our Calculus teacher the first week of school.. ALL work
A function from a set D to a set R is a rule that assigns a unique element in R to each element in D.
 1.2 Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1.2 FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1.2 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function 2. Find the domain of a function
1.2 Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1.2 FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1.2 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function 2. Find the domain of a function
4.7. Newton s Method. Procedure for Newton s Method HISTORICAL BIOGRAPHY
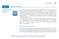 4. Newton s Method 99 4. Newton s Method HISTORICAL BIOGRAPHY Niels Henrik Abel (18 189) One of the basic problems of mathematics is solving equations. Using the quadratic root formula, we know how to
4. Newton s Method 99 4. Newton s Method HISTORICAL BIOGRAPHY Niels Henrik Abel (18 189) One of the basic problems of mathematics is solving equations. Using the quadratic root formula, we know how to
10.5 Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions
 790 Foundations of Trigonometr 0.5 Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions In this section, we return to our discussion of the circular (trigonometric functions as functions of real numbers and pick up where
790 Foundations of Trigonometr 0.5 Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions In this section, we return to our discussion of the circular (trigonometric functions as functions of real numbers and pick up where
4.3 Exercises. local maximum or minimum. The second derivative is. e 1 x 2x 1. f x x 2 e 1 x 1 x 2 e 1 x 2x x 4
 SECTION 4.3 HOW DERIVATIVES AFFECT THE SHAPE OF A GRAPH 297 local maimum or minimum. The second derivative is f 2 e 2 e 2 4 e 2 4 Since e and 4, we have f when and when 2 f. So the curve is concave downward
SECTION 4.3 HOW DERIVATIVES AFFECT THE SHAPE OF A GRAPH 297 local maimum or minimum. The second derivative is f 2 e 2 e 2 4 e 2 4 Since e and 4, we have f when and when 2 f. So the curve is concave downward
1. d = 1. or Use Only in Pilot Program F Review Exercises 131
 or Use Onl in Pilot Program F 0 0 Review Eercises. Limit proof Suppose f is defined for all values of near a, ecept possibl at a. Assume for an integer N 7 0, there is another integer M 7 0 such that f
or Use Onl in Pilot Program F 0 0 Review Eercises. Limit proof Suppose f is defined for all values of near a, ecept possibl at a. Assume for an integer N 7 0, there is another integer M 7 0 such that f
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE. Functions & Graphs
 STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
KEY IDEAS. Chapter 1 Function Transformations. 1.1 Horizontal and Vertical Translations Pre-Calculus 12 Student Workbook MHR 1
 Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations A translation can move the graph of a function up or down (vertical translation) and right or left (horizontal translation). A translation
Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations A translation can move the graph of a function up or down (vertical translation) and right or left (horizontal translation). A translation
APPENDIXES. B Coordinate Geometry and Lines C. D Trigonometry E F. G The Logarithm Defined as an Integral H Complex Numbers I
 APPENDIXES A Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values B Coordinate Geometr and Lines C Graphs of Second-Degree Equations D Trigonometr E F Sigma Notation Proofs of Theorems G The Logarithm Defined as
APPENDIXES A Numbers, Inequalities, and Absolute Values B Coordinate Geometr and Lines C Graphs of Second-Degree Equations D Trigonometr E F Sigma Notation Proofs of Theorems G The Logarithm Defined as
Model Inverse Variation. p Write and graph inverse variation equations. VOCABULARY. Inverse variation. Constant of variation. Branches of a hyperbola
 12.1 Model Inverse Variation Goal p Write and graph inverse variation equations. Your Notes VOCABULARY Inverse variation Constant of variation Hperbola Branches of a hperbola Asmptotes of a hperbola Eample
12.1 Model Inverse Variation Goal p Write and graph inverse variation equations. Your Notes VOCABULARY Inverse variation Constant of variation Hperbola Branches of a hperbola Asmptotes of a hperbola Eample
Limits 4: Continuity
 Limits 4: Continuit 55 Limits 4: Continuit Model : Continuit I. II. III. IV. z V. VI. z a VII. VIII. IX. Construct Your Understanding Questions (to do in class). Which is the correct value of f (a) in
Limits 4: Continuit 55 Limits 4: Continuit Model : Continuit I. II. III. IV. z V. VI. z a VII. VIII. IX. Construct Your Understanding Questions (to do in class). Which is the correct value of f (a) in
Chapter 4 Analytic Trigonometry
 Analtic Trigonometr Chapter Analtic Trigonometr Inverse Trigonometric Functions The trigonometric functions act as an operator on the variable (angle, resulting in an output value Suppose this process
Analtic Trigonometr Chapter Analtic Trigonometr Inverse Trigonometric Functions The trigonometric functions act as an operator on the variable (angle, resulting in an output value Suppose this process
Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions
 CHAPTER 3 Eponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions 3.1 Eponential and Logistic Functions 3.2 Eponential and Logistic Modeling 3.3 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 3.4 Properties of Logarithmic
CHAPTER 3 Eponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions 3.1 Eponential and Logistic Functions 3.2 Eponential and Logistic Modeling 3.3 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 3.4 Properties of Logarithmic
Section 1.5 Formal definitions of limits
 Section.5 Formal definitions of limits (3/908) Overview: The definitions of the various tpes of limits in previous sections involve phrases such as arbitraril close, sufficientl close, arbitraril large,
Section.5 Formal definitions of limits (3/908) Overview: The definitions of the various tpes of limits in previous sections involve phrases such as arbitraril close, sufficientl close, arbitraril large,
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge
 Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of work b Horia Varlan;
Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of work b Horia Varlan;
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. D) D: (-, 0) (0, )
 Midterm Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the domain and graph the function. ) G(t) = t - 3 ) 3 - -3 - - 3 - - -3
Midterm Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the domain and graph the function. ) G(t) = t - 3 ) 3 - -3 - - 3 - - -3
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Name Date Chapter Polnomial and Rational Functions Section.1 Quadratic Functions Objective: In this lesson ou learned how to sketch and analze graphs of quadratic functions. Important Vocabular Define
Name Date Chapter Polnomial and Rational Functions Section.1 Quadratic Functions Objective: In this lesson ou learned how to sketch and analze graphs of quadratic functions. Important Vocabular Define
Quick Review 4.1 (For help, go to Sections 1.2, 2.1, 3.5, and 3.6.)
 Section 4. Etreme Values of Functions 93 EXPLORATION Finding Etreme Values Let f,.. Determine graphicall the etreme values of f and where the occur. Find f at these values of.. Graph f and f or NDER f,,
Section 4. Etreme Values of Functions 93 EXPLORATION Finding Etreme Values Let f,.. Determine graphicall the etreme values of f and where the occur. Find f at these values of.. Graph f and f or NDER f,,
UNCORRECTED. To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: y = x 1 y 2 = x
 5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
Table of Contents. Module 1
 Table of Contents Module 1 11 Order of Operations 16 Signed Numbers 1 Factorization of Integers 17 Further Signed Numbers 13 Fractions 18 Power Laws 14 Fractions and Decimals 19 Introduction to Algebra
Table of Contents Module 1 11 Order of Operations 16 Signed Numbers 1 Factorization of Integers 17 Further Signed Numbers 13 Fractions 18 Power Laws 14 Fractions and Decimals 19 Introduction to Algebra
Trigonometric Functions
 Trigonometric Functions This section reviews radian measure and the basic trigonometric functions. C ' θ r s ' ngles ngles are measured in degrees or radians. The number of radians in the central angle
Trigonometric Functions This section reviews radian measure and the basic trigonometric functions. C ' θ r s ' ngles ngles are measured in degrees or radians. The number of radians in the central angle
Glossary. Also available at BigIdeasMath.com: multi-language glossary vocabulary flash cards. An equation that contains an absolute value expression
 Glossar This student friendl glossar is designed to be a reference for ke vocabular, properties, and mathematical terms. Several of the entries include a short eample to aid our understanding of important
Glossar This student friendl glossar is designed to be a reference for ke vocabular, properties, and mathematical terms. Several of the entries include a short eample to aid our understanding of important
4.3 Mean-Value Theorem and Monotonicity
 .3 Mean-Value Theorem and Monotonicit 1. Mean Value Theorem Theorem: Suppose that f is continuous on the interval a, b and differentiable on the interval a, b. Then there eists a number c in a, b such
.3 Mean-Value Theorem and Monotonicit 1. Mean Value Theorem Theorem: Suppose that f is continuous on the interval a, b and differentiable on the interval a, b. Then there eists a number c in a, b such
Review Exercises for Chapter 3. Review Exercises for Chapter r v 0 2. v ft sec. x 1 2 x dx f x x 99.4.
 Review Eercises for Chapter 6. r v 0 sin. Let f, 00, d 0.6. v 0 00 ftsec changes from 0 to dr 00 cos d 6 0 d 0 r dr 80 00 6 96 feet 80 cos 0 96 feet 8080 f f fd d f 99. 00 0.6 9.97 00 Using a calculator:
Review Eercises for Chapter 6. r v 0 sin. Let f, 00, d 0.6. v 0 00 ftsec changes from 0 to dr 00 cos d 6 0 d 0 r dr 80 00 6 96 feet 80 cos 0 96 feet 8080 f f fd d f 99. 00 0.6 9.97 00 Using a calculator:
2-6. _ k x and y = _ k. The Graph of. Vocabulary. Lesson
 Chapter 2 Lesson 2-6 BIG IDEA The Graph of = _ k and = _ k 2 The graph of the set of points (, ) satisfing = k_, with k constant, is a hperbola with the - and -aes as asmptotes; the graph of the set of
Chapter 2 Lesson 2-6 BIG IDEA The Graph of = _ k and = _ k 2 The graph of the set of points (, ) satisfing = k_, with k constant, is a hperbola with the - and -aes as asmptotes; the graph of the set of
Functions and Graphs TERMINOLOGY
 5 Functions and Graphs TERMINOLOGY Arc of a curve: Part or a section of a curve between two points Asmptote: A line towards which a curve approaches but never touches Cartesian coordinates: Named after
5 Functions and Graphs TERMINOLOGY Arc of a curve: Part or a section of a curve between two points Asmptote: A line towards which a curve approaches but never touches Cartesian coordinates: Named after
Limits. or Use Only in Pilot Program F The Idea of Limits 2.2 Definitions of Limits 2.3 Techniques for Computing.
 Limits or Use Onl in Pilot Program F 03 04. he Idea of Limits. Definitions of Limits.3 echniques for Computing Limits.4 Infinite Limits.5 Limits at Infinit.6 Continuit.7 Precise Definitions of Limits Biologists
Limits or Use Onl in Pilot Program F 03 04. he Idea of Limits. Definitions of Limits.3 echniques for Computing Limits.4 Infinite Limits.5 Limits at Infinit.6 Continuit.7 Precise Definitions of Limits Biologists
Differentiation and applications
 FS O PA G E PR O U N C O R R EC TE D Differentiation and applications. Kick off with CAS. Limits, continuit and differentiabilit. Derivatives of power functions.4 C oordinate geometr applications of differentiation.5
FS O PA G E PR O U N C O R R EC TE D Differentiation and applications. Kick off with CAS. Limits, continuit and differentiabilit. Derivatives of power functions.4 C oordinate geometr applications of differentiation.5
1.5. Analyzing Graphs of Functions. The Graph of a Function. What you should learn. Why you should learn it. 54 Chapter 1 Functions and Their Graphs
 0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
Algebra/Pre-calc Review
 Algebra/Pre-calc Review The following pages contain various algebra and pre-calculus topics that are used in the stud of calculus. These pages were designed so that students can refresh their knowledge
Algebra/Pre-calc Review The following pages contain various algebra and pre-calculus topics that are used in the stud of calculus. These pages were designed so that students can refresh their knowledge
AP Calculus I Summer Packet
 AP Calculus I Summer Packet This will be your first grade of AP Calculus and due on the first day of class. Please turn in ALL of your work and the attached completed answer sheet. I. Intercepts The -intercept
AP Calculus I Summer Packet This will be your first grade of AP Calculus and due on the first day of class. Please turn in ALL of your work and the attached completed answer sheet. I. Intercepts The -intercept
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
Review Topics for MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus Table of Contents
 Math 1400 - Mano Table of Contents - Review - page 1 of 2 Review Topics for MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus Table of Contents MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus is one of the Marquette Core Courses for Mathematical
Math 1400 - Mano Table of Contents - Review - page 1 of 2 Review Topics for MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus Table of Contents MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus is one of the Marquette Core Courses for Mathematical
4Cubic. polynomials UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 4Cubic polnomials 4.1 Kick off with CAS 4. Polnomials 4.3 The remainder and factor theorems 4.4 Graphs of cubic polnomials 4.5 Equations of cubic polnomials 4.6 Cubic models and applications 4.7 Review
4Cubic polnomials 4.1 Kick off with CAS 4. Polnomials 4.3 The remainder and factor theorems 4.4 Graphs of cubic polnomials 4.5 Equations of cubic polnomials 4.6 Cubic models and applications 4.7 Review
Section 1.2: A Catalog of Functions
 Section 1.: A Catalog of Functions As we discussed in the last section, in the sciences, we often tr to find an equation which models some given phenomenon in the real world - for eample, temperature as
Section 1.: A Catalog of Functions As we discussed in the last section, in the sciences, we often tr to find an equation which models some given phenomenon in the real world - for eample, temperature as
Chapter 18 Quadratic Function 2
 Chapter 18 Quadratic Function Completed Square Form 1 Consider this special set of numbers - the square numbers or the set of perfect squares. 4 = = 9 = 3 = 16 = 4 = 5 = 5 = Numbers like 5, 11, 15 are
Chapter 18 Quadratic Function Completed Square Form 1 Consider this special set of numbers - the square numbers or the set of perfect squares. 4 = = 9 = 3 = 16 = 4 = 5 = 5 = Numbers like 5, 11, 15 are
2.1 Rates of Change and Limits AP Calculus
 . Rates of Change and Limits AP Calculus. RATES OF CHANGE AND LIMITS Limits Limits are what separate Calculus from pre calculus. Using a it is also the foundational principle behind the two most important
. Rates of Change and Limits AP Calculus. RATES OF CHANGE AND LIMITS Limits Limits are what separate Calculus from pre calculus. Using a it is also the foundational principle behind the two most important
8 Differential Calculus 1 Introduction
 8 Differential Calculus Introduction The ideas that are the basis for calculus have been with us for a ver long time. Between 5 BC and 5 BC, Greek mathematicians were working on problems that would find
8 Differential Calculus Introduction The ideas that are the basis for calculus have been with us for a ver long time. Between 5 BC and 5 BC, Greek mathematicians were working on problems that would find
and y f ( x ). given the graph of y f ( x ).
 FUNCTIONS AND RELATIONS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES:. Concept of function f : f ( ) : domain, range; image (value). Odd and even functions Composite functions f g; Identit function. One-to-one and man-to-one functions.
FUNCTIONS AND RELATIONS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES:. Concept of function f : f ( ) : domain, range; image (value). Odd and even functions Composite functions f g; Identit function. One-to-one and man-to-one functions.
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
Exercise Set 4.3: Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Eercise Set.: Unit Circle Trigonometr Sketch each of the following angles in standard position. (Do not use a protractor; just draw a quick sketch of each angle. Sketch each of the following angles in
Eercise Set.: Unit Circle Trigonometr Sketch each of the following angles in standard position. (Do not use a protractor; just draw a quick sketch of each angle. Sketch each of the following angles in
6.4 graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
 SECTION 6. graphs of logarithmic functions 9 9 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Identif the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. 6. graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
SECTION 6. graphs of logarithmic functions 9 9 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Identif the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. 6. graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
8.3. Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions. 570 Chapter 8: Techniques of Integration
 570 Chapter 8: Techniques of Integration 8.3 Integration of Rational Functions b Partial Fractions This section shows how to epress a rational function (a quotient of polnomials) as a sum of simpler fractions,
570 Chapter 8: Techniques of Integration 8.3 Integration of Rational Functions b Partial Fractions This section shows how to epress a rational function (a quotient of polnomials) as a sum of simpler fractions,
A.5. Complex Numbers AP-12. The Development of the Real Numbers
 AP- A.5 Comple Numbers Comple numbers are epressions of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers and i is a smbol for -. Unfortunatel, the words real and imaginar have connotations that somehow
AP- A.5 Comple Numbers Comple numbers are epressions of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers and i is a smbol for -. Unfortunatel, the words real and imaginar have connotations that somehow
67. (a) Use a computer algebra system to find the partial fraction CAS. 68. (a) Find the partial fraction decomposition of the function CAS
 SECTION 7.5 STRATEGY FOR INTEGRATION 483 6. 2 sin 2 2 cos CAS 67. (a) Use a computer algebra sstem to find the partial fraction decomposition of the function 62 63 Find the area of the region under the
SECTION 7.5 STRATEGY FOR INTEGRATION 483 6. 2 sin 2 2 cos CAS 67. (a) Use a computer algebra sstem to find the partial fraction decomposition of the function 62 63 Find the area of the region under the
Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Graphing
 8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
Analytic Trigonometry
 CHAPTER 5 Analtic Trigonometr 5. Fundamental Identities 5. Proving Trigonometric Identities 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities 5.4 Multiple-Angle Identities 5.5 The Law of Sines 5.6 The Law of Cosines It
CHAPTER 5 Analtic Trigonometr 5. Fundamental Identities 5. Proving Trigonometric Identities 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities 5.4 Multiple-Angle Identities 5.5 The Law of Sines 5.6 The Law of Cosines It
C H A P T E R 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry
 C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
LIMITS AND CONTINUITY
 Chapter LIMITS AND CONTINUITY OVERVIEW The concept of a it is a central idea that distinguishes calculus from algebra and trigonometr. It is fundamental to finding the tangent to a curve or the velocit
Chapter LIMITS AND CONTINUITY OVERVIEW The concept of a it is a central idea that distinguishes calculus from algebra and trigonometr. It is fundamental to finding the tangent to a curve or the velocit
1.6 CONTINUITY OF TRIGONOMETRIC, EXPONENTIAL, AND INVERSE FUNCTIONS
 .6 Continuit of Trigonometric, Eponential, and Inverse Functions.6 CONTINUITY OF TRIGONOMETRIC, EXPONENTIAL, AND INVERSE FUNCTIONS In this section we will discuss the continuit properties of trigonometric
.6 Continuit of Trigonometric, Eponential, and Inverse Functions.6 CONTINUITY OF TRIGONOMETRIC, EXPONENTIAL, AND INVERSE FUNCTIONS In this section we will discuss the continuit properties of trigonometric
Section 1.2: Relations, from College Algebra: Corrected Edition by Carl Stitz, Ph.D. and Jeff Zeager, Ph.D. is available under a Creative Commons
 Section.: Relations, from College Algebra: Corrected Edition b Carl Stitz, Ph.D. and Jeff Zeager, Ph.D. is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike.0 license. 0, Carl Stitz.
Section.: Relations, from College Algebra: Corrected Edition b Carl Stitz, Ph.D. and Jeff Zeager, Ph.D. is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike.0 license. 0, Carl Stitz.
Finding Limits Graphically and Numerically. An Introduction to Limits
 60_00.qd //0 :05 PM Page 8 8 CHAPTER Limits and Their Properties Section. Finding Limits Graphicall and Numericall Estimate a it using a numerical or graphical approach. Learn different was that a it can
60_00.qd //0 :05 PM Page 8 8 CHAPTER Limits and Their Properties Section. Finding Limits Graphicall and Numericall Estimate a it using a numerical or graphical approach. Learn different was that a it can
APPENDIX D Rotation and the General Second-Degree Equation
 APPENDIX D Rotation and the General Second-Degree Equation Rotation of Aes Invariants Under Rotation After rotation of the - and -aes counterclockwise through an angle, the rotated aes are denoted as the
APPENDIX D Rotation and the General Second-Degree Equation Rotation of Aes Invariants Under Rotation After rotation of the - and -aes counterclockwise through an angle, the rotated aes are denoted as the
Gregory Hartman, Ph.D. Contributing Authors Troy Siemers, Ph.D. Brian Heinold, Ph.D. Dimplekumar Chalishajar, Ph.D. Editor Jennifer Bowen, Ph.D.
 AP E XCalculus I Version 30 Custom Edition for Math 00, Universit of Lethbridge Gregor Hartman, PhD Department of Applied Mathematics Virginia Militar Institute Contributing Authors Tro Siemers, PhD Department
AP E XCalculus I Version 30 Custom Edition for Math 00, Universit of Lethbridge Gregor Hartman, PhD Department of Applied Mathematics Virginia Militar Institute Contributing Authors Tro Siemers, PhD Department
Finding Limits Graphically and Numerically. An Introduction to Limits
 8 CHAPTER Limits and Their Properties Section Finding Limits Graphicall and Numericall Estimate a it using a numerical or graphical approach Learn different was that a it can fail to eist Stud and use
8 CHAPTER Limits and Their Properties Section Finding Limits Graphicall and Numericall Estimate a it using a numerical or graphical approach Learn different was that a it can fail to eist Stud and use
5. Zeros. We deduce that the graph crosses the x-axis at the points x = 0, 1, 2 and 4, and nowhere else. And that s exactly what we see in the graph.
 . Zeros Eample 1. At the right we have drawn the graph of the polnomial = ( 1) ( 2) ( 4). Argue that the form of the algebraic formula allows ou to see right awa where the graph is above the -ais, where
. Zeros Eample 1. At the right we have drawn the graph of the polnomial = ( 1) ( 2) ( 4). Argue that the form of the algebraic formula allows ou to see right awa where the graph is above the -ais, where
Math Review Packet #5 Algebra II (Part 2) Notes
 SCIE 0, Spring 0 Miller Math Review Packet #5 Algebra II (Part ) Notes Quadratic Functions (cont.) So far, we have onl looked at quadratic functions in which the term is squared. A more general form of
SCIE 0, Spring 0 Miller Math Review Packet #5 Algebra II (Part ) Notes Quadratic Functions (cont.) So far, we have onl looked at quadratic functions in which the term is squared. A more general form of
Answer Explanations. The SAT Subject Tests. Mathematics Level 1 & 2 TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE
 The SAT Subject Tests Answer Eplanations TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE Mathematics Level & Visit sat.org/stpractice to get more practice and stud tips for the Subject Test
The SAT Subject Tests Answer Eplanations TO PRACTICE QUESTIONS FROM THE SAT SUBJECT TESTS STUDENT GUIDE Mathematics Level & Visit sat.org/stpractice to get more practice and stud tips for the Subject Test
Chapter 1 Prerequisites for Calculus
 Section. Chapter Prerequisites for Calculus Section. Lines (pp. ) Quick Review.. + ( ) + () +. ( +). m. m ( ) ( ). (a) ( )? 6 (b) () ( )? 6. (a) 7? ( ) + 7 + Yes (b) ( ) + 9 No Yes No Section. Eercises.
Section. Chapter Prerequisites for Calculus Section. Lines (pp. ) Quick Review.. + ( ) + () +. ( +). m. m ( ) ( ). (a) ( )? 6 (b) () ( )? 6. (a) 7? ( ) + 7 + Yes (b) ( ) + 9 No Yes No Section. Eercises.
Section 2.6 Limits at infinity and infinite limits 2 Lectures. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 2.6 Limits at infinity and infinite its 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS 0: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Infinite Limits / 29 Finite its as ±. 2 Horizontal Asympotes. 3 Infinite its. 4
Section 2.6 Limits at infinity and infinite its 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS 0: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Infinite Limits / 29 Finite its as ±. 2 Horizontal Asympotes. 3 Infinite its. 4
QUIZ ON CHAPTERS 1 AND 2 - SOLUTIONS REVIEW / LIMITS AND CONTINUITY; MATH 150 SPRING 2017 KUNIYUKI 105 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 100 POINTS = 100%
 QUIZ ON CHAPTERS AND 2 - SOLUTIONS REVIEW / LIMITS AND CONTINUITY; MATH 50 SPRING 207 KUNIYUKI 05 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 00 POINTS = 00% ) For a), b), and c) below, bo in the correct answer. (6 points total;
QUIZ ON CHAPTERS AND 2 - SOLUTIONS REVIEW / LIMITS AND CONTINUITY; MATH 50 SPRING 207 KUNIYUKI 05 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 00 POINTS = 00% ) For a), b), and c) below, bo in the correct answer. (6 points total;
CHAPTER 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 CHAPTER Polnomial and Rational Functions Section. Quadratic Functions..................... 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree.......... Section. Real Zeros of Polnomial Functions............
CHAPTER Polnomial and Rational Functions Section. Quadratic Functions..................... 9 Section. Polnomial Functions of Higher Degree.......... Section. Real Zeros of Polnomial Functions............
LESSON #28 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
Chapter 2 Polynomial, Power, and Rational Functions
 Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling 6 Chapter Polnomial, Power, and Rational Functions Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling Eploration. $000 per ear.. The equation will
Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling 6 Chapter Polnomial, Power, and Rational Functions Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling Eploration. $000 per ear.. The equation will
Math RE - Calculus I Functions Page 1 of 10. Topics of Functions used in Calculus
 Math 0-03-RE - Calculus I Functions Page of 0 Definition of a function f() : Topics of Functions used in Calculus A function = f() is a relation between variables and such that for ever value onl one value.
Math 0-03-RE - Calculus I Functions Page of 0 Definition of a function f() : Topics of Functions used in Calculus A function = f() is a relation between variables and such that for ever value onl one value.
Cubic and quartic functions
 3 Cubic and quartic functions 3A Epanding 3B Long division of polnomials 3C Polnomial values 3D The remainder and factor theorems 3E Factorising polnomials 3F Sum and difference of two cubes 3G Solving
3 Cubic and quartic functions 3A Epanding 3B Long division of polnomials 3C Polnomial values 3D The remainder and factor theorems 3E Factorising polnomials 3F Sum and difference of two cubes 3G Solving
Limits and Their Properties
 Limits and Their Properties The it of a function is the primar concept that distinguishes calculus from algebra and analtic geometr. The notion of a it is fundamental to the stud of calculus. Thus, it
Limits and Their Properties The it of a function is the primar concept that distinguishes calculus from algebra and analtic geometr. The notion of a it is fundamental to the stud of calculus. Thus, it
Continuity, End Behavior, and Limits. Unit 1 Lesson 3
 Unit Lesson 3 Students will be able to: Interpret ke features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities, and sketch graphs showing ke features given a verbal description of the relationship. Ke Vocabular:
Unit Lesson 3 Students will be able to: Interpret ke features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities, and sketch graphs showing ke features given a verbal description of the relationship. Ke Vocabular:
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION
 4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.4 Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at
4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.4 Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at
CHAPTER 1 Functions, Graphs, and Limits
 CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula.......... Section. Graphs of Equations........................ 8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope....................
CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula.......... Section. Graphs of Equations........................ 8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope....................
2.1 Rates of Change and Limits AP Calculus
 .1 Rates of Change and Limits AP Calculus.1 RATES OF CHANGE AND LIMITS Limits Limits are what separate Calculus from pre calculus. Using a it is also the foundational principle behind the two most important
.1 Rates of Change and Limits AP Calculus.1 RATES OF CHANGE AND LIMITS Limits Limits are what separate Calculus from pre calculus. Using a it is also the foundational principle behind the two most important
Tangent Lines. Limits 1
 Limits Tangent Lines The concept of the tangent line to a circle dates back at least to the earl das of Greek geometr, that is, at least 5 ears. The tangent line to a circle with centre O at a point A
Limits Tangent Lines The concept of the tangent line to a circle dates back at least to the earl das of Greek geometr, that is, at least 5 ears. The tangent line to a circle with centre O at a point A
CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus
 PART II CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models..................... 8 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............ 87 Section P. Functions and Their Graphs................
PART II CHAPTER P Preparation for Calculus Section P. Graphs and Models..................... 8 Section P. Linear Models and Rates of Change............ 87 Section P. Functions and Their Graphs................
1. For each of the following, state the domain and range and whether the given relation defines a function. b)
 Eam Review Unit 0:. For each of the following, state the domain and range and whether the given relation defines a function. (,),(,),(,),(5,) a) { }. For each of the following, sketch the relation and
Eam Review Unit 0:. For each of the following, state the domain and range and whether the given relation defines a function. (,),(,),(,),(5,) a) { }. For each of the following, sketch the relation and
3.5 Continuity of a Function One Sided Continuity Intermediate Value Theorem... 23
 Chapter 3 Limit and Continuity Contents 3. Definition of Limit 3 3.2 Basic Limit Theorems 8 3.3 One sided Limit 4 3.4 Infinite Limit, Limit at infinity and Asymptotes 5 3.4. Infinite Limit and Vertical
Chapter 3 Limit and Continuity Contents 3. Definition of Limit 3 3.2 Basic Limit Theorems 8 3.3 One sided Limit 4 3.4 Infinite Limit, Limit at infinity and Asymptotes 5 3.4. Infinite Limit and Vertical
SEPARABLE EQUATIONS 2.2
 46 CHAPTER FIRST-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 4. Chemical Reactions When certain kinds of chemicals are combined, the rate at which the new compound is formed is modeled b the autonomous differential equation
46 CHAPTER FIRST-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 4. Chemical Reactions When certain kinds of chemicals are combined, the rate at which the new compound is formed is modeled b the autonomous differential equation
Math 123 Summary of Important Algebra & Trigonometry Concepts Chapter 1 & Appendix D, Stewart, Calculus Early Transcendentals
 Math Summar of Important Algebra & Trigonometr Concepts Chapter & Appendi D, Stewart, Calculus Earl Transcendentals Function a rule that assigns to each element in a set D eactl one element, called f (
Math Summar of Important Algebra & Trigonometr Concepts Chapter & Appendi D, Stewart, Calculus Earl Transcendentals Function a rule that assigns to each element in a set D eactl one element, called f (
Chapter 3: Three faces of the derivative. Overview
 Overview We alread saw an algebraic wa of thinking about a derivative. Geometric: zooming into a line Analtic: continuit and rational functions Computational: approimations with computers 3. The geometric
Overview We alread saw an algebraic wa of thinking about a derivative. Geometric: zooming into a line Analtic: continuit and rational functions Computational: approimations with computers 3. The geometric
